a43807066a928b6a8815e779901c834d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Model-based Communication Networks, Valued Information at the Right Time (VIRT) & Rich Semantic Track (RST): Filtering Information by Value to Improve Collaborative Decision-Making Project Report on CEC Collaboration Rick Hayes-Roth hayes-roth@nps. edu June 15, 2007 #1

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration #2

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration #3
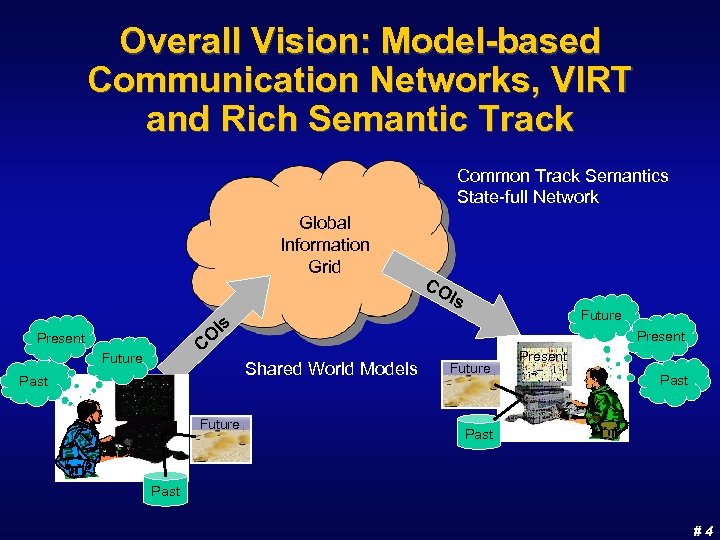
Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT and Rich Semantic Track Common Track Semantics State-full Network Global Information Grid CO Is O C Present Future Past Future Is Present Shared World Models Future Present Past #4
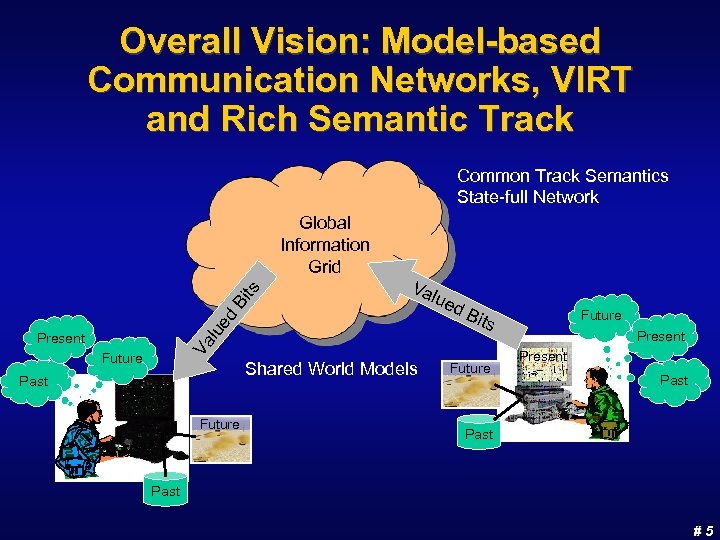
Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT and Rich Semantic Track Common Track Semantics State-full Network Va lu ed Bi ts Global Information Grid Future Past d. B its Va Present lue Shared World Models Future Present Past #5

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration #6

CEC/VIRT Project Key Results n Advanced theory and implementation of Valued Information at the Right Time (VIRT) and Rich Semantic Track (RST) u Demonstrated significant reductions in bandwidth from 2 -5 orders of magnitude in initial studies to 45 -90% in CEC-specific simulated message streams n Created research opportunities for NPS faculty and students n Created research and development initiatives with government and industry n Developed simulation framework for advanced studies of VIRT and RST #7

CEC/VIRT Project Results (1) n Prepared/published/presented several papers u “Model-based Communication Networks and VIRT: Filtering Information by Value to Improve Collaborative Decision. Making” u “Towards a Rich Semantic Model of Track: Essential Foundation for Information Sharing” u “Two Theories of Process Design for Information Superiority: Smart Pull vs. Smart Push” u VIRT Technical Architecture Specification (Draft) u “Hyper-Nodes for Emerging Command Control Networks: The 8 th Layer” (with Alex Bordetsky) u “Model-Based Communication Networks and VIRT: Orders of Magnitude Better for Information Superiority” u “Decision Making in Very Large Networks” (with Peter Denning) u “Semantic Reasoning for Adaptive Management of Telecommunications Networks” (with J. C. Hoag) n Established VIRT as key focus of W 2 COG u VIRT driving various groups’ efforts #8

CEC/VIRT Project Results (2) n Recruited & mentored three NPS thesis students n Mentoring two NPS Ph. D students n Helped PACOM start up CMA JCTD around sharing of rich track information; leading design and development of the CMA data model n Advising Joint Track Management (JTM) Architecture Working Group n Acquired workstation & CEC simulation data n Completed first computational model of CECVIRT concepts in thesis research #9

CEC/VIRT Project Results (3) n Designed and implemented CEC-VIRT simulation framework for continuing test and experimentation n Conducted computational analysis of CEC simulated message streams n Mapped CEP-to-Track-User message elements to abstract Rich Semantic Track model n Initiated design and development of Semantic Web representations of RST n Designed expressions of VIRT Conditions of Interest using Semantic Web technologies in CEC context n Initiated design and development of formalized theory of RST n Defined initial measures of performance for evaluating VIRT applications # 10
VIRT Implementation and Testing n Described VIRT Product Line Architecture approach n Built collaboration with industry to generate a draft technical architecture for VIRT n Hayes-Roth paper showed 5 orders of magnitude reduction in bandwidth using Smart Push Implementation n LCDR Acevedo thesis describing application of VIRT concepts in context of the CEC -Under modeling assumptions, Theory 2 Smart Push model showed a decrease of nearly 200 times the bandwidth of Theory 1, Smart Pull model # 11

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments u Drill-down on Analysis of CEC Message Streams n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration # 12

CEC/VIRT Message Stream Analysis n Simulated message streams provided by JHU/APL n Focus on application of VIRT at an intermediary node (“VIRT Track User”) between the CEC network and the general GIG network n Value determined by “GIG User” Conditions of Interest (COIs) relating to expected position and velocity, track identification, and engagement status n Computed bit traffic reduction of 45 -90% in short duration, highly dynamic air tracking scenarios n Demonstrated capability to “tune” bit traffic flows based on user-defined thresholds in accuracy of estimations # 13
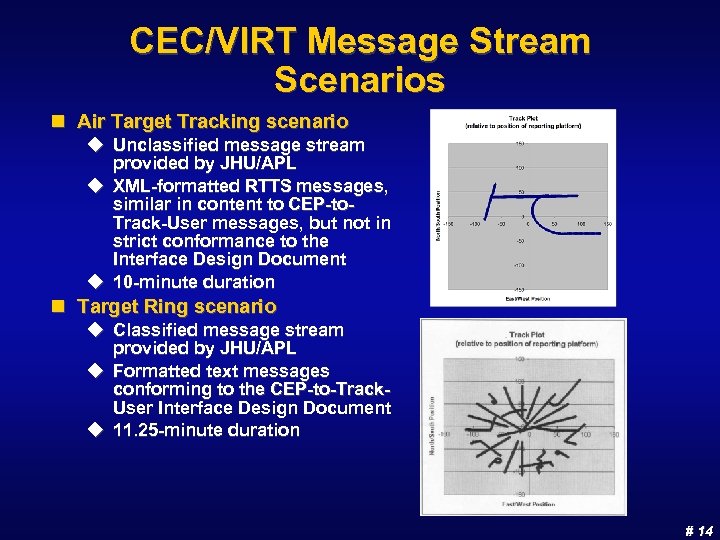
CEC/VIRT Message Stream Scenarios n Air Target Tracking scenario u Unclassified message stream provided by JHU/APL u XML-formatted RTTS messages, similar in content to CEP-to. Track-User messages, but not in strict conformance to the Interface Design Document u 10 -minute duration n Target Ring scenario u Classified message stream provided by JHU/APL u Formatted text messages conforming to the CEP-to-Track. User Interface Design Document u 11. 25 -minute duration # 14

Operational Assumptions (both scenarios) n Detected aircraft are initially behaving in accordance with expectations n Intermediary node (Track User) between the CEC network and the general user (GIG User) shares the same expectations of target behavior as the GIG User n Track User node is given knowledge of GIG User COIs n Only a significant deviation from expected behavior is considered “valued information” Under these assumptions, what portion of the message stream is passed to the user node? # 15

CEC/VIRT Conditions of Interest (both scenarios) n Significant change in expected motion of air tracks based on decision thresholds for the magnitude of change in expected position and expected velocity n Significant change in Track ID information (e. g. , from FRIEND to HOSTILE) n Significant change in Track IFF information (e. g. , change in IFF mode responses) n Start and end of engagements n Assumption/Operational Decision: No need to send CEC network-specific Cooperating Unit, Time, and Status messages # 16
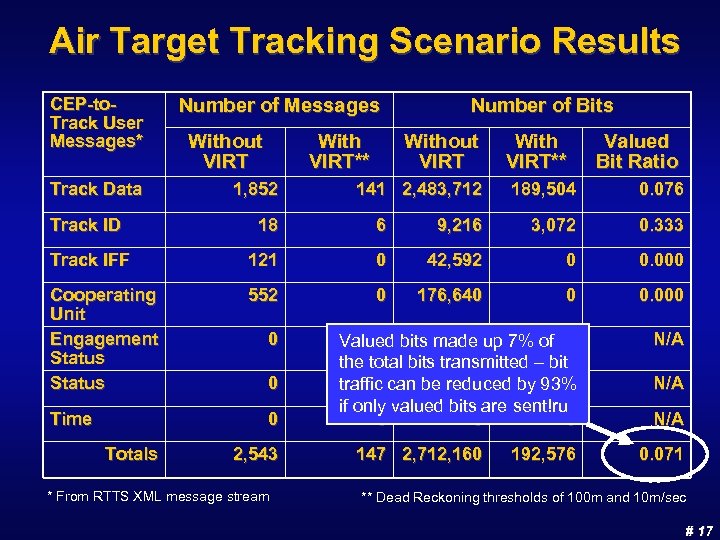
Air Target Tracking Scenario Results CEP-to. Track User Messages* Track Data Number of Messages Without VIRT With VIRT** 1, 852 Number of Bits Without VIRT 141 2, 483, 712 With VIRT** Valued Bit Ratio 189, 504 0. 076 Track ID 18 6 9, 216 3, 072 0. 333 Track IFF 121 0 42, 592 0 0. 000 Cooperating Unit Engagement Status 552 0 176, 640 0 0. 000 0 0 Valued bits made up 7% of 0 the total bits transmitted – bit 0 0 0 traffic can be reduced by 93% if only valued bits are sent!ru 0 0 0 N/A Time 0 0 0 Totals 2, 543 * From RTTS XML message stream 147 2, 712, 160 192, 576 N/A 0. 071 ** Dead Reckoning thresholds of 100 m and 10 m/sec # 17

Air Target Tracking Scenario Discussion n Results used position and velocity information in all 3 dimensions n If initial shared awareness is assumed, only 1 of the 18 Track ID messages needed to be sent (change from ASSUMED FRIEND to UNKNOWN) n None of the 552 Cooperating Unit messages needed to be sent (CEC domain only) n None of the 121 Track IFF messages needed to be sent (information of significance provided in the Track ID message) n Portion of Track Data messages sent depended on criteria applied (position or velocity) and threshold setting u 92% reduction in Track Data bit traffic at 100 m position threshold and 10 m/sec velocity threshold # 18
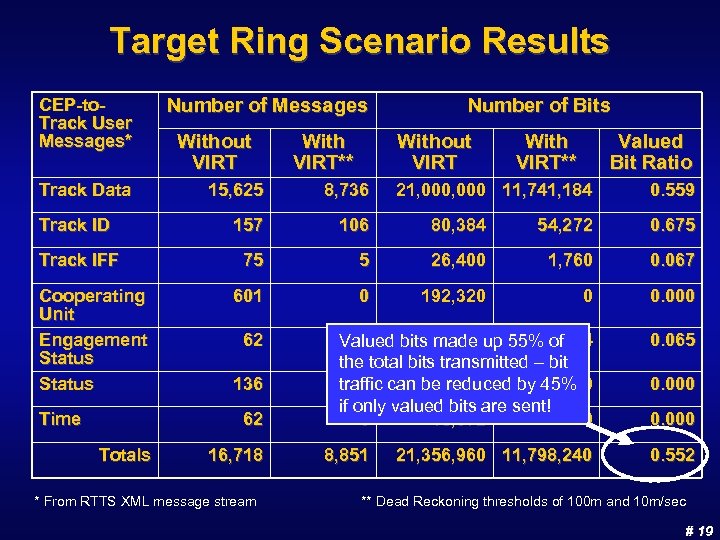
Target Ring Scenario Results CEP-to. Track User Messages* Track Data Number of Messages Without VIRT With VIRT** Number of Bits Without VIRT With VIRT** Valued Bit Ratio 15, 625 8, 736 Track ID 157 106 80, 384 54, 272 0. 675 Track IFF 75 5 26, 400 1, 760 0. 067 601 0 192, 320 0 0. 000 4 Valued bits 15, 872 up 55% 1, 024 made of the total bits transmitted – bit 0 26, 112 traffic can be reduced by 45% 0 if only valued bits are sent! 0 15, 872 0 0. 065 Cooperating Unit Engagement Status Time 62 136 62 Totals 16, 718 * From RTTS XML message stream 8, 851 21, 000 11, 741, 184 21, 356, 960 11, 798, 240 0. 559 0. 000 0. 552 ** Dead Reckoning thresholds of 100 m and 10 m/sec # 19

Target Ring Scenario Discussion n Results used position and velocity information in all 3 dimensions (east/west, north/south, and altitude) n Passed initial Track ID messages and changes in reported attributes u Refinements to Track ID COIs may be possible n Only sent 5 of 75 Track IFF messages, representing conditions raising suspicion about the track n None of the 601 Cooperating Unit messages, 136 Status messages, and 62 Time messages needed to be sent (CEC domain only) n Portion of Track Data messages sent depended on criteria applied (position or velocity) and threshold setting u 44% reduction in Track Data bit traffic at 100 m position threshold and 10 m/sec velocity threshold # 20

CEC Message Stream Analysis Conclusions n Can achieve significant reduction in bit traffic from attention to user information needs (COIs) n Demonstrated mechanisms for enabling CEC message traffic to be filtered for non-CEC users n Opportunity for further research into userspecified COIs and message processing using more of the message content (e. g. , certainty and accuracy data) # 21

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration # 22

Rich Semantic Track Model n Need practical ontologies for important domains n Tracks are common information elements in numerous military and non-military domains u A common “informal” concept in military operations u Now vital in multiple domains: aircraft, ships, vehicles, people, cargo, … u Semantic hub + translator generators => information sharing n Provides vocabulary for expressing COIs n Provides logical constructs for evaluating COIs # 23
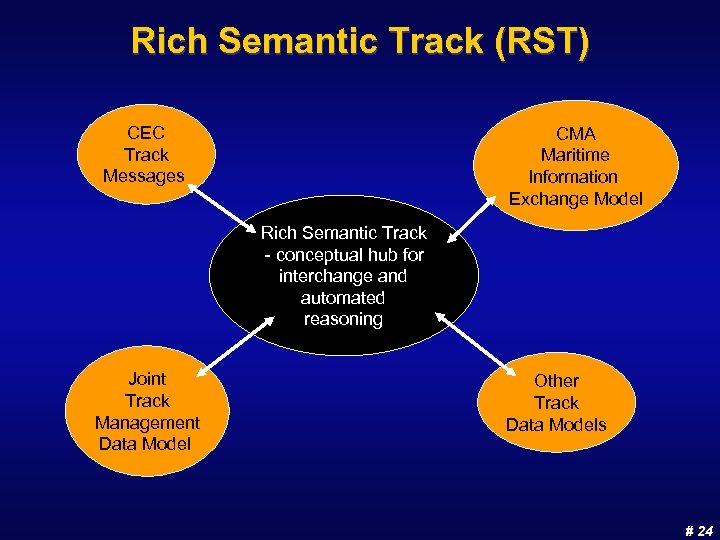
Rich Semantic Track (RST) CEC Track Messages CMA Maritime Information Exchange Model Rich Semantic Track - conceptual hub for interchange and automated reasoning Joint Track Management Data Model Other Track Data Models # 24
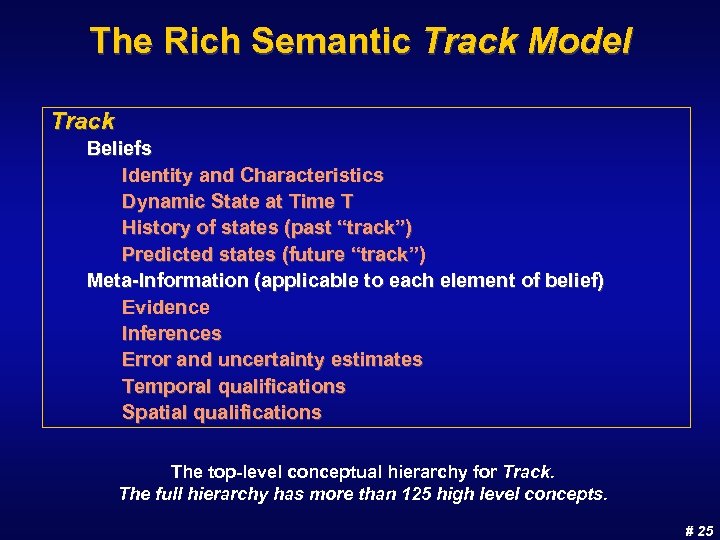
The Rich Semantic Track Model Track Beliefs Identity and Characteristics Dynamic State at Time T History of states (past “track”) Predicted states (future “track”) Meta-Information (applicable to each element of belief) Evidence Inferences Error and uncertainty estimates Temporal qualifications Spatial qualifications The top-level conceptual hierarchy for Track. The full hierarchy has more than 125 high level concepts. # 25

CEC/VIRT Project n Investigated mapping of CEC track data to RST conceptual model n Constructed various RST representations for software and web-based implementations u Formal logic representation for automating mappings across track data models u Semantic Web representations for web-based data interchange and machine reasoning n Constructed various web-based expressions of COIs # 26
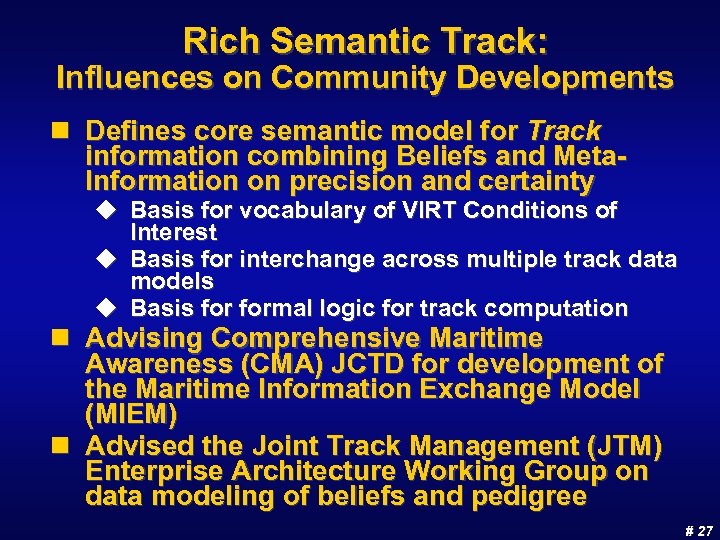
Rich Semantic Track: Influences on Community Developments n Defines core semantic model for Track information combining Beliefs and Meta. Information on precision and certainty u Basis for vocabulary of VIRT Conditions of Interest u Basis for interchange across multiple track data models u Basis formal logic for track computation n Advising Comprehensive Maritime Awareness (CMA) JCTD for development of the Maritime Information Exchange Model (MIEM) n Advised the Joint Track Management (JTM) Enterprise Architecture Working Group on data modeling of beliefs and pedigree # 27
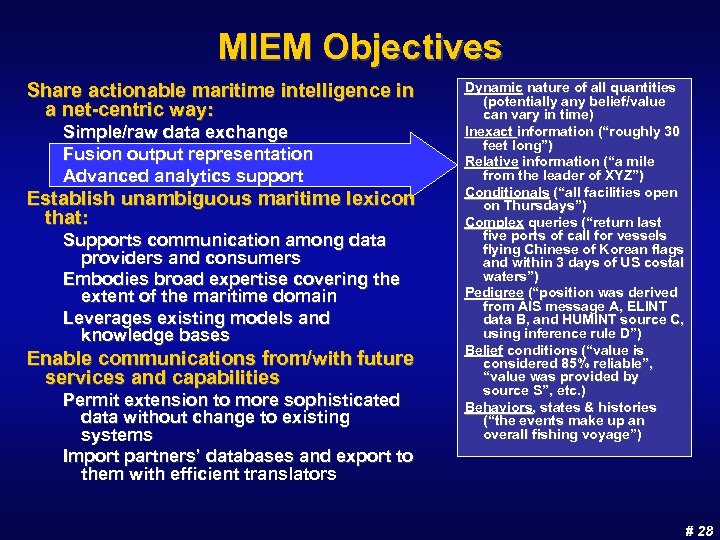
MIEM Objectives Share actionable maritime intelligence in a net-centric way: Simple/raw data exchange Fusion output representation Advanced analytics support Establish unambiguous maritime lexicon that: Supports communication among data providers and consumers Embodies broad expertise covering the extent of the maritime domain Leverages existing models and knowledge bases Enable communications from/with future services and capabilities Permit extension to more sophisticated data without change to existing systems Import partners’ databases and export to them with efficient translators Dynamic nature of all quantities (potentially any belief/value can vary in time) Inexact information (“roughly 30 feet long”) Relative information (“a mile from the leader of XYZ”) Conditionals (“all facilities open on Thursdays”) Complex queries (“return last five ports of call for vessels flying Chinese of Korean flags and within 3 days of US costal waters”) Pedigree (“position was derived from AIS message A, ELINT data B, and HUMINT source C, using inference rule D”) Belief conditions (“value is considered 85% reliable”, “value was provided by source S”, etc. ) Behaviors, states & histories (“the events make up an overall fishing voyage”) # 28
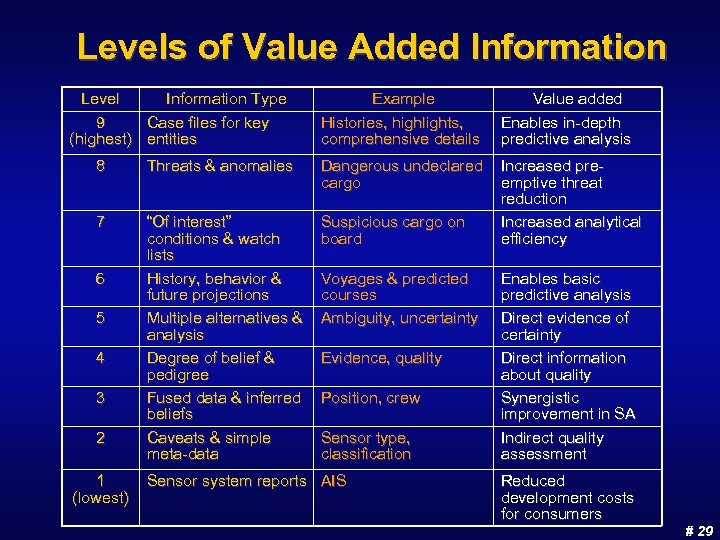
Levels of Value Added Information Level Information Type 9 Case files for key (highest) entities Example Histories, highlights, comprehensive details Value added Enables in-depth predictive analysis Increased preemptive threat reduction Increased analytical efficiency 8 Threats & anomalies Dangerous undeclared cargo 7 “Of interest” conditions & watch lists History, behavior & future projections Multiple alternatives & analysis Degree of belief & pedigree Fused data & inferred beliefs Caveats & simple meta-data Suspicious cargo on board 6 5 4 3 2 1 (lowest) Voyages & predicted courses Ambiguity, uncertainty Evidence, quality Position, crew Sensor type, classification Sensor system reports AIS Enables basic predictive analysis Direct evidence of certainty Direct information about quality Synergistic improvement in SA Indirect quality assessment Reduced development costs for consumers # 29
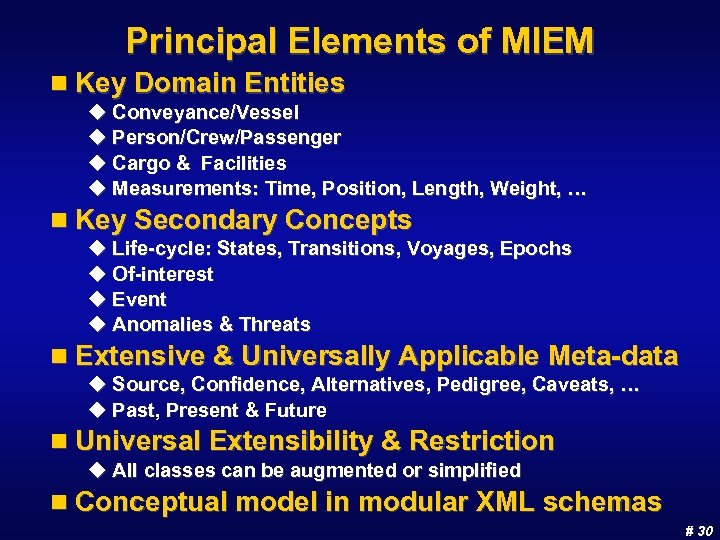
Principal Elements of MIEM n Key Domain Entities u Conveyance/Vessel u Person/Crew/Passenger u Cargo & Facilities u Measurements: Time, Position, Length, Weight, … n Key Secondary Concepts u Life-cycle: States, Transitions, Voyages, Epochs u Of-interest u Event u Anomalies & Threats n Extensive & Universally Applicable Meta-data u Source, Confidence, Alternatives, Pedigree, Caveats, … u Past, Present & Future n Universal Extensibility & Restriction u All classes can be augmented or simplified n Conceptual model in modular XML schemas # 30
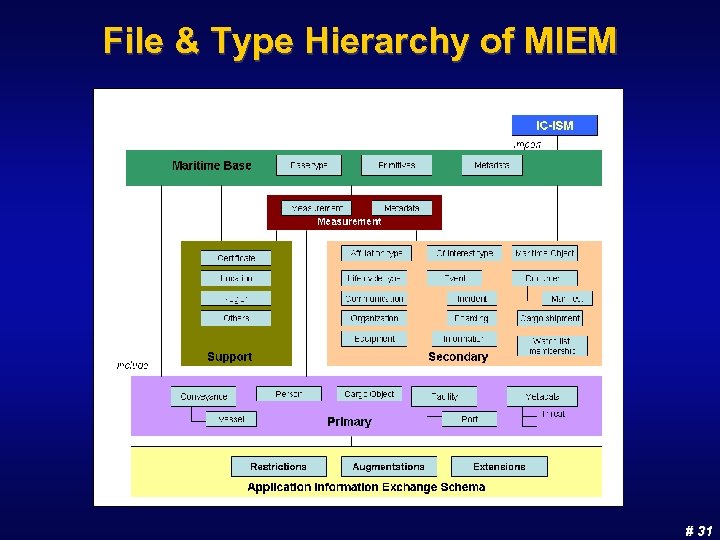
File & Type Hierarchy of MIEM # 31
Basis for Further Research, Development and Experimentation n Refine the RST model based on applications in CEC, CMA, and JTM domains n Continue development of a higher order abstract formalization of RST (formal theory of Track) for extended reasoning capabilities and cross-domain mappings n Refine expressions of RST concepts using Semantic Web standards to promote data interchange and automated interpretation in the GIG architecture n Continue integration of software implementations of RST into VIRT/CEC simulation framework for test and experimentation # 32

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration # 33
Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring n Strong semantic representations of Track data improve automated search, information filtering and reasoning n Improved computer interpretation and processing of data provides better information products and reduces human processing load n Semantics of military orders implies critical conditions of interest – automated derivation of COIs from orders creates valued information flows # 34
Condition Monitoring is Key n Conditions of Interest (COIs) u Computable expressions (“continuous queries”) u Describe critical assumptions (like CCIRs) u Depend on operator’s evolving context ¦ Usually reflects phase of a mission & current status n High-value events are detected u u Data describing the event match the COI The event is “news” The COI assures the event is still “relevant” Bits reporting the event flow with priority n Low-value data does not flow u Generally relevant data not matching a COI u Repeated and redundant data, not newsworthy # 35

Outline n Overall Vision: Model-based Communication Networks, VIRT, and Rich Semantic Track n CEC/VIRT Project Results and Accomplishments n Rich Semantic Track Definition and Influence on Community Developments n Semantic Modeling and Condition Monitoring: Making Information Delivery More Precise and Reducing Work Load n Opportunities for Further Collaboration # 36

Opportunities for Further Collaboration (1) n Recommended next steps for CEC & IWS u Develop and implement VIRT principles inside the CEC network and SIAP (e. g. , variable length messages sending only message fields that have significantly changed value) u Develop & deliver VIRT track data using COIs to demonstrate timely sharing of valued info u Spearhead development of rich track model for SIAP u Develop enhanced toolkit for and methods for using a rich semantic track model ¦ Semantic V&V ¦ Interface & service code generators ¦ Track storage & query using XML ¦ COI specification, event computing, and AAR learning # 37

Opportunities for Further Collaboration (2) n Recommendation for JTM Enterprise Architecture Working Group u Examine MIEM products of the CMA JCTD u Identify common concepts and model components u Collaborate in developing interchange mechanisms for passing data between the models # 38

Opportunities for Further Collaboration (3) n Requested Funding for NPS u Extend formalization of RST for further experimentation ¦ COI expressions ¦ Computing with uncertainty ¦ Intermediary for automated exchange of data across multiple track representations (MIEM, JTM, others) u Research automated derivation of COIs from plans and orders u Investigate Web-based techniques to create smart push of valued information from autogenerated COIs # 39

Conclusion n New problems & opportunities combine to change our concept of “collaborative communication networks” n Humans must use computers to reduce information glut n Collaborators need to employ common models to share model state n Operators and domain practitioners will use semantic technologies to create and evolve the needed models n Each consumer’s plans and beliefs determine the value of information n Computers can implement knowledge of decisionmakers and current state to determine the flow of bits n Significant increases in productivity will result # 40
a43807066a928b6a8815e779901c834d.ppt