
MODAL VERBS Must / have to / may / might / should / ought to / needn’t / will

Obligation / necessity You must take your medicine. You have to / need to take your medicine. You should take your medicine.

Must / should present or future Have to in all tenses I had to study for the test yesterday. I will have to find a new house soon.

Lack of necessity I don’t have / don’t need to get up early today. I needn’t get up early today.

Prohibition You mustn’t/ can’t/ may not smoke in the hospital.

advice

Ability / inability Present can – can’t Past could- couldn’t He can play the violin. He could write before he started school. But They were able to find the street although they didn’t have a map.

In all tenses be able to He will be able to help us tomorrow. Getting the job requires being able to speak Chinese. You should be able to buy a car soon.

Possibility It may / might / can / could rain later.

Permission May / Can / Might / Could I go out ?

Request Can / Could / Will / Would you help me with the bags, please?

certainty It must be abandoned. It can’t / couldn’t be inhabited.

Offer Shall /May I help you?

prediction The concert should / ought to / will start soon.

PAST Modal + have + past participle

certainty He can’t have studied.

prediction Peter hasn’t arrived yet. He may / might / could have missed the bus.

Expectations not fulfilled I could have done better. I should have tried harder. I shouldn’t have made that stupid mistake.

I would have bought the shoes, but I didn’t have enough money.

Everything went fine. I needn’t have worried so much.
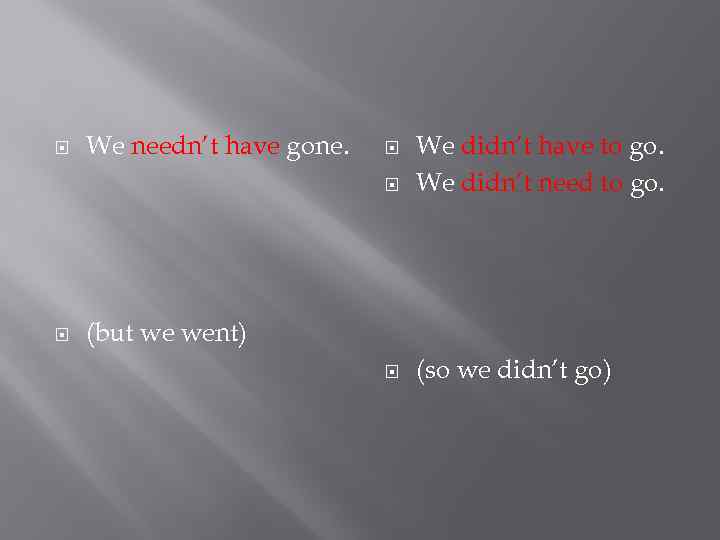
We needn’t have gone. We didn’t have to go. We didn’t need to go. (so we didn’t go) (but we went)