17b8a5d3ea9b301ef1c615f5a2bf5194.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29


MODAL VERBS • CAN • COULD • MAY • MIGHT • MUST • SHOULD • OUGHT TO • NEED • WOULD • SHALL • WILL

USE: • ESPRIMERE UNA CAPACITà: I can play tennis So giocare a tennis • CHIEDERE INFORMAZIONI: Where can I get a map of the town? Dove posso trovare una piantina della città? ESPRIMERE POSSIBILITà O DARE INFORMAZIONI: In Dublin you can meet a lot of tourists A Dublino si possono incontrare molti turisti

• CHIEDERE QUALCOSA A QUALCUNO: Can I have a drink, please? Posso avere qualcosa da bere, per favore? • OFFRIRE IL PROPRIO AIUTO: Can I help you? Posso aiutarti? • PER PARLARE DI Ciò CHE è PERMESSO O NO: In Britain you can leave school at 16 In Gran Bretagna si può lasciare la scuola a sedici anni IN QUEST’ULTIMO CASO SI Può USARE ANCHE: Be allowed to Es. In Britain you aren’t allowed to drive at 16

VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they can swim NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they cannot/can’t go QUESTIONS Can I/You/he/she/it/we/they play the guitar

ATTENTION • La forma can è uguale per tutte le persone • E’ sempre seguito dalla forma base del verbo (senza il to) • È utilizzato solo al presente, per costruire gli altri tempi si utilizza: be able to

COULD (POTREBBE) corrisponde al passato e al condizionale di CAN USE: • ESPRIMERE UNA POSSIBILITA’ O UNA PROBABILITA’ INCERTA You could be happy. Potresti essere felice • ESPRIMERE UN TENTATIVO D’INDOVINARE QUALCOSA That mobile phone could be Pete’s. Quel cellulare potrebbe essere di Pete. • ESPRIMERE CAPACITA’ E POSSIBILITA’ DEL PASSATO. She couldn’t get the bus yesterday. Non ha potuto prendere l’autobus ieri.

• ESPRIME INCERTEZZA • SI USA AL TEMPO PRESENTE • SI TRADUCE CON: PUO’ DARSI CHE ES. You may be going on a trip soon. Può darsi che presto tu faccia un viaggio

• ESPRIME INCERTEZZA • SI USA AL TEMPO CONDIZIONALE • SI TRADUCE: POTREBBE DARSI CHE ES. It might rain Potrebbe darsi che piove

USE: • DARE UN ORDINE: You must stay in class during the break. Dovete restare in classe durante l’intervallo. • DIRE CIO’ CHE è PRESCRITTO DALLA LEGGE O DA UN REGOLAMENTO: You must drive on the left in Britain. In Gran Bretagna si deve tenere la sinistra giudando. • ESPRIMERE UN OBBLIGO O UNA NECESSITA’ PERSONALE: I mustn’t be so lazy. Non devo essere così pigro.

• DARE UN CONSIGLIO O UN SUGGERIMENTO: You must read this book Devi leggere questo libro. • RIFERIRE OBBLIGHI CHE DERIVANO DA AVVISI O ANNUNCI PUBBLICI: Patients must not leave the hospital without permission. I pazienti non devono lasciare l’ospedale senza autorizzazione.

VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they must study NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they must not/mutn’t go QUESTIONS Must I/You/he/she/it/we/they study?

ATTENTION La forma must è uguale per tutte le persone E’ sempre seguito dalla forma base del verbo (senza il to) È utilizzato solo al presente MUST può essere sostituito da HAVE TO: • Verbo ordinario • Traduce tutti i tempi indica dovere, obbligo e necessità nella forma affermativa • Nella forma negativa indica non è necessario Es. You don’t have to get a visa to go to Britain. Non è necessario chiedere il visto per andare in Gran Bretagna

SHOULD corrisponde al condizionale di “DOVERE”. USE: • CHIEDERE E DARE CONSIGLI O PARERI • DIRE QUAL E’ LA COSA MIGLIORE DA FARE ES. You shouldn’t go out tonight Non dovresti uscire stasera.

ATTENTION Should è un verbo modale quindi: • La forma è uguale per tutte le persone • È sempre seguito dalla forma base del verbo (infinito senza il to) VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they should study NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they should not/shouldn’t go QUESTIONS Should I/You/he/she/it/we/they study?

OUGHT TO ha un significato simile a should e corrisponde al condizionale di dovere. Usa ought to invece di should per dire qual è la cosa migliore da fare, cioè per esprimere un consiglio piuttosto che un dovere. ES. We ought to go home now. Dovremmo andare a casa adesso. ATTENTION!!! • E’ uguale per tutte le persone • È sempre seguito dalla forma base del verbo(senza il to)

VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they ought to go NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they ought not to go QUESTIONS Ought I/You/he/she/it/we/they to go?

Il verbo NEED è un verbo particolare detto semi-modale, perché viene utilizzato sia come verbo modale che come verbo non modale. Assume un significato diverso nelle due forme, ma spesso i due usi si sovrappongono. NEED-MODAL VERB È raramente utilizzato in forma affermativa. Do you think I need wear a coat today? Pensi che io debba indossare (= sia necessario che io indossi)un cappotto oggi? L’espressione do you think che precede I need rende la frase interrogativa. I don’t suppose you need tell him the truth. Non credo che sia necessario che tu gli dica la verità. L’espressione I don’t suppose rende la frase negativa.

TO NEED-MAIN VERB Nel significato di aver bisogno di… si utilizza il verbo non modale to need. È un verbo regolare, il cui paradigma è need – needed. Può essere coniugato in tutti i tempi verbali, ma non è utilizzato nella –ing form. Alla terza persona singolare del Simple Present prende normalmente la s. Prende normalmente l’ausiliare do / does e did al Simple Present ed al Simple Past. È seguito dall’Infinito (con to). I need to buy some fruit for dinner. Ho bisogno di comperare della frutta per cena. Do you need any money? Hai bisogno di soldi?

WOULD non corrisponde a un verbo italiano. Si usa per lo più per formare il condizionale. VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they would/ ’d go NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they would not/wouldn’t go QUESTIONS Would I/You/he/she/it/we/they go? RICORDA: • WOULD è un verbo modale • La forma è uguale per tutte le persone • È sempre seguito dalla forma base del verbo (senza il to)
USAGE • CONDIZIONALE They would choose another film. Avrebbero scelto un altro film. • NEL DISCORSO INDIRETTO PER TRASFORMARE UN DISCORSO DIRETTO CON WILL Jenny: ‘I will come back at three’ Jenny said she would come back at three’ Jenny disse che sarebbe tornata alle tre. • WOULD + LIKE PER ESPRIMERE IL CONDIZIONALE DI ‘VOLERE’ E ‘PIACERE’ I’d like a coffe Vorrei un caffè

USAGE: • PER OFFRIRE QUALCOSA O PER PROPORRE QUALCOSA A QUALCUNO: Shall we go home? Andiamo a casa? ATTENTION!!! Non usare shall per accettare o rifiutare le offerte e le proposte fatte. ES. Shall we watch tv? Guardiamo la tv? Yes, good idea. Si ottima idea. NO: Yes, we shall • USA (WHAT) SHALL+SOGGETTO+ FORMA BASE PER CHIEDERE UN CONSIGLIO A QUALCUNO: What shall we go and see? Cosa andiamo a vedere? SHALL E’ UN VERBO MODALE, QUINDI E’ UGUALE PER TUTTE LE PERSONE ED E’ SEGUITO DALLA FORMA BASE DEL VERBO (SENZA IL TO)

WILL NON CORRISPONDE A UN VERBO ITALIANO. SI USA PER LO PIU’ PER FORMARE IL FUTURO, NEI QUI CASI ELENCATI: • FARE UNA PREVISIONE SUL FUTURO The shops will be crowded on Saturday. I negozi saranno affollati il sabato • EPRIME UNA DECISIONE IMMEDIATA I’m tired. I think I’ll go to bed. Sono stanca. Penso che andrò a letto • OFFRIRTI DI FARE QUALCOSA PER GLI ALTRI I’ll make a coffè. Ti faccio un caffè.

• FARE UNA PROMESSA I promise I’ll meet you tomorrow after school. Ti prometto che ci vedremo domani dopo scuola • FARE PREVISIONI METEREOLOGICHE It will be cold tomorrow. Domani farà freddo.

VERB TABLES POSITIVE: I/You/he/she/it/we/they will go NEGATIVE I/You/he/she/it/we/they will not/won’t go QUESTIONS Will I/You/he/she/it/we/they go?
I verbi modali in inglese non hanno alcuni modi e tempi (vengono sostituiti da altri verbi) e presentano delle particolari caratteristiche: - Sono invariabili - Non usano l’ausiliare nelle forme interrogativa, negativa e interrogativo-negativa - I verbi che li seguono sono all’infinito senza il to (ad eccezione di ought) - Non sono mai seguiti da un complemento oggetto
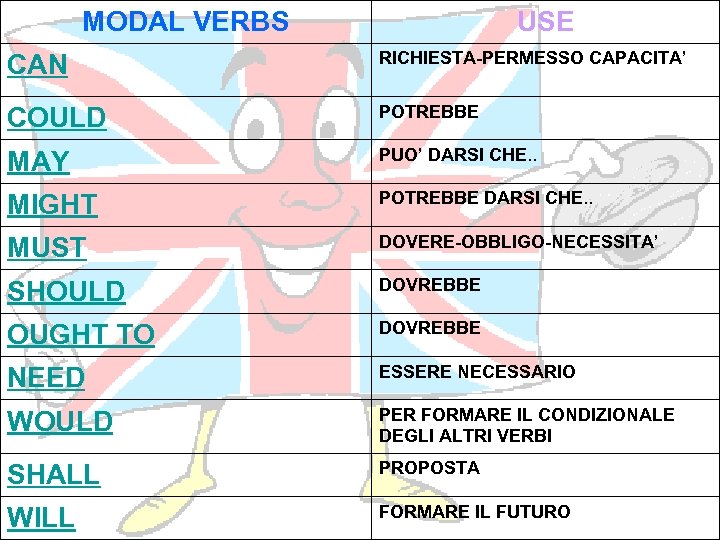
MODAL VERBS USE CAN RICHIESTA-PERMESSO CAPACITA’ COULD POTREBBE MAY PUO’ DARSI CHE. . MIGHT POTREBBE DARSI CHE. . MUST DOVERE-OBBLIGO-NECESSITA’ SHOULD DOVREBBE OUGHT TO DOVREBBE NEED ESSERE NECESSARIO WOULD PER FORMARE IL CONDIZIONALE DEGLI ALTRI VERBI SHALL PROPOSTA WILL FORMARE IL FUTURO

FONTI SCRITTE: • Grammatica inglese Nardella • www. english gratis. com • Libro “Right Now” • Appunti Prof. Mossuto FONTI AUDIO: • ARE YOU IN LOVE, BACK TO LIFE (GIOVANNI ALLEVI) VOCE: • PASQUALE PISANI

LICEO SCIENTIFICO “ETTORE MAJORANA” Via Platone, 11 92100 Agrigento tel. 092221940 Classe: 2°G : Realizzazione: alunna Assello Clara ANNO SCOLASTICO 2009/10
17b8a5d3ea9b301ef1c615f5a2bf5194.ppt