a9baa4bea3e4a4bebb58038d679a5294.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

MOBILE RFID PRIVACY PROTECTION Katayoon Moazzami & Debashis Roy

Outline Introduction Mobile RFID Components Architecture Privacy Issues in RFID Proposed Solutions for Privacy Issues in RFID Privacy protection using Mobile Agent Another Privacy Protection Scheme for Mobile RFID Comparison of MARP and the Other Method for RFID Privacy Protection Conclusion and future work
Introduction RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) is an automatic contactless identification system It is based on EPC (Electronic product code) It uses RF signal for communication can be a good substitute for barcode system used in manufacturing, supply chain management and inventory control

Papers that will be Discussed 1) H. Lee, J. Kim. "Privacy Threats and Issues in Mobile RFID. " The First International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security (ARES '06), 2006. 2) S. C. Kim, S. S. Yeo, S. K. Kim. "MARP: Mobile Agent for RFID Privacy Protection. " 7 th Smart Card Research and Advanced Application IFIP Conference (CARDIS '06), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2006, pp. 300 -312. 3) I. J. Kim, E. Y. Choi, D. H. Lee. "Secure Mobile RFID System Against Privacy and Security Problems. " Third International Workshop on Security, Privacy and Trust in Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Sec. Per. U’ 07), 2007, pp. 67 -72. 4) Radio-frequency identification, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rfid

Mobile RFID “Mobile RFID (M-RFID) can be defined as services that provide information on objects equipped with an RFID tag over a telecommunication network” - C. Seidler, “RFID Opportunities for mobile telecommunication services”, ITU-T Lighthouse Technical Paper, May 2005. Reader is embedded in a mobile device
Components of Mobile RFID System RFID Tag Consists of two parts Microchip Antenna Three kinds of tags Passive Active Semi-passive Use EPC (Electronic Product Code) structure to store information
Components of Mobile RFID System (contd. ) Mobile Reader Base Station Manages communication among the reader and the servers Network Servers Object Information Server (OIS) Contains Object information about an object Name Server (ONS) Contains the URL of OIS
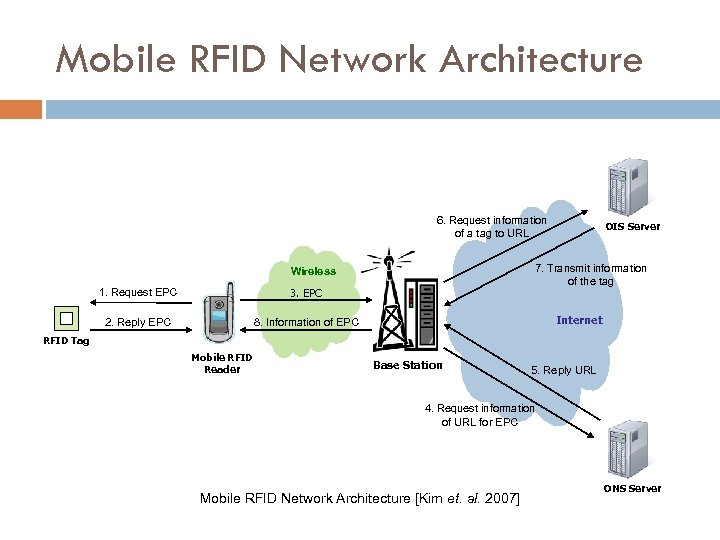
Mobile RFID Network Architecture 6. Request information of a tag to URL 7. Transmit information of the tag Wireless 1. Request EPC 3. EPC 2. Reply EPC OIS Server 8. Information of EPC Internet RFID Tag Mobile RFID Reader Base Station 5. Reply URL 4. Request information of URL for EPC Mobile RFID Network Architecture [Kim et. al. 2007] ONS Server

Mobile RFID Network Architecture A mobile reader requests EPC from a tag The tag sends EPC to the mobile reader The mobile reader sends the received EPC to a base station The base station requests URL of a server which includes information of EPC to ONS server sends the requested URL to the base station Using the received URL the base station requests information of EPC from OIS server sends information of EPC to the base station The base station sends information of EPC to the mobile reader

Privacy Issues in RFID Traceability Information Leakage Gathering information about user without authorization Impersonation Tracking the movement of an user or an object Acting as a legitimate user by making a clone tag Additional Privacy Issues for Mobile RFID Reading range of the tag increases Privacy of the reader carrying user

Proposed Solutions for Privacy Issues in RFID The Kill Command Tag password tag can be password protected Encryption Deactivates the tag for further reading Encryption of tag data using cryptography Proxying Approach An additional mobile device is used as proxy Reader communicates with tag through the proxy Blocking Uses a privacy bit to restrict public scanning of the tag
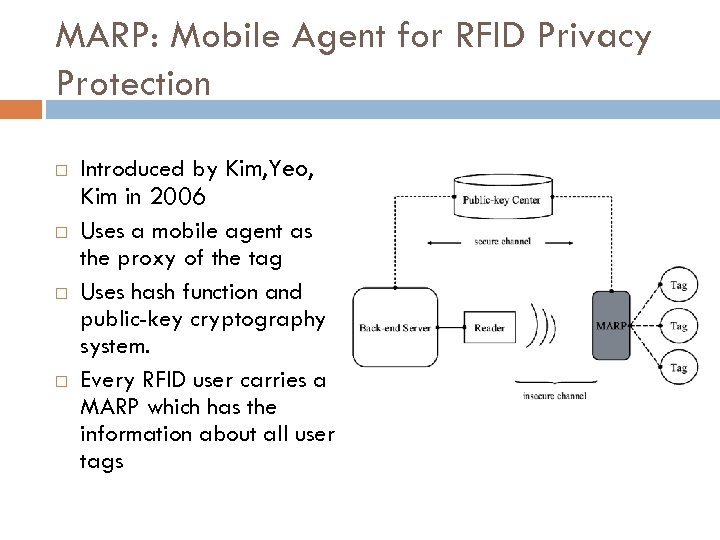
MARP: Mobile Agent for RFID Privacy Protection Introduced by Kim, Yeo, Kim in 2006 Uses a mobile agent as the proxy of the tag Uses hash function and public-key cryptography system. Every RFID user carries a MARP which has the information about all user tags

The MARP Method MARP method has four phases Initial Setup phase Privacy Protection phase (tag sleep mode) Authentication phase (tag wake mode) Main scheme

The MARP Method (contd. ) Initial Setup Phase Every reader belongs to a specific group and has its own group ID and public key Tag has its PIN and tag ID MARP contains the reader’s group ID and public key MARP also has the tag IDs, PIN and hashed secret data The server contains the tag related and the reader group related information

The MARP Method (contd. ) Privacy Protect Phase MARP obtains the secret information of the tag puts the tag into sleep mode communicates with the reader on behalf of the tag after authenticating the reader Authentication Phase Server checks the validity of tag
The MARP Method (contd. ) Main Scheme The authentication between the tag and MARP, between the MARP and the reader and between the server and tag are done collectively Overall scenario using MARP The PIN of the RFID tag is stored in the shop’s DB after arrival of a good A consumer purchases the good and the PIN of the tag is transmitted to the consumer’s MARP. Some of the tag’s secret information is obtained by the MARP through authentication using the tag’s PIN. The consumer registers the tag and changes the PIN for keeping security. Any reader communicates with the MARP instead of the tag using public key cryptosystem. If the good transferred to another user, the PIN information of the good is sent to the new user. The new user will register the tag and change the PIN.
Analysis of MARP Traceability Only authenticated readers and tags can join the communication A tag uses keyed hash function with different random number in every session (indistinguishable to attackers) Information leakage MARP use public-key system to encrypt data Impersonation MARP only has parts of tag’s information The server authenticates the tag before communication

Another Privacy Protection Scheme for Mobile RFID Introduced by Kim, Choi, Lee in 2007. Reader is embedded in a mobile device carried by the user Uses only Hash function and random number No public key encryption No use of additional proxy device This scheme has three phases: Identification phase Initial setup Privacy protection phase
Another Privacy Protection Scheme for Mobile RFID (contd. ) Identification Phase Mobile reader obtains a certificate Cj from the local server Mobile reader sends a query to the tag along with the certificate The tag sends NID=IDTi h. KTi(Cj) to reader and reader sends NID to the server The server checks whether Cj is valid and sends tag data to the reader. Initial Setup Phase Reader receives a key K from the server This key is used to protect privacy
Another Privacy Protection Scheme for Mobile RFID (contd. ) Privacy Protection Phase The mobile reader generates a random number RRi and sends it to the tag The tag generates another random number RT i and sends PID=IDTi RTi and KID=h. KTi(RRi) RTi to the reader The reader computes RTi = KID h. Kj(RRi) and IDTi=PID RTi and sends IDTi to the server The server sends the tag data to the reader.
Analysis Information leakage The tag uses a random number and hash function to send information to the reader It is almost impossible for the adversary to predict the random number Traceability The reader cannot distinguish between the outputs of the tags around it if it does not have the correct key and random number Impersonation The tag refreshes its random number in each session.
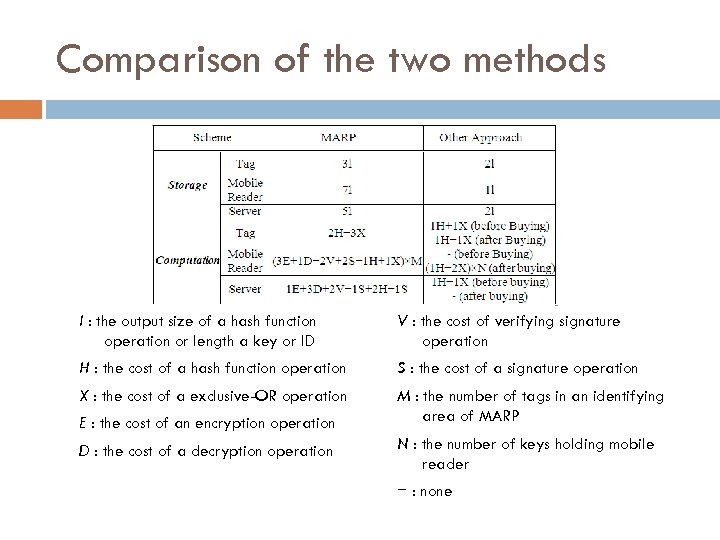
Comparison of the two methods l : the output size of a hash function operation or length a key or ID V : the cost of verifying signature operation H : the cost of a hash function operation S : the cost of a signature operation X : the cost of a exclusive-OR operation M : the number of tags in an identifying area of MARP E : the cost of an encryption operation D : the cost of a decryption operation N : the number of keys holding mobile reader − : none

Our Idea Instead of arbitrarily generating the random number the tag should use a function of its hardware ID (HID) and time(t) to generate the random number (RTi) RTi = f(HIDtag, t) Only the legitimate readers will have the HIDtag. The reader can authenticate the tag.

Conclusion & Future Work Privacy of the reader carrying user ? ?

Thank you for your patience Any questions
a9baa4bea3e4a4bebb58038d679a5294.ppt