01439faa6e10a11a5735617409c7811a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
MOBILE ETHERNET-BASED NETWORKING AND TRANSPORT SERVICES Jenia Feldman Supervisor: Prof. Ran Giladi Communication Systems Engineering Department Ben - Gurion University, Israel

Introduction Research Goals 4 G MEF HETNA Summary
INTRODUCTION Increasing number of mobile users and the evolving of wireless technologies derive the need for more bandwidth. 4 G cellular networks use packet core networks for data services based on L 2 (Ethernet) and L 3 (IP) Carrier Ethernet (standardized by the MEF) is evolving towards being used as access for Mobile Backhaul Recent developments of scalable Ethernet-based network architectures, support traffic engineering, Qo. S/Co. S and mobility The Ethernet technology provides an attractive solution for these bandwidth and performance requirements

RESEARCH GOALS Studying the existing work on the subject of mobile Ethernet-based networking (MEF, Wi. MAX, and LTE) Examining the compatibility of HETNA with 4 G networks protocols HETNA and MEF Mobile Backhaul
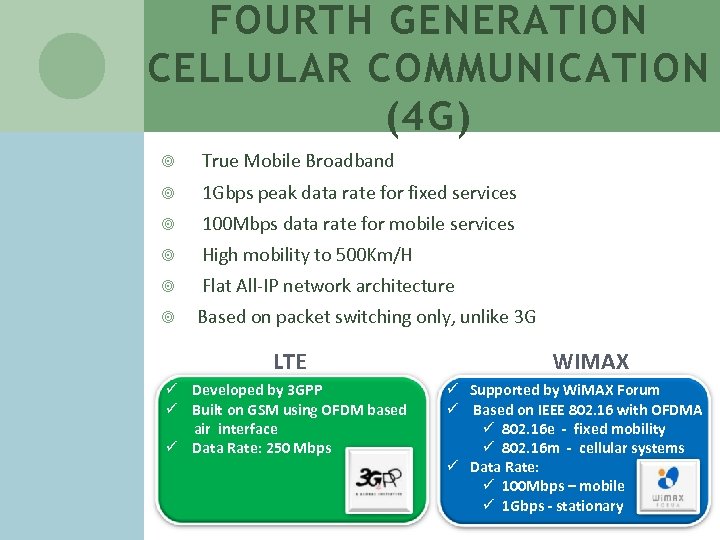
FOURTH GENERATION CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (4 G) True Mobile Broadband 1 Gbps peak data rate for fixed services 100 Mbps data rate for mobile services High mobility to 500 Km/H Flat All-IP network architecture Based on packet switching only, unlike 3 G LTE ü Developed by 3 GPP ü Built on GSM using OFDM based air interface ü Data Rate: 250 Mbps WIMAX ü Supported by Wi. MAX Forum ü Based on IEEE 802. 16 with OFDMA ü 802. 16 e - fixed mobility ü 802. 16 m - cellular systems ü Data Rate: ü 100 Mbps – mobile ü 1 Gbps - stationary
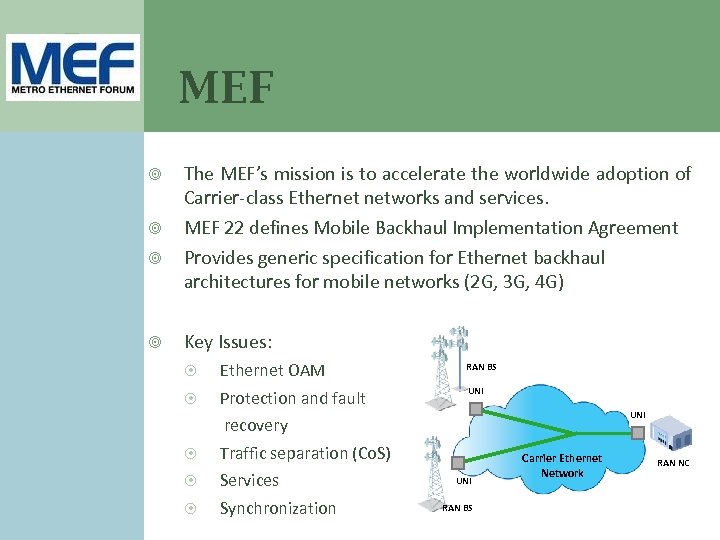
MEF The MEF’s mission is to accelerate the worldwide adoption of Carrier-class Ethernet networks and services. MEF 22 defines Mobile Backhaul Implementation Agreement Provides generic specification for Ethernet backhaul architectures for mobile networks (2 G, 3 G, 4 G) Key Issues: Ethernet OAM RAN BS Protection and fault UNI recovery Traffic separation (Co. S) Services Synchronization UNI RAN BS Carrier Ethernet Network RAN NC
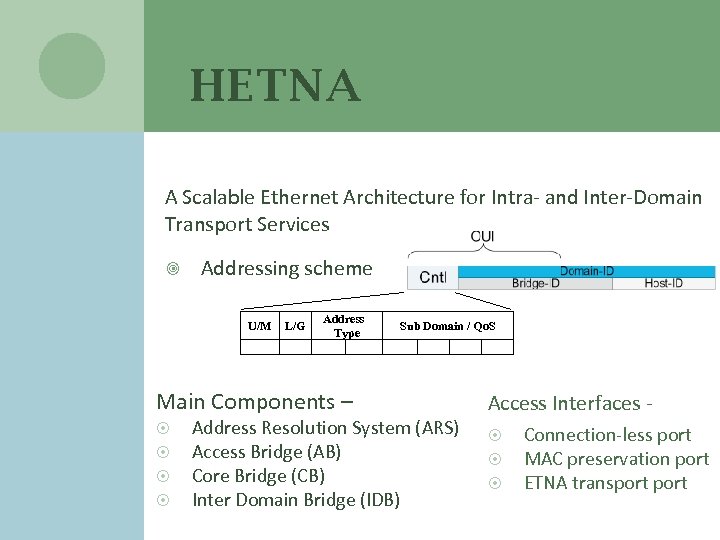
HETNA A Scalable Ethernet Architecture for Intra- and Inter-Domain Transport Services Addressing scheme U/M L/G Address Type Sub Domain / Qo. S Main Components – Access Interfaces - Address Resolution System (ARS) Access Bridge (AB) Core Bridge (CB) Inter Domain Bridge (IDB) Connection-less port MAC preservation port ETNA transport
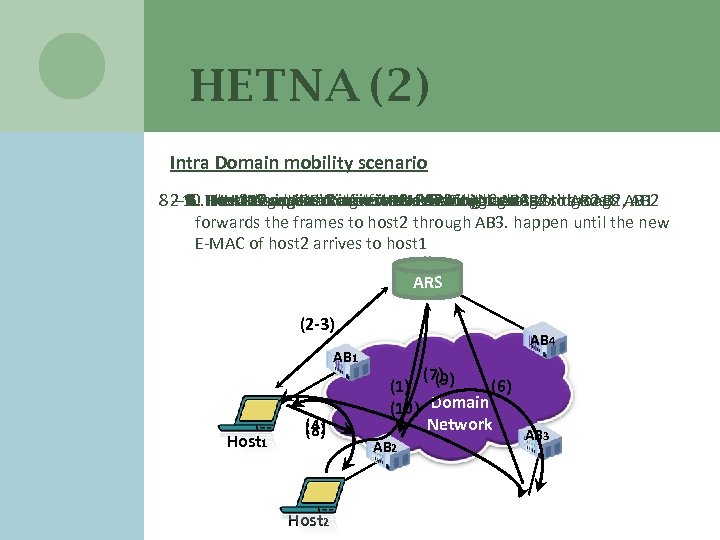
HETNA (2) Intra Domain mobility scenario 8 2 -3. Host 2 changes atoitself the. Host 2 E-MAC AB 3 bridge AB 2, AB 1 – 10. The ARS sends location in Notification between to AB 2 9. Host 1 registers itself resumes directly message the hosts AB 2 7. 6. Host 2 registers areto Host 2 through access 5. Host 1 uses ARP Redirect the ARS through AB 2 4. The communication in AB 3 ARS through address through 1. keeps sending communicating and Host 2 receive detects it forwards the frames to host 2 through AB 3. happen until the new E-MAC of host 2 arrives to host 1 ARS (2 -3) AB 1 Host 1 (4) (8) Host 2 AB 4 (7) (1) (9) (6) (10) Domain Network AB 2 AB 3
SUMMARY Examining the compatibility of HETNA with 4 G networks protocols HETNA and MEF Mobile Backhaul
01439faa6e10a11a5735617409c7811a.ppt