99f6e428c07b3e61b667d933ec1e7b6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Mobile Computing Systems and Application - CSE 598/494 Fall 2011 Sandeep K. S. Gupta School of Computing, Informatics and Decision Systems Engineering Arizona State University

Mobile Computing • What is mobile computing? – Computing that is not obstructed while the location of it changes Mobile computing = + ? • Mobile computing draws from – Wireless communications and networking • Ability to communicate via wireless links – Ubiquitous and pervasive computing • Ability to provide computing anywhere and anytime (ubiquitous), usually in a seamless manner, potentially not perceived (pervasive)

Mobile Computing – Examples • Mobile Medicine 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 911 Call and dispatch Ambulance arrives/departs Closest hospital Access patient records Send vital signs Update patient records Page hospital personnel Order medical supplies

Examples contd… • Party on Friday – Update Smart Phone’s calendar with guests names. – Make a note to order food from Dinner-on-Wheels. – Update shopping list based on the guests drinking preferences. – Don’t forget to swipe that last can of beer’s UPS label. – The shopping list is always up-to-date. – Auto. PC detects a near Supermarket that advertises sales. – It accesses the shopping list and your calendar on the Smart Phone. – It informs you the soda and beer are on sale, and reminds you. that your next appointment is in 1 hour. – There is enough time based on the latest traffic report.

Systems and Applications • Systems Smart phones • Applications – – Mobile Healthcare Environment monitoring Military applications Entertainment Medical Sensors
platforms design and development applications challenges CSE 494/598 Operating Systems HCI Mobile Networks SW devel methods

Definitions – Health n What is health? ¨ Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO)

Definitions – Social Networking n What is social networking? ¨ Social networking is about enabling interactions with individuals who share interests

Definitions – Smartphones n Smartphone ¨ a device that combines the functions of a cellular phone and a handheld computer = + ? n n Characteristics: 5˝-10˝ screen, possible keyboard, cellular capability, embedded operating system, storage, internet applications, organizer, calendar Examples Blackberry ¨ i. Phone ¨ G 1 ¨

Definitions – Mobile Internet Devices n Mobile Internet Device (MID) ¨ a multimedia-capable handheld computer providing wireless Internet access = + ? n Characteristics: 4˝-6˝ screen, no keyboard, near-general purpose O/S, HSDPA capability, no telephony n Examples

Definitions – UMPCs n Ultra-Mobile PCs (a. k. a Netbooks) ¨ n n a portable personal computer (may be a Tablet. PC) of very small factor (5˝-10˝) Characteristics: 5˝-10˝ screen, possible slate design, true general-purpose O/S, wifi/wimax capability Examples Samsung Q 1 ¨ Sony VAIO UX ¨ OQO 02 ¨

Why talk about all the above? n Technology convergence ¨ What technology will survive? n A significant shift in consumer computing since laptops ¨ What will happen to laptops? n Change in application development paradigm ¨ No keyboard, no mouse/pad, small screens

Smart Phone and Health ECG monitoring Heart phone Embryo monitoring i. Phone as a medical device http: //mobihealthnews. com/2580/timeline-the-iphone-as-medical-tool/ Vue. Me: medical imaging Surgical Radiology: Educational App Anxiety Connect: Health + Social Networking

Pervasive Healthcare Use Pervasive Computing for day-to-day healthcare management to enable realtime, continuous patient monitoring EEG EKG BP GPS Mp 3 Camera Sp. O 2 Body Area Network Features v Utilize in-vivo and in-vitro medical sensors Nano-scale Blood Glucose level detector Developed @ UIUC Lifeshirt noninvasive monitoring Developed @ Vivometrics Medical Tele-sensor Can measure and transmit Body temperature Developed @ Oak Ridge National Laboratory PDA/phone Gateway v Physical presence of caregivers required only during emergencies GOAL: Enable independent living, general wellness and disease management. Motion v Mobile patients. No time & space restrictions for Sensor health monitoring Home-based Care Applications v Body Area Network Enabling Technology: Better quality of care and reduced medical errors Sports Health Management Disaster Relief Management v Early detection of ailments and actuation through automated health data analysis Medical Facility Management

Body Area Networks (BAN) • Principal enabling technology for the medical device plane in pervasive health care • Network of wearable or implanted medical devices – Wireless multi-hop communication – Devices can be physiological sensors, environmental sensors, actuators or energy scavenging sources • Base Station – generally a mobile phone acting as a gateway • Heterogeneous hardware and software

Mobile Health Examples • Proactive Health Project @ Intel – Developing sensor network based pervasive computing systems • Managing daily health and wellness of people at homes • Proactively anticipate patient’s need and improve quality of life. • Code Blue Project Sensor network based health monitoring @ Harvard – Developing sensor network based medical applications for: • Emergency Care • Disaster Management • Stroke patient rehabilitation • Ayushman Project @ ASU • Reliable Non-intrusive Secure Real-time Automated health monitoring – E. g. : BP, pulse, Sp. O 2, ECG • Aware Project @ the Center Pervasive Healthcare, University of Aarhus, Denmark. – Applying context aware computing to hospital scenarios – Developing context aware hospital bed, pill box which is aware of its patients. No restriction to mobility of human Mobile phone enables mobility management

Ayushman*: A Pervasive Healthcare System • Project @ IMPACT Lab, Arizona State University Environmental Sensors (Temperature etc) • To provide a dependable, nonintrusive, secure, real-time automated health monitoring. • Should be scalable and flexible enough to be used in diverse scenarios from home based monitoring to disaster relief, with minimal customization. • To provide a realistic environment (test-bed) for testing communication protocols and systems for medical applications. Internet Stargate Gateway External Gateway Central Server Medical Sensors (EKG, BP) controlled By Mica 2 motes Medical Professional Body Based Intelligence Home/Ward Based Intelligence Medical Facility Based Intelligence Vision

Course Goal To understand what are the fundamental challenges in MC and what are some of the solutions towards solving these fundamental challenges

Course Goals - Indirect • To get you a high-paying job • To enrich you with new ideas • To train you in (mobile) systems oriented thinking • To prepare you for research/profession in mobile computing – but more generally – in “adaptive” (nextgeneration) computer systems

Course Pre-req • Knowledge of Computer Networks, Operating Systems, Computer Architecture • Programming experience with Java, C. • Experience with basic operation of embedded systems such as android phones. • Willingness to learn!

Course/Reference Book(s) + Material 1. Fundamentals of Mobile and Pervasive Computing – F. Adelstein, S. K. S. Gupta, G. G. Richard III, and L. Schwiebert – Mc. Graw Hill. – Book Website – Link at bottom of http: //impact. asu. edu • Reference Books: – Principles of Wireless Networks – Pahlavan and Krishnamurty – Mobile Computing- Imielinski and Korth – Protocols and Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks - Karl and Willing – Wireless Sensor Networks – Raghavendra, Znati et al. • Reading List – will be posted on the class web site.

Topics – Tentative List • Mobile Computing Application, Services and Standards – Mobile Info access and dissemination • Sensing (Physiological + Environmental sensing), Communication (Zigbee, Bluetooth, Wi. Fi), Storage (Flash, Ram) – Mobility and Location Management • Connectivity, data access, personalization – Mobile Healthcare • Interfacing mobile phones with physiological sensors, long term monitoring • Wireless Sensor networking, applications and services – Localization • Positioning of sensors, context aware applications – Energy efficient communication duty cycling • Macro Level Issues – Cyber-physical Systems – Energy consumption – Sustainability, Safety, and Security

Course Mechanics • Assignment + Exams + Quizzes: 40% – Exams – take home, Midterm – around 23 Nov 2011 – Assignments –implementation heavy course, first one next class • Paper presentation: 20%, presentation schedule coming soon • Term Project: 40% – In groups of three max, will be formed soon. – Three phases: a) proposal, b) midterm report, and c) final report (counted as the final exam) • Extra: 10% – Self-directed presentation – related to this class

Assignment Schedule • Assignment 1: Android Programming – Write an app in Google phones to develop an UI for patient monitoring • Assignment 2: Android + Sensor Programming – Program sensor to sense accelerometer signals and send to the android phone for display in the UI developed in assignment 1. • Assignment 3: Parallel programming in sensors – Real-time simultaneous sensing, computation and communication • Assignment 4: Patient tracking – Use localization schemes to track a patient in a hospital wearing sensors • Assignment 5: Mobile Healthcare App – Detection of motion artifacts in medical devices using accelerometer • Assignment 6: Energy and Sustainability (optional for undergrads) – Power profiling of sensors and scavenging sources – Heating effects in embedded systems

Distinction between Grad and Undergrad course • Assignment 6 – Extra credit for undergrads – Compulsory for grads

Cheating/Plagarism Policy • Strictly prohibited • See University policy • Minimum punishment – zero in the assignment

“ No Distraction” Policy • No Laptops/Netbooks/Cell Phone/News Papers etc. • Laptops/Netbooks may be permitted – only with instructor’s permission

Class Format • Lecture (5 -75 min) – As class progresses the lecture time will decrease (on average) • One or Two Paper presentation (1/2 hr each) – Starting soon! • 5 min. mid-break – if desired • Note: slides of presenters should be provided to TA one day in advance.

Class Cyberpresence • http: //impact. asu. edu/cse 598 fa 11. html – – Class assignments Slides Reference material Announcement • Visit regularly for latest information

What can you expect from this course? • Lots of in-class/ on-line interaction • Interesting and challenging assignments and exam questions • Reading technical papers – classical as well as state-of-art • Technical Writing – critiquing, summarizing • Help/Tutorials by instructor/Grader on difficult material • And lot more!

Contacting Me or TA • Instructor – Email: sandeep. gupta@asu. edu • Subject line: CSE 494 Fa 11/CSE 598 Fa 11 – – – • Office: BY 522 Phone: 5 -3806 Office Hours: M W 3: 30 -5 pm Call me || come to my office hrs || Set up an appointment http: //impact. asu. edu TA: Ayan Banerjee – Email: abanerj 3@asu. edu – Office BY 517 BD

• What do I do when I am not teaching? – Introduction to IMPACT – Mobile Computing Lab
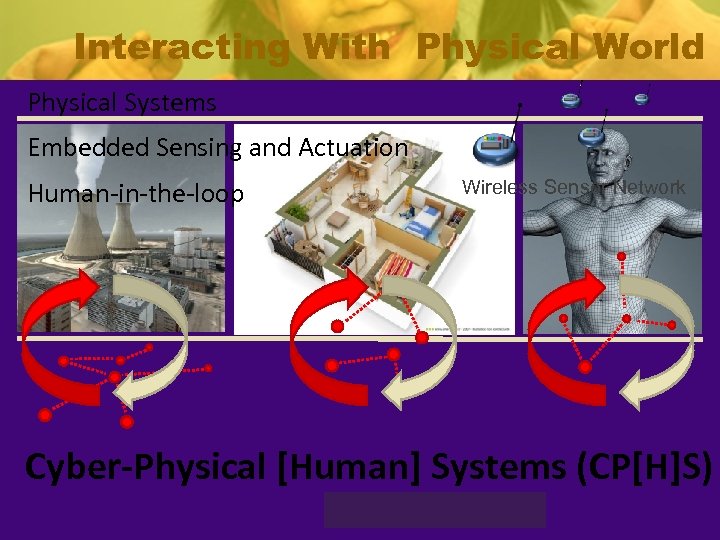
Interacting With Physical World Physical Systems Embedded Sensing and Actuation Human-in-the-loop Wireless Sensor Network Cyber-Physical [Human] Systems (CP[H]S) CSE 420/598 Spring 2007

IMPACT Lab • Dr. Sandeep Gupta @ School of Computing, Informatics and Decision Systems Engineering Use-inspired, Human-centric research in distributed cyber-physical systems Medical Device Safety Analysis Mobile Ad-hoc Networks Pervasive Health Monitoring Criticality Aware. Systems Thermal Management for Data Centers Intelligent Container Collaboration with FDA BEST PAPER AWARD: Security Solutions for Pervasive Health. Care – ICISIP 2006. BOOK: Fundamentals of Mobile and Pervasive Computing, Publisher: Mc. Graw-Hill Dec. 2004 • TCP Co-Chair: • TCP Chair • Area Editor Green. Com’ 07 http: //www. bodynets. org http: //impact. asu. edu/ greencom Email: Sandeep. Gupta@asu. edu Best Researcher Senior Faculty Award

IMPACT Lab Members and Collaborators • Faculty • Sandeep K. S. Gupta (Professor) • Students • • Zahra Abbasi (CSE Phd) Priyanka Bagade (CSE Phd) Ayan Banerjee (CSE Phd) Joshua Fergussen (CSE Phd) Sayan Kole (CSE Phd) Madhurima Pore (CSE Phd) Robin Rose (ME Ms) Wei Wu (CSE Phd) • Collaborators • • • FDA University of Washington Intel Corp. University of Pennsylvania Xerox http: //impact. asu. edu

IMPACT: Research Thrusts • Challenges – Traffic congestion, Energy Scarcity, Climate Change, Medical Cost … • Smart Infrastructure – distributed CPS (Cyber. Physical Embedded System (of systems)) • Criticality (Context)-awareness to enhance dependability (security, safety, reliability) of CPS systems • Unifying Framework to enhance our understanding in developing (energy) efficient, sustainable, assured CPS • Model-based Design and Development to harness complexity (simultaneously ensure safety, security, efficiency etc. ) as well cost. • Enhanced Usability and Interoperability to reduce manageability overhead and enhance

NSF REU • Opportunity for undergraduate students to work closely with impact lab researchers in a funded project • Gain research experience while working on projects of their interest • Contact Dr. Gupta during his office hours for more details

What’s Next? • Chapter 1: Mobile Adaptive Computing • Background survey • Interesting read – – – – Apps Bring Past, Present and Future Into Focus: http: //www. nytimes. com/2011/07/10/nyregion/appsbring-past-present-and-future-into-focus. html? hpw Google, Already Dominant in Mobile Search, Isn’t Resting: http: //www. nytimes. com/2011/04/25/technology/25 mobile. html? _r=1 Your Brain on Computers – Series: http: //topics. nytimes. com/top/features/timestopics/series/your_brain_on_computers/index. html MIT students build mobile applications in 13 weeks: http: //techcrunch. com/2008/12/12/mit-students-build -mobile-applications-in-13 -weeks/ Hal’s MIT Course: Building mobile applications with Android: http: //people. csail. mit. edu/hal/mobile-appsspring-08/ Locale App for Android Phones “Wouldn’t Even Be Possible on the i. Phone, ” Says Winner of $275 K Developer Challenge: http: //www. xconomy. com/boston/2008/10/02/locale-app-for-android-phoneswouldnt-even-be-possible-on-the-iphone-says-winner-of-275 k-developer-challenge/ Power-Hungry Devices: http: //www. nytimes. com/2011/07/05/opinion/05 tue 2. html? src=recg Cellphone Use Tied to Brain Changes: http: //well. blogs. nytimes. com/2011/02/22/cellphone-use-tied-tochanges-in-brain-activity/? hp

Some Quotes from Randy Pausch “The Last Lecture” http: //www. mediabistro. com/galleycat/original/randy-pausch. jpg “Have something to bring to the table, because that will make you more welcome. ” “You’ve got to get the fundamentals down because otherwise the fancy stuff isn’t going to work. “ “The brick walls are not there to keep us out. The brick walls are there to give us a chance to show badly we want something. Because the brick walls are there to stop the people who don’t want it badly enough. ” “Be prepared. Luck is truly where preparation meets opportunity. ”
99f6e428c07b3e61b667d933ec1e7b6c.ppt