ee1358e1d3816fff1318870a10c61c6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 174

MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS

2
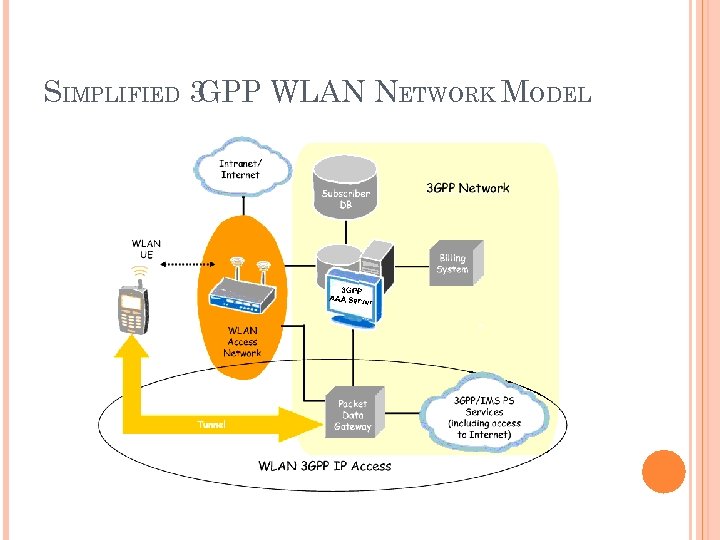
SIMPLIFIED 3 GPP WLAN NETWORK MODEL
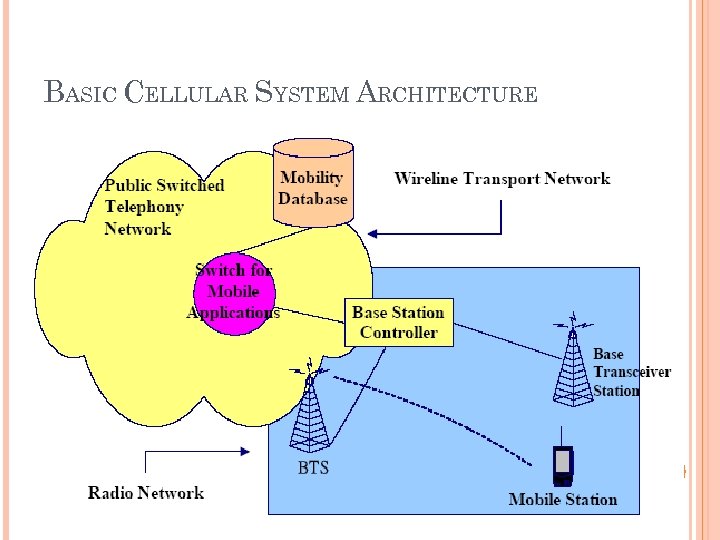
BASIC CELLULAR SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE

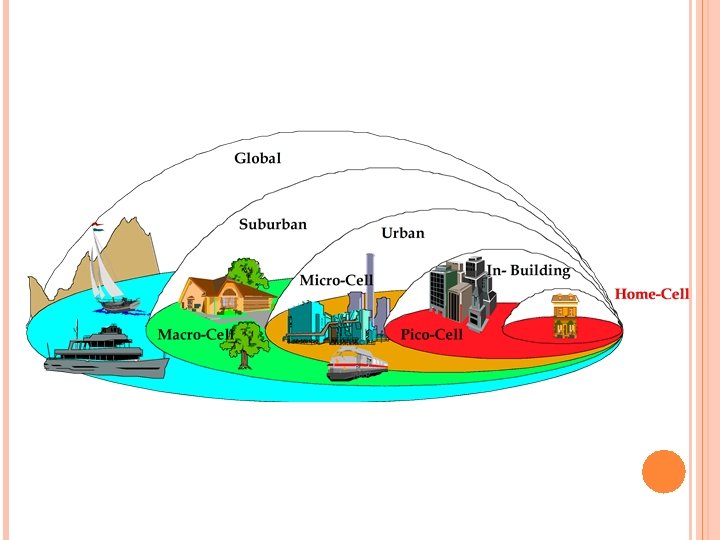
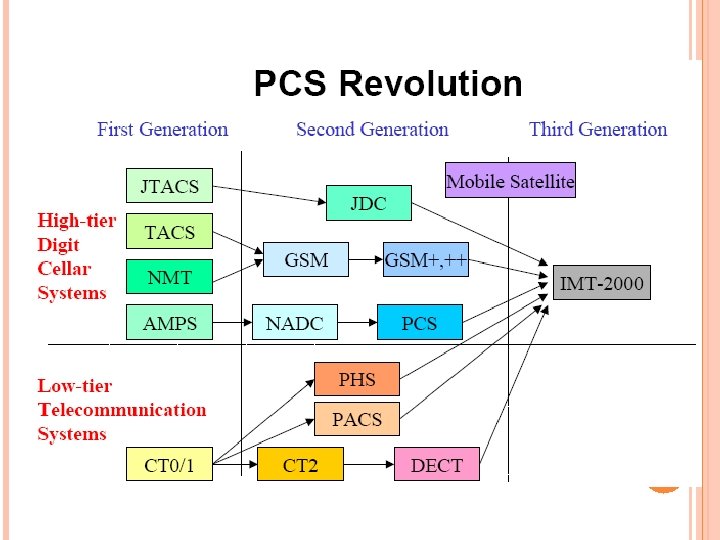
MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Low tier wireless systems High tier cellular telephony

DECT LOW TIER WIRELESS SYSTEMS Low tier cordless telephony CT 2 (Cordless Telephone, Second Generation) DECT (Digital European [Enhanced] Cordless Telephone) Low tier personal communications system (PCS) PHS (Personal Handy phone System) PACS (Personal Access Communications System) PHS

特色 低傳輸功率 適合長時間通話 涵蓋範圍小 基地台數目多 低傳輸延遲 移動範圍小 網路複雜度低 低成本
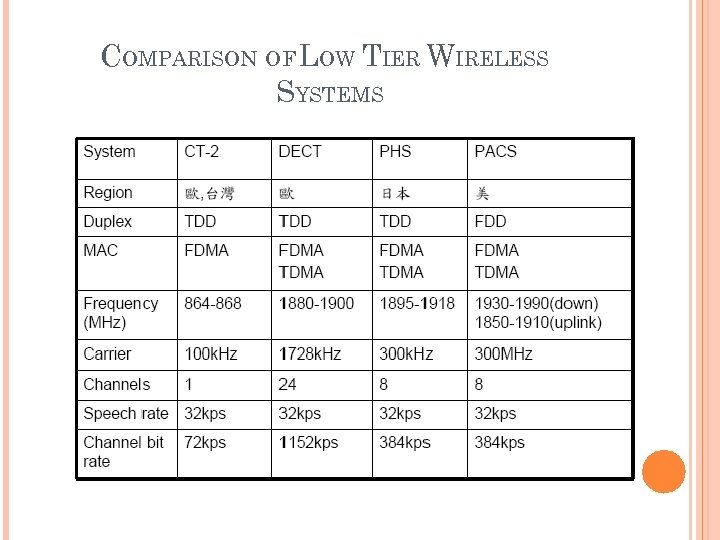
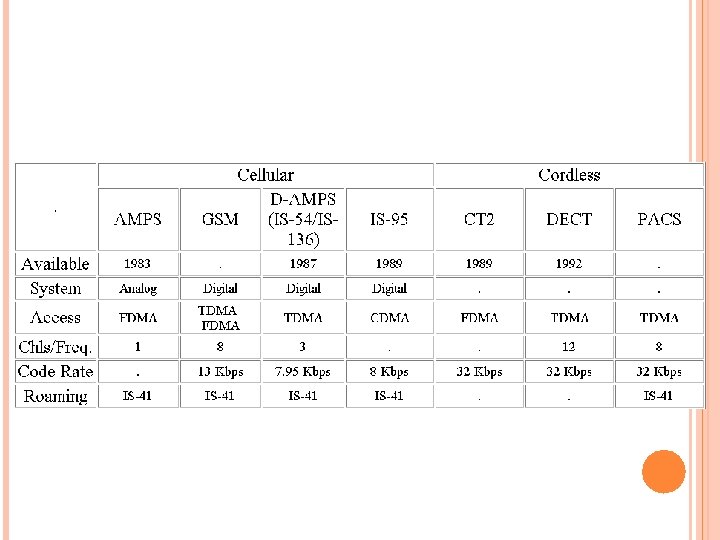
COMPARISON OF LOW TIER WIRELESS SYSTEMS
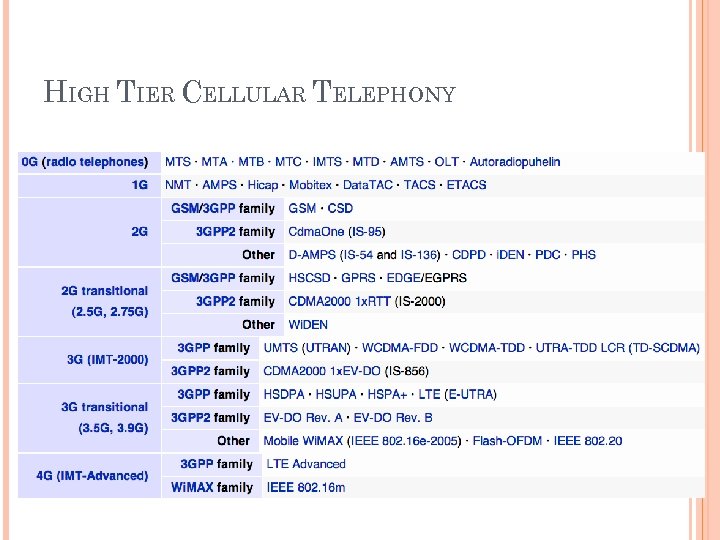
HIGH TIER CELLULAR TELEPHONY

特色 支援手機的高度移動性 涵蓋區域大 基地台和手機使用較高的傳輸功率 手機需要較高的訊號處理功率 通訊網路複雜度高 微細胞(microcell)概念的發展 為增加系統容量(capacity) 微細胞涵蓋區域小 微細胞的基地台建置成本低於大範圍cell的基地台

FEMTOCELL ACCESS TO THECORE MOBILE NETWORK VIA BROADBAND INTERNET
Hierarchical Cell Structure
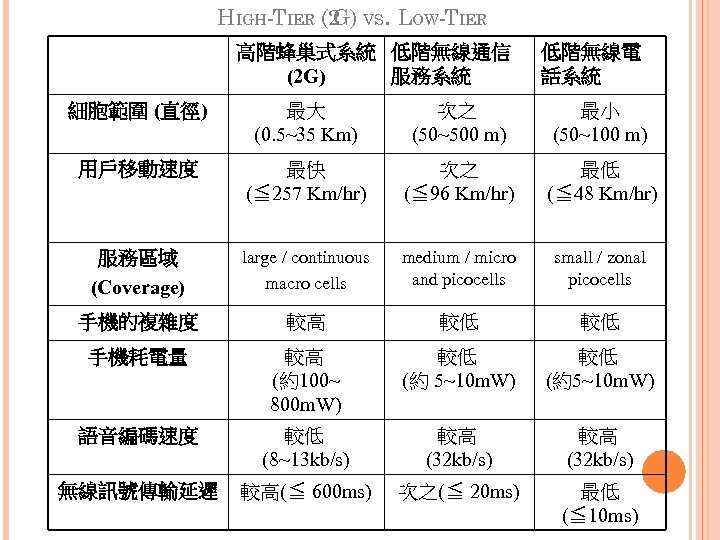
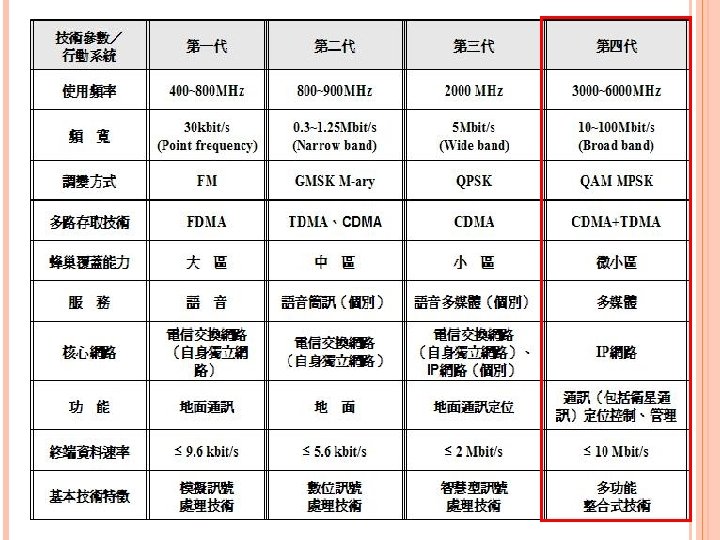
HIGH-TIER (2 VS. LOW-TIER G) 高階蜂巢式系統 低階無線通信 服務系統 (2 G) 低階無線電 話系統 細胞範圍 (直徑) 最大 (0. 5~35 Km) 次之 (50~500 m) 最小 (50~100 m) 用戶移動速度 最快 (≦ 257 Km/hr) 次之 (≦ 96 Km/hr) 最低 (≦ 48 Km/hr) 服務區域 (Coverage) large / continuous macro cells medium / micro and picocells small / zonal picocells 手機的複雜度 較高 較低 較低 手機耗電量 較高 (約100~ 800 m. W) 較低 (約 5~10 m. W) 較低 (約5~10 m. W) 語音編碼速度 較低 (8~13 kb/s) 較高 (32 kb/s) 無線訊號傳輸延遲 較高(≦ 600 ms) 次之(≦ 20 ms) 最低 (≦ 10 ms)
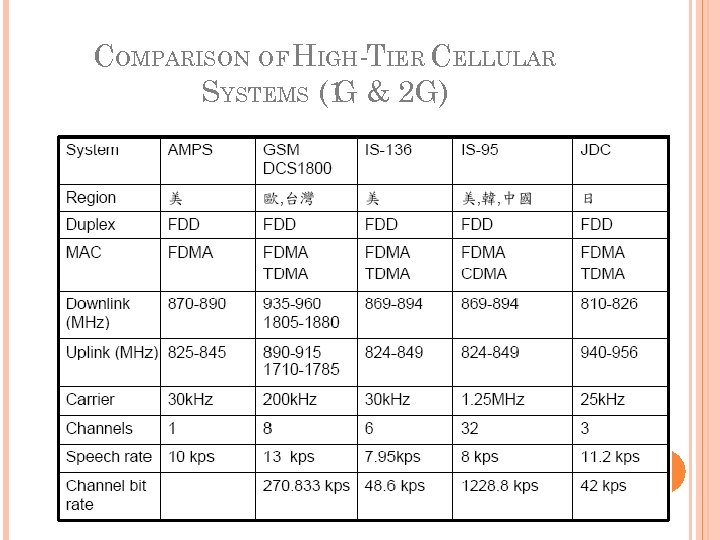
COMPARISON OF HIGH-TIER CELLULAR SYSTEMS (1 & 2 G) G
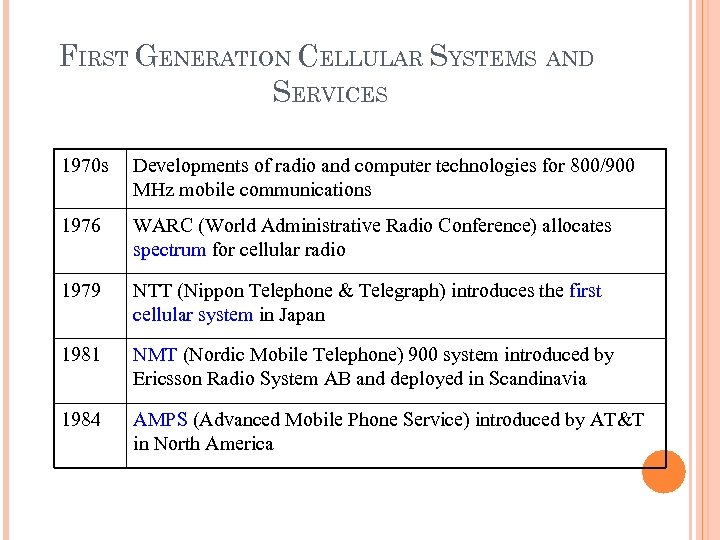
FIRST GENERATION CELLULAR SYSTEMS AND SERVICES 1970 s Developments of radio and computer technologies for 800/900 MHz mobile communications 1976 WARC (World Administrative Radio Conference) allocates spectrum for cellular radio 1979 NTT (Nippon Telephone & Telegraph) introduces the first cellular system in Japan 1981 NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone) 900 system introduced by Ericsson Radio System AB and deployed in Scandinavia 1984 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service) introduced by AT&T in North America

1 G 1980年開始的類比式通訊系統 僅提供「類比語音」的單一服務 類比訊號傳輸 利用聲音所產生的聲波頻率作為傳送方式 通話對方的收話器也依聲波形狀直接接收 類比訊號是連續的,傳送時受到雜訊的干擾,很難保持 波形不失真 很難對訊號做處理及增加系統功能,如AMPS系統使用類 比技術,易被盜拷竊聽

無線電話(cordless telephony) 使用者經由手機收發電話 手機以無線訊號與一固定主機溝通 主機再連至外界公眾交換電話網路(PSTN)或交 換機(PBX) 服務對象:一極小範圍內移動的人 此與作較廣範圍通訊的蜂巢式電話有不同的訴 求族群 針對無線電話所提出的標準有 CT 1、 CT 2、CT 3及數位歐洲無線電訊(DECT)
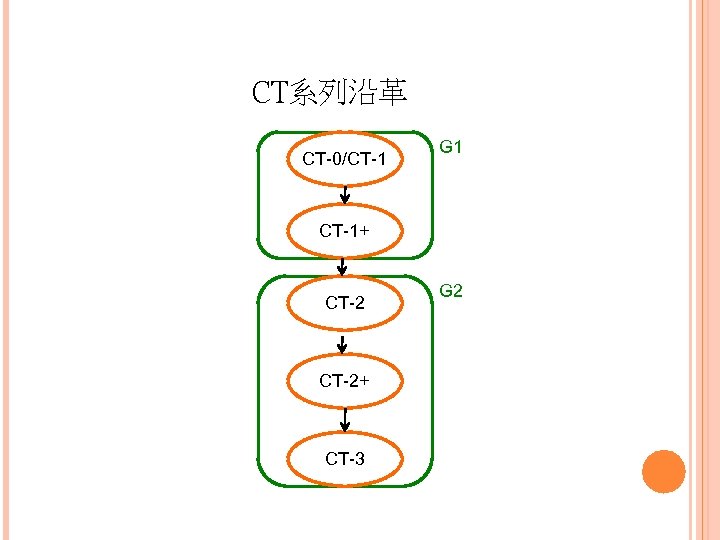
CT系列沿革 CT-0/CT-1 G 1 CT-1+ CT-2+ CT-3 G 2

CT-0 英國發展出MPT 1322 使用類比(analog) 通話品質差 FM (CT-0)標準

CT-1 CEPT (Conference Europeenne des Postes et Telecommunications,歐洲郵電會議)對於高要求而 發展 900 MHz analog FM CT-1 使用FDMA/FDD技術 適於家用場合

CT-1+ 加入Telepoint (遠點)概念,使用於公共場合 Telepoint是一種在主機有效範圍內作收發話的公共進出 方法,結合公共電話與類比無線電話 約在公共基地台 100 m範圍內,可用無線電話撥打 電話出去 不能接收電話 移出基地台範圍,電話就斷線 CT 1(或CT 0)代表第一代無線電話 通常具備兩個無線頻道的類比式無線話機 雖然其可靠度、安全性皆不高且易受干擾、傳送距離 又短,但至少開啟無線電話之先例

AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service) 第一套類比式蜂巢電話系統 1964年,開始構想該系統 1970年代由貝爾實驗室發展完成 採用分頻多重擷取(FDMA)技術

50 MHZ的無線電頻寬分配給AMPS使用 824 -849 MHz (25 MHz)及869 -894 MHz (25 MHz) 該頻寬被切割成 832個頻道 416條下行頻道(downlinks) 由基地台到手機的傳輸通道 416條上行頻道(uplinks) 由手機到基地台的傳輸通道

頻率使用方式 所有AMPS細胞被分組成群(cluster) 頻率分配原則 容許不同群的細胞使用相同頻率,但須保證不 會互相干擾 同一群內的細胞因距離較近必須使用不同的頻 率以避免干擾 AMPS的漫遊管理標準 EIA/TIA IS-41

趨勢 數位式系統能容納較高的用戶密度,進而提供較 低的通話價錢及高品質的服務 數位式蜂巢系統取代AMPS
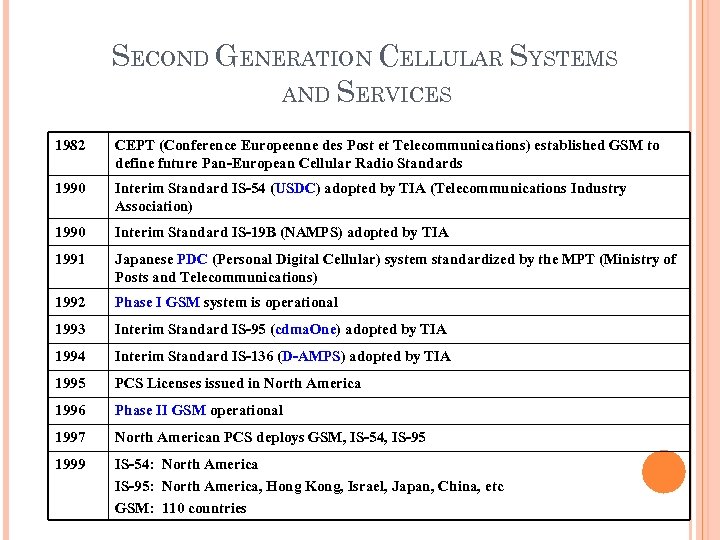
SECOND GENERATION CELLULAR SYSTEMS AND SERVICES 1982 CEPT (Conference Europeenne des Post et Telecommunications) established GSM to define future Pan-European Cellular Radio Standards 1990 Interim Standard IS-54 (USDC) adopted by TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) 1990 Interim Standard IS-19 B (NAMPS) adopted by TIA 1991 Japanese PDC (Personal Digital Cellular) system standardized by the MPT (Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications) 1992 Phase I GSM system is operational 1993 Interim Standard IS-95 (cdma. One) adopted by TIA 1994 Interim Standard IS-136 (D-AMPS) adopted by TIA 1995 PCS Licenses issued in North America 1996 Phase II GSM operational 1997 North American PCS deploys GSM, IS-54, IS-95 1999 IS-54: North America IS-95: North America, Hong Kong, Israel, Japan, China, etc GSM: 110 countries

2 G 從 1990年開始的數位式通訊系統 數位訊號傳輸 聲波先經壓縮 重新編碼成 0與1字元 接收方收到數位編碼訊號後重新組碼,恢復原聲 波形狀 可對系統加以運算,增加額外系統功能

傳輸優點 通訊品質較高 系統容量較大 通訊保密性較佳 可結合其它數位科技提供多樣化通訊服務 「語音+數據」的結合(語音為主,數據為輔) 手機可傳送簡單文字或利用筆記型電腦上網

Example:GSM手機 可透過WAP技術無線上網 網路連線以電路交換(circuit-switch)方式,而網際網 路上資料傳遞以封包交換(packet-switch)方式 不同的交換架構,彼此間網路都是獨立運作,並 不互連 Example:PHS手機 通話費比GSM系統便宜約50%~60% 待機時間長達 700小時,連續通話時間可達 6 -8小時, 可將近一個月才充電一次 發射功率只有10毫瓦,是GSM的1/60至 1/100 在時速 100公里的狀態下,也可通話
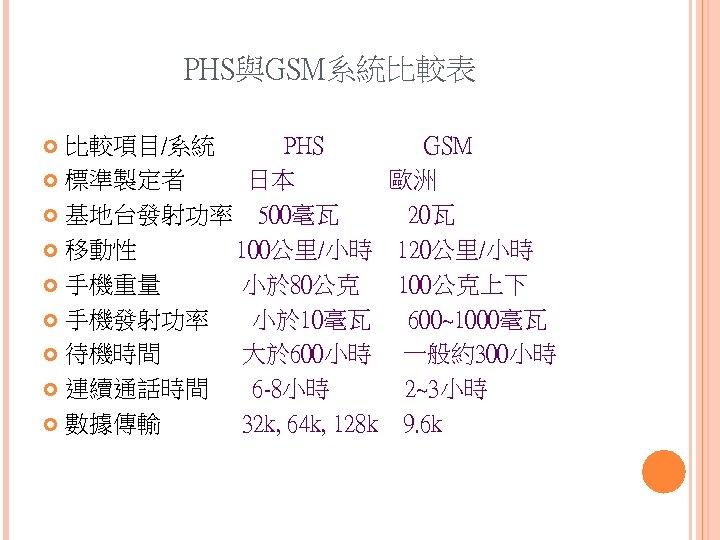
PHS與GSM系統比較表 比較項目/系統 PHS GSM 標準製定者 日本 歐洲 基地台發射功率 500毫瓦 20瓦 移動性 100公里/小時 120公里/小時 手機重量 小於 80公克 100公克上下 手機發射功率 小於 10毫瓦 600~1000毫瓦 待機時間 大於 600小時 一般約300小時 連續通話時間 6 -8小時 2~3小時 數據傳輸 32 k, 64 k, 128 k 9. 6 k

可執行國際漫遊協定 採用電路交換技術,通訊網路效率較低 傳輸速率只有9. 6 Kbps (GSM) 最高可達 64 Kbps (PHS) 語音壓縮 GSM將64 K語音壓縮至 9. 6 K,失真較為嚴重 PHS將64 K語音壓縮至 32 K,通話音質較佳

CT-2 1989年在英國開始商業性營運 商業或家用系統的CT-2可雙向撥打與接收電話( 因位置固定) Telepoint公共電話系統仍只能單向打電話,無法 雙向通訊,也無交遞(handoff) 無線電頻寬分配 864 -868 MHz 每個頻道寬 100 KHz,共 40條FDMA語音頻道 每個頻道的語音編碼速率為 32 kbps

採分時雙 (Time Division Duplexing,TDD) 手機(uplink)及主機(downlink)不管傳送或接收訊號 都在同一頻道上,而用交叉使用時槽(timeinterleaved)的方式來分隔收發動作 可經由語音編解碼器(speech codec)提供數據傳輸 服務 速率約在 2. 4 kbps~4. 8 kbps 註:codec (coder/decoder):將類比訊號轉換為數位 訊號的裝置 手機最大發射功率約在 10 m. W左右,非常省電

CT-2+ 為使手機可以漫遊(roaming),加入訊號系統,產 生共通空中介面(Common Air Interface,CAI) CT 2/CAI可讓不同廠商的手機與基地台(主機)相通 提供雙向通訊和handoff

CT-3 架構在CT-2/CT-2+技術上,易利信提出CT-3作為 大範圍WPBX (Wireless PBX)標準 該標準發展成DECT

DECT 1992年發表,被歐洲採用為無線電話標準 以超微細胞(pico cell)方式在高密度用戶區提供服 務 無線電頻寬分配 1880 -1900 MHz 使用TDMA技術將每個頻道切割成 12個語音通道 與CT 2相同,採TDD雙 模式 語音通道編碼速率為 32 kbps Cell size: Micro-cell約直徑 100~500公尺 Pico-cell約直徑小於 100公尺

採動態通道分配(Dynamic Channel Allocation, DCA) 可動態轉換不同的timeslot 時槽轉換(time slot transfer):將通話線路由一個 時槽轉移至另一個時槽(避免干擾) 使頻道能有效率地使用並增強通話品質 可經由私用交換機(Private Branch Exchange,PBX) 與公眾電話網路(PSTN)相連 具無縫式交遞(seamless handoff)能力 可與GSM互連以提供使用者漫遊能力 有DECT與GSM結合的系統(dual mode),在室內使 用DECT,快速移動使用GSM

提供服務 區域性的資料傳輸服務 (connectionless datagram service) 群播(multicast) 廣播(broadcast) 虛擬通道(virtual circuits) 認證(authentication) 資料保密(confidentiality)

PHS 1993年由日本RCR (Research and development Center for Radio system)製訂的標準 一種數位低階個人通訊服務系統,適用於居家、 辦公室及室外環境 以無線電擷取方式提供用戶公眾電話網路或數據 網路的服務 採用TDMA技術,每個頻率可提供四個電話通道 無線電頻寬分配 1895~1918. 1 MHz 此頻寬可容納77個語音通道,通道寬度為 300 KHz 37個通道(1895 MHz-1906 MHz)用於家庭/辦公室環境 40個通道(1906. 1 MHz-1918. l MHz)用於公眾系統

與DECT相同 PHS亦採用動態式通道分配技術 與DECT不同 PHS使用專屬控制通道(dedicated control channel) 預先選擇的通道係用來傳送系統及控制信令 (signaling)等資訊 語音編碼速率為 32 kbps,使用TDD雙 模式

PHS 選擇性地提供線路交遞功能 支援傳真服務,速度介於 4. 2~7. 8 kbps 支援全雙 的數據機傳輸服務(full-duplex modem), 速度介於 2. 4~9. 6 kbps 主要系統是純粹的數位化封包傳輸系統 進行數據資料傳輸沒有GSM先天上設計的缺陷 數據傳輸: 32~64 k,128 K 大眾電信PHS低功率行動電話(www. phs. com. tw)

PACS 結合PHS和無線存取通訊系統(Wireless Access Communications System) 由Belllcore發展的低階個人通訊服務系統,為美 國標準之一 無線電頻寬分配 1930 -1990 MHz (base station transmission) 1850 -1910 MHz (handset transmission) PACS採用TDMA技術,每個頻率可提供 8個語音 通道

與CT 2、PHS和DECT相同 PACS每個通道的語音編碼速率均為 32 kbps 與CT 2、PHS和 DECT不同 PACS同時提供TDD與FDD兩種雙 模式 在FDD模式下,上行通道(uplink)與下行通道 (downlink)使用不同的頻率傳送 漫遊管理採用類似於IS-41的標準 PACS 提供 電路交換方式(circuit switching)協定 分封交換方式(packet switching)協定—應用在數據 傳輸

DAMPS Digital AMPS EIA/TIA IS-136 Digital Cellular System 1987年,在美國開始發展 規格 早期規格為EIA/TIA IS-54修訂後的後續規格為IS-136 使用數位TDMA技術,DAMPS稱為 ADC (American Digital Cellular) NA-TDMA (North American TDMA)

數位化後可提供來電顯示、認證、語音加密等功 能 利用TDMA技術 IS-136的每個載送頻率可提供三個語音通道 容量為AMPS的三倍 無線電頻寬分配 869 -894 MHz (base station transmission) 824 -849 MHz (handset transmission)

通道使用型態 full-rate 語音通道使用兩個timeslot傳語音,數據傳輸為 13 kbps 因一些數據使用錯誤偵測及錯誤修正,真正的語音 使用為 8 kbps half-rate 語音通道使用一個timeslot傳語音,資料傳輸率為 5 kbps,真正的語音使用約為 4 kbps

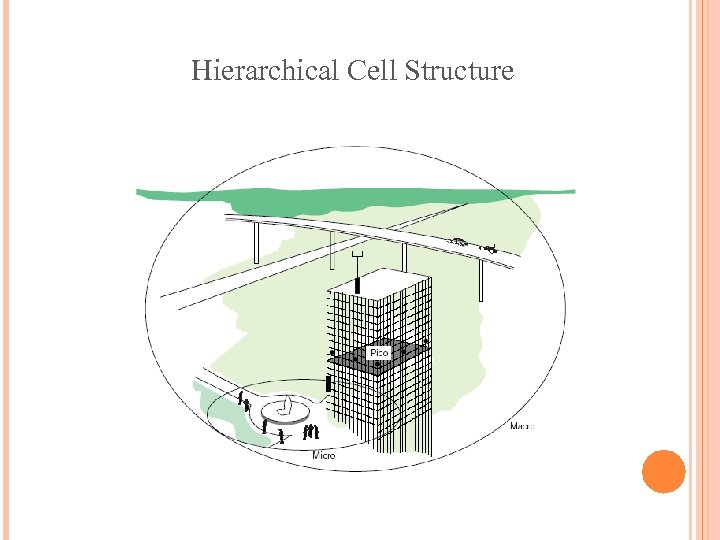
IS-136使用與AMPS相同的頻段 IS-136的其它特性 點對點的短訊服務(point-to-point short messaging) 廣播訊息(broadcast messaging) 群組定址(group addressing) 私人用戶群(private user group) 階層式細胞架構(hierarchical cell structure)
Hierarchical Cell Structure

DAMPS利用時槽呼叫通道(slotted 提供手機睡眠模式(sleep mode)以降低手機耗電量 DAMPS的漫遊管理標準 paging channel) IS-41

EIA/TIA IS-95 沿革 1940美國軍方開始使用CDMA 1970 -1980展頻技術開始商業上的應用. 1993美國採用Qualcomm的CDMA做為IS-95標準. Qualcomm在 1996開始營運,該系統稱為cdma. One (i. e. , IS-95) 南韓在 1991決定將IS-95商業化、本土化,1997發 展成功

IS-95的無線電擷取方式採用CDMA的DSSS技術 CDMA最基本概念是所有用戶共享一個很大的頻寬 一起傳送訊號,但各自使用不同的碼來萃取出自 己的資料 此編碼技術能將頻寬做最佳化的應用 CDMA的容量比TDMA大 3 -6倍 CDMA的語音編碼速率為 8 kbps或 13 kbps 當語音編碼速率為 8 kbps時,IS-95的容量約為 AMPS (FDMA技術)的9倍

IS-95提供soft handoff,比較不受到干擾,使用 RAKE receiver技術解決multipath fading的問題 IS-95 手機在通話期間,持續接收兩個以上基地台 之間通訊,在多路徑(multipath)改變時,手機能選 擇採用訊號較佳的基地台的訊號,提供較佳的通 話品質 IS-95之air-interface的演進 cdma. One IS-95 A → cdma. One IS-95 B → cdma 2000 1 XEV (CDMA MC FDD)

IS-95之core network漫遊管理標準的演進 cdma. One採用IS-41 → cdma 2000 採用IS-41+Simple IP → cdma 2000 1 x. EV(cdma MC FDD) 採用IS-41+Mobile IP

GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) 數位蜂巢式行動電話系統 由歐洲郵政電信組織(Conference Europeenne des Postes et Telecommunications, CEPT)及其後繼者 歐洲電信標準協會(European Telecommunications Standard Institute, ETSI)於 1983年開始發展 目標:提供一套橫跨歐洲國家的相容性行動電話 服務

無線電頻寬分配 uplink (handset transmission) 890 -915 MHz (25 MHz) downlink (base station transmission) 935 -960 MHz (25 MHz) 技術突破 結合FDMA/TDMA/FDD
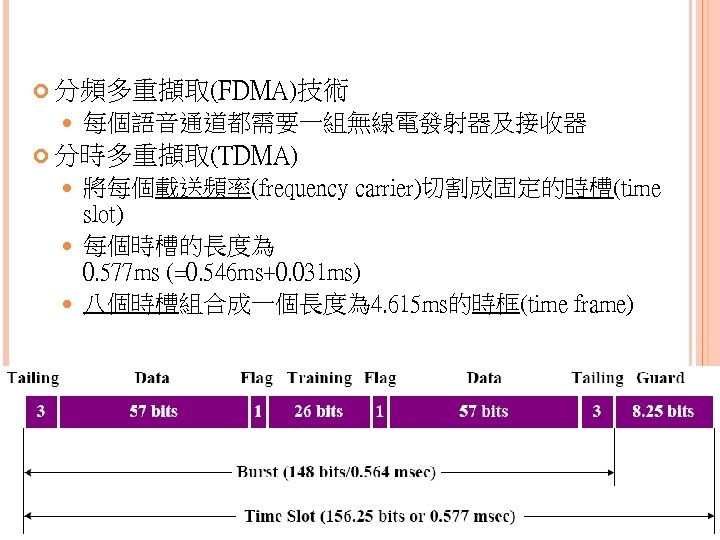
分頻多重擷取(FDMA)技術 每個語音通道都需要一組無線電發射器及接收器 分時多重擷取(TDMA) 將每個載送頻率(frequency carrier)切割成固定的時槽(time slot) 每個時槽的長度為 0. 577 ms (=0. 546 ms+0. 031 ms) 八個時槽組合成一個長度為 4. 615 ms的時框(time frame)
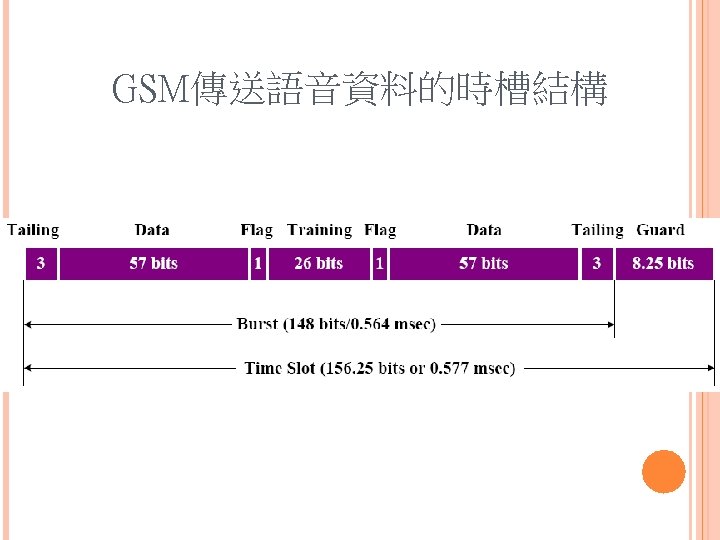
GSM傳送語音資料的時槽結構

每個時槽相當於一個語音通道,所以GSM的每一 個載送頻率提供 8個語音通道 各通道的語音編碼(speech coding)速率為l 3 Kbps GSM基地台的無線電硬體能讓 8個語音通道共用 GSM的漫遊管理 依據GSM MAP (Mobile Application Part)規格(與IS-41 類似)
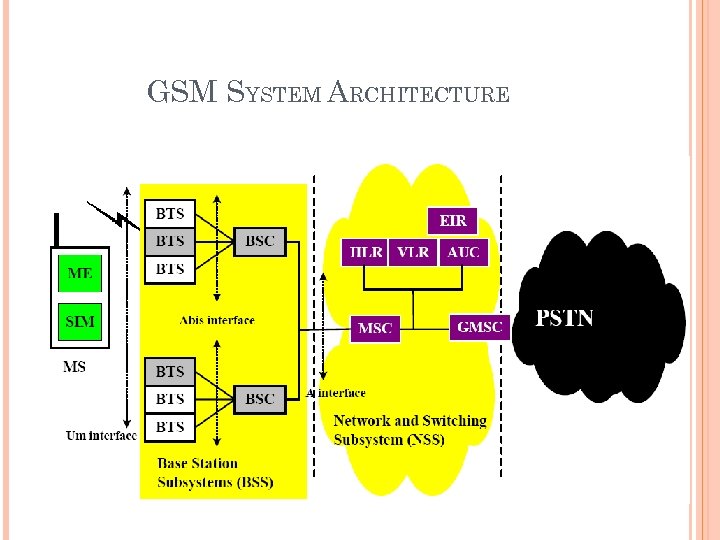
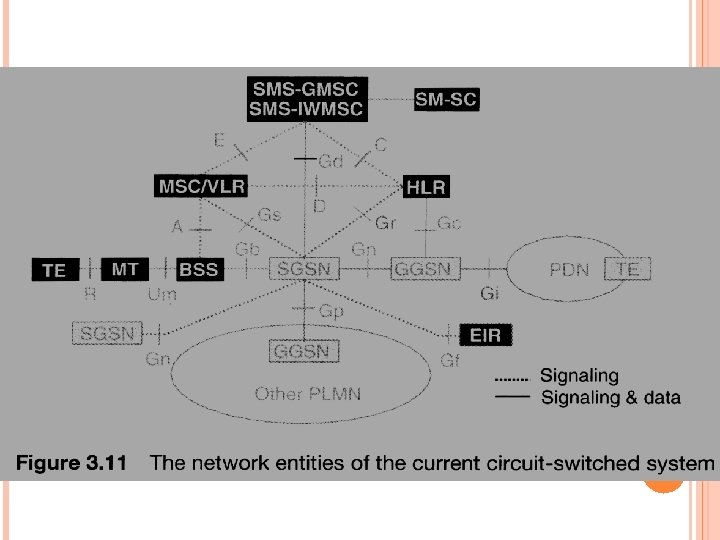
GSM SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
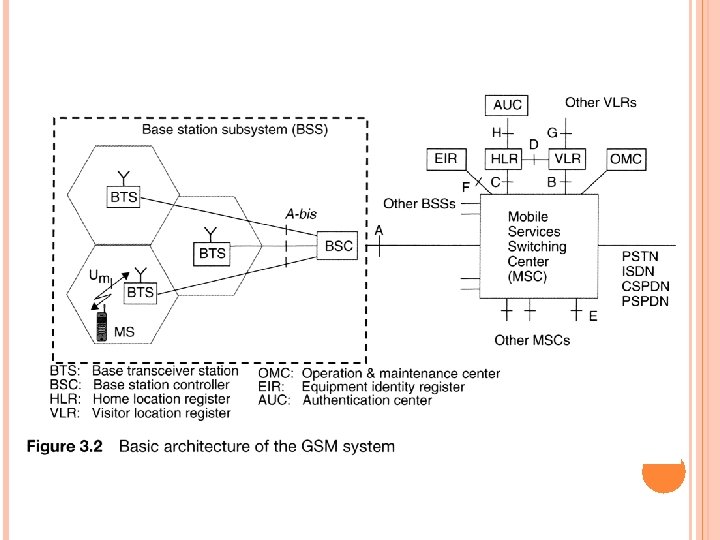

名詞 NSS:網路及交換子系統(Network and Switch Subsystem) MSC:行動交換中心(Mobile Switching Center) BSS:基地台子系統(Base Station Subsystem) BSC:基站控制台(Base Station Controller) BTS:基地收發台(Base Transceiver Station) MS:手機(Mobile Station) ME:手機通訊模組(Mobile Equipment) SIM:使用者認証模組(Subscriber Identity Module)

2. 5 G GSM+ 高速電路交換數據服務(High Speed Circuit Switched Data, HSCSD) 通用無線封包通訊數據服務(General Packet Radio Service, GPRS) GSM++ 全球增強型數據提昇率(Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution,EDGE)
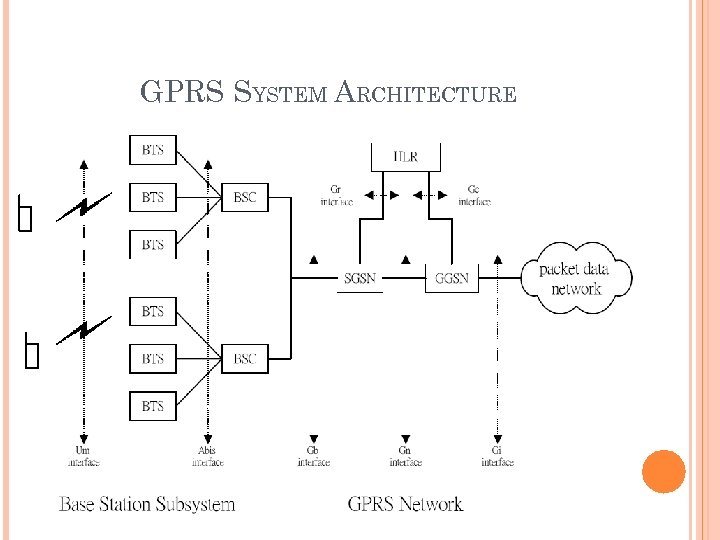
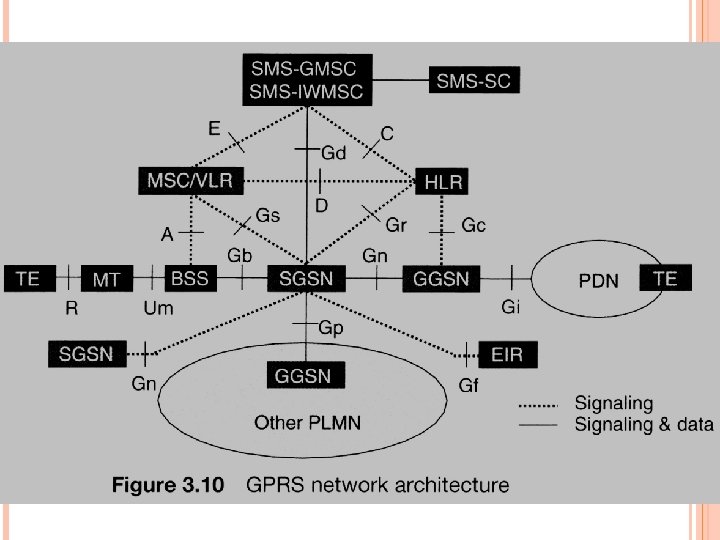
GPRS SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
GPRS General Packet Radio Service 由窄頻過渡到寬頻的中間技術 每位用戶瞬間最多可使用八個時槽,傳輸速率可高達 171. 2 Kbps (21. 4 Kbps× 8 ) 是封包交換數據的標準技術 在現有GSM網路上,加上幾個數據交換節點 在基地台系統方面,增加 通道編碼單元(Channel Coding Unit,CCU) 封包控制單元(Packet Control Unit,PCU)

通道編碼單元(CCU) 提供四種不同編碼模式,提供不同等級的錯誤保護(error protection)能力 四種不同編碼方式,其每個時槽可提供的傳輸速率也不同 CS-1 (9. 05 K)保護最嚴密 CS-2 (13. 4 K) CS-3 (15. 6 K) CS-4 (21. 4 K)完全未加任何保護

封包控制單元(PCU) 量測無線電訊號 拆解與組合數據封包 數據交換節點具處理封包能力,使得GSM網路能和 網際網路互連 具立即連線特性,使用者隨時都在上線的狀態 計費按數據交換量,而非連線時間

功能 點對點載送服務,包括非連接導向,如IP及連接導向 身份識別 利用加密演算法保護分封數據的安全性 透過GPRS載送短訊(SMS over GPRS) 支援分封數據計費 點對點及點對多點服務 預付費、計算訊息提示及其它加值服務 引入不同服務等級Qo. S

EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution),為 2 G和2. 5 G (GPRS)的延伸,有時被稱為 2. 75 G,是 另一種達到 3 G資料傳輸速率的技術 以GSM標準為架構 能將GPRS功能發揮到極限 利用不同調變技術(GMSK及8 PSK)提高傳輸速率 可透過無線網路提供寬頻多媒體服務 EDGE支援電路交換及封包交換模式 在封包交換方面EDGE和GPRS很類似 在電路交換上則和GSM很類似

傳輸速度可達 384 kbps 可應用在諸如無線多媒體、電子郵件、網路資訊娛樂及 視訊會議上 ISP導入EDGE的優點為成本低及網路影響度低 影響所及在於無線接續(Radio Access)網路端 基地台(BTS) 基地台控制中心(BSC) 並無負作用於應用程式端及電路或封包交換等不同介面 電路交換仍舊透過MSC (Mobile Switching Center)維護 封包交換則透過SGSN (GPRS Support Node)維護

3 G 「數據+多媒體」的結合 以數據資料為主 傳輸率可達 2 Mbps,以提供多媒體影像傳送服務 目標 一統各家規格,達到一支手機擁有各種無線電介面 可seamless跨越不同系統 可與2 G並存 提供更高系統容量 更高的資料傳輸速率

特色 能整合各項地面的行動電話網路(包括GSM、CDMA及TDMA) 和衛星通訊 支援多模式操作介面 可透過共同標準以達全球漫遊(旅行者在各國移動時不用轉換 當地行動電話系統) 能符合高速數據傳輸條件 強化空中傳輸及網路安全性(防個人資料遭入侵或盜取) 主要通訊協定 W-CDMA/UMTS (日本與歐洲推動) CDMA 2000 (美國主導) TD-SCDMA (中國大陸推動,由大唐電信與西門子共同制定)

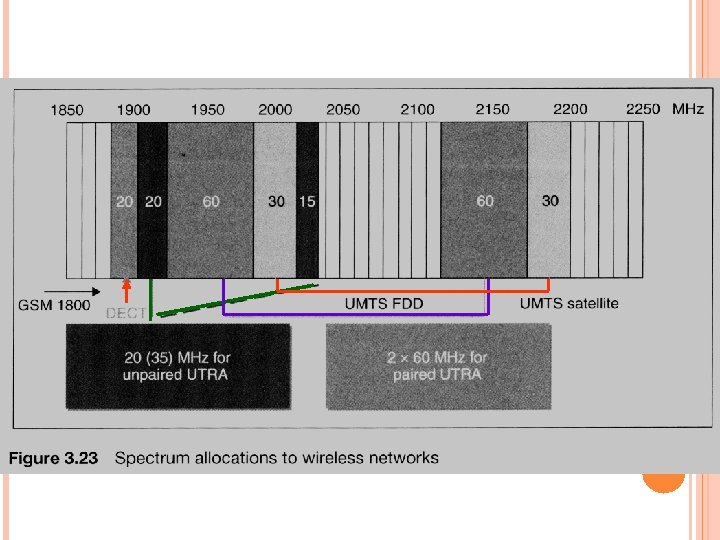
W-CDMA W-CDMA(Wideband CDMA,寬頻分碼多重存取) 又名CDMA Direct Spread 能架在現有GSM網路上 UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System) 頻譜分配 營運模式(modes of operation) 20 +15 MHz for unpaired UTRA TDD mode used by TD-CDMA 1900 ~ 1920 + 2010 ~ 2025 35 Mz
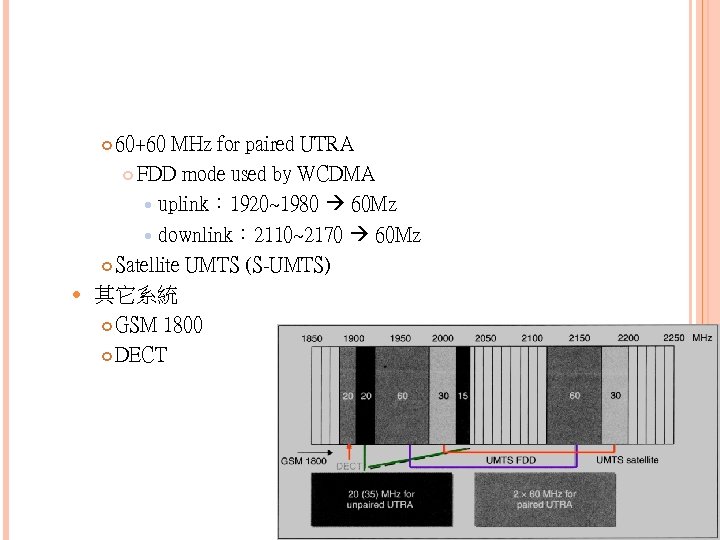
60+60 MHz for paired UTRA FDD mode used by WCDMA uplink: 1920~1980 60 Mz downlink: 2110~2170 60 Mz Satellite UMTS (S-UMTS) 其它系統 GSM 1800 DECT

CDMA 2000 又名CDMA Multi-Carrier 為CDMA開發組織CDG (CDMA Development Group)所發展 出的第三代行動電話標準 從窄頻cdma. One (IS-95)標準衍生而出

CDMA 2000系統計有四個不同的衍生版本 CDMA 2000 1 x (高品質語音,307 kbps) CDMA 2000 3 x. MC (高品質語音,大於 384 kbps) 又稱為多載波(Multi Carrier,MC) 結合3個1. 25 MHz的載波而形成 3. 75 MHz頻寬 CDMA 2000 1 x. EV-DO (2. 4 Mbps,data only) DO (Data Optimization),利用新的調變技術(8 PSK, 16 QAM)可達到 2. 4 Mbps的傳輸速率 CDMA 2000 1 x. EV-DV (Evolution-Data/Voice) (4. 8 Mbps,更高 容量的語音與資料傳輸)

TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous CDMA) 規格是由CWTS (China Wireless Telecommunication Standards)所制定 技術開發主要由CATT (China Academy of Telecommunication Technology)和西門子(Siemens)所負責

TD-SCDMA的重要參數 頻帶: 2010~2025 中國) Hz 頻寬: 1. 6 MHz 最小) 碼片率(chip rate): 1. 28 Mbp 訊框長度: 10 時槽數目: 7 調變架構:QPSK或PS 功率控制率: 200 H 最高資料傳輸 : 2. 048 bps (電路及封包交換資料)
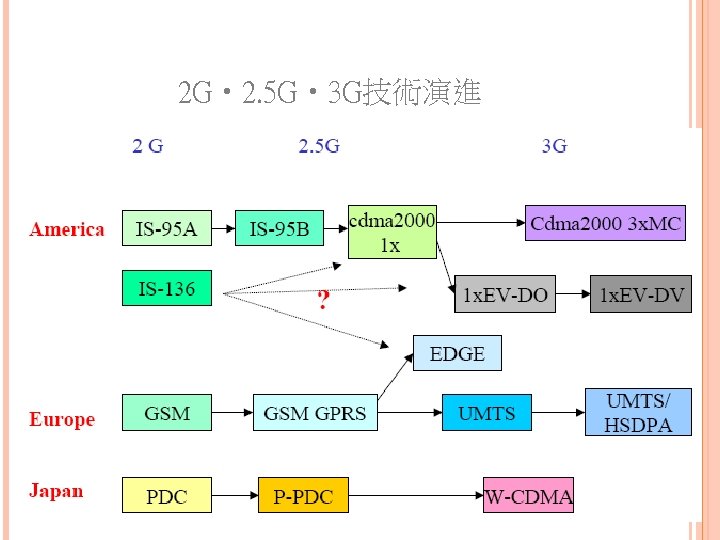
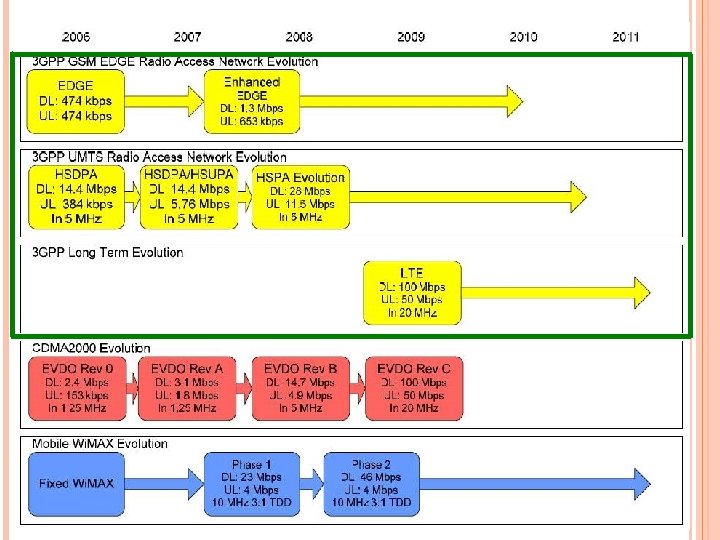
2 G • 2. 5 G • 3 G技術演進

AIR INTERFACE的演進 CDMA IS-95 A (voice,14. 4 kbps) → IS-95 B (voice, 64 kbp,已被略過) → cdma 2000 1 x (高品質語音, 307 kbps) → cdma 2000 3 x. MC (高品質語音,大於 384 kbps) → 1 x. EV-DO (2. 4 Mbps,data only) → 1 x. EV-DV (更高 容量的語音與資料傳輸) IS-136 (voice,9. 6 kbp) → ? (可能是cdma 2000 1 x或 1 x. EV-DO)
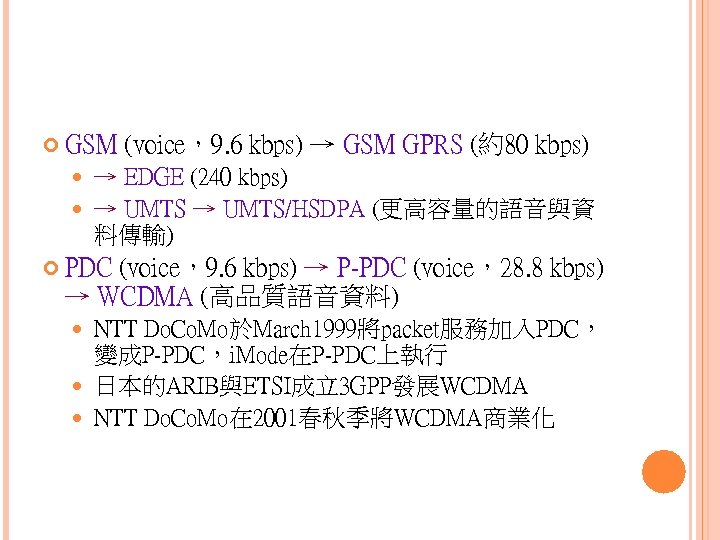
GSM (voice,9. 6 kbps) → GSM GPRS (約80 kbps) → EDGE (240 kbps) → UMTS/HSDPA (更高容量的語音與資 料傳輸) PDC (voice,9. 6 kbps) → P-PDC (voice,28. 8 kbps) → WCDMA (高品質語音資料) NTT Do. Co. Mo於March 1999將packet服務加入PDC, 變成P-PDC,i. Mode在P-PDC上執行 日本的ARIB與ETSI成立3 GPP發展WCDMA NTT Do. Co. Mo在 2001春秋季將WCDMA商業化

RD 3 GPP (THE 3 GENERATION PARTNERSHIP PROJECT) A collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations Make a globally applicable third generation (3 G) mobile phone system specification within the scope of the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) project of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) 3 GPP specifications are based on evolved Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) specifications 3 GPP standardization encompasses Radio, Core Network and Service architecture

IMT-2000 Fulfill one's dream of anywhere, anytime communications a reality The global standard for third generation (3 G) wireless communications as defined by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Compatibility of services within IMT-2000 and with the fixed networks high quality small terminal for worldwide use worldwide roaming capability for multimedia applications, and a wide range of services and terminals

Important component of IMT-2000 is the ability to provide high bearer rate capabilities 2 Mbps for fixed environment 384 kbps for indoor/outdoor and pedestrian environments 144 kbps for vehicular environment Radio interface standards for IMT-2000 1999, ITU approved five radio interfaces for IMT 2000 as a part of the ITU-R M. 1457 Recommendation 2007, additionally approved a new standard as the sixth IMT-2000 radio interface

The six IMT-2000 radio interface standards IMT-DS Direct-Sequence known as W-CDMA or UTRA-FDD used in UMTS Note:UTRA -- UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access IMT-MC Multi-Carrier known as CDMA 2000 the successor to 2 G CDMA (IS-95)

IMT-TD Time-Division TD-CDMA (Time Division - Code Division Multiple Access) standardized in UMTS by the 3 GPP as UTRA TDD-HCR (high chip rate) 3. 84 Mcps, 5 MHz bandwidth TD-SCDMA (Time Division - Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) standardized in UMTS by the 3 GPP as UTRA TDD-LCR (low chip rate) 1. 28 Mcps, 1. 6 MHz bandwidth

IMT-SC Single Carrier known as EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) EDGE Evolution, added in Release 7 of the 3 GPP standard, provides reduced latency and potential speeds of 1 Mbps by using even more complex coding functions IMT-OFDMA TDD WMAN better known as Wi. MAX

IMT-FT Frequency Time known as DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) DECT IMT-2000: up to 2. 5 Mbps user data rate (1999) Beyond IMT-2000: up to 15 Mbps (single and wide carrier 64 -QAM modulation)
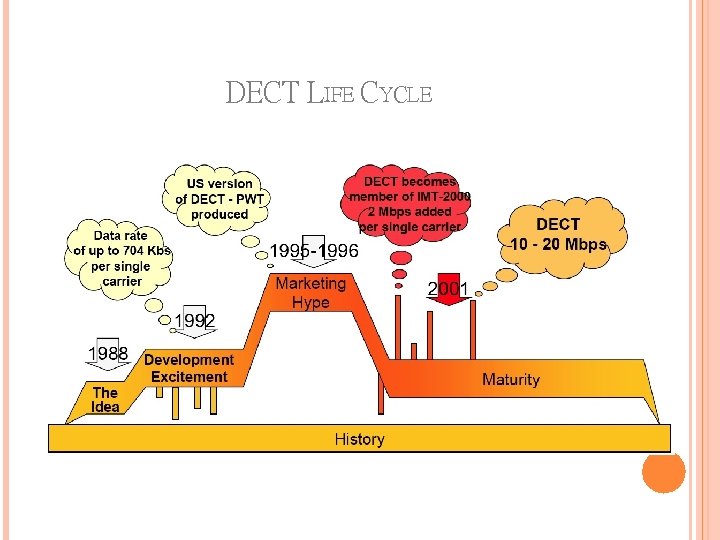
DECT LIFE CYCLE
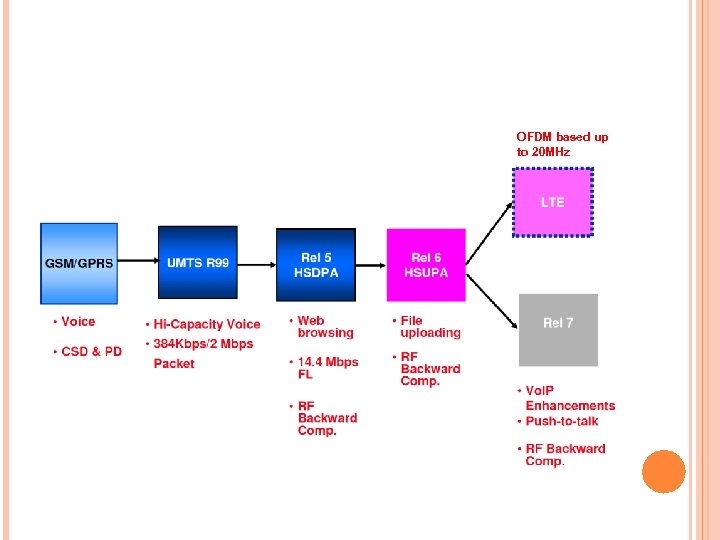
OFDM based up to 20 MHz
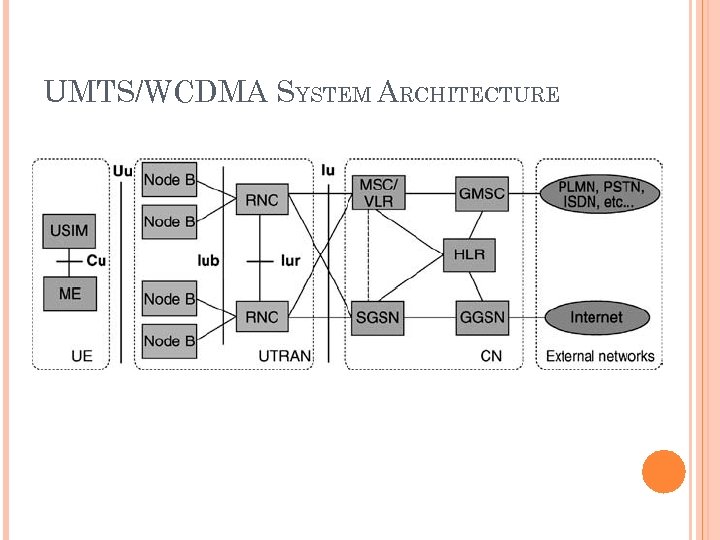
UMTS/WCDMA SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE

IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM (IMS) An architectural framework for delivering Internet Protocol (IP) multimedia services Originally designed by the wireless standards body 3 rd Generation Partnership Project (3 GPP), as a part of the vision for evolving mobile networks beyond GSM Its original formulation (3 GPP R 5) represented an approach to delivering "Internet services" over GPRS this vision was later updated by 3 GPP, 3 GPP 2 and TISPAN by requiring support of networks other than GPRS, such as Wireless LAN, CDMA 2000 and fixed line

To ease the integration with the Internet, IMS uses IETF protocols wherever possible, e. g. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) According to the 3 GPP, IMS is not intended to standardize applications but rather to aid the access of multimedia and voice applications from wireless and wireline terminals, i. e. create a form of Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC) This is done by having a horizontal control layer that isolates the access network from the service layer From a logical architecture perspective, services need not have their own control functions, as the control layer is a common horizontal layer
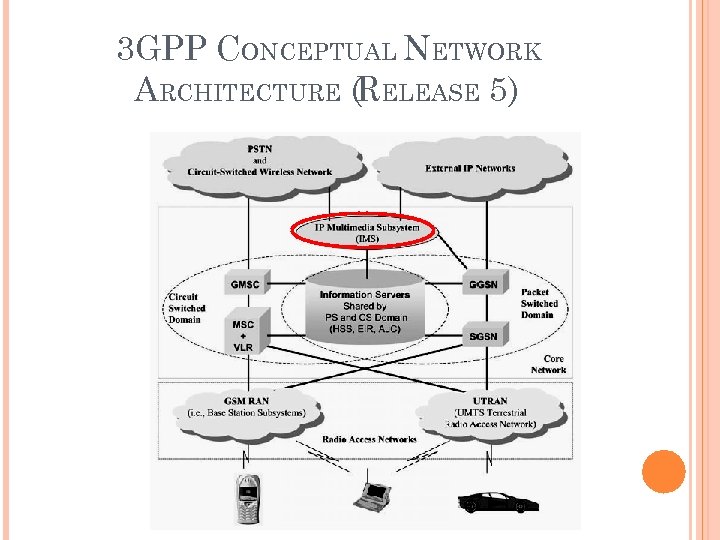
3 GPP CONCEPTUAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE (RELEASE 5)

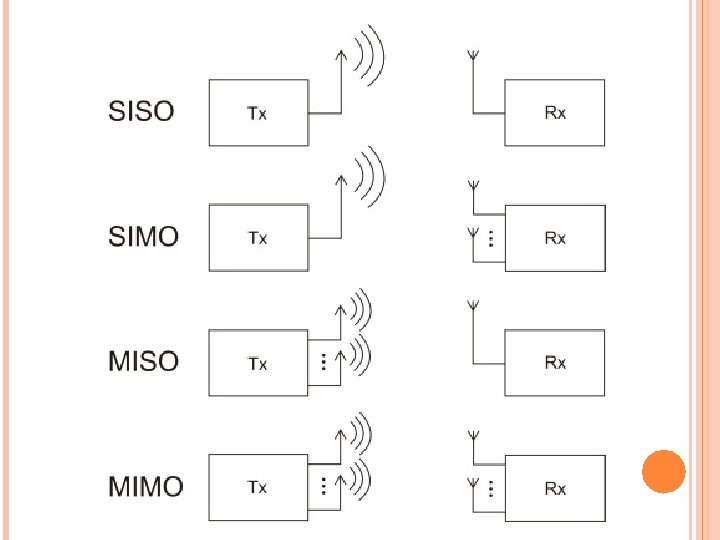
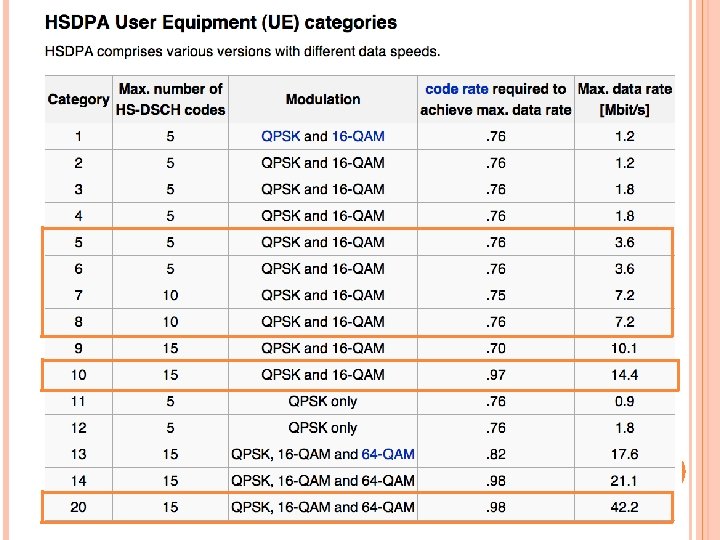
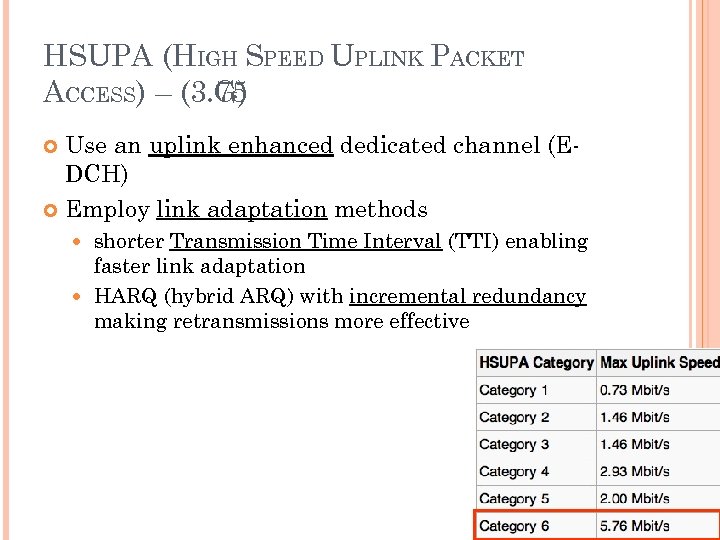
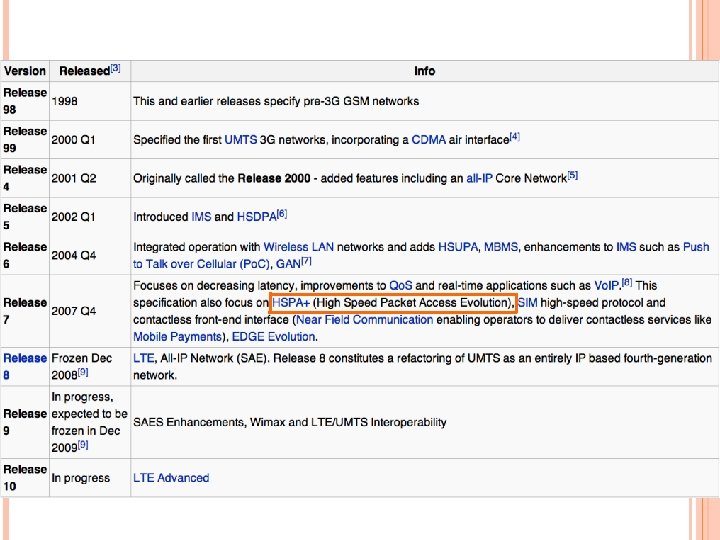
HSDPA (HIGH-SPEED DOWNLINK PACKET ACCESS) – (3. 5 G) An enhanced 3 G mobile telephony communications protocol in the High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA) family Also coined 3. 5 G, 3 G+ or turbo 3 G Allows networks based on Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) to have higher data transfer speeds and capacity Current HSDPA deployments support down-link speeds of 1. 8, 3. 6, 7. 2, 14. 4 Mbps Further speed increases are available with HSPA+, which provides speeds of up to 42. 2 Mbps downlink

HSDPA (High-Speed Data Packet Access) 3 GPP在R 5制訂高速下載封包存取技術,以增加UMTS下載 封包的傳輸速度 新增 一個傳輸通道HS-DSCH (High Speed Downlink Shared Channel) 此共享通道可傳送突發性暴增資料的(bursty data)能 力 一個在Node B的MAC子層MAC-hs (High Speed Medium Access protocol),提供兩項關鍵技術 混合自動回覆(Hybrid Automatic Re. Quest, HARQ) 適應型調變編碼(Adaptive Modulation and Coding, AMC)

結合下列技術,將最大下載傳輸速率大幅提升到 10 Mbps 以上(上傳 384 Kbps) 適應性調變編碼(Adaptive Modulation and Coding,AMC) 混合自動重複(Hybrid Automatic Re. Quest,HARQ) 多重輸入與多重輸出(Multiple Input Multiple Output, MIMO) 快速細胞選擇(Fast Cell Selection,FCS)

Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC) (or Link adaptation) a term used in wireless communications to denote the matching of the modulation, coding and other signal and protocol parameters to the conditions on the radio link

the signal and protocol parameters change as the radio link conditions change, e. g. the pathloss the interference due to signals coming from other transmitters the sensitivity of the receiver the available transmitter power margin, etc. in HSDPA of UMTS this can take place every 2 ms

Hybrid ARQ (HARQ) a variation of the ARQ error control method Standard ARQ error-detection (ED) information bits are added to data to be transmitted (such as cyclic redundancy check,CRC) Hybrid ARQ forward error correction (FEC) bits are also added to the existing error detection (ED) bits

Hybrid ARQ performs better than ordinary ARQ in poor signal conditions, but in its simplest form this comes at the expense of significantly lower throughput in good signal conditions there is typically a signal quality cross-over point below which simple Hybrid ARQ is better, and above which basic ARQ is better
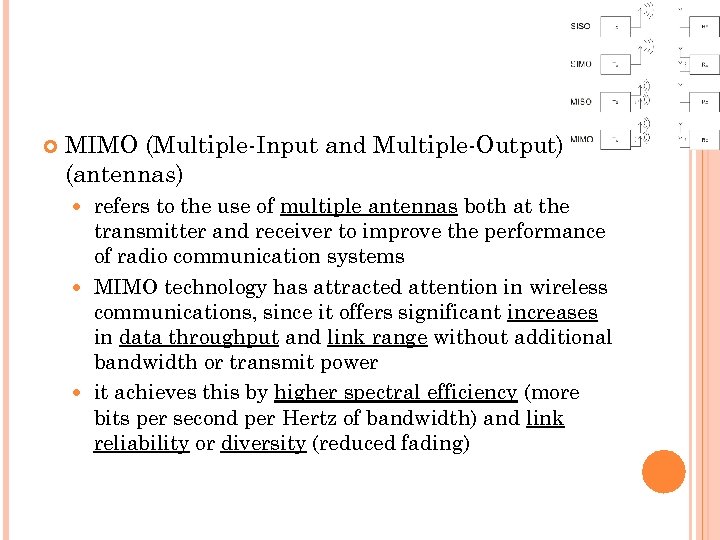
MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) (antennas) refers to the use of multiple antennas both at the transmitter and receiver to improve the performance of radio communication systems MIMO technology has attracted attention in wireless communications, since it offers significant increases in data throughput and link range without additional bandwidth or transmit power it achieves this by higher spectral efficiency (more bits per second per Hertz of bandwidth) and link reliability or diversity (reduced fading)

FCS (Fast Cell Selection) 使用FCS機制,手機可指定一個通道品質最佳的細胞作為 服務細胞 雖然手機中的Active Set中有許多可收到訊號的細胞,但 在FCS機制中,手機只能由單一細胞下載資料封包 此做法可有效降低干擾狀況與增加系統容量
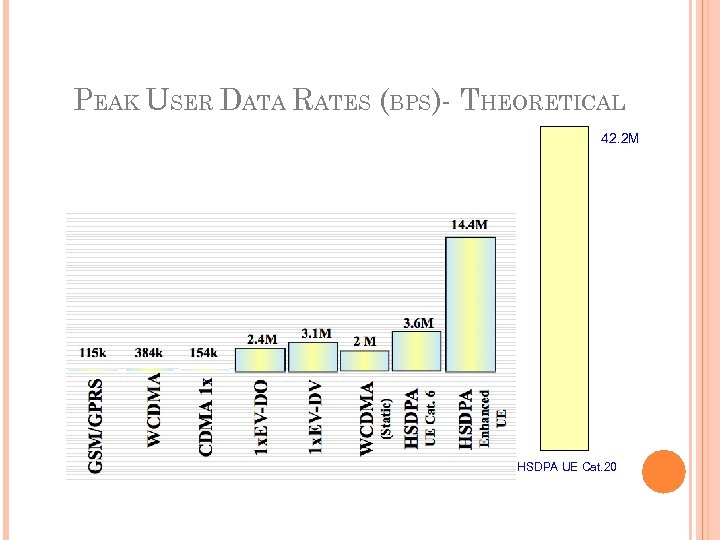
PEAK USER DATA RATES (BPS)- THEORETICAL 42. 2 M HSDPA UE Cat. 20
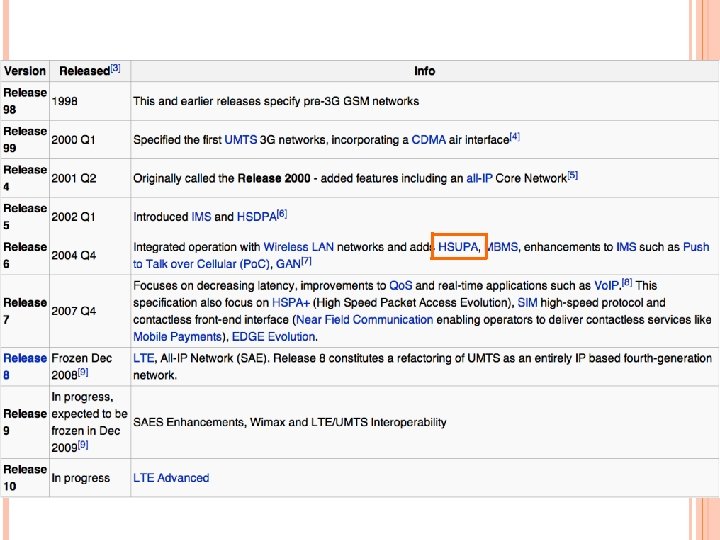
HSUPA (HIGH SPEED UPLINK PACKET ACCESS) – (3. 75 G) Use an uplink enhanced dedicated channel (EDCH) Employ link adaptation methods shorter Transmission Time Interval (TTI) enabling faster link adaptation HARQ (hybrid ARQ) with incremental redundancy making retransmissions more effective

PTT (PUSH-TO-TALK) Also known as Press-To-Transmit A method of conversing on half-duplex communication lines, including two-way radio Using a momentary button to switch from voice reception mode to transmit mode

GAN (GENERIC ACCESS NETWORK) UMA (Unlicensed Mobile Access) the commercial name of the 3 GPP GAN, or GAN standard The most common application of GAN is in a dual -mode handset service where subscribers can seamlessly roam and handover between local area networks and wide area networks using a GSM/Wi-Fi dual-mode mobile phone GAN enables the convergence of mobile, fixed and Internet telephony, sometimes called Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC)

HSOPA (HIGH SPEED OFDM PACKET ACCESS) – (3. 9 G) A proposed part of 3 GPP's Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for UMTS systems HSOPA is also often referred to as Super 3 G If adopted, HSOPA succeeds HSDPA and HSUPA technologies specified in 3 GPP releases 5 and 6 Unlike HSDPA or HSUPA, HSOPA is an entirely new air interface system, unrelated to and incompatible with W-CDMA

HSOPA features flexible bandwidth usage with 1. 25 MHz to 20 MHz bandwidths by comparison, W-CDMA uses fixed size 5 MHz chunks of spectrum increased spectral efficiency at 2 -4 times more than that in 3 GPP release 6, peak transfer rates of 100 Mbps for downlink and 50 Mbps for uplink

latency times of around 20 ms for round trip time from user terminal to RAN, approximately the same as a combined HSDPA/HSUPA system, but much better than "classic" W-CDMA uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antenna technology to support up to 10 times as many users as WCDMA based systems, with lower processing power required on each handset
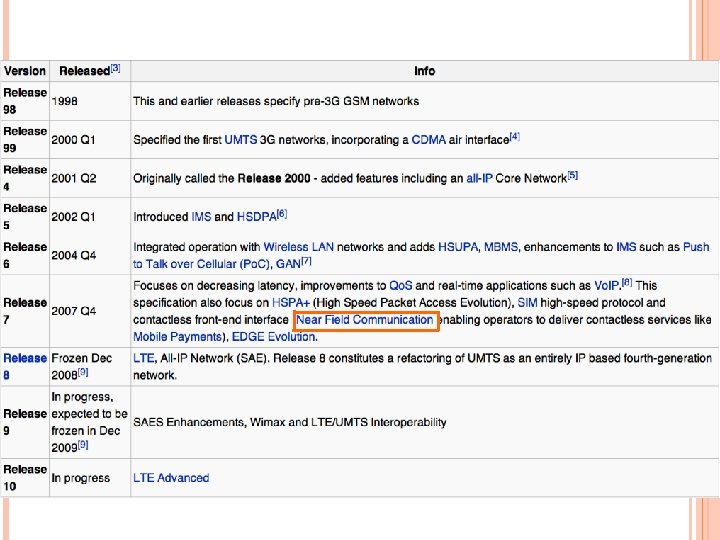

NFC (NEAR FIELD COMMUNICATION) A short-range high frequency wireless communication technology which enables the exchange of data between devices over about a 10 centimeter (around 4 inches) distance The technology is a simple extension of the ISO 14443 proximity-card standard (contactless card, RFID) that combines the interface of a smartcard and a reader into a single device

an NFC device can communicate with both existing ISO 14443 smartcards and readers, as well as with other NFC devices, and is thereby compatible with existing contactless infrastructure already in use for public transportation and payment NFC is primarily aimed at usage in mobile phones
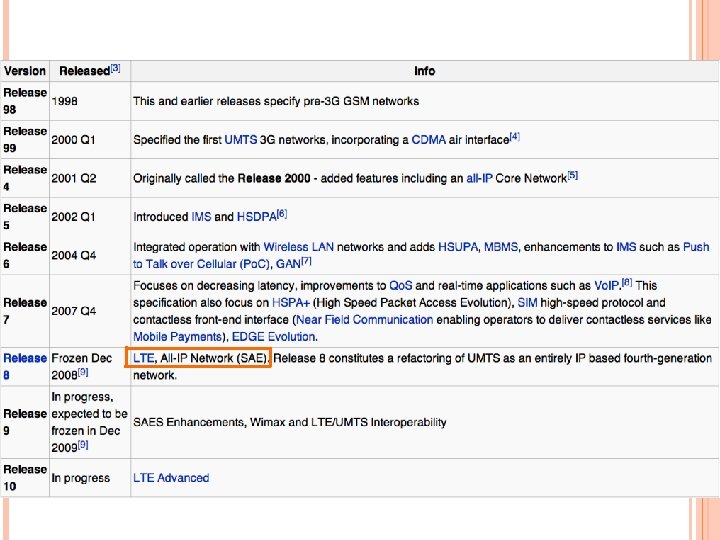

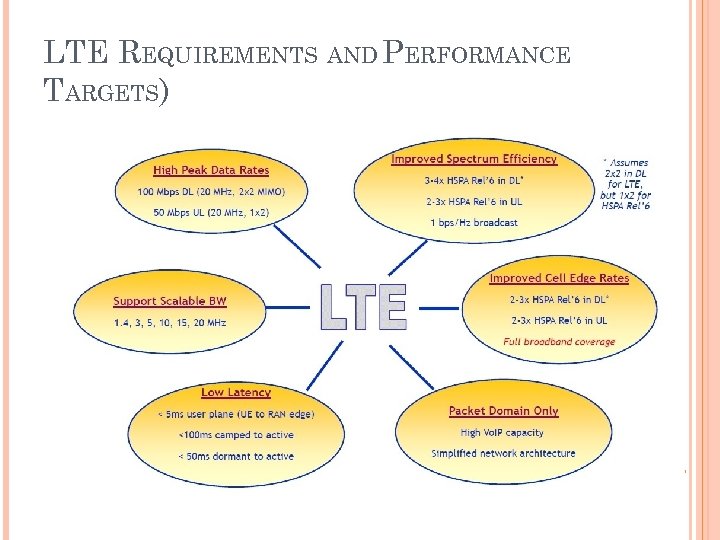
LTE (LONG TERM EVOLUTION) LTE meets key requirements of next generation networks downlink peak rates: at least 100 Mbit/s uplink peak rates: 50 Mbit/s RAN (Radio Access Network) round-trip times: less than 10 ms

Goals improve spectral efficiency lower costs improve services make use of new spectrum better integration with other open standards

Main advantages high throughput low latency plug and play FDD and TDD in the same platform superior end-user experience simple architecture resulting in low Operating Expenditures (OPEX) seamless connection to existing networks, such as GSM, CDMA and HSPA
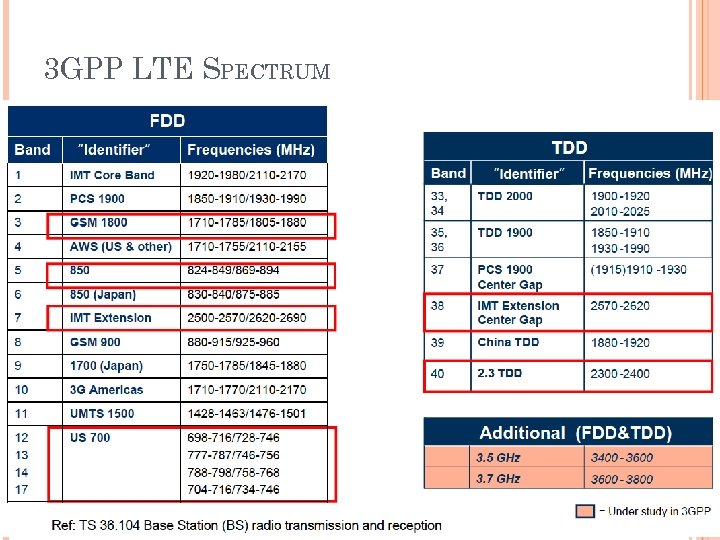
3 GPP LTE SPECTRUM
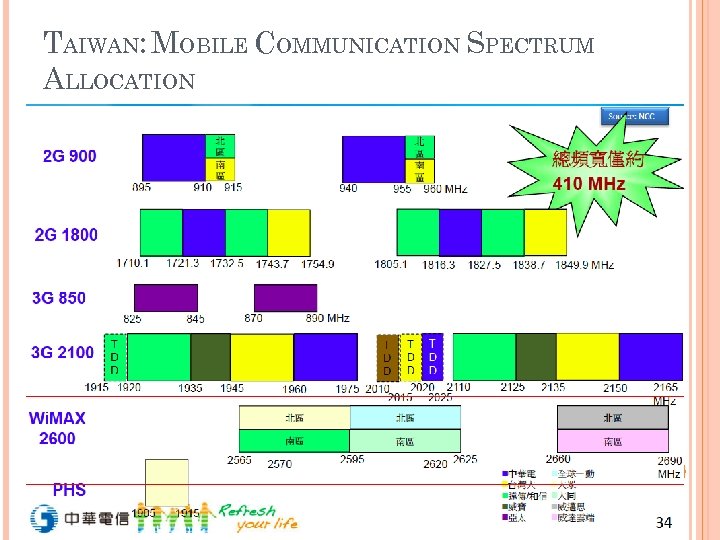
TAIWAN: MOBILE COMMUNICATION SPECTRUM ALLOCATION
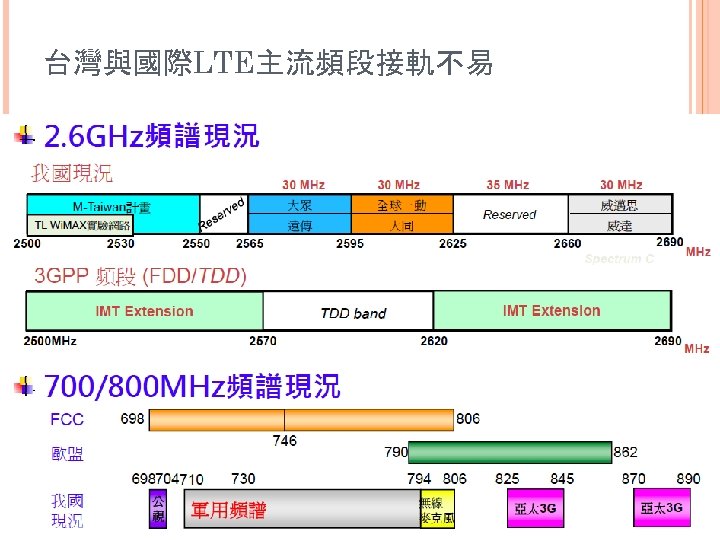
台灣與國際LTE主流頻段接軌不易
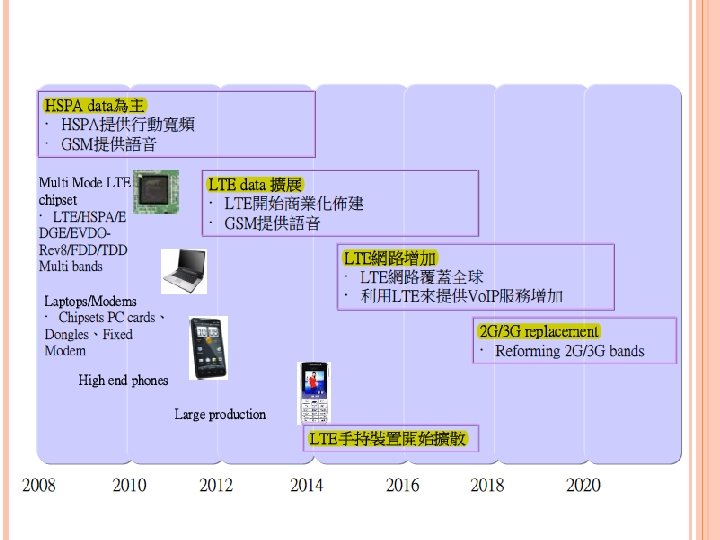
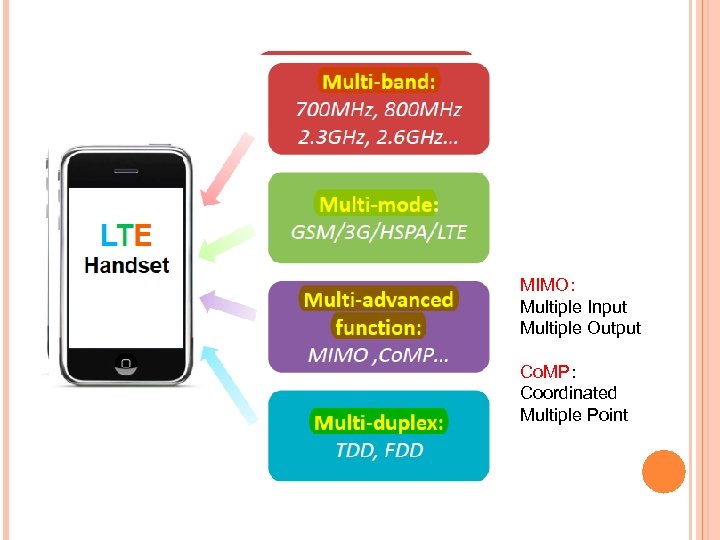
MIMO: Multiple Input Multiple Output Co. MP: Coordinated Multiple Point
LTE REQUIREMENTS AND PERFORMANCE TARGETS)
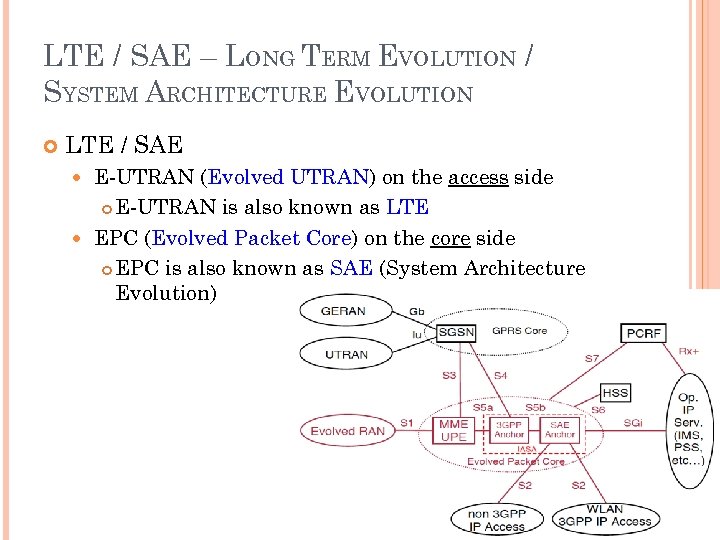
LTE / SAE – LONG TERM EVOLUTION / SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION LTE / SAE E-UTRAN (Evolved UTRAN) on the access side E-UTRAN is also known as LTE EPC (Evolved Packet Core) on the core side EPC is also known as SAE (System Architecture Evolution)
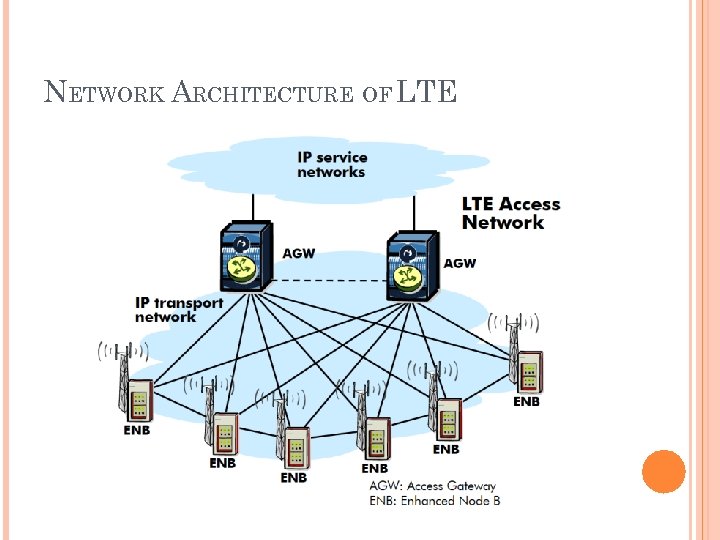
NETWORK ARCHITECTURE OF LTE
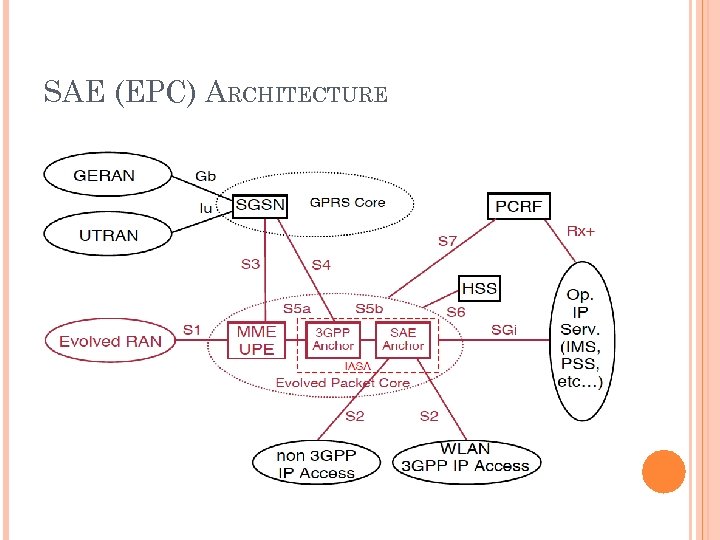
SAE (EPC) ARCHITECTURE

SAE (EPC) ARCHITECTURE – FUNCTIONS PER ELEMENT MME (Mobility Management Entity) manages and stores the UE control plane context, generates temporary id, UE authentication, authorization of TA/PLMN, mobility management UPE (User Plane Entity) manages and stores UE context, DL UP termination in LTE_IDLE, ciphering, mobility anchor, packet routing and forwarding, initiation of paging 3 GPP anchor (Serving Gateway, S-GW) mobility anchor between 2 G/3 G and LTE SAE anchor (PDN Gateway, P-GW) mobility anchor between 3 GPP and non 3 GPP (IWLAN, etc)
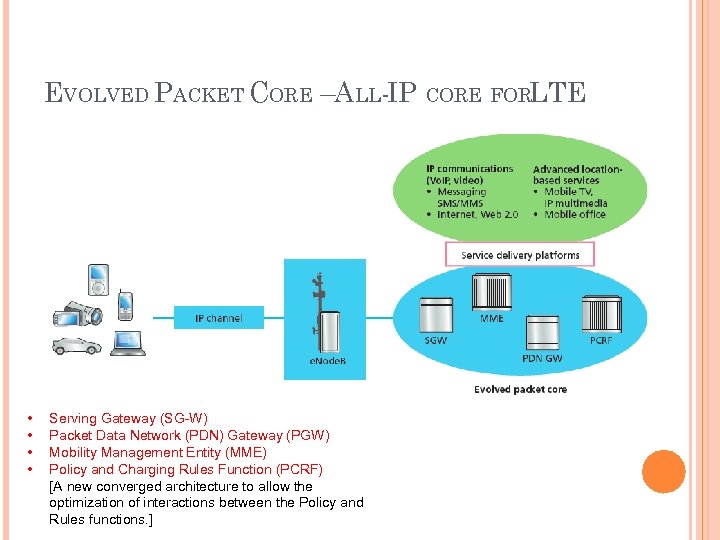
EVOLVED PACKET CORE –ALL-IP CORE FORLTE • • Serving Gateway (SG-W) Packet Data Network (PDN) Gateway (PGW) Mobility Management Entity (MME) Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) [A new converged architecture to allow the optimization of interactions between the Policy and Rules functions. ]
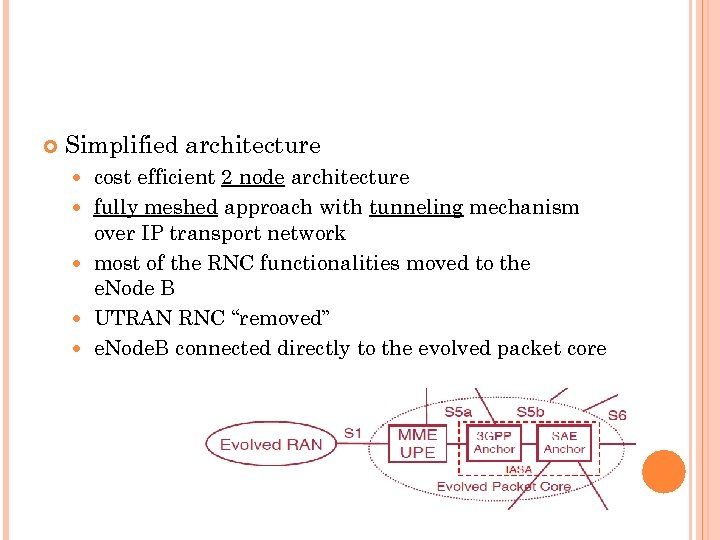
Simplified architecture cost efficient 2 node architecture fully meshed approach with tunneling mechanism over IP transport network most of the RNC functionalities moved to the e. Node B UTRAN RNC “removed” e. Node. B connected directly to the evolved packet core
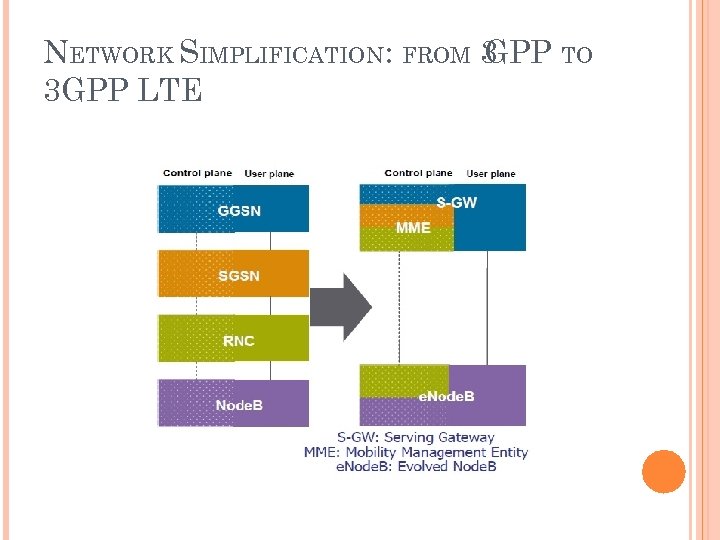
NETWORK SIMPLIFICATION: FROM 3 GPP TO 3 GPP LTE
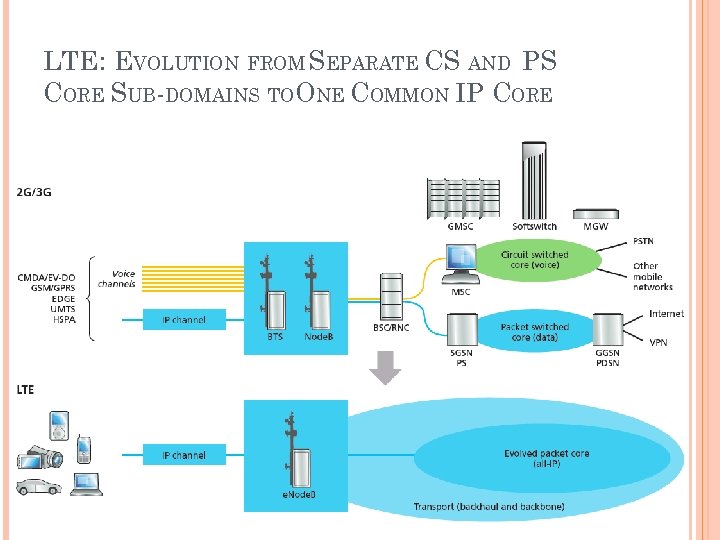
LTE: EVOLUTION FROM SEPARATE CS AND PS CORE SUB-DOMAINS TOONE COMMON IP CORE
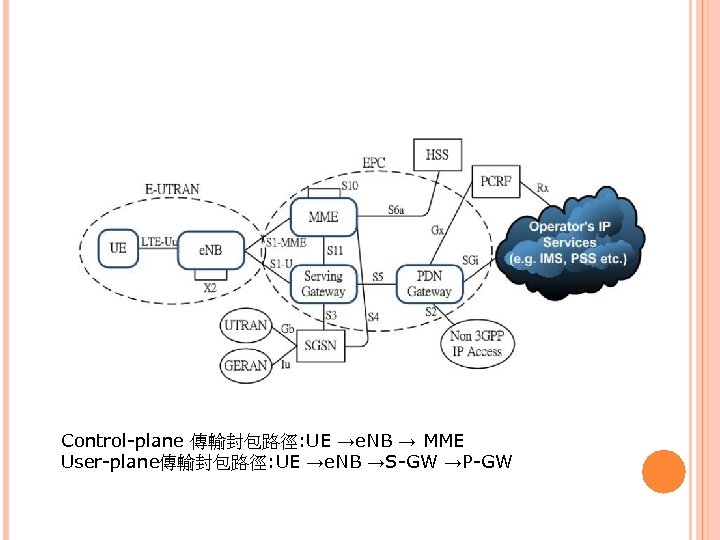
Control-plane 傳輸封包路徑: UE →e. NB → MME User-plane傳輸封包路徑: UE →e. NB →S-GW →P-GW
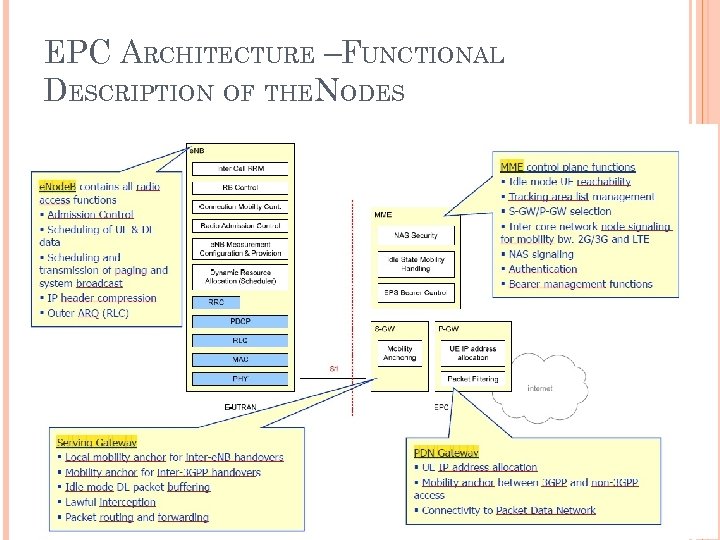
EPC ARCHITECTURE –FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THENODES
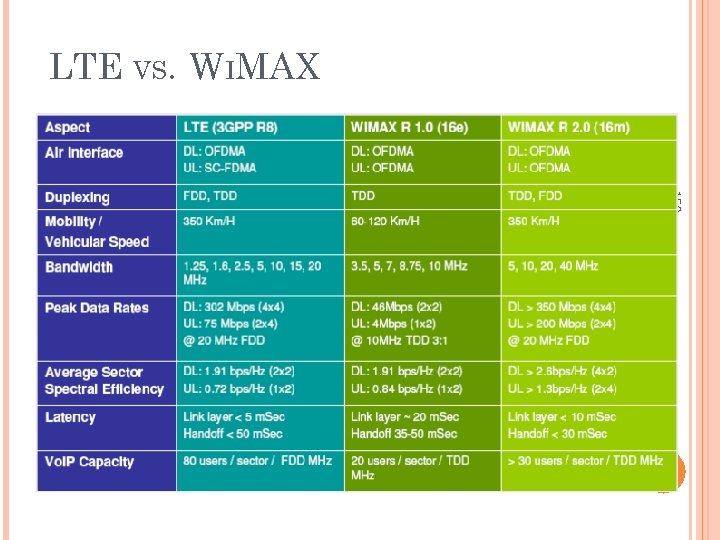
LTE VS. WIMAX 150

RD 3 GPP 2 (THE 3 GENERATION PARTNERSHIP PROJECT 2) The 3 rd Generation Partnership Project 2 (3 GPP 2) is a collaboration between telecommunications associations to make a globally applicable third generation (3 G) mobile phone system specification within the scope of the ITU's IMT-2000 project 3 GPP 2 is the standardization group for CDMA 2000, the set of 3 G standards based on earlier 2 G CDMA technology
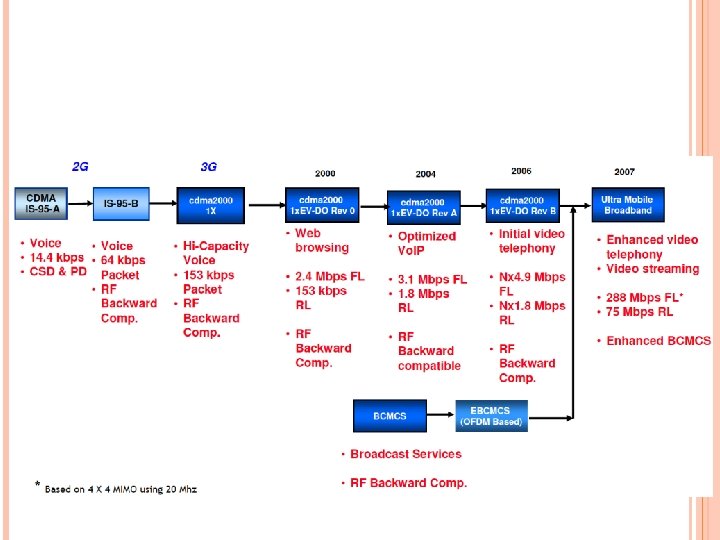
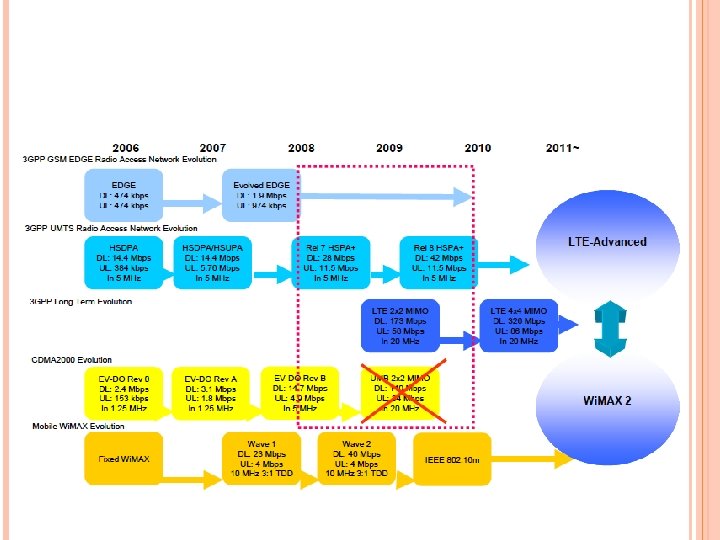
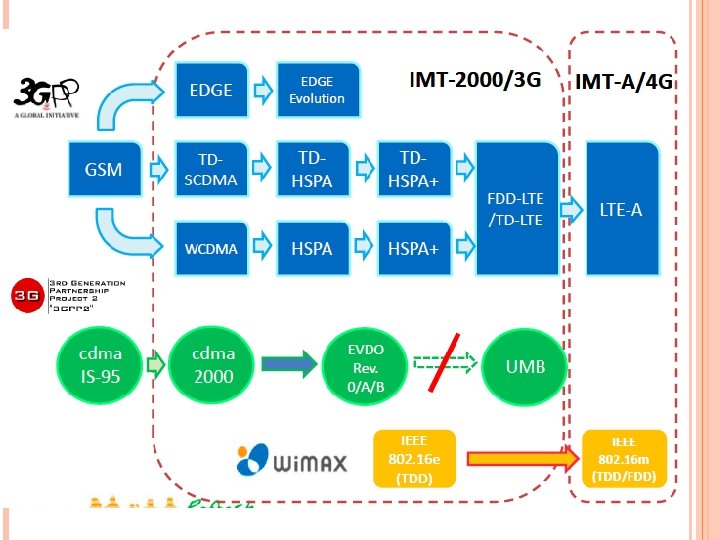

4 G A fully IP-based integrated system of systems and network of networks Convergence of wired and wireless networks as well as computer, consumer electronics, communication technology Be capable of providing 100 Mbps and 1 Gbps, respectively, in outdoor and indoor environments End-to-end quality of service and high security Offering any kind of services anytime, anywhere, at affordable cost and one billing
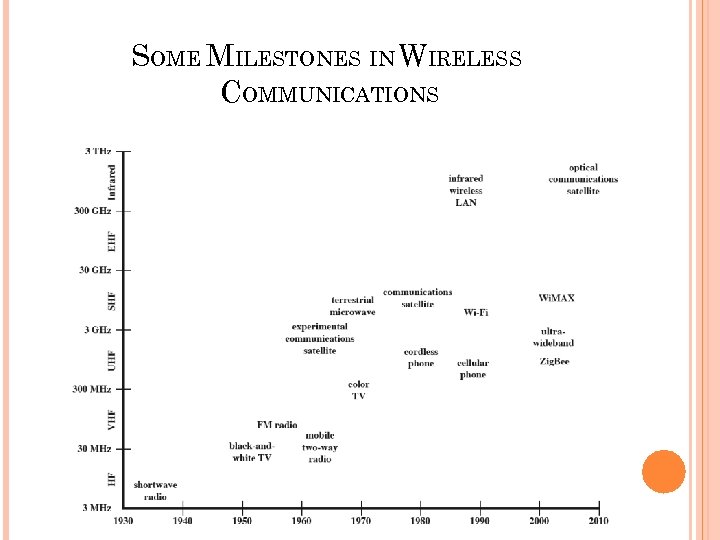
SOME MILESTONES IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS
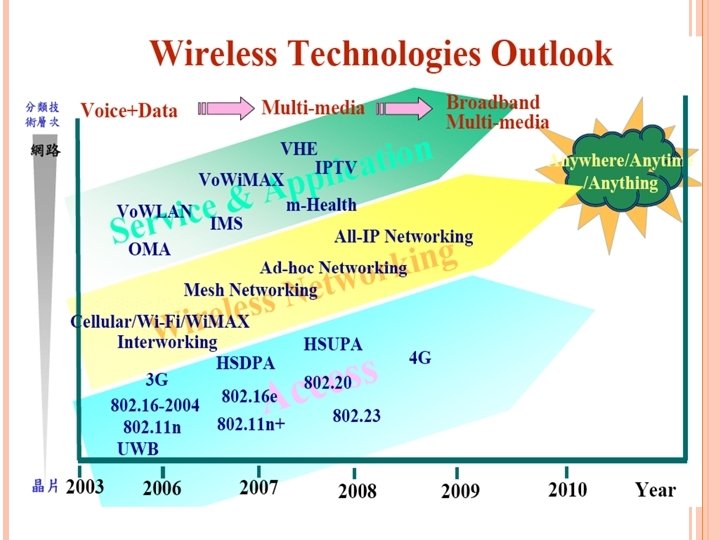
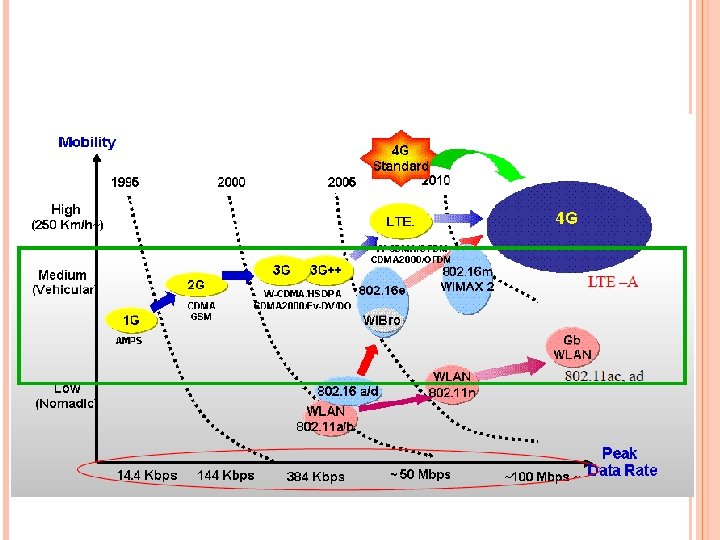

4 G is being developed to accommodate the quality of service (Qo. S) and rate requirements set by forthcoming applications like wireless broadband access Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) video chat mobile TV HDTV content Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) minimal service like voice and data other streaming services for “anytime-anywhere”
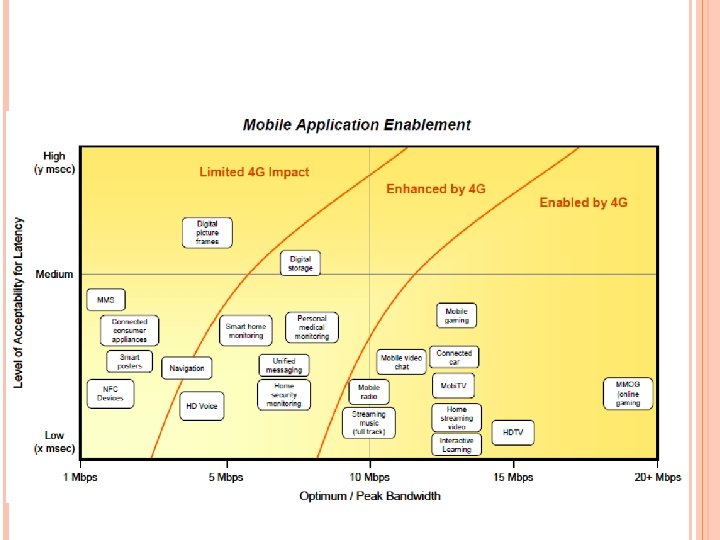

Objectives a spectrally efficient system (in bits/s/Hz and bits/s/Hz/site) high network capacity: more simultaneous users per cell a nominal data rate of 100 Mbps while the client physically moves at high speeds relative to the station, and 1 Gbps while client and station are in relatively fixed positions as defined by the ITU-R a data rate of at least 100 Mbps between any two points in the world smooth handoff across heterogeneous networks

seamless connectivity and global roaming across multiple networks high quality of service for next generation multimedia support (real time audio, high speed data, HDTV video content, mobile TV, etc) interoperability with existing wireless standards an all IP, packet switched network
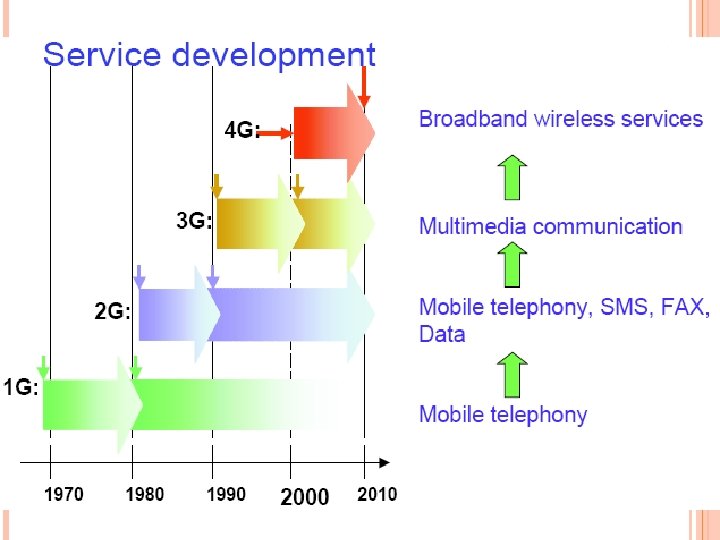
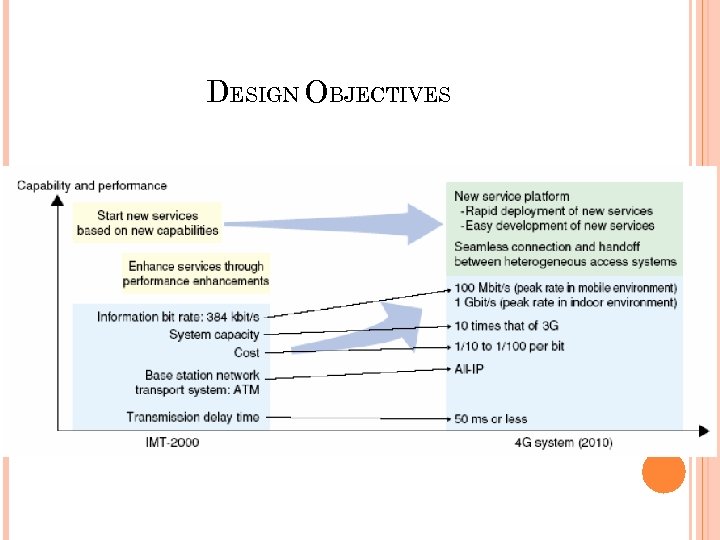
DESIGN OBJECTIVES

4 G concept supports user driven, user controlled services and context-aware applications User controlled services user has freedom and flexibility to select any desired service with reasonable Qo. S and affordable price, anytime, anywhere

Context-aware applications the behavior of the application adapts itself to user context changes user context includes user profile and preferences user terminal and network capabilities user environment and mobility

Network level concepts interworking / integration / convergence (cell & WLAN, cell & broadcast) of all existing and emerging fixed and mobile (wired and wireless) networks including broadcast
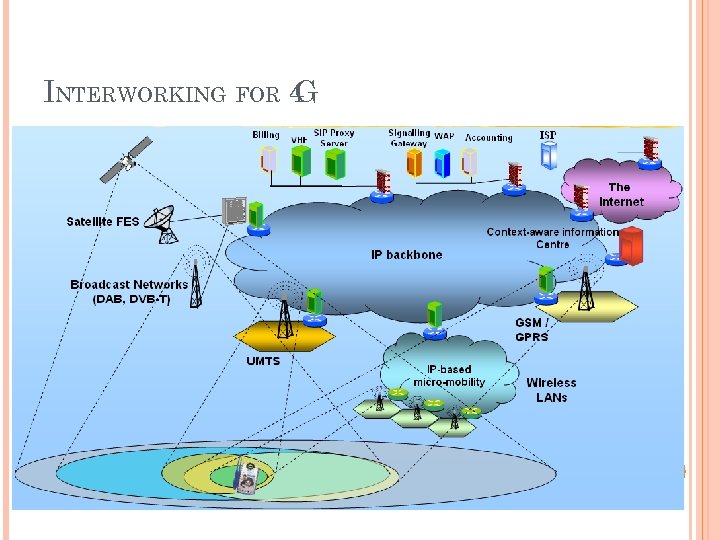
INTERWORKING FOR 4 G
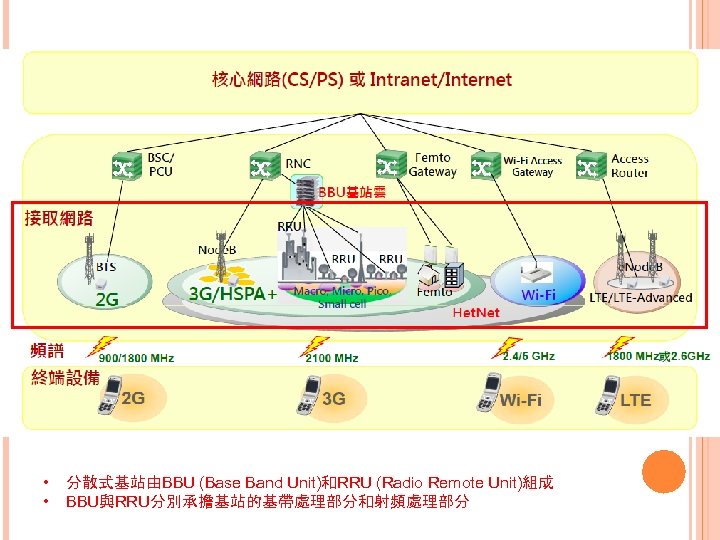
• • 分散式基站由BBU (Base Band Unit)和RRU (Radio Remote Unit)組成 BBU與RRU分別承擔基站的基帶處理部分和射頻處理部分
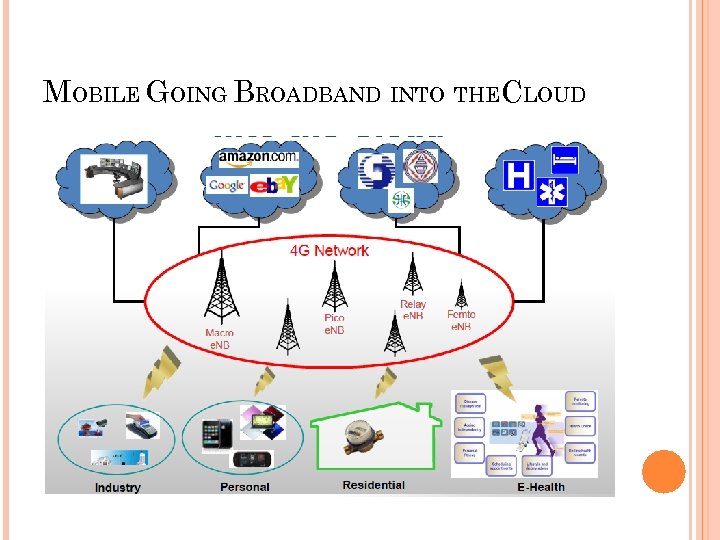
MOBILE GOING BROADBAND INTO THECLOUD
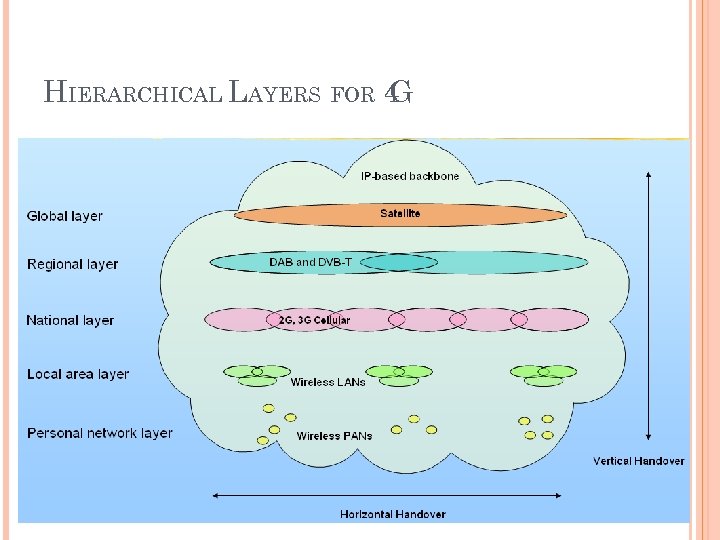
HIERARCHICAL LAYERS FOR 4 G
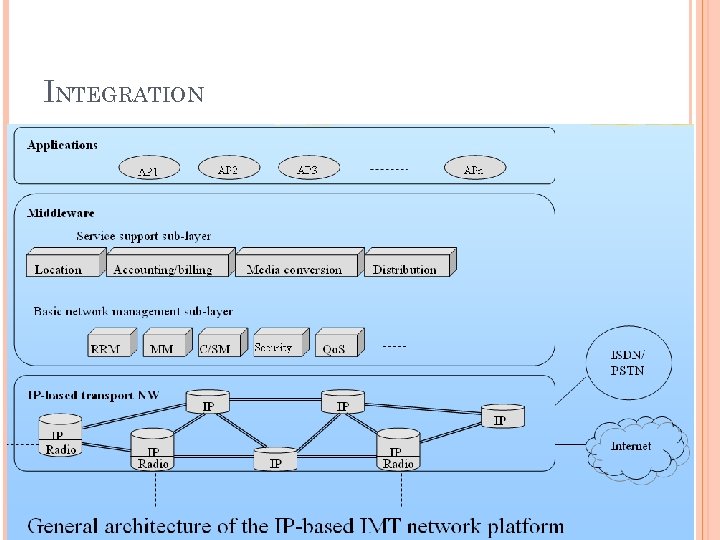
INTEGRATION
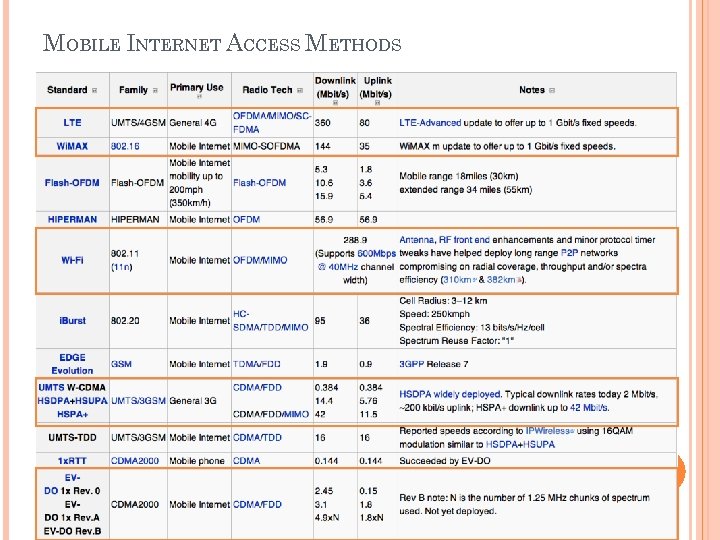
MOBILE INTERNET ACCESS METHODS
ee1358e1d3816fff1318870a10c61c6e.ppt