0d7e00485aed3149f815ea4ed167a62f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
MNIA Introduction to Health Informatics The Basics of Data Norma Alberg Epidemiologist Databases March 17, 2008
Databases in Health Care § Definitions § Record Structure § “Wild Cards” (ie. local chart numbers) § Relational Databases § Unique identifiers (MHSC, PHIN) § Maintenance § Data Entry § Standardized coding structures (mutually exclusive) Databases March 17, 2008
“Ah, those Databases! Databases March 17, 2008

What is a Database? A Database, • Is essentially a tool for storing information for later sorting and retrieval of specific records, based on inclusion criteria determined by the end-user. • The main element of its structure is a FIELD of information. Databases March 17, 2008

Why do we need a Database? Nursing Informatics, • “Integrates nursing science, computer science, and information science to manage and communicate data, information, and knowledge in nursing practice. Nursing informatics facilitates the integration of data, information, and knowledge to support clients, nurses, and other providers in their decision-making in all roles and settings. " (Staggers & Bagley-Thompson, 2002). – Source www. CNIA. ca Databases March 17, 2008
What is File Structure? A Template for a single record is established to determine the required fields of information. This defines the file structure. – – – Field name Type of information Size (length) Code structure Linkages (code lists, numeric, text…) Data entry criteria (acceptable ranges and types) Databases March 17, 2008
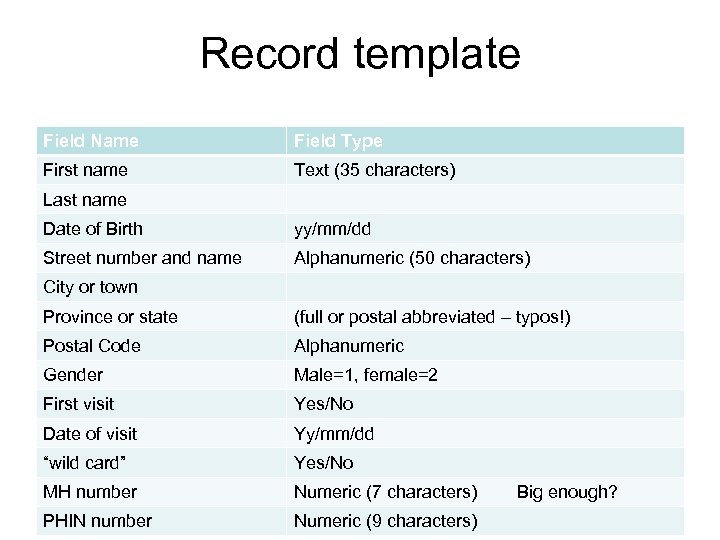
Record template Field Name Field Type First name Text (35 characters) Last name Date of Birth yy/mm/dd Street number and name Alphanumeric (50 characters) City or town Province or state (full or postal abbreviated – typos!) Postal Code Alphanumeric Gender Male=1, female=2 First visit Yes/No Date of visit Yy/mm/dd “wild card” Yes/No MH number Numeric (7 characters) Big enough? PHIN number Numeric (9 characters)

Relational Databases Example - Manitoba Health Contact visit (Diagnosis…) Mental Health Immunizations Client File (PHIN, MHSC…) Physician codes PHC care Facility codes Databases March 17, 2008
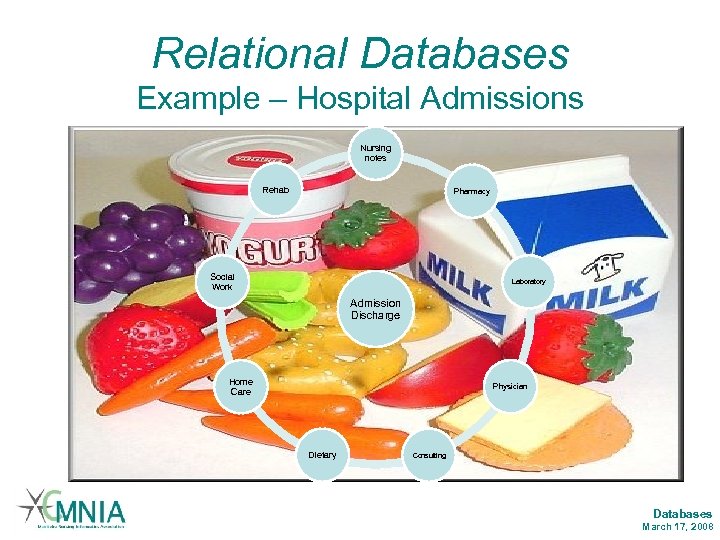
Relational Databases Example – Hospital Admissions Nursing notes Rehab Pharmacy Social Work Laboratory Admission Discharge Home Care Physician Dietary Consulting Databases March 17, 2008

Relational Databases • • What can they do? Cohort Studies (Study on Aging) Health Care Delivery Trends (LOS) Patient Transfer Patterns (rural-urban) Utilization Patterns (Ca, occup, chronic) Illness Severity and outcome Risk Factor Identification And so on and so on…… Databases March 17, 2008
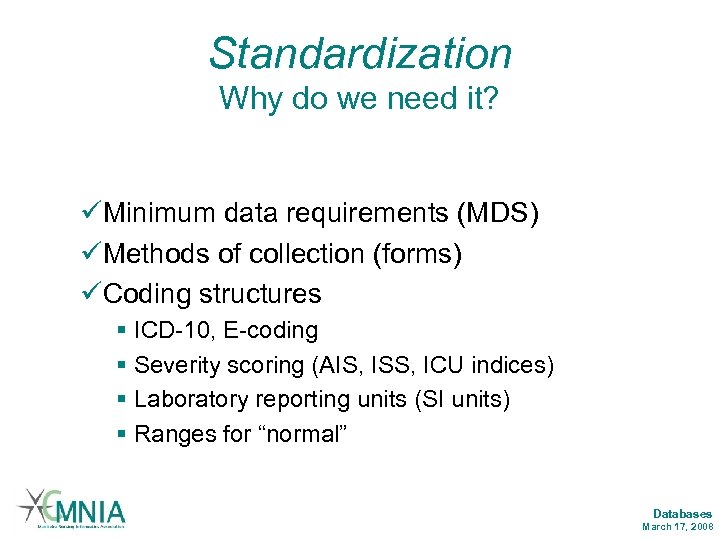
Standardization Why do we need it? üMinimum data requirements (MDS) üMethods of collection (forms) üCoding structures § ICD-10, E-coding § Severity scoring (AIS, ISS, ICU indices) § Laboratory reporting units (SI units) § Ranges for “normal” Databases March 17, 2008
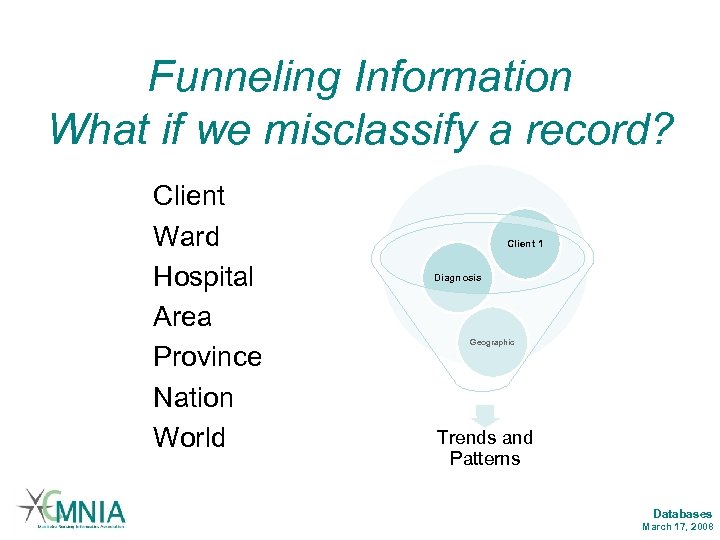
Funneling Information What if we misclassify a record? Client Ward Hospital Area Province Nation World Client 1 Diagnosis Geographic Trends and Patterns Databases March 17, 2008

How do we fit in to the big picture? Canadian representation on HL 7 international board, Toronto, March 6, 2008 - • • Canada Health Infoway's (Infoway) Chief Technology Officer, Dennis Giokas, was recently appointed to the Health Level 7 (HL 7) International board. Giokas' appointment will help Canada shape the strategic direction of HL 7, which is critical to the interoperability and standardization that is fundamental to the success of the interoperable electronic health record (i. EHR). "Canada is a strong contributor to the global acceleration of electronic health records and we look forward to their continued collaboration, and to leveraging their strengths and experience, " said HL 7 Board Chair Dr. Ed Hammond. Infoway uses HL 7 in defining the interoperability standards that are used in every clinical domain and demographic registry Infoway invests in. Thus they are critical to the 245 Infoway-funded electronic health projects currently underway across Canada. The appointment of Mr. Giokas will ensure the needs of Canadian patients, clinicians and vendors are well represented on the international stage.
Some of the Challenges of Maintaining Databases Optimizing RELIABILITY § Trained personnel § Inter-rater reliability § Commitment to end product § Timeliness on data entry § Up-to-date on standards changes § Responsive to client needs § Multiple stake holders Databases March 17, 2008

Plan it well and things may actually roll your way. GOOD LUCK !
0d7e00485aed3149f815ea4ed167a62f.ppt