d65209bf8c4c7cbdf6d0062d1ca6307d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 106
 MM 04 - Goods Receipt & Invoice Verification November , 2000 Ó XX Consulting 2000
MM 04 - Goods Receipt & Invoice Verification November , 2000 Ó XX Consulting 2000
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 2
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 2
 General Concept l Goods receipt with reference to a purchase order allows: n n Invoice verification based on quantity received. n Purchase order history update. n Inventory quantity and value update. n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Delivery notification. n l Data to be copied from the purchase order to the goods receipt document. Automatic update to G/L accounts. If a goods receipt does not contain a purchase order number on the delivery slip, a search for the correct purchase order number can be performed using the material number or the vendor number. 3
General Concept l Goods receipt with reference to a purchase order allows: n n Invoice verification based on quantity received. n Purchase order history update. n Inventory quantity and value update. n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Delivery notification. n l Data to be copied from the purchase order to the goods receipt document. Automatic update to G/L accounts. If a goods receipt does not contain a purchase order number on the delivery slip, a search for the correct purchase order number can be performed using the material number or the vendor number. 3
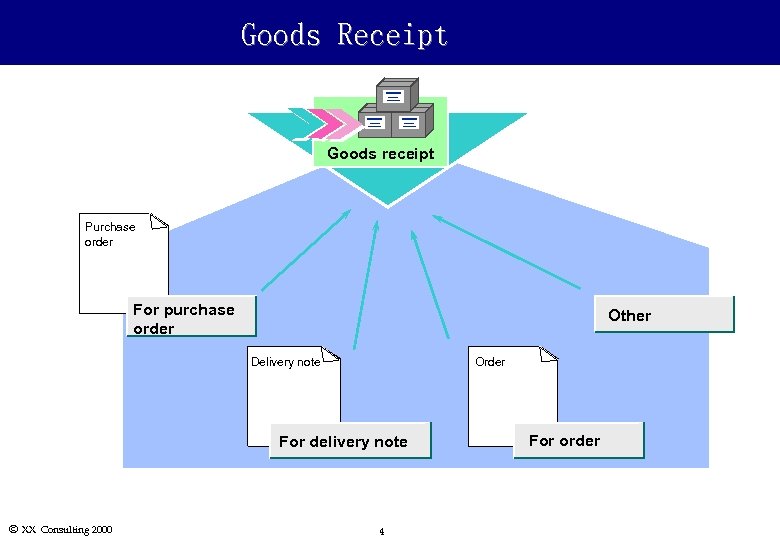 Goods Receipt Goods receipt Purchase order For purchase order Other Delivery note Order For delivery note Ó XX Consulting 2000 4 For order
Goods Receipt Goods receipt Purchase order For purchase order Other Delivery note Order For delivery note Ó XX Consulting 2000 4 For order
 Goods Receipt Destinations l Stock: Material destined for the warehouse is given a storage location. Goods receipts for the warehouse can be posted to three different stock types: n Unrestricted-use n Quality inspection n Blocked stock (valuated) Material intended for consumption (e. g. , l Consumption: charged to a cost center or a project) can be assigned a recipient or unloading point. Conditionally accepted l Goods Receipt Blocked Stock: material is usually recorded into GR blocked stock. In the stock overview, there is a separate column for blocked stock. The material is not valuated until released from blocked stock but the inventory quantity is updated immediately. Ó XX Consulting 2000 5
Goods Receipt Destinations l Stock: Material destined for the warehouse is given a storage location. Goods receipts for the warehouse can be posted to three different stock types: n Unrestricted-use n Quality inspection n Blocked stock (valuated) Material intended for consumption (e. g. , l Consumption: charged to a cost center or a project) can be assigned a recipient or unloading point. Conditionally accepted l Goods Receipt Blocked Stock: material is usually recorded into GR blocked stock. In the stock overview, there is a separate column for blocked stock. The material is not valuated until released from blocked stock but the inventory quantity is updated immediately. Ó XX Consulting 2000 5
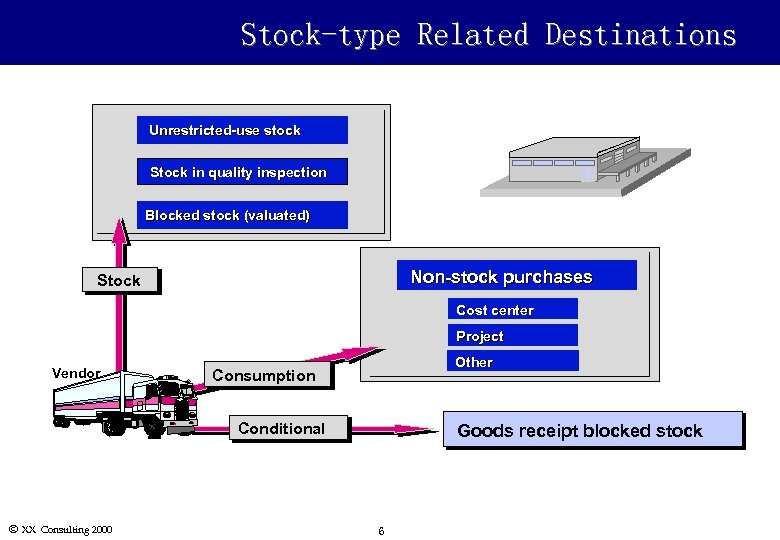 Stock-type Related Destinations Unrestricted-use stock Stock in quality inspection Blocked stock (valuated) Non-stock purchases Stock Cost center Project Vendor Other Consumption Conditional Ó XX Consulting 2000 Goods receipt blocked stock 6
Stock-type Related Destinations Unrestricted-use stock Stock in quality inspection Blocked stock (valuated) Non-stock purchases Stock Cost center Project Vendor Other Consumption Conditional Ó XX Consulting 2000 Goods receipt blocked stock 6
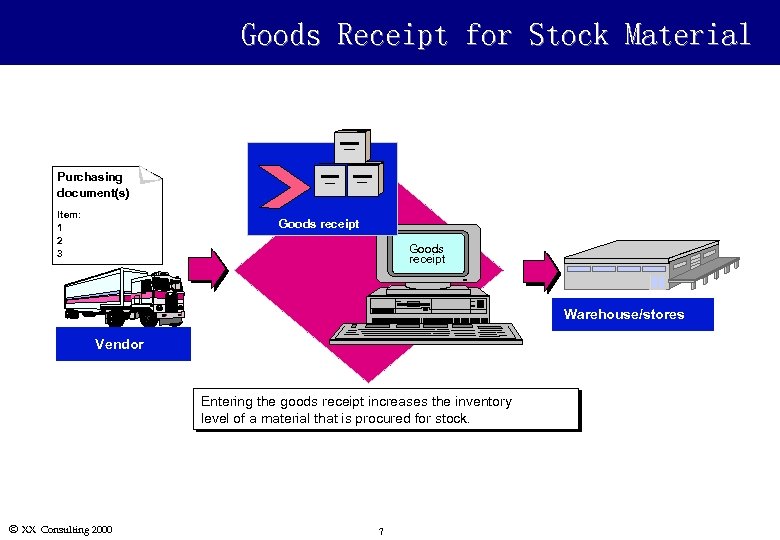 Goods Receipt for Stock Material Purchasing document(s) Item: 1 2 3 Goods receipt Warehouse/stores Vendor Entering the goods receipt increases the inventory level of a material that is procured for stock. Ó XX Consulting 2000 7
Goods Receipt for Stock Material Purchasing document(s) Item: 1 2 3 Goods receipt Warehouse/stores Vendor Entering the goods receipt increases the inventory level of a material that is procured for stock. Ó XX Consulting 2000 7
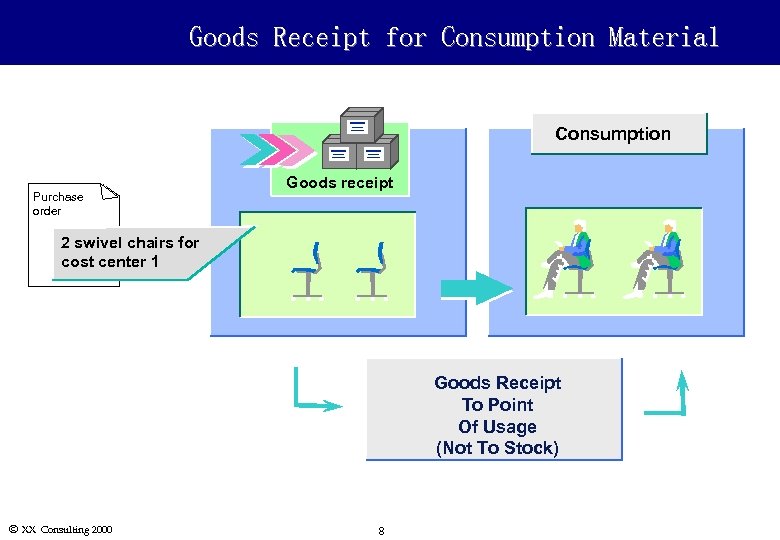 Goods Receipt for Consumption Material Consumption Purchase order Goods receipt 2 swivel chairs for cost center 1 Goods Receipt To Point Of Usage (Not To Stock) Ó XX Consulting 2000 8
Goods Receipt for Consumption Material Consumption Purchase order Goods receipt 2 swivel chairs for cost center 1 Goods Receipt To Point Of Usage (Not To Stock) Ó XX Consulting 2000 8
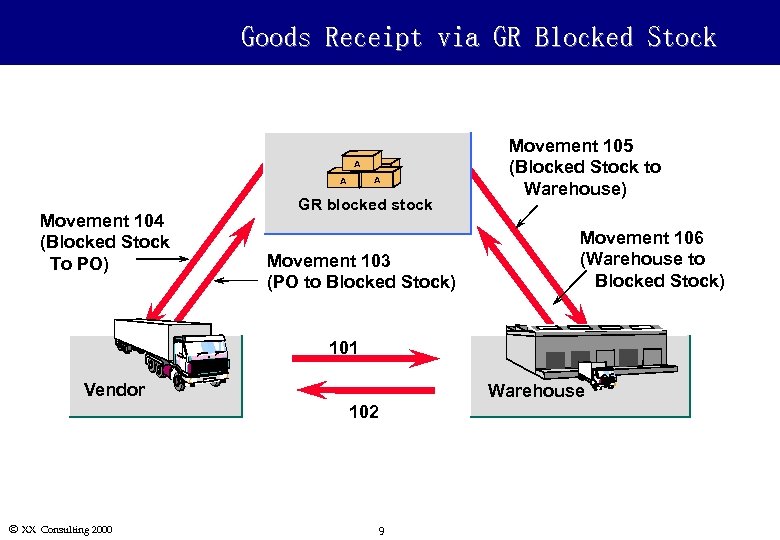 Goods Receipt via GR Blocked Stock A A Movement 104 (Blocked Stock To PO) A A GR blocked stock Movement 103 (PO to Blocked Stock) Movement 105 (Blocked Stock to Warehouse) Movement 106 (Warehouse to Blocked Stock) 101 Vendor Warehouse 102 Ó XX Consulting 2000 9
Goods Receipt via GR Blocked Stock A A Movement 104 (Blocked Stock To PO) A A GR blocked stock Movement 103 (PO to Blocked Stock) Movement 105 (Blocked Stock to Warehouse) Movement 106 (Warehouse to Blocked Stock) 101 Vendor Warehouse 102 Ó XX Consulting 2000 9
 Movement Type Concept l Movement types differentiate among the following stock transactions: n n Goods issue n l Goods receipt Stock transfer Movement type determines which: n n General ledger stock or consumption accounts are updated. n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock types are updated. n l Quantity fields are updated. Fields are displayed during document entry. A three-digit code identifies the particular movement to be performed (e. g. , 101 = purchase order receipt). 10
Movement Type Concept l Movement types differentiate among the following stock transactions: n n Goods issue n l Goods receipt Stock transfer Movement type determines which: n n General ledger stock or consumption accounts are updated. n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock types are updated. n l Quantity fields are updated. Fields are displayed during document entry. A three-digit code identifies the particular movement to be performed (e. g. , 101 = purchase order receipt). 10
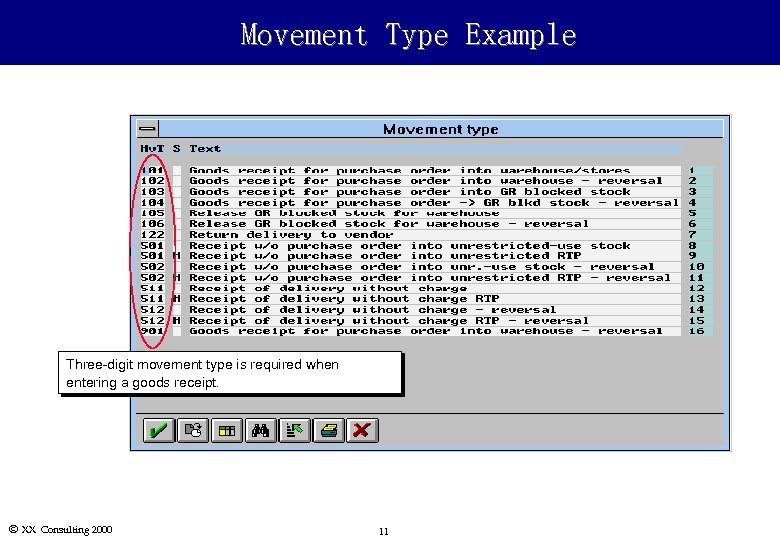 Movement Type Example Three-digit movement type is required when entering a goods receipt. Ó XX Consulting 2000 11
Movement Type Example Three-digit movement type is required when entering a goods receipt. Ó XX Consulting 2000 11
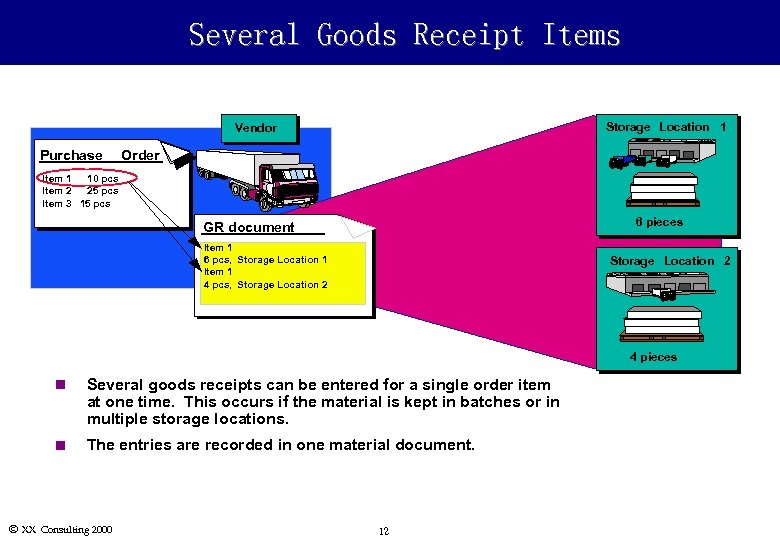 Several Goods Receipt Items Storage Location 1 Vendor Purchase Order Item 1 10 pcs Item 2 25 pcs Item 3 15 pcs 6 pieces GR document Item 1 6 pcs, Storage Location 1 Item 1 4 pcs, Storage Location 2 4 pieces n Several goods receipts can be entered for a single order item at one time. This occurs if the material is kept in batches or in multiple storage locations. n The entries are recorded in one material document. Ó XX Consulting 2000 12
Several Goods Receipt Items Storage Location 1 Vendor Purchase Order Item 1 10 pcs Item 2 25 pcs Item 3 15 pcs 6 pieces GR document Item 1 6 pcs, Storage Location 1 Item 1 4 pcs, Storage Location 2 4 pieces n Several goods receipts can be entered for a single order item at one time. This occurs if the material is kept in batches or in multiple storage locations. n The entries are recorded in one material document. Ó XX Consulting 2000 12
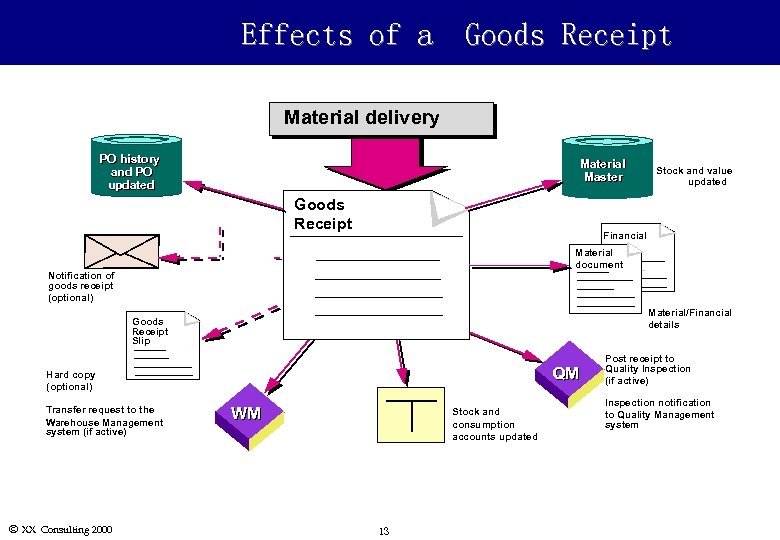 Effects of a Goods Receipt Material delivery PO history and PO updated Material Master Goods Receipt Financial Material document Notification of goods receipt (optional) Material/Financial details Goods Receipt Slip QM Hard copy (optional) Transfer request to the Warehouse Management system (if active) Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock and value updated WM Stock and consumption accounts updated 13 Post receipt to Quality Inspection (if active) Inspection notification to Quality Management system
Effects of a Goods Receipt Material delivery PO history and PO updated Material Master Goods Receipt Financial Material document Notification of goods receipt (optional) Material/Financial details Goods Receipt Slip QM Hard copy (optional) Transfer request to the Warehouse Management system (if active) Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock and value updated WM Stock and consumption accounts updated 13 Post receipt to Quality Inspection (if active) Inspection notification to Quality Management system
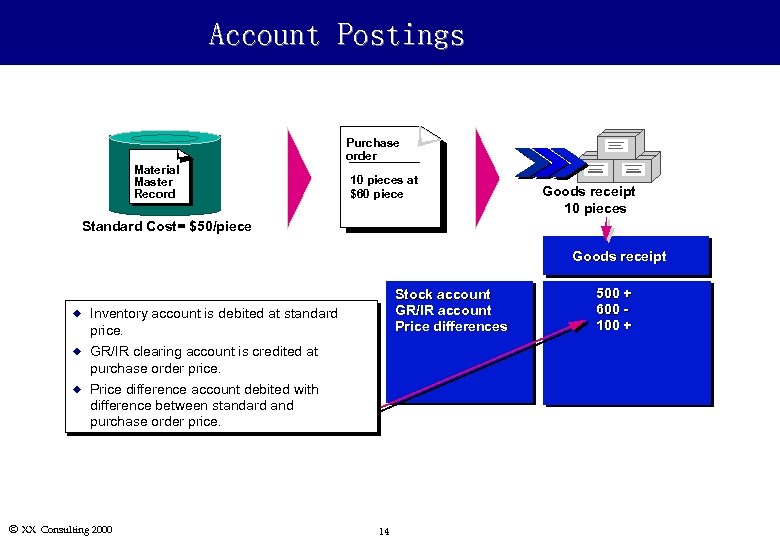 Account Postings Material Master Record Purchase order 10 pieces at $60 piece Goods receipt 10 pieces Standard Cost= $50/piece Goods receipt u Inventory account is debited at standard price. u GR/IR clearing account is credited at purchase order price. u Stock account GR/IR account Price differences Price difference account debited with difference between standard and purchase order price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 14 500 + 600 100 +
Account Postings Material Master Record Purchase order 10 pieces at $60 piece Goods receipt 10 pieces Standard Cost= $50/piece Goods receipt u Inventory account is debited at standard price. u GR/IR clearing account is credited at purchase order price. u Stock account GR/IR account Price differences Price difference account debited with difference between standard and purchase order price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 14 500 + 600 100 +
 The Document Concept l A document is proof that a business transaction or posting occurred. l In the SAP R/3 System, documents are generated and stored for every goods movement. There are two types of documents: n n l Material documents Accounting documents movement. record inventory impacts and changes. record the financial impact of a goods Once a goods movement has been posted, quantities, materials, movement types and organizational levels cannot be changed. Only data such as text can be changed. Mistakes are corrected with a new document. Documents can be canceled or reversed. Ó XX Consulting 2000 15
The Document Concept l A document is proof that a business transaction or posting occurred. l In the SAP R/3 System, documents are generated and stored for every goods movement. There are two types of documents: n n l Material documents Accounting documents movement. record inventory impacts and changes. record the financial impact of a goods Once a goods movement has been posted, quantities, materials, movement types and organizational levels cannot be changed. Only data such as text can be changed. Mistakes are corrected with a new document. Documents can be canceled or reversed. Ó XX Consulting 2000 15
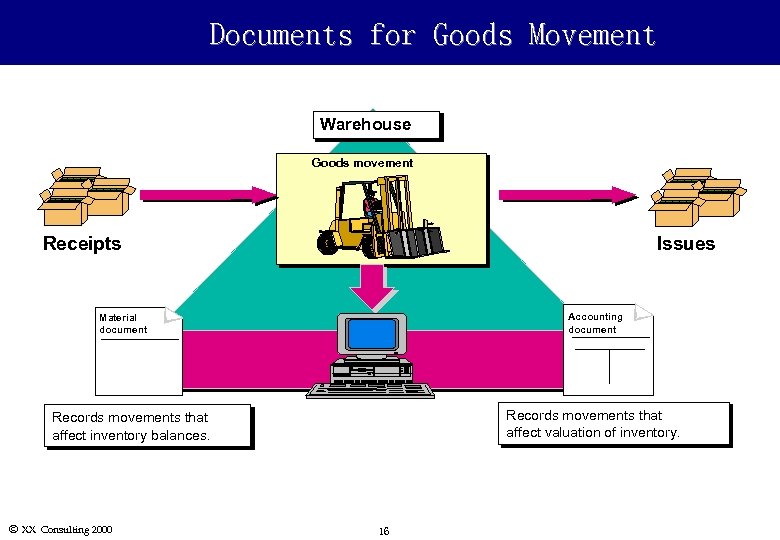 Documents for Goods Movement Warehouse Goods movement Receipts Issues Accounting document Material document Records movements that affect valuation of inventory. Records movements that affect inventory balances. Ó XX Consulting 2000 16
Documents for Goods Movement Warehouse Goods movement Receipts Issues Accounting document Material document Records movements that affect valuation of inventory. Records movements that affect inventory balances. Ó XX Consulting 2000 16
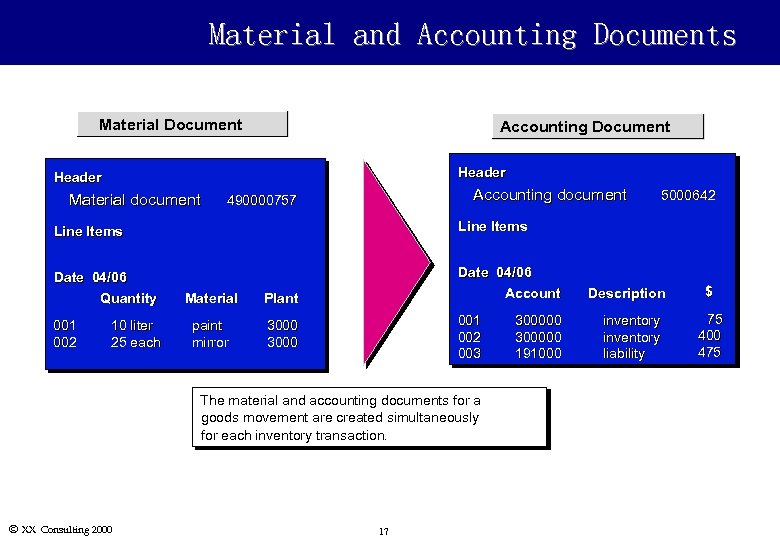 Material and Accounting Documents Material Document Accounting Document Header Material document Accounting document 490000757 Line Items Date 04/06 Quantity Date 04/06 Account 5000642 001 002 10 liter 25 each Material Plant paint mirror 3000 001 002 003 The material and accounting documents for a goods movement are created simultaneously for each inventory transaction. Ó XX Consulting 2000 17 300000 191000 Description inventory liability $ 75 400 475
Material and Accounting Documents Material Document Accounting Document Header Material document Accounting document 490000757 Line Items Date 04/06 Quantity Date 04/06 Account 5000642 001 002 10 liter 25 each Material Plant paint mirror 3000 001 002 003 The material and accounting documents for a goods movement are created simultaneously for each inventory transaction. Ó XX Consulting 2000 17 300000 191000 Description inventory liability $ 75 400 475
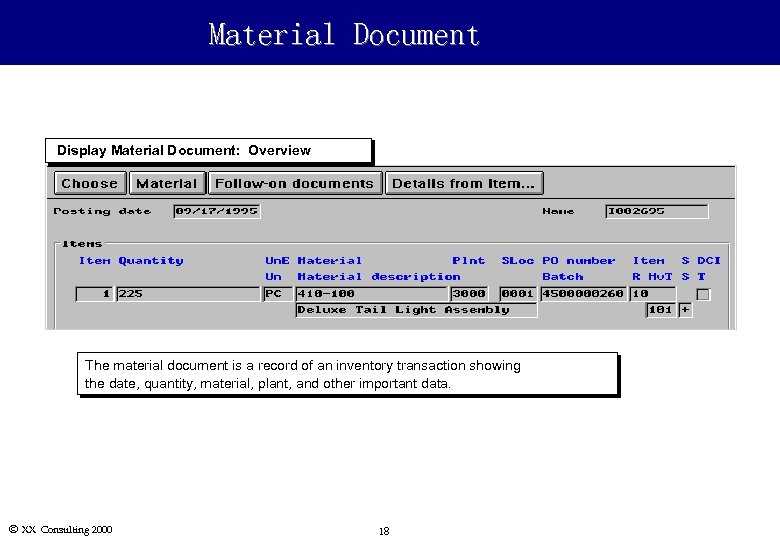 Material Document Display Material Document: Overview The material document is a record of an inventory transaction showing the date, quantity, material, plant, and other important data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 18
Material Document Display Material Document: Overview The material document is a record of an inventory transaction showing the date, quantity, material, plant, and other important data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 18
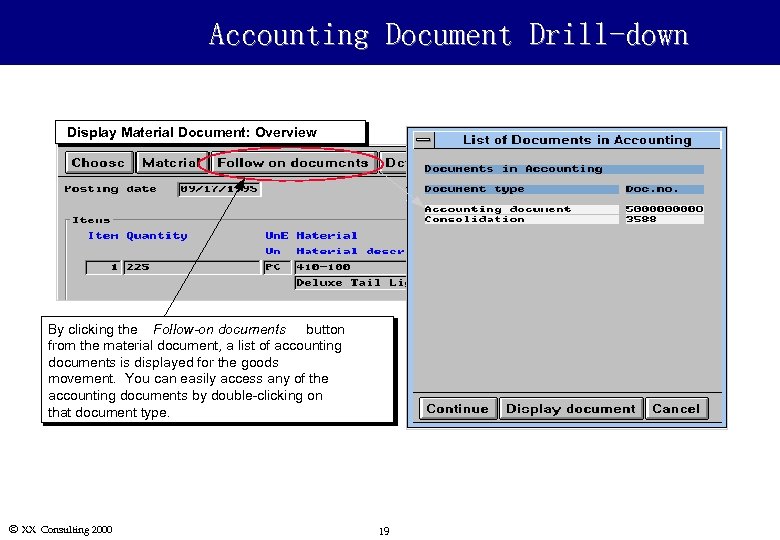 Accounting Document Drill-down Display Material Document: Overview By clicking the Follow-on documents button from the material document, a list of accounting documents is displayed for the goods movement. You can easily access any of the accounting documents by double-clicking on that document type. Ó XX Consulting 2000 19
Accounting Document Drill-down Display Material Document: Overview By clicking the Follow-on documents button from the material document, a list of accounting documents is displayed for the goods movement. You can easily access any of the accounting documents by double-clicking on that document type. Ó XX Consulting 2000 19
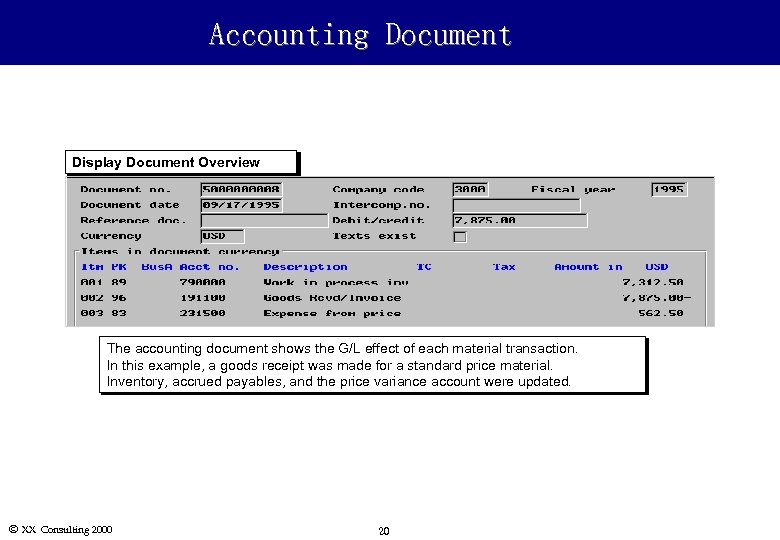 Accounting Document Display Document Overview The accounting document shows the G/L effect of each material transaction. In this example, a goods receipt was made for a standard price material. Inventory, accrued payables, and the price variance account were updated. Ó XX Consulting 2000 20
Accounting Document Display Document Overview The accounting document shows the G/L effect of each material transaction. In this example, a goods receipt was made for a standard price material. Inventory, accrued payables, and the price variance account were updated. Ó XX Consulting 2000 20
 Summary Material document and accounting document are created after goods receipt. Ó XX Consulting 2000 21
Summary Material document and accounting document are created after goods receipt. Ó XX Consulting 2000 21
 Exercise for Goods Receipt Now it’s time for you to do: MM 04 - Exercise 10 30 minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 22
Exercise for Goods Receipt Now it’s time for you to do: MM 04 - Exercise 10 30 minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 22
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reports Ó XX Consulting 2000 23
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reports Ó XX Consulting 2000 23
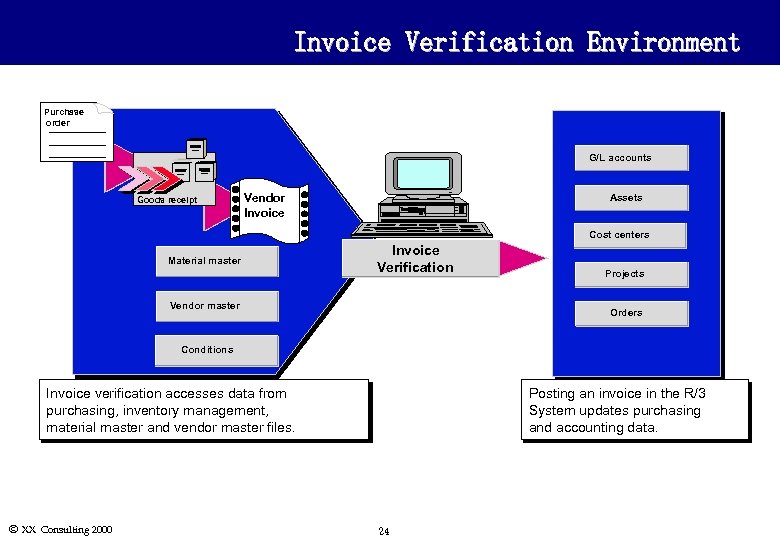 Invoice Verification Environment Purchase order G/L accounts Goods receipt Vendor Invoice Assets Cost centers Material master Invoice Verification Vendor master Projects Orders Conditions Invoice verification accesses data from purchasing, inventory management, material master and vendor master files. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Posting an invoice in the R/3 System updates purchasing and accounting data. 24
Invoice Verification Environment Purchase order G/L accounts Goods receipt Vendor Invoice Assets Cost centers Material master Invoice Verification Vendor master Projects Orders Conditions Invoice verification accesses data from purchasing, inventory management, material master and vendor master files. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Posting an invoice in the R/3 System updates purchasing and accounting data. 24
 Types of Invoice Verification : All purchase order items may l Purchase order-based be settled regardless of partial deliveries. : Goods receipt must already have l Goods receipt-based been entered for the quantity invoiced. Each receipt is entered and settled individually. Invoices for quantities greater than receipt quantities cannot be posted. This type of invoice verification must be specified in the purchase order. : Invoice is directly posted to a l Vendor invoice-based material, general ledger, or a fixed asset account if a purchase order or a goods receipt does not exist in the R/3 System. l Evaluated Receipt Settlement (pay on receipt): is automatically created upon goods receipt based on purchase order terms and receipt quantity. Ó XX Consulting 2000 25 Invoice
Types of Invoice Verification : All purchase order items may l Purchase order-based be settled regardless of partial deliveries. : Goods receipt must already have l Goods receipt-based been entered for the quantity invoiced. Each receipt is entered and settled individually. Invoices for quantities greater than receipt quantities cannot be posted. This type of invoice verification must be specified in the purchase order. : Invoice is directly posted to a l Vendor invoice-based material, general ledger, or a fixed asset account if a purchase order or a goods receipt does not exist in the R/3 System. l Evaluated Receipt Settlement (pay on receipt): is automatically created upon goods receipt based on purchase order terms and receipt quantity. Ó XX Consulting 2000 25 Invoice
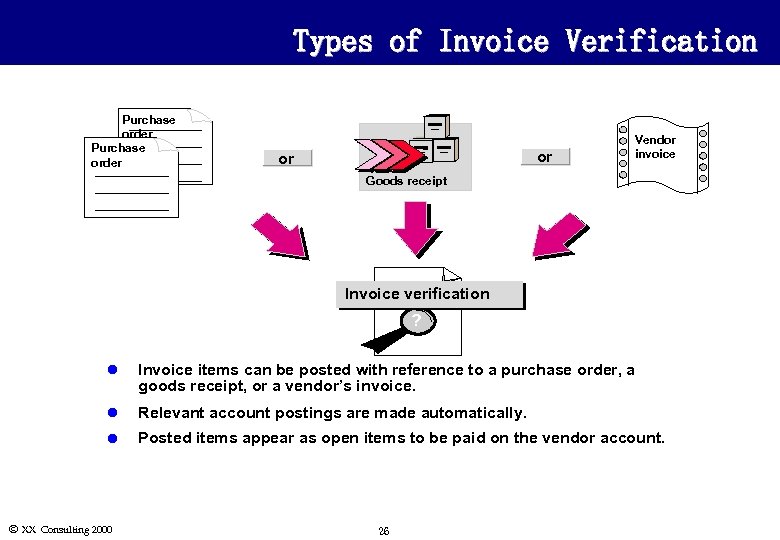 Types of Invoice Verification Purchase order or or Vendor invoice Goods receipt Invoice verification ? l Invoice items can be posted with reference to a purchase order, a goods receipt, or a vendor’s invoice. l Relevant account postings are made automatically. l Posted items appear as open items to be paid on the vendor account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 26
Types of Invoice Verification Purchase order or or Vendor invoice Goods receipt Invoice verification ? l Invoice items can be posted with reference to a purchase order, a goods receipt, or a vendor’s invoice. l Relevant account postings are made automatically. l Posted items appear as open items to be paid on the vendor account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 26
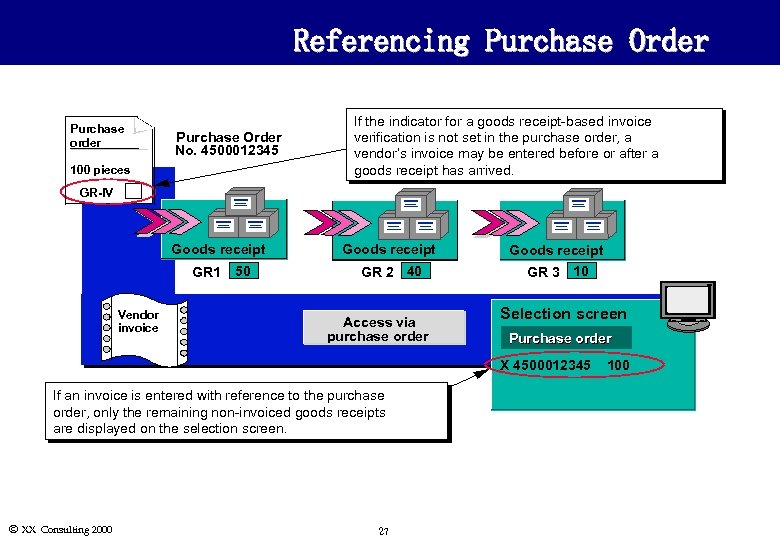 Referencing Purchase Order Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces If the indicator for a goods receipt-based invoice verification is not set in the purchase order, a vendor’s invoice may be entered before or after a goods receipt has arrived. GR-IV Goods receipt GR 1 Vendor invoice 50 Goods receipt GR 2 40 GR 3 10 Access via purchase order Selection screen Purchase order X 4500012345 If an invoice is entered with reference to the purchase order, only the remaining non-invoiced goods receipts are displayed on the selection screen. Ó XX Consulting 2000 27 100
Referencing Purchase Order Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces If the indicator for a goods receipt-based invoice verification is not set in the purchase order, a vendor’s invoice may be entered before or after a goods receipt has arrived. GR-IV Goods receipt GR 1 Vendor invoice 50 Goods receipt GR 2 40 GR 3 10 Access via purchase order Selection screen Purchase order X 4500012345 If an invoice is entered with reference to the purchase order, only the remaining non-invoiced goods receipts are displayed on the selection screen. Ó XX Consulting 2000 27 100
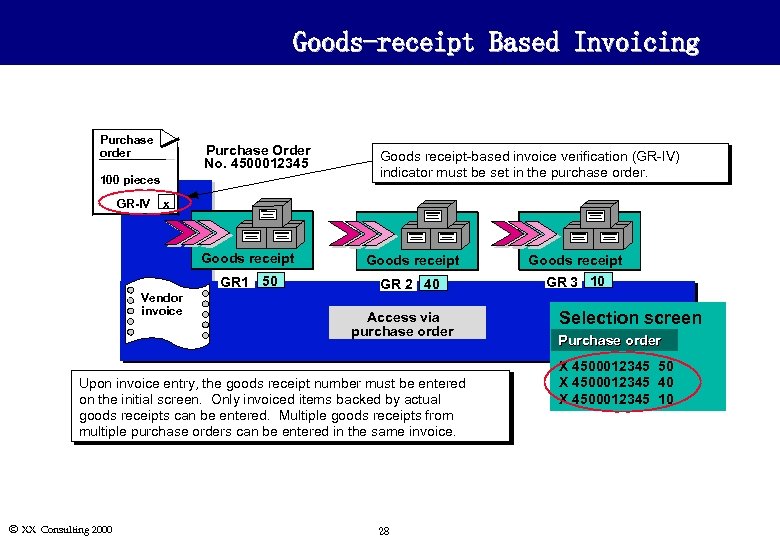 Goods-receipt Based Invoicing Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces GR-IV Goods receipt-based invoice verification (GR-IV) indicator must be set in the purchase order. x Goods receipt GR 1 50 Vendor invoice Goods receipt GR 2 40 GR 3 10 Access via purchase order Upon invoice entry, the goods receipt number must be entered on the initial screen. Only invoiced items backed by actual goods receipts can be entered. Multiple goods receipts from multiple purchase orders can be entered in the same invoice. Ó XX Consulting 2000 28 Selection screen Purchase order X 4500012345 50 X 4500012345 40 X 4500012345 10
Goods-receipt Based Invoicing Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces GR-IV Goods receipt-based invoice verification (GR-IV) indicator must be set in the purchase order. x Goods receipt GR 1 50 Vendor invoice Goods receipt GR 2 40 GR 3 10 Access via purchase order Upon invoice entry, the goods receipt number must be entered on the initial screen. Only invoiced items backed by actual goods receipts can be entered. Multiple goods receipts from multiple purchase orders can be entered in the same invoice. Ó XX Consulting 2000 28 Selection screen Purchase order X 4500012345 50 X 4500012345 40 X 4500012345 10
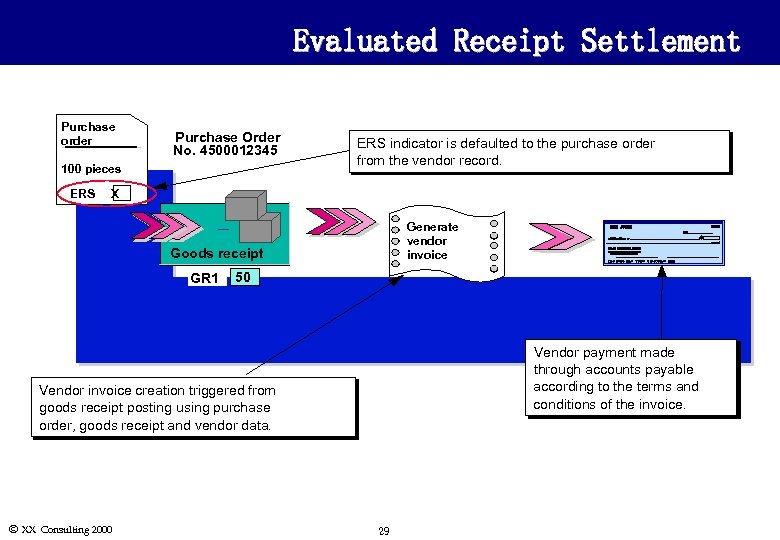 Evaluated Receipt Settlement Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces ERS indicator is defaulted to the purchase order from the vendor record. X Generate vendor invoice Goods receipt GR 1 50 Vendor payment made through accounts payable according to the terms and conditions of the invoice. Vendor invoice creation triggered from goods receipt posting using purchase order, goods receipt and vendor data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 29
Evaluated Receipt Settlement Purchase order Purchase Order No. 4500012345 100 pieces ERS indicator is defaulted to the purchase order from the vendor record. X Generate vendor invoice Goods receipt GR 1 50 Vendor payment made through accounts payable according to the terms and conditions of the invoice. Vendor invoice creation triggered from goods receipt posting using purchase order, goods receipt and vendor data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 29
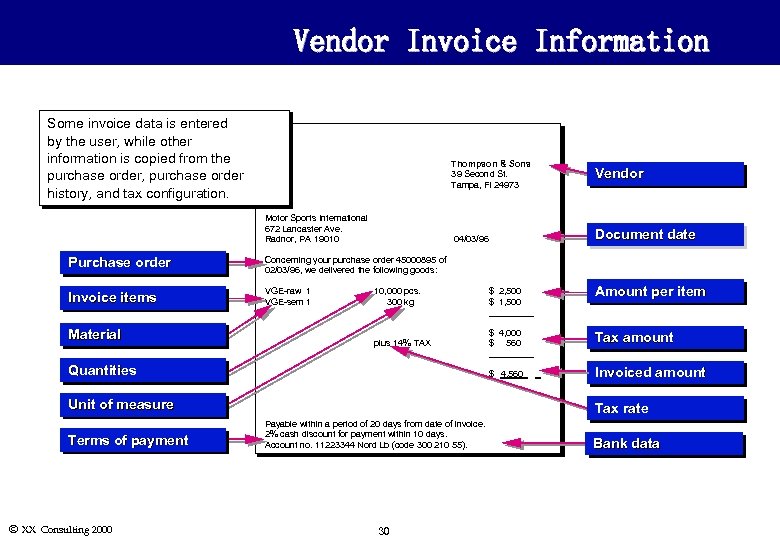 Vendor Invoice Information Some invoice data is entered by the user, while other information is copied from the purchase order, purchase order history, and tax configuration. Thompson & Sons 39 Second St. Tampa, Fl 24973 Motor Sports International 672 Lancaster Ave. Radnor, PA 19010 04/03/96 Purchase order VGE-raw 1 VGE-sem 1 Document date Concerning your purchase order 45000895 of 02/03/96, we delivered the following goods: Invoice items Vendor Material 10, 000 pcs. 300 kg plus 14% TAX Quantities Ó XX Consulting 2000 Amount per item $ 4, 000 $ 560 _____ Tax amount $ 4, 560_ _ Unit of measure Terms of payment $ 2, 500 $ 1, 500 _____ Invoiced amount Tax rate Payable within a period of 20 days from date of invoice. 2% cash discount for payment within 10 days. Account no. 11223344 Nord Lb (code 300 210 55). 30 Bank data
Vendor Invoice Information Some invoice data is entered by the user, while other information is copied from the purchase order, purchase order history, and tax configuration. Thompson & Sons 39 Second St. Tampa, Fl 24973 Motor Sports International 672 Lancaster Ave. Radnor, PA 19010 04/03/96 Purchase order VGE-raw 1 VGE-sem 1 Document date Concerning your purchase order 45000895 of 02/03/96, we delivered the following goods: Invoice items Vendor Material 10, 000 pcs. 300 kg plus 14% TAX Quantities Ó XX Consulting 2000 Amount per item $ 4, 000 $ 560 _____ Tax amount $ 4, 560_ _ Unit of measure Terms of payment $ 2, 500 $ 1, 500 _____ Invoiced amount Tax rate Payable within a period of 20 days from date of invoice. 2% cash discount for payment within 10 days. Account no. 11223344 Nord Lb (code 300 210 55). 30 Bank data
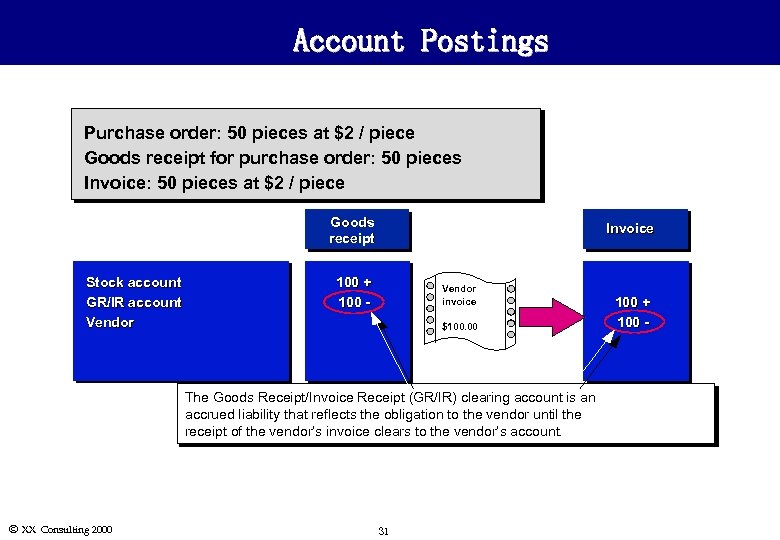 Account Postings Purchase order: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt for purchase order: 50 pieces Invoice: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Invoice 100 + 100 - Vendor invoice $100. 00 The Goods Receipt/Invoice Receipt (GR/IR) clearing account is an accrued liability that reflects the obligation to the vendor until the receipt of the vendor’s invoice clears to the vendor’s account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 31 100 + 100 -
Account Postings Purchase order: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt for purchase order: 50 pieces Invoice: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Invoice 100 + 100 - Vendor invoice $100. 00 The Goods Receipt/Invoice Receipt (GR/IR) clearing account is an accrued liability that reflects the obligation to the vendor until the receipt of the vendor’s invoice clears to the vendor’s account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 31 100 + 100 -
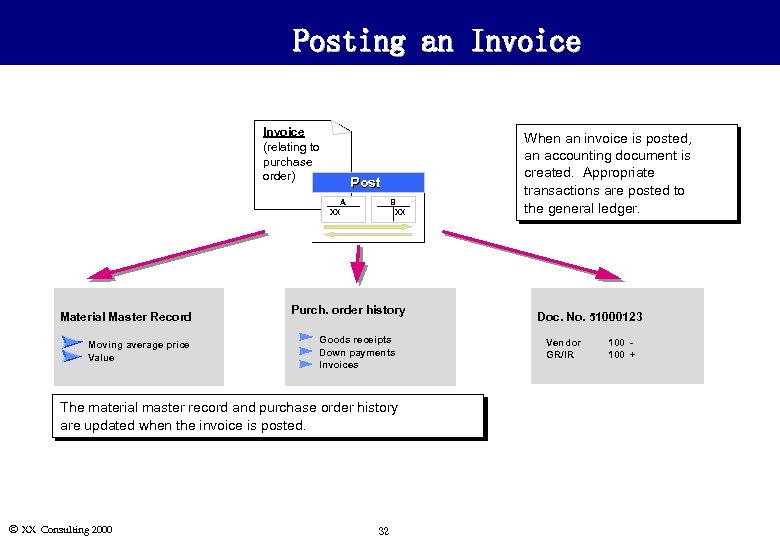 Posting an Invoice (relating to purchase order) Post A XX Material Master Record Moving average price Value B XX Purch. order history Goods receipts Down payments Invoices The material master record and purchase order history are updated when the invoice is posted. Ó XX Consulting 2000 32 When an invoice is posted, an accounting document is created. Appropriate transactions are posted to the general ledger. Doc. No. 51000123 Vendor GR/IR 100 +
Posting an Invoice (relating to purchase order) Post A XX Material Master Record Moving average price Value B XX Purch. order history Goods receipts Down payments Invoices The material master record and purchase order history are updated when the invoice is posted. Ó XX Consulting 2000 32 When an invoice is posted, an accounting document is created. Appropriate transactions are posted to the general ledger. Doc. No. 51000123 Vendor GR/IR 100 +
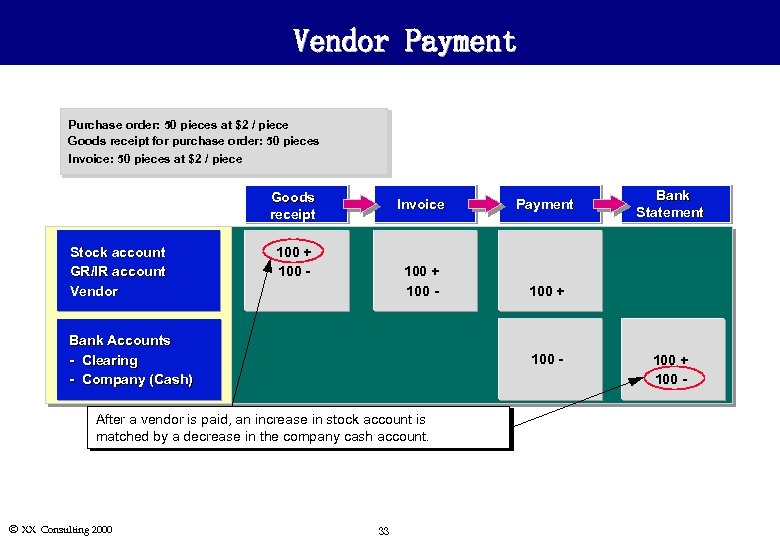 Vendor Payment Purchase order: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt for purchase order: 50 pieces Invoice: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Invoice 100 + 100 - Payment 100 + Bank Accounts - Clearing - Company (Cash) 100 - After a vendor is paid, an increase in stock account is matched by a decrease in the company cash account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 33 Bank Statement 100 + 100 -
Vendor Payment Purchase order: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt for purchase order: 50 pieces Invoice: 50 pieces at $2 / piece Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Invoice 100 + 100 - Payment 100 + Bank Accounts - Clearing - Company (Cash) 100 - After a vendor is paid, an increase in stock account is matched by a decrease in the company cash account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 33 Bank Statement 100 + 100 -
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 34
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 34
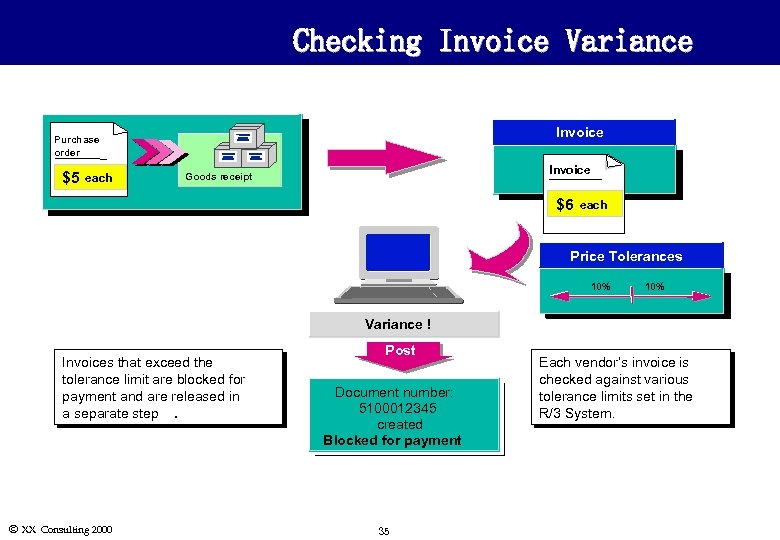 Checking Invoice Variance Invoice Purchase order $5 each Invoice Goods receipt $6 each Price Tolerances 10% Variance ! Invoices that exceed the tolerance limit are blocked for payment and are released in a separate step. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Post Document number: 5100012345 created Blocked for payment 35 Each vendor’s invoice is checked against various tolerance limits set in the R/3 System.
Checking Invoice Variance Invoice Purchase order $5 each Invoice Goods receipt $6 each Price Tolerances 10% Variance ! Invoices that exceed the tolerance limit are blocked for payment and are released in a separate step. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Post Document number: 5100012345 created Blocked for payment 35 Each vendor’s invoice is checked against various tolerance limits set in the R/3 System.
 Types of Invoice Variance l There are several types of variances that can be checked by the SAP R/3 System during invoice verification: Delivered quantity differs from the invoiced quantity. n Quantity: n Price: n Order price quantity Purchase order price differs from the invoice price. : Goods receipt (or purchase order) order price quantity differs from invoice order price quantity. n l Date: Invoice receipt date is before planned delivery date. Any one purchase order line item may have one or more variances that would cause the invoice to be blocked for payment by the R/3 System. Ó XX Consulting 2000 36
Types of Invoice Variance l There are several types of variances that can be checked by the SAP R/3 System during invoice verification: Delivered quantity differs from the invoiced quantity. n Quantity: n Price: n Order price quantity Purchase order price differs from the invoice price. : Goods receipt (or purchase order) order price quantity differs from invoice order price quantity. n l Date: Invoice receipt date is before planned delivery date. Any one purchase order line item may have one or more variances that would cause the invoice to be blocked for payment by the R/3 System. Ó XX Consulting 2000 36
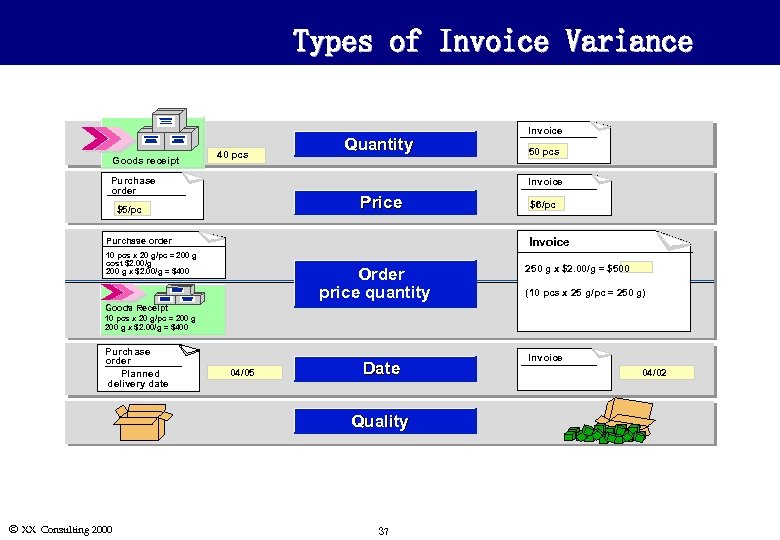 Types of Invoice Variance Goods receipt 40 pcs Purchase order Quantity Invoice 50 pcs Invoice Price $5/pc $6/pc Invoice Purchase order 10 pcs x 20 g/pc = 200 g cost $2. 00/g 200 g x $2. 00/g = $400 Order price quantity 250 g x $2. 00/g = $500 (10 pcs x 25 g/pc = 250 g) Goods Receipt 10 pcs x 20 g/pc = 200 g x $2. 00/g = $400 Purchase order Planned delivery date 04/05 Date Quality Ó XX Consulting 2000 37 Invoice 04/02
Types of Invoice Variance Goods receipt 40 pcs Purchase order Quantity Invoice 50 pcs Invoice Price $5/pc $6/pc Invoice Purchase order 10 pcs x 20 g/pc = 200 g cost $2. 00/g 200 g x $2. 00/g = $400 Order price quantity 250 g x $2. 00/g = $500 (10 pcs x 25 g/pc = 250 g) Goods Receipt 10 pcs x 20 g/pc = 200 g x $2. 00/g = $400 Purchase order Planned delivery date 04/05 Date Quality Ó XX Consulting 2000 37 Invoice 04/02
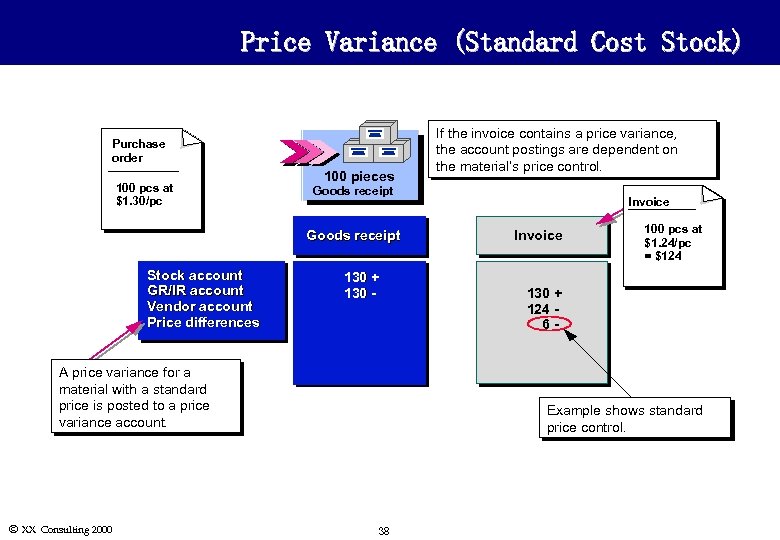 Price Variance (Standard Cost Stock) Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor account Price differences 130 + 130 - A price variance for a material with a standard price is posted to a price variance account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the account postings are dependent on the material’s price control. Invoice 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124 130 + 124 6 - Example shows standard price control. 38
Price Variance (Standard Cost Stock) Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor account Price differences 130 + 130 - A price variance for a material with a standard price is posted to a price variance account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the account postings are dependent on the material’s price control. Invoice 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124 130 + 124 6 - Example shows standard price control. 38
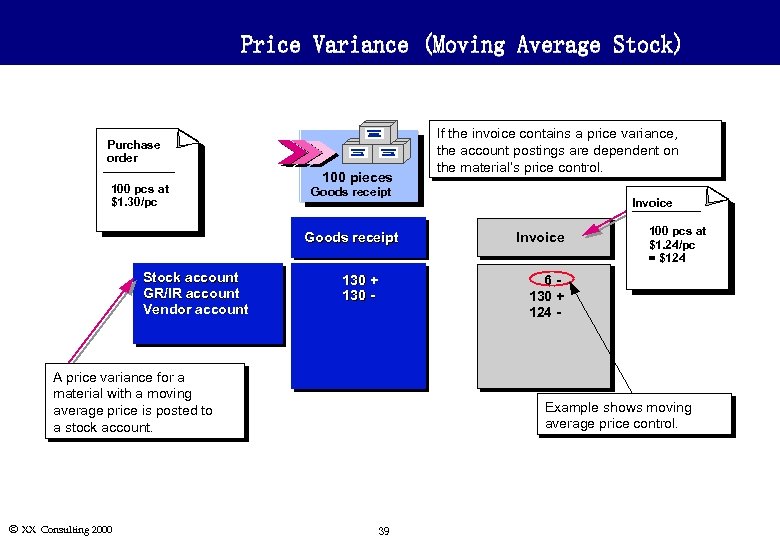 Price Variance (Moving Average Stock) Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor account 130 + 130 - Invoice 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124 6130 + 124 - A price variance for a material with a moving average price is posted to a stock account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the account postings are dependent on the material’s price control. Example shows moving average price control. 39
Price Variance (Moving Average Stock) Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor account 130 + 130 - Invoice 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124 6130 + 124 - A price variance for a material with a moving average price is posted to a stock account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the account postings are dependent on the material’s price control. Example shows moving average price control. 39
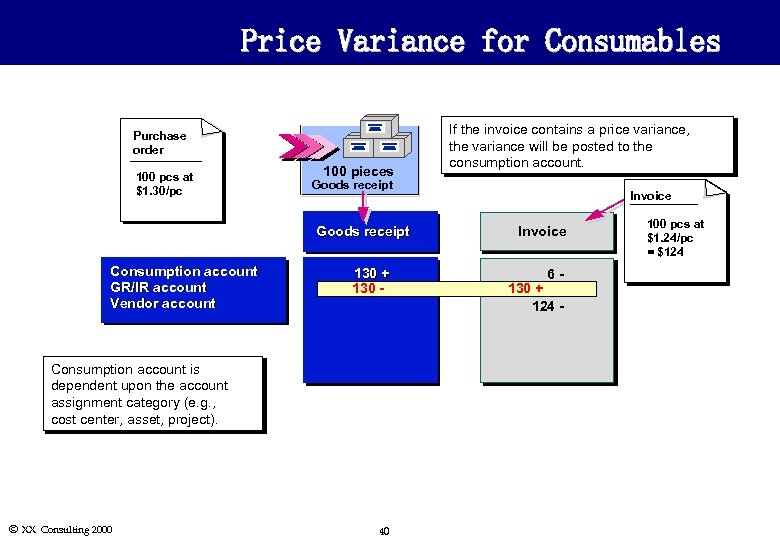 Price Variance for Consumables Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Consumption account GR/IR account Vendor account 130 + 130 -130 Consumption account is dependent upon the account assignment category (e. g. , cost center, asset, project). Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the variance will be posted to the consumption account. 40 Invoice 6130 + + 124 - 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124
Price Variance for Consumables Purchase order 100 pcs at $1. 30/pc 100 pieces Goods receipt Consumption account GR/IR account Vendor account 130 + 130 -130 Consumption account is dependent upon the account assignment category (e. g. , cost center, asset, project). Ó XX Consulting 2000 If the invoice contains a price variance, the variance will be posted to the consumption account. 40 Invoice 6130 + + 124 - 100 pcs at $1. 24/pc = $124
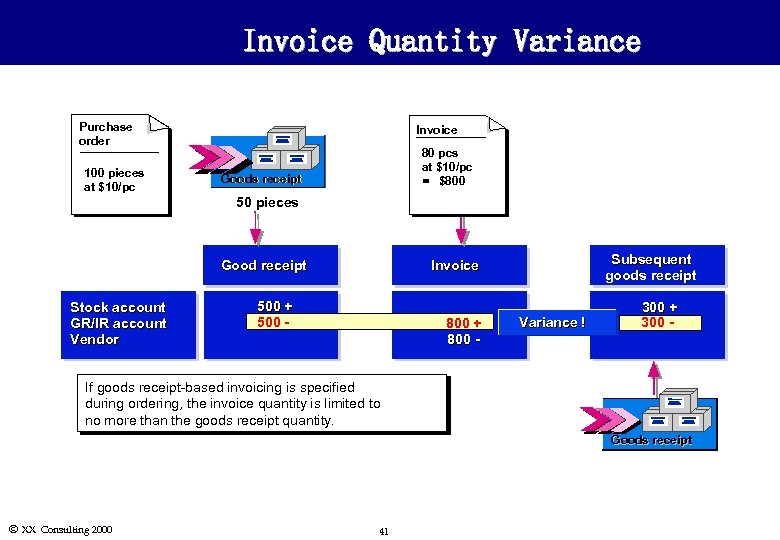 Invoice Quantity Variance Purchase order 100 pieces at $10/pc Invoice 80 pcs at $10/pc = $800 Goods receipt 50 pieces Good receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Subsequent goods receipt Invoice 500 + 500 - 800 -+ 800 - Variance ! 300 + 300 - If goods receipt-based invoicing is specified during ordering, the invoice quantity is limited to no more than the goods receipt quantity. Goods receipt Ó XX Consulting 2000 41
Invoice Quantity Variance Purchase order 100 pieces at $10/pc Invoice 80 pcs at $10/pc = $800 Goods receipt 50 pieces Good receipt Stock account GR/IR account Vendor Subsequent goods receipt Invoice 500 + 500 - 800 -+ 800 - Variance ! 300 + 300 - If goods receipt-based invoicing is specified during ordering, the invoice quantity is limited to no more than the goods receipt quantity. Goods receipt Ó XX Consulting 2000 41
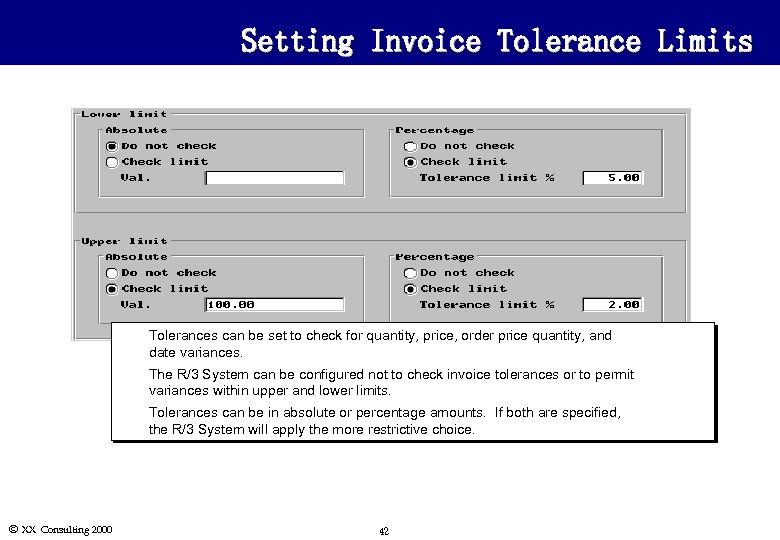 Setting Invoice Tolerance Limits u u The R/3 System can be configured not to check invoice tolerances or to permit variances within upper and lower limits. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Tolerances can be set to check for quantity, price, order price quantity, and date variances. Tolerances can be in absolute or percentage amounts. If both are specified, the R/3 System will apply the more restrictive choice. 42
Setting Invoice Tolerance Limits u u The R/3 System can be configured not to check invoice tolerances or to permit variances within upper and lower limits. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Tolerances can be set to check for quantity, price, order price quantity, and date variances. Tolerances can be in absolute or percentage amounts. If both are specified, the R/3 System will apply the more restrictive choice. 42
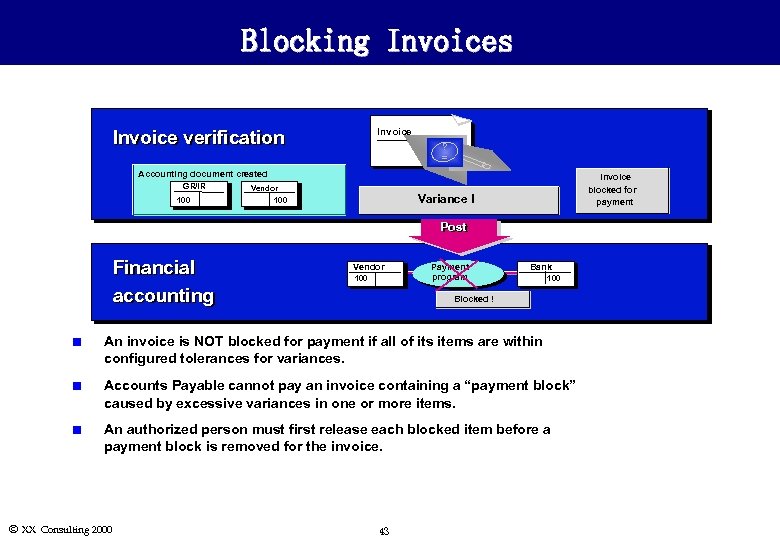 Blocking Invoices Invoice verification ? = Accounting document created GR/IR 100 Vendor 100 Invoice blocked for payment Variance ! Post Financial accounting Vendor 100 Payment program Bank 100 Blocked ! n An invoice is NOT blocked for payment if all of its items are within configured tolerances for variances. n Accounts Payable cannot pay an invoice containing a “payment block” caused by excessive variances in one or more items. n An authorized person must first release each blocked item before a payment block is removed for the invoice. Ó XX Consulting 2000 43
Blocking Invoices Invoice verification ? = Accounting document created GR/IR 100 Vendor 100 Invoice blocked for payment Variance ! Post Financial accounting Vendor 100 Payment program Bank 100 Blocked ! n An invoice is NOT blocked for payment if all of its items are within configured tolerances for variances. n Accounts Payable cannot pay an invoice containing a “payment block” caused by excessive variances in one or more items. n An authorized person must first release each blocked item before a payment block is removed for the invoice. Ó XX Consulting 2000 43
 Invoice Blocking Reasons l One or several excessive variances in any one invoice line item will cause a payment block of the entire invoice. l The SAP R/3 System will automatically calculate blocking reasons for: n Quantity n Price n Order Price Quantity n Date l An invoice may be blocked manually at the time of posting. Ó XX Consulting 2000 44
Invoice Blocking Reasons l One or several excessive variances in any one invoice line item will cause a payment block of the entire invoice. l The SAP R/3 System will automatically calculate blocking reasons for: n Quantity n Price n Order Price Quantity n Date l An invoice may be blocked manually at the time of posting. Ó XX Consulting 2000 44
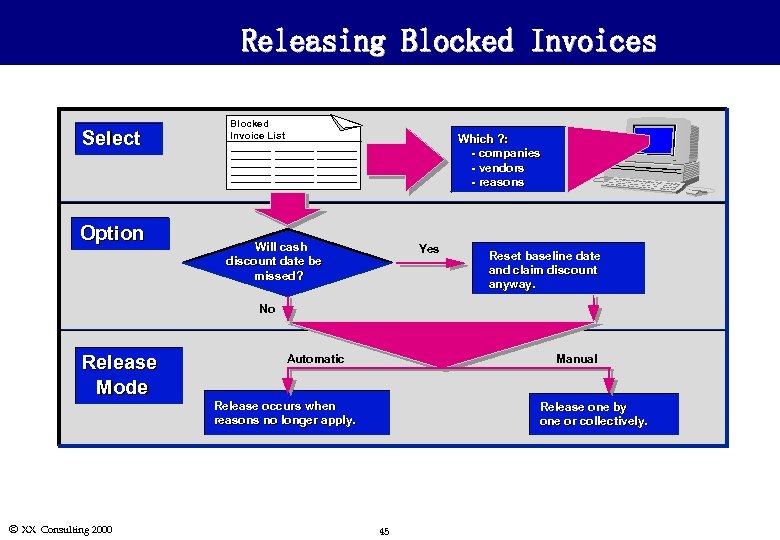 Releasing Blocked Invoices Select Option Blocked Invoice List Which ? : - companies - vendors - reasons Will cash discount date be missed? Yes Reset baseline date and claim discount anyway. No Release Mode Ó XX Consulting 2000 Automatic Manual Release occurs when reasons no longer apply. Release one by one or collectively. 45
Releasing Blocked Invoices Select Option Blocked Invoice List Which ? : - companies - vendors - reasons Will cash discount date be missed? Yes Reset baseline date and claim discount anyway. No Release Mode Ó XX Consulting 2000 Automatic Manual Release occurs when reasons no longer apply. Release one by one or collectively. 45
 Automatic Release l The Automatic release function will release all invoices blocked for quantity, price or date reasons that are no longer valid. For example: n n Ó XX Consulting 2000 An invoice, which arrived early and was blocked for date variance, can be automatically released for payment upon reaching the planned delivery date. n l An invoice, blocked because the invoice quantity exceeded the receipt quantity, can be automatically released after a subsequent delivery because the quantity variance will no longer exist. An invoice, blocked because the invoice price was greater than the purchase order price, can be automatically released for payment if the purchase order price was changed to equal the invoice price. The user must initiate the release of the range of invoices in the R/3 System even though the blocking reasons are no longer valid. 46
Automatic Release l The Automatic release function will release all invoices blocked for quantity, price or date reasons that are no longer valid. For example: n n Ó XX Consulting 2000 An invoice, which arrived early and was blocked for date variance, can be automatically released for payment upon reaching the planned delivery date. n l An invoice, blocked because the invoice quantity exceeded the receipt quantity, can be automatically released after a subsequent delivery because the quantity variance will no longer exist. An invoice, blocked because the invoice price was greater than the purchase order price, can be automatically released for payment if the purchase order price was changed to equal the invoice price. The user must initiate the release of the range of invoices in the R/3 System even though the blocking reasons are no longer valid. 46
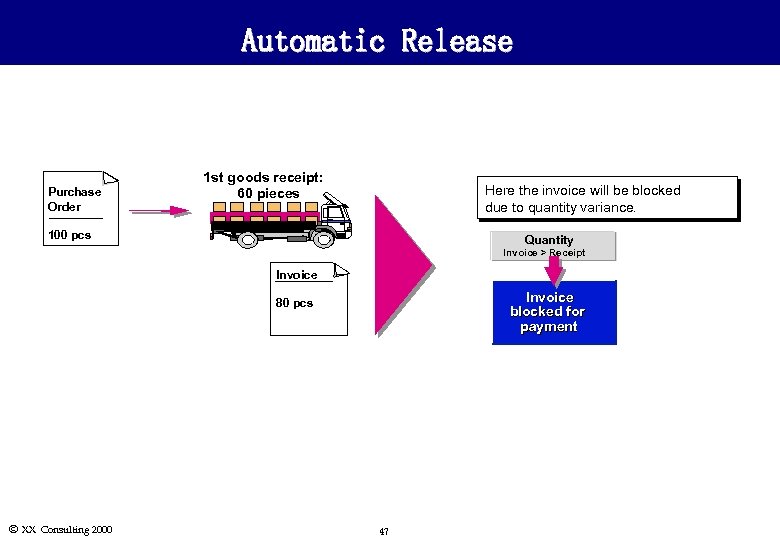 Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Ó XX Consulting 2000 47
Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Ó XX Consulting 2000 47
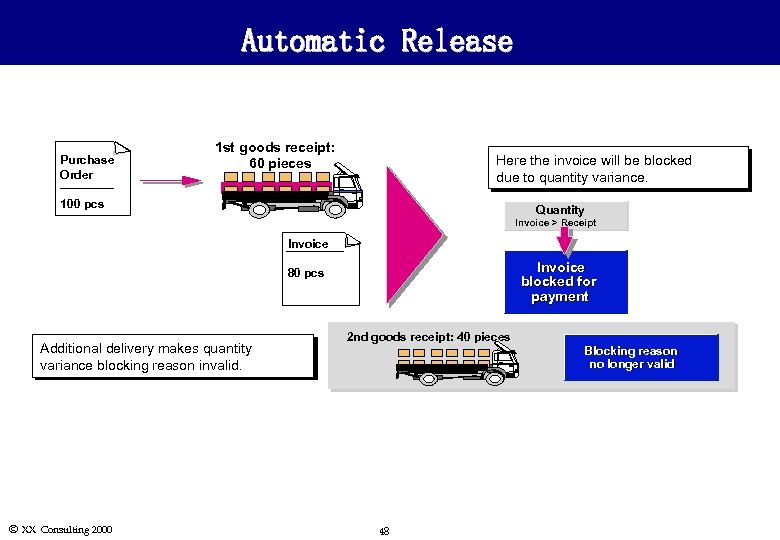 Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Additional delivery makes quantity variance blocking reason invalid. Ó XX Consulting 2000 2 nd goods receipt: 40 pieces Blocking reason no longer valid 48
Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Additional delivery makes quantity variance blocking reason invalid. Ó XX Consulting 2000 2 nd goods receipt: 40 pieces Blocking reason no longer valid 48
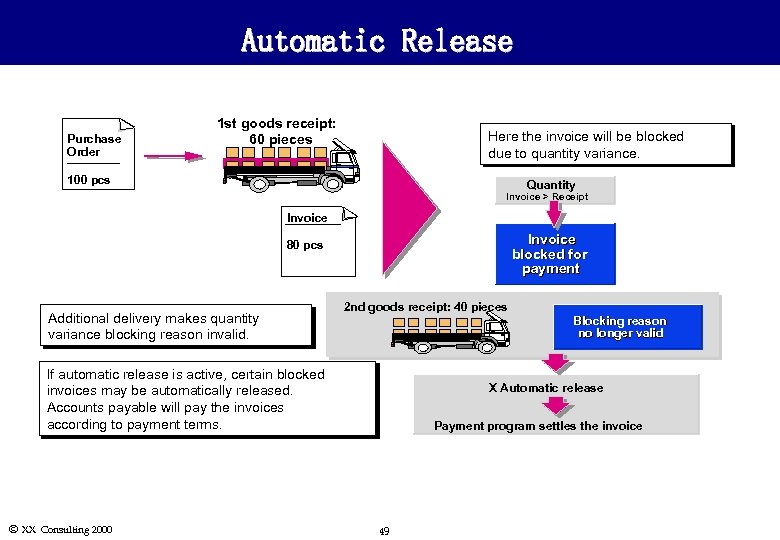 Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Additional delivery makes quantity variance blocking reason invalid. 2 nd goods receipt: 40 pieces Blocking reason no longer valid If automatic release is active, certain blocked invoices may be automatically released. Accounts payable will pay the invoices according to payment terms. Ó XX Consulting 2000 X Automatic release Payment program settles the invoice 49
Automatic Release Purchase Order 1 st goods receipt: 60 pieces Here the invoice will be blocked due to quantity variance. 100 pcs Quantity Invoice > Receipt Invoice blocked for payment 80 pcs Additional delivery makes quantity variance blocking reason invalid. 2 nd goods receipt: 40 pieces Blocking reason no longer valid If automatic release is active, certain blocked invoices may be automatically released. Accounts payable will pay the invoices according to payment terms. Ó XX Consulting 2000 X Automatic release Payment program settles the invoice 49
 Manual Release l Manual release allows blocking reason(s) for an invoice item to be selected individually and deleted. l When the last blocking reason is deleted for all line items in an invoice, the entire invoice is then released for payment. l Manual release of invoices can be done through: n Individual release: Cursor is placed on an individual invoice line item blocking reason and that reason is deleted. n Collective release : Cursor is placed on range of invoice items which are to be released for payment. l When invoices are released, the document number remains on the screen until the transaction is completed. l Items can only be reblocked by A/P. Ó XX Consulting 2000 50
Manual Release l Manual release allows blocking reason(s) for an invoice item to be selected individually and deleted. l When the last blocking reason is deleted for all line items in an invoice, the entire invoice is then released for payment. l Manual release of invoices can be done through: n Individual release: Cursor is placed on an individual invoice line item blocking reason and that reason is deleted. n Collective release : Cursor is placed on range of invoice items which are to be released for payment. l When invoices are released, the document number remains on the screen until the transaction is completed. l Items can only be reblocked by A/P. Ó XX Consulting 2000 50
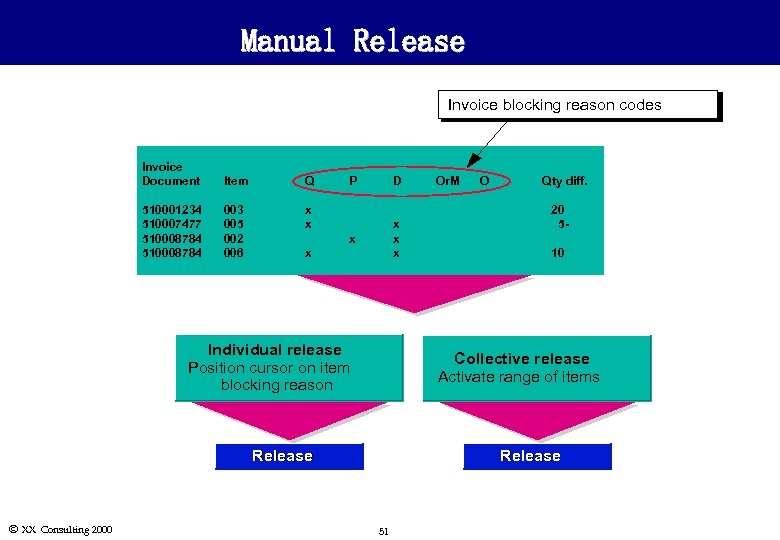 Manual Release Invoice blocking reason codes Invoice Document Item Q 510001234 510007477 510008784 003 005 002 006 x x P D x x x Individual release Position cursor on item blocking reason O Qty diff. 20 510 Collective release Activate range of items Release Ó XX Consulting 2000 Or. M Release 51
Manual Release Invoice blocking reason codes Invoice Document Item Q 510001234 510007477 510008784 003 005 002 006 x x P D x x x Individual release Position cursor on item blocking reason O Qty diff. 20 510 Collective release Activate range of items Release Ó XX Consulting 2000 Or. M Release 51
 Summary • When you enter an invoice referencing a purchase order, the system suggests almost all of the required information. You only have to enter a small amount of information manually. • The R/3 system checks every invoice item for variances on the basis of content and price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 52
Summary • When you enter an invoice referencing a purchase order, the system suggests almost all of the required information. You only have to enter a small amount of information manually. • The R/3 system checks every invoice item for variances on the basis of content and price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 52
 Exercise for Invoice Verification Now it’s time for you to do: MM 04 - Exercise 11 45 minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 53
Exercise for Invoice Verification Now it’s time for you to do: MM 04 - Exercise 11 45 minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 53
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 54
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 54
 General Concepts l Material valuation determines and records the value of stock material. l Unit price, stock quantity, and total value are maintained in the material master. l Valuation: n Links Materials Management with Financial Accounting by updating the General Ledger. n Occurs automatically whenever a goods movement transaction (quantity change) or invoice is posted. n Can be performed manually by: w Changing standard or moving average prices. w Posting subsequent debits and credits in invoice verification. Ó XX Consulting 2000 55
General Concepts l Material valuation determines and records the value of stock material. l Unit price, stock quantity, and total value are maintained in the material master. l Valuation: n Links Materials Management with Financial Accounting by updating the General Ledger. n Occurs automatically whenever a goods movement transaction (quantity change) or invoice is posted. n Can be performed manually by: w Changing standard or moving average prices. w Posting subsequent debits and credits in invoice verification. Ó XX Consulting 2000 55
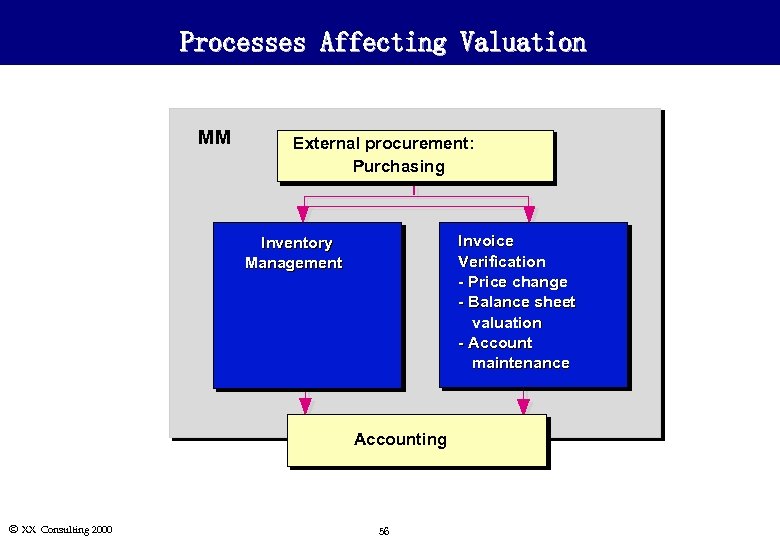 Processes Affecting Valuation MM External procurement: Purchasing Invoice Verification - Price change - Balance sheet valuation - Account maintenance Inventory Management Accounting Ó XX Consulting 2000 56
Processes Affecting Valuation MM External procurement: Purchasing Invoice Verification - Price change - Balance sheet valuation - Account maintenance Inventory Management Accounting Ó XX Consulting 2000 56
 Standard vs. Moving Average Price l Materials are valuated using two types of price control: n Standard price n Moving average price l Standard price requires that all postings be carried out at one price for a set period of time. All variances are posted to price difference accounts. l Moving average price requires that materials be valuated at goods receipt value. Moving average prices are automatically adjusted in the material master when variances occur. l Price control should be set in the material master (accounting view) when a material is created. Ó XX Consulting 2000 57
Standard vs. Moving Average Price l Materials are valuated using two types of price control: n Standard price n Moving average price l Standard price requires that all postings be carried out at one price for a set period of time. All variances are posted to price difference accounts. l Moving average price requires that materials be valuated at goods receipt value. Moving average prices are automatically adjusted in the material master when variances occur. l Price control should be set in the material master (accounting view) when a material is created. Ó XX Consulting 2000 57
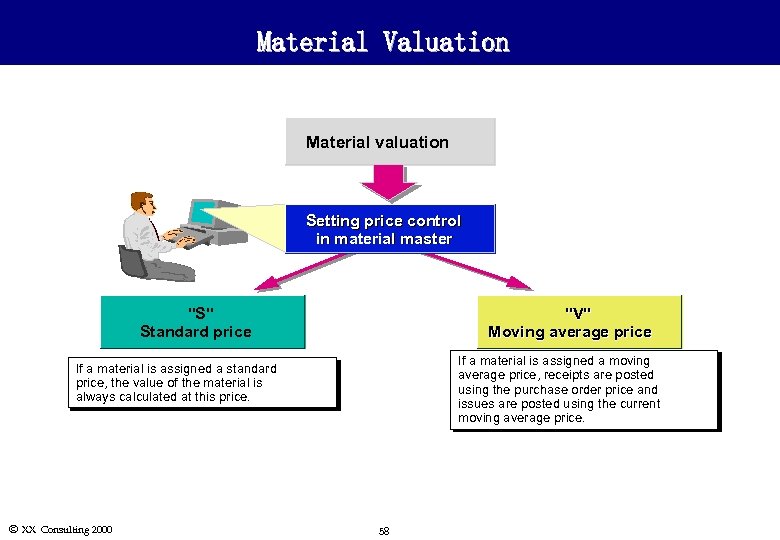 Material Valuation Material valuation Setting price control in material master "S" Standard price "V" Moving average price If a material is assigned a moving average price, receipts are posted using the purchase order price and issues are posted using the current moving average price. If a material is assigned a standard price, the value of the material is always calculated at this price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 58
Material Valuation Material valuation Setting price control in material master "S" Standard price "V" Moving average price If a material is assigned a moving average price, receipts are posted using the purchase order price and issues are posted using the current moving average price. If a material is assigned a standard price, the value of the material is always calculated at this price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 58
 Valuation Class l Material type determines the valuation class that can be assigned to a material. l Valuation class groups different materials with similar properties so separate stock accounts do not have to be maintained for every material. l The R/3 System uses valuation class for automatic account determination. This class is used to determine which stock account should be posted to when an inventory transaction occurs. Ó XX Consulting 2000 59
Valuation Class l Material type determines the valuation class that can be assigned to a material. l Valuation class groups different materials with similar properties so separate stock accounts do not have to be maintained for every material. l The R/3 System uses valuation class for automatic account determination. This class is used to determine which stock account should be posted to when an inventory transaction occurs. Ó XX Consulting 2000 59
 Valuation Class l Material type determines the valuation class that can be assigned to a material. l Valuation class groups different materials with similar properties so separate stock accounts do not have to be maintained for every material. l The R/3 System uses valuation class for automatic account determination. This class is used to determine which stock account should be posted to when an inventory transaction occurs. Ó XX Consulting 2000 60
Valuation Class l Material type determines the valuation class that can be assigned to a material. l Valuation class groups different materials with similar properties so separate stock accounts do not have to be maintained for every material. l The R/3 System uses valuation class for automatic account determination. This class is used to determine which stock account should be posted to when an inventory transaction occurs. Ó XX Consulting 2000 60
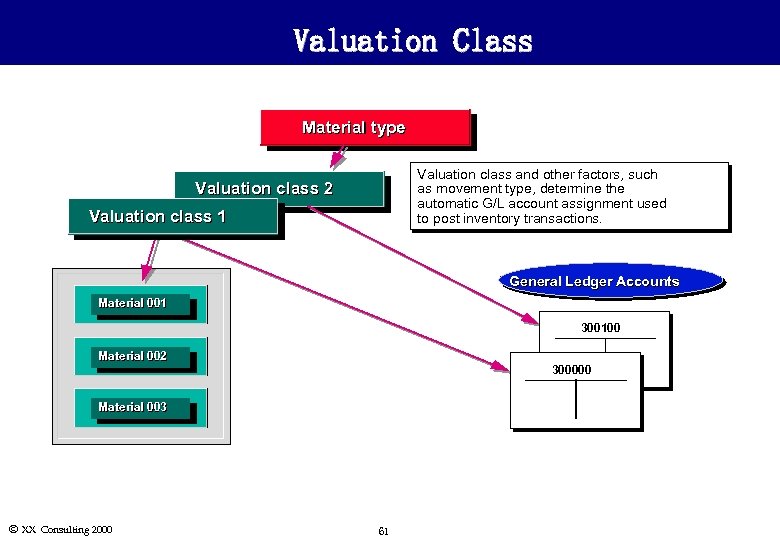 Valuation Class Material type Valuation class and other factors, such as movement type, determine the automatic G/L account assignment used to post inventory transactions. Valuation class 2 Valuation class 1 General Ledger Accounts Material 001 300100 Material 002 300000 Material 003 Ó XX Consulting 2000 61
Valuation Class Material type Valuation class and other factors, such as movement type, determine the automatic G/L account assignment used to post inventory transactions. Valuation class 2 Valuation class 1 General Ledger Accounts Material 001 300100 Material 002 300000 Material 003 Ó XX Consulting 2000 61
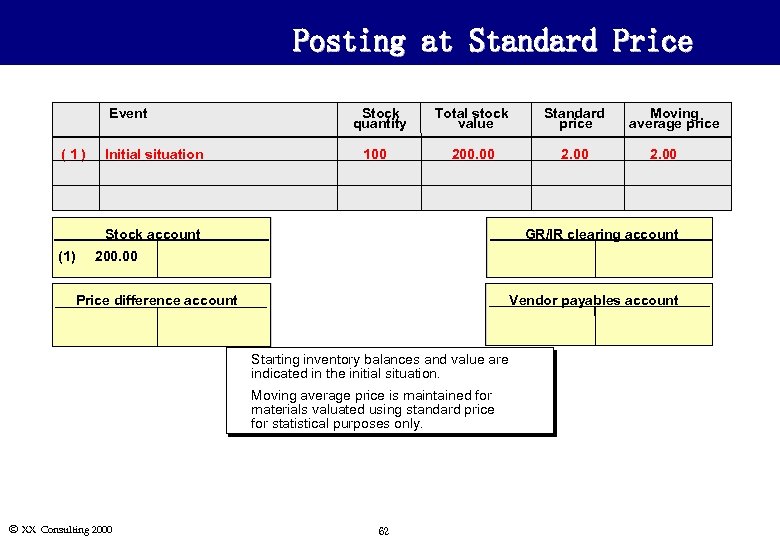 Posting at Standard Price Event (1) Stock quantity Initial situation 100 Total stock value Standard price 200. 00 2. 00 Stock account (1) Moving average price 2. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 Price difference account Vendor payables account u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Starting inventory balances and value are indicated in the initial situation. Moving average price is maintained for materials valuated using standard price for statistical purposes only. 62
Posting at Standard Price Event (1) Stock quantity Initial situation 100 Total stock value Standard price 200. 00 2. 00 Stock account (1) Moving average price 2. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 Price difference account Vendor payables account u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Starting inventory balances and value are indicated in the initial situation. Moving average price is maintained for materials valuated using standard price for statistical purposes only. 62
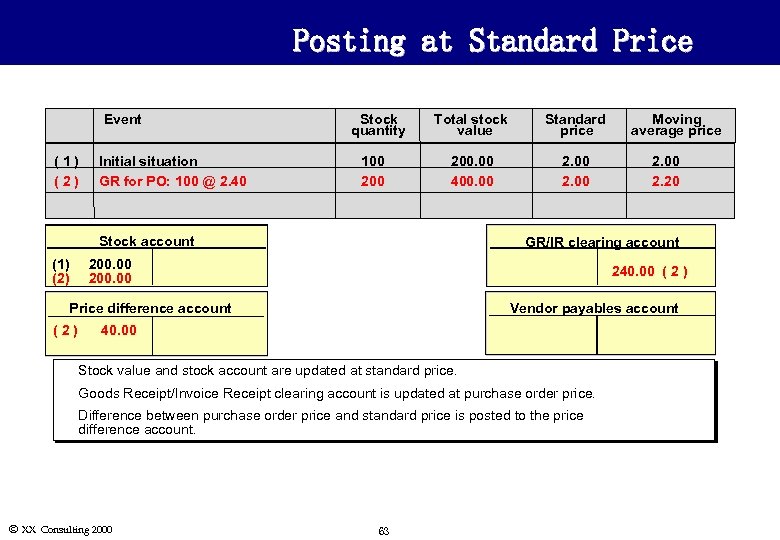 Posting at Standard Price Event (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 Stock quantity 100 200 Total stock value Standard price 200. 00 400. 00 2. 00 Stock account (1) (2) 240. 00 ( 2 ) Price difference account Vendor payables account 40. 00 u Stock value and stock account are updated at standard price. u Goods Receipt/Invoice Receipt clearing account is updated at purchase order price. u Difference between purchase order price and standard price is posted to the price difference account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 2. 20 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 (2) Moving average price 63
Posting at Standard Price Event (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 Stock quantity 100 200 Total stock value Standard price 200. 00 400. 00 2. 00 Stock account (1) (2) 240. 00 ( 2 ) Price difference account Vendor payables account 40. 00 u Stock value and stock account are updated at standard price. u Goods Receipt/Invoice Receipt clearing account is updated at purchase order price. u Difference between purchase order price and standard price is posted to the price difference account. Ó XX Consulting 2000 2. 20 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 (2) Moving average price 63
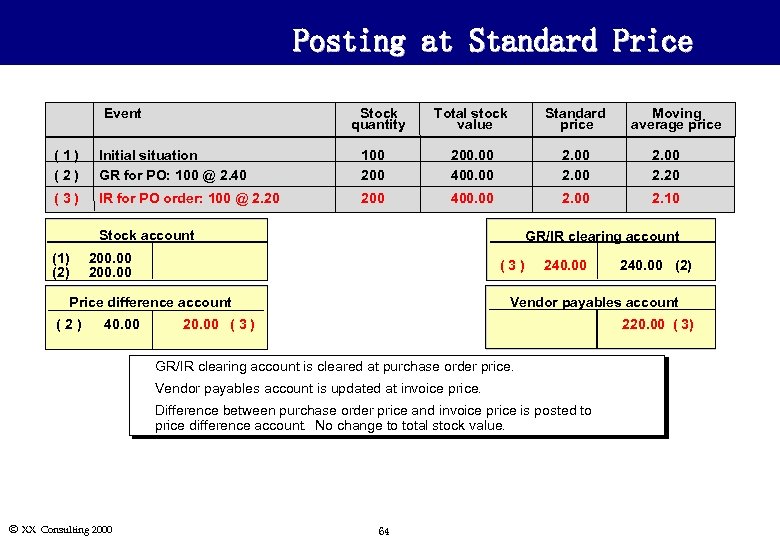 Posting at Standard Price Event Stock quantity Total stock value Standard price Moving average price (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 100 200. 00 400. 00 2. 20 (3) IR for PO order: 100 @ 2. 20 200 400. 00 2. 10 Stock account (1) (2) GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 (3) Price difference account (2) 40. 00 240. 00 Vendor payables account 20. 00 ( 3 ) 220. 00 ( 3) u GR/IR clearing account is cleared at purchase order price. u Vendor payables account is updated at invoice price. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 240. 00 (2) Difference between purchase order price and invoice price is posted to price difference account. No change to total stock value. 64
Posting at Standard Price Event Stock quantity Total stock value Standard price Moving average price (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 100 200. 00 400. 00 2. 20 (3) IR for PO order: 100 @ 2. 20 200 400. 00 2. 10 Stock account (1) (2) GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 (3) Price difference account (2) 40. 00 240. 00 Vendor payables account 20. 00 ( 3 ) 220. 00 ( 3) u GR/IR clearing account is cleared at purchase order price. u Vendor payables account is updated at invoice price. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 240. 00 (2) Difference between purchase order price and invoice price is posted to price difference account. No change to total stock value. 64
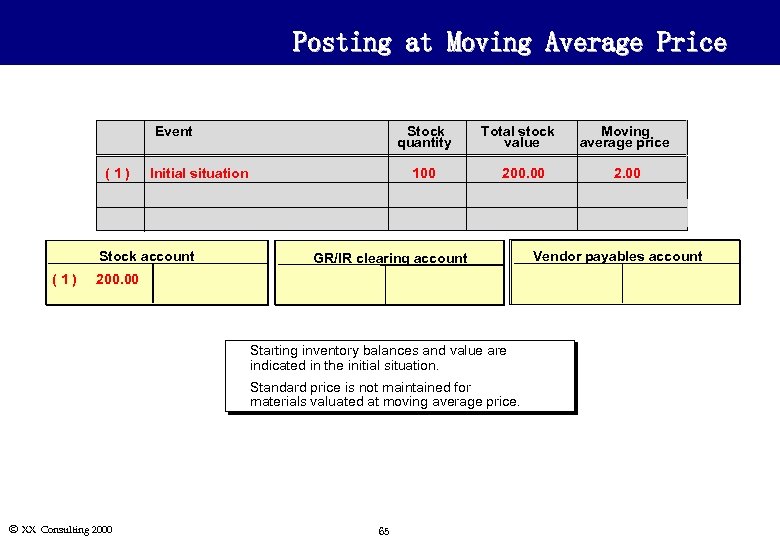 Posting at Moving Average Price Event (1) Stock quantity Initial situation Stock account (1) 100 Total stock value 200. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Starting inventory balances and value are indicated in the initial situation. Standard price is not maintained for materials valuated at moving average price. 65 Moving average price 2. 00 Vendor payables account
Posting at Moving Average Price Event (1) Stock quantity Initial situation Stock account (1) 100 Total stock value 200. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Starting inventory balances and value are indicated in the initial situation. Standard price is not maintained for materials valuated at moving average price. 65 Moving average price 2. 00 Vendor payables account
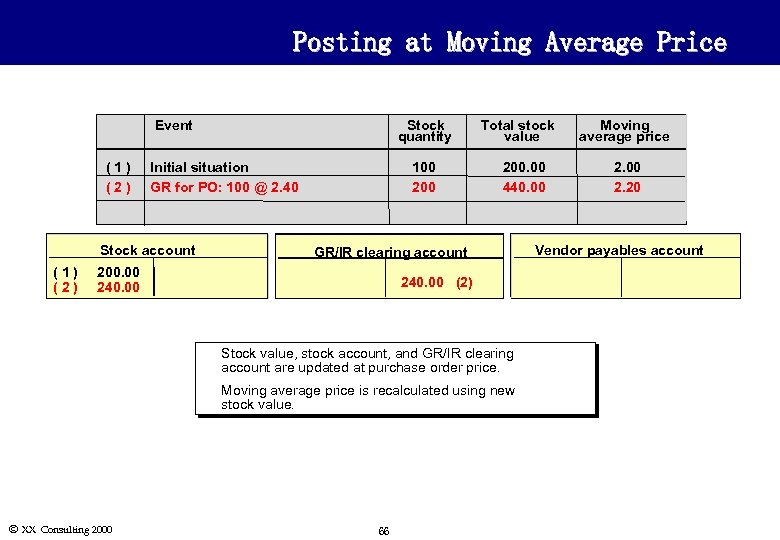 Posting at Moving Average Price Event (1) (2) Stock quantity Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 Stock account (1) (2) 100 200 Total stock value 200. 00 440. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 240. 00 (2) u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock value, stock account, and GR/IR clearing account are updated at purchase order price. Moving average price is recalculated using new stock value. 66 Moving average price 2. 00 2. 20 Vendor payables account
Posting at Moving Average Price Event (1) (2) Stock quantity Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 Stock account (1) (2) 100 200 Total stock value 200. 00 440. 00 GR/IR clearing account 200. 00 240. 00 (2) u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 Stock value, stock account, and GR/IR clearing account are updated at purchase order price. Moving average price is recalculated using new stock value. 66 Moving average price 2. 00 2. 20 Vendor payables account
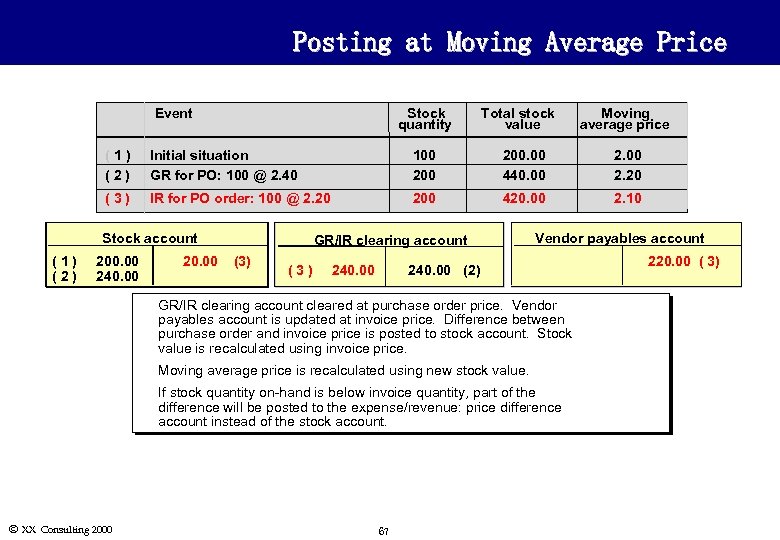 Posting at Moving Average Price Event Stock quantity Total stock value Moving average price (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 100 200. 00 440. 00 2. 20 (3) IR for PO order: 100 @ 2. 20 200 420. 00 2. 10 Stock account (1) (2) 200. 00 240. 00 20. 00 GR/IR clearing account (3) 240. 00 Vendor payables account 240. 00 (2) u u Moving average price is recalculated using new stock value. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 GR/IR clearing account cleared at purchase order price. Vendor payables account is updated at invoice price. Difference between purchase order and invoice price is posted to stock account. Stock value is recalculated using invoice price. If stock quantity on-hand is below invoice quantity, part of the difference will be posted to the expense/revenue: price difference account instead of the stock account. 67 220. 00 ( 3)
Posting at Moving Average Price Event Stock quantity Total stock value Moving average price (1) (2) Initial situation GR for PO: 100 @ 2. 40 100 200. 00 440. 00 2. 20 (3) IR for PO order: 100 @ 2. 20 200 420. 00 2. 10 Stock account (1) (2) 200. 00 240. 00 20. 00 GR/IR clearing account (3) 240. 00 Vendor payables account 240. 00 (2) u u Moving average price is recalculated using new stock value. u Ó XX Consulting 2000 GR/IR clearing account cleared at purchase order price. Vendor payables account is updated at invoice price. Difference between purchase order and invoice price is posted to stock account. Stock value is recalculated using invoice price. If stock quantity on-hand is below invoice quantity, part of the difference will be posted to the expense/revenue: price difference account instead of the stock account. 67 220. 00 ( 3)
 Valuation Area l Valuation area specifies the level at which a material is valuated. Valuation levels: n Company code n Plant l If stock is valuated at the company code level, all stocks of a material in the company are valuated together at the same price. l If stock is valuated at the plant level, all stocks of a material in an individual plant are valuated together at one price. Stocks in other plants are not included in the valuation area and can be valuated at a different price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 68
Valuation Area l Valuation area specifies the level at which a material is valuated. Valuation levels: n Company code n Plant l If stock is valuated at the company code level, all stocks of a material in the company are valuated together at the same price. l If stock is valuated at the plant level, all stocks of a material in an individual plant are valuated together at one price. Stocks in other plants are not included in the valuation area and can be valuated at a different price. Ó XX Consulting 2000 68
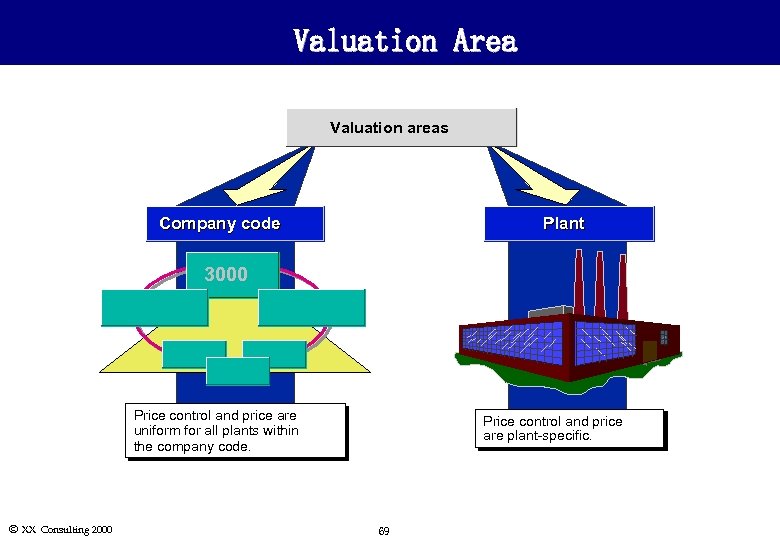 Valuation Area Valuation areas Plant Company code 3000 Price control and price are uniform for all plants within the company code. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Price control and price are plant-specific. 69
Valuation Area Valuation areas Plant Company code 3000 Price control and price are uniform for all plants within the company code. Ó XX Consulting 2000 Price control and price are plant-specific. 69
 Exercise for Material Valuation Now it’s time for you to do exercise: No exercise! Ó XX Consulting 2000 70
Exercise for Material Valuation Now it’s time for you to do exercise: No exercise! Ó XX Consulting 2000 70
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 71
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 71
 General Concepts l Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is often the source of demand for purchased materials in an organization. l Depending on material master settings and parameters selected when running MRP, demand from MRP can generate: n Planned orders : Can be converted to purchase requisitions or purchase orders. n Purchase requisitions: n Stock transport orders n Schedule releases : Orders against scheduling agreements, are also called delivery plans. Can be converted to purchase orders. : Orders between plants. l Note: MRP is covered in detail in the Manufacturing Planning course. Ó XX Consulting 2000 72
General Concepts l Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is often the source of demand for purchased materials in an organization. l Depending on material master settings and parameters selected when running MRP, demand from MRP can generate: n Planned orders : Can be converted to purchase requisitions or purchase orders. n Purchase requisitions: n Stock transport orders n Schedule releases : Orders against scheduling agreements, are also called delivery plans. Can be converted to purchase orders. : Orders between plants. l Note: MRP is covered in detail in the Manufacturing Planning course. Ó XX Consulting 2000 72
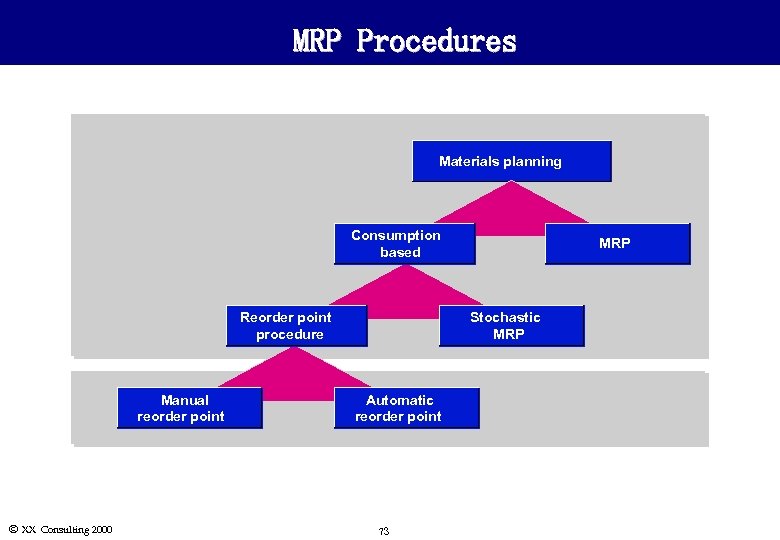 MRP Procedures Materials planning Consumption based Reorder point procedure Manual reorder point Ó XX Consulting 2000 MRP Stochastic MRP Automatic reorder point 73
MRP Procedures Materials planning Consumption based Reorder point procedure Manual reorder point Ó XX Consulting 2000 MRP Stochastic MRP Automatic reorder point 73
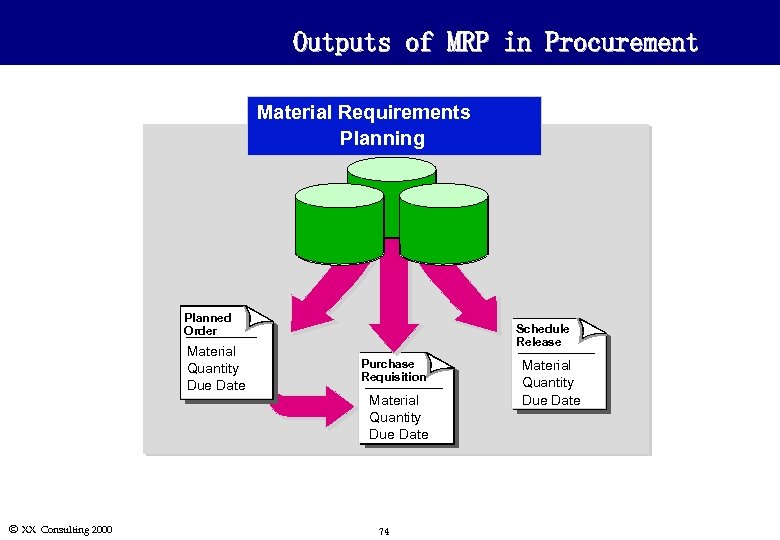 Outputs of MRP in Procurement Material Requirements Planning Planned Order Material Quantity Due Date Ó XX Consulting 2000 Schedule Release Purchase Requisition Material Quantity Due Date 74 Material Quantity Due Date
Outputs of MRP in Procurement Material Requirements Planning Planned Order Material Quantity Due Date Ó XX Consulting 2000 Schedule Release Purchase Requisition Material Quantity Due Date 74 Material Quantity Due Date
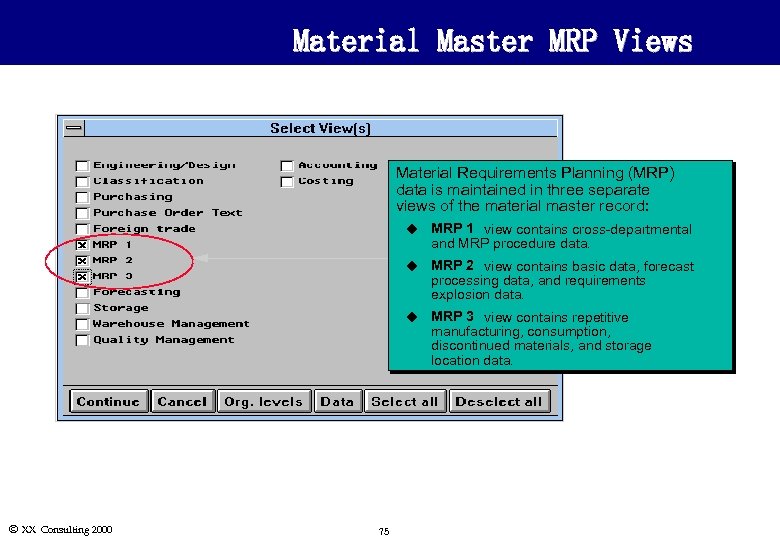 Material Master MRP Views Material Requirements Planning (MRP) data is maintained in three separate views of the material master record: u MRP 1 view contains cross-departmental and MRP procedure data. u MRP 2 view contains basic data, forecast processing data, and requirements explosion data. u MRP 3 view contains repetitive manufacturing, consumption, discontinued materials, and storage location data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 75
Material Master MRP Views Material Requirements Planning (MRP) data is maintained in three separate views of the material master record: u MRP 1 view contains cross-departmental and MRP procedure data. u MRP 2 view contains basic data, forecast processing data, and requirements explosion data. u MRP 3 view contains repetitive manufacturing, consumption, discontinued materials, and storage location data. Ó XX Consulting 2000 75
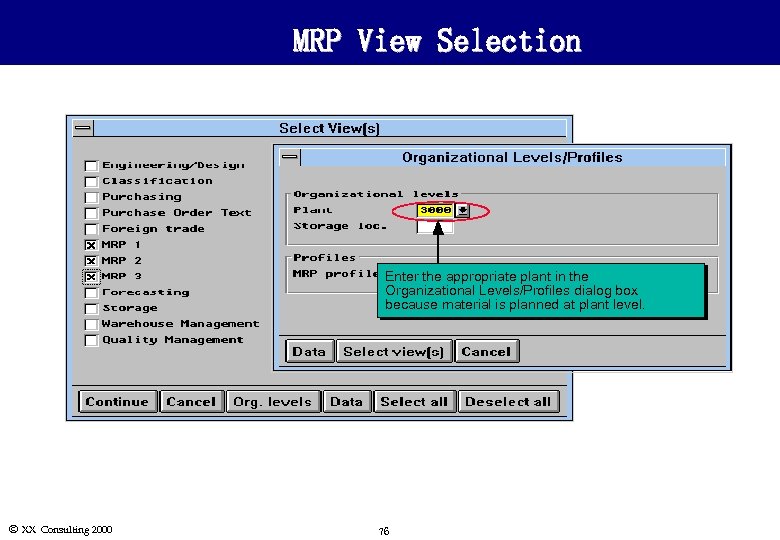 MRP View Selection Enter the appropriate plant in the Organizational Levels/Profiles dialog box because material is planned at plant level. Ó XX Consulting 2000 76
MRP View Selection Enter the appropriate plant in the Organizational Levels/Profiles dialog box because material is planned at plant level. Ó XX Consulting 2000 76
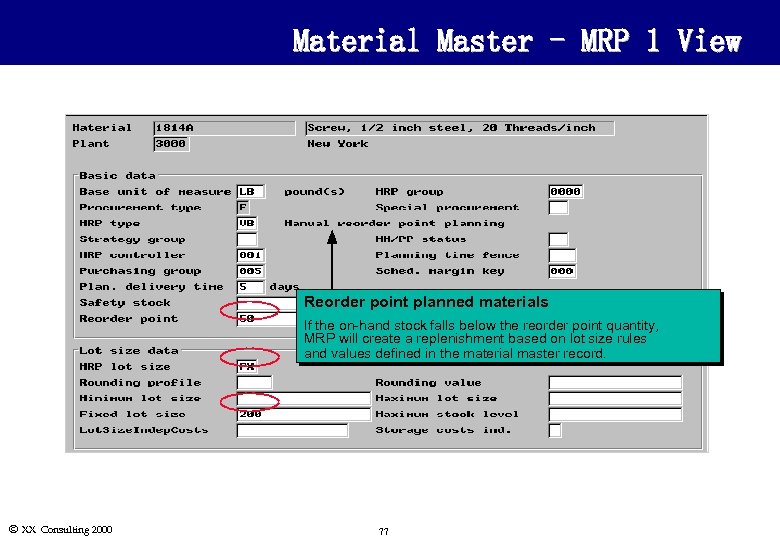 Material Master - MRP 1 View Reorder point planned materials If the on-hand stock falls below the reorder point quantity, MRP will create a replenishment based on lot size rules and values defined in the material master record. Ó XX Consulting 2000 77
Material Master - MRP 1 View Reorder point planned materials If the on-hand stock falls below the reorder point quantity, MRP will create a replenishment based on lot size rules and values defined in the material master record. Ó XX Consulting 2000 77
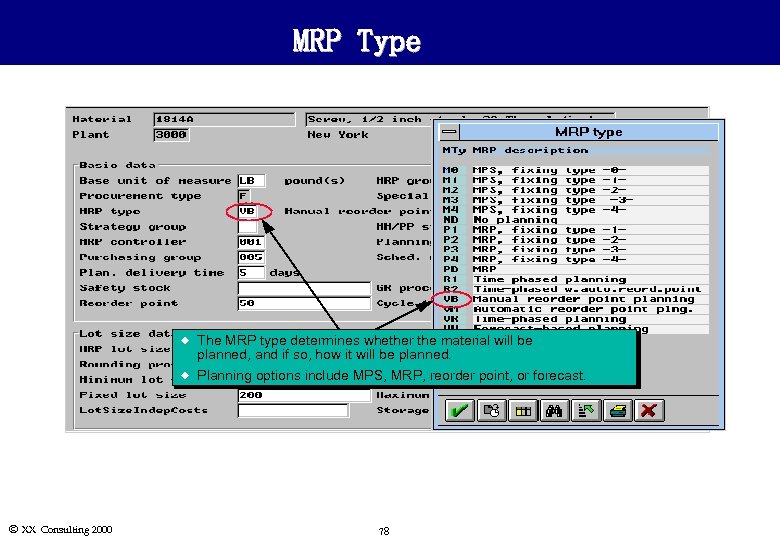 MRP Type u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 The MRP type determines whether the material will be planned, and if so, how it will be planned. Planning options include MPS, MRP, reorder point, or forecast. 78
MRP Type u u Ó XX Consulting 2000 The MRP type determines whether the material will be planned, and if so, how it will be planned. Planning options include MPS, MRP, reorder point, or forecast. 78
 Exercise for Procurement Now it’s time for you to do exercise: No exercise! Ó XX Consulting 2000 79
Exercise for Procurement Now it’s time for you to do exercise: No exercise! Ó XX Consulting 2000 79
 Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 80
Schedule • Topic One: Goods Receipt • Topic Two: Invoice Verification • Vendor Invoice Processing • Invoice Variance • Topic Three: Material Valuation • Topic Four: Procurement • Topic Five: Reporting and Analysis Ó XX Consulting 2000 80
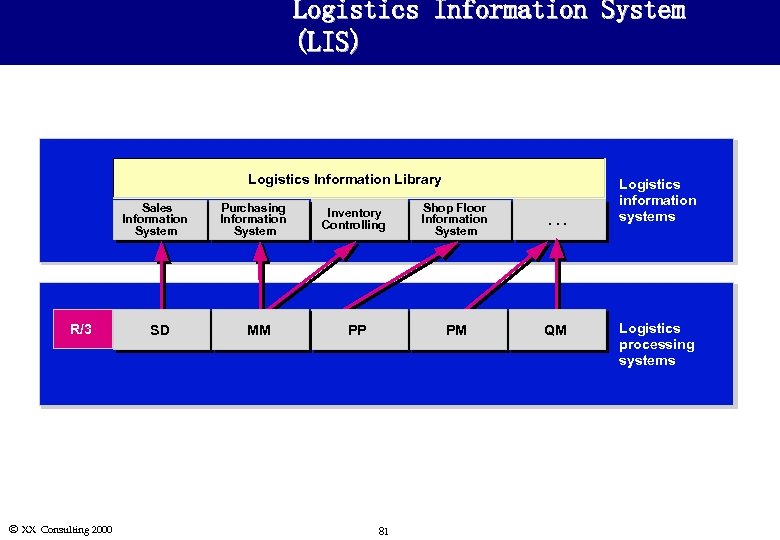 Logistics Information System (LIS) Logistics Information Library Sales Information System R/3 Ó XX Consulting 2000 SD Purchasing Information System MM PP 81 Shop Floor Information System . . . PM Inventory Controlling QM Logistics information systems Logistics processing systems
Logistics Information System (LIS) Logistics Information Library Sales Information System R/3 Ó XX Consulting 2000 SD Purchasing Information System MM PP 81 Shop Floor Information System . . . PM Inventory Controlling QM Logistics information systems Logistics processing systems
 General Concepts l Standard purchasing reports and analyses provide an overview of purchasing transaction data. l Transaction-level detail and summary-level analyses can be completed quickly and efficiently using the tools available in the R/3 System. l Examples of standard reports and analyses include: n n Number of purchase orders by material n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Order values by vendor Average value of purchase orders by purchasing group 82
General Concepts l Standard purchasing reports and analyses provide an overview of purchasing transaction data. l Transaction-level detail and summary-level analyses can be completed quickly and efficiently using the tools available in the R/3 System. l Examples of standard reports and analyses include: n n Number of purchase orders by material n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Order values by vendor Average value of purchase orders by purchasing group 82
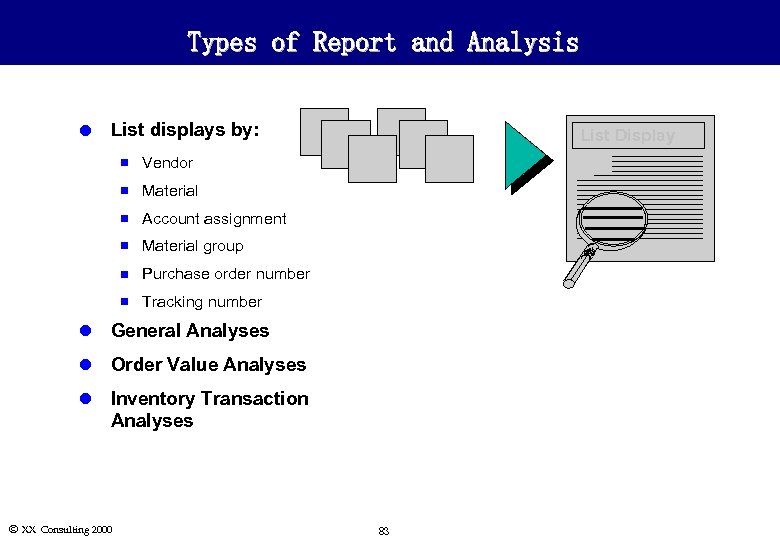 Types of Report and Analysis l List displays by: n Vendor n Material n Account assignment n Material group n Purchase order number n List Display Tracking number l General Analyses l Order Value Analyses l Inventory Transaction Analyses Ó XX Consulting 2000 83
Types of Report and Analysis l List displays by: n Vendor n Material n Account assignment n Material group n Purchase order number n List Display Tracking number l General Analyses l Order Value Analyses l Inventory Transaction Analyses Ó XX Consulting 2000 83
 General Concepts l A list is the output of a report program. l Lists can be used to manage daily functions and report on routine activities. Purchasing examples include lists of: n Purchasing requisitions that must be converted into purchase orders. n Purchase orders without receipts. l Lists can be tailored to the specific requirements of the user. n n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Selection criteria and data ranges are entered to specify the amount of information displayed in the list. Presentation of data may be modified using sorts and total displays. 84
General Concepts l A list is the output of a report program. l Lists can be used to manage daily functions and report on routine activities. Purchasing examples include lists of: n Purchasing requisitions that must be converted into purchase orders. n Purchase orders without receipts. l Lists can be tailored to the specific requirements of the user. n n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Selection criteria and data ranges are entered to specify the amount of information displayed in the list. Presentation of data may be modified using sorts and total displays. 84
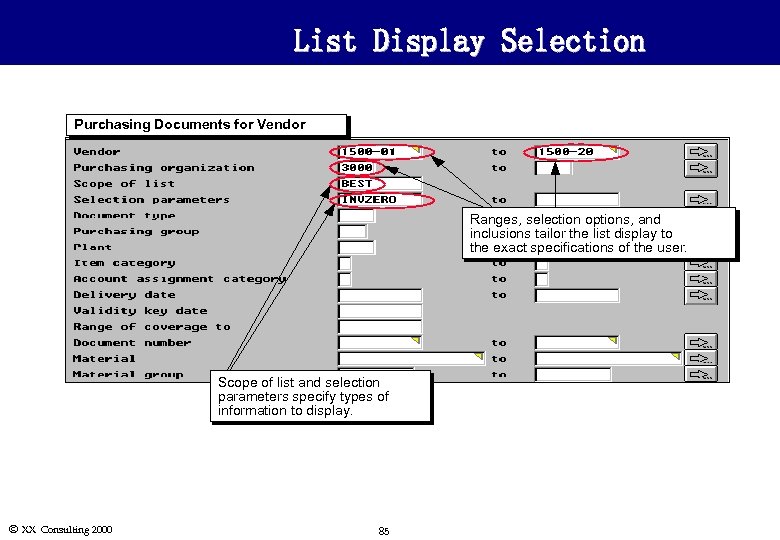 List Display Selection Purchasing Documents for Vendor Ranges, selection options, and inclusions tailor the list display to the exact specifications of the user. Scope of list and selection parameters specify types of information to display. Ó XX Consulting 2000 85
List Display Selection Purchasing Documents for Vendor Ranges, selection options, and inclusions tailor the list display to the exact specifications of the user. Scope of list and selection parameters specify types of information to display. Ó XX Consulting 2000 85
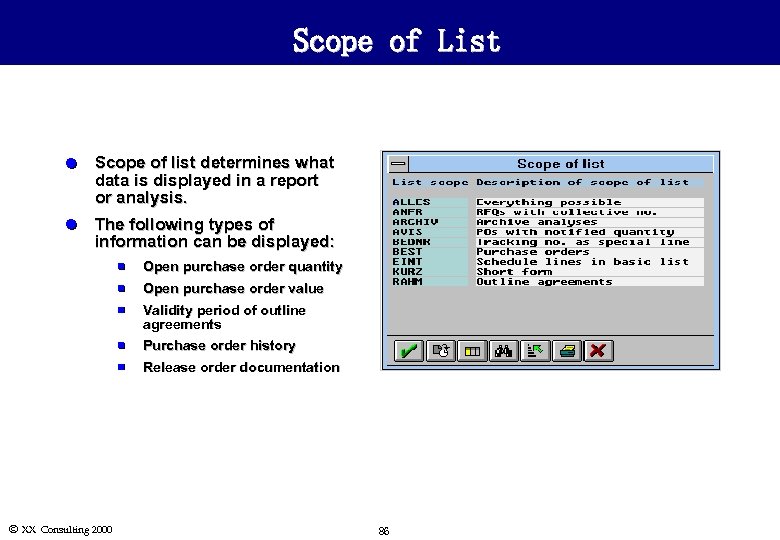 Scope of List l Scope of list determines what data is displayed in a report or analysis. l The following types of information can be displayed: n n Open purchase order quantity Open purchase order value n n Purchase order history n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Validity period of outline agreements Release order documentation 86
Scope of List l Scope of list determines what data is displayed in a report or analysis. l The following types of information can be displayed: n n Open purchase order quantity Open purchase order value n n Purchase order history n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Validity period of outline agreements Release order documentation 86
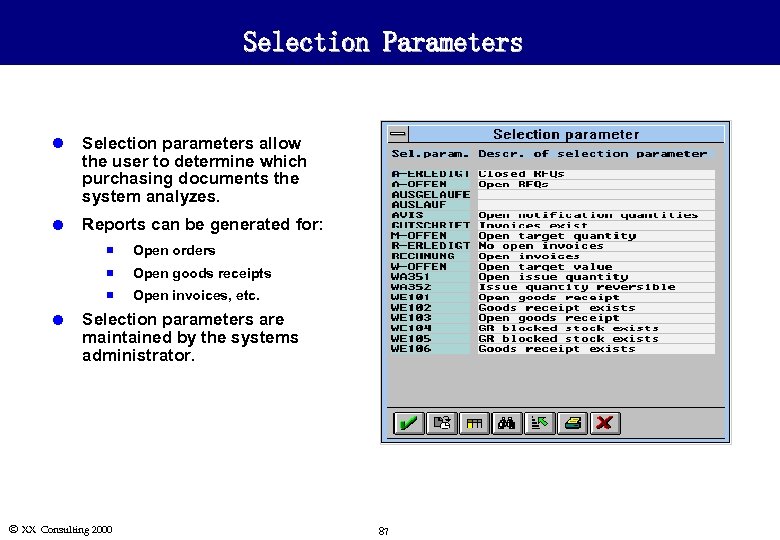 Selection Parameters l Selection parameters allow the user to determine which purchasing documents the system analyzes. l Reports can be generated for: n n Open goods receipts n l Open orders Open invoices, etc. Selection parameters are maintained by the systems administrator. Ó XX Consulting 2000 87
Selection Parameters l Selection parameters allow the user to determine which purchasing documents the system analyzes. l Reports can be generated for: n n Open goods receipts n l Open orders Open invoices, etc. Selection parameters are maintained by the systems administrator. Ó XX Consulting 2000 87
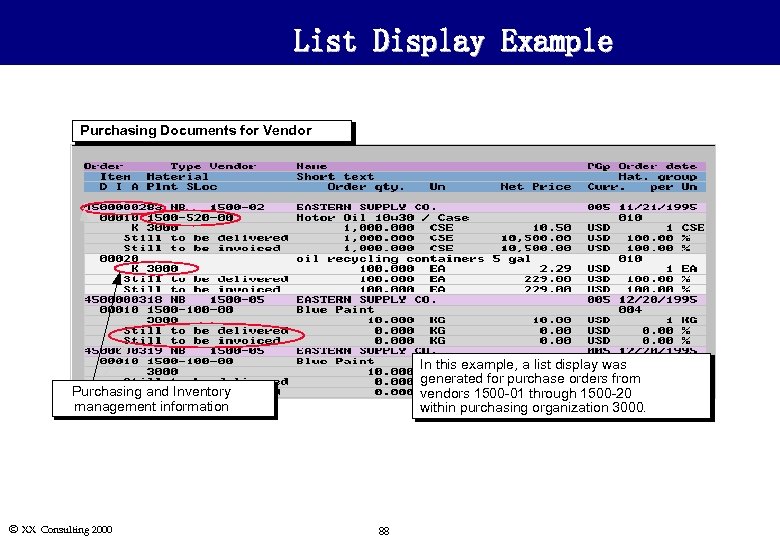 List Display Example Purchasing Documents for Vendor In this example, a list display was generated for purchase orders from vendors 1500 -01 through 1500 -20 within purchasing organization 3000. Purchasing and Inventory management information Ó XX Consulting 2000 88
List Display Example Purchasing Documents for Vendor In this example, a list display was generated for purchase orders from vendors 1500 -01 through 1500 -20 within purchasing organization 3000. Purchasing and Inventory management information Ó XX Consulting 2000 88
 General Concepts of Variant l Variants are groups of user-defined selection criteria that have been saved for later use when calling up frequently generated reports and analyses. l Variants reduce data-entry time and allow users to easily access only the information that is relevant to their area, department, plant, etc. l A report may have any number of variants attached. Ó XX Consulting 2000 89
General Concepts of Variant l Variants are groups of user-defined selection criteria that have been saved for later use when calling up frequently generated reports and analyses. l Variants reduce data-entry time and allow users to easily access only the information that is relevant to their area, department, plant, etc. l A report may have any number of variants attached. Ó XX Consulting 2000 89
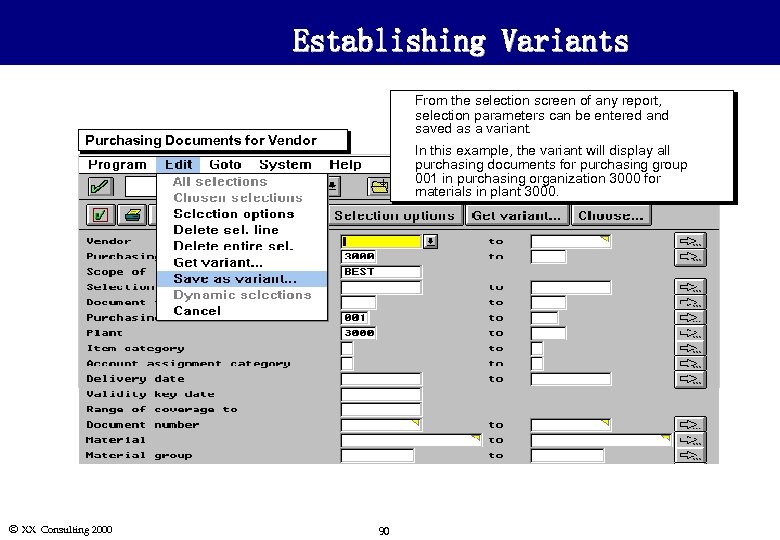 Establishing Variants u u Purchasing Documents for Vendor From the selection screen of any report, selection parameters can be entered and saved as a variant. In this example, the variant will display all purchasing documents for purchasing group 001 in purchasing organization 3000 for materials in plant 3000. R ã SAP AG Ó XX Consulting 2000 90
Establishing Variants u u Purchasing Documents for Vendor From the selection screen of any report, selection parameters can be entered and saved as a variant. In this example, the variant will display all purchasing documents for purchasing group 001 in purchasing organization 3000 for materials in plant 3000. R ã SAP AG Ó XX Consulting 2000 90
 Saving Variants Purchasing Documents for Vendor The variant name and description must be entered when the variant is saved. Ó XX Consulting 2000 91
Saving Variants Purchasing Documents for Vendor The variant name and description must be entered when the variant is saved. Ó XX Consulting 2000 91
 General Concepts l General analyses allow you to review purchase orders, contracts, scheduling agreements, or requests for quotations by: n Vendor n Material group n Purchasing group l Selection criteria and settings allow you to modify the content and layout of the analysis. Ó XX Consulting 2000 92
General Concepts l General analyses allow you to review purchase orders, contracts, scheduling agreements, or requests for quotations by: n Vendor n Material group n Purchasing group l Selection criteria and settings allow you to modify the content and layout of the analysis. Ó XX Consulting 2000 92
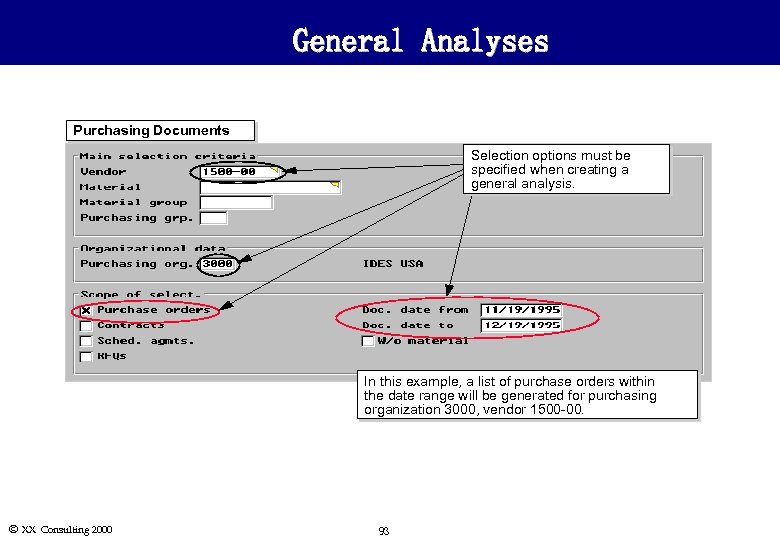 General Analyses Purchasing Documents Selection options must be specified when creating a general analysis. In this example, a list of purchase orders within the date range will be generated for purchasing organization 3000, vendor 1500 -00. Ó XX Consulting 2000 93
General Analyses Purchasing Documents Selection options must be specified when creating a general analysis. In this example, a list of purchase orders within the date range will be generated for purchasing organization 3000, vendor 1500 -00. Ó XX Consulting 2000 93
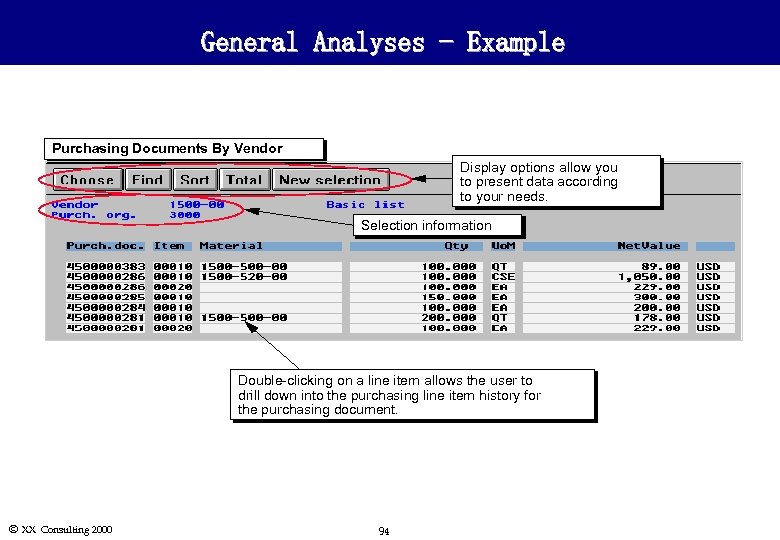 General Analyses - Example Purchasing Documents By Vendor Display options allow you to present data according to your needs. Selection information Double-clicking on a line item allows the user to drill down into the purchasing line item history for the purchasing document. Ó XX Consulting 2000 94
General Analyses - Example Purchasing Documents By Vendor Display options allow you to present data according to your needs. Selection information Double-clicking on a line item allows the user to drill down into the purchasing line item history for the purchasing document. Ó XX Consulting 2000 94
 General Concepts l Order value analyses allow you to analyze purchasing patterns using one or several of the following options: n Totals analysis n ABC analysis n Analyses with comparison periods n Frequency analysis l Purchasing data may be totaled by: n n Purchasing group n Vendor n Plant n Material group n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Purchasing organization Material 95
General Concepts l Order value analyses allow you to analyze purchasing patterns using one or several of the following options: n Totals analysis n ABC analysis n Analyses with comparison periods n Frequency analysis l Purchasing data may be totaled by: n n Purchasing group n Vendor n Plant n Material group n Ó XX Consulting 2000 Purchasing organization Material 95
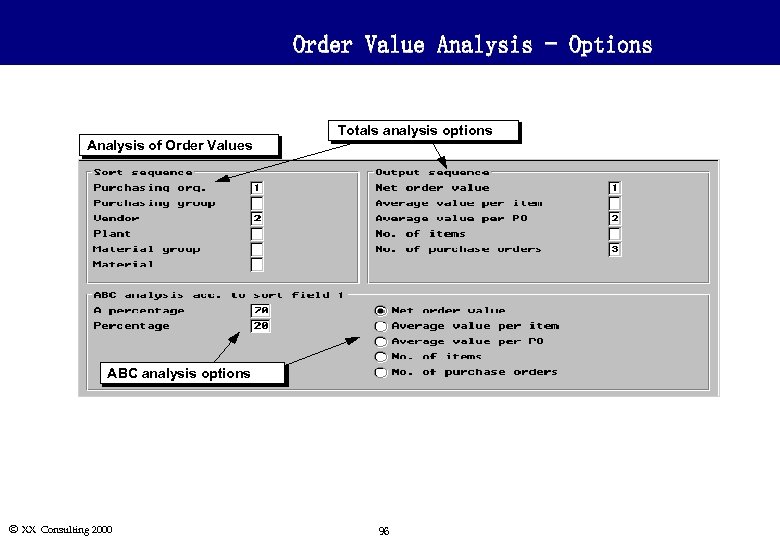 Order Value Analysis - Options Analysis of Order Values Totals analysis options ABC analysis options Ó XX Consulting 2000 96
Order Value Analysis - Options Analysis of Order Values Totals analysis options ABC analysis options Ó XX Consulting 2000 96
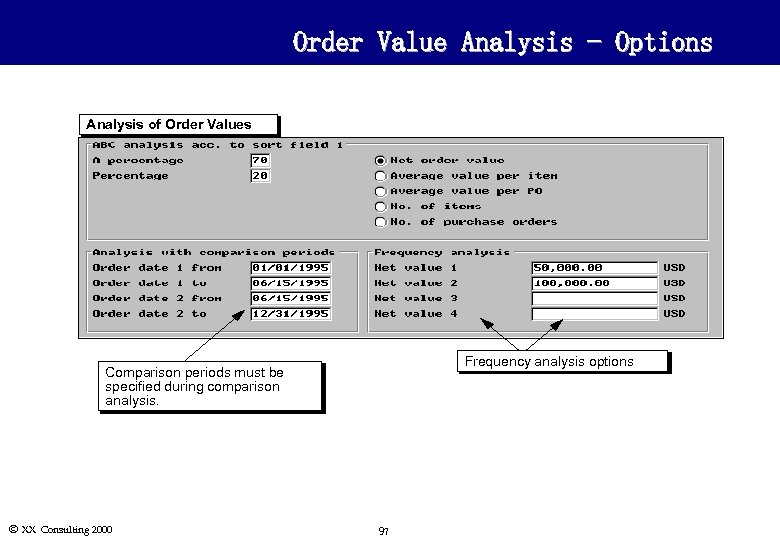 Order Value Analysis - Options Analysis of Order Values Frequency analysis options Comparison periods must be specified during comparison analysis. Ó XX Consulting 2000 97
Order Value Analysis - Options Analysis of Order Values Frequency analysis options Comparison periods must be specified during comparison analysis. Ó XX Consulting 2000 97
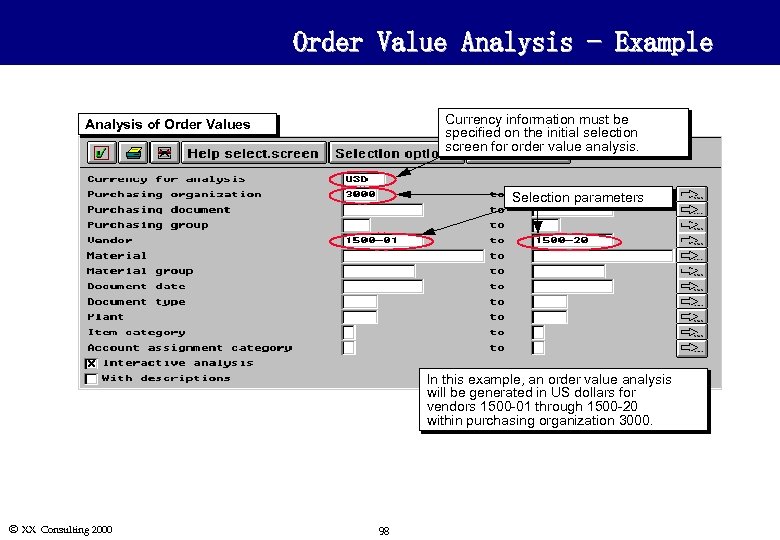 Order Value Analysis - Example Currency information must be specified on the initial selection screen for order value analysis. Analysis of Order Values Selection parameters In this example, an order value analysis will be generated in US dollars for vendors 1500 -01 through 1500 -20 within purchasing organization 3000. Ó XX Consulting 2000 98
Order Value Analysis - Example Currency information must be specified on the initial selection screen for order value analysis. Analysis of Order Values Selection parameters In this example, an order value analysis will be generated in US dollars for vendors 1500 -01 through 1500 -20 within purchasing organization 3000. Ó XX Consulting 2000 98
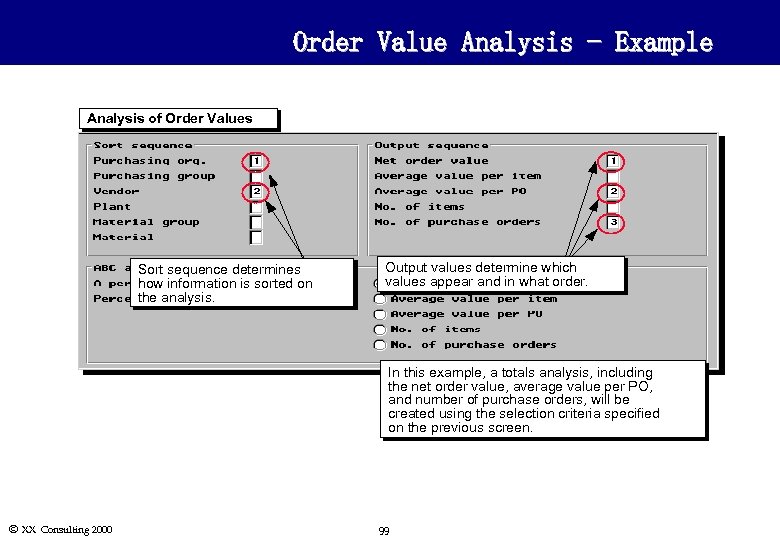 Order Value Analysis - Example Analysis of Order Values Sort sequence determines how information is sorted on the analysis. Output values determine which values appear and in what order. In this example, a totals analysis, including the net order value, average value per PO, and number of purchase orders, will be created using the selection criteria specified on the previous screen. Ó XX Consulting 2000 99
Order Value Analysis - Example Analysis of Order Values Sort sequence determines how information is sorted on the analysis. Output values determine which values appear and in what order. In this example, a totals analysis, including the net order value, average value per PO, and number of purchase orders, will be created using the selection criteria specified on the previous screen. Ó XX Consulting 2000 99
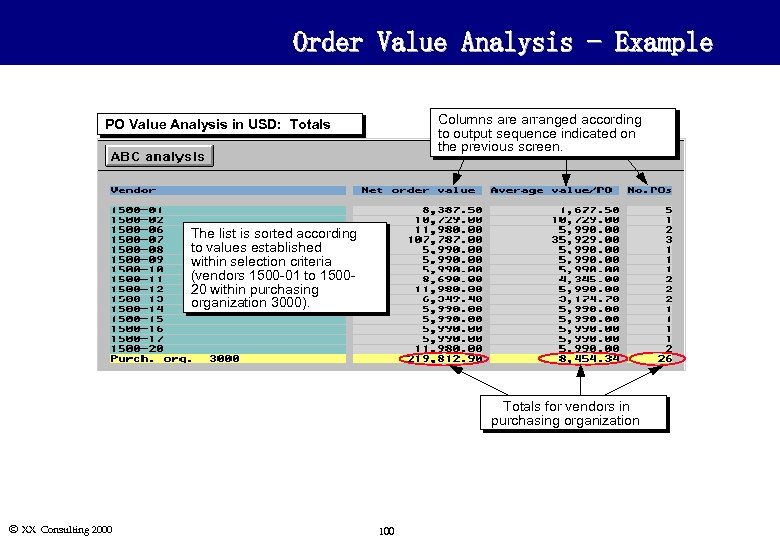 Order Value Analysis - Example Columns are arranged according to output sequence indicated on the previous screen. PO Value Analysis in USD: Totals The list is sorted according to values established within selection criteria (vendors 1500 -01 to 150020 within purchasing organization 3000). Totals for vendors in purchasing organization Ó XX Consulting 2000 100
Order Value Analysis - Example Columns are arranged according to output sequence indicated on the previous screen. PO Value Analysis in USD: Totals The list is sorted according to values established within selection criteria (vendors 1500 -01 to 150020 within purchasing organization 3000). Totals for vendors in purchasing organization Ó XX Consulting 2000 100
 General Concepts l Inventory Transaction Analyses display information about: n Material movements n Material stocks l Inventory Transaction Analyses can be used to: n Review the transaction history for a material n Determine the current stock balance for a material l Inventory list displays may be created for all types of material transactions. Ó XX Consulting 2000 101
General Concepts l Inventory Transaction Analyses display information about: n Material movements n Material stocks l Inventory Transaction Analyses can be used to: n Review the transaction history for a material n Determine the current stock balance for a material l Inventory list displays may be created for all types of material transactions. Ó XX Consulting 2000 101
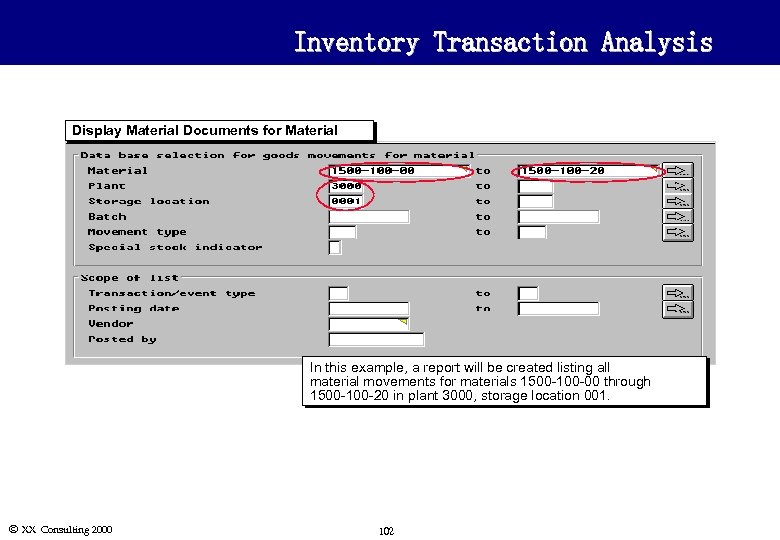 Inventory Transaction Analysis Display Material Documents for Material In this example, a report will be created listing all material movements for materials 1500 -100 -00 through 1500 -100 -20 in plant 3000, storage location 001. Ó XX Consulting 2000 102
Inventory Transaction Analysis Display Material Documents for Material In this example, a report will be created listing all material movements for materials 1500 -100 -00 through 1500 -100 -20 in plant 3000, storage location 001. Ó XX Consulting 2000 102
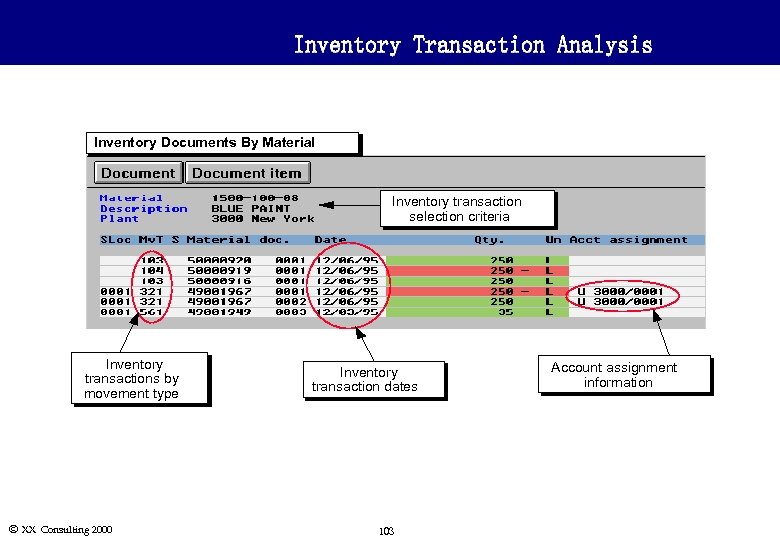 Inventory Transaction Analysis Inventory Documents By Material Inventory transaction selection criteria Inventory transactions by movement type Ó XX Consulting 2000 Inventory transaction dates 103 Account assignment information
Inventory Transaction Analysis Inventory Documents By Material Inventory transaction selection criteria Inventory transactions by movement type Ó XX Consulting 2000 Inventory transaction dates 103 Account assignment information
 Exercise for Reporting and Analysis Now it’s time for you to do exercise: MM 04 - Exercise 12 30 Minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 104
Exercise for Reporting and Analysis Now it’s time for you to do exercise: MM 04 - Exercise 12 30 Minutes Ó XX Consulting 2000 104
 Course Evaluation and Quiz • Your input in course evaluation form is appreciated. • Please take the quiz. Ó XX Consulting 2000 105
Course Evaluation and Quiz • Your input in course evaluation form is appreciated. • Please take the quiz. Ó XX Consulting 2000 105
 Congratulations ! Ó XX Consulting 2000 106
Congratulations ! Ó XX Consulting 2000 106


