b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107
 MLIF: The Multi Lingual Information Framework ISO WD 24616 Samuel CRUZ-LARA Samuel. Cruz-Lara@loria. fr LORIA / INRIA, France
MLIF: The Multi Lingual Information Framework ISO WD 24616 Samuel CRUZ-LARA Samuel. Cruz-Lara@loria. fr LORIA / INRIA, France
![Outline Introduction MLIF [ISO WD 24616] Ongoing activities Actions Date Extension Request Conclusion Pisa, Outline Introduction MLIF [ISO WD 24616] Ongoing activities Actions Date Extension Request Conclusion Pisa,](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-2.jpg) Outline Introduction MLIF [ISO WD 24616] Ongoing activities Actions Date Extension Request Conclusion Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 2 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Outline Introduction MLIF [ISO WD 24616] Ongoing activities Actions Date Extension Request Conclusion Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 2 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Introduction
Introduction
 Introduction The “Multi Lingual Information Framework” MLIF ISO AWI 24616 (TC 37/SC 4 WG 3) Nasredine Semmar (CEA, France), WG 3 Convenor Samuel Cruz. Lara (LORIA / INRIA, France), MLIF Project Leader Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 4 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Introduction The “Multi Lingual Information Framework” MLIF ISO AWI 24616 (TC 37/SC 4 WG 3) Nasredine Semmar (CEA, France), WG 3 Convenor Samuel Cruz. Lara (LORIA / INRIA, France), MLIF Project Leader Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 4 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 New Work Item Proposal ISO TC 37/SC 4 Meeting China, Beijing August 2006 ISO AWI 24616 Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 5 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
New Work Item Proposal ISO TC 37/SC 4 Meeting China, Beijing August 2006 ISO AWI 24616 Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 5 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope This standard aims at proposing a specification platform for a computeroriented representation of multilingual data within a large variety of applications such as translation memories, localization, computer-aided translation, multimedia, or electronic document management. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 6 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope This standard aims at proposing a specification platform for a computeroriented representation of multilingual data within a large variety of applications such as translation memories, localization, computer-aided translation, multimedia, or electronic document management. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 6 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
![Scope As with the “Terminological Markup Framework”, used in terminology [ISO 16642], the MLIF Scope As with the “Terminological Markup Framework”, used in terminology [ISO 16642], the MLIF](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-7.jpg) Scope As with the “Terminological Markup Framework”, used in terminology [ISO 16642], the MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories that will be integrated within the TC 37 Data Category Registry [ISO/DIS 12620. 2] in order to allow the description of any specific domain. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 7 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope As with the “Terminological Markup Framework”, used in terminology [ISO 16642], the MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories that will be integrated within the TC 37 Data Category Registry [ISO/DIS 12620. 2] in order to allow the description of any specific domain. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 7 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope The standard will thus provide a way to validate any instance of this metamodel, as well as, interoperability principles with numerous translation and localization standards. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 8 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope The standard will thus provide a way to validate any instance of this metamodel, as well as, interoperability principles with numerous translation and localization standards. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 8 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The extremely fast evolution of the technological development in the sector of Communication and Information Technologies, and in particular, in the field of natural language processing, makes particularly acute the question of standardization. The issues related to this standardization are of an industrial, economic and cultural nature. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 9 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The extremely fast evolution of the technological development in the sector of Communication and Information Technologies, and in particular, in the field of natural language processing, makes particularly acute the question of standardization. The issues related to this standardization are of an industrial, economic and cultural nature. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 9 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The control of the interoperability between the industrial standards currently used for localization (XLIFF) , translation memory (TMX) , or any other Multi Lingual Markup Language (ML 2), constitutes a major objective for a coherent and global management of these data. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 10 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The control of the interoperability between the industrial standards currently used for localization (XLIFF) , translation memory (TMX) , or any other Multi Lingual Markup Language (ML 2), constitutes a major objective for a coherent and global management of these data. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 10 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The MLIF could be associated to several multimedia standards such as MPEG-4 [ISO/IEC 14496], MPEG-7 [ISO/IEC 15938], and W 3 C SMIL, in order to handle multilingual data within several multimedia applications such as, interactive TV, video conferencing, subtitling, karaoke and accessibility. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 11 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The MLIF could be associated to several multimedia standards such as MPEG-4 [ISO/IEC 14496], MPEG-7 [ISO/IEC 15938], and W 3 C SMIL, in order to handle multilingual data within several multimedia applications such as, interactive TV, video conferencing, subtitling, karaoke and accessibility. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 11 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The MLIF may also be used in cultural heritage related activities such as, digital museums, e-learning and electronic document management. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 12 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The MLIF may also be used in cultural heritage related activities such as, digital museums, e-learning and electronic document management. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 12 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification As with the “Terminological Markup Framework” (TMF), used in terminology, the MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 13 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification As with the “Terminological Markup Framework” (TMF), used in terminology, the MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 13 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification These data categories will be derived as a subset of a Data Category Registry (DCR) [ISO/DIS 12620. 2], in order to ensure interoperability between several multilingual applications and corpora. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 14 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification These data categories will be derived as a subset of a Data Category Registry (DCR) [ISO/DIS 12620. 2], in order to ensure interoperability between several multilingual applications and corpora. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 14 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification A Data Category Specification (DCS) will define, in combination with the metamodel, the various constraints that apply to a given domain-specific information structure or interchange format. A DCS and a metamodel represent the organization of an individual application and the organization of a specific domain. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 15 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification A Data Category Specification (DCS) will define, in combination with the metamodel, the various constraints that apply to a given domain-specific information structure or interchange format. A DCS and a metamodel represent the organization of an individual application and the organization of a specific domain. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 15 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The MLIF should be considered as a unified conceptual representation of multilingual content. The MLIF is not meant to replace or to compete with any other existing standard such as TMX or XLIFF. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 16 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The MLIF should be considered as a unified conceptual representation of multilingual content. The MLIF is not meant to replace or to compete with any other existing standard such as TMX or XLIFF. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 16 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification Rather, the MLIF is being designed with the objective of providing a common conceptual model and a platform allowing interoperability among several translation and localization standards, and by extension, their committed tools. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 17 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification Rather, the MLIF is being designed with the objective of providing a common conceptual model and a platform allowing interoperability among several translation and localization standards, and by extension, their committed tools. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 17 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The asset of MLIF is the interoperability which allows experts to gather, under the same conceptual unit, various tools and representations related to multilingual data. In addition, MLIF will also make it possible to evaluate and to compare these multilingual resources and tools. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 18 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The asset of MLIF is the interoperability which allows experts to gather, under the same conceptual unit, various tools and representations related to multilingual data. In addition, MLIF will also make it possible to evaluate and to compare these multilingual resources and tools. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 18 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification The description of all different XML elements will be done by using Relax. NG [ISO/IEC 19757 -2] with the help of ODD, which is the creation and documentation language for XML schemas proposed by the TEI (Text Encoding Initiative). This follows a recent decision taken by the World Wide Web Consortium. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 19 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification The description of all different XML elements will be done by using Relax. NG [ISO/IEC 19757 -2] with the help of ODD, which is the creation and documentation language for XML schemas proposed by the TEI (Text Encoding Initiative). This follows a recent decision taken by the World Wide Web Consortium. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 19 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Purpose and Justification MLIF will also provide a variety of filters allowing transformations between several MLIF-compatible formats, as well as, several automatic validation tools. The adoption of this new work item proposal may allow to instantiate the business plan proposal of TC 37/SC 4 in the perspective of creating a work specification on multilingual content (WG 3). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 20 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Purpose and Justification MLIF will also provide a variety of filters allowing transformations between several MLIF-compatible formats, as well as, several automatic validation tools. The adoption of this new work item proposal may allow to instantiate the business plan proposal of TC 37/SC 4 in the perspective of creating a work specification on multilingual content (WG 3). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 20 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF ISO WD 24616
MLIF ISO WD 24616
 Introduction The scope of research and development in the localization and translation memory (TM) process development is very large, and numerous independent groups are working on these aspects, such as LISA, OASIS, W 3 C, ISO, etc. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 22 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Introduction The scope of research and development in the localization and translation memory (TM) process development is very large, and numerous independent groups are working on these aspects, such as LISA, OASIS, W 3 C, ISO, etc. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 22 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Introduction Under the guidance of the abovementioned groups, many formats have been developed. Some of the major formats of specific interest for localization and TM are TMX (LISA/OSCAR) and XLIFF (OASIS). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 23 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Introduction Under the guidance of the abovementioned groups, many formats have been developed. Some of the major formats of specific interest for localization and TM are TMX (LISA/OSCAR) and XLIFF (OASIS). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 23 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Introduction There are many identical requirements for all the formats irrespective of the differences in final output. For example, all the formats aim at being user-friendly, easy-to-learn, and at reusing existing databases or knowledge. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 24 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Introduction There are many identical requirements for all the formats irrespective of the differences in final output. For example, all the formats aim at being user-friendly, easy-to-learn, and at reusing existing databases or knowledge. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 24 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Introduction All these formats work well in the specific field they are designed for, but they lack a synergy that would make them interoperable when using one type of information in a slightly different context, giving rise to the fear of competition between them. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 25 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Introduction All these formats work well in the specific field they are designed for, but they lack a synergy that would make them interoperable when using one type of information in a slightly different context, giving rise to the fear of competition between them. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 25 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
![Scope As with “Terminological Markup Framework” TMF [ISO 16642] in terminology, MLIF will introduce Scope As with “Terminological Markup Framework” TMF [ISO 16642] in terminology, MLIF will introduce](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-26.jpg) Scope As with “Terminological Markup Framework” TMF [ISO 16642] in terminology, MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories [ISO/DIS 12620. 2], as a means of ensuring interoperability between several multilingual applications and corpora. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 26 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope As with “Terminological Markup Framework” TMF [ISO 16642] in terminology, MLIF will introduce a metamodel in combination with chosen data categories [ISO/DIS 12620. 2], as a means of ensuring interoperability between several multilingual applications and corpora. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 26 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope MLIF deals with multilingual corpora, multilingual fragments, and the translation relations between them. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 27 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope MLIF deals with multilingual corpora, multilingual fragments, and the translation relations between them. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 27 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope In each domain where MLIF can be used, we may consider a specific granularity of segmentation and description, built on MAF [ISO CD 24611], Synaf [ISO CD 24615], TMF [ISO 16642] or LAF [ISO CD 24612] respectively, for morphological description, syntactical annotation, terminological description, and linguistic annotation. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 28 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope In each domain where MLIF can be used, we may consider a specific granularity of segmentation and description, built on MAF [ISO CD 24611], Synaf [ISO CD 24615], TMF [ISO 16642] or LAF [ISO CD 24612] respectively, for morphological description, syntactical annotation, terminological description, and linguistic annotation. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 28 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope MLIF will thus describe elementary linguistic segments (i. e. sentence, syntactical component, word, …). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 29 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope MLIF will thus describe elementary linguistic segments (i. e. sentence, syntactical component, word, …). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 29 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope Supporting the construction and the interoperability of localization and “Translation Memories” (TM) resources, MLIF deals with the description of a metamodel for multilingual content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 30 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope Supporting the construction and the interoperability of localization and “Translation Memories” (TM) resources, MLIF deals with the description of a metamodel for multilingual content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 30 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Scope MLIF will not propose a closed list of description features. Rather, it will provide a list of Data Categories, which is much easier to update and extend. This list represents a point of reference for multilingual information in the context of various application scenarios. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 31 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Scope MLIF will not propose a closed list of description features. Rather, it will provide a list of Data Categories, which is much easier to update and extend. This list represents a point of reference for multilingual information in the context of various application scenarios. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 31 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Normative References ISO 16642 Computer applications in terminology -- Terminological Markup Framework. ISO CD 24615 Syntactical Annotation Framework. ISO/DIS 12620. 2 Computer applications in terminology -- Data categories. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 32 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Normative References ISO 16642 Computer applications in terminology -- Terminological Markup Framework. ISO CD 24615 Syntactical Annotation Framework. ISO/DIS 12620. 2 Computer applications in terminology -- Data categories. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 32 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Normative References ISO/IEC 639 -1, Information technology - ISO 639: 1988, Code for the representation of names of languages. ISO 639 -2 Code for the representation of names and languages-part 2: Alpha-3 code. ISO 8601 Data elements and interchange formats - Information interchange - Representation of dates and times. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 33 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Normative References ISO/IEC 639 -1, Information technology - ISO 639: 1988, Code for the representation of names of languages. ISO 639 -2 Code for the representation of names and languages-part 2: Alpha-3 code. ISO 8601 Data elements and interchange formats - Information interchange - Representation of dates and times. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 33 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Starting point of MLIF The MLIF promotes the use of a common framework for the future development of several different formats: TMX, XLIFF, … The MLIF can be considered as a parent for all these formats, since all of them deal with multilingual data expressed in the form of segments or text units. They all can be stored, manipulated and translated in a similar manner. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 34 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Starting point of MLIF The MLIF promotes the use of a common framework for the future development of several different formats: TMX, XLIFF, … The MLIF can be considered as a parent for all these formats, since all of them deal with multilingual data expressed in the form of segments or text units. They all can be stored, manipulated and translated in a similar manner. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 34 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
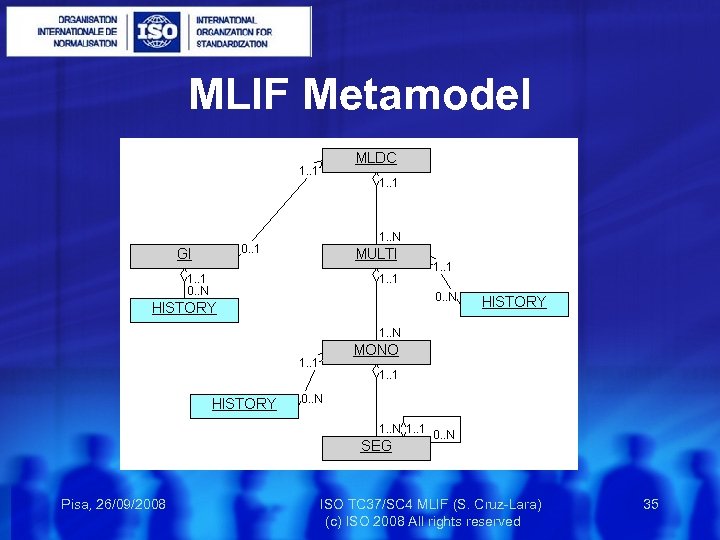 MLIF Metamodel Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 35 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 35 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Metamodel Multi Lingual Data Collection (MLDC) Represents a collection of data containing global information and several multilingual units. Global Information (GI) Represents technical and administrative information applying to the entire data collection. Example: title of the data collection, revision history, … Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 36 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel Multi Lingual Data Collection (MLDC) Represents a collection of data containing global information and several multilingual units. Global Information (GI) Represents technical and administrative information applying to the entire data collection. Example: title of the data collection, revision history, … Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 36 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Metamodel Multi Lingual Component (MULTI) This component represents a unique multilingual entry. Mono Lingual Component (MONO) Part of a multilingual component containing information related to one language. Segment Component (SEG) Textual content itself (may be “decorated” with several attributes as in Syn. AF [ISO CD 24615]) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 37 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel Multi Lingual Component (MULTI) This component represents a unique multilingual entry. Mono Lingual Component (MONO) Part of a multilingual component containing information related to one language. Segment Component (SEG) Textual content itself (may be “decorated” with several attributes as in Syn. AF [ISO CD 24615]) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 37 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Metamodel History Component This generic component allows to trace modifications on the component it is anchored to (i. e. versioning). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 38 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel History Component This generic component allows to trace modifications on the component it is anchored to (i. e. versioning). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 38 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Metamodel In order to provide a larger description of the linguistic content, the MLIF metamodel allows anchoring of other metamodels, such as MAF (morphological description), Syn. AF (syntactical annotation), TMF (terminological description), LAF (linguistic annotation), or any other metamodel based on ISO 12620. 2. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 39 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel In order to provide a larger description of the linguistic content, the MLIF metamodel allows anchoring of other metamodels, such as MAF (morphological description), Syn. AF (syntactical annotation), TMF (terminological description), LAF (linguistic annotation), or any other metamodel based on ISO 12620. 2. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 39 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
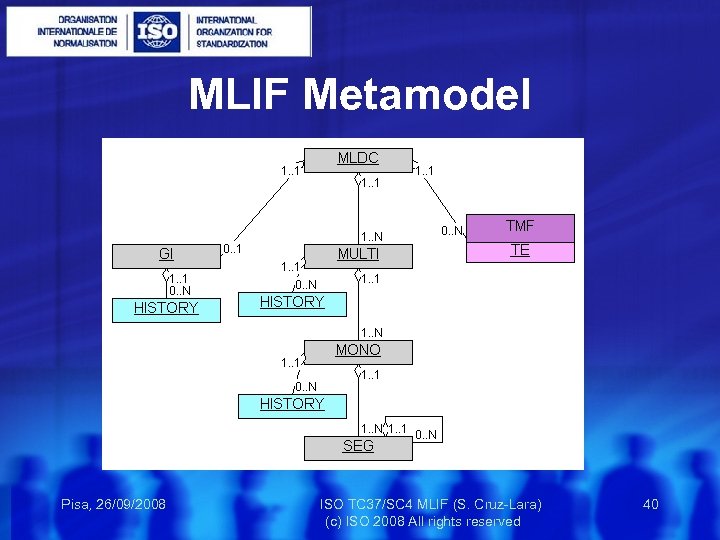 MLIF Metamodel Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 40 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Metamodel Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 40 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
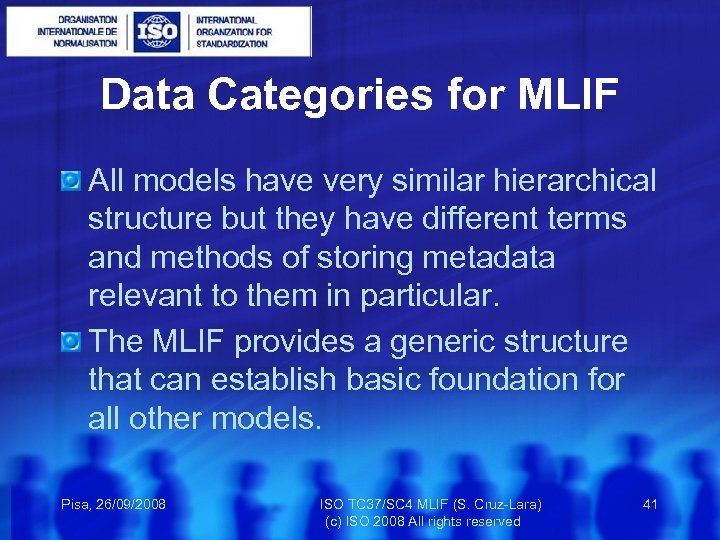 Data Categories for MLIF All models have very similar hierarchical structure but they have different terms and methods of storing metadata relevant to them in particular. The MLIF provides a generic structure that can establish basic foundation for all other models. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 41 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF All models have very similar hierarchical structure but they have different terms and methods of storing metadata relevant to them in particular. The MLIF provides a generic structure that can establish basic foundation for all other models. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 41 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
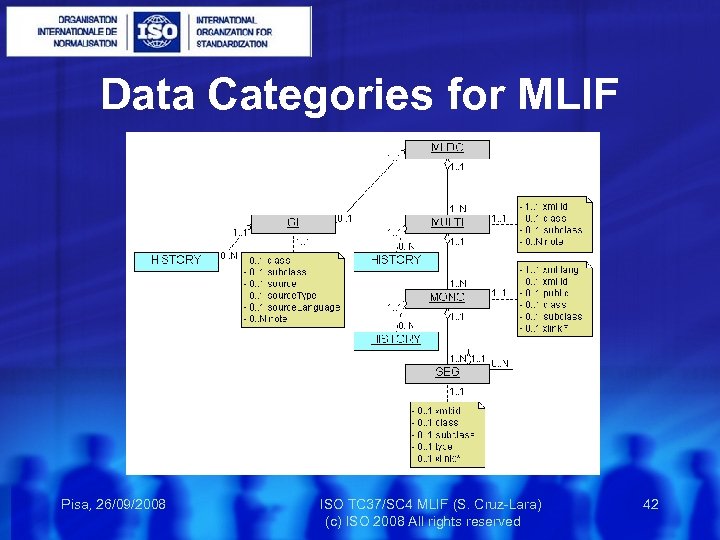 Data Categories for MLIF Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 42 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 42 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /domain/ Specifies the domain on which the MLDC is dependent. /project/ Specifies a project within the domain on which the MLDC is dependent. /source/ “A complete citation of the bibliographic information pertaining to a document or other resource. “[ISO 12620] Reference to a resource from which the present resource is derived. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 43 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /domain/ Specifies the domain on which the MLDC is dependent. /project/ Specifies a project within the domain on which the MLDC is dependent. /source/ “A complete citation of the bibliographic information pertaining to a document or other resource. “[ISO 12620] Reference to a resource from which the present resource is derived. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 43 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /source. Type/ “In multilingual and translation-oriented language resource or terminology management, the kind of text used to document the selection of lexical or terminological equivalents, collocations, and the like. “[ISO 12620] “Both parallel and background texts serve as sources for information used in documenting multilingual terminology entries. “[ISO 12620] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 44 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /source. Type/ “In multilingual and translation-oriented language resource or terminology management, the kind of text used to document the selection of lexical or terminological equivalents, collocations, and the like. “[ISO 12620] “Both parallel and background texts serve as sources for information used in documenting multilingual terminology entries. “[ISO 12620] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 44 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /source. Language/ “In a translation-oriented language resource or terminology database, the language that is taken as the language in which the original text is written. ” [ISO 12620] /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 45 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Global Information (GI) /source. Language/ “In a translation-oriented language resource or terminology database, the language that is taken as the language in which the original text is written. ” [ISO 12620] /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 45 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
![Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-46.jpg) Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 46 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 46 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 47 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Multilingual Component (MULTI) /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 47 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /language. Identifier/ A unique identifier in a language resource entry that indicates the name of a language. [source: ISO 12620] XML equivalent “xml: lang” /language. Level/ Specifies the language level of the unique language identifier associated to the monolingual component (e. g. adults, children, scientist, slang, …) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 48 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /language. Identifier/ A unique identifier in a language resource entry that indicates the name of a language. [source: ISO 12620] XML equivalent “xml: lang” /language. Level/ Specifies the language level of the unique language identifier associated to the monolingual component (e. g. adults, children, scientist, slang, …) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 48 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
![Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-49.jpg) Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 49 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 49 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 50 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 50 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /xlink/: Is a data category refinement composed by several data categories. It is used to identify a name or a resource: /uri/: can be represented by an xlink: href attribute. /type/: can be represented by an xlink: type attribute. /label/: can be represented by an xlink: label attribute. /title/: can be represented by an xlink: title attribute. /from/: can be represented by an xlink: from attribute. /to/: can be represented by an xlink: to attribute. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 51 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Monolingual Component (MONO) /xlink/: Is a data category refinement composed by several data categories. It is used to identify a name or a resource: /uri/: can be represented by an xlink: href attribute. /type/: can be represented by an xlink: type attribute. /label/: can be represented by an xlink: label attribute. /title/: can be represented by an xlink: title attribute. /from/: can be represented by an xlink: from attribute. /to/: can be represented by an xlink: to attribute. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 51 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
![Data categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Data categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-52.jpg) Data categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 52 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /identifier/ A unique name [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] Dublin Core equivalent: DC: Identifier [source: IMDI_Source_Tag] XML equivalent “xml: id” [source: http: //www. w 3. org/TR/xml-id] Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 52 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 53 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /class/ A hierarchical high level description of the component it is anchored to. /subclass/ A hierarchical low level description of the component it is anchored to. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 53 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /xlink/: Is a data category refinement composed by several data categories. It is used to identify a name or a resource: /uri/: can be represented by an xlink: href attribute. /type/: can be represented by an xlink: type attribute. /label/: can be represented by an xlink: label attribute. /title/: can be represented by an xlink: title attribute. /from/: can be represented by an xlink: from attribute. /to/: can be represented by an xlink: to attribute. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 54 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF Segment Component (SEG) /xlink/: Is a data category refinement composed by several data categories. It is used to identify a name or a resource: /uri/: can be represented by an xlink: href attribute. /type/: can be represented by an xlink: type attribute. /label/: can be represented by an xlink: label attribute. /title/: can be represented by an xlink: title attribute. /from/: can be represented by an xlink: from attribute. /to/: can be represented by an xlink: to attribute. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 54 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF The History. Component is a generic component allowing to trace modifications on the component it is anchored to (e. g. , creation, modification, validation). It can be anchored onto any component of the metamodel. In MLIF metamodel, the History. Component may be anchored to the Global. Information or to the Mono. Lingual. Component. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 55 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF The History. Component is a generic component allowing to trace modifications on the component it is anchored to (e. g. , creation, modification, validation). It can be anchored onto any component of the metamodel. In MLIF metamodel, the History. Component may be anchored to the Global. Information or to the Mono. Lingual. Component. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 55 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF In the Global. Information component, the History. Component keeps all information related to any modification on the context or on the domain; In the Mono. Lingual. Component, the History. Component allows keeping all evolutions or any enhancement of the content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 56 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF In the Global. Information component, the History. Component keeps all information related to any modification on the context or on the domain; In the Mono. Lingual. Component, the History. Component allows keeping all evolutions or any enhancement of the content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 56 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF History. Component /transaction/ One of the steps involved in the creation, approval, and use of a specific component (approval, check, exportation, importation, input, modification, origination, standardization, user. Access, withdrawal). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 57 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF History. Component /transaction/ One of the steps involved in the creation, approval, and use of a specific component (approval, check, exportation, importation, input, modification, origination, standardization, user. Access, withdrawal). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 57 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Data Categories for MLIF History. Component /date/ A date. The date is encoded according to a profile of [ISO 8601] as described in [W 3 CDTF] and follows the YYYY-MM-DD format. /author/ The person responsible for the creation of the content. /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 58 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Data Categories for MLIF History. Component /date/ A date. The date is encoded according to a profile of [ISO 8601] as described in [W 3 CDTF] and follows the YYYY-MM-DD format. /author/ The person responsible for the creation of the content. /note/ This is an optional descriptor providing further information on any part of a content. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 58 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF example 1
MLIF example 1
 MLIF example 2
MLIF example 2
 MLIF example 3
MLIF example 3
 Ongoing Activities
Ongoing Activities
 Ongoing activities MLIF can be used in e-learning, interactive television programs and any other application having a user interface. It may be very helpful for future interactive television broadcasting. Within ITEA’s “Jules Verne” and “Passepartout” projects, we have identified several potential implementations of MLIF in association with interactive TV and multimedia. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 63 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Ongoing activities MLIF can be used in e-learning, interactive television programs and any other application having a user interface. It may be very helpful for future interactive television broadcasting. Within ITEA’s “Jules Verne” and “Passepartout” projects, we have identified several potential implementations of MLIF in association with interactive TV and multimedia. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 63 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Ongoing activities The MLIF and multimedia association presents ample opportunity for giving value to different languages and cultures, as is the case in Europe and Asia. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 64 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Ongoing activities The MLIF and multimedia association presents ample opportunity for giving value to different languages and cultures, as is the case in Europe and Asia. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 64 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Ongoing activities Within the framework of ITEA “Passepartout” project, we have experimented with some basic scenarios by using: XMT (“e. Xtensible MPEG 4 Textual format”) and, W 3 C SMIL (“Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language”). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 65 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Ongoing activities Within the framework of ITEA “Passepartout” project, we have experimented with some basic scenarios by using: XMT (“e. Xtensible MPEG 4 Textual format”) and, W 3 C SMIL (“Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language”). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 65 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Ongoing activities We are currently collaborating with the W 3 C SYMM (SYnchronized Multi. Media) Working Group SMIL (Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language) SMILText New text container element Multilinguality (yes) Linguistic granularity (no) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 66 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Ongoing activities We are currently collaborating with the W 3 C SYMM (SYnchronized Multi. Media) Working Group SMIL (Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language) SMILText New text container element Multilinguality (yes) Linguistic granularity (no) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 66 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 SMILText This module defines new functionality for SMIL 3. 0. It extends the media types available for SMIL, but does not alter any other existing functionality from SMIL 2. 1 or earlier versions. Editors: Dick Bulterman (CWI, The Netherlands), Sjoerd Mullender (CWI, The Netherlands), Samuel Cruz-Lara (LORIA / INRIA, France) TEXT IS BEAUTIFUL ! Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 67 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
SMILText This module defines new functionality for SMIL 3. 0. It extends the media types available for SMIL, but does not alter any other existing functionality from SMIL 2. 1 or earlier versions. Editors: Dick Bulterman (CWI, The Netherlands), Sjoerd Mullender (CWI, The Netherlands), Samuel Cruz-Lara (LORIA / INRIA, France) TEXT IS BEAUTIFUL ! Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 67 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 SMILText The SMILText modules provide a text container element with an explicit content model for defining in-line text, and a set of additional elements and attributes to control explicit in-line text rendering. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 68 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
SMILText The SMILText modules provide a text container element with an explicit content model for defining in-line text, and a set of additional elements and attributes to control explicit in-line text rendering. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 68 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 SMILText Since the SMILText elements and attributes are defined in a series of modules, designers of other markup languages can reuse these modules when they need to include a simple form of timed text functionality into their language. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 69 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
SMILText Since the SMILText elements and attributes are defined in a series of modules, designers of other markup languages can reuse these modules when they need to include a simple form of timed text functionality into their language. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 69 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Ongoing activities We have recently joint four new projects where MLIF should be used: ITEA 2 SEMby. SEM (INRIA - S. Cruz-Lara) ITEA 2 METAVERSE 1 (INRIA - S. Cruz. Lara) FP 7 -ICT MEDAR (CEA - N. Semmar) ANR WEBCROSSLING (CEA - N. Semmar) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 71 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Ongoing activities We have recently joint four new projects where MLIF should be used: ITEA 2 SEMby. SEM (INRIA - S. Cruz-Lara) ITEA 2 METAVERSE 1 (INRIA - S. Cruz. Lara) FP 7 -ICT MEDAR (CEA - N. Semmar) ANR WEBCROSSLING (CEA - N. Semmar) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 71 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 SEMby. SEM This project will provide an innovative and comprehensive Semantic Services Management System, based on a common open infrastructure, to allow management of tomorrow mixed systems (made of thousands elementary software and hardware components) with facilities to build ad-hoc dynamic visualisations of the managed systems for information, management and SLA verification purposes. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 72 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
SEMby. SEM This project will provide an innovative and comprehensive Semantic Services Management System, based on a common open infrastructure, to allow management of tomorrow mixed systems (made of thousands elementary software and hardware components) with facilities to build ad-hoc dynamic visualisations of the managed systems for information, management and SLA verification purposes. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 72 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 SEMby. SEM To do so, it will extensively use semantic description with the help of a « new standard » that it will provide. Keywords: Software Engineering, UML, OMG (SBVR, MOF, KDM, … Countries: Finland, France, and Turkey INRIA’s contribution: Multilingual Ontologies Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 73 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
SEMby. SEM To do so, it will extensively use semantic description with the help of a « new standard » that it will provide. Keywords: Software Engineering, UML, OMG (SBVR, MOF, KDM, … Countries: Finland, France, and Turkey INRIA’s contribution: Multilingual Ontologies Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 73 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 METAVERSE 1 The Metaverse 1 (global standards among real and virtual worlds) project will provide a standardized global framework that enables the interoperability between virtual worlds (as for example Second Life, World of Warcraft, IMVU, Google Earth and many others) and the real world (sensors, actuators, vision and rendering, social and welfare systems, banking, insurance, travel, real estate and many others). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 74 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
METAVERSE 1 The Metaverse 1 (global standards among real and virtual worlds) project will provide a standardized global framework that enables the interoperability between virtual worlds (as for example Second Life, World of Warcraft, IMVU, Google Earth and many others) and the real world (sensors, actuators, vision and rendering, social and welfare systems, banking, insurance, travel, real estate and many others). Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 74 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 METAVERSE 1 The ‘Metaverse for all’ will be a special attention point aiming at the e-Inclusion of minorities in the society. Countries: Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Israel, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, and Spain INRIA’s contribution: Standardise the management and the representation of multilingual textual data Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 75 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
METAVERSE 1 The ‘Metaverse for all’ will be a special attention point aiming at the e-Inclusion of minorities in the society. Countries: Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Israel, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, and Spain INRIA’s contribution: Standardise the management and the representation of multilingual textual data Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 75 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 FP 7 -ICT MEDAR Supporting the development of tools and resources in Machine Translation and Multi. Lingual Information Retrieval on the basis of other partners technologies and open source code CEA’s contribution: Multilingual Information Retrieval Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 76 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
FP 7 -ICT MEDAR Supporting the development of tools and resources in Machine Translation and Multi. Lingual Information Retrieval on the basis of other partners technologies and open source code CEA’s contribution: Multilingual Information Retrieval Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 76 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 ANR Web. Crossling Developing a Machine Translation prototype based on Multi. Lingual Information Retrieval technology CEA’s contribution: Multilingual Information Retrieval Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 77 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
ANR Web. Crossling Developing a Machine Translation prototype based on Multi. Lingual Information Retrieval technology CEA’s contribution: Multilingual Information Retrieval Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 77 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Actions
Actions
![Actions MLIF is an ISO “Working Draft” [ISO WD 24616]. A Committee of Experts Actions MLIF is an ISO “Working Draft” [ISO WD 24616]. A Committee of Experts](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-78.jpg) Actions MLIF is an ISO “Working Draft” [ISO WD 24616]. A Committee of Experts for MLIF has been constituted The proposal we have just presented needs comments, remarks, … so it will be shortly sent to the Committee of Experts Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 79 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Actions MLIF is an ISO “Working Draft” [ISO WD 24616]. A Committee of Experts for MLIF has been constituted The proposal we have just presented needs comments, remarks, … so it will be shortly sent to the Committee of Experts Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 79 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Experts Committee Member bodies Annelies Kesting - NEN (The Netherlands) Bettina Seitl - ON (Austria) Young-Shik Kang - KATS (Republic of Korea) Marketa Jindrakova - CNI (Czech Republic) Roberto Ravaglia - UNI (Italy) Surayuth Boonmatat - TISI (Thailand) Toni Hittema - AFNOR (France) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 80 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Experts Committee Member bodies Annelies Kesting - NEN (The Netherlands) Bettina Seitl - ON (Austria) Young-Shik Kang - KATS (Republic of Korea) Marketa Jindrakova - CNI (Czech Republic) Roberto Ravaglia - UNI (Italy) Surayuth Boonmatat - TISI (Thailand) Toni Hittema - AFNOR (France) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 80 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Experts Committee Experts Dewi Bryn Jones - Canolfan Bedwyr (UK) Elena Montiel - UPM (Spain) Elsa Sklavounou - SYSTRAN (France) Emmanuel Planas - Lingua et Machina (France) Felix Sasaki - W 3 C Gerhard Budin - University of Vienna (Austria) Guadalupe Aguado de Cea - UPM (Spain) Harry Bunt - Tilburg University (The Netherlands) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 81 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Experts Committee Experts Dewi Bryn Jones - Canolfan Bedwyr (UK) Elena Montiel - UPM (Spain) Elsa Sklavounou - SYSTRAN (France) Emmanuel Planas - Lingua et Machina (France) Felix Sasaki - W 3 C Gerhard Budin - University of Vienna (Austria) Guadalupe Aguado de Cea - UPM (Spain) Harry Bunt - Tilburg University (The Netherlands) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 81 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Experts Committee Experts Key-Sun Choi - KORTERM/KAIST (Korea) Kiyong Lee - Korea University (Korea) Laurent Romary - Max Planck Digital Library (Germany), INRIA (France) Mourad Amine - Université de Montréal (Canada) Nasredine Semmar CEA (France) Nicoletta Calzolari ILC-CNR (Italy) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 82 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Experts Committee Experts Key-Sun Choi - KORTERM/KAIST (Korea) Kiyong Lee - Korea University (Korea) Laurent Romary - Max Planck Digital Library (Germany), INRIA (France) Mourad Amine - Université de Montréal (Canada) Nasredine Semmar CEA (France) Nicoletta Calzolari ILC-CNR (Italy) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 82 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 MLIF Experts Committee Experts Samuel Cruz-Lara - LORIA / INRIA (France) Stéphane Albucher - Business Objects (France) Wim Peters - University of Sheffield (UK) Yves Savourel ENLASO - (USA) Julien Ducret - SAFARI Consulting (France) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 83 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF Experts Committee Experts Samuel Cruz-Lara - LORIA / INRIA (France) Stéphane Albucher - Business Objects (France) Wim Peters - University of Sheffield (UK) Yves Savourel ENLASO - (USA) Julien Ducret - SAFARI Consulting (France) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 83 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Actions The basis of the discussion must be the new proposal Metamodel & Data Categories Do we need to modify them? Do we need to take into account any new aspect? How can we progress? Use cases!!! Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 84 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Actions The basis of the discussion must be the new proposal Metamodel & Data Categories Do we need to modify them? Do we need to take into account any new aspect? How can we progress? Use cases!!! Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 84 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
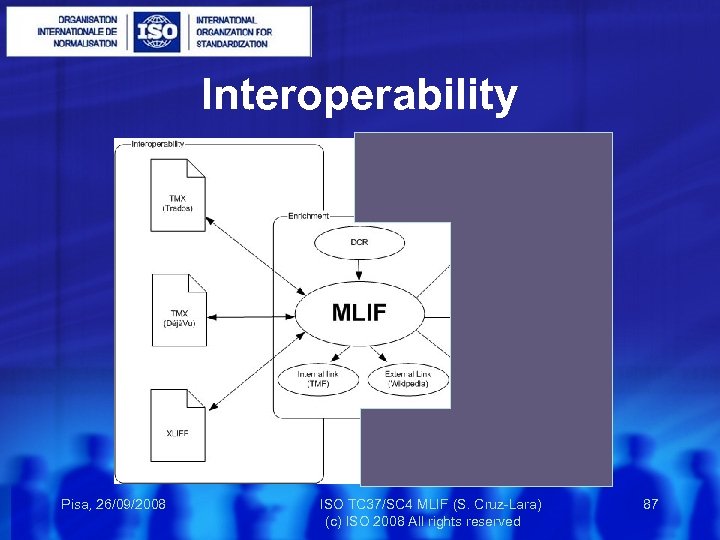
 Actions Use Cases Interoperability Publishing Linguistic Granularity Segmentation Related Standards Multimedia Multilingual Ontologies … Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 85 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Actions Use Cases Interoperability Publishing Linguistic Granularity Segmentation Related Standards Multimedia Multilingual Ontologies … Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 85 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
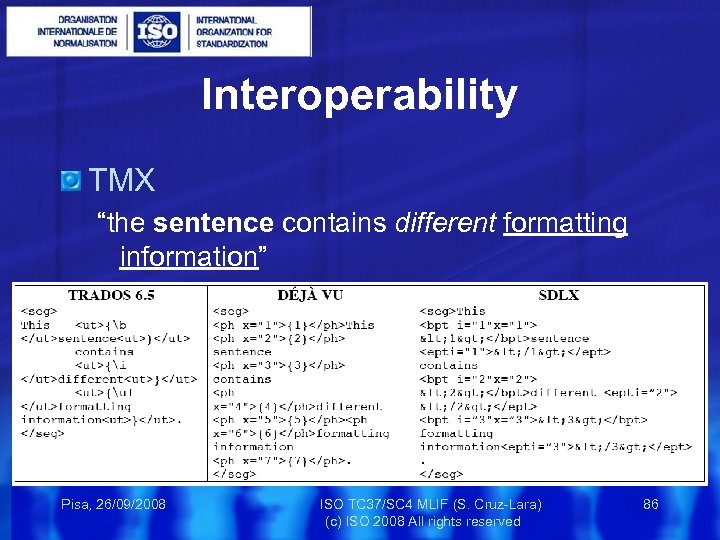 Interoperability TMX “the sentence contains different formatting information” Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 86 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Interoperability TMX “the sentence contains different formatting information” Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 86 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Interoperability Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 87 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Interoperability Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 87 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Interoperability TMX & MLIF
Interoperability TMX & MLIF
 Interoperability TMX & MLIF
Interoperability TMX & MLIF
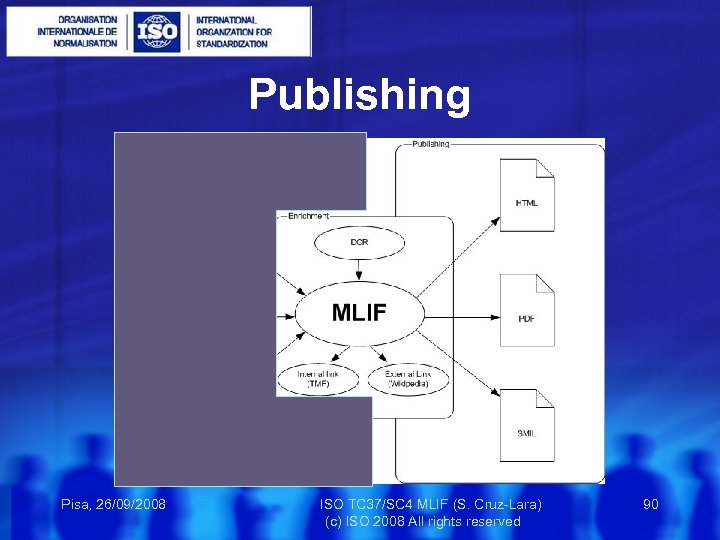 Publishing Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 90 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Publishing Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 90 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
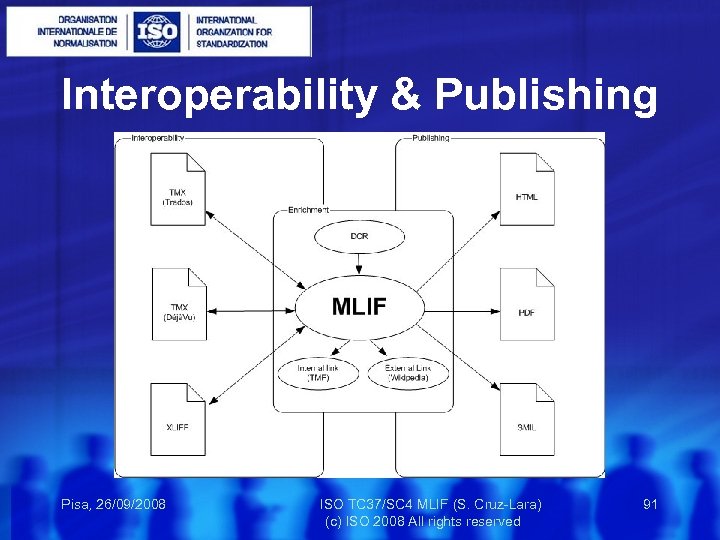 Interoperability & Publishing Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 91 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Interoperability & Publishing Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 91 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Linguistic Properties Sentence, word, lemma, POS, … Time related issues? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 92 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Linguistic Properties Sentence, word, lemma, POS, … Time related issues? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 92 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Linguistic Properties Example by: Nasredine Semmar
Linguistic Properties Example by: Nasredine Semmar
 Segmentation How segmentation issues will be taken into account by MLIF? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 94 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Segmentation How segmentation issues will be taken into account by MLIF? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 94 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Related Standards TEI (Text Encoding Initiative) The description of all different XML elements will be done by using Relax. NG [ISO 19757 -2] with the help of ODD, which is the creation and documentation language for XML schemas proposed by the TEI. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 95 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Related Standards TEI (Text Encoding Initiative) The description of all different XML elements will be done by using Relax. NG [ISO 19757 -2] with the help of ODD, which is the creation and documentation language for XML schemas proposed by the TEI. Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 95 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Related Standards W 3 C ITS (International Tag Set) ITS is a set of rules, expressed in elements, that provide information on how parts of a given DTD or XML Schema are related to specific internationalization & localization properties. Should ITS may be used inside MLIF (as ITS may be used in SMILText)? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 96 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Related Standards W 3 C ITS (International Tag Set) ITS is a set of rules, expressed in elements, that provide information on how parts of a given DTD or XML Schema are related to specific internationalization & localization properties. Should ITS may be used inside MLIF (as ITS may be used in SMILText)? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 96 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Multimedia W 3 C SMILText Multilinguality (yes) Linguistic Granularity (no) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 97 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Multimedia W 3 C SMILText Multilinguality (yes) Linguistic Granularity (no) Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 97 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
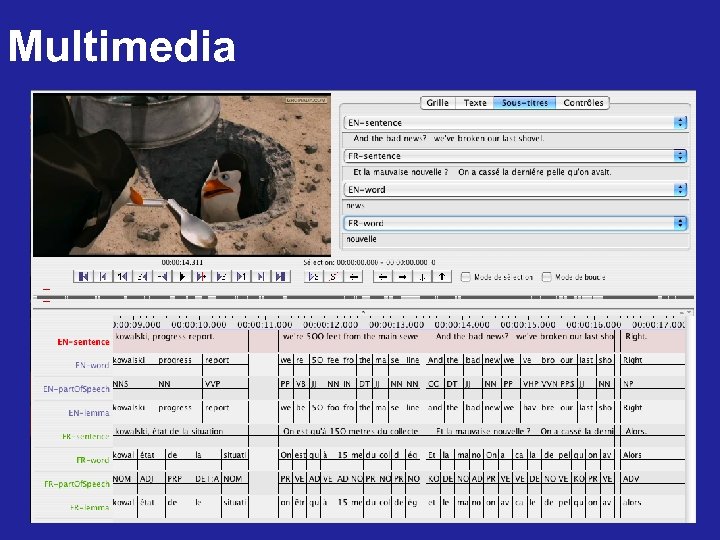 Multimedia
Multimedia
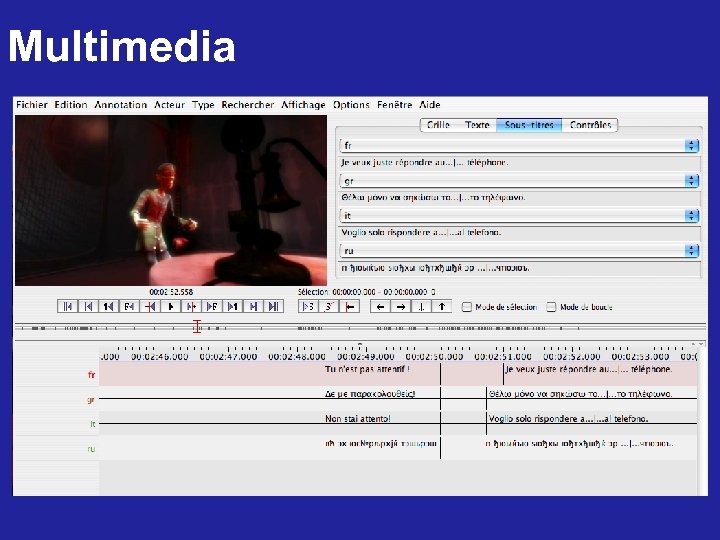 Multimedia
Multimedia
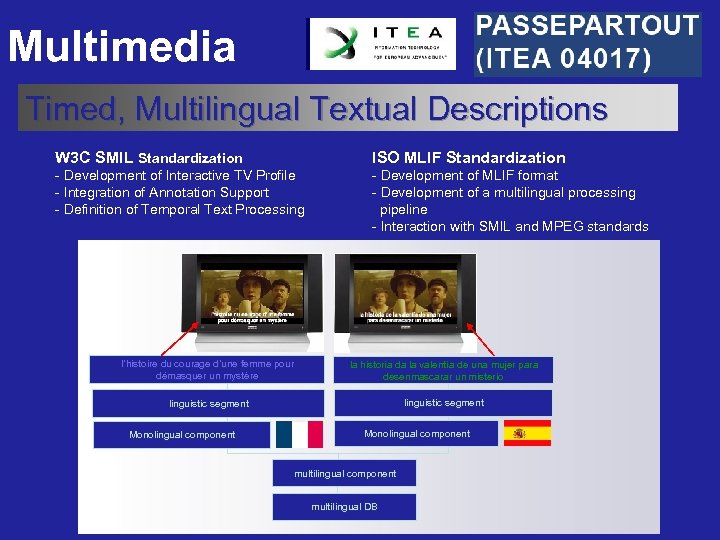 Multimedia Timed, Multilingual Textual Descriptions W 3 C SMIL Standardization - Development of Interactive TV Profile - Integration of Annotation Support - Definition of Temporal Text Processing ISO MLIF Standardization - Development of MLIF format - Development of a multilingual processing pipeline - Interaction with SMIL and MPEG standards l’histoire du courage d’une femme pour démasquer un mystère la historia da la valentía de una mujer para desenmascarar un misterio desenmascarar un linguistic segment Monolingual component multilingual DB
Multimedia Timed, Multilingual Textual Descriptions W 3 C SMIL Standardization - Development of Interactive TV Profile - Integration of Annotation Support - Definition of Temporal Text Processing ISO MLIF Standardization - Development of MLIF format - Development of a multilingual processing pipeline - Interaction with SMIL and MPEG standards l’histoire du courage d’une femme pour démasquer un mystère la historia da la valentía de una mujer para desenmascarar un misterio desenmascarar un linguistic segment Monolingual component multilingual DB
 Multilingual Ontologies In what way can MLIF be related to Multilingual Ontologies? ITEA 2 SEMby. SEM Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 101 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Multilingual Ontologies In what way can MLIF be related to Multilingual Ontologies? ITEA 2 SEMby. SEM Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 101 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Date Extension Request
Date Extension Request
![MLIF [ISO CD 24616] Current state: Warning Urgent actions to do? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO MLIF [ISO CD 24616] Current state: Warning Urgent actions to do? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO](https://present5.com/presentation/b51e27f187d24fe12420109881d48716/image-102.jpg) MLIF [ISO CD 24616] Current state: Warning Urgent actions to do? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 103 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
MLIF [ISO CD 24616] Current state: Warning Urgent actions to do? Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 103 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Date Extension Request Current Proposed DIS 2008 -10 -13 2009 -10 -13 FDIS 2010 -04 -13 2011 -04 -13 IS 2010 -10 -13 2011 -10 -13 Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 104 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Date Extension Request Current Proposed DIS 2008 -10 -13 2009 -10 -13 FDIS 2010 -04 -13 2011 -04 -13 IS 2010 -10 -13 2011 -10 -13 Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 104 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Conclusion
Conclusion
 Conclusion We suggest to develop several use cases in order to test and to validate the new metamodel and related data categories Each use case should be leaded by one or several members of the MLIF Experts Committee Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 106 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Conclusion We suggest to develop several use cases in order to test and to validate the new metamodel and related data categories Each use case should be leaded by one or several members of the MLIF Experts Committee Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 106 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Conclusion A new working draft of MLIF, taken into account all proposed use cases, should be submitted to the Committee of Experts soon Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 107 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Conclusion A new working draft of MLIF, taken into account all proposed use cases, should be submitted to the Committee of Experts soon Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 107 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
 Thank you! Thank you for your attention Any question? Mailing list mlif@loria. fr Web site http: //mlif. loria. fr Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 108 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved
Thank you! Thank you for your attention Any question? Mailing list mlif@loria. fr Web site http: //mlif. loria. fr Pisa, 26/09/2008 ISO TC 37/SC 4 MLIF (S. Cruz-Lara) 108 (c) ISO 2008 All rights reserved


