89fd0459d6ced4f3f832059a5bf987f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

MKTG 504 - CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WHO, WHEN, HOW, WHERE. . Dr. Dennis Pitta University of Baltimore

CONSUMER BEHAVIOR The subject of human behavior that is concerned with the decisions and acts of individuals in purchasing and using products.

BUYING BEHAVIOR The decision processes and actions of individuals involved in buying and using products.
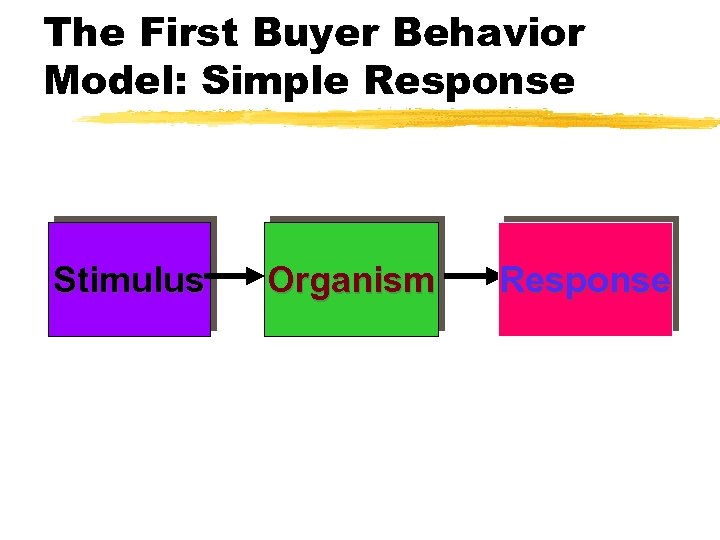
The First Buyer Behavior Model: Simple Response Stimulus Organism Response

ECONOMIC (HU) MAN MODEL Income is spent on goods providing UTILITY MARGINAL UTILITY CONCEPT PROBLEMS WITH THE MODEL: z. MAN NOT ALWAYS RATIONAL z. NO PERFECT INFORMATON

USES FOR THE ECONOMIC HUMAN MODEL z. USEFUL FOR EXPENSIVE GOODS z. PROVIDES ANALYSIS OFECONOMIC VARIABLES FOR WHCIH DATA EXISTS. (E. G. , ELASTICITY - at what price will utility decrease? )
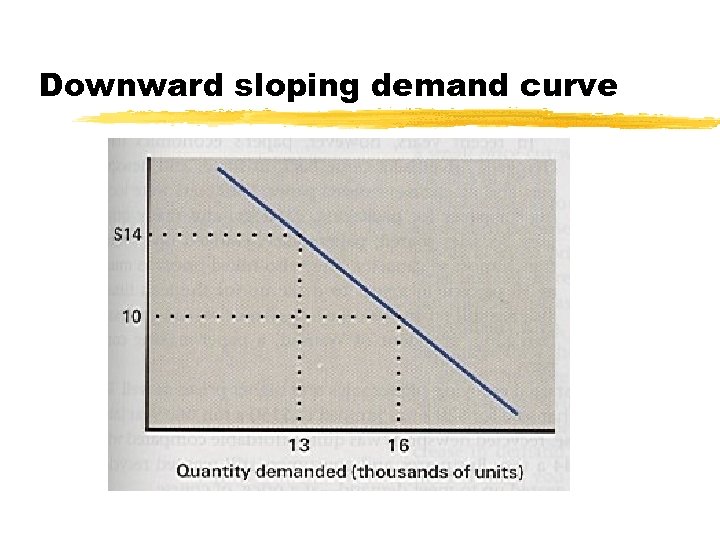
Downward sloping demand curve
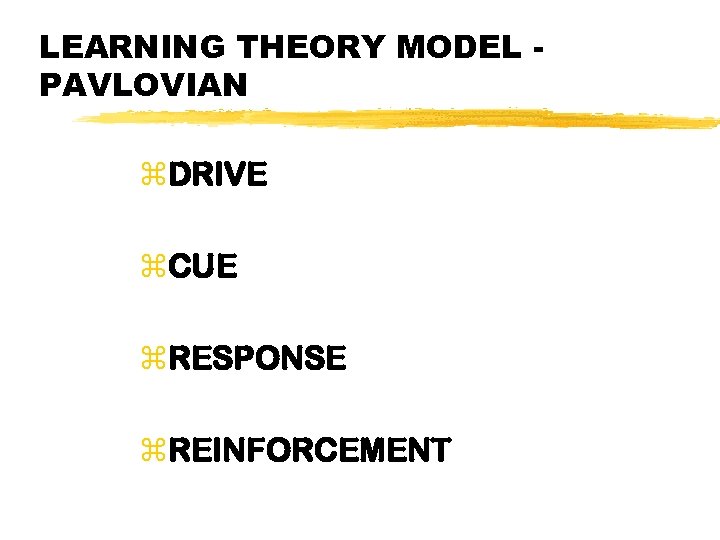
LEARNING THEORY MODEL PAVLOVIAN z. DRIVE z. CUE z. RESPONSE z. REINFORCEMENT

USES FOR LEARNING THEORY MODEL MANY: BRAND LOYALTY BRAND NAMES

PROBLEMS WITH THE LEARNING THEORY MODEL NEGLECTS: z. PERCEPTIONS z. INTERPERSONAL INFLUENCES z. SUBCONCIOUS

MOTIVATION MODEL: FREUDIAN (SYMBOLIC PRODUCT) Uses PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUES MOTIVATIONAL RESEARCH PROBLEMS WITH THE MODEL: z. COSTLY z. INTERPRETATION? ? ?

A projective test - the Thematic Apperception Test

Typical directions…. Study the picture on the right until your imagination begins to form a story about it. There are no rules except that your story should have a beginning (what has happened in the story so far), middle (what is happening now), and an end (how things turn out).

Another example of projective techniques. . .

Describe the person who composed this shopping list (List A or List B) z 10 pounds of potatoes z 5 pound of sugar z 3 pounds of ground z 1 lb of ground coffee <--> 16 oz instant z 1 loaf of white bread z 2 pounds of carrots z 1 box of laundry detergent z 1 pound of tomatoes z 2 qts milk
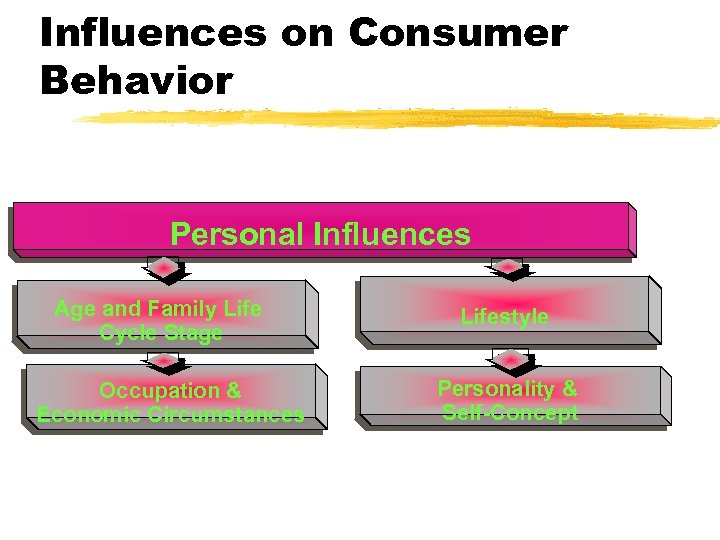
Influences on Consumer Behavior Personal Influences Age and Family Life Cycle Stage Occupation & Economic Circumstances Lifestyle Personality & Self-Concept
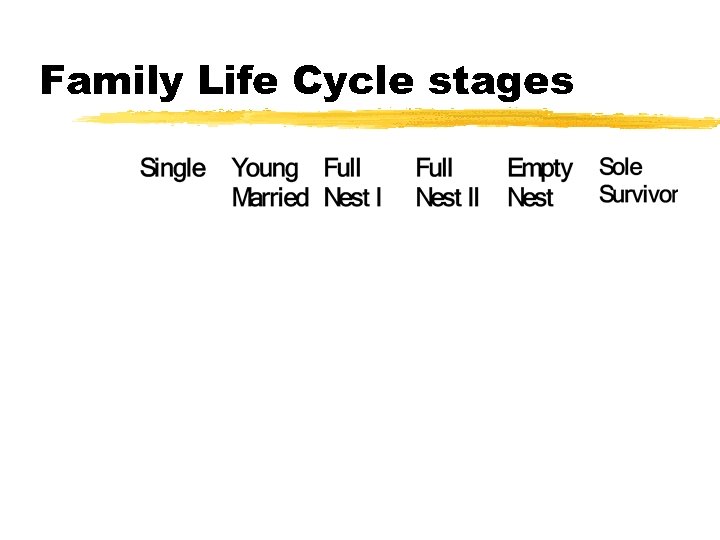
Family Life Cycle stages
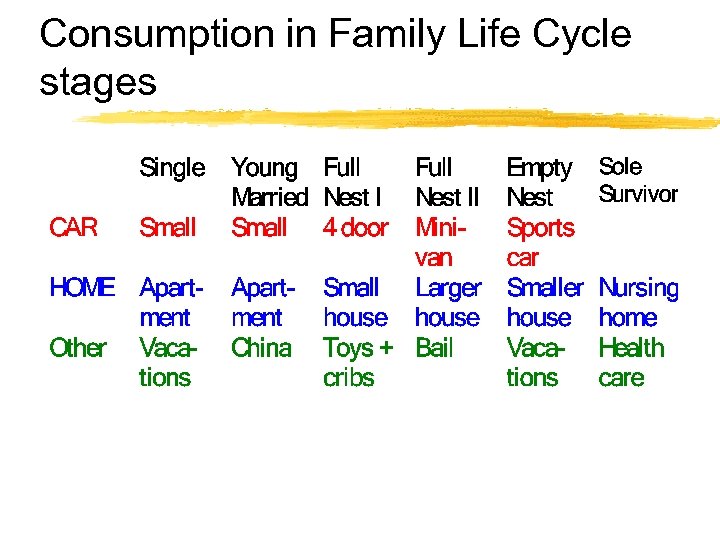
Consumption in Family Life Cycle stages

SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGICAL MODEL MANY FACTORS AFFECT BEHAVIOR: z. INDIVIDUAL z. FAMILY z. REFERENCE GROUPS y(Opinion Leadership) z. SOCIAL CLASS z. CULTURE

Personal Influence : PERSONALITY Personality = The collection of relatively permanent tendencies to behavior in consistent ways in certain situations.

Personal Influence: ATTITUDES Attitudes = Enduring feelings, evaluations, and responses - tendencies directed toward an object or idea. May be positive or negative. Attitudes does not equal buying intentions. Resistant to changes.

Components of attitudes z. BELIEFS about an object (bi) z. EVALUATION of those beliefs as good or bad (e i) z. Ao= biei
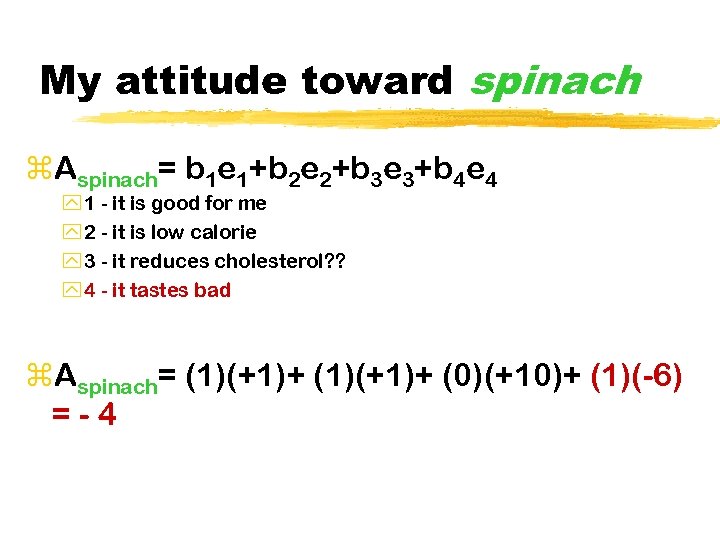
My attitude toward spinach z. Aspinach= b 1 e 1+b 2 e 2+b 3 e 3+b 4 e 4 y 1 - it is good for me y 2 - it is low calorie y 3 - it reduces cholesterol? ? y 4 - it tastes bad z. Aspinach= (1)(+1)+ (0)(+10)+ (1)(-6) =-4

How do you change a person’s attitude? z. Change the beliefs - not the evaluation z. Example: 9 out of 10 doctors eat spinach to lower their cholesterol

Do you see the black dots?

Personal Influence : Perceptions?

Personal Influence: PERCEPTION Perception = The process through which an individual selects relevant stimuli from the environment, organizes them and assigns meaning to them. SELECTIVE EXPOSURE SELECTIVE DISTORTION SELECTIVE RETENTION

Is this perceived?

Personal Influence: MOTIVATION Motivation = The driving force that causes a person to take action to satisfy specific needs or wants. Example: Maslow’s hierarchy. Physiological Safety Love and belonging Esteem Self-esteem

How believable is Maslow? z. There is no evidence that needs beyond safety needs exist widely throughout society.

Personal Influence: LEARNING Learning = The process through which a relatively permanent change in behavior results from the consequences of past behavior.

Source of Learning Direct Experience = actual use Indirect Experience = information obtained from others or observation of the behavior of others.

Result of Learning Brand Loyalty -> learned through positive reinforcement. Extinction -> weakening of well-established habit by unsatisfactory experiences.
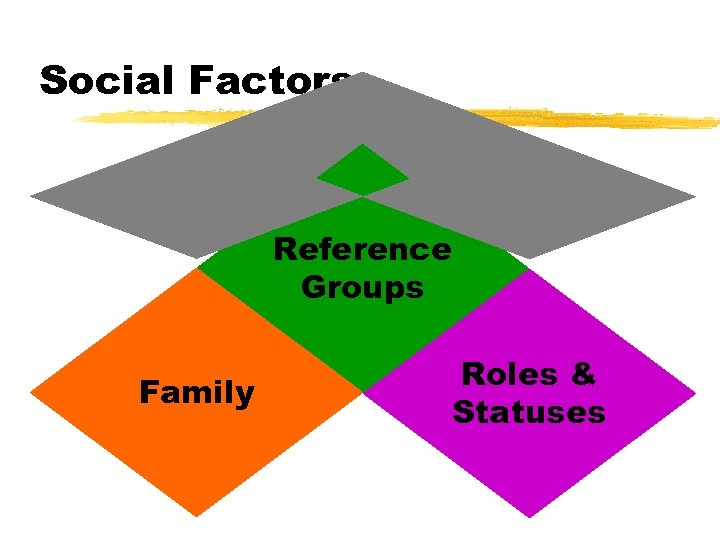
Social Factors Reference Groups Family Roles & Statuses
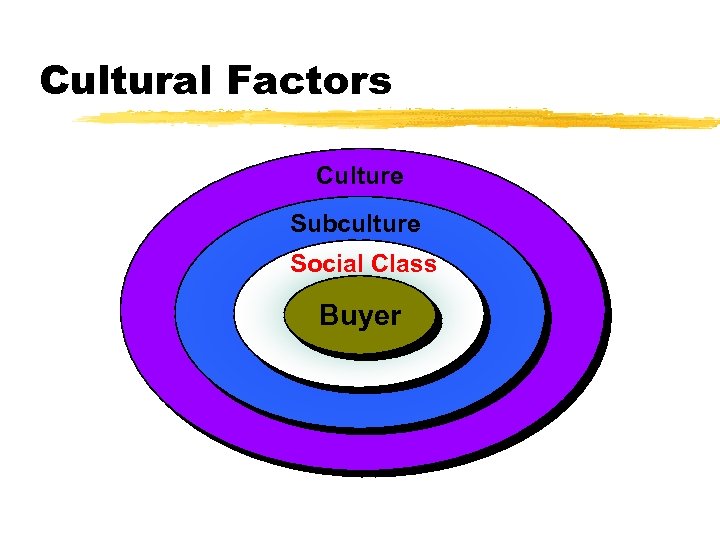
Cultural Factors Culture Subculture Social Class Buyer

Diffusion of Innovation CONCERNED WITH THE ADOPTION OF NEW PRODUCTS

How do products diffuse through the population over time?
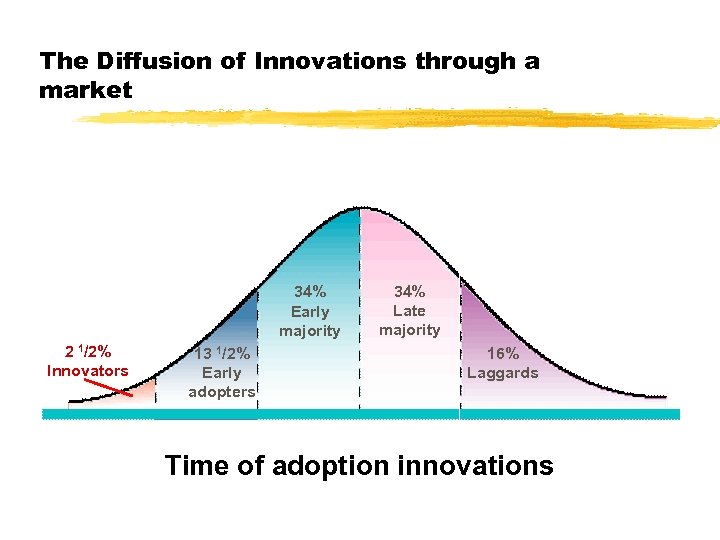
The Diffusion of Innovations through a market 34% Early majority 2 1/2% Innovators 13 1/2% Early adopters 34% Late majority 16% Laggards Time of adoption innovations

Which group pays the most money for a product or service?

Which group expects to pay the least money for a product or service?

Buying is work - let’s look at the effort needed to buy something….

How much effort do you spend to buy gum? z________________

How much effort do you spend to buy a new textbook? z________________

How much effort do you spend to buy your first house? z________________
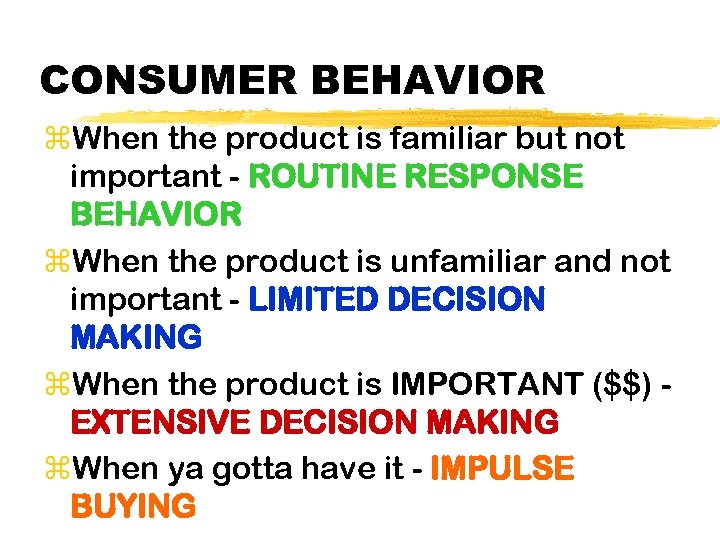
CONSUMER BEHAVIOR z. When the product is familiar but not important - ROUTINE RESPONSE BEHAVIOR z. When the product is unfamiliar and not important - LIMITED DECISION MAKING z. When the product is IMPORTANT ($$) EXTENSIVE DECISION MAKING z. When ya gotta have it - IMPULSE BUYING

z. When your car blows blue smoke, makes a funny very loud noise and dies…. what do you do?
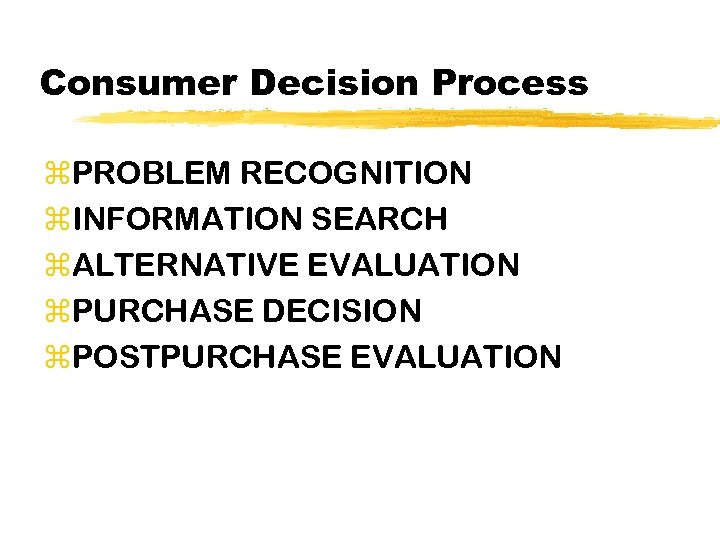
Consumer Decision Process z. PROBLEM RECOGNITION z. INFORMATION SEARCH z. ALTERNATIVE EVALUATION z. PURCHASE DECISION z. POSTPURCHASE EVALUATION
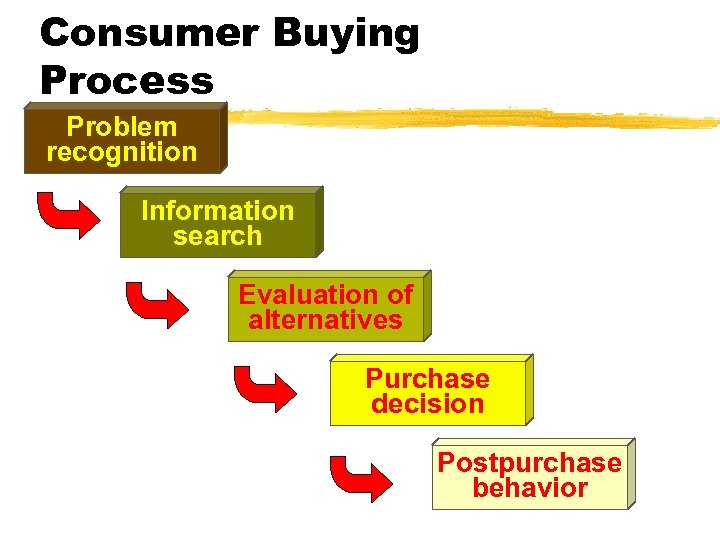
Consumer Buying Process Problem recognition Information search Evaluation of alternatives Purchase decision Postpurchase behavior
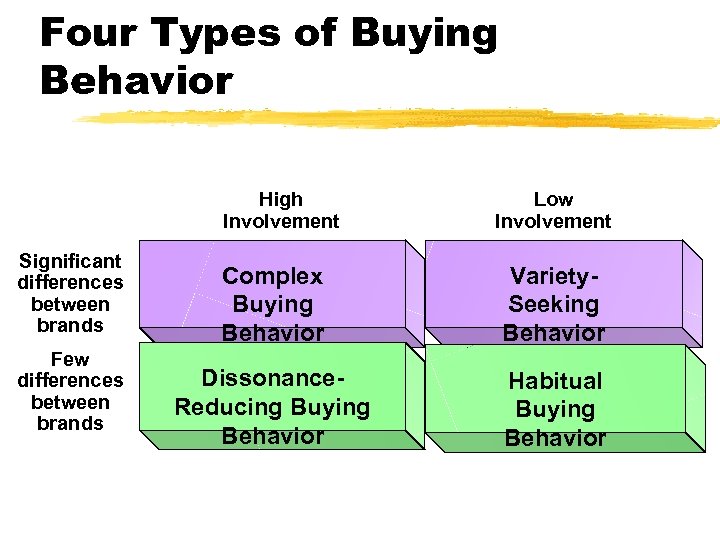
Four Types of Buying Behavior High Involvement Significant differences between brands Few differences between brands Low Involvement Complex Buying Behavior Variety. Seeking Behavior Dissonance. Reducing Buying Behavior Habitual Buying Behavior

How does organization buying behavior differ from consumer buyer behavior?

Organizational Buying Behavior z CHARACTERISTICS y. Derived Demand y. Fewer Buyers y. More Concentrated Geographically y. Greater $ per Transaction

Organizational Buying Behavior z DIFFERENCES FROM CONSUMER BEHAVIOR y. More Rational (Value Analysis) y. Large Volume Purchases y. Many Individuals Involved y. Evaluation Specific y. Service and Leasing Important

Organizational Buying Behavior “THE BUYING CENTER” BASED ON ROLES z USER - ACTUALLY USES IT z BUYER - BUYS IT (PROCESSES THE PAPERWORK) z INFLUENCER - SHAPES THE EXPECTATIONS FOR IT z GATEKEEPER - INFLUENCES THE FLOW OF INFORMATION ABOUT THE DECISION z DECIDER - ACTUALLY MAKES THE DECISION

Which role is the most important?

Organizational Buying Behavior BUY TASKS z. NEW TASK - NEW PRODUCT- NEW VENDOR z. STRAIGHT REBUY - OLD PRODUCT NEW VENDOR z. MODIFIED REBUY - NEW PRODUCT OLD VENDOR/ OR OLD PRODUCT NEW VENDOR

Organizational Buying Behavior NAIS( old SIC) CODE - STANDARD INDUSTRIAL CLASSIFICATION z A WAY OF LUMPING LIKE COMPANIES TOGETHER z EXAMPLE y 27 -> PRINTING, PUBLISHING, AND ALLIED INDUSTRIES y 272 -> PERIODICALS: PUBLISHING, PUBLISHING AND PRINTING y 2721 -> COMIC BOOKS, MAGAZINES, PERIODICALS, STATISTICAL REPORTS, TRADE JOURNALS

UPCOMING TOPIC z. PRODUCT
89fd0459d6ced4f3f832059a5bf987f5.ppt