82a88d95371c675a7b93207b76bb7489.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 MKTG 3110 Fall 2015 Mrs. Tamara L. Cohen Marketing Concepts Class #7 Marketing in the Big Wide World
MKTG 3110 Fall 2015 Mrs. Tamara L. Cohen Marketing Concepts Class #7 Marketing in the Big Wide World
 Valentine’s Day around the world USA – express love for sweethearts, spouse, teachers, parents, others JAPAN – 2 different dates; 2 different levels FRANCE – strong association since Middle Ages ITALY – in Turin betrothed couples announced engagement on V. Day LATIN AMERICA - El Día del Amor y la Amistad SOUTH KOREA – White Day & Black Day SOUTH AFRICA – only for lovers or crushes; anonymous cards
Valentine’s Day around the world USA – express love for sweethearts, spouse, teachers, parents, others JAPAN – 2 different dates; 2 different levels FRANCE – strong association since Middle Ages ITALY – in Turin betrothed couples announced engagement on V. Day LATIN AMERICA - El Día del Amor y la Amistad SOUTH KOREA – White Day & Black Day SOUTH AFRICA – only for lovers or crushes; anonymous cards
 Thailand
Thailand
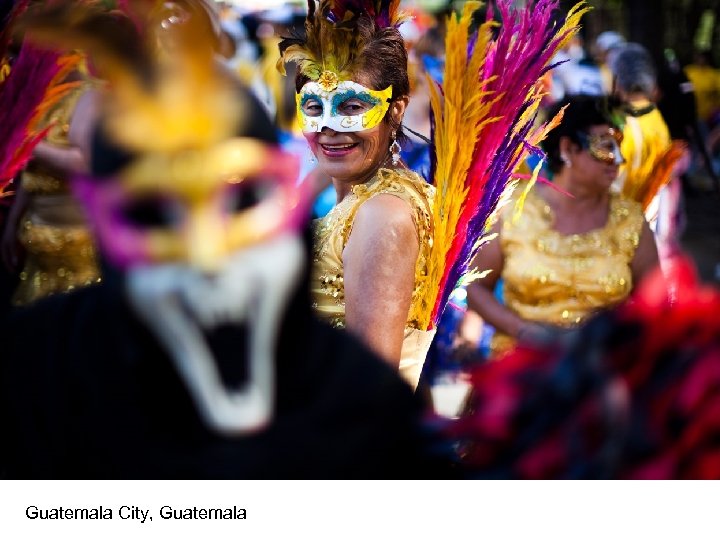 Guatemala City, Guatemala
Guatemala City, Guatemala
 Shanghai, China
Shanghai, China
 Germering, Germany
Germering, Germany
 Manila, Philippines
Manila, Philippines
 Gaza City, Palestine
Gaza City, Palestine
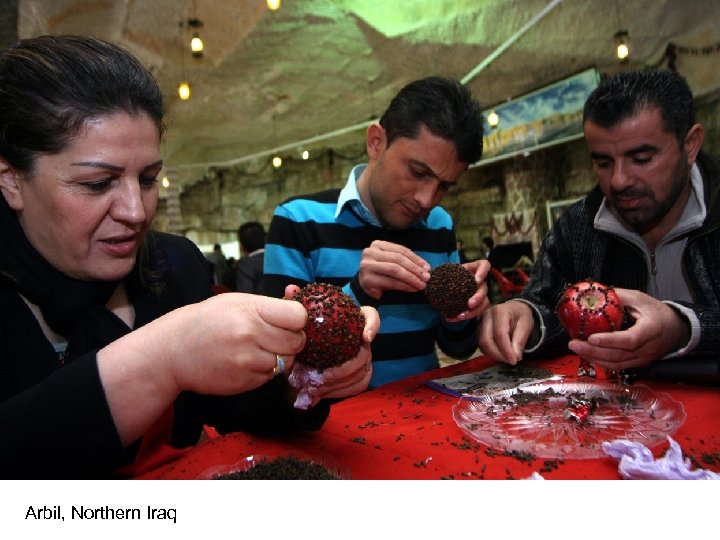 Arbil, Northern Iraq
Arbil, Northern Iraq
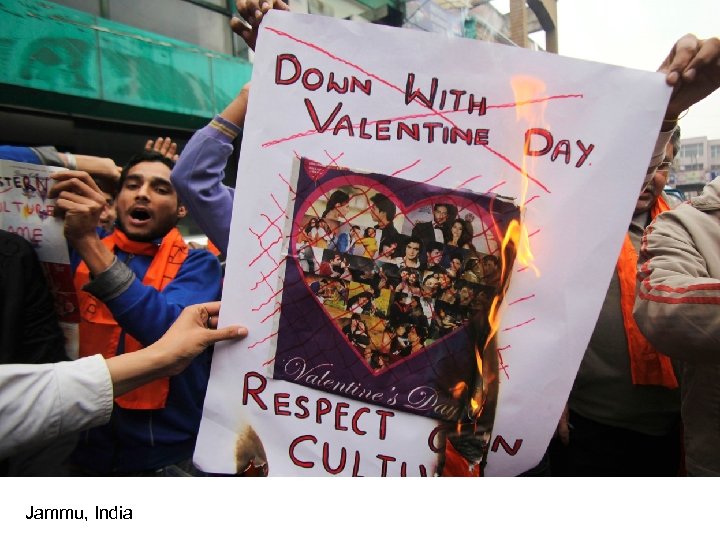 Jammu, India
Jammu, India
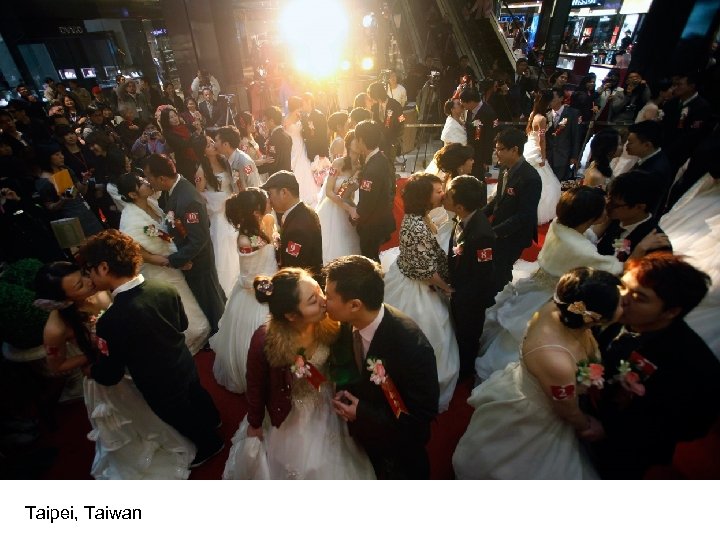 Taipei, Taiwan
Taipei, Taiwan
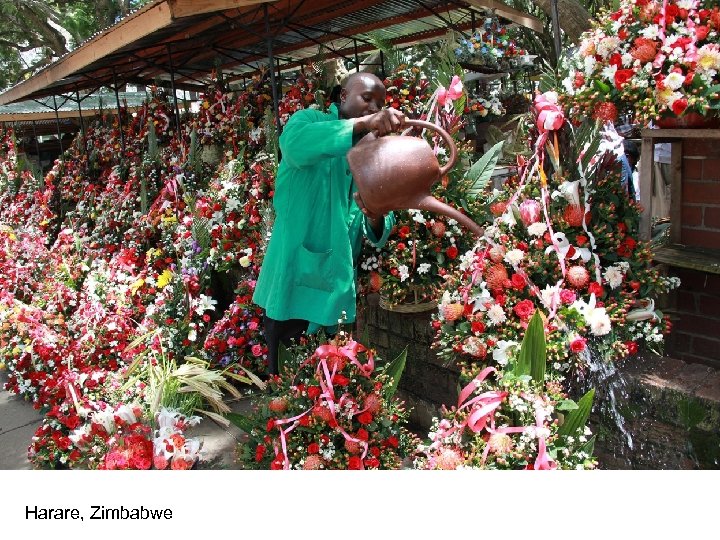 Harare, Zimbabwe
Harare, Zimbabwe
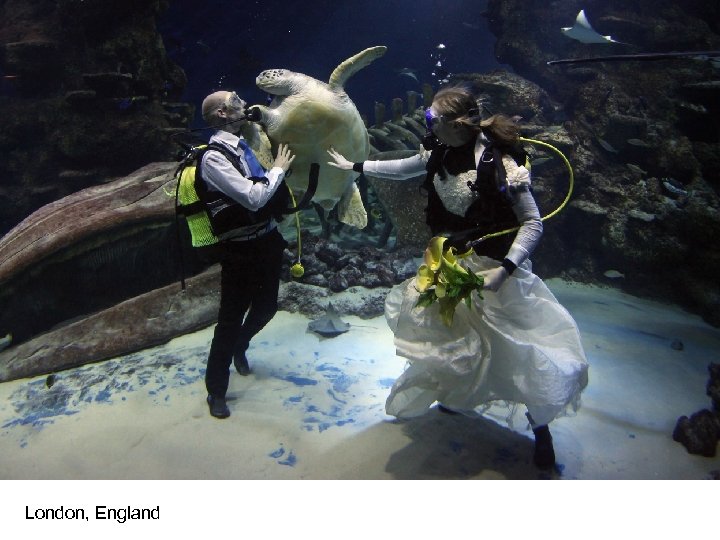 London, England
London, England
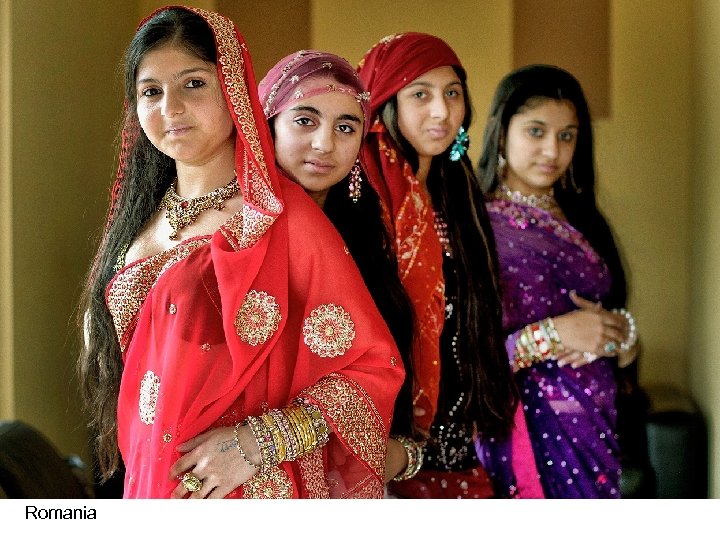 Romania
Romania
 KEY TERMS • Balance of Trade – SURPLUS – DEFICIT • Emerging Markets • Barter / Countertrade • Tariffs • Quotas • Global competition Global companies Global consumers Global brands • Globalization • Dumping • Semiotics • Ethnocentrism • Currency exchange rates
KEY TERMS • Balance of Trade – SURPLUS – DEFICIT • Emerging Markets • Barter / Countertrade • Tariffs • Quotas • Global competition Global companies Global consumers Global brands • Globalization • Dumping • Semiotics • Ethnocentrism • Currency exchange rates
 KEY CONCEPTS • Protectionism • World Trade Organization (WTO) • Cultural diversity • values, customs, symbols • language problems • Strategic alliances • European Union • NAFTA • • Bottom of the Pyramid Microfinance Political risk Market entry strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. Exporting Licensing / Franchising Joint Ventures Foreign Direct Investment
KEY CONCEPTS • Protectionism • World Trade Organization (WTO) • Cultural diversity • values, customs, symbols • language problems • Strategic alliances • European Union • NAFTA • • Bottom of the Pyramid Microfinance Political risk Market entry strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. Exporting Licensing / Franchising Joint Ventures Foreign Direct Investment
 How much world trade is there? • A LOT (±$20 trillion) US & world trade • “International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, & services across international borders… Without international trade, nations would be limited to the goods and services produced within their own borders. ” • What grows global markets? • Balance of Trade DEFICIT • Biggest US trading partners 1. 2. 3. 4. Globalization Greater access to markets Global competition Multinational corporations Canada, China, Mexico, Japan, Germany
How much world trade is there? • A LOT (±$20 trillion) US & world trade • “International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, & services across international borders… Without international trade, nations would be limited to the goods and services produced within their own borders. ” • What grows global markets? • Balance of Trade DEFICIT • Biggest US trading partners 1. 2. 3. 4. Globalization Greater access to markets Global competition Multinational corporations Canada, China, Mexico, Japan, Germany
 People accelerate global trade. Who are the ‘Globalizers’?
People accelerate global trade. Who are the ‘Globalizers’?
 Process of Globalization • Global transactions touch us every day • Imports & exports come from & go to remote areas • Technology & e-business facilitate spread of trade
Process of Globalization • Global transactions touch us every day • Imports & exports come from & go to remote areas • Technology & e-business facilitate spread of trade
 Growth in Emerging Economies “We used to design the same products for global requirements and distribute the same product globally … we started … talking to emerging country customers, designing a product for emerging countries, and initially launching the product in only emerging countries. ”¹ Dell LISTENED Changes in Dell’s global strategy: • sales & distribution • ‘experience centers’
Growth in Emerging Economies “We used to design the same products for global requirements and distribute the same product globally … we started … talking to emerging country customers, designing a product for emerging countries, and initially launching the product in only emerging countries. ”¹ Dell LISTENED Changes in Dell’s global strategy: • sales & distribution • ‘experience centers’
 Emerging Markets BUZZZZ § 28 - 150 emerging markets worldwide § 4 Tigers = Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan § 4 Lions = Egypt, Morocco, Tunisia, South Africa BRIC = Brazil, Russia, India, China CIVETS = Colombia, Indonesia, Vietnam, Egypt, Turkey, South Africa
Emerging Markets BUZZZZ § 28 - 150 emerging markets worldwide § 4 Tigers = Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan § 4 Lions = Egypt, Morocco, Tunisia, South Africa BRIC = Brazil, Russia, India, China CIVETS = Colombia, Indonesia, Vietnam, Egypt, Turkey, South Africa
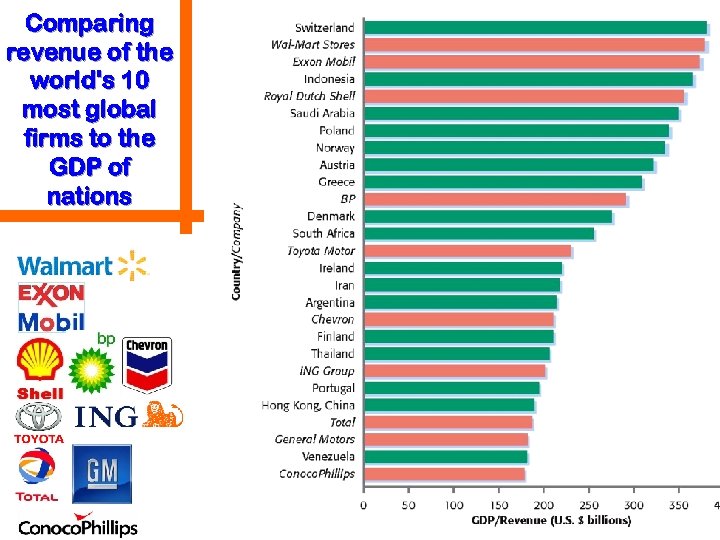 Comparing revenue of the world's 10 most global firms to the GDP of nations
Comparing revenue of the world's 10 most global firms to the GDP of nations
 Countertrade Global marketer must know: Which markets will require countertrade? • • Eastern Europe old USSR states some Latin American countries some African countries Why countertrade? • when cash reserves low Countertrade may include 1. 2. direct exchange of goods part payment in goods, part in cash
Countertrade Global marketer must know: Which markets will require countertrade? • • Eastern Europe old USSR states some Latin American countries some African countries Why countertrade? • when cash reserves low Countertrade may include 1. 2. direct exchange of goods part payment in goods, part in cash
 Pepsi’s famous barter deal with Russia 1959 Pepsi introduced to Russia • 1972 Pepsi concentrate bartered for Stolichnaya vodka. • 1990 Pepsi barter trade with Russia reached $3 billion • 2005 Coke > Pepsi in Russia
Pepsi’s famous barter deal with Russia 1959 Pepsi introduced to Russia • 1972 Pepsi concentrate bartered for Stolichnaya vodka. • 1990 Pepsi barter trade with Russia reached $3 billion • 2005 Coke > Pepsi in Russia
 Barter Ships for oil Brazil proposed that South Korea supply drill ships, in return for stakes in Brazil’s Santos oil fields, which Korea would also manage
Barter Ships for oil Brazil proposed that South Korea supply drill ships, in return for stakes in Brazil’s Santos oil fields, which Korea would also manage
 Counterpurchase Fred Krupp Huttenwerke AG of Germany sold $9 million of large capacity hydraulic cranes to Machinoimport in USSR used countertrade tools & equipment in German plants, or resold them.
Counterpurchase Fred Krupp Huttenwerke AG of Germany sold $9 million of large capacity hydraulic cranes to Machinoimport in USSR used countertrade tools & equipment in German plants, or resold them.
 Marketing in a borderless economic world? Is Protectionism really waning? Tariffs still most common barrier to entry Quotas discouraged by WTO GATT limited trade barriers & promoted world trade through reduction of tariffs; not address non-tariff barriers WTO deals with rules of trade between nations; ensures trade flows smoothly did
Marketing in a borderless economic world? Is Protectionism really waning? Tariffs still most common barrier to entry Quotas discouraged by WTO GATT limited trade barriers & promoted world trade through reduction of tariffs; not address non-tariff barriers WTO deals with rules of trade between nations; ensures trade flows smoothly did
 World Trade Organization members & observers
World Trade Organization members & observers
 Protectionism hinders world trade when countries raise prices & limit supply through tariff & quota policies PROTECTIONISM TARIFFS QUOTAS INCREASE PRICE LIMIT SUPPLY DECREASE WORLD TRADE
Protectionism hinders world trade when countries raise prices & limit supply through tariff & quota policies PROTECTIONISM TARIFFS QUOTAS INCREASE PRICE LIMIT SUPPLY DECREASE WORLD TRADE
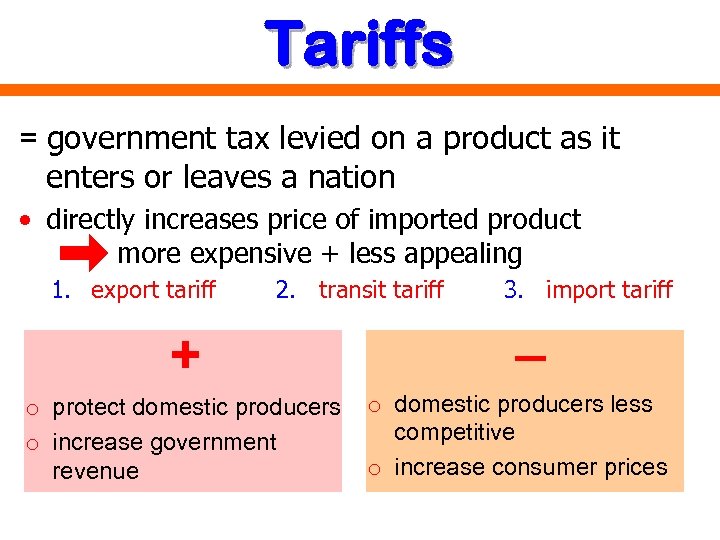 Tariffs = government tax levied on a product as it enters or leaves a nation • directly increases price of imported product more expensive + less appealing 1. export tariff 2. transit tariff + o protect domestic producers o increase government revenue 3. import tariff _ o domestic producers less competitive o increase consumer prices
Tariffs = government tax levied on a product as it enters or leaves a nation • directly increases price of imported product more expensive + less appealing 1. export tariff 2. transit tariff + o protect domestic producers o increase government revenue 3. import tariff _ o domestic producers less competitive o increase consumer prices
 Quotas = restriction on quantity of a good that can enter or leave a country during a certain time • most common non-tariff barrier IMPORT QUOTA o protects domestic producers o foreign companies compete for market access competition consumer prices consumer choices EXPORT QUOTA supply of product in home market, e. g. natural resources essential to local business or longterm survival supply on world market global price
Quotas = restriction on quantity of a good that can enter or leave a country during a certain time • most common non-tariff barrier IMPORT QUOTA o protects domestic producers o foreign companies compete for market access competition consumer prices consumer choices EXPORT QUOTA supply of product in home market, e. g. natural resources essential to local business or longterm survival supply on world market global price
 Strategic Alliances • Countries form strategic alliances to cooperate to reduce or eliminate barriers to facilitate the international flow of products, people, and capital. PROS specialization efficiency trade consumption standards of living political benefits CONS trade diverted to cheaper countries protectionism national sovereignty divergent rules /standards
Strategic Alliances • Countries form strategic alliances to cooperate to reduce or eliminate barriers to facilitate the international flow of products, people, and capital. PROS specialization efficiency trade consumption standards of living political benefits CONS trade diverted to cheaper countries protectionism national sovereignty divergent rules /standards
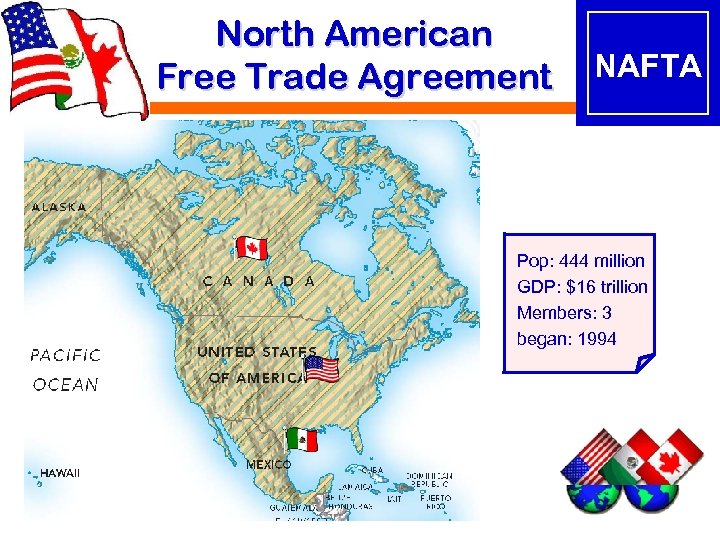 North American Free Trade Agreement NAFTA Pop: 444 million GDP: $16 trillion Members: 3 began: 1994
North American Free Trade Agreement NAFTA Pop: 444 million GDP: $16 trillion Members: 3 began: 1994
 European Union Pop: 500 million GDP: $15 trillion Members: 28 began: 1951
European Union Pop: 500 million GDP: $15 trillion Members: 28 began: 1951
 Association of South. East Asian Nations GOALS: • Promote economic, social, and cultural development • Safeguard economic and political stability • Serve as a forum to resolve disputes Pop: 633 million GDP: $1. 1 trillion Members: 10 Began: 1967
Association of South. East Asian Nations GOALS: • Promote economic, social, and cultural development • Safeguard economic and political stability • Serve as a forum to resolve disputes Pop: 633 million GDP: $1. 1 trillion Members: 10 Began: 1967
 Global Competition § when companies originate, produce & market their products & services worldwide § widens competitive landscape for marketers § can give rise to global strategic alliances
Global Competition § when companies originate, produce & market their products & services worldwide § widens competitive landscape for marketers § can give rise to global strategic alliances
 Global Companies § international company § multinational company (MNC) § transnational company
Global Companies § international company § multinational company (MNC) § transnational company
 Global companies & marketing strategy
Global companies & marketing strategy
 Global Brands § brand is marketed under the same name in multiple countries, using similar and centrally-coordinated marketing programs § strong corporate identity § same product formulation, same benefits, consistent advertising across borders § e. g. Mc. Donald’s’ “food, fun, and families” in 118 countries; but some aspects customized
Global Brands § brand is marketed under the same name in multiple countries, using similar and centrally-coordinated marketing programs § strong corporate identity § same product formulation, same benefits, consistent advertising across borders § e. g. Mc. Donald’s’ “food, fun, and families” in 118 countries; but some aspects customized
 Global Consumers § consumer groups living in many countries or regions of the world, who have similar needs or seek similar features & benefits from products or services § global middle class; youth market; elites § companies that have developed these markets:
Global Consumers § consumer groups living in many countries or regions of the world, who have similar needs or seek similar features & benefits from products or services § global middle class; youth market; elites § companies that have developed these markets:
 Networked Global Marketspace § Internet enables exchange of goods, services & information anywhere, any time, & at lower price § global electronic commerce grown especially by B 2 B § most active B 2 B commerce countries: US, Canada, UK, Germany, Sweden, Japan, India, China, Taiwan
Networked Global Marketspace § Internet enables exchange of goods, services & information anywhere, any time, & at lower price § global electronic commerce grown especially by B 2 B § most active B 2 B commerce countries: US, Canada, UK, Germany, Sweden, Japan, India, China, Taiwan
 Networked Global Marketspace:
Networked Global Marketspace:
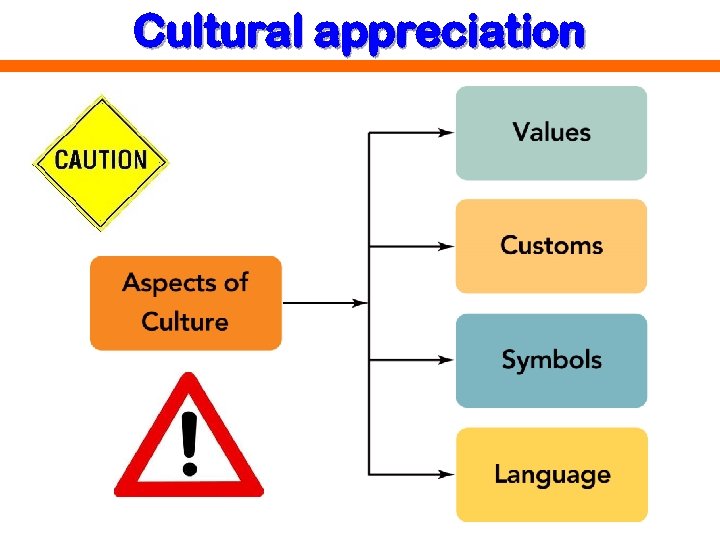 Cultural appreciation
Cultural appreciation
 Cultural literacy Cross-cultural analysis Values Customs Cultural symbols Language Ethnocentrism
Cultural literacy Cross-cultural analysis Values Customs Cultural symbols Language Ethnocentrism
 In-class exercise
In-class exercise

 Language Blunders Japanese knife manufacturer labeled its exports to the United States with “Caution: Blade extremely sharp! Keep out of children. ” English sign in a Moscow hotel read, “You are welcome to visit the cemetery where famous Russians are buried daily, except Thursday. ” Sign for non-Japanese-speaking guests in a Tokyo hotel read, “You are respectfully requested to take advantage of the chambermaids. ” Sign in English at Copenhagen ticket office read, “We take your bags and send them in all directions. ” Braniff Airlines’ English-language slogan “Fly in Leather” was
Language Blunders Japanese knife manufacturer labeled its exports to the United States with “Caution: Blade extremely sharp! Keep out of children. ” English sign in a Moscow hotel read, “You are welcome to visit the cemetery where famous Russians are buried daily, except Thursday. ” Sign for non-Japanese-speaking guests in a Tokyo hotel read, “You are respectfully requested to take advantage of the chambermaids. ” Sign in English at Copenhagen ticket office read, “We take your bags and send them in all directions. ” Braniff Airlines’ English-language slogan “Fly in Leather” was
 Mixed Signals • Middle East, West Africa, South America, Iran, Sardinia, Bangladesh: rude, insulting; obscene gesture • Italy, Germany, Greece, Hungary: #1, or ‘okay’ • Russia, Finland, Australia: ‘good’, ‘well done’ • UK: farewell or greeting between young men • Japan: male gender • Egypt, Iraq, Israel: ‘perfect’ • SCUBA diving: “go up (to the surface)” • Hitchhiker: “I need a ride”
Mixed Signals • Middle East, West Africa, South America, Iran, Sardinia, Bangladesh: rude, insulting; obscene gesture • Italy, Germany, Greece, Hungary: #1, or ‘okay’ • Russia, Finland, Australia: ‘good’, ‘well done’ • UK: farewell or greeting between young men • Japan: male gender • Egypt, Iraq, Israel: ‘perfect’ • SCUBA diving: “go up (to the surface)” • Hitchhiker: “I need a ride”
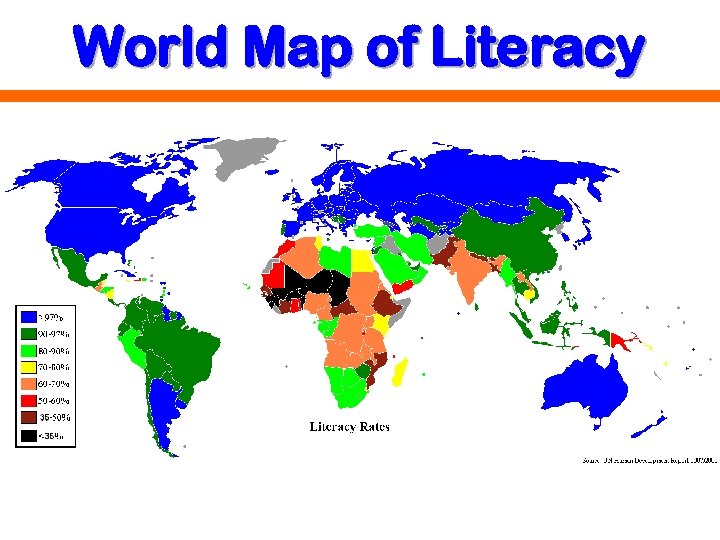 World Map of Literacy
World Map of Literacy
 Economic Considerations • Developed or developing country • Economic infrastructure - communications, transportation, financial, distribution systems • Consumer income & purchasing power • Currency exchange rates - price of one currency in terms of another • Bottom of the Pyramid 2. 5 billion people; < $2. 50/day • Microfinance - offering small, collateral-free loans to people outside conventional capital markets
Economic Considerations • Developed or developing country • Economic infrastructure - communications, transportation, financial, distribution systems • Consumer income & purchasing power • Currency exchange rates - price of one currency in terms of another • Bottom of the Pyramid 2. 5 billion people; < $2. 50/day • Microfinance - offering small, collateral-free loans to people outside conventional capital markets
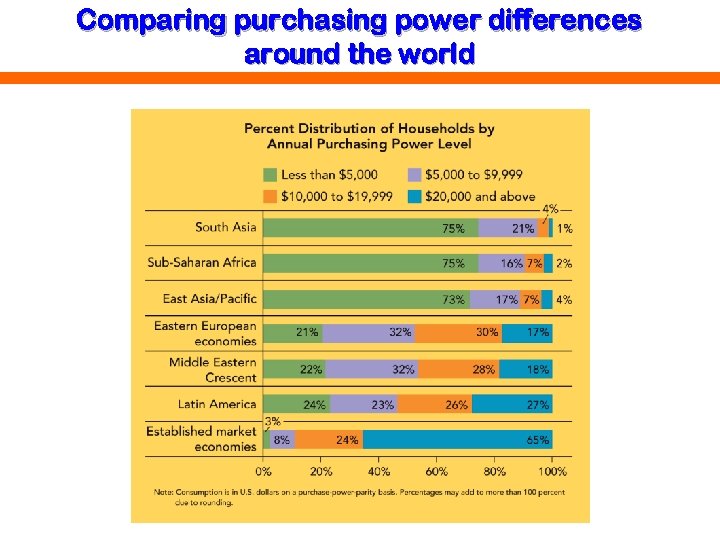 Comparing purchasing power differences around the world
Comparing purchasing power differences around the world
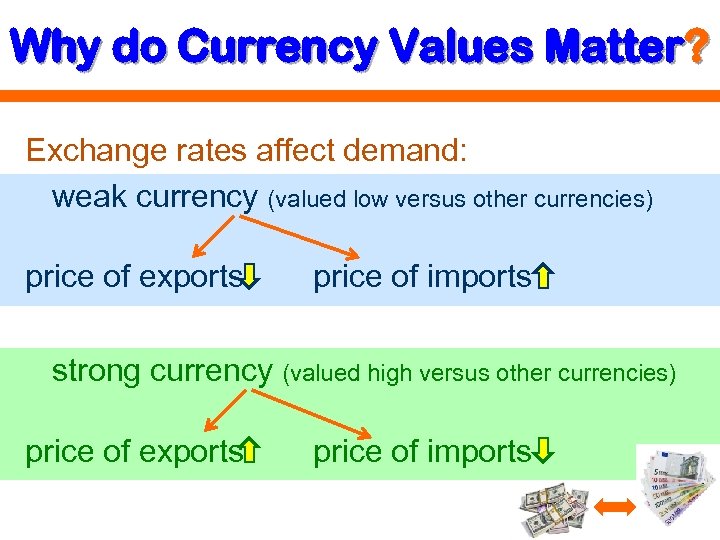 Why do Currency Values Matter? Exchange rates affect demand: weak currency (valued low versus other currencies) price of exports price of imports strong currency (valued high versus other currencies) price of exports price of imports
Why do Currency Values Matter? Exchange rates affect demand: weak currency (valued low versus other currencies) price of exports price of imports strong currency (valued high versus other currencies) price of exports price of imports
 Political Risk Conflict & violence Terrorism & kidnapping Property seizure Policy changes Local content requirements Trade regulations
Political Risk Conflict & violence Terrorism & kidnapping Property seizure Policy changes Local content requirements Trade regulations
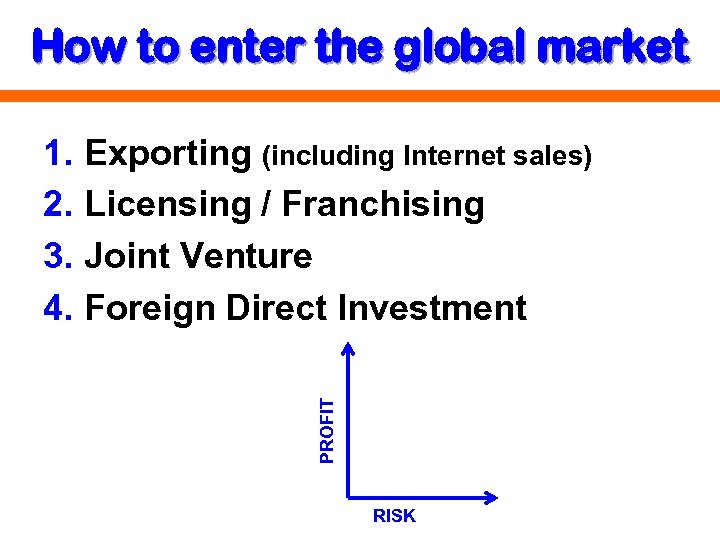 How to enter the global market PROFIT 1. Exporting (including Internet sales) 2. Licensing / Franchising 3. Joint Venture 4. Foreign Direct Investment RISK
How to enter the global market PROFIT 1. Exporting (including Internet sales) 2. Licensing / Franchising 3. Joint Venture 4. Foreign Direct Investment RISK
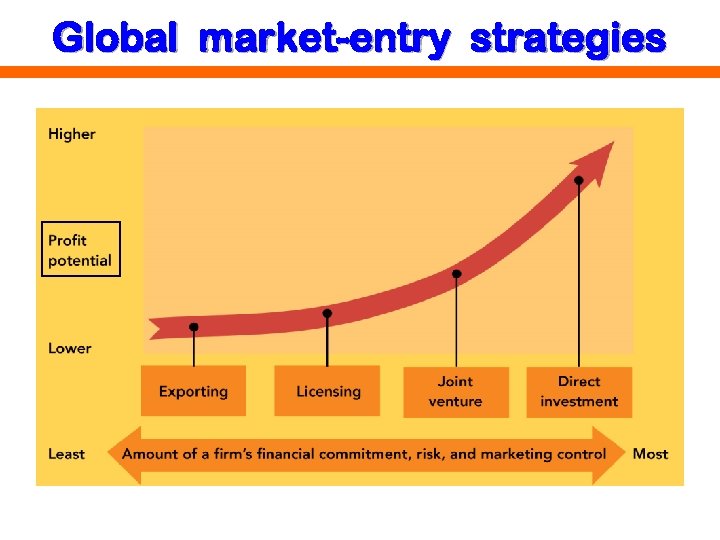 Global market-entry strategies
Global market-entry strategies
 1. Exporting accounts for ± 10% of global economic activity. • Internet marketing initially focused on domestic sales. International internet marketing developed from companies receiving orders from customers overseas. • Direct exporting = company sells to a customer in another country; most common initial approach • Indirect exporting = company sells to a buyer (importer or distribution) in home country, who in turn exports the product • Direct sales especially for high tech & big ticket industrial products
1. Exporting accounts for ± 10% of global economic activity. • Internet marketing initially focused on domestic sales. International internet marketing developed from companies receiving orders from customers overseas. • Direct exporting = company sells to a customer in another country; most common initial approach • Indirect exporting = company sells to a buyer (importer or distribution) in home country, who in turn exports the product • Direct sales especially for high tech & big ticket industrial products
 2. Franchising & Licensing Franchising Licensing • Company has greater control over sale of product in foreign market • Primary use in service sector • Ongoing assistance required from franchiser • Company has less control over sale of product in foreign market • Primary use in manufacturing • Usually involves one-time transfer of property
2. Franchising & Licensing Franchising Licensing • Company has greater control over sale of product in foreign market • Primary use in service sector • Ongoing assistance required from franchiser • Company has less control over sale of product in foreign market • Primary use in manufacturing • Usually involves one-time transfer of property
 Franchises in the Global Marketplace
Franchises in the Global Marketplace
 3. Joint Venture (JV) Company created & jointly owned by 2 or more entities to achieve a common objective Advantages Ø reduce risk by sharing investment penetrate markets usually reserved for locals Ø access to local party’s distribution channels Ø Disadvantages partner conflict if objectives change, cooperation & trust fade Ø control may be unpredictable if local government involved in JV Ø
3. Joint Venture (JV) Company created & jointly owned by 2 or more entities to achieve a common objective Advantages Ø reduce risk by sharing investment penetrate markets usually reserved for locals Ø access to local party’s distribution channels Ø Disadvantages partner conflict if objectives change, cooperation & trust fade Ø control may be unpredictable if local government involved in JV Ø
 4. Foreign Direct Investment = purchase of physical assets or a significant ownership share of company overseas, 10% in order to control management • FDI usually involves management participation, joint venture, transfer of technology or expertise, or any combination • FDI focuses on productive assets: factories, land, organizations • FDI INFLOW (=INWARD FDI) when investments made in home country by overseas investors • FDI OUTFLOWS (=OUTWARD FDI) when home country investors make investments overseas • FDIs can be made by individuals, private or public companies, governments, or any combination
4. Foreign Direct Investment = purchase of physical assets or a significant ownership share of company overseas, 10% in order to control management • FDI usually involves management participation, joint venture, transfer of technology or expertise, or any combination • FDI focuses on productive assets: factories, land, organizations • FDI INFLOW (=INWARD FDI) when investments made in home country by overseas investors • FDI OUTFLOWS (=OUTWARD FDI) when home country investors make investments overseas • FDIs can be made by individuals, private or public companies, governments, or any combination
 China & FDI • FDI in China occurs through IJVs, cooperative enterprises, & solely foreign-owned enterprises • China acknowledges that FDI has been crucial in its ‘economic miracle’ • More of China’s FDI comes from East Asia, especially Hong Kong (½), then Taiwan, USA, Japan, Korea • Most FDI is in manufacturing • China has tightly controlled flow of FDI into services sector • 2 main FDI objectives: 1. promoting exports 2. transferring technology
China & FDI • FDI in China occurs through IJVs, cooperative enterprises, & solely foreign-owned enterprises • China acknowledges that FDI has been crucial in its ‘economic miracle’ • More of China’s FDI comes from East Asia, especially Hong Kong (½), then Taiwan, USA, Japan, Korea • Most FDI is in manufacturing • China has tightly controlled flow of FDI into services sector • 2 main FDI objectives: 1. promoting exports 2. transferring technology
 FDI into Europe • Most global FDI goes into Western Europe • Much FDI activity is consolidation due to opening markets & removing barriers • New Central & Eastern European markets attracting FDI too • FDI attracted to higher value-added activities that benefit from well-educated work force • UK & France remain FDI leaders in Europe
FDI into Europe • Most global FDI goes into Western Europe • Much FDI activity is consolidation due to opening markets & removing barriers • New Central & Eastern European markets attracting FDI too • FDI attracted to higher value-added activities that benefit from well-educated work force • UK & France remain FDI leaders in Europe
 CARS in INDIA: Examples of different Entry Modes • Maruti Suzuki India is a wholly owned subsidiary of Maruti Japan's Suzuki Motor, and is the biggest automobile Swift manufacturer in India. • General Motors India Private Limited is a joint venture (50: 50 partnership) between GM & SAIC. BMW • BMW exports some cars to India as CBUs, despite 105% import tax. • Tata Motors & Fiat established a Chevy strategic alliance in 2005, which Beat FIAT grew into a JV shortly afterwards. Tata makes power trains for both Tata & Fiat models (backward integration). Tata distributes and markets Fiat cars in India (forward integration).
CARS in INDIA: Examples of different Entry Modes • Maruti Suzuki India is a wholly owned subsidiary of Maruti Japan's Suzuki Motor, and is the biggest automobile Swift manufacturer in India. • General Motors India Private Limited is a joint venture (50: 50 partnership) between GM & SAIC. BMW • BMW exports some cars to India as CBUs, despite 105% import tax. • Tata Motors & Fiat established a Chevy strategic alliance in 2005, which Beat FIAT grew into a JV shortly afterwards. Tata makes power trains for both Tata & Fiat models (backward integration). Tata distributes and markets Fiat cars in India (forward integration).
 Next class: Marketing Research Market Segmentation Preparation: Read Ch. 8 & Ch. 9 (assigned pages) Homework #6: Market Segmentation
Next class: Marketing Research Market Segmentation Preparation: Read Ch. 8 & Ch. 9 (assigned pages) Homework #6: Market Segmentation


