180849725736edeb30cbc5f7b413a927.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 MKTG 3110 -004 Fall 2014 Mrs. Tamara L. Cohen Marketing Concepts Class #1 Introduction to Marketing Concepts
MKTG 3110 -004 Fall 2014 Mrs. Tamara L. Cohen Marketing Concepts Class #1 Introduction to Marketing Concepts
 Course Introduction § introduce fundamentals of marketing § marketing is basic to our society o o “conventional” consumer products B 2 B markets not-for-profit markets marketing of services
Course Introduction § introduce fundamentals of marketing § marketing is basic to our society o o “conventional” consumer products B 2 B markets not-for-profit markets marketing of services
 Course Objectives q Understand that marketing focuses on identifying & satisfying consumer needs, therefore is critical to success of organizations. q Appreciate value to Marketing function of relationships at various levels & among various interest groups. q Develop awareness of impact of environmental factors on consumer behavior & marketing functions; include global context. q Study each element of Marketing Mix q Comprehend integration of marketing concepts into marketing strategy. q Appreciate social responsibility & ethics in marketing.
Course Objectives q Understand that marketing focuses on identifying & satisfying consumer needs, therefore is critical to success of organizations. q Appreciate value to Marketing function of relationships at various levels & among various interest groups. q Develop awareness of impact of environmental factors on consumer behavior & marketing functions; include global context. q Study each element of Marketing Mix q Comprehend integration of marketing concepts into marketing strategy. q Appreciate social responsibility & ethics in marketing.
 Textbook Marketing − by Roger Kerin, Steven Hartley & William Rudelius − 11 th edition; 2013 − published by Mc. Graw-Hill Irwin − ISBN-13: 978 -0 -07 -802889 -2 Ø Buy new or used Ø Rent Ø Digital
Textbook Marketing − by Roger Kerin, Steven Hartley & William Rudelius − 11 th edition; 2013 − published by Mc. Graw-Hill Irwin − ISBN-13: 978 -0 -07 -802889 -2 Ø Buy new or used Ø Rent Ø Digital
 About ME Education Professional Personal q MBA, Wharton School, q International Travel Consultant - CLT q Founder & Vice President, Garden Essentials, Inc. - CLT q Marketing Manager, Beacon Sweets, Inc. – Newark, NJ q Marketing Manager, Beacon Sweets & Chocolates (Pty) Ltd – South Africa q Born & raised in South Africa q Married; 5 kids q Avid traveler q International experience q Languages University of Pennsylvania q BS, University of Cape Town, South Africa What I Bring to the Class … Tamara L. Cohen q I have traveled on 5 continents, and worked in Domestic and Multinational Marketing capacities on 3 continents. q Experience marketing consumer products q Experience marketing services q Experience in business-to-business marketing q Entrepreneurial experience
About ME Education Professional Personal q MBA, Wharton School, q International Travel Consultant - CLT q Founder & Vice President, Garden Essentials, Inc. - CLT q Marketing Manager, Beacon Sweets, Inc. – Newark, NJ q Marketing Manager, Beacon Sweets & Chocolates (Pty) Ltd – South Africa q Born & raised in South Africa q Married; 5 kids q Avid traveler q International experience q Languages University of Pennsylvania q BS, University of Cape Town, South Africa What I Bring to the Class … Tamara L. Cohen q I have traveled on 5 continents, and worked in Domestic and Multinational Marketing capacities on 3 continents. q Experience marketing consumer products q Experience marketing services q Experience in business-to-business marketing q Entrepreneurial experience
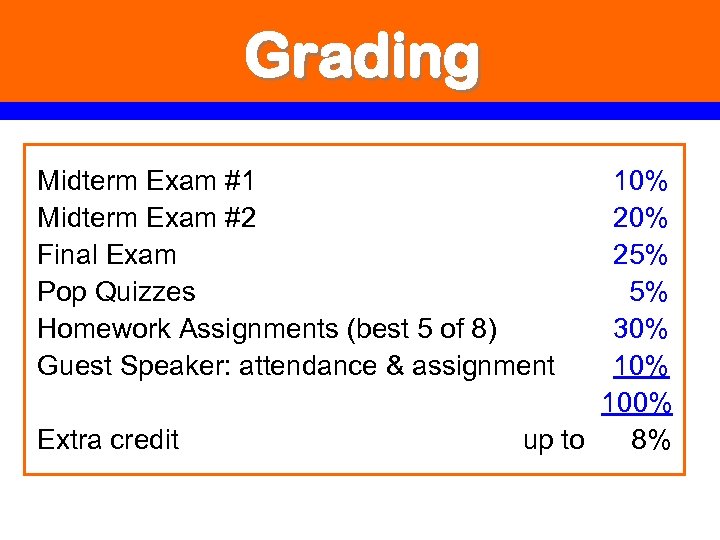 Grading Midterm Exam #1 Midterm Exam #2 Final Exam Pop Quizzes Homework Assignments (best 5 of 8) Guest Speaker: attendance & assignment Extra credit 10% 25% 5% 30% 100% up to 8%
Grading Midterm Exam #1 Midterm Exam #2 Final Exam Pop Quizzes Homework Assignments (best 5 of 8) Guest Speaker: attendance & assignment Extra credit 10% 25% 5% 30% 100% up to 8%
 Tests & Exams ü Multiple choice questions ü Fill-in-the-blank ü Short answers Exams are based on: q material presented / discussed in class q terms and information from the text book q homework material q guest speaker material
Tests & Exams ü Multiple choice questions ü Fill-in-the-blank ü Short answers Exams are based on: q material presented / discussed in class q terms and information from the text book q homework material q guest speaker material
 Home work DUE a 3: 30 t pm • • 8 homework assignments 5 best grades count + 1% if all 8 completed Due dates & details in SYLLABUS & HOMEWORK page on web site • MAXIMUM 150 words • Executive MEMO format; 12 -point type; double space; WORD format • Writing Resource Center bonus
Home work DUE a 3: 30 t pm • • 8 homework assignments 5 best grades count + 1% if all 8 completed Due dates & details in SYLLABUS & HOMEWORK page on web site • MAXIMUM 150 words • Executive MEMO format; 12 -point type; double space; WORD format • Writing Resource Center bonus
 Executive Memo Format MEMO TO: me FROM: you DATE: due date SUBJECT: one line only WORD COUNT: ≤ 150 This is the body of your memo (i. e. homework assignment). Remember: 12 -point type, double space, WORD format End: References (if used)
Executive Memo Format MEMO TO: me FROM: you DATE: due date SUBJECT: one line only WORD COUNT: ≤ 150 This is the body of your memo (i. e. homework assignment). Remember: 12 -point type, double space, WORD format End: References (if used)
 Guest Speaker November 24 5% + 5% Scott Gakenheimer • MANDATORY ASSIGNMENT = 5% • MANDATORY ATTENDANCE = 5% o Arrive on time o Leave on time o No wandering in and out o Sign in o NO SCREENS
Guest Speaker November 24 5% + 5% Scott Gakenheimer • MANDATORY ASSIGNMENT = 5% • MANDATORY ATTENDANCE = 5% o Arrive on time o Leave on time o No wandering in and out o Sign in o NO SCREENS
 Class Participation up to + 4% • CLASSROOM DISCUSSIONS • ATTENDANCE in regular classes is not mandatory. Exam material comes principally from lectures, and also from assigned readings. • CELL PHONE use in class is distracting and discourteous. You will be asked to leave the room, and your participation may be penalized. • BONUS POINTS for worthwhile contributions in class • OBSERVE Classroom Etiquette (next slide)
Class Participation up to + 4% • CLASSROOM DISCUSSIONS • ATTENDANCE in regular classes is not mandatory. Exam material comes principally from lectures, and also from assigned readings. • CELL PHONE use in class is distracting and discourteous. You will be asked to leave the room, and your participation may be penalized. • BONUS POINTS for worthwhile contributions in class • OBSERVE Classroom Etiquette (next slide)
 Classroom Etiquette ü No cell phone calls or texting ü Bring laptop computers, i. Pads, etc, only for taking notes ü No refreshments ü ü Arrive on time. Leave on time. No wandering in and out of class Display name tents in every class If you plan to use a laptop in class, please sit in the BACK ROWS.
Classroom Etiquette ü No cell phone calls or texting ü Bring laptop computers, i. Pads, etc, only for taking notes ü No refreshments ü ü Arrive on time. Leave on time. No wandering in and out of class Display name tents in every class If you plan to use a laptop in class, please sit in the BACK ROWS.
 Extra Credit up to + 8% 1. Writing Resource Center (WRC) +3% • Take any homework assignment to WRC & email official report to instructor • Extra credit +25% of your grade on that assignment • Maximum 2 assignment extra credits 2. Complete all 8 homework assignments +1% 3. Bonus points for in-class contributions +4%
Extra Credit up to + 8% 1. Writing Resource Center (WRC) +3% • Take any homework assignment to WRC & email official report to instructor • Extra credit +25% of your grade on that assignment • Maximum 2 assignment extra credits 2. Complete all 8 homework assignments +1% 3. Bonus points for in-class contributions +4%
 Where to find this info.
Where to find this info.
 break
break
 What is Marketing?
What is Marketing?
 KEY TERMS • NEEDS versus WANTS • DEMANDS • Market • Target market • Customer value • Relationship marketing • Relationship management
KEY TERMS • NEEDS versus WANTS • DEMANDS • Market • Target market • Customer value • Relationship marketing • Relationship management
 KEY CONCEPTS • The Four Ps = Marketing Mix 1. 2. 3. 4. Product Price Promotion Place • Marketing program • Marketing concept
KEY CONCEPTS • The Four Ps = Marketing Mix 1. 2. 3. 4. Product Price Promotion Place • Marketing program • Marketing concept
 What is MARKETING? “… the activity for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that benefit the organization, its stakeholders and society at large” • discover needs & wants of prospective customers, and • satisfy those needs & wants
What is MARKETING? “… the activity for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that benefit the organization, its stakeholders and society at large” • discover needs & wants of prospective customers, and • satisfy those needs & wants
 What is MARKETING? “Marketing is used to identify the customer, satisfy the customer, and keep the customer. ”
What is MARKETING? “Marketing is used to identify the customer, satisfy the customer, and keep the customer. ”
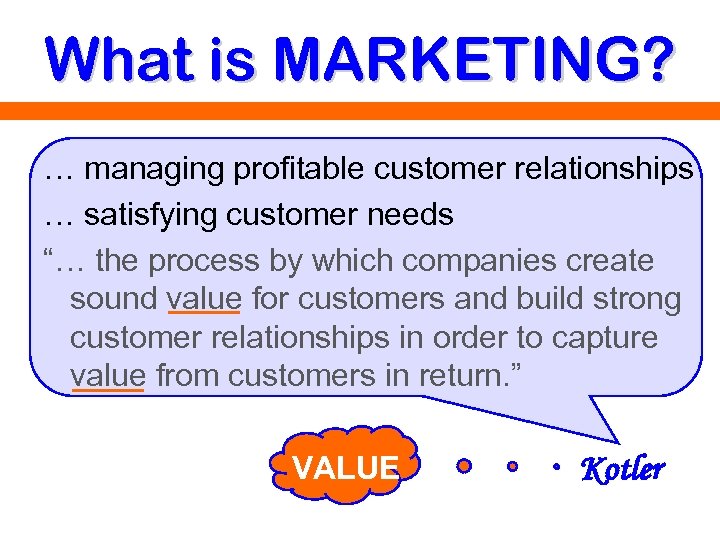 What is MARKETING? … managing profitable customer relationships … satisfying customer needs “… the process by which companies create sound value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. ” VALUE Kotler
What is MARKETING? … managing profitable customer relationships … satisfying customer needs “… the process by which companies create sound value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. ” VALUE Kotler
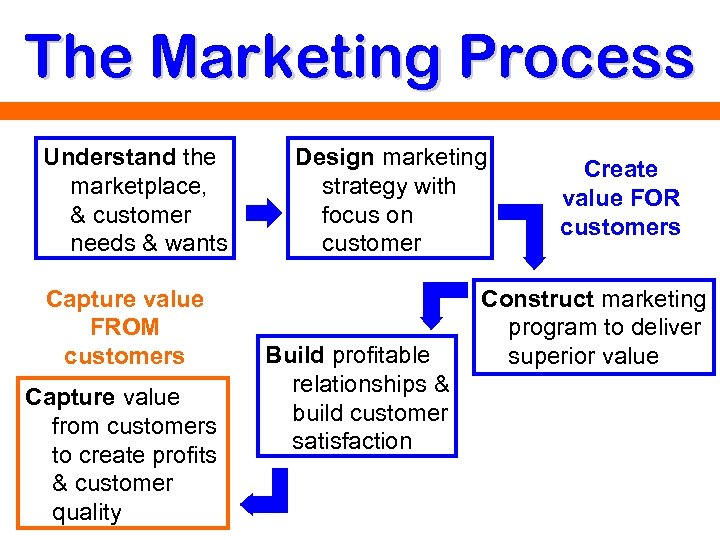 The Marketing Process Understand the marketplace, & customer needs & wants Capture value FROM customers Capture value from customers to create profits & customer quality Design marketing strategy with focus on customer Build profitable relationships & build customer satisfaction Create value FOR customers Construct marketing program to deliver superior value
The Marketing Process Understand the marketplace, & customer needs & wants Capture value FROM customers Capture value from customers to create profits & customer quality Design marketing strategy with focus on customer Build profitable relationships & build customer satisfaction Create value FOR customers Construct marketing program to deliver superior value
 What is MARKETING? Managing expectations
What is MARKETING? Managing expectations
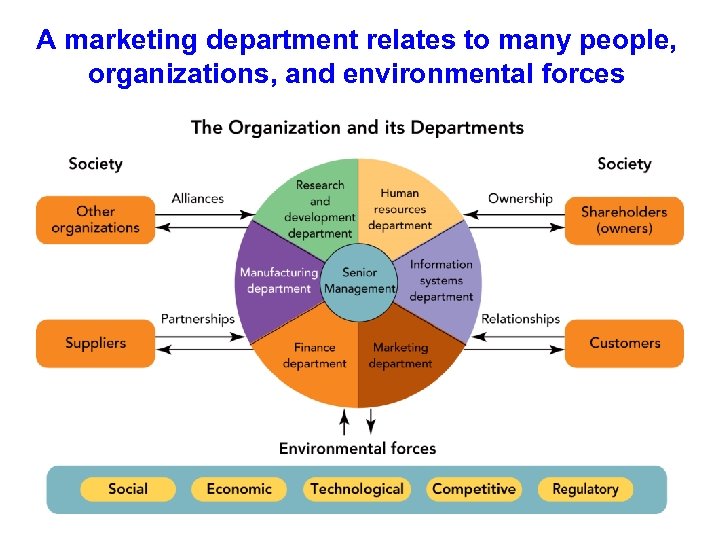 A marketing department relates to many people, organizations, and environmental forces
A marketing department relates to many people, organizations, and environmental forces
 What is needed for MARKETING to happen Parties with unsatisfied needs Desire and ability to be satisfied Way for parties to communicate Something to exchange
What is needed for MARKETING to happen Parties with unsatisfied needs Desire and ability to be satisfied Way for parties to communicate Something to exchange
 MARKETING breakdown Ø Parties with unmet needs Consumers with taste for peanut butter-&-chocolate combination Ø Desire & ability to be satisfied Consumers with money to buy these chocolates; stores stocking these chocolates for sale Ø Ways to communicate Advertising expensive & dominated by major players; browsing exposure too small & slow for high-volume consumer goods Ø Something to exchange Consumers had money to spend; store-owners had chocolates on shelves
MARKETING breakdown Ø Parties with unmet needs Consumers with taste for peanut butter-&-chocolate combination Ø Desire & ability to be satisfied Consumers with money to buy these chocolates; stores stocking these chocolates for sale Ø Ways to communicate Advertising expensive & dominated by major players; browsing exposure too small & slow for high-volume consumer goods Ø Something to exchange Consumers had money to spend; store-owners had chocolates on shelves
 Challenge of NEW products How does marketing discover needs that don’t exist (yet)? Consumers may not know what they need or want. Most new products fail: - 94% fail - 33, 000 consumable products introduced in US annually Strategies to avoid new product failure: 1. Focus on consumer benefit 2. Learn from past
Challenge of NEW products How does marketing discover needs that don’t exist (yet)? Consumers may not know what they need or want. Most new products fail: - 94% fail - 33, 000 consumable products introduced in US annually Strategies to avoid new product failure: 1. Focus on consumer benefit 2. Learn from past
 Dr. Care Vanilla-Mint Aerosol Toothpaste What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
Dr. Care Vanilla-Mint Aerosol Toothpaste What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
 Hot Pockets Panini Microwaveable Snacks What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
Hot Pockets Panini Microwaveable Snacks What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
 AT&T Cruise. Cast What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
AT&T Cruise. Cast What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
 Pepsi Max What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
Pepsi Max What “benefits” and what “showstoppers? ”
 How MARKETING discovers consumer NEEDS versus WANTS Need Does Marketing persuade people to buy the “wrong” things? Market Target Market Want
How MARKETING discovers consumer NEEDS versus WANTS Need Does Marketing persuade people to buy the “wrong” things? Market Target Market Want
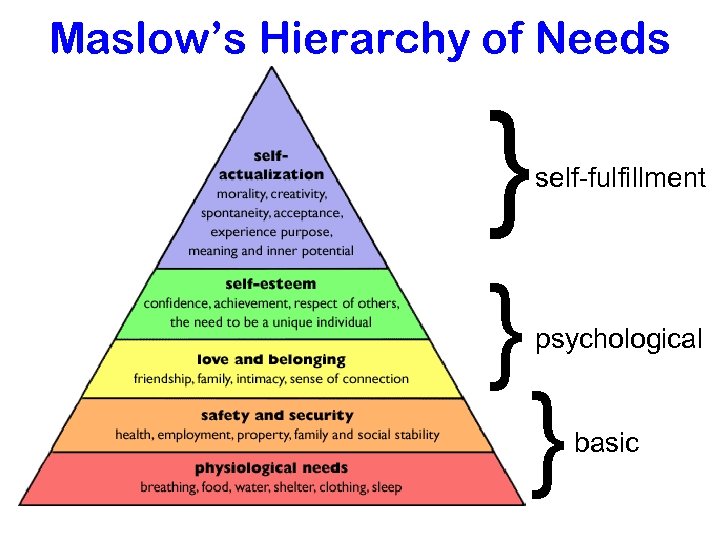 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs } } self-fulfillment psychological } basic
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs } } self-fulfillment psychological } basic
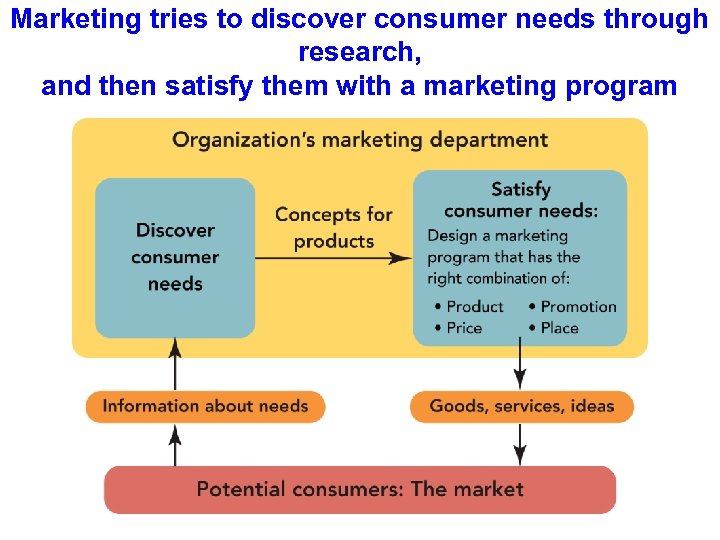 Marketing tries to discover consumer needs through research, and then satisfy them with a marketing program
Marketing tries to discover consumer needs through research, and then satisfy them with a marketing program
 Marketing’s 4 Ps PRODUCT PRICE a good or service or idea to satisfy a consumer need amount consumer pays for good (can be cash or kind) PROMOTION PLACE means of communication means of delivering product to between buyer and seller e. g. consumer, i. e. distribution advertising, public relations, selling, sales promotion
Marketing’s 4 Ps PRODUCT PRICE a good or service or idea to satisfy a consumer need amount consumer pays for good (can be cash or kind) PROMOTION PLACE means of communication means of delivering product to between buyer and seller e. g. consumer, i. e. distribution advertising, public relations, selling, sales promotion
 4 Ps Example: PRODUCT PRICE breakfast cereal PROMOTION PLACE
4 Ps Example: PRODUCT PRICE breakfast cereal PROMOTION PLACE
 4 Ps Example: SERVICE PRODUCT = SERVICE PROMOTION PLACE
4 Ps Example: SERVICE PRODUCT = SERVICE PROMOTION PLACE
 4 Ps Example: IDEA PRODUCT = IDEA PRICE PROMOTION PLACE
4 Ps Example: IDEA PRODUCT = IDEA PRICE PROMOTION PLACE
 Customer Value = benefits = utility = unique combination of benefits received by targeted buyers - includes quality, convenience, on-time delivery, before- and after-sales service at specific price
Customer Value = benefits = utility = unique combination of benefits received by targeted buyers - includes quality, convenience, on-time delivery, before- and after-sales service at specific price
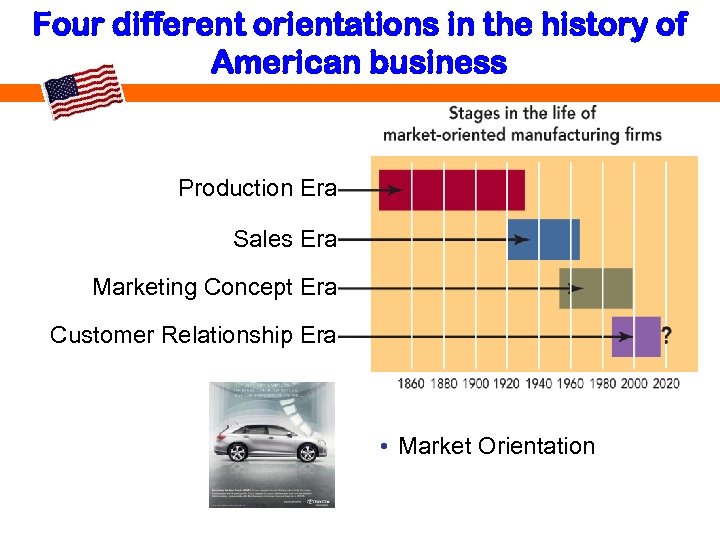 Four different orientations in the history of American business Production Era Sales Era Marketing Concept Era Customer Relationship Era • Market Orientation
Four different orientations in the history of American business Production Era Sales Era Marketing Concept Era Customer Relationship Era • Market Orientation
 Customer Relationship Management = process of identifying prospective buyers, understanding them thoroughly, & developing favorable long-term perceptions of the organization so buyers will choose them in the marketplace. Fundamental commitment to market orientation facilitates relationship management. Customer experience: What companies think they are providing = what customers say they are receiving? (Remember: Manage expectations. )
Customer Relationship Management = process of identifying prospective buyers, understanding them thoroughly, & developing favorable long-term perceptions of the organization so buyers will choose them in the marketplace. Fundamental commitment to market orientation facilitates relationship management. Customer experience: What companies think they are providing = what customers say they are receiving? (Remember: Manage expectations. )
 Breadth & Depth of Marketing Q: WHO markets? A: EVERYONE Q: WHAT is marketed? A: EVERYTHING Goods Services Ideas
Breadth & Depth of Marketing Q: WHO markets? A: EVERYONE Q: WHAT is marketed? A: EVERYTHING Goods Services Ideas
 10 companies control everything you buy
10 companies control everything you buy
 Next class: Marketing & Strategy Preparation: Read Ch. 1 pp. 4 -5; p. 7 fig. 1 -2; pp. 9 -11; pp. 18 -19 Ch. 2 p. 26; pp. 32 -33; p. 39 SWOT
Next class: Marketing & Strategy Preparation: Read Ch. 1 pp. 4 -5; p. 7 fig. 1 -2; pp. 9 -11; pp. 18 -19 Ch. 2 p. 26; pp. 32 -33; p. 39 SWOT


