6ec3e79f76542816d115fc67ca107904.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

 Mixed Signal Design Space Exploration through Analog Platforms F. De Bernardinis , P. Nuzzo , A. Sangiovanni Vincentelli UC Berkeley University of Pisa, Italy
Mixed Signal Design Space Exploration through Analog Platforms F. De Bernardinis , P. Nuzzo , A. Sangiovanni Vincentelli UC Berkeley University of Pisa, Italy
 Outline Introduction Analog Platforms definition design flow Performance Models definition optimization of approximation process Mixed-Signal Case Study pipeline ADC design with platforms optimization and results Conclusions 3
Outline Introduction Analog Platforms definition design flow Performance Models definition optimization of approximation process Mixed-Signal Case Study pipeline ADC design with platforms optimization and results Conclusions 3
 Introduction Mixed-Signal Design: heterogeneous problem to be coped at system level most remunerative tradeoffs across A/D interface scant attention in the past Platform Based Design originates as an answer to engineering and economic issues widely accepted in the design community moves design focus to composition of library elements Analog Design Flows limited synthesis capabilities struggle with device and circuit complexity 4
Introduction Mixed-Signal Design: heterogeneous problem to be coped at system level most remunerative tradeoffs across A/D interface scant attention in the past Platform Based Design originates as an answer to engineering and economic issues widely accepted in the design community moves design focus to composition of library elements Analog Design Flows limited synthesis capabilities struggle with device and circuit complexity 4
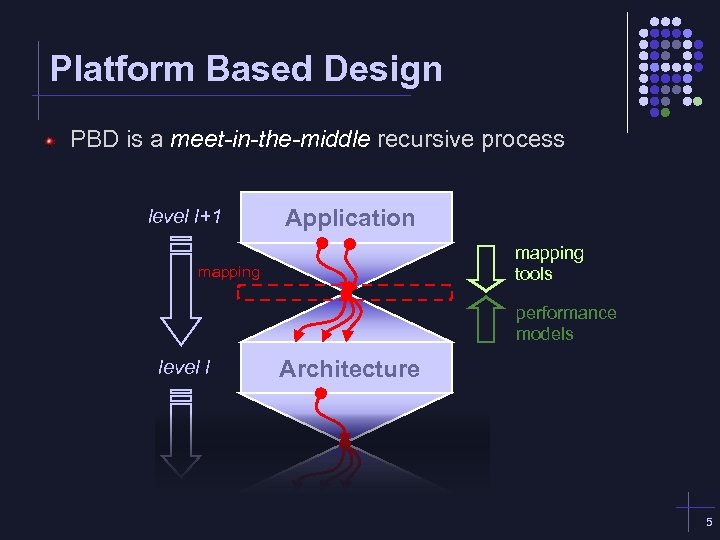 Platform Based Design PBD is a meet-in-the-middle recursive process level l+1 Application mapping tools mapping performance models level l Architecture 5
Platform Based Design PBD is a meet-in-the-middle recursive process level l+1 Application mapping tools mapping performance models level l Architecture 5
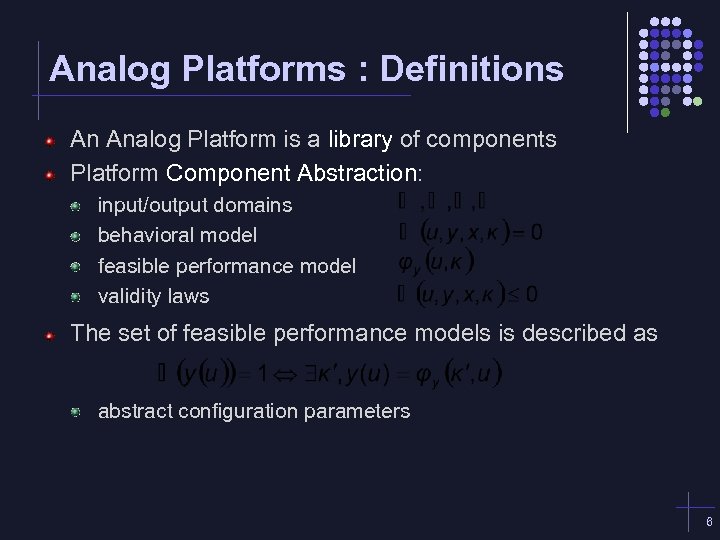 Analog Platforms : Definitions An Analog Platform is a library of components Platform Component Abstraction: input/output domains behavioral model feasible performance model validity laws The set of feasible performance models is described as abstract configuration parameters 6
Analog Platforms : Definitions An Analog Platform is a library of components Platform Component Abstraction: input/output domains behavioral model feasible performance model validity laws The set of feasible performance models is described as abstract configuration parameters 6
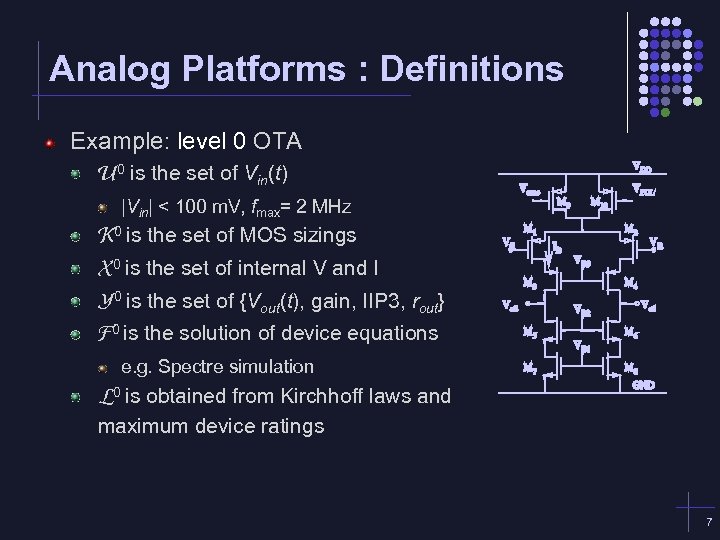 Analog Platforms : Definitions Example: level 0 OTA U 0 is the set of Vin(t) |Vin| < 100 m. V, fmax= 2 MHz K 0 is the set of MOS sizings X 0 is the set of internal V and I Y 0 is the set of {Vout(t), gain, IIP 3, rout} F 0 is the solution of device equations e. g. Spectre simulation L 0 is obtained from Kirchhoff laws and maximum device ratings 7
Analog Platforms : Definitions Example: level 0 OTA U 0 is the set of Vin(t) |Vin| < 100 m. V, fmax= 2 MHz K 0 is the set of MOS sizings X 0 is the set of internal V and I Y 0 is the set of {Vout(t), gain, IIP 3, rout} F 0 is the solution of device equations e. g. Spectre simulation L 0 is obtained from Kirchhoff laws and maximum device ratings 7
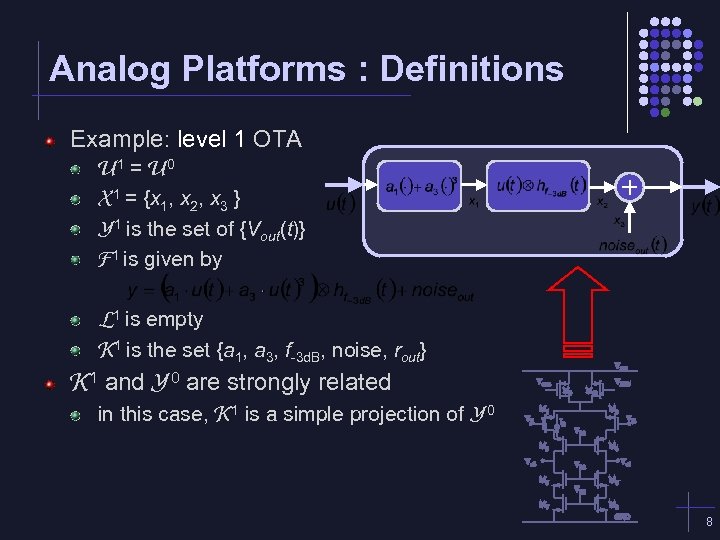 Analog Platforms : Definitions Example: level 1 OTA U 1 = U 0 X 1 = {x 1, x 2, x 3 } Y 1 is the set of {Vout(t)} F 1 is given by L 1 is empty K 1 is the set {a 1, a 3, f-3 d. B, noise, rout} K 1 and Y 0 are strongly related in this case, K 1 is a simple projection of Y 0 8
Analog Platforms : Definitions Example: level 1 OTA U 1 = U 0 X 1 = {x 1, x 2, x 3 } Y 1 is the set of {Vout(t)} F 1 is given by L 1 is empty K 1 is the set {a 1, a 3, f-3 d. B, noise, rout} K 1 and Y 0 are strongly related in this case, K 1 is a simple projection of Y 0 8
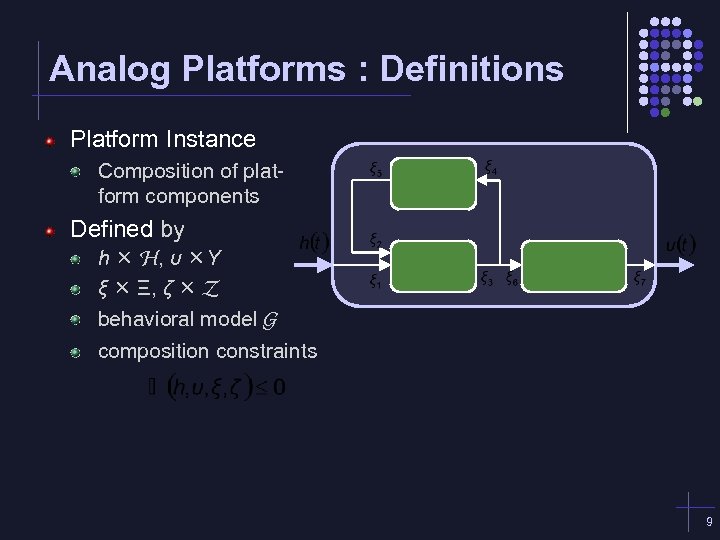 Analog Platforms : Definitions Platform Instance Composition of platform components Defined by h H, υ Υ ξ Ξ, ζ Z behavioral model G composition constraints 9
Analog Platforms : Definitions Platform Instance Composition of platform components Defined by h H, υ Υ ξ Ξ, ζ Z behavioral model G composition constraints 9
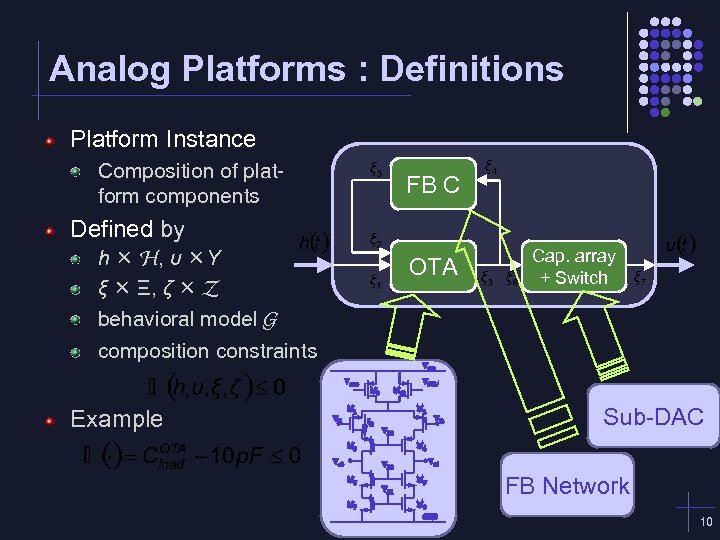 Analog Platforms : Definitions Platform Instance Composition of platform components FB C Defined by h H, υ Υ ξ Ξ, ζ Z behavioral model G OTA Cap. array + Switch composition constraints Example Sub-DAC FB Network 10
Analog Platforms : Definitions Platform Instance Composition of platform components FB C Defined by h H, υ Υ ξ Ξ, ζ Z behavioral model G OTA Cap. array + Switch composition constraints Example Sub-DAC FB Network 10
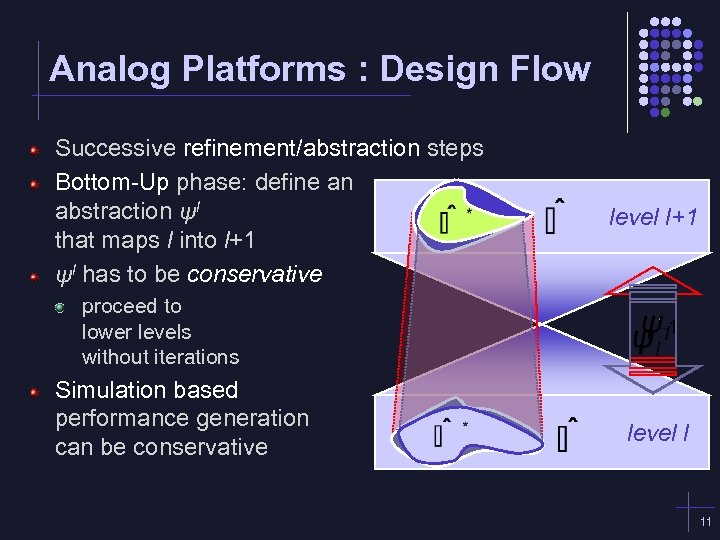 Analog Platforms : Design Flow Successive refinement/abstraction steps Bottom-Up phase: define an abstraction ψl that maps l into l+1 ψl has to be conservative level l+1 proceed to lower levels without iterations Simulation based performance generation can be conservative level l 11
Analog Platforms : Design Flow Successive refinement/abstraction steps Bottom-Up phase: define an abstraction ψl that maps l into l+1 ψl has to be conservative level l+1 proceed to lower levels without iterations Simulation based performance generation can be conservative level l 11
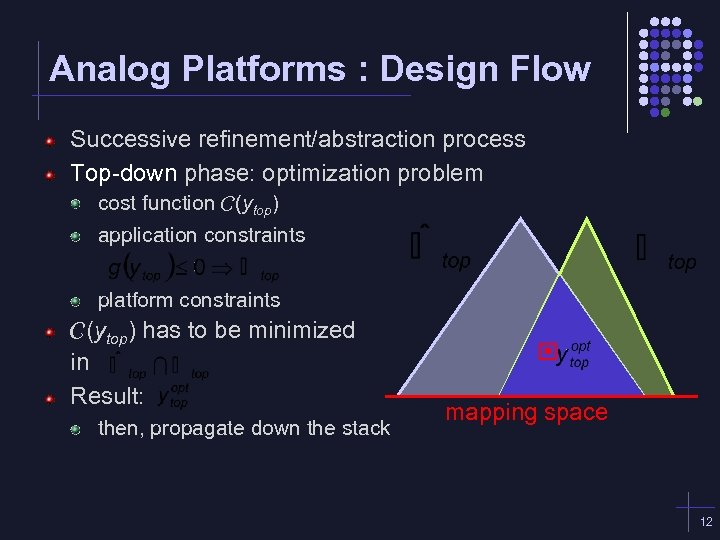 Analog Platforms : Design Flow Successive refinement/abstraction process Top-down phase: optimization problem cost function C(ytop) application constraints platform constraints C(ytop) has to be minimized in Result: then, propagate down the stack mapping space 12
Analog Platforms : Design Flow Successive refinement/abstraction process Top-down phase: optimization problem cost function C(ytop) application constraints platform constraints C(ytop) has to be minimized in Result: then, propagate down the stack mapping space 12
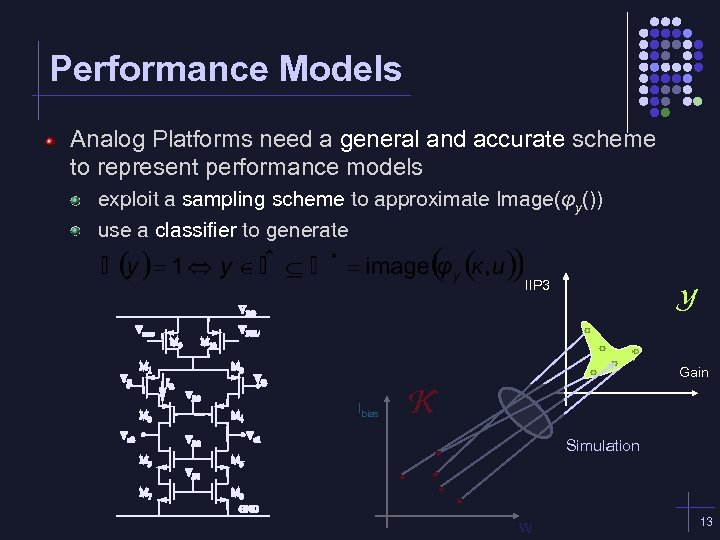 Performance Models Analog Platforms need a general and accurate scheme to represent performance models exploit a sampling scheme to approximate Image(φy()) use a classifier to generate IIP 3 Ibias Y Gain K Simulation W 13
Performance Models Analog Platforms need a general and accurate scheme to represent performance models exploit a sampling scheme to approximate Image(φy()) use a classifier to generate IIP 3 Ibias Y Gain K Simulation W 13
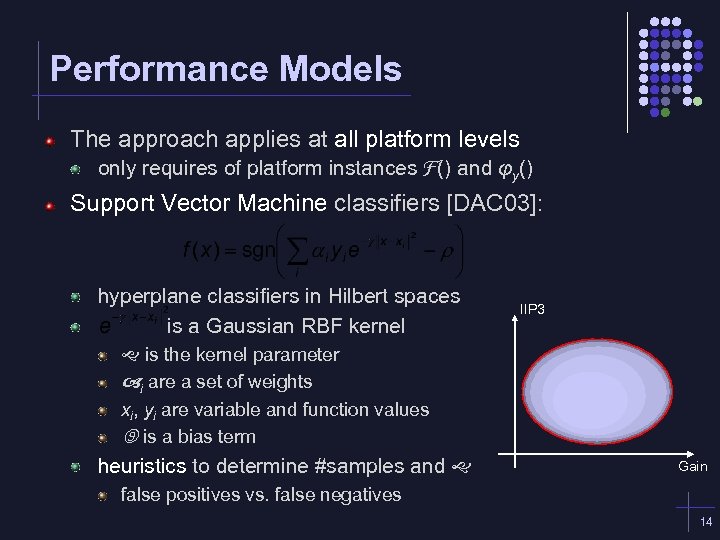 Performance Models The approach applies at all platform levels only requires of platform instances F() and φy() Support Vector Machine classifiers [DAC 03]: hyperplane classifiers in Hilbert spaces is a Gaussian RBF kernel IIP 3 is the kernel parameter i are a set of weights xi, yi are variable and function values is a bias term heuristics to determine #samples and Gain false positives vs. false negatives 14
Performance Models The approach applies at all platform levels only requires of platform instances F() and φy() Support Vector Machine classifiers [DAC 03]: hyperplane classifiers in Hilbert spaces is a Gaussian RBF kernel IIP 3 is the kernel parameter i are a set of weights xi, yi are variable and function values is a bias term heuristics to determine #samples and Gain false positives vs. false negatives 14
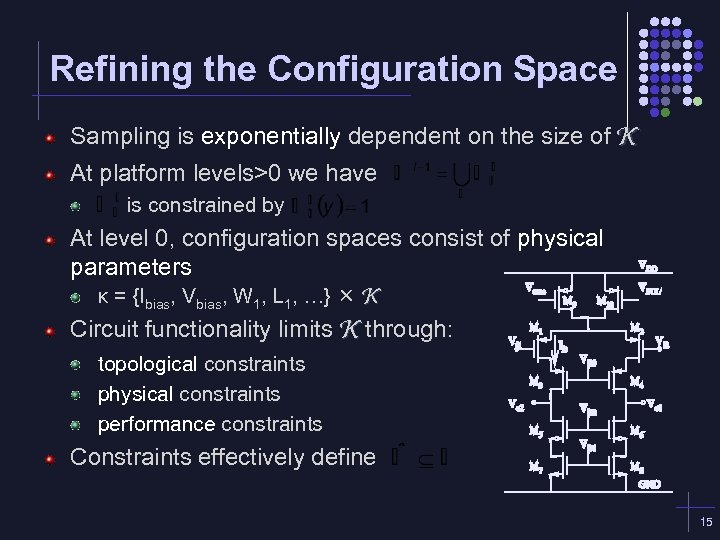 Refining the Configuration Space Sampling is exponentially dependent on the size of K At platform levels>0 we have is constrained by At level 0, configuration spaces consist of physical parameters κ = {Ibias, Vbias, W 1, L 1, …} K Circuit functionality limits K through: topological constraints physical constraints performance constraints Constraints effectively define 15
Refining the Configuration Space Sampling is exponentially dependent on the size of K At platform levels>0 we have is constrained by At level 0, configuration spaces consist of physical parameters κ = {Ibias, Vbias, W 1, L 1, …} K Circuit functionality limits K through: topological constraints physical constraints performance constraints Constraints effectively define 15
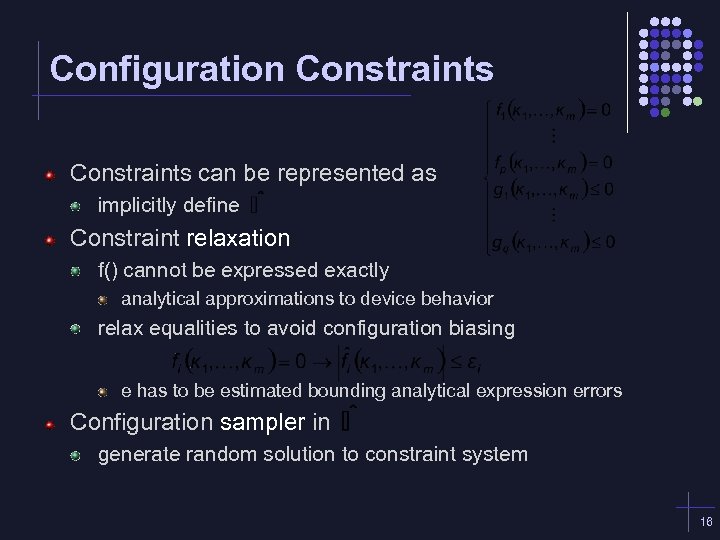 Configuration Constraints can be represented as implicitly define Constraint relaxation f() cannot be expressed exactly analytical approximations to device behavior relax equalities to avoid configuration biasing e has to be estimated bounding analytical expression errors Configuration sampler in generate random solution to constraint system 16
Configuration Constraints can be represented as implicitly define Constraint relaxation f() cannot be expressed exactly analytical approximations to device behavior relax equalities to avoid configuration biasing e has to be estimated bounding analytical expression errors Configuration sampler in generate random solution to constraint system 16
![Analog Constraint Graphs Exploit bipartite graph representation [Donald] An ACG is an undirected bipartite Analog Constraint Graphs Exploit bipartite graph representation [Donald] An ACG is an undirected bipartite](https://present5.com/presentation/6ec3e79f76542816d115fc67ca107904/image-17.jpg) Analog Constraint Graphs Exploit bipartite graph representation [Donald] An ACG is an undirected bipartite graph ( , , ), where are the design variables are equations on design variables ACGs represent under-constrained systems of equations with a set of inequalities A scheduling operation can be defined to provide efficient executable samplers in r. B=WB/LB W 1 VGS 1 r 2 r. M=WM/LM L 1 L 2 IB W 2 VGS 2 17
Analog Constraint Graphs Exploit bipartite graph representation [Donald] An ACG is an undirected bipartite graph ( , , ), where are the design variables are equations on design variables ACGs represent under-constrained systems of equations with a set of inequalities A scheduling operation can be defined to provide efficient executable samplers in r. B=WB/LB W 1 VGS 1 r 2 r. M=WM/LM L 1 L 2 IB W 2 VGS 2 17
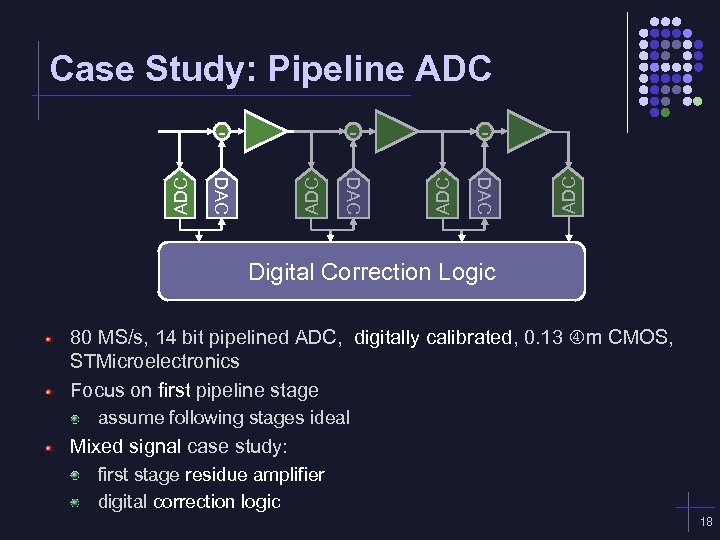 Case Study: Pipeline ADC ADC ADC DAC DAC - Digital Correction Logic 80 MS/s, 14 bit pipelined ADC, digitally calibrated, 0. 13 m CMOS, STMicroelectronics Focus on first pipeline stage assume following stages ideal Mixed signal case study: first stage residue amplifier digital correction logic 18
Case Study: Pipeline ADC ADC ADC DAC DAC - Digital Correction Logic 80 MS/s, 14 bit pipelined ADC, digitally calibrated, 0. 13 m CMOS, STMicroelectronics Focus on first pipeline stage assume following stages ideal Mixed signal case study: first stage residue amplifier digital correction logic 18
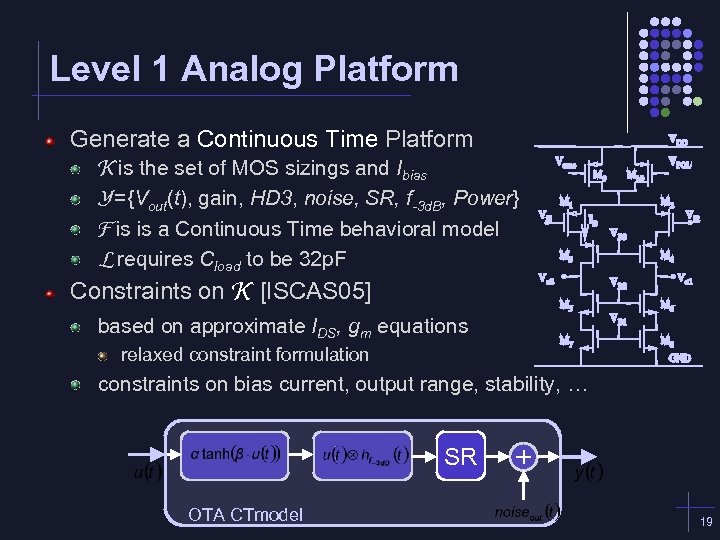 Level 1 Analog Platform Generate a Continuous Time Platform K is the set of MOS sizings and Ibias Y={Vout(t), gain, HD 3, noise, SR, f-3 d. B, Power} F is is a Continuous Time behavioral model L requires Cload to be 32 p. F Constraints on K [ISCAS 05] based on approximate IDS, gm equations relaxed constraint formulation constraints on bias current, output range, stability, … SR OTA CTmodel 19
Level 1 Analog Platform Generate a Continuous Time Platform K is the set of MOS sizings and Ibias Y={Vout(t), gain, HD 3, noise, SR, f-3 d. B, Power} F is is a Continuous Time behavioral model L requires Cload to be 32 p. F Constraints on K [ISCAS 05] based on approximate IDS, gm equations relaxed constraint formulation constraints on bias current, output range, stability, … SR OTA CTmodel 19
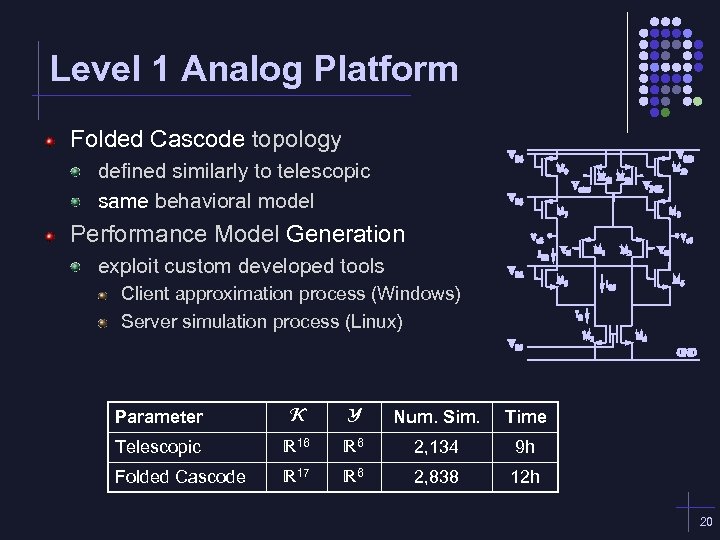 Level 1 Analog Platform Folded Cascode topology defined similarly to telescopic same behavioral model Performance Model Generation exploit custom developed tools Client approximation process (Windows) Server simulation process (Linux) Parameter K Y Num. Sim. Time Telescopic R 16 R 6 2, 134 9 h Folded Cascode R 17 R 6 2, 838 12 h 20
Level 1 Analog Platform Folded Cascode topology defined similarly to telescopic same behavioral model Performance Model Generation exploit custom developed tools Client approximation process (Windows) Server simulation process (Linux) Parameter K Y Num. Sim. Time Telescopic R 16 R 6 2, 134 9 h Folded Cascode R 17 R 6 2, 838 12 h 20
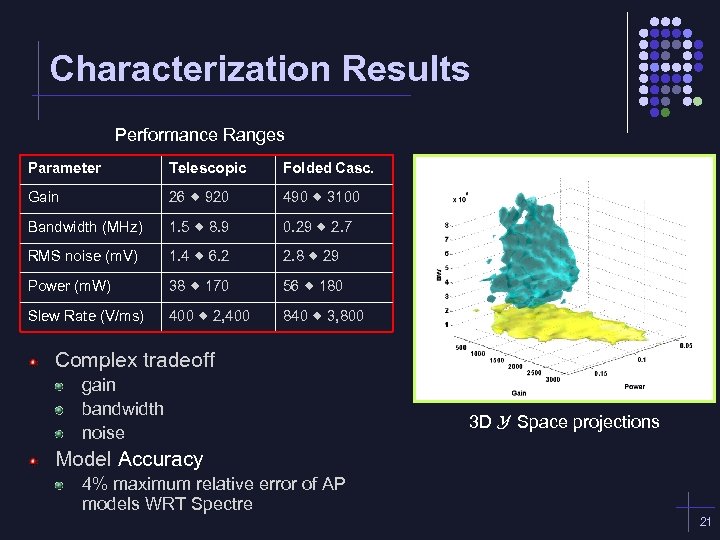 Characterization Results Performance Ranges Parameter Telescopic Folded Casc. Gain 26 920 490 3100 Bandwidth (MHz) 1. 5 8. 9 0. 29 2. 7 RMS noise (m. V) 1. 4 6. 2 2. 8 29 Power (m. W) 38 170 56 180 Slew Rate (V/ms) 400 2, 400 840 3, 800 Complex tradeoff gain bandwidth noise 3 D Y Space projections Model Accuracy 4% maximum relative error of AP models WRT Spectre 21
Characterization Results Performance Ranges Parameter Telescopic Folded Casc. Gain 26 920 490 3100 Bandwidth (MHz) 1. 5 8. 9 0. 29 2. 7 RMS noise (m. V) 1. 4 6. 2 2. 8 29 Power (m. W) 38 170 56 180 Slew Rate (V/ms) 400 2, 400 840 3, 800 Complex tradeoff gain bandwidth noise 3 D Y Space projections Model Accuracy 4% maximum relative error of AP models WRT Spectre 21
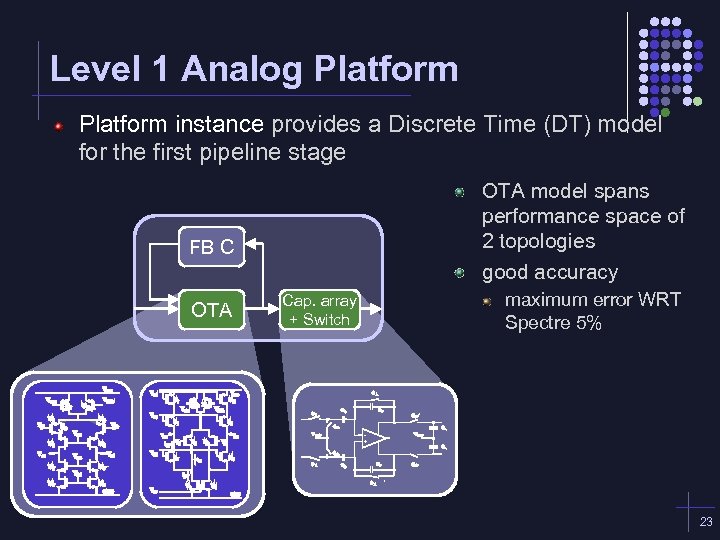 Level 1 Analog Platform instance provides a Discrete Time (DT) model for the first pipeline stage OTA model spans performance space of 2 topologies good accuracy FB C OTA Cap. array + Switch maximum error WRT Spectre 5% 23
Level 1 Analog Platform instance provides a Discrete Time (DT) model for the first pipeline stage OTA model spans performance space of 2 topologies good accuracy FB C OTA Cap. array + Switch maximum error WRT Spectre 5% 23
![Level 1 Digital Platform Digital post-process [Murmann 03]: adjust gain linearize system 0. 4 Level 1 Digital Platform Digital post-process [Murmann 03]: adjust gain linearize system 0. 4](https://present5.com/presentation/6ec3e79f76542816d115fc67ca107904/image-23.jpg) Level 1 Digital Platform Digital post-process [Murmann 03]: adjust gain linearize system 0. 4 Transfer Characteristic Estimation 1 st Stage: 1 LSB = 0. 1 V B FSR = 0. 8 V A Characterization as a component Vres(V) y = a 1 x+a 3 x 3 0 bounds on accuracy of â 1 and â 3 simulate the algorithm: (a 1, a 3) (â 1, â 3) P(P, a 1, a 3 , â 1, â 3)=1 Polynomial Inversion -0. 4 -0. 05 compute predictor/corrector implementation scheme performance model for accuracy: P(P, â 1, â 3)=1 0 V (V) in 0. 05 24
Level 1 Digital Platform Digital post-process [Murmann 03]: adjust gain linearize system 0. 4 Transfer Characteristic Estimation 1 st Stage: 1 LSB = 0. 1 V B FSR = 0. 8 V A Characterization as a component Vres(V) y = a 1 x+a 3 x 3 0 bounds on accuracy of â 1 and â 3 simulate the algorithm: (a 1, a 3) (â 1, â 3) P(P, a 1, a 3 , â 1, â 3)=1 Polynomial Inversion -0. 4 -0. 05 compute predictor/corrector implementation scheme performance model for accuracy: P(P, â 1, â 3)=1 0 V (V) in 0. 05 24
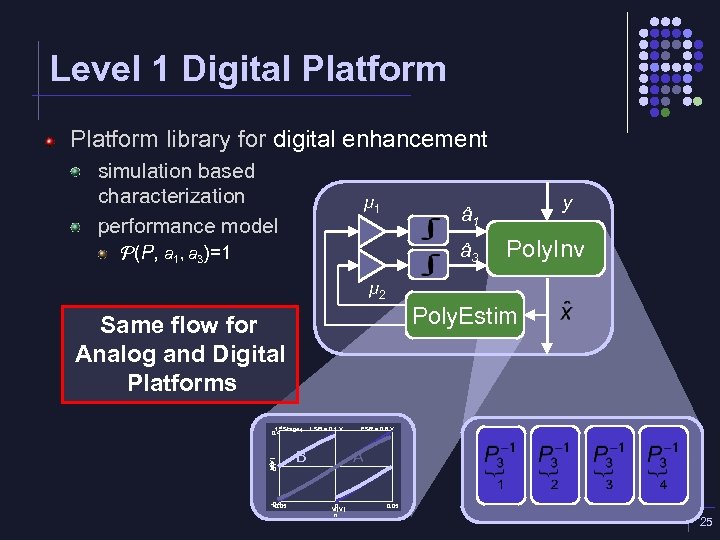 Level 1 Digital Platform library for digital enhancement simulation based characterization performance model μ 1 y â 1 P(P, a 1, a 3)=1 â 3 Poly. Inv μ 2 Poly. Estim Same flow for Analog and Digital Platforms V(V) res 1 st Stage: 1 0. 4 0 -0. 4 -0. 05 LSB = 0. 1 V B FSR = 0. 8 V A 0 Vi (V) n 0. 05 25
Level 1 Digital Platform library for digital enhancement simulation based characterization performance model μ 1 y â 1 P(P, a 1, a 3)=1 â 3 Poly. Inv μ 2 Poly. Estim Same flow for Analog and Digital Platforms V(V) res 1 st Stage: 1 0. 4 0 -0. 4 -0. 05 LSB = 0. 1 V B FSR = 0. 8 V A 0 Vi (V) n 0. 05 25
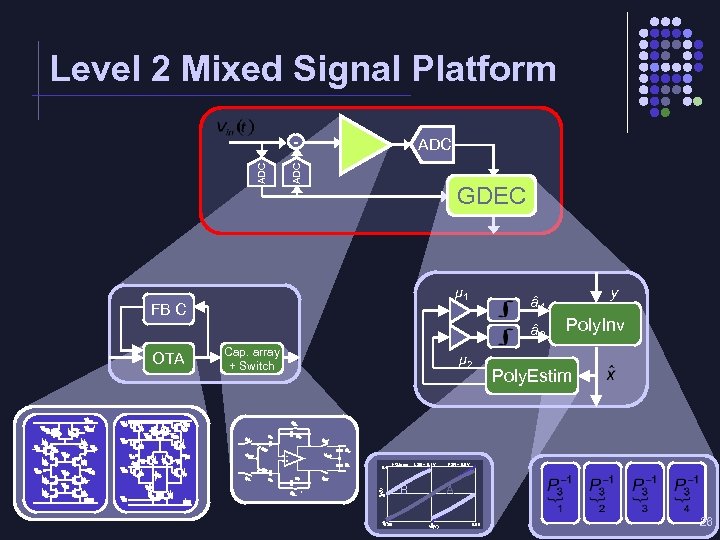 Level 2 Mixed Signal Platform ADC ADC - GDEC μ 1 FB C â 3 Cap. array + Switch μ 2 0. 4 1 st Stage: 1 V (V) res OTA 0 -0. 4 -0. 05 LSB = 0. 1 V B y â 1 Poly. Inv Poly. Estim FSR = 0. 8 V A 0 V (V) in 0. 05 26
Level 2 Mixed Signal Platform ADC ADC - GDEC μ 1 FB C â 3 Cap. array + Switch μ 2 0. 4 1 st Stage: 1 V (V) res OTA 0 -0. 4 -0. 05 LSB = 0. 1 V B y â 1 Poly. Inv Poly. Estim FSR = 0. 8 V A 0 V (V) in 0. 05 26
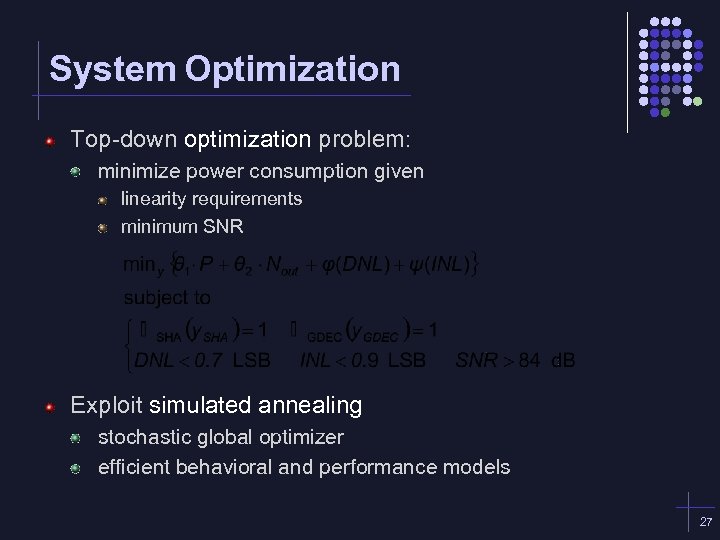 System Optimization Top-down optimization problem: minimize power consumption given linearity requirements minimum SNR Exploit simulated annealing stochastic global optimizer efficient behavioral and performance models 27
System Optimization Top-down optimization problem: minimize power consumption given linearity requirements minimum SNR Exploit simulated annealing stochastic global optimizer efficient behavioral and performance models 27
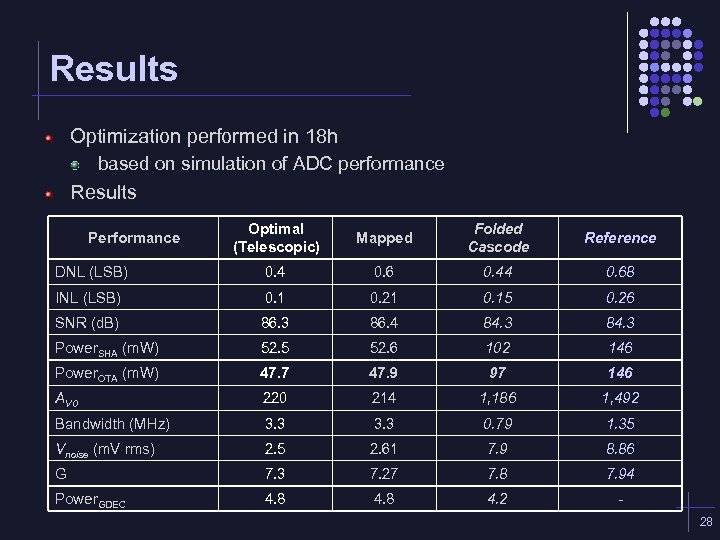 Results Optimization performed in 18 h based on simulation of ADC performance Results Optimal (Telescopic) Mapped Folded Cascode Reference DNL (LSB) 0. 4 0. 6 0. 44 0. 68 INL (LSB) 0. 1 0. 21 0. 15 0. 26 SNR (d. B) 86. 3 86. 4 84. 3 Power. SHA (m. W) 52. 5 52. 6 102 146 Power. OTA (m. W) 47. 7 47. 9 97 146 AV 0 220 214 1, 186 1, 492 Bandwidth (MHz) 3. 3 0. 79 1. 35 Vnoise (m. V rms) 2. 5 2. 61 7. 9 8. 86 G 7. 3 7. 27 7. 8 7. 94 Power. GDEC 4. 8 4. 2 - Performance 28
Results Optimization performed in 18 h based on simulation of ADC performance Results Optimal (Telescopic) Mapped Folded Cascode Reference DNL (LSB) 0. 4 0. 6 0. 44 0. 68 INL (LSB) 0. 1 0. 21 0. 15 0. 26 SNR (d. B) 86. 3 86. 4 84. 3 Power. SHA (m. W) 52. 5 52. 6 102 146 Power. OTA (m. W) 47. 7 47. 9 97 146 AV 0 220 214 1, 186 1, 492 Bandwidth (MHz) 3. 3 0. 79 1. 35 Vnoise (m. V rms) 2. 5 2. 61 7. 9 8. 86 G 7. 3 7. 27 7. 8 7. 94 Power. GDEC 4. 8 4. 2 - Performance 28
 Conclusions A mixed signal design exploration methodology has been presented Analog platforms have been formally defined Simulation based performance models have been exploited: conservative approximations of feasible spaces approximated with SVMs A challenging ADC design has been presented analog and digital platforms the mixed signal design exploration has been solved with SA Results demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach automatic topology selection power reduced by 64% WRT reference design 29
Conclusions A mixed signal design exploration methodology has been presented Analog platforms have been formally defined Simulation based performance models have been exploited: conservative approximations of feasible spaces approximated with SVMs A challenging ADC design has been presented analog and digital platforms the mixed signal design exploration has been solved with SA Results demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach automatic topology selection power reduced by 64% WRT reference design 29
 Thanks. 30
Thanks. 30


