d19d0ffb706af63238fbc82dde0e3d57.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Mitsubishi’s Quality Assurance ■ Introduction of Mitsubishi ■ Challenges for Achieving high-quality works ■ Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier Naoki Miyakoshi General Manager Nuclear Quality and Safety Management Nuclear Energy Systems Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. 0
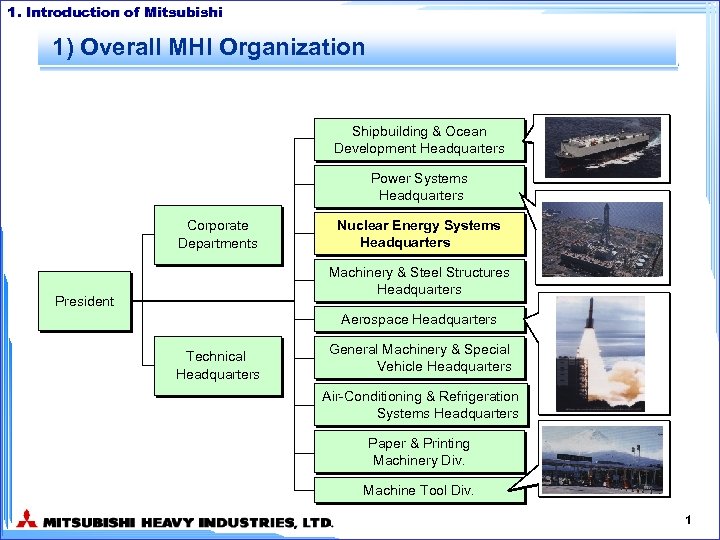
1. Introduction of Mitsubishi 1) Overall MHI Organization Shipbuilding & Ocean Development Headquarters Power Systems Headquarters Corporate Departments Nuclear Energy Systems Headquarters Machinery & Steel Structures Headquarters President Aerospace Headquarters Technical Headquarters General Machinery & Special Vehicle Headquarters Air-Conditioning & Refrigeration Systems Headquarters Paper & Printing Machinery Div. Machine Tool Div. 1
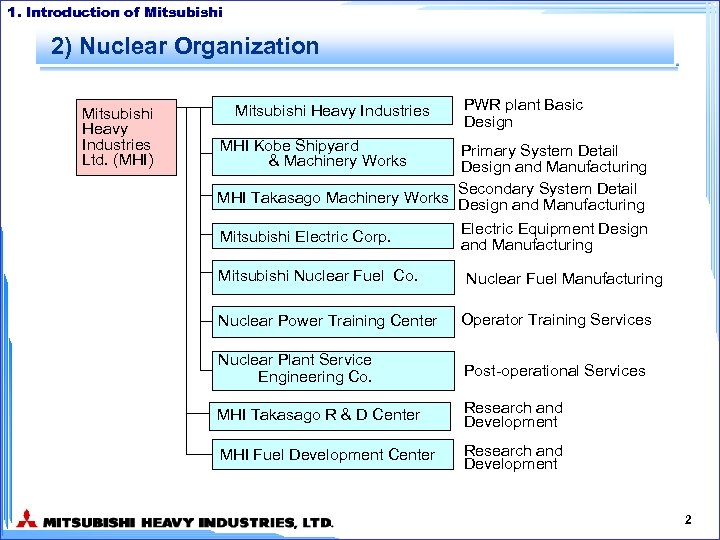
1. Introduction of Mitsubishi 2) Nuclear Organization Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (MHI) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries PWR plant Basic Design MHI Kobe Shipyard & Machinery Works Primary System Detail Design and Manufacturing Secondary System Detail MHI Takasago Machinery Works Design and Manufacturing Mitsubishi Electric Corp. Mitsubishi Nuclear Fuel Co. Electric Equipment Design and Manufacturing Nuclear Fuel Manufacturing Nuclear Power Training Center Operator Training Services Nuclear Plant Service Engineering Co. Post-operational Services MHI Takasago R & D Center Research and Development MHI Fuel Development Center Research and Development 2
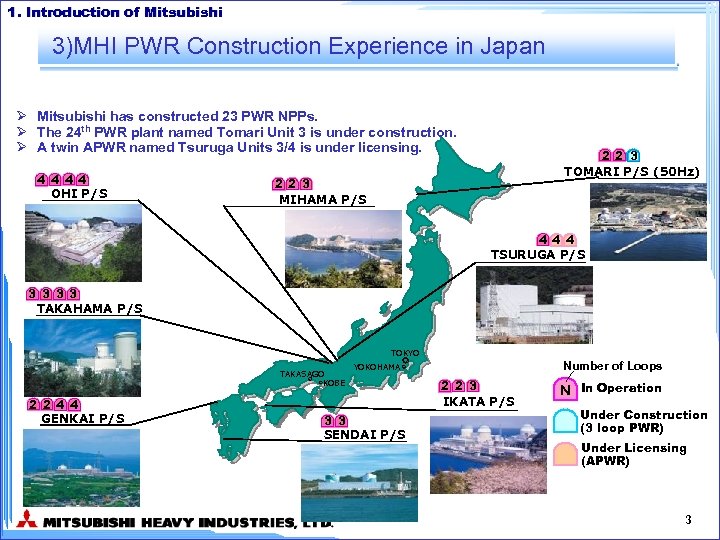
1. Introduction of Mitsubishi 3)MHI PWR Construction Experience in Japan Ø Mitsubishi has constructed 23 PWR NPPs. Ø The 24 th PWR plant named Tomari Unit 3 is under construction. Ø A twin APWR named Tsuruga Units 3/4 is under licensing. 4 4 OHI P/S 2 2 3 TOMARI P/S (50 Hz) 2 2 3 MIHAMA P/S 4 4 4 TSURUGA P/S 3 3 TAKAHAMA P/S TOKYO TAKASAGO KOBE 2 2 4 4 GENKAI P/S Number of Loops YOKOHAMA 3 3 SENDAI P/S 2 2 3 IKATA P/S N In Operation Under Construction (3 loop PWR) Under Licensing (APWR) 3
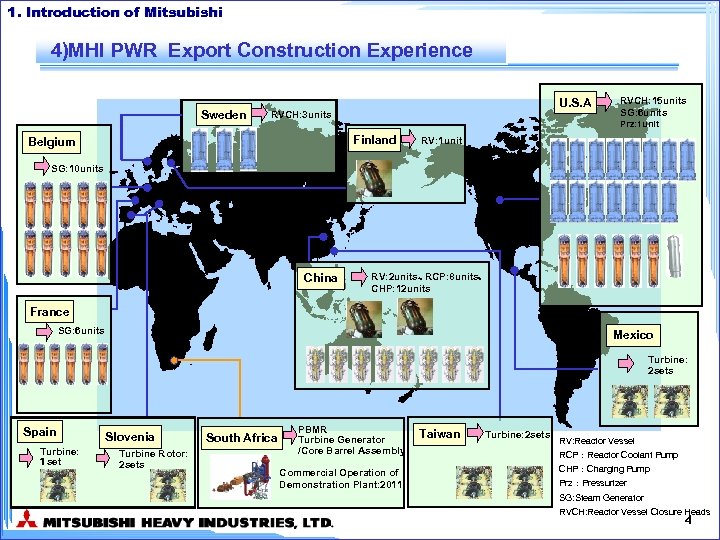
1. Introduction of Mitsubishi 4)MHI PWR Export Construction Experience Sweden U. S. A RVCH: 3 units Prz: 1 unit Finland Belgium RVCH: 15 units SG: 6 units RV: 1 unit SG: 10 units China RV: 2 units、RCP: 8 units、 CHP: 12 units France SG: 6 units Mexico Turbine: 2 sets Spain Turbine: 1 set Slovenia South Africa Turbine Rotor: 2 sets PBMR Turbine Generator /Core Barrel Assembly Commercial Operation of Demonstration Plant: 2011 Taiwan Turbine: 2 sets RV: Reactor Vessel RCP:Reactor Coolant Pump CHP:Charging Pump Prz:Pressurizer SG: Steam Generator RVCH: Reactor Vessel Closure Heads 4
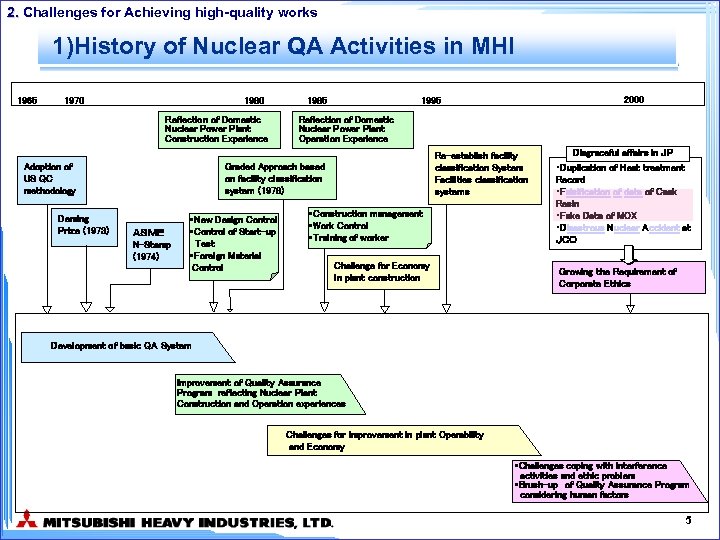
2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 1)History of Nuclear QA Activities in MHI 1965 1970 1980 Reflection of Domestic Nuclear Power Plant Construction Experience Adoption of US QC methodology Deming Prize (1973) 1985 Reflection of Domestic Nuclear Power Plant Operation Experience Re-establish facility classification System Facilities classification systems Graded Approach based on facility classification system (1978) ASME N-Stamp (1974) ・New Design Control ・Control of Start-up Test ・Foreign Material Control 2000 1995 ・Construction management ・Work Control ・Training of worker Challenge for Economy in plant construction Disgraceful affairs in JP ・Duplication of Heat treatment Record ・Falsification of data of Cask Resin ・Fake Data of MOX ・Disastrous Nuclear Accident at JCO Growing the Requirement of Corporate Ethics Development of basic QA System Improvement of Quality Assurance Program reflecting Nuclear Plant Construction and Operation experiences Challenges for improvement in plant Operability and Economy ・Challenges coping with interference activities and ethic problem ・Brush-up of Quality Assurance Program considering human factors 5

2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 1) History of Nuclear QA Activities in MHI Ⅰst Era(1965 -1978) - Introduction of American Style Quality Assurance (10 CFR 50 App. B) - Establishment of Nuclear Quality Assurance Program Ⅱnd Era(1979 -1985) - Improvement of Quality Assurance Program reflecting Nuclear Plant Construction and Operation experiences Ⅲrd Era(1986 -1995) - Challenges for improvement in plant Operability and Economy Ⅳth Era(1996 - ) - Challenges coping with interference activities and ethic problem - Brush-up of Quality Assurance Program considering human factors 6

2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 3) Representative Activities up to now - Graded Approach for Quality Assurance Classification of systems and components based on nuclear safety and plant reliability ⇒Example① -Systems to assure that approved licensing items are translated into working documents and surely inspected - Establishment of Construction management program Integrate plant construction planning Plant scheduling Comprehensive design check Comprehensive facility inspection ⇒Example② - New design and construction method control - Foreign material control - Start-up test control - Preventive actions from other plant experiences 7
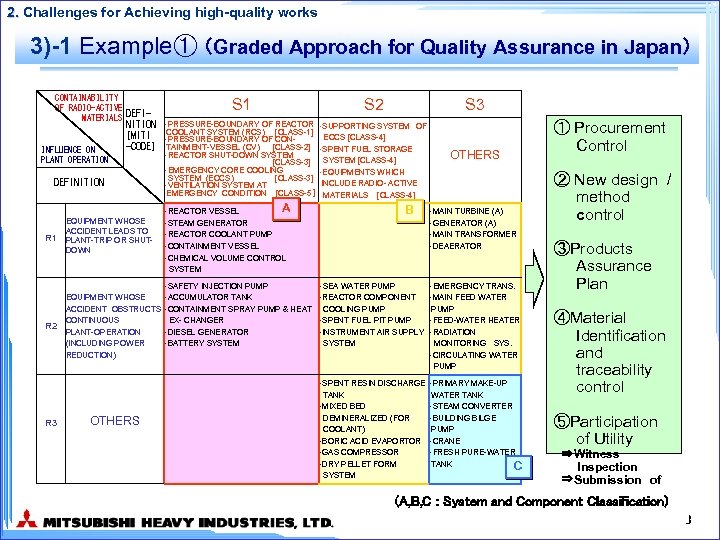
2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 3)-1 Example① (Graded Approach for Quality Assurance in Japan) CONTAINABILITY OF RADIO-ACTIVE MATERIALS DEFI- INFLUENCE ON PLANT OPERATION NITION [MITI -CODE] DEFINITION R 1 EQUIPMENT WHOSE ACCIDENT LEADS TO PLANT-TRIP OR SHUTDOWN R 2 EQUIPMENT WHOSE ACCIDENT OBSTRUCTS CONTINUOUS PLANT-OPERATION (INCLUDING POWER REDUCTION) R 3 OTHERS S 1 S 2 ・PRESSURE-BOUNDARY OF REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM (RCS) [CLASS-1] ・PRESSURE-BOUNDARY OF CONTAINMENT-VESSEL (CV) [CLASS-2] ・REACTOR SHUT-DOWN SYSTEM [CLASS-3] ・EMERGENCY CORE COOLING SYSTEM (ECCS) [CLASS-3] ・VENTILATION SYSTEM AT EMERGENCY CONDITION [CLASS-5] ・SUPPORTING SYSTEM OF ECCS [CLASS-4] ・SPENT FUEL STORAGE SYSTEM [CLASS-4] ・EQUIPMENTS WHICH INCLUDE RADIO- ACTIVE MATERIALS [CLASS-4] A ・REACTOR VESSEL ・STEAM GENERATOR ・REACTOR COOLANT PUMP ・CONTAINMENT VESSEL ・CHEMICAL VOLUME CONTROL SYSTEM ・SAFETY INJECTION PUMP ・ACCUMULATOR TANK ・CONTAINMENT SPRAY PUMP & HEAT EX- CHANGER ・DIESEL GENERATOR ・BATTERY SYSTEM S 3 B OTHERS ・MAIN TURBINE (A) ・GENERATOR (A) ・MAIN TRANSFORMER ・DEAERATOR ・SEA WATER PUMP ・REACTOR COMPONENT COOLING PUMP ・SPENT FUEL PIT PUMP ・INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM ・EMERGENCY TRANS. ・MAIN FEED WATER PUMP ・FEED-WATER HEATER ・RADIATION MONITORING SYS. ・CIRCULATING WATER PUMP ・SPENT RESIN DISCHARGE TANK ・MIXED BED DEMINERALIZED (FOR COOLANT) ・BORIC ACID EVAPORTOR ・GAS COMPRESSOR ・DRY PELLET FORM SYSTEM ・PRIMARY MAKE-UP WATER TANK ・STEAM CONVERTER ・BUILDING BILGE PUMP ・CRANE ・FRESH PURE-WATER TANK C ① Procurement Control ② New design / method control ③Products Assurance Plan ④Material Identification and traceability control ⑤Participation of Utility ⇒Witness Inspection ⇒Submission of Documents (A, B, C : System and Component Classification) 8
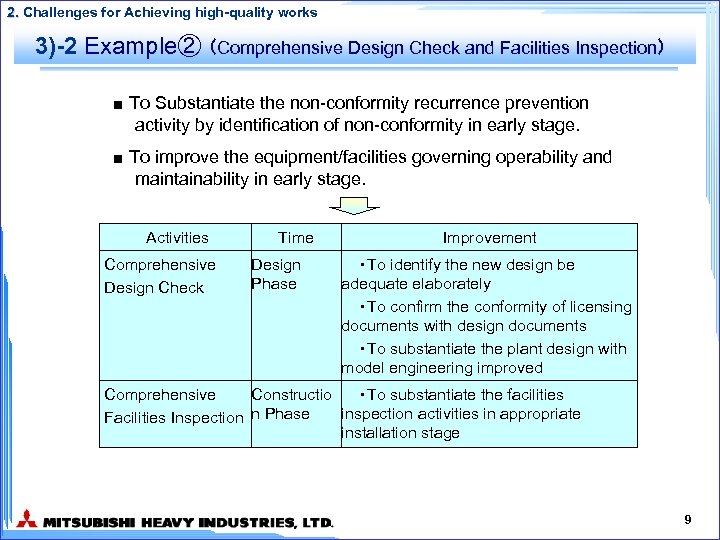
2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 3)-2 Example② (Comprehensive Design Check and Facilities Inspection) ■ To Substantiate the non-conformity recurrence prevention activity by identification of non-conformity in early stage. ■ To improve the equipment/facilities governing operability and maintainability in early stage. Activities Comprehensive Design Check Time Design Phase Improvement ・To identify the new design be adequate elaborately ・To confirm the conformity of licensing documents with design documents ・To substantiate the plant design with model engineering improved Comprehensive Constructio ・To substantiate the facilities inspection activities in appropriate Facilities Inspection n Phase installation stage 9

2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 4) Backgrounds which support Quality Activities - Regarding Craftsmanship as one of most important Feedback system from worker to engineer - Precise and Concrete Work Instruction to be a practical and effective work instruction such as caution mark, failure points, figures, and numerical criteria to be a observable work instruction through review activities from worker’s view points - Good Communication among design, manufacturing and construction and maintenance people intensive kick-off meeting ⇒Through study for new job and brainwashing of new requirements at early stage of the job reading out the procedures with all participants - High Motivation Meister patrol 3 layers meeting (manager-foreman-worker) Award system for “Kaizen” plan Indoctrination for worker (CAI) ⇒Example③ 10
2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 4) ⇒Example③ ( CAI for Worker ) Criteria Assumed Situation , Risk Caution Point 11

2. Challenges for Achieving high-quality works 5) Challenges for next Construction - Coping with Changes of Regulatory Inspection system in Japan - Coping with new NRC requirements for next Construction in US 10 CFR 21, CGI, ITAAC, Construction Inspection, RAP---- New Documentation System using advanced IT tool Measures to assure that DC and COL items are translated into working documents and surely inspected - MHI original personnel performance improvement program - Improvement of Procurement Control System 12
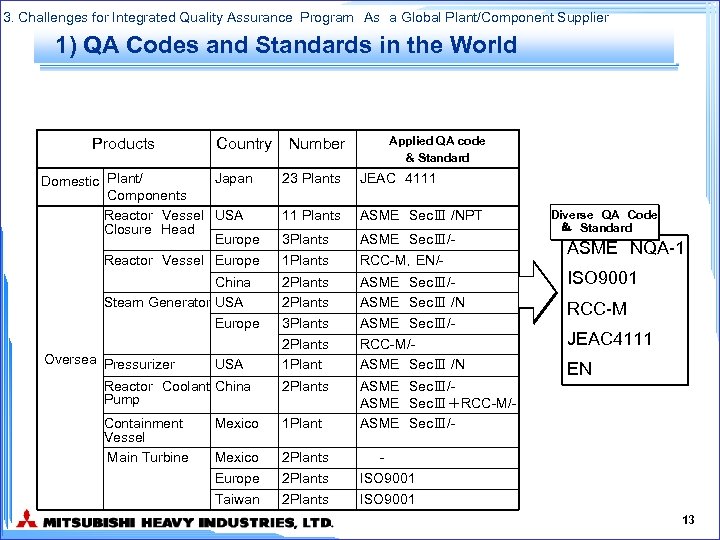
3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier 1) QA Codes and Standards in the World Products Country Japan Domestic Plant/ Components Reactor Vessel USA Closure Head Europe Reactor Vessel Europe Number Applied QA code & Standard 23 Plants JEAC 4111 11 Plants ASME SecⅢ /NPT 3 Plants 1 Plants ASME SecⅢ/RCC-M,EN/- 2 Plants 3 Plants 2 Plants 1 Plant ASME SecⅢ/ASME SecⅢ /N ASME SecⅢ/RCC-M/ASME SecⅢ /N Reactor Coolant China Pump 2 Plants Containment Vessel Main Turbine Mexico 1 Plant ASME SecⅢ/ASME SecⅢ+RCC-M/ASME SecⅢ/- Mexico Europe Taiwan 2 Plants ISO 9001 China Steam Generator USA Europe Oversea Pressurizer USA Diverse QA Code & Standard ASME NQA-1 ISO 9001 RCC-M JEAC 4111 EN 13
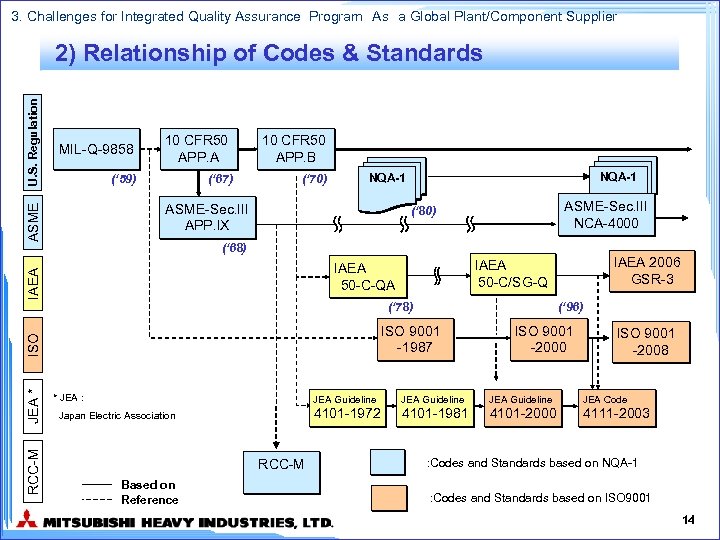
3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier MIL-Q-9858 10 CFR 50 APP. A (‘ 59) (‘ 67) 10 CFR 50 APP. B (‘ 70) NQA-1 ASME-Sec. III APP. IX ASME U. S. Regulation 2) Relationship of Codes & Standards ASME-Sec. III NCA-4000 (‘ 80) (‘ 68) IAEA (‘ 78) ISO JEA * RCC-M (‘ 96) ISO 9001 -1987 * JEA : IAEA 2006 GSR-3 IAEA 50 -C/SG-Q IAEA 50 -C-QA ISO 9001 -2000 ISO 9001 -2008 JEA Guideline RCC-M Based on Reference JEA Guideline JEA Code 4101 -1972 Japan Electric Association JEA Guideline 4101 -1981 4101 -2000 4111 -2003 : Codes and Standards based on NQA-1 : Codes and Standards based on ISO 9001 14

3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier 3) Reconciliation of ISO 9001 & NQA-1 ISO 9001: (QMS) NQA-1: (QA) The target of ISO 9001 is to make a strong organization by assessing the organization’s ability to meet customer, regulatory and the organization’s own requirements and performing the continuous improvement. The target of NQA-1 is to achieve nuclear safety and NQA-1 requires “organization” to establish quality assurance program to assure that all necessary works are properly done. In order to initiate more effective QA activities than the past, it is important to develop and integrate the concepts of the above two standards. Ref. Sector Standard In each industry, global standard is made as the sector standard by adding the industrial specific requirements to ISO 9001. Automotive Industry ISO/TS 16949 Medical Industry ISO 13485 Aviation Industry AS 9100 15
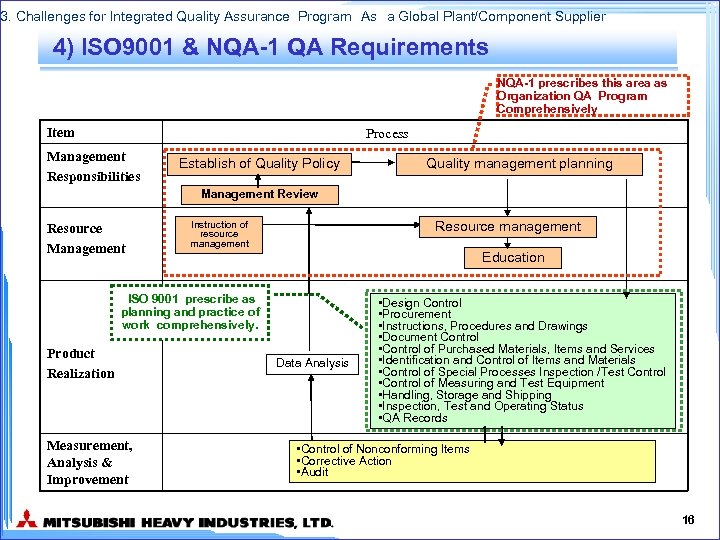
3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier 4) ISO 9001 & NQA-1 QA Requirements NQA-1 prescribes this area as Organization QA Program Comprehensively Item Process Management Responsibilities Establish of Quality Policy Quality management planning Management Review Resource Management Resource management Instruction of resource management Education ISO 9001 prescribe as planning and practice of work comprehensively. Product Realization Measurement, Analysis & Improvement Data Analysis • Design Control • Procurement • Instructions, Procedures and Drawings • Document Control • Control of Purchased Materials, Items and Services • Identification and Control of Items and Materials • Control of Special Processes Inspection /Test Control • Control of Measuring and Test Equipment • Handling, Storage and Shipping • Inspection, Test and Operating Status • QA Records • Control of Nonconforming Items • Corrective Action • Audit 16
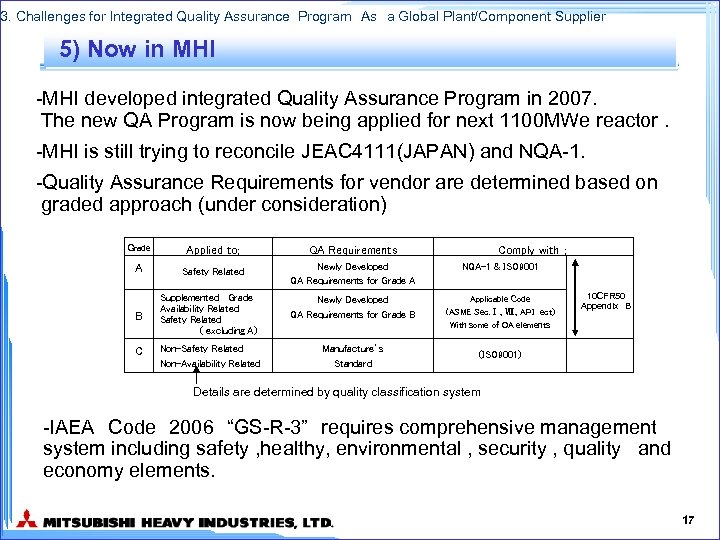
3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier 5) Now in MHI -MHI developed integrated Quality Assurance Program in 2007. The new QA Program is now being applied for next 1100 MWe reactor. -MHI is still trying to reconcile JEAC 4111(JAPAN) and NQA-1. -Quality Assurance Requirements for vendor are determined based on graded approach (under consideration) Grade Applied to; QA Requirements A Safety Related Newly Developed QA Requirements for Grade A NQA-1 & ISO 9001 Newly Developed QA Requirements for Grade B Applicable Code (ASME Sec. Ⅰ、Ⅷ、API ect) With some of QA elements B C Supplemented Grade Availability Related Safety Related ( excluding A) Non-Safety Related Non-Availability Related Manufacture’s Standard Comply with ; 10 CFR 50 Appendix B (ISO 9001) Details are determined by quality classification system -IAEA Code 2006 “GS-R-3” requires comprehensive management system including safety , healthy, environmental , security , quality and economy elements. 17
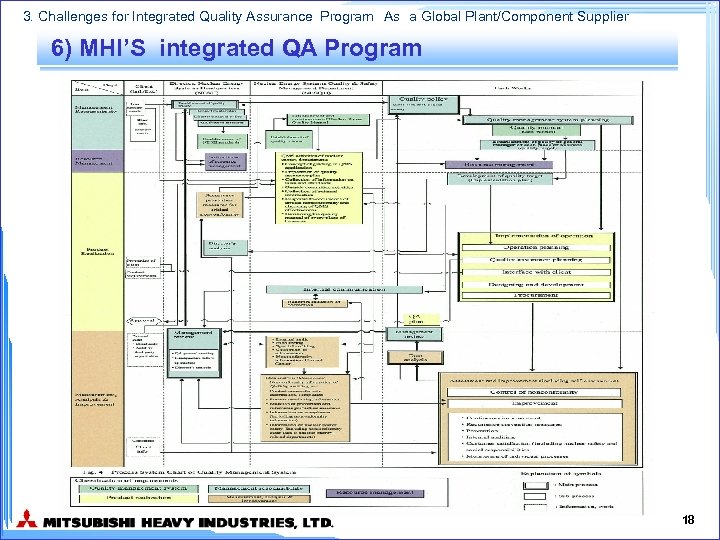
3. Challenges for Integrated Quality Assurance Program As a Global Plant/Component Supplier 6) MHI’S integrated QA Program 18
d19d0ffb706af63238fbc82dde0e3d57.ppt