5-1 Mitral valve disease.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Mitral Valve Disease
Mitral Valve Disease
 Normal Valves Connective tissue leaflets attached to atrial and ventricular muscle Dense collagenous core (Fibrosa) near the outflow surface Loose connective tissue (Spongiosa) close to the inflow surface Maintain unidirectional blood flow; leaflet apposition and overlap provide leakproof seal 심장판막질환의 이해
Normal Valves Connective tissue leaflets attached to atrial and ventricular muscle Dense collagenous core (Fibrosa) near the outflow surface Loose connective tissue (Spongiosa) close to the inflow surface Maintain unidirectional blood flow; leaflet apposition and overlap provide leakproof seal 심장판막질환의 이해
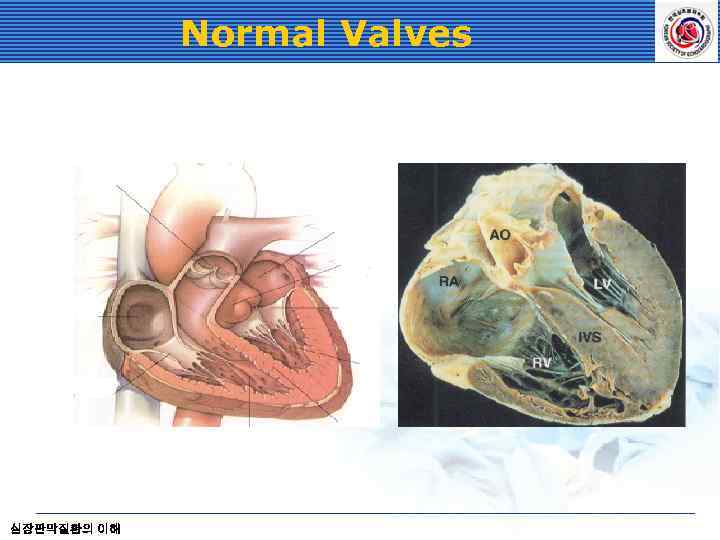 Normal Valves 심장판막질환의 이해
Normal Valves 심장판막질환의 이해
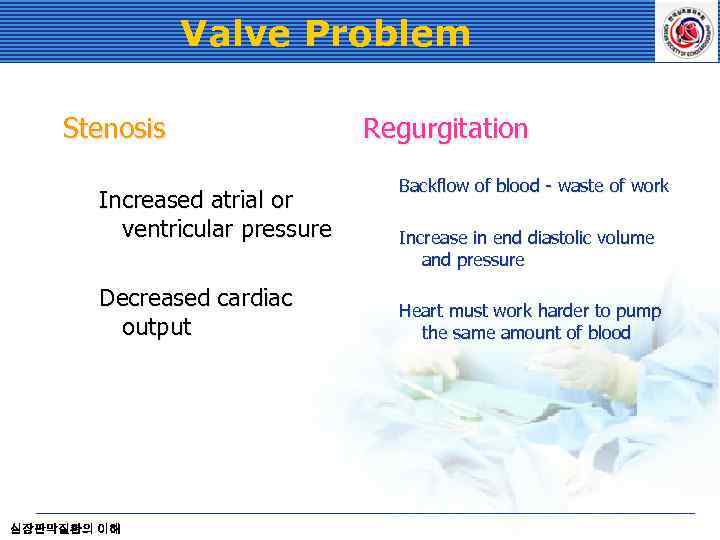 Valve Problem Stenosis Increased atrial or ventricular pressure Decreased cardiac output 심장판막질환의 이해 Regurgitation Backflow of blood - waste of work Increase in end diastolic volume and pressure Heart must work harder to pump the same amount of blood
Valve Problem Stenosis Increased atrial or ventricular pressure Decreased cardiac output 심장판막질환의 이해 Regurgitation Backflow of blood - waste of work Increase in end diastolic volume and pressure Heart must work harder to pump the same amount of blood
 Pathology STENOSIS Failure of a valve to open completely, thereby impeding forward flow Pure or Mixed Single or Multiple Valves 심장판막질환의 이해 REGURGITATION (INSUFFICIENCY) Failure of a valve to close completely, thereby allowing reversed flow
Pathology STENOSIS Failure of a valve to open completely, thereby impeding forward flow Pure or Mixed Single or Multiple Valves 심장판막질환의 이해 REGURGITATION (INSUFFICIENCY) Failure of a valve to close completely, thereby allowing reversed flow
 Etiology
Etiology
 심장판막질환의 이해
심장판막질환의 이해
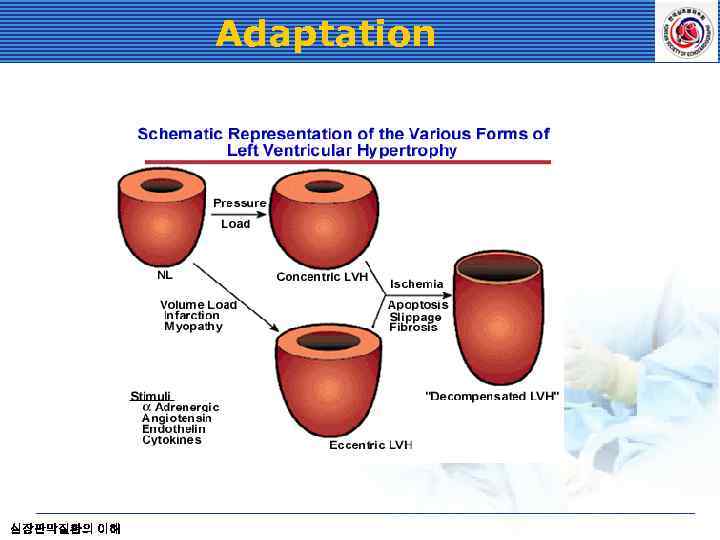 Adaptation 심장판막질환의 이해
Adaptation 심장판막질환의 이해
 Mitral Stenosis
Mitral Stenosis
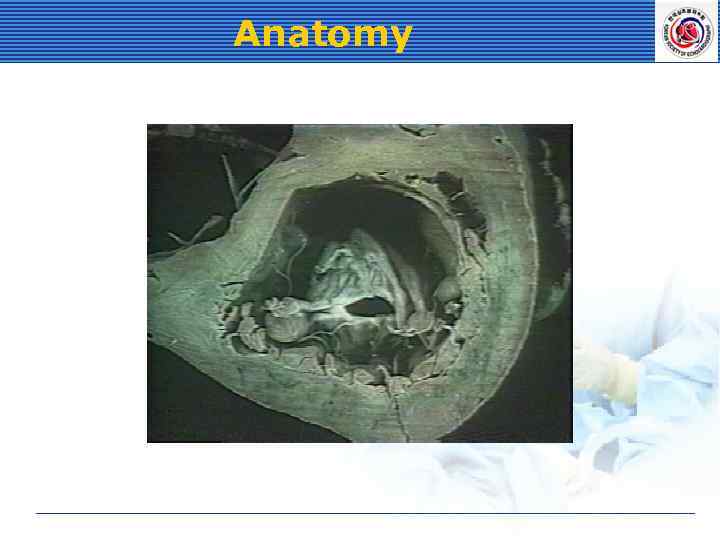 Anatomy
Anatomy
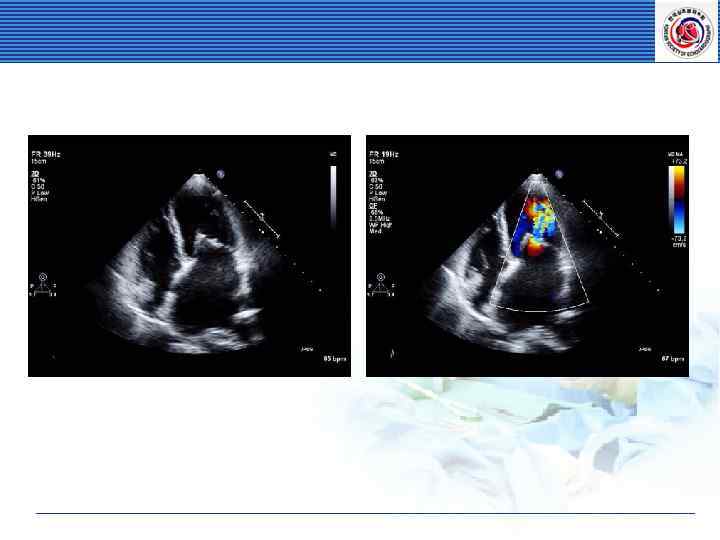
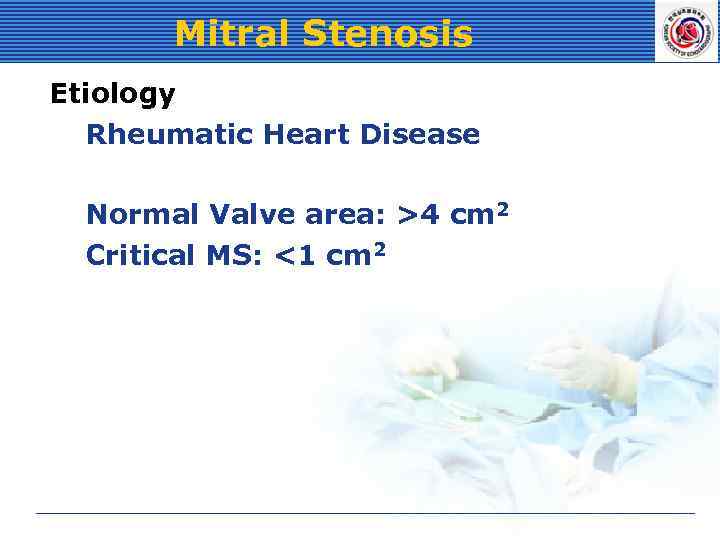 Mitral Stenosis Etiology Rheumatic Heart Disease Normal Valve area: >4 cm 2 Critical MS: <1 cm 2
Mitral Stenosis Etiology Rheumatic Heart Disease Normal Valve area: >4 cm 2 Critical MS: <1 cm 2
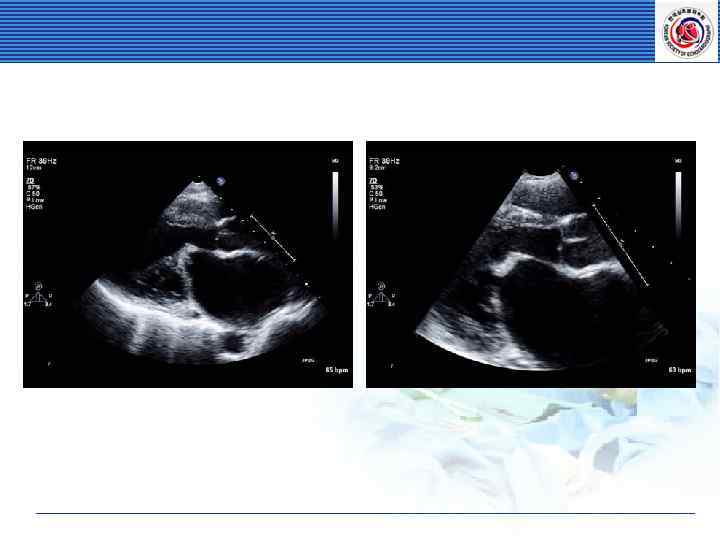
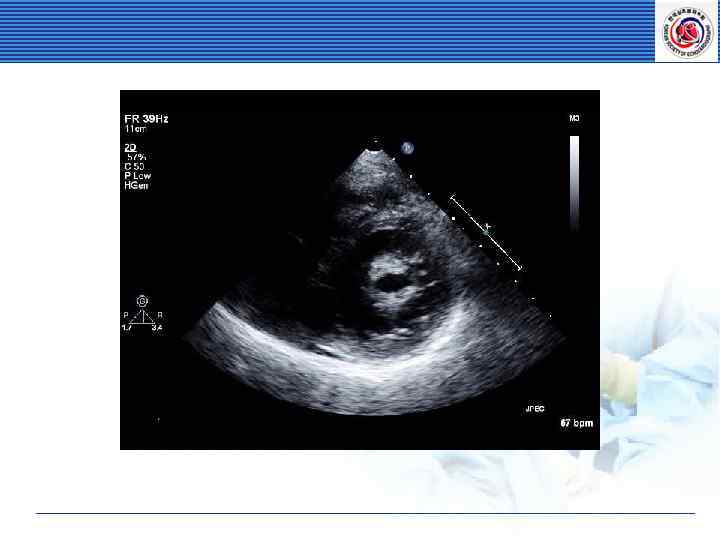
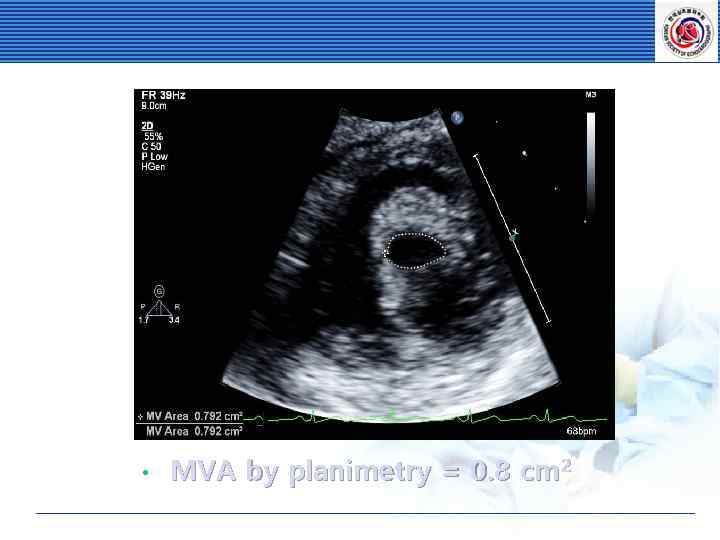 • MVA by planimetry = 0. 8 cm 2
• MVA by planimetry = 0. 8 cm 2
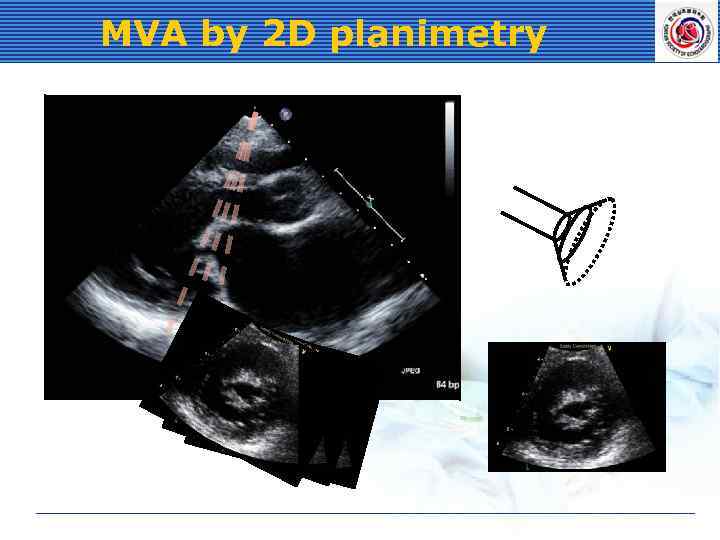 MVA by 2 D planimetry
MVA by 2 D planimetry
 Doppler in MS Pressure gradient MVA
Doppler in MS Pressure gradient MVA
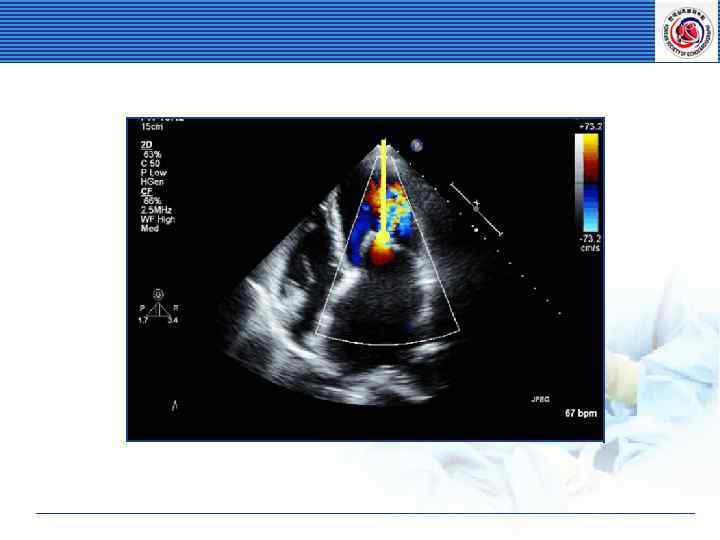
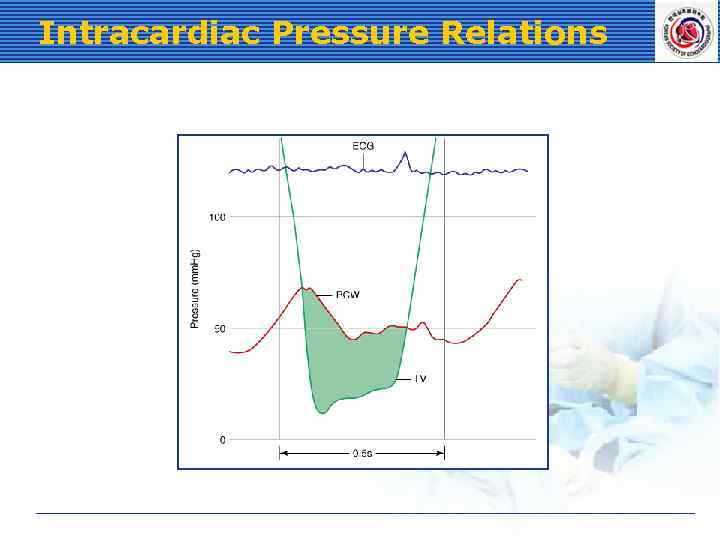 Intracardiac Pressure Relations
Intracardiac Pressure Relations
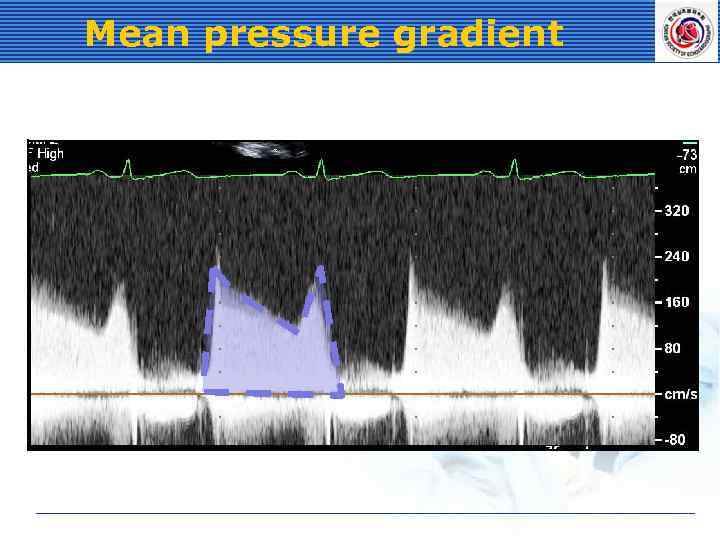 Mean pressure gradient
Mean pressure gradient
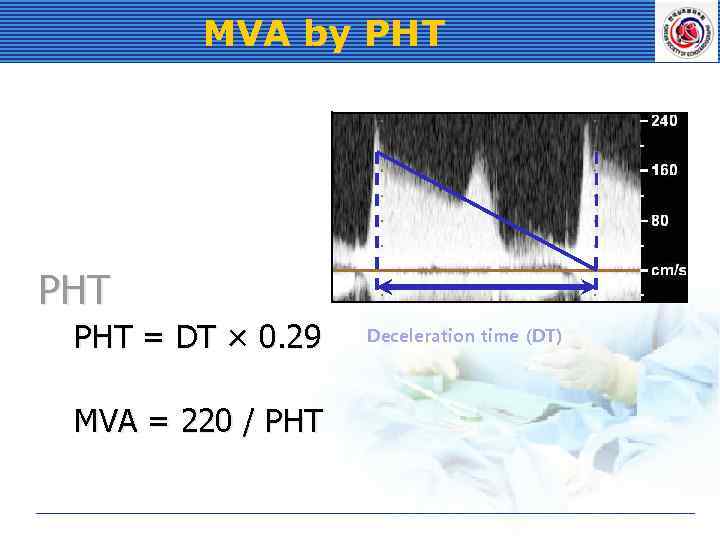 MVA by PHT PHT = DT × 0. 29 MVA = 220 / PHT Deceleration time (DT)
MVA by PHT PHT = DT × 0. 29 MVA = 220 / PHT Deceleration time (DT)
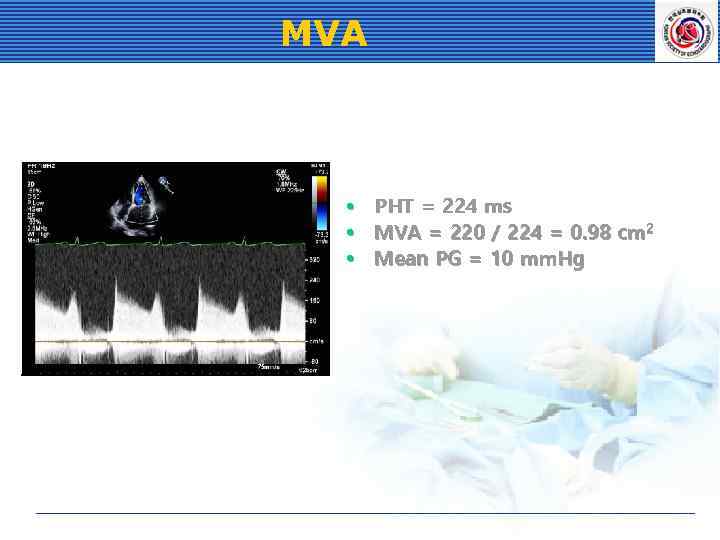 MVA • PHT = 224 ms • MVA = 220 / 224 = 0. 98 cm 2 • Mean PG = 10 mm. Hg
MVA • PHT = 224 ms • MVA = 220 / 224 = 0. 98 cm 2 • Mean PG = 10 mm. Hg
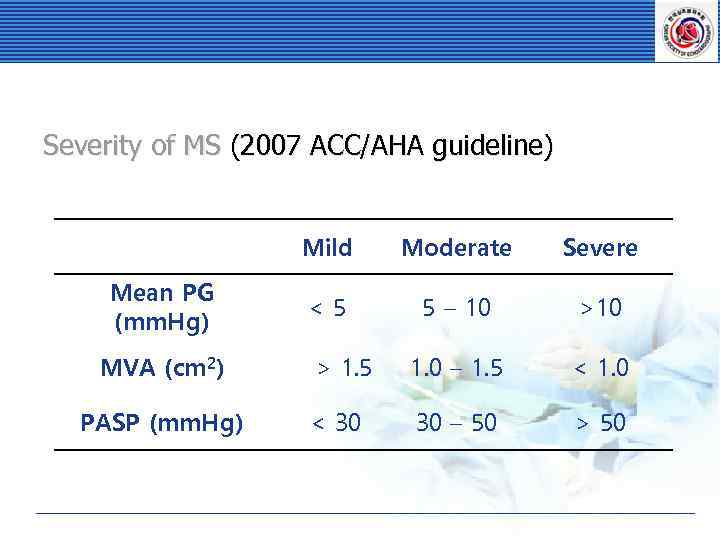 Severity of MS (2007 ACC/AHA guideline) Mild Mean PG (mm. Hg) MVA (cm 2) PASP (mm. Hg) Moderate Severe <5 5 – 10 > 1. 5 1. 0 – 1. 5 < 1. 0 < 30 30 – 50 > 50
Severity of MS (2007 ACC/AHA guideline) Mild Mean PG (mm. Hg) MVA (cm 2) PASP (mm. Hg) Moderate Severe <5 5 – 10 > 1. 5 1. 0 – 1. 5 < 1. 0 < 30 30 – 50 > 50
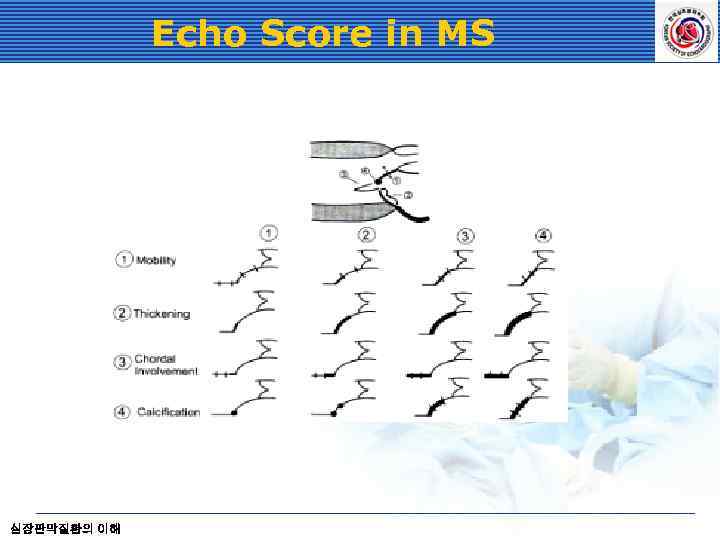 Echo Score in MS 심장판막질환의 이해
Echo Score in MS 심장판막질환의 이해
 Mitral Regurgitation 심장판막질환의 이해
Mitral Regurgitation 심장판막질환의 이해
 Etiology Valvular Myxomatous CT Disease Rheumatic Endocarditis Chordae Annulus Calcification Papillary Muscles CAD (Ischemia, Infarction) Infiltrative disorders LV Dilatation & Functional Prolapse 심장판막질환의 이해
Etiology Valvular Myxomatous CT Disease Rheumatic Endocarditis Chordae Annulus Calcification Papillary Muscles CAD (Ischemia, Infarction) Infiltrative disorders LV Dilatation & Functional Prolapse 심장판막질환의 이해
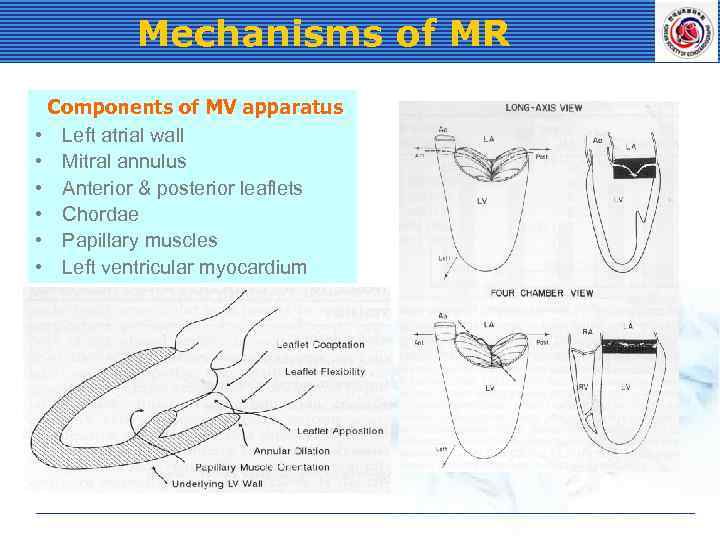 Mechanisms of MR Components of MV apparatus • Left atrial wall • Mitral annulus • Anterior & posterior leaflets • Chordae • Papillary muscles • Left ventricular myocardium
Mechanisms of MR Components of MV apparatus • Left atrial wall • Mitral annulus • Anterior & posterior leaflets • Chordae • Papillary muscles • Left ventricular myocardium
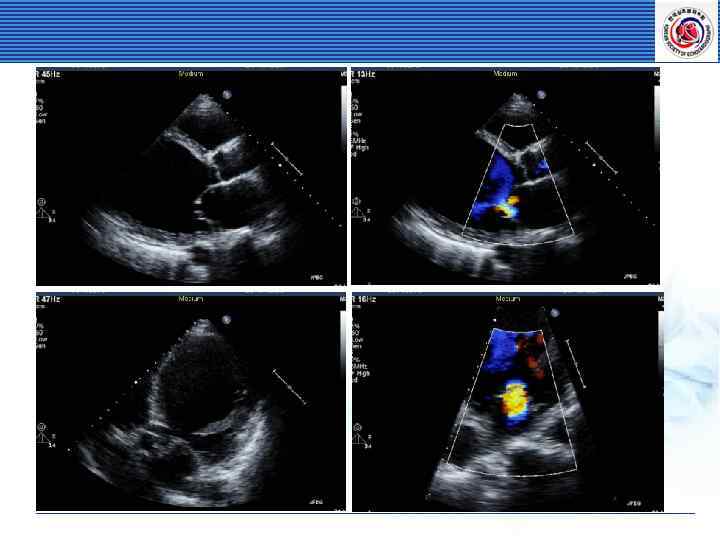
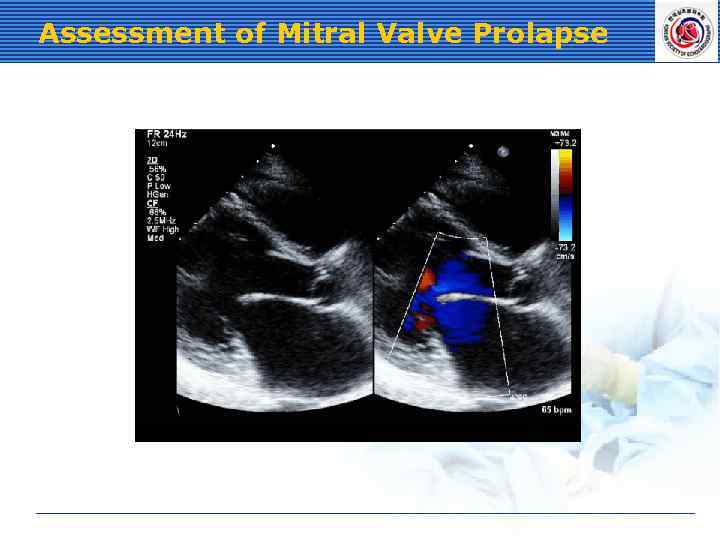 Assessment of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Assessment of Mitral Valve Prolapse
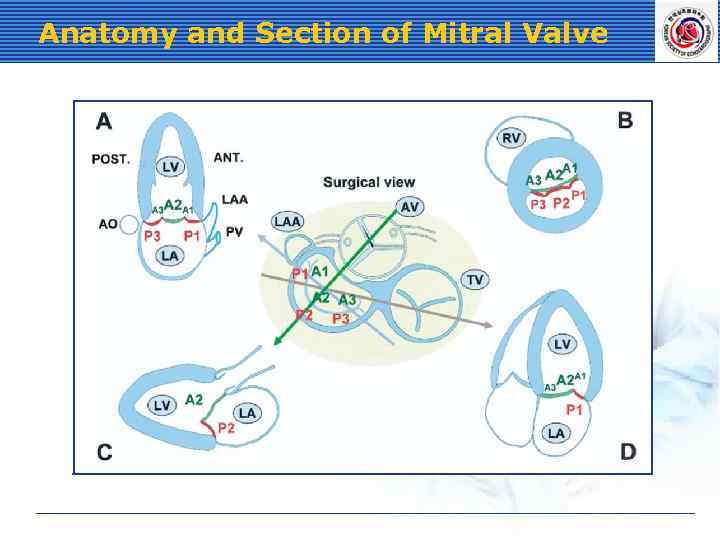 Anatomy and Section of Mitral Valve
Anatomy and Section of Mitral Valve
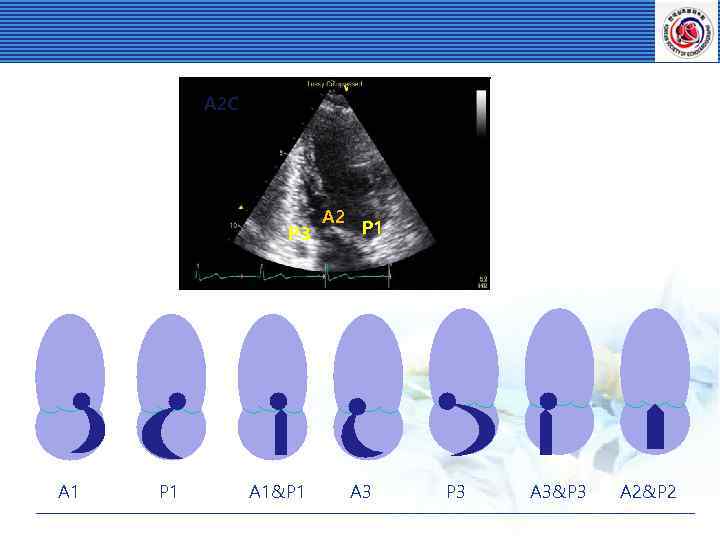 A 2 C P 3 A 1 P 1 A 1&P 1 A 2 P 1 A 3 P 3 A 3&P 3 A 2&P 2
A 2 C P 3 A 1 P 1 A 1&P 1 A 2 P 1 A 3 P 3 A 3&P 3 A 2&P 2
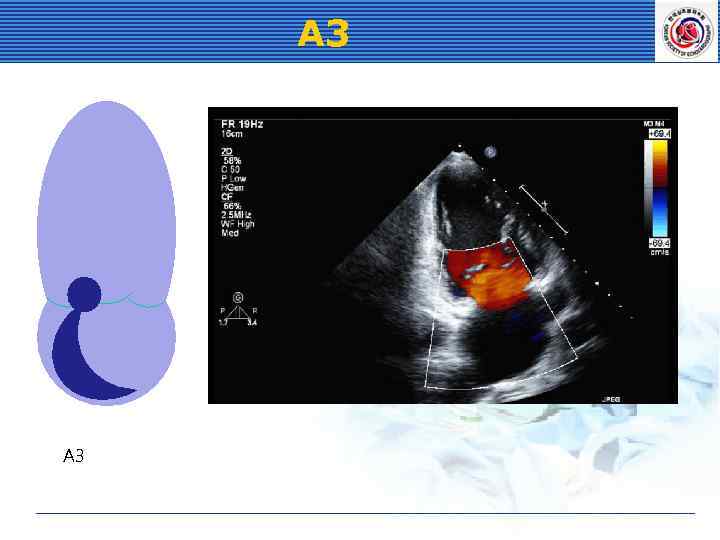 A 3
A 3
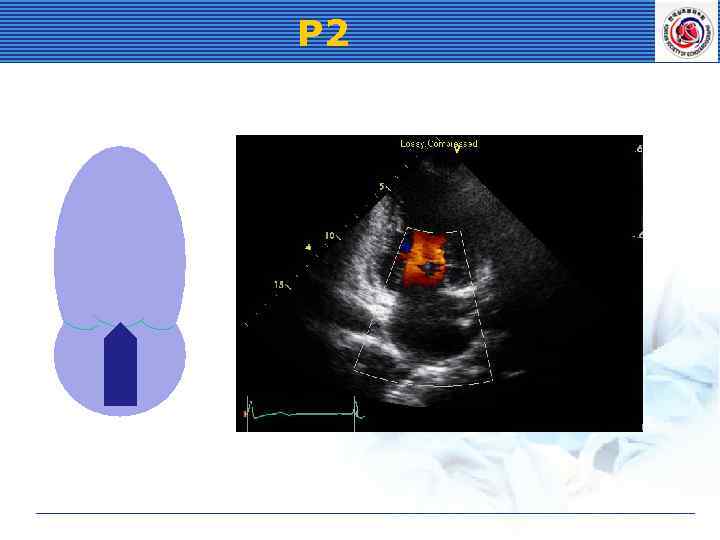 P 2
P 2
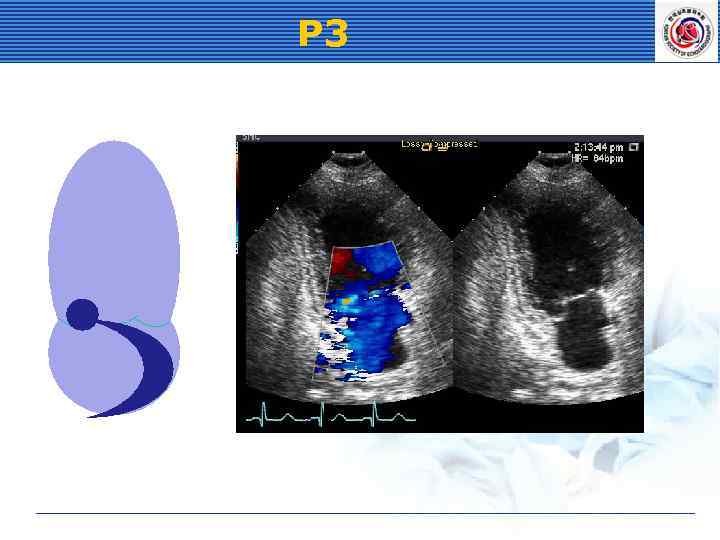 P 3
P 3
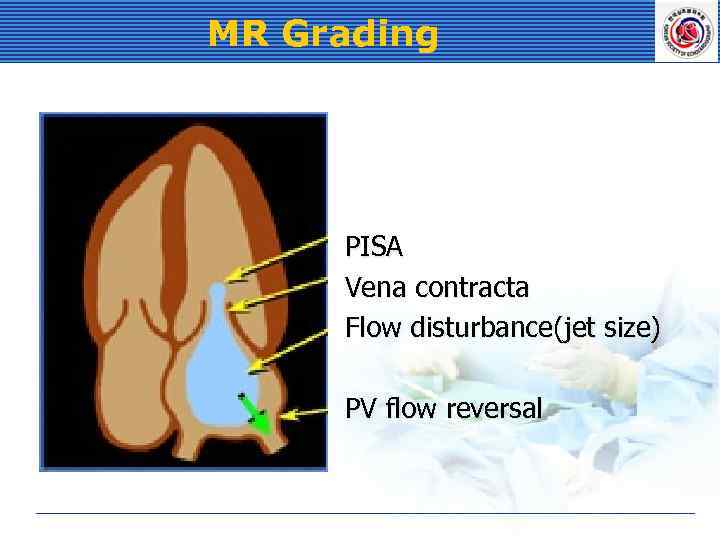 MR Grading PISA Vena contracta Flow disturbance(jet size) PV flow reversal
MR Grading PISA Vena contracta Flow disturbance(jet size) PV flow reversal
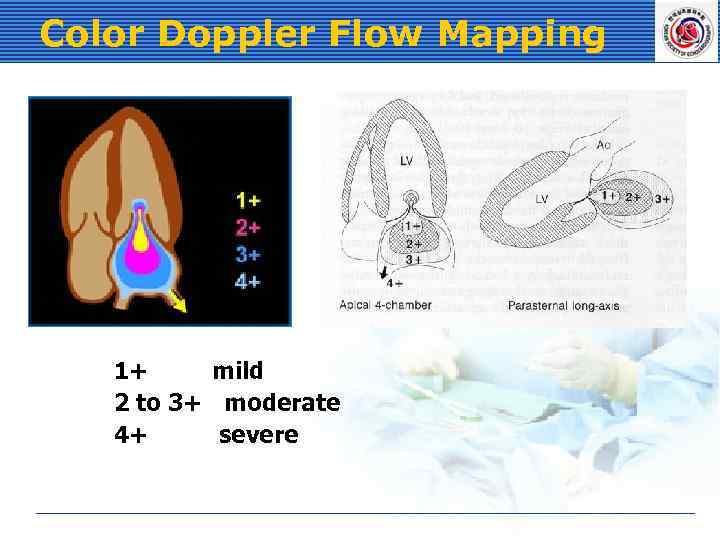 Color Doppler Flow Mapping 1+ mild 2 to 3+ moderate 4+ severe
Color Doppler Flow Mapping 1+ mild 2 to 3+ moderate 4+ severe
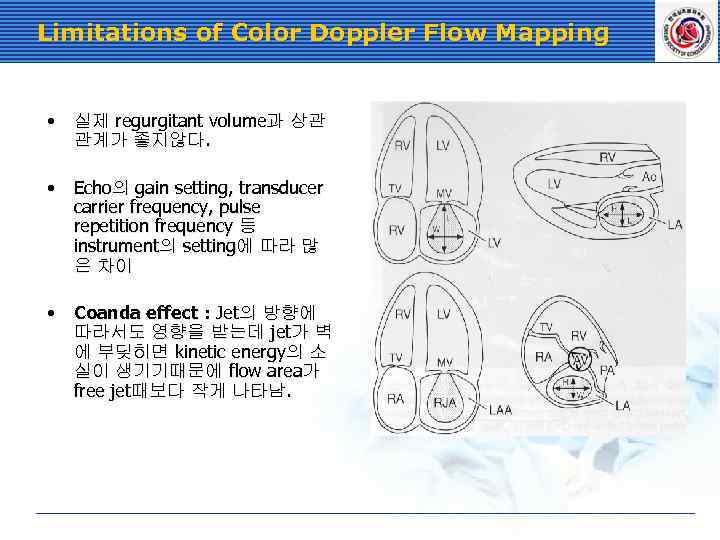 Limitations of Color Doppler Flow Mapping • 실제 regurgitant volume과 상관 관계가 좋지않다. • Echo의 gain setting, transducer carrier frequency, pulse repetition frequency 등 instrument의 setting에 따라 많 은 차이 • Coanda effect : Jet의 방향에 따라서도 영향을 받는데 jet가 벽 에 부딪히면 kinetic energy의 소 실이 생기기때문에 flow area가 free jet때보다 작게 나타남.
Limitations of Color Doppler Flow Mapping • 실제 regurgitant volume과 상관 관계가 좋지않다. • Echo의 gain setting, transducer carrier frequency, pulse repetition frequency 등 instrument의 setting에 따라 많 은 차이 • Coanda effect : Jet의 방향에 따라서도 영향을 받는데 jet가 벽 에 부딪히면 kinetic energy의 소 실이 생기기때문에 flow area가 free jet때보다 작게 나타남.
 Vena Contracta Width § Narrowest cross-sectional area of a jet § Relatively independent of hemodynamic variables and instrument settings § Simple and accurately reflects regurgitant flow § Smaller than anatomical orifice area Proximal flow about 20% convergence § Vena contracta width > 0. 5 cm severe MR
Vena Contracta Width § Narrowest cross-sectional area of a jet § Relatively independent of hemodynamic variables and instrument settings § Simple and accurately reflects regurgitant flow § Smaller than anatomical orifice area Proximal flow about 20% convergence § Vena contracta width > 0. 5 cm severe MR
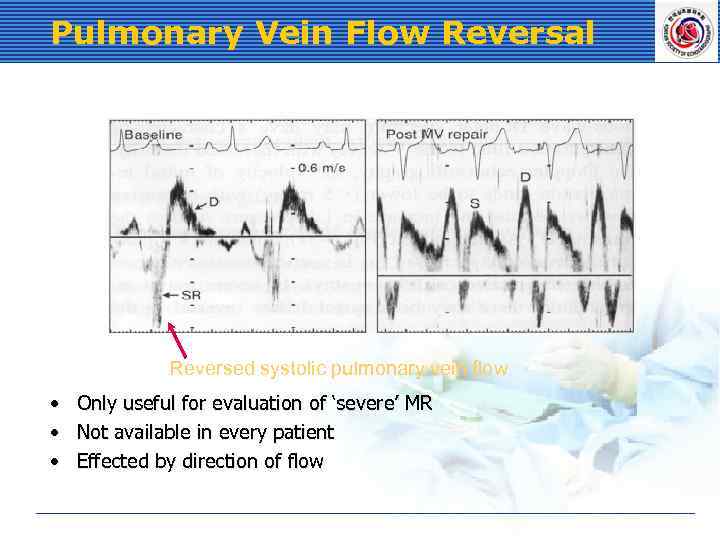 Pulmonary Vein Flow Reversal Reversed systolic pulmonary vein flow • • • Only useful for evaluation of ‘severe’ MR Not available in every patient Effected by direction of flow
Pulmonary Vein Flow Reversal Reversed systolic pulmonary vein flow • • • Only useful for evaluation of ‘severe’ MR Not available in every patient Effected by direction of flow
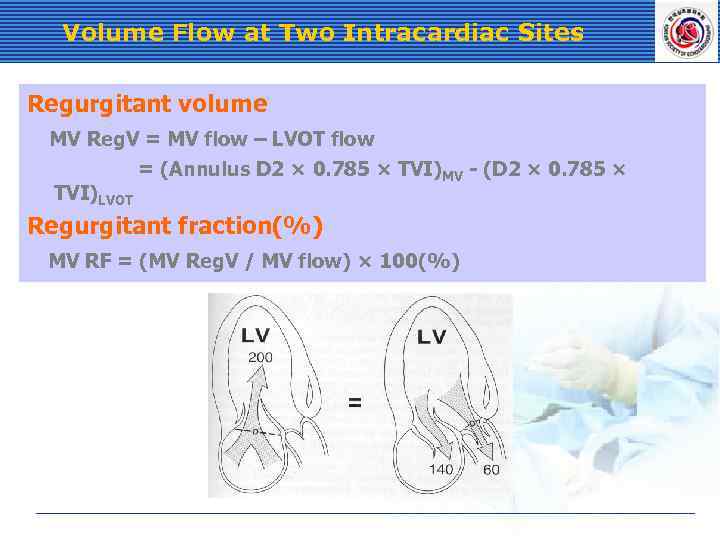 Volume Flow at Two Intracardiac Sites Regurgitant volume MV Reg. V = MV flow – LVOT flow = (Annulus D 2 × 0. 785 × TVI)MV - (D 2 × 0. 785 × TVI)LVOT Regurgitant fraction(%) MV RF = (MV Reg. V / MV flow) × 100(%)
Volume Flow at Two Intracardiac Sites Regurgitant volume MV Reg. V = MV flow – LVOT flow = (Annulus D 2 × 0. 785 × TVI)MV - (D 2 × 0. 785 × TVI)LVOT Regurgitant fraction(%) MV RF = (MV Reg. V / MV flow) × 100(%)
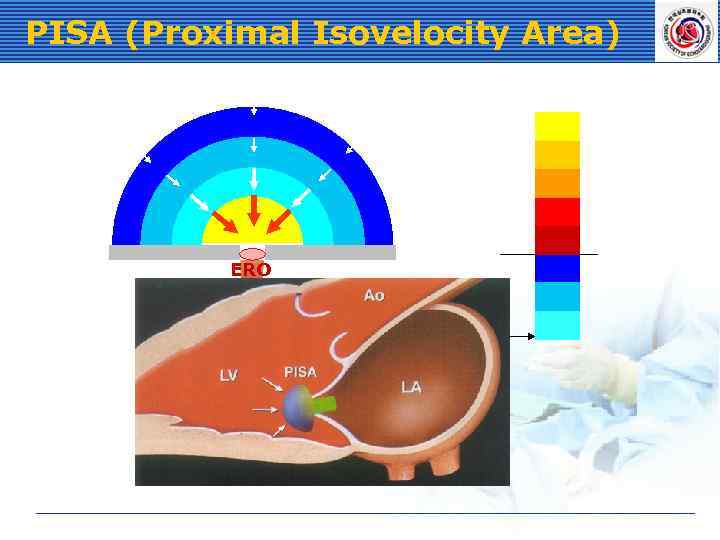 PISA (Proximal Isovelocity Area) ERO Aliasing Velocity (Va)
PISA (Proximal Isovelocity Area) ERO Aliasing Velocity (Va)
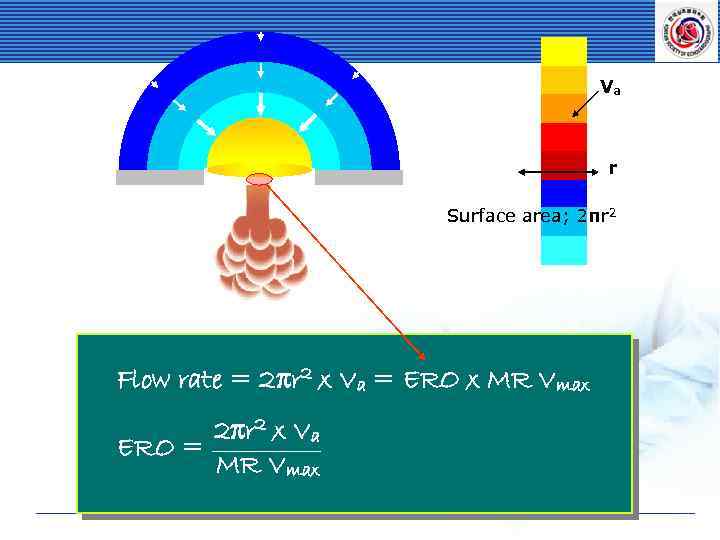 Va r Surface area; 2πr 2 Flow rate = 2πr 2 x Va = ERO x MR Vmax 2πr 2 x Va ERO = MR Vmax
Va r Surface area; 2πr 2 Flow rate = 2πr 2 x Va = ERO x MR Vmax 2πr 2 x Va ERO = MR Vmax
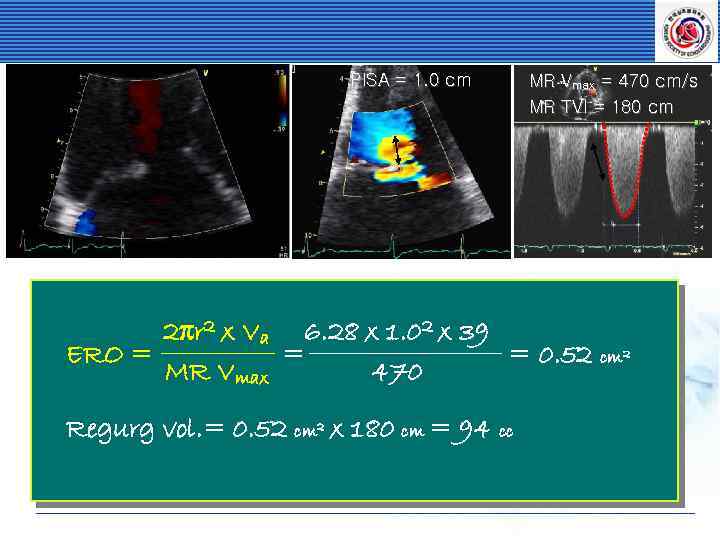 PISA = 1. 0 cm MR Vmax = 470 cm/s MR TVI = 180 cm 2πr 2 x Va 6. 28 x 1. 02 x 39 = = 0. 52 cm 2 ERO = 470 MR Vmax Regurg vol. = 0. 52 cm 2 x 180 cm = 94 cc
PISA = 1. 0 cm MR Vmax = 470 cm/s MR TVI = 180 cm 2πr 2 x Va 6. 28 x 1. 02 x 39 = = 0. 52 cm 2 ERO = 470 MR Vmax Regurg vol. = 0. 52 cm 2 x 180 cm = 94 cc
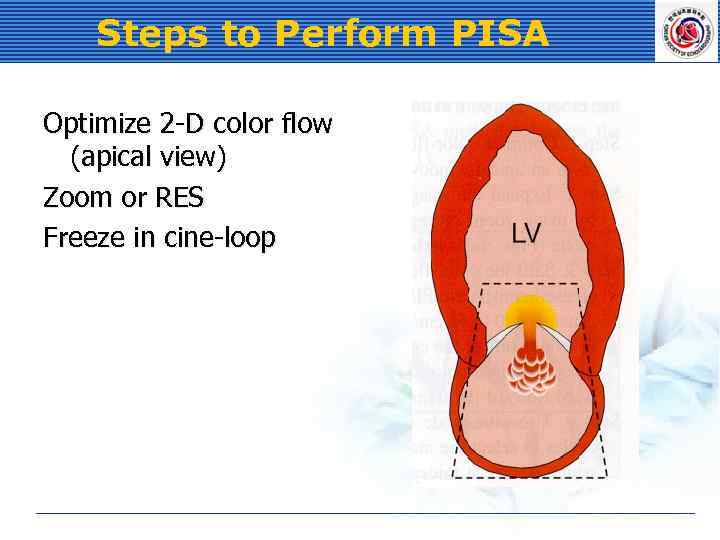 Steps to Perform PISA Optimize 2 -D color flow (apical view) Zoom or RES Freeze in cine-loop
Steps to Perform PISA Optimize 2 -D color flow (apical view) Zoom or RES Freeze in cine-loop
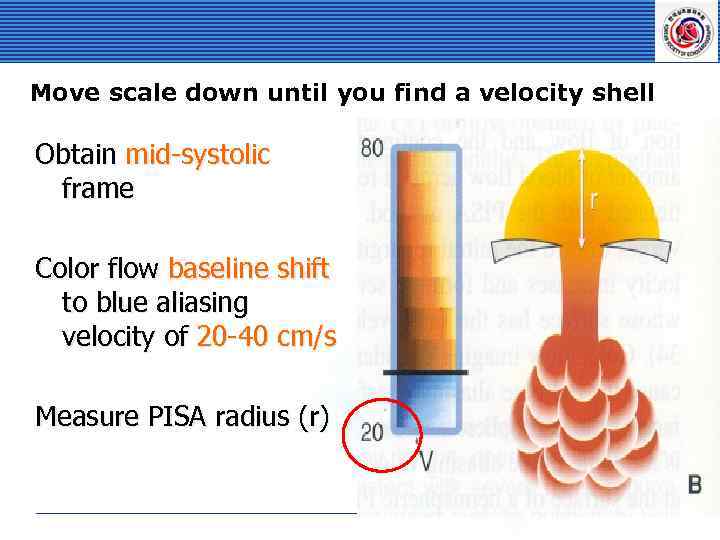 Move scale down until you find a velocity shell Obtain mid-systolic frame Color flow baseline shift to blue aliasing velocity of 20 -40 cm/s Measure PISA radius (r)
Move scale down until you find a velocity shell Obtain mid-systolic frame Color flow baseline shift to blue aliasing velocity of 20 -40 cm/s Measure PISA radius (r)
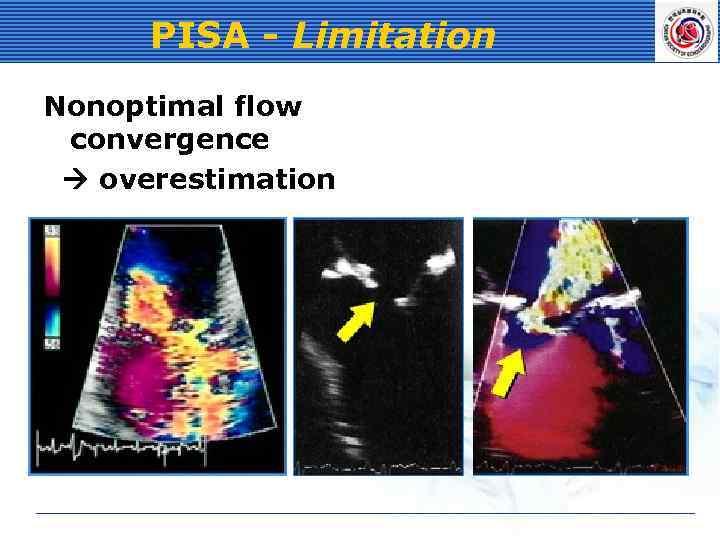 PISA - Limitation Nonoptimal flow convergence overestimation
PISA - Limitation Nonoptimal flow convergence overestimation
 PISA - Limitation PISA can change over Time
PISA - Limitation PISA can change over Time
 PISA - Limitation Nonoptimal flow convergence Phasic changes Eccentric jets suboptimal PISA Interobserver variability Isovelocity surface not always hemisphere
PISA - Limitation Nonoptimal flow convergence Phasic changes Eccentric jets suboptimal PISA Interobserver variability Isovelocity surface not always hemisphere
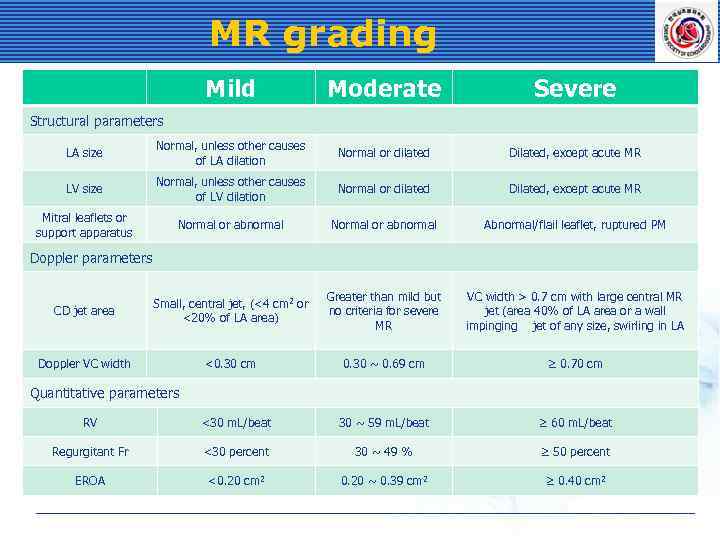 MR grading Mild Moderate Severe LA size Normal, unless other causes of LA dilation Normal or dilated Dilated, except acute MR LV size Normal, unless other causes of LV dilation Normal or dilated Dilated, except acute MR Mitral leaflets or support apparatus Normal or abnormal Abnormal/flail leaflet, ruptured PM CD jet area Small, central jet, (<4 cm 2 or <20% of LA area) Greater than mild but no criteria for severe MR VC width > 0. 7 cm with large central MR jet (area 40% of LA area or a wall impinging jet of any size, swirling in LA Doppler VC width <0. 30 cm 0. 30 ~ 0. 69 cm ≥ 0. 70 cm Structural parameters Doppler parameters Quantitative parameters RV <30 m. L/beat 30 ~ 59 m. L/beat ≥ 60 m. L/beat Regurgitant Fr <30 percent 30 ~ 49 % ≥ 50 percent EROA <0. 20 cm 2 0. 20 ~ 0. 39 cm 2 ≥ 0. 40 cm 2
MR grading Mild Moderate Severe LA size Normal, unless other causes of LA dilation Normal or dilated Dilated, except acute MR LV size Normal, unless other causes of LV dilation Normal or dilated Dilated, except acute MR Mitral leaflets or support apparatus Normal or abnormal Abnormal/flail leaflet, ruptured PM CD jet area Small, central jet, (<4 cm 2 or <20% of LA area) Greater than mild but no criteria for severe MR VC width > 0. 7 cm with large central MR jet (area 40% of LA area or a wall impinging jet of any size, swirling in LA Doppler VC width <0. 30 cm 0. 30 ~ 0. 69 cm ≥ 0. 70 cm Structural parameters Doppler parameters Quantitative parameters RV <30 m. L/beat 30 ~ 59 m. L/beat ≥ 60 m. L/beat Regurgitant Fr <30 percent 30 ~ 49 % ≥ 50 percent EROA <0. 20 cm 2 0. 20 ~ 0. 39 cm 2 ≥ 0. 40 cm 2


