858ce1edf41ff186f822b86630565232.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Securing Wireless LAN using Cisco-based technology Campus Crew Study Group Paul Matijevic Ed Mc. Culloch Peter Mozdzierz Greg Schrader June 2007
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Securing Wireless LAN using Cisco-based technology Campus Crew Study Group Paul Matijevic Ed Mc. Culloch Peter Mozdzierz Greg Schrader June 2007
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Outline • • Scenario Solution Rationale Concerns
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Outline • • Scenario Solution Rationale Concerns
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Scenario • Deploy a wireless LAN infrastructure • Provide coverage for the following areas of a manufacturing environment: – Office – Shop floor • Security goals: – protect data confidentiality and integrity – authenticate and authorize each user – provide scalability and central manageability
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Scenario • Deploy a wireless LAN infrastructure • Provide coverage for the following areas of a manufacturing environment: – Office – Shop floor • Security goals: – protect data confidentiality and integrity – authenticate and authorize each user – provide scalability and central manageability
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • Hardware purchased: – 8 Cisco 1200 Access Points (enterprise grade) • Assigned different channels to minimize interference • Assigning use of only channels 1, 6, and 11 minimizes interference by maximizing distance between carrier frequencies – Cisco 802. 11 b/g computer hardware • PCI adapters and PCMCIA cards
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • Hardware purchased: – 8 Cisco 1200 Access Points (enterprise grade) • Assigned different channels to minimize interference • Assigning use of only channels 1, 6, and 11 minimizes interference by maximizing distance between carrier frequencies – Cisco 802. 11 b/g computer hardware • PCI adapters and PCMCIA cards
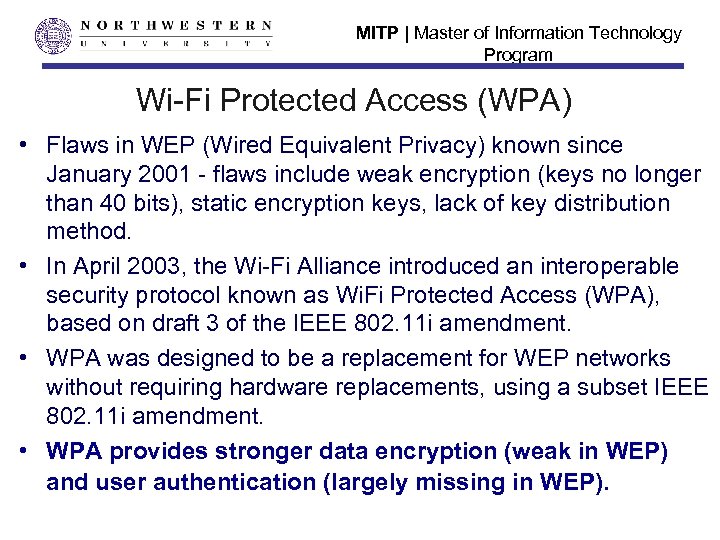
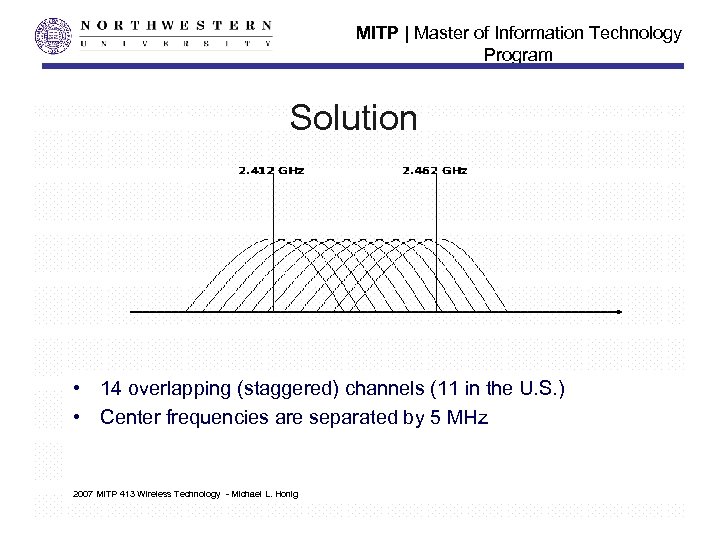 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • 14 overlapping (staggered) channels (11 in the U. S. ) • Center frequencies are separated by 5 MHz 2007 MITP 413 Wireless Technology - Michael L. Honig
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • 14 overlapping (staggered) channels (11 in the U. S. ) • Center frequencies are separated by 5 MHz 2007 MITP 413 Wireless Technology - Michael L. Honig
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • Security considerations: – Encryption Algorithm mechanism – Message Integrity mechanism – Authentication Framework mechanism – Authentication Algorithm mechanism
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • Security considerations: – Encryption Algorithm mechanism – Message Integrity mechanism – Authentication Framework mechanism – Authentication Algorithm mechanism
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) • Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) known since January 2001 - flaws include weak encryption (keys no longer than 40 bits), static encryption keys, lack of key distribution method. • In April 2003, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced an interoperable security protocol known as Wi. Fi Protected Access (WPA), based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802. 11 i amendment. • WPA was designed to be a replacement for WEP networks without requiring hardware replacements, using a subset IEEE 802. 11 i amendment. • WPA provides stronger data encryption (weak in WEP) and user authentication (largely missing in WEP).
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) • Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) known since January 2001 - flaws include weak encryption (keys no longer than 40 bits), static encryption keys, lack of key distribution method. • In April 2003, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced an interoperable security protocol known as Wi. Fi Protected Access (WPA), based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802. 11 i amendment. • WPA was designed to be a replacement for WEP networks without requiring hardware replacements, using a subset IEEE 802. 11 i amendment. • WPA provides stronger data encryption (weak in WEP) and user authentication (largely missing in WEP).
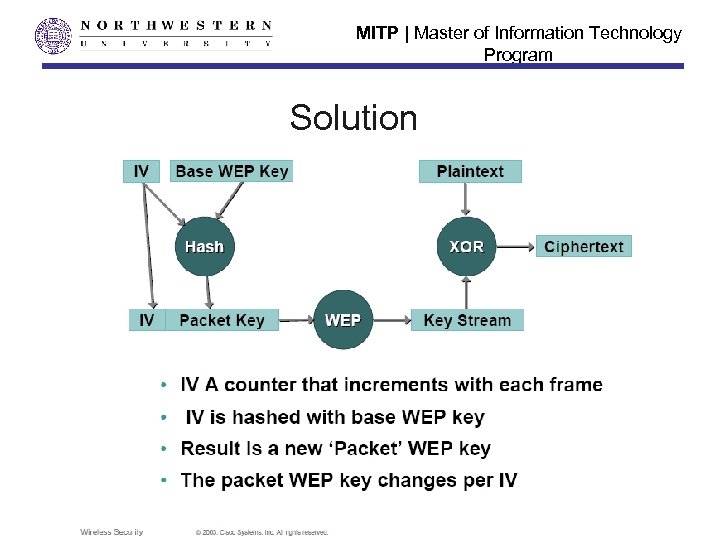
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA Security Enhancements • WPA includes Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and 802. 1 x mechanisms. • The combination of these two mechanisms provides dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication • TKIP adds the following strengths to WEP: – 48 -bit initialization vectors, use one-way hash function instead of XOR – Per-packet key construction and distribution: WPA automatically generates a new unique encryption key periodically for each client. In fact, WPA uses a unique key for each 802. 11 frame. This avoids the same key staying in use for weeks or months as they do with WEP – Message integrity code: guard against forgery attacks.
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA Security Enhancements • WPA includes Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and 802. 1 x mechanisms. • The combination of these two mechanisms provides dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication • TKIP adds the following strengths to WEP: – 48 -bit initialization vectors, use one-way hash function instead of XOR – Per-packet key construction and distribution: WPA automatically generates a new unique encryption key periodically for each client. In fact, WPA uses a unique key for each 802. 11 frame. This avoids the same key staying in use for weeks or months as they do with WEP – Message integrity code: guard against forgery attacks.
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Message Integrity Solution • • • Using TKIP-MIC (message integrity check) MIC ensures data frames have not been tampered with and authenticity of source addresses – Also prevents WEP reuse 8 byte field placed between data portion of 802. 11 frame and 4 byte ICV (integrity Check Value) protecting both payload and header
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Message Integrity Solution • • • Using TKIP-MIC (message integrity check) MIC ensures data frames have not been tampered with and authenticity of source addresses – Also prevents WEP reuse 8 byte field placed between data portion of 802. 11 frame and 4 byte ICV (integrity Check Value) protecting both payload and header
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA 2 • In July 2004, the IEEE approved the full IEEE 802. 11 i specification, which was quickly followed by a new interoperability testing certification from the Wi. Fi Alliance known as WPA 2. • Strong encryption and authentication for infrastructure and adhoc networks (WPA 1 is limited to infrastructure networks) • Support for the CCMP (Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol) encryption mechanism based on the AES as an alternative to the TKIP protocol – AES is the equivalent of the RC 4 algorithm used by WPA. – CCMP is the equivalent of TKIP in WPA. Changing even one bit in a message produces a totally different result. CCMP utilizes 128 -bit keys, with a 48 -bit initialization vector (IV) for replay detection
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA 2 • In July 2004, the IEEE approved the full IEEE 802. 11 i specification, which was quickly followed by a new interoperability testing certification from the Wi. Fi Alliance known as WPA 2. • Strong encryption and authentication for infrastructure and adhoc networks (WPA 1 is limited to infrastructure networks) • Support for the CCMP (Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol) encryption mechanism based on the AES as an alternative to the TKIP protocol – AES is the equivalent of the RC 4 algorithm used by WPA. – CCMP is the equivalent of TKIP in WPA. Changing even one bit in a message produces a totally different result. CCMP utilizes 128 -bit keys, with a 48 -bit initialization vector (IV) for replay detection
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA 2 • TKIP was designed as an interim solution for wireless security, with the goal of providing sufficient security for 5 years while organizations transitioned to the full IEEE 802. 11 i security mechanism. • As of March 2006, the WPA 2 certification became mandatory for all new equipment certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance, ensuring that any reasonably modern hardware will support both WPA 1 and WPA 2.
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program WPA 2 • TKIP was designed as an interim solution for wireless security, with the goal of providing sufficient security for 5 years while organizations transitioned to the full IEEE 802. 11 i security mechanism. • As of March 2006, the WPA 2 certification became mandatory for all new equipment certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance, ensuring that any reasonably modern hardware will support both WPA 1 and WPA 2.
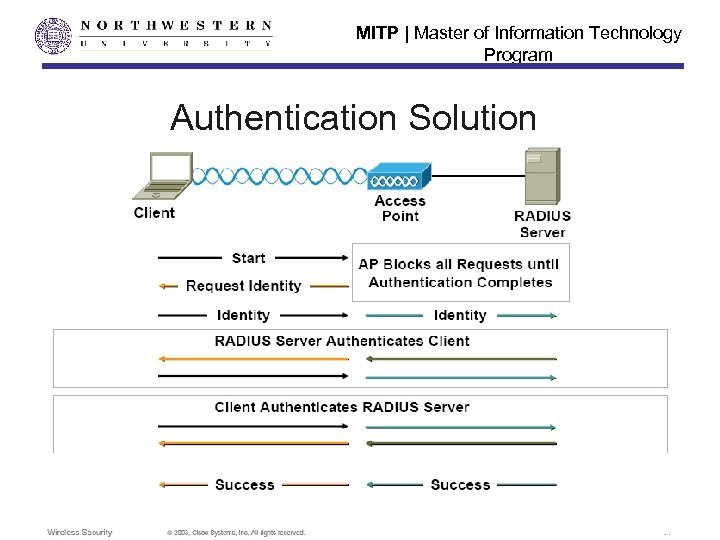
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution • Facilitates authentication messages sent between AP’s and clients • 802. 1 x authentication used – Protocol resides at layer 2 - supports EAP (extensible authentication protocol) – Provides centralized policy control with timeout triggers • AP’s blocked until authentication process complete • RADIUS (Remote Access Dial-In User Service) server used – Low deployment complexity
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution • Facilitates authentication messages sent between AP’s and clients • 802. 1 x authentication used – Protocol resides at layer 2 - supports EAP (extensible authentication protocol) – Provides centralized policy control with timeout triggers • AP’s blocked until authentication process complete • RADIUS (Remote Access Dial-In User Service) server used – Low deployment complexity
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution • Authentication Algorithm – Validates each users network access credentials – RADIUS server stores strong passwords • 25 alphanumeric characters • Non-dictionary phrases – Passwords encrypted and stored in users wireless profiles – Cisco’s LEAP (lightweight extensible authentication protocol) used • Allows for clients to re-authenticate frequently
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Authentication Solution • Authentication Algorithm – Validates each users network access credentials – RADIUS server stores strong passwords • 25 alphanumeric characters • Non-dictionary phrases – Passwords encrypted and stored in users wireless profiles – Cisco’s LEAP (lightweight extensible authentication protocol) used • Allows for clients to re-authenticate frequently
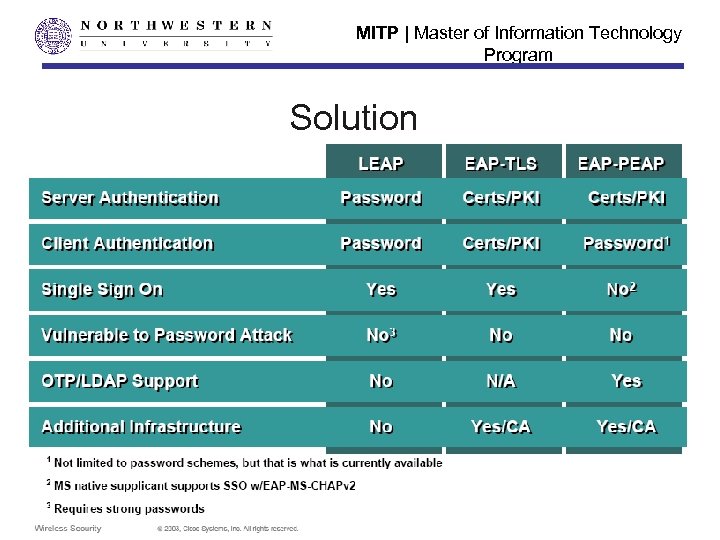 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • • Additional security – MAC address authentication – Valid addresses authenticated against list in RADIUS server – AP’s also possess a copy of users, passwords and valid MAC addresses MAC and IP address spoofing is very difficult with 802. 11 X implementations
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution • • Additional security – MAC address authentication – Valid addresses authenticated against list in RADIUS server – AP’s also possess a copy of users, passwords and valid MAC addresses MAC and IP address spoofing is very difficult with 802. 11 X implementations
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Concerns • LEAP allows clients to acquire a new WEP key that does not expire - could be hacked – Considered minimal risk in this case • Employees installing their own WLAN devices – AP’s configured to collect rogue SSID info • Do. S attacks could occur against AP’s – Alarms configured to observe flooding behavior – Logs track details of usage and are reviewed regularly – Telnet disabled in favor of SSH
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Concerns • LEAP allows clients to acquire a new WEP key that does not expire - could be hacked – Considered minimal risk in this case • Employees installing their own WLAN devices – AP’s configured to collect rogue SSID info • Do. S attacks could occur against AP’s – Alarms configured to observe flooding behavior – Logs track details of usage and are reviewed regularly – Telnet disabled in favor of SSH
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Concerns • Wireless IDS is not installed – WIDS understands data level patterns / signatures (like wired IDS) and also RF signatures of attacks – Current hardware does not include IDS • At the time of purchase, software IDS was not an option – Newer versions of Cisco AP’s include IDS capability • AP’s are upgradeable (as of 2005) • Firmware upgrade would install software wireless IDS
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Concerns • Wireless IDS is not installed – WIDS understands data level patterns / signatures (like wired IDS) and also RF signatures of attacks – Current hardware does not include IDS • At the time of purchase, software IDS was not an option – Newer versions of Cisco AP’s include IDS capability • AP’s are upgradeable (as of 2005) • Firmware upgrade would install software wireless IDS
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Questions? Other than Ron…
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Questions? Other than Ron…
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Other EAP • EAP-MD 5 • LEAP (Lightweight EAP) – CISCO authentication that provides mutual authentication and dynamic WEP key generation • EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security) – offers full authentication consistent with PKI public/private keys, PKI and digital certificates – Needs client certificate in order to authenticate client – Users login from different computers in coffee shops – Users are more familiar with the idea of passwords. Certificates may require some training.
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Other EAP • EAP-MD 5 • LEAP (Lightweight EAP) – CISCO authentication that provides mutual authentication and dynamic WEP key generation • EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security) – offers full authentication consistent with PKI public/private keys, PKI and digital certificates – Needs client certificate in order to authenticate client – Users login from different computers in coffee shops – Users are more familiar with the idea of passwords. Certificates may require some training.
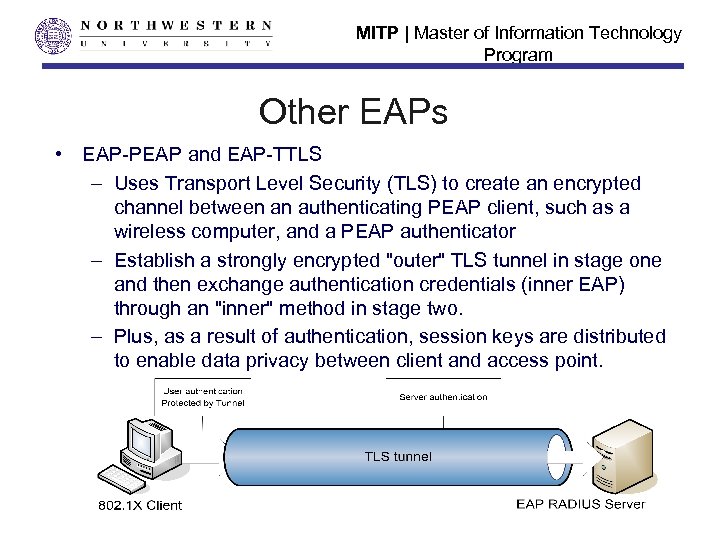 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Other EAPs • EAP-PEAP and EAP-TTLS – Uses Transport Level Security (TLS) to create an encrypted channel between an authenticating PEAP client, such as a wireless computer, and a PEAP authenticator – Establish a strongly encrypted "outer" TLS tunnel in stage one and then exchange authentication credentials (inner EAP) through an "inner" method in stage two. – Plus, as a result of authentication, session keys are distributed to enable data privacy between client and access point.
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Other EAPs • EAP-PEAP and EAP-TTLS – Uses Transport Level Security (TLS) to create an encrypted channel between an authenticating PEAP client, such as a wireless computer, and a PEAP authenticator – Establish a strongly encrypted "outer" TLS tunnel in stage one and then exchange authentication credentials (inner EAP) through an "inner" method in stage two. – Plus, as a result of authentication, session keys are distributed to enable data privacy between client and access point.
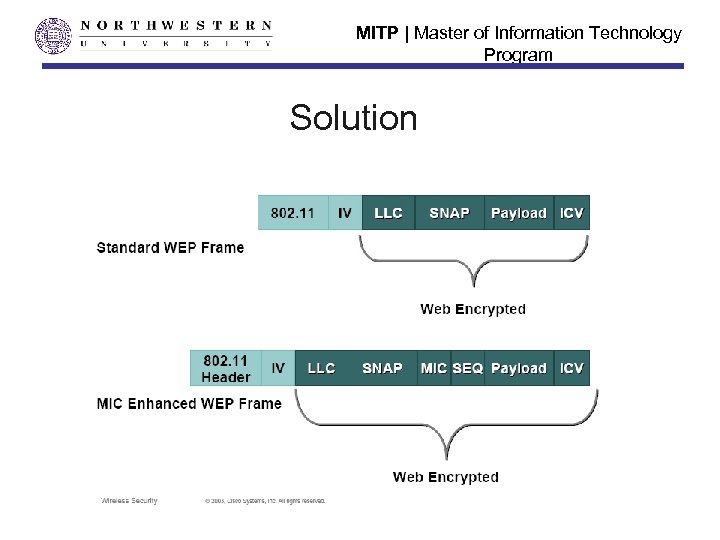 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution
 MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution Rationale • WEP encryption and static-WEP key vulnerabilities are patched with 802. 11 X protocols • Authentication vulnerabilities minimized by use of strong, non-dictionary passwords • Cisco TKIP protocol preferred over WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) – TKIP session key rotation is dynamic – Changes every 4 hours and 40 minutes
MITP | Master of Information Technology Program Solution Rationale • WEP encryption and static-WEP key vulnerabilities are patched with 802. 11 X protocols • Authentication vulnerabilities minimized by use of strong, non-dictionary passwords • Cisco TKIP protocol preferred over WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) – TKIP session key rotation is dynamic – Changes every 4 hours and 40 minutes


