9 class MITOSIS & MEIOSIS.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31

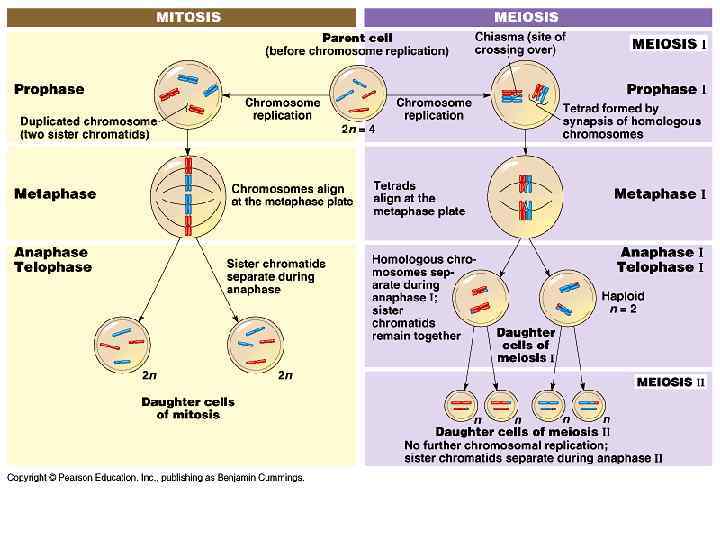
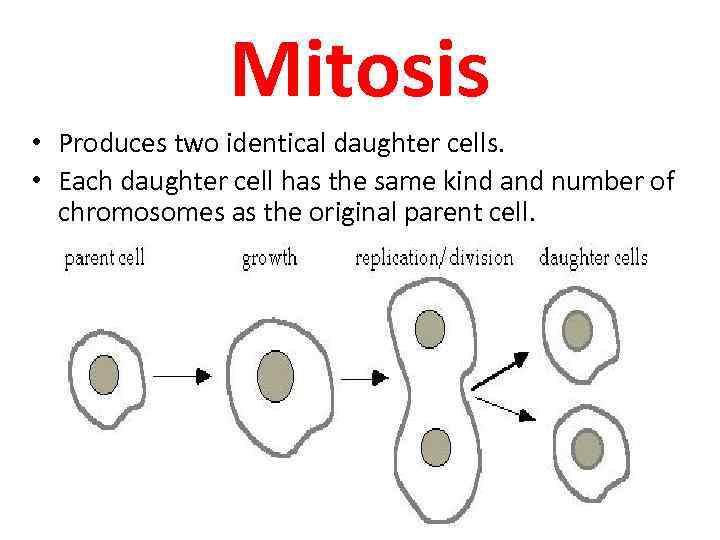 Mitosis • Produces two identical daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has the same kind and number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
Mitosis • Produces two identical daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has the same kind and number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
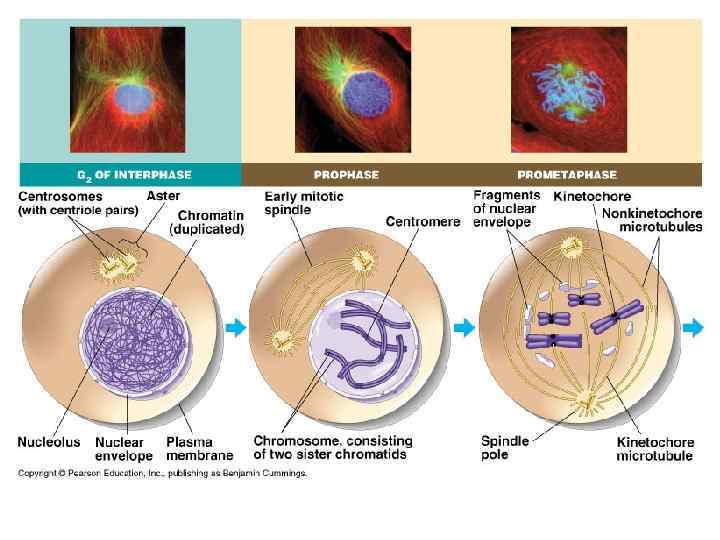
 The Stages of Mitosis § Prophase § The cell’s chromatin tightens. § The chromosome consist of two sister chromatids, which are attached at the centromere. § Two centrioles move to opposite poles of cell, and start to form spindle fibers (consist of microtubules).
The Stages of Mitosis § Prophase § The cell’s chromatin tightens. § The chromosome consist of two sister chromatids, which are attached at the centromere. § Two centrioles move to opposite poles of cell, and start to form spindle fibers (consist of microtubules).
 Cellular Reproduction § The nuclear envelope seems to disappear. § Spindle fibers attach to the sister chromatids at the kinetochore (region in centromere).
Cellular Reproduction § The nuclear envelope seems to disappear. § Spindle fibers attach to the sister chromatids at the kinetochore (region in centromere).
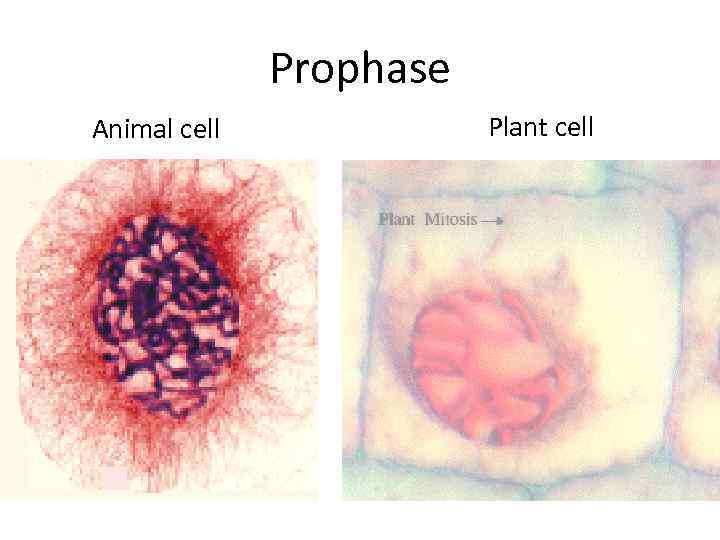 Prophase Animal cell Plant cell
Prophase Animal cell Plant cell
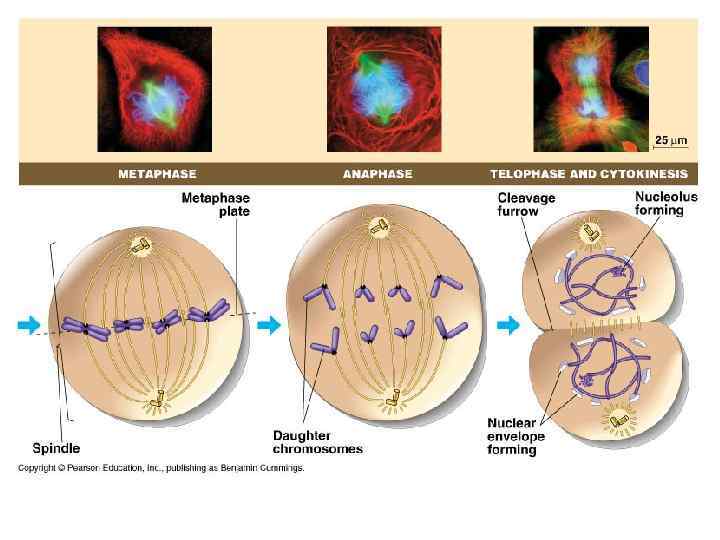
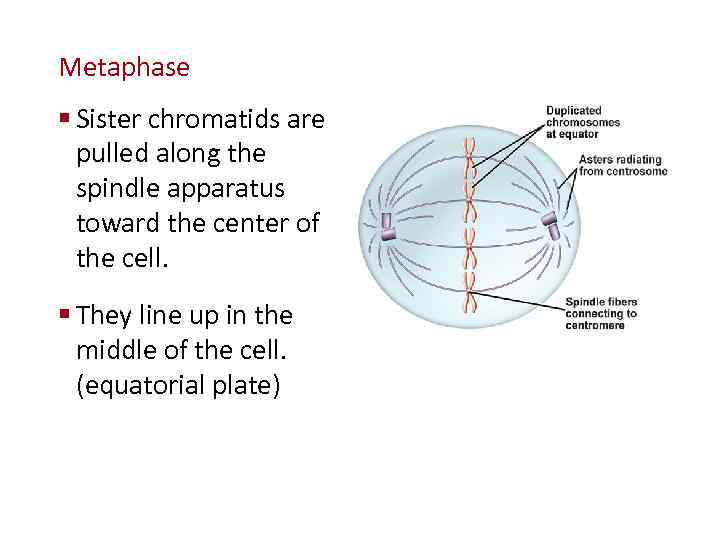 Cellular Reproduction Metaphase § Sister chromatids are pulled along the spindle apparatus toward the center of the cell. § They line up in the middle of the cell. (equatorial plate)
Cellular Reproduction Metaphase § Sister chromatids are pulled along the spindle apparatus toward the center of the cell. § They line up in the middle of the cell. (equatorial plate)
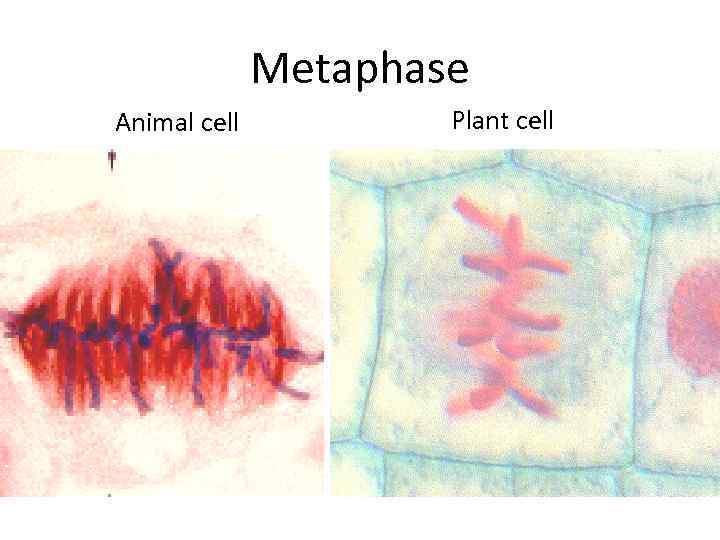 Metaphase Animal cell Plant cell
Metaphase Animal cell Plant cell
 Cellular Reproduction Anaphase § The microtubules of the spindle apparatus begin to shorten. § The sister chromatids separate. § The chromosomes move toward the poles of the cell.
Cellular Reproduction Anaphase § The microtubules of the spindle apparatus begin to shorten. § The sister chromatids separate. § The chromosomes move toward the poles of the cell.
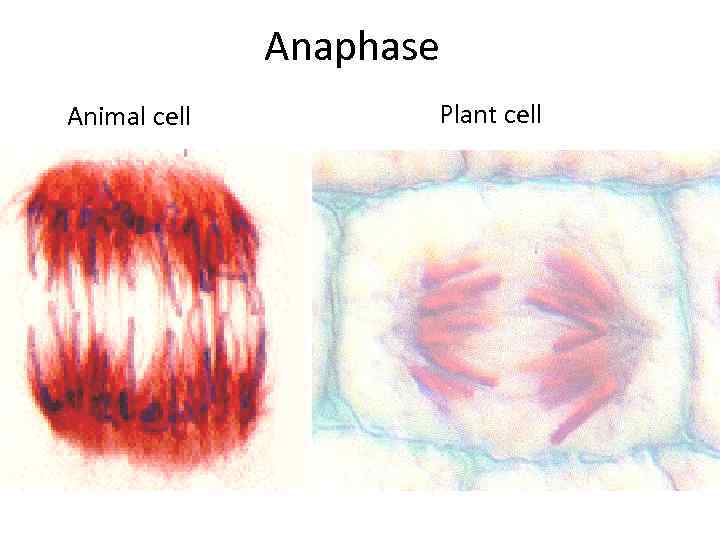 Anaphase Animal cell Plant cell
Anaphase Animal cell Plant cell
 Cellular Reproduction Telophase § The chromosomes arrive at the poles and begin to relax. § Two new nuclear membranes begin to form and the nucleoli reappear. § The spindle apparatus disassembles.
Cellular Reproduction Telophase § The chromosomes arrive at the poles and begin to relax. § Two new nuclear membranes begin to form and the nucleoli reappear. § The spindle apparatus disassembles.
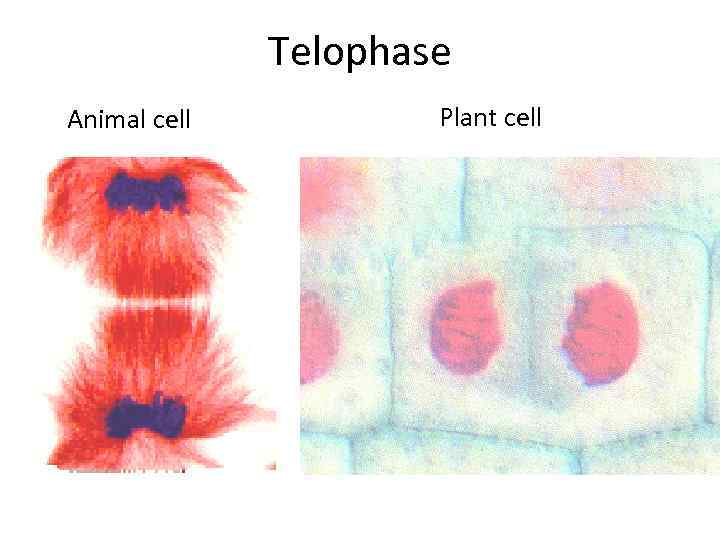 Telophase Animal cell Plant cell
Telophase Animal cell Plant cell
 Cellular Reproduction Cytokinesis § In animal cells, microfilaments constrict, or pinch, the cytoplasm. § In plant cells, a new structure, called a cell plate, forms.
Cellular Reproduction Cytokinesis § In animal cells, microfilaments constrict, or pinch, the cytoplasm. § In plant cells, a new structure, called a cell plate, forms.
 MEIOSIS
MEIOSIS
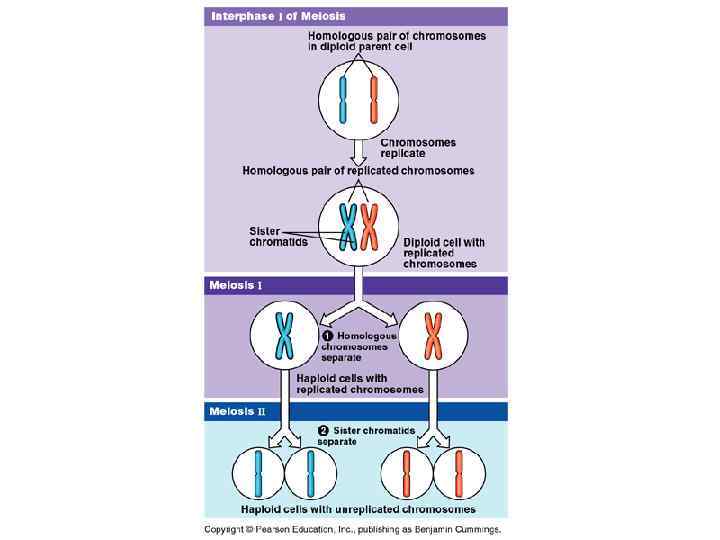
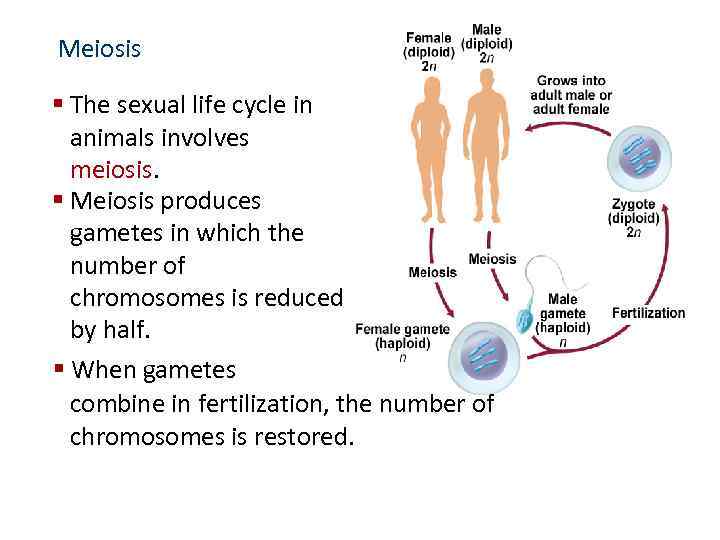 Meiosis § The sexual life cycle in animals involves meiosis. § Meiosis produces gametes in which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. § When gametes combine in fertilization, the number of chromosomes is restored.
Meiosis § The sexual life cycle in animals involves meiosis. § Meiosis produces gametes in which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. § When gametes combine in fertilization, the number of chromosomes is restored.
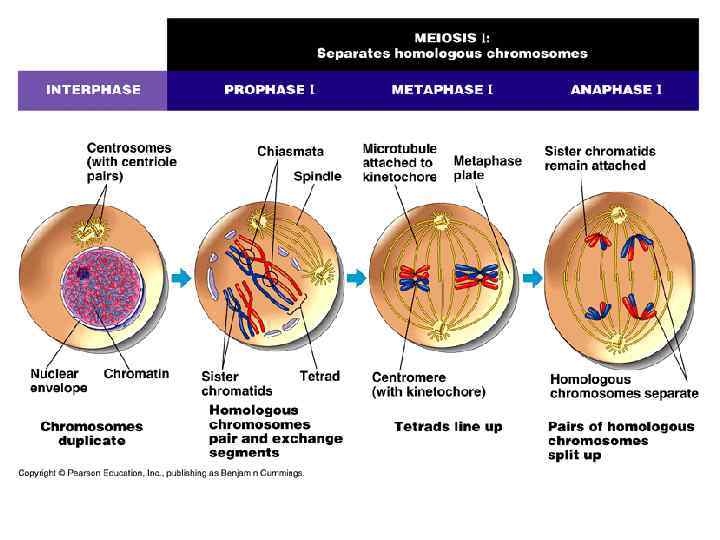
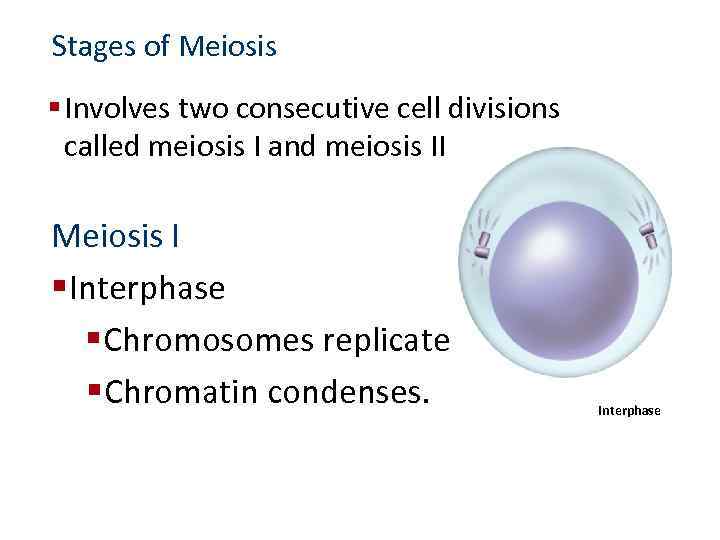 Stages of Meiosis § Involves two consecutive cell divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II Meiosis I § Interphase § Chromosomes replicate. § Chromatin condenses. Interphase
Stages of Meiosis § Involves two consecutive cell divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II Meiosis I § Interphase § Chromosomes replicate. § Chromatin condenses. Interphase
 Meiosis I § Prophase I § Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs. § Each chromosome consists of two chromatids. § The nuclear envelope breaks down. § Spindles form. Prophase I
Meiosis I § Prophase I § Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs. § Each chromosome consists of two chromatids. § The nuclear envelope breaks down. § Spindles form. Prophase I
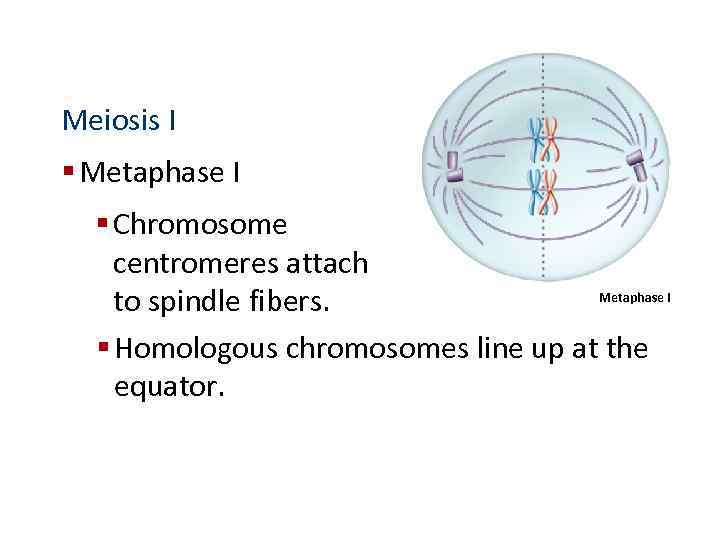 Meiosis I § Metaphase I § Chromosome centromeres attach Metaphase I to spindle fibers. § Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator.
Meiosis I § Metaphase I § Chromosome centromeres attach Metaphase I to spindle fibers. § Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator.
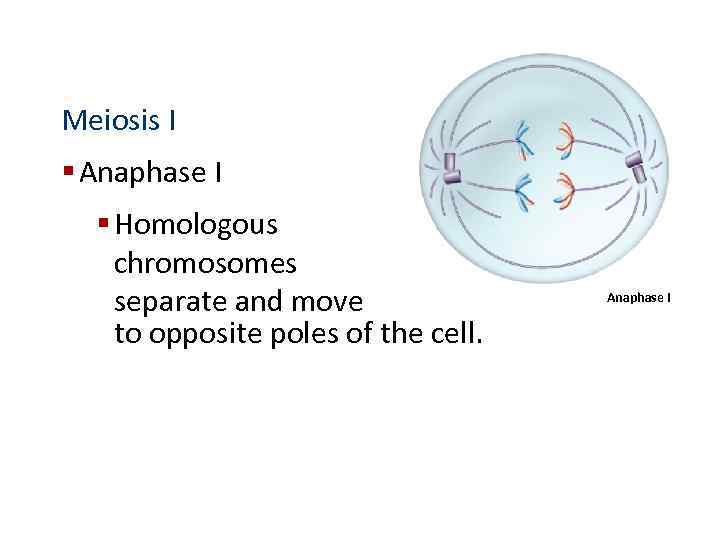 Meiosis I § Anaphase I § Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Anaphase I
Meiosis I § Anaphase I § Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Anaphase I
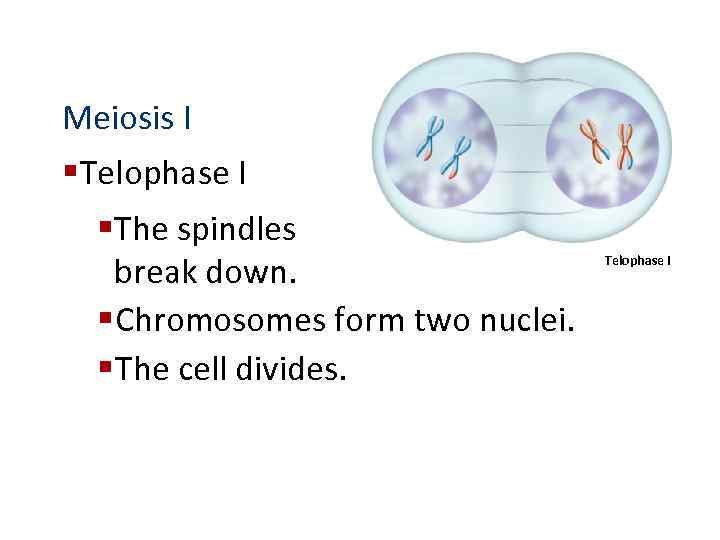 Meiosis I § Telophase I § The spindles break down. § Chromosomes form two nuclei. § The cell divides. Telophase I
Meiosis I § Telophase I § The spindles break down. § Chromosomes form two nuclei. § The cell divides. Telophase I
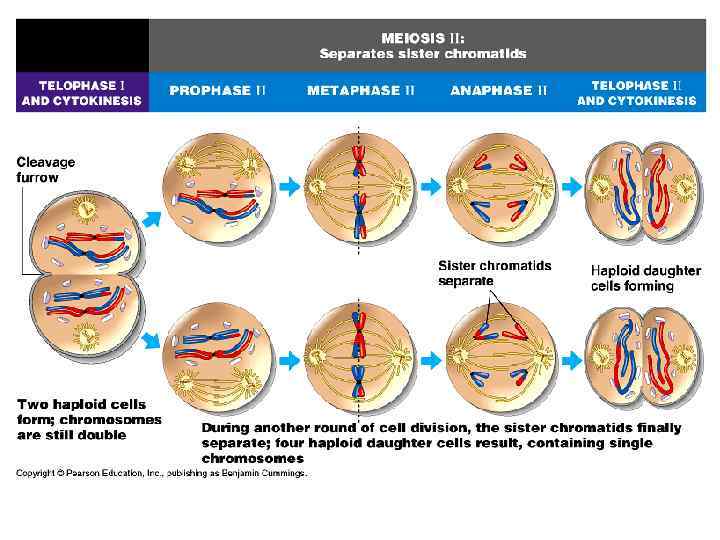
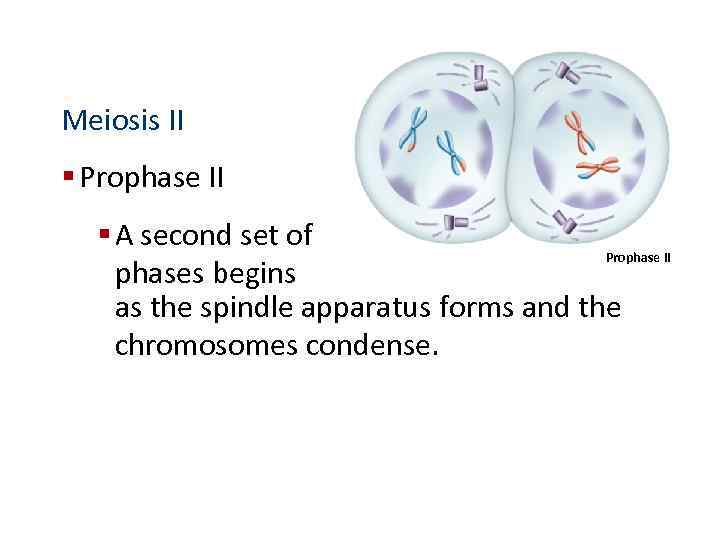 Meiosis II § Prophase II § A second set of Prophase II phases begins as the spindle apparatus forms and the chromosomes condense.
Meiosis II § Prophase II § A second set of Prophase II phases begins as the spindle apparatus forms and the chromosomes condense.
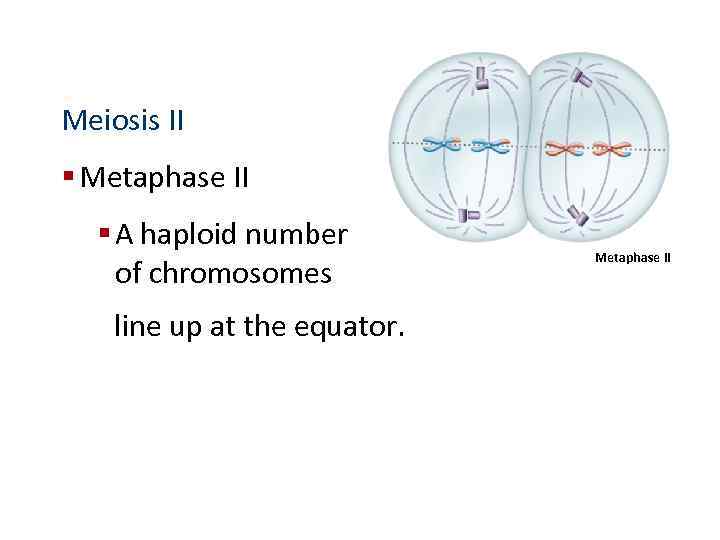 Meiosis II § Metaphase II § A haploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. Metaphase II
Meiosis II § Metaphase II § A haploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. Metaphase II
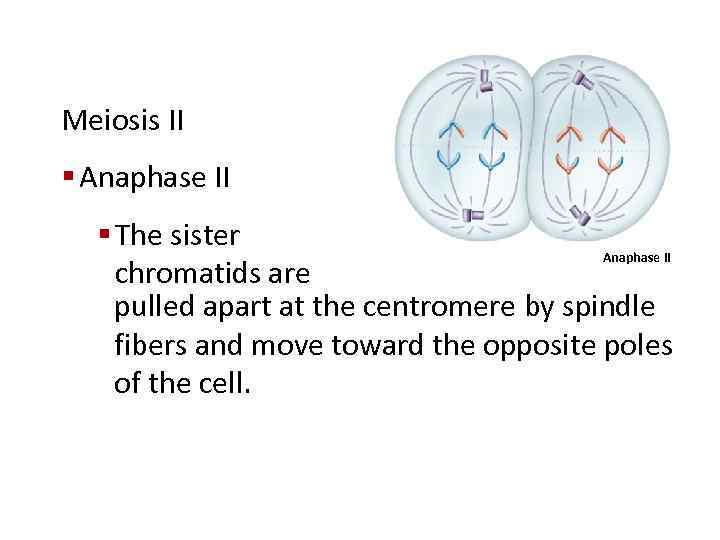 Meiosis II § Anaphase II § The sister Anaphase II chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere by spindle fibers and move toward the opposite poles of the cell.
Meiosis II § Anaphase II § The sister Anaphase II chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere by spindle fibers and move toward the opposite poles of the cell.
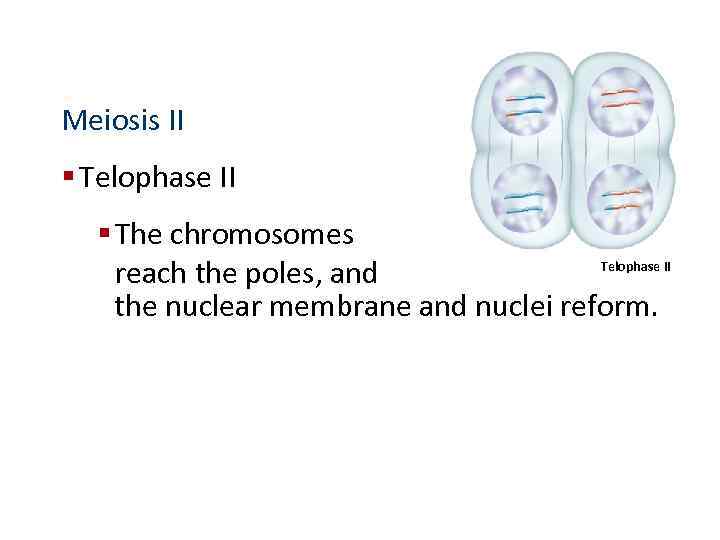 Meiosis II § Telophase II § The chromosomes Telophase II reach the poles, and the nuclear membrane and nuclei reform.
Meiosis II § Telophase II § The chromosomes Telophase II reach the poles, and the nuclear membrane and nuclei reform.
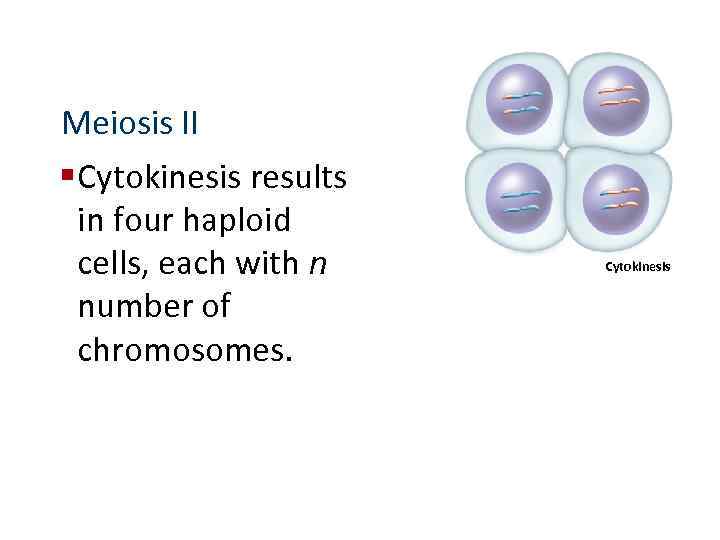 Meiosis II § Cytokinesis results in four haploid cells, each with n number of chromosomes. Cytokinesis
Meiosis II § Cytokinesis results in four haploid cells, each with n number of chromosomes. Cytokinesis
 The Importance of Meiosis § Meiosis consists of two sets of divisions § Produces four haploid daughter cells that are not identical § Results in genetic variation
The Importance of Meiosis § Meiosis consists of two sets of divisions § Produces four haploid daughter cells that are not identical § Results in genetic variation