72f6e93b9a3b30d98aa2961991938200.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Mitigating the Energy Crisis using Simulation for Enhanced Oil Recovery Analyzing oil fields grain by grain David Holmes, John Williams Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Peter Tilke Mathematics and Modeling Department Schlumberger-Doll Research December 9 th, 2008 www. milner-photo. com/industrial/home. html
Mitigating the Energy Crisis using Simulation for Enhanced Oil Recovery Analyzing oil fields grain by grain David Holmes, John Williams Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Peter Tilke Mathematics and Modeling Department Schlumberger-Doll Research December 9 th, 2008 www. milner-photo. com/industrial/home. html
 Outline n Enhanced Oil Recovery – Problem Statement – Modeling Challenges n Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework – Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core – Dynamic Execution Management n Testing and Applications n Conclusions
Outline n Enhanced Oil Recovery – Problem Statement – Modeling Challenges n Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework – Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core – Dynamic Execution Management n Testing and Applications n Conclusions
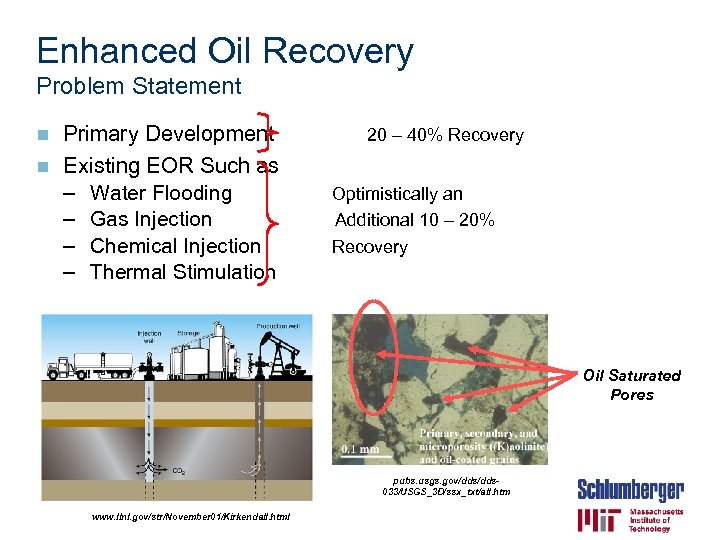 Enhanced Oil Recovery Problem Statement Primary Development n Existing EOR Such as – Water Flooding – Gas Injection – Chemical Injection – Thermal Stimulation n 20 – 40% Recovery Optimistically an Additional 10 – 20% Recovery Oil Saturated Pores pubs. usgs. gov/dds 033/USGS_3 D/ssx_txt/all. htm www. llnl. gov/str/November 01/Kirkendall. html
Enhanced Oil Recovery Problem Statement Primary Development n Existing EOR Such as – Water Flooding – Gas Injection – Chemical Injection – Thermal Stimulation n 20 – 40% Recovery Optimistically an Additional 10 – 20% Recovery Oil Saturated Pores pubs. usgs. gov/dds 033/USGS_3 D/ssx_txt/all. htm www. llnl. gov/str/November 01/Kirkendall. html
 Enhanced Oil Recovery Problem Statement n The Department of Energy (DOE) estimates that using ‘Next Generation EOR’ the United States could generate an additional 240 billion barrels of recoverable oil resources n This corresponds to approximately 30 years supply at current consumption n Developing new EOR is critical to maintaining our way of life http: //photo. net/photodb/photo? photo_id=52193 http: //www. shmolnick. com/images/traffic_jam
Enhanced Oil Recovery Problem Statement n The Department of Energy (DOE) estimates that using ‘Next Generation EOR’ the United States could generate an additional 240 billion barrels of recoverable oil resources n This corresponds to approximately 30 years supply at current consumption n Developing new EOR is critical to maintaining our way of life http: //photo. net/photodb/photo? photo_id=52193 http: //www. shmolnick. com/images/traffic_jam
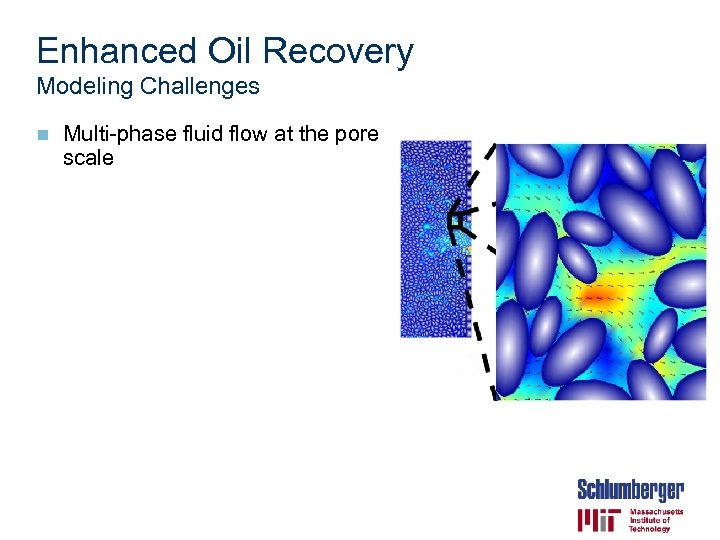 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale
 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n www. co 2 crc. com. au/aboutgeo/storage. html
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n www. co 2 crc. com. au/aboutgeo/storage. html
 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks n www. thewaterexperts. com/welldevel opment. htm
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks n www. thewaterexperts. com/welldevel opment. htm
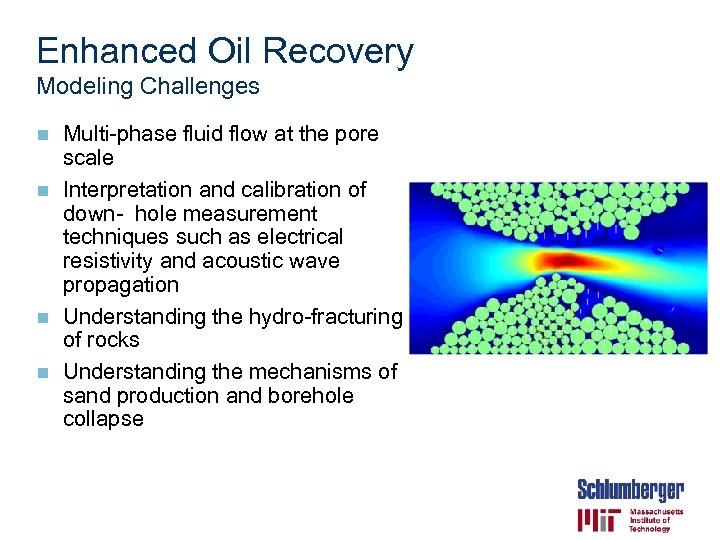 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks n Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse n
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale n Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation n Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks n Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse n
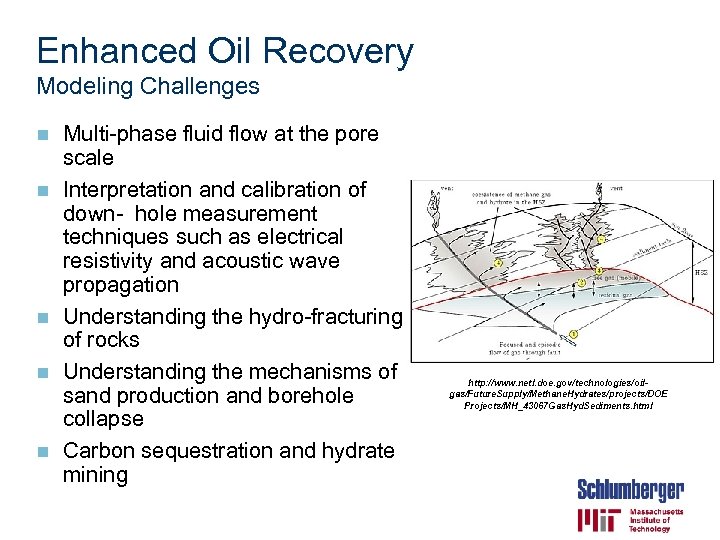 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n n n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse Carbon sequestration and hydrate mining http: //www. netl. doe. gov/technologies/oilgas/Future. Supply/Methane. Hydrates/projects/DOE Projects/MH_43067 Gas. Hyd. Sediments. html
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n n n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse Carbon sequestration and hydrate mining http: //www. netl. doe. gov/technologies/oilgas/Future. Supply/Methane. Hydrates/projects/DOE Projects/MH_43067 Gas. Hyd. Sediments. html
 Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n n n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse Carbon sequestration and hydrate mining Architecting integrated multiphysics software systems that
Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling Challenges n n n Multi-phase fluid flow at the pore scale Interpretation and calibration of down- hole measurement techniques such as electrical resistivity and acoustic wave propagation Understanding the hydro-fracturing of rocks Understanding the mechanisms of sand production and borehole collapse Carbon sequestration and hydrate mining Architecting integrated multiphysics software systems that
 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Concurrency Packages Conventional parallel simulation implementations use MPI n A powerful new library for multi-core is Microsoft’s CCR n Further room for generalization for simulation applications n Challenges to Concurrency General challenges – Synchronization – Thread safety – Load balance n Challenges unique to simulation in parallel – Spatial reasoning and task distribution n
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Concurrency Packages Conventional parallel simulation implementations use MPI n A powerful new library for multi-core is Microsoft’s CCR n Further room for generalization for simulation applications n Challenges to Concurrency General challenges – Synchronization – Thread safety – Load balance n Challenges unique to simulation in parallel – Spatial reasoning and task distribution n
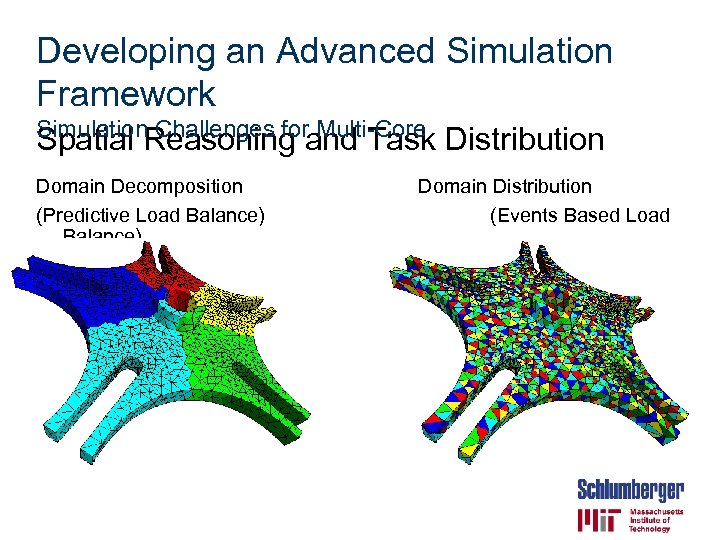 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Spatial Reasoning and Task Distribution Domain Decomposition (Predictive Load Balance) Domain Distribution (Events Based Load
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Spatial Reasoning and Task Distribution Domain Decomposition (Predictive Load Balance) Domain Distribution (Events Based Load
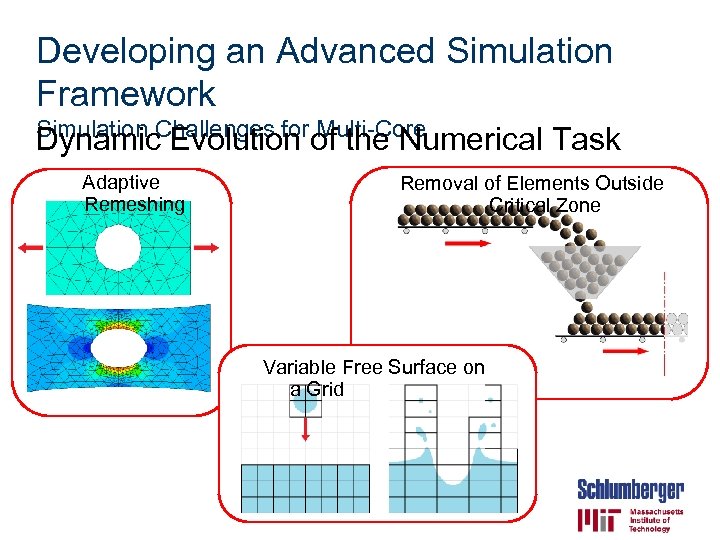 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Dynamic Evolution of the Numerical Task Adaptive Remeshing Removal of Elements Outside Critical Zone Variable Free Surface on a Grid
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Simulation Challenges for Multi-Core Dynamic Evolution of the Numerical Task Adaptive Remeshing Removal of Elements Outside Critical Zone Variable Free Surface on a Grid
 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Dynamic Execution Managementand Microsoft’s Concurrency Runtime (CCR) n Acknowledgements George Chrysanthakopoulos n Coordination Primary Concurrency Tools – Port – Receiver Henrik Nielsen
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Dynamic Execution Managementand Microsoft’s Concurrency Runtime (CCR) n Acknowledgements George Chrysanthakopoulos n Coordination Primary Concurrency Tools – Port – Receiver Henrik Nielsen
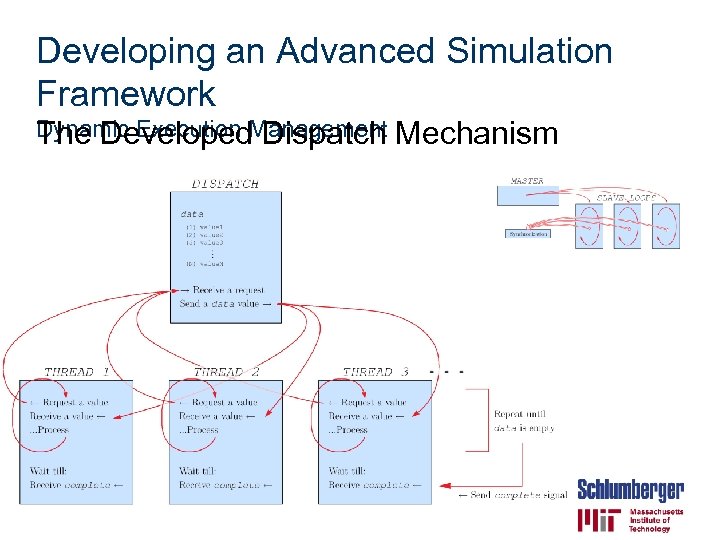 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Dynamic Execution Management Mechanism The Developed Dispatch
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework Dynamic Execution Management Mechanism The Developed Dispatch
 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework n Advantages Dynamic Execution Management – Perfectly load balanced to within required operations on 1 data point – Accommodates any CPU number – Accommodates variable CPU efficiency/availability and remains load balanced n Programming Challenges – Dispatch must know when all data has been received – Dispatch must recognize when data has been distributed – All processes must complete before finalization
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework n Advantages Dynamic Execution Management – Perfectly load balanced to within required operations on 1 data point – Accommodates any CPU number – Accommodates variable CPU efficiency/availability and remains load balanced n Programming Challenges – Dispatch must know when all data has been received – Dispatch must recognize when data has been distributed – All processes must complete before finalization
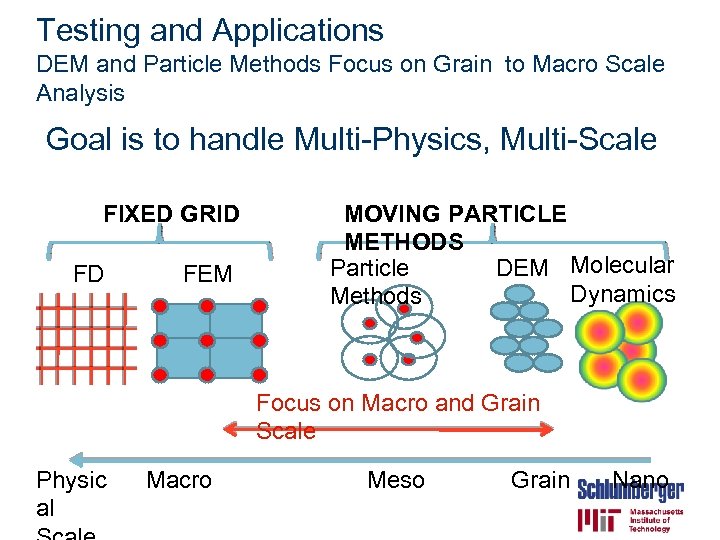 Testing and Applications DEM and Particle Methods Focus on Grain to Macro Scale Analysis Goal is to handle Multi-Physics, Multi-Scale FIXED GRID FD FEM MOVING PARTICLE METHODS Particle DEM Molecular Dynamics Methods Focus on Macro and Grain Scale Physic al Macro Meso Grain Nano
Testing and Applications DEM and Particle Methods Focus on Grain to Macro Scale Analysis Goal is to handle Multi-Physics, Multi-Scale FIXED GRID FD FEM MOVING PARTICLE METHODS Particle DEM Molecular Dynamics Methods Focus on Macro and Grain Scale Physic al Macro Meso Grain Nano
 Testing and Applications
Testing and Applications
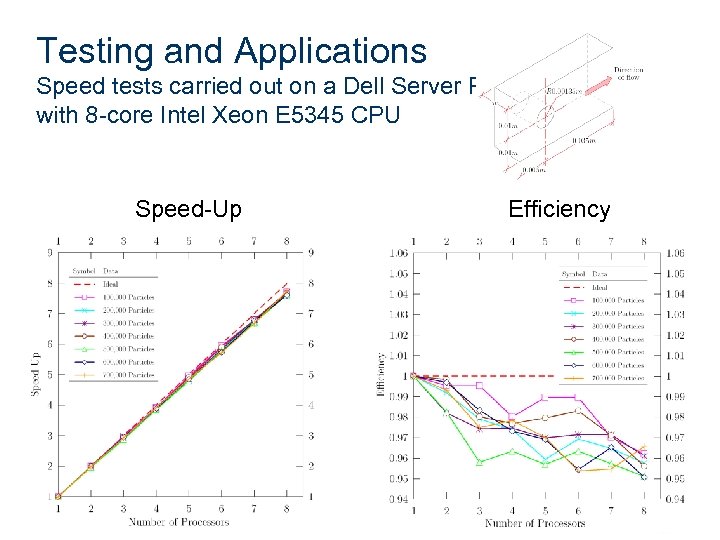 Testing and Applications Speed tests carried out on a Dell Server PE 2900 with 8 -core Intel Xeon E 5345 CPU Speed-Up Efficiency
Testing and Applications Speed tests carried out on a Dell Server PE 2900 with 8 -core Intel Xeon E 5345 CPU Speed-Up Efficiency
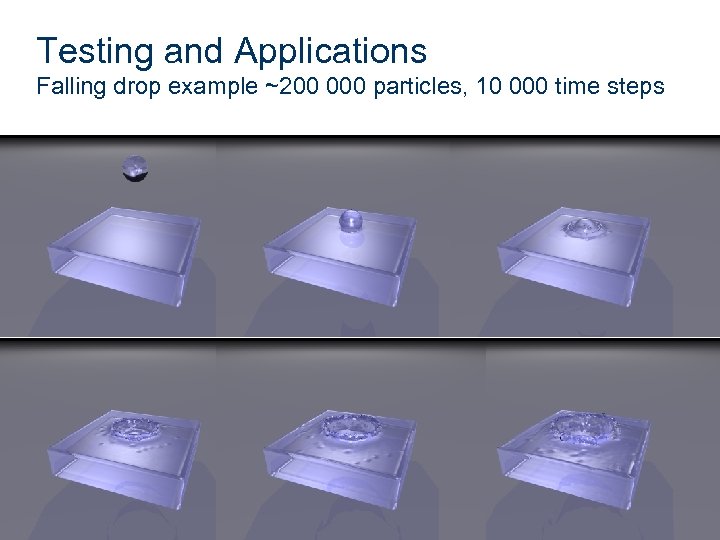 Testing and Applications Falling drop example ~200 000 particles, 10 000 time steps
Testing and Applications Falling drop example ~200 000 particles, 10 000 time steps
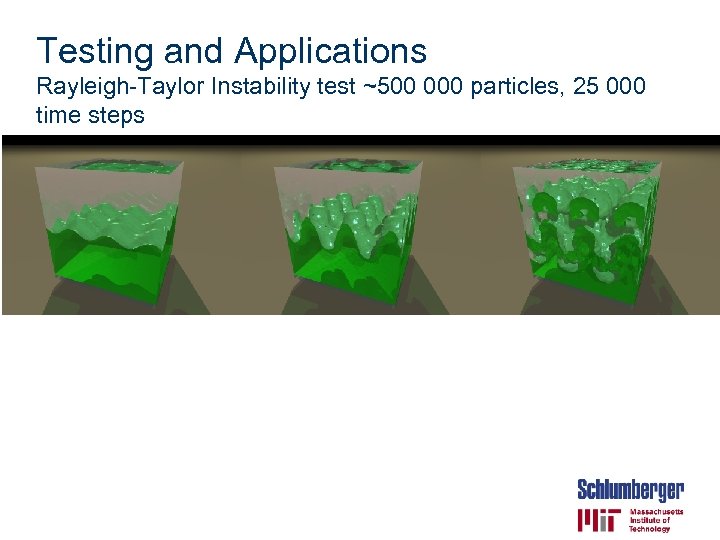 Testing and Applications Rayleigh-Taylor Instability test ~500 000 particles, 25 000 time steps
Testing and Applications Rayleigh-Taylor Instability test ~500 000 particles, 25 000 time steps
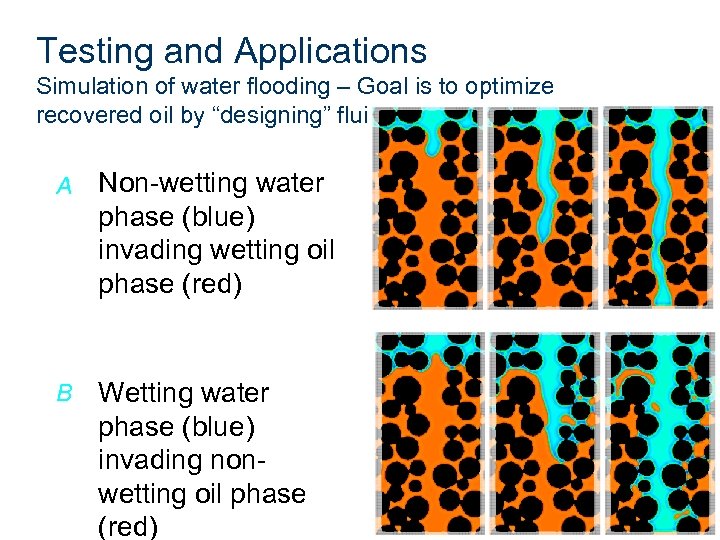 Testing and Applications Simulation of water flooding – Goal is to optimize recovered oil by “designing” fluids A Non-wetting water phase (blue) invading wetting oil phase (red) B Wetting water phase (blue) invading nonwetting oil phase (red)
Testing and Applications Simulation of water flooding – Goal is to optimize recovered oil by “designing” fluids A Non-wetting water phase (blue) invading wetting oil phase (red) B Wetting water phase (blue) invading nonwetting oil phase (red)
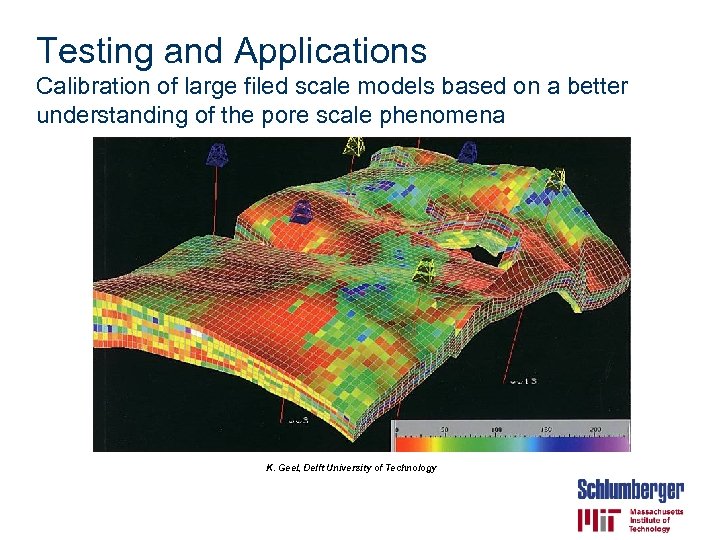 Testing and Applications Calibration of large filed scale models based on a better understanding of the pore scale phenomena K. Geel, Delft University of Technology
Testing and Applications Calibration of large filed scale models based on a better understanding of the pore scale phenomena K. Geel, Delft University of Technology
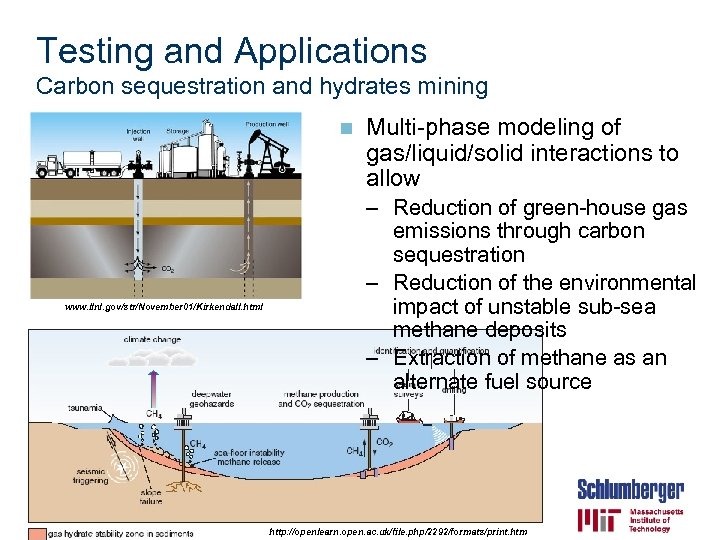 Testing and Applications Carbon sequestration and hydrates mining n www. llnl. gov/str/November 01/Kirkendall. html Multi-phase modeling of gas/liquid/solid interactions to allow – Reduction of green-house gas emissions through carbon sequestration – Reduction of the environmental impact of unstable sub-sea methane deposits – Extraction of methane as an alternate fuel source http: //openlearn. open. ac. uk/file. php/2292/formats/print. htm
Testing and Applications Carbon sequestration and hydrates mining n www. llnl. gov/str/November 01/Kirkendall. html Multi-phase modeling of gas/liquid/solid interactions to allow – Reduction of green-house gas emissions through carbon sequestration – Reduction of the environmental impact of unstable sub-sea methane deposits – Extraction of methane as an alternate fuel source http: //openlearn. open. ac. uk/file. php/2292/formats/print. htm
 Conclusions
Conclusions
 Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework n Conventional CCR example of Dynamic Execution Management a repeated scatter-gather Scatte r Parall el Gathe r
Developing an Advanced Simulation Framework n Conventional CCR example of Dynamic Execution Management a repeated scatter-gather Scatte r Parall el Gathe r


