4781b27e4931351dbb714ac6933f05e1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

MITEC – June 6, 2006 IBM System i 5 Introducing. . . The IBM Toolbox for Java Jeff Lee – jlee@us. ibm. com

IBM System i 5 Trademarks and Disclaimers 8 IBM Corporation 1994 -2006. All rights reserved. References in this document to IBM products or services do not imply that IBM intends to make them available in every country. The following terms are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both: AS/400 e-business on demand i 5/OS AS/400 e IBM OS/400 e. Server IBM (logo) System i 5 i. Series Rational is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation and Rational Software Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. Intel, Intel Logo, Intel Inside logo, Intel Centrino logo, Celeron, Intel Xeon, Intel Speed. Step, Itanium, and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both. Microsoft, Windows NT, and the Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries. Java and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both. Other company, product or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. Information is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind. All customer examples described are presented as illustrations of how those customers have used IBM products and the results they may have achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics may vary by customer. Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from a supplier of these products, published announcement material, or other publicly available sources and does not constitute an endorsement of such products by IBM. Sources for non-IBM list prices and performance numbers are taken from publicly available information, including vendor announcements and vendor worldwide homepages. IBM has not tested these products and cannot confirm the accuracy of performance, capability, or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions on the capability of non-IBM products should be addressed to the supplier of those products. All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. Contact your local IBM office or IBM authorized reseller for the full text of the specific Statement of Direction. Some information addresses anticipated future capabilities. Such information is not intended as a definitive statement of a commitment to specific levels of performance, function or delivery schedules with respect to any future products. Such commitments are only made in IBM product announcements. The information is presented here to communicate IBM's current investment and development activities as a good faith effort to help with our customers' future planning. Performance is based on measurements and projections using standard IBM benchmarks in a controlled environment. The actual throughput or performance that any user will experience will vary depending upon considerations such as the amount of multiprogramming in the user's job stream, the I/O configuration, the storage configuration, and the workload processed. Therefore, no assurance can be given that an individual user will achieve throughput or performance improvements equivalent to the ratios stated here. Photographs shown are of engineering prototypes. Changes may be incorporated in production models. 2 © 2006 IBM Corporation
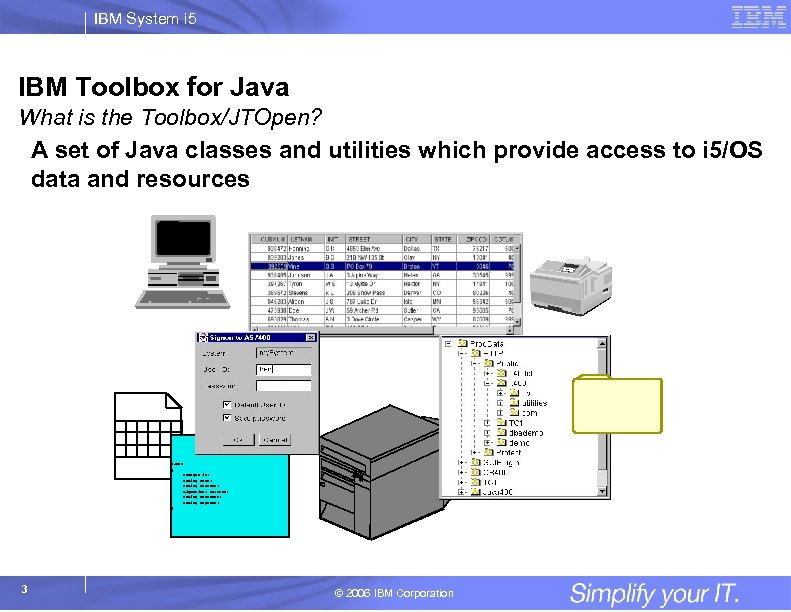
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java What is the Toolbox/JTOpen? A set of Java classes and utilities which provide access to i 5/OS data and resources class { Integer id; String name; String address; Big. Decimal balance; String ccnumber; String expdate; } 3 © 2006 IBM Corporation
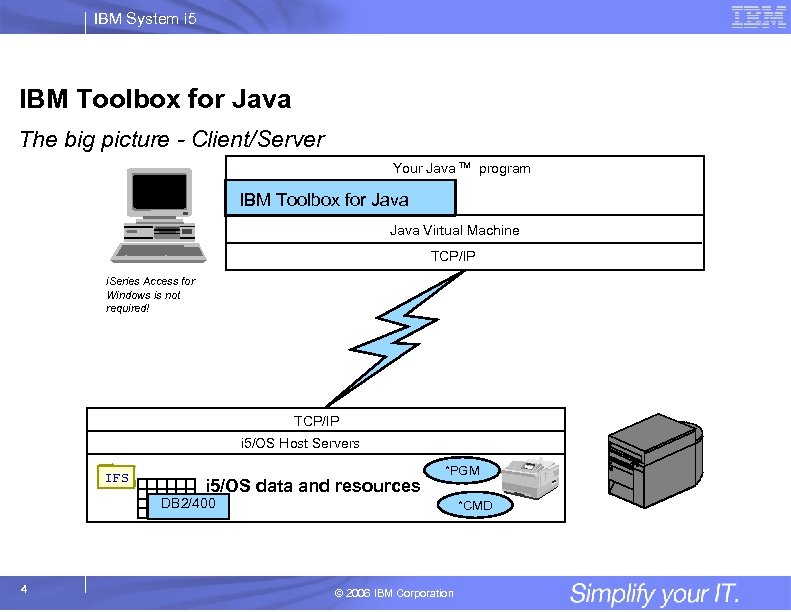
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java The big picture - Client/Server Your Java TM program IBM Toolbox for Java Virtual Machine TCP/IP i. Series Access for Windows is not required! TCP/IP i 5/OS Host Servers IFS i 5/OS data and resources *PGM DB 2/400 4 *CMD © 2006 IBM Corporation
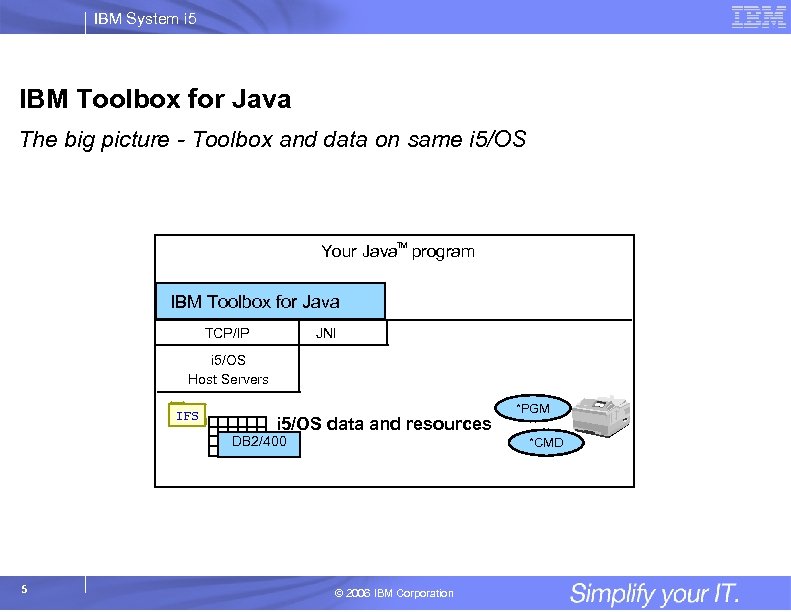
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java The big picture - Toolbox and data on same i 5/OS Your Java. TM program IBM Toolbox for Java TCP/IP JNI i 5/OS Host Servers IFS i 5/OS data and resources DB 2/400 5 *PGM *CMD © 2006 IBM Corporation
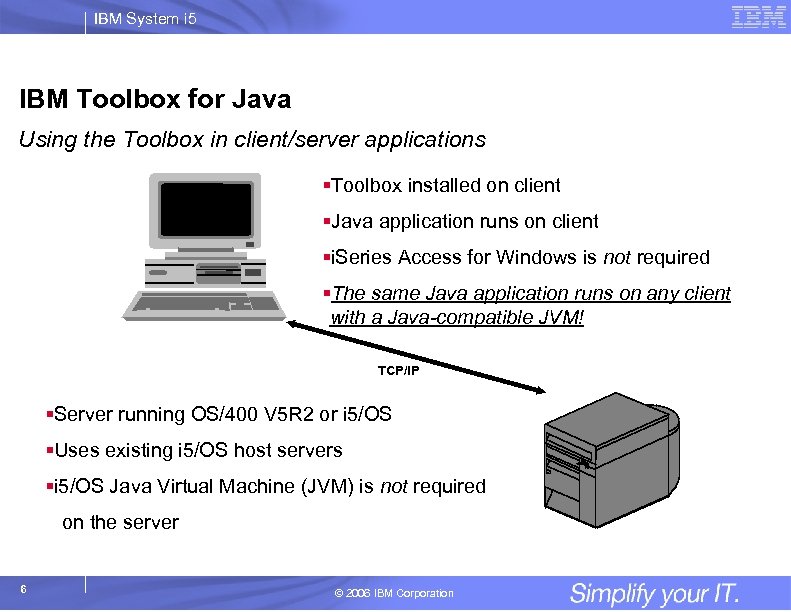
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Using the Toolbox in client/server applications §Toolbox installed on client §Java application runs on client §i. Series Access for Windows is not required §The same Java application runs on any client with a Java-compatible JVM! TCP/IP §Server running OS/400 V 5 R 2 or i 5/OS §Uses existing i 5/OS host servers §i 5/OS Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is not required on the server 6 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Using the Toolbox in server applications §Toolbox installed on i 5/OS §Java application runs on i 5/OS §Use Toolbox instead of JNI §"Local" sockets used to communicate between Toolbox and servers §Direct API calls used in some cases to avoid the servers §i 5/OS with Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is required 7 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Using the Toolbox in Internet-based servlets §Web browser displays HTML HTTP §No Java on the client §Server running OS/400 V 5 R 2 or i 5/OS TCP/IP §Toolbox installed on web server §Java servlet runs on web server §Java-enabled web server is required 8 §Uses existing i 5/OS host servers (Web server and data server can be the same machine) © 2006 IBM Corporation §i 5/OS Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is not required

IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Supported platforms: §i 5/OS, Linux, Windows, AIX, Solaris, Netscape Communicator, Microsoft Internet Explorer Requires Java 1. 1. 8 or greater, and supports Java 2. Note: Many new functions require Java 1. 4. Divided into packages: §com. ibm. as 400. access - APIs for accessing i 5/OS data and resources §com. ibm. as 400. resource - Framework for accessing list-based data §com. ibm. as 400. vaccess - GUI components §com. ibm. as 400. data - Program call markup language §com. ibm. as 400. ui. * - Graphical Toolbox §com. ibm. as 400. util. * - HTML, XSL-FO (*NEW*) and Servlet components §com. ibm. as 400. micro. * - APIs for wireless devices §utilities - utility classes such as Jar. Maker, JPing, Run. Java. Application, About. Toolbox 9 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Packaging Licensed program 5722 -JC 1 (no additional charge) Downloadable from Toolbox or JTOpen websites (no additional charge) Ships with i 5/OS Jar files: §jt 400. jar - Base function + GUI components §jt 400 Native. jar - Base function only, intended for use on i 5/OS JVM §jt 400 Proxy. jar - Proxy support, subset of jt 400. jar §jt 400 Servlet. jar - HTML, XSL-FO, and Servlet components §jt 400 Micro. jar - Wireless support §uitools. jar, jui 400. jar, util 400. jar, x 4 j 400. jar - Graphical Toolbox §tes. jar - System Debugger Use the Jar. Maker utility to reduce the size of jt 400. jar or any other jar file 10 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 JTOpen (Open Source) All of the primary Toolbox packages are open source! http: //jt 400. sourceforge. net §Part of IBM's open source development community §Use source as a debug tool §Submit new function under the IBM Public License (IPL) §Modify source for your use §Submit problem reports and bug fixes Two versions of the Toolbox: §Licensed program Ÿ Supported by IBM Ÿ Fixes delivered by PTFs §Open source version Ÿ Supported by open source community Ÿ Now officially supported by IBM Service! Ÿ Includes source from non-IBM contributors Ÿ New functions and fixes available here first! 11 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Popular Toolbox Functions §Database access via JDBC §Database access via a record-level I/O and DDS interface §Command Call §Program Call via both Java code and XML §Data Queues / User Spaces / Data Areas §Access files in i. Series Integrated File System §Access Print object (spooled files, printers, queues, . . . ) §Access i. Series objects (Jobs, Users, System Values, etc. ) §Built-in automatic data conversion §HTML / Servlet wrappers §Wireless APIs §XML-based GUI Builder §Components are Java Beans 12 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java i 5/OS Functions Built on the Toolbox §i. Series Navigator and Management Central §i. Series Access for Web §i. Series Connect (B 2 B) §IBM Host On Demand §Plus Many More. . . 13 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Access Classes: Low-level Java APIs to Access Data §User Authentication and Identification §Command Call §Connection Pools §Clustered Hashtables §Data Area §Data Description §Data Conversion §Data Queues §Environment Variables §FTP §IFS 14 §JDBC §Jobs §Messages §Net. Server §Print §Permissions §Program Call §Record-level Database Access §Save File §System Status §System Values §Users and Groups §User Space © 2006 IBM Corporation
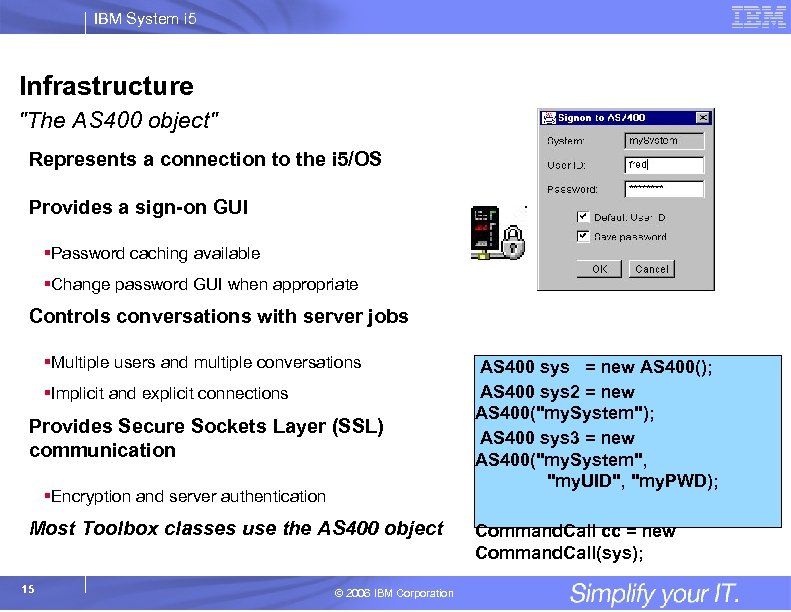
IBM System i 5 Infrastructure "The AS 400 object" Represents a connection to the i 5/OS Provides a sign-on GUI §Password caching available §Change password GUI when appropriate Controls conversations with server jobs §Multiple users and multiple conversations §Implicit and explicit connections Provides Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) communication §Encryption and server authentication Most Toolbox classes use the AS 400 object 15 © 2006 IBM Corporation AS 400 sys = new AS 400(); AS 400 sys 2 = new AS 400("my. System"); AS 400 sys 3 = new AS 400("my. System", "my. UID", "my. PWD); Command. Call cc = new Command. Call(sys);

IBM System i 5 JDBC The Java standard for database access Write Java programs in terms of standard JDBC interfaces, then plug in any JDBC driver - to work with any database! §Java gives you platform independence, JDBC gives you database independence java. sql package in Java Developers Kit SQL is used extensively §Based on X/Open SQL Call Level Interface Also supports: §Database definitions, manipulations, and queries §Stored procedures §Catalog methods §Transactions (commit, rollback, isolation levels, distributed) 16 © 2006 IBM Corporation
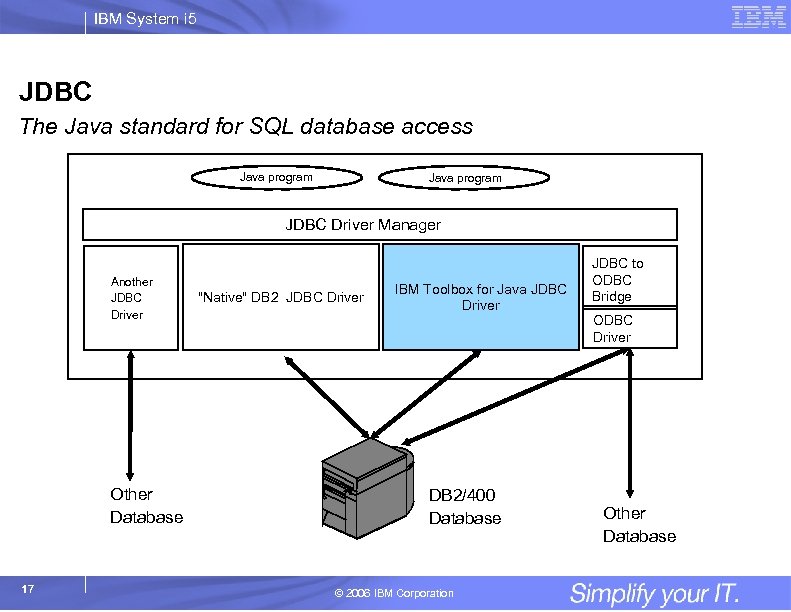
IBM System i 5 JDBC The Java standard for SQL database access Java program JDBC Driver Manager Another JDBC Driver Other Database 17 "Native" DB 2 JDBC Driver IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC Driver DB 2/400 Database © 2006 IBM Corporation JDBC to ODBC Bridge ODBC Driver Other Database
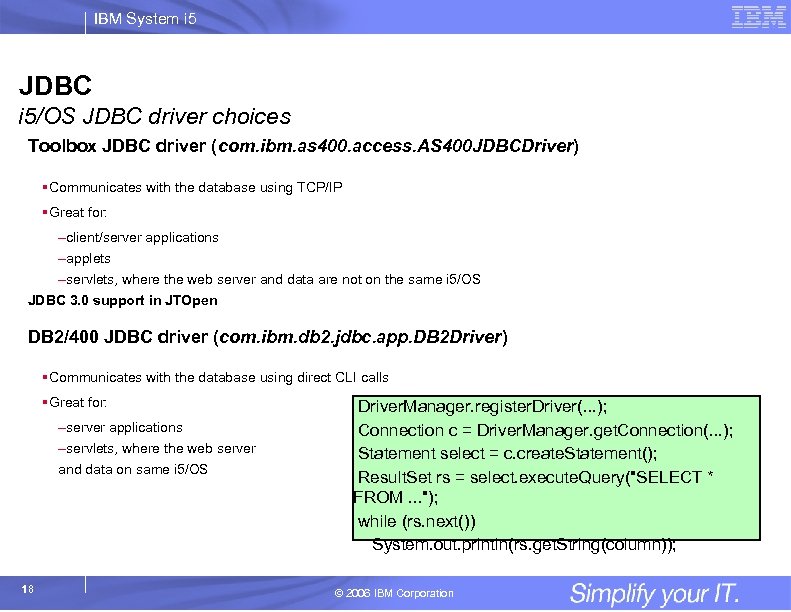
IBM System i 5 JDBC i 5/OS JDBC driver choices Toolbox JDBC driver (com. ibm. as 400. access. AS 400 JDBCDriver) §Communicates with the database using TCP/IP §Great for: –client/server applications –applets –servlets, where the web server and data are not on the same i 5/OS JDBC 3. 0 support in JTOpen DB 2/400 JDBC driver (com. ibm. db 2. jdbc. app. DB 2 Driver) §Communicates with the database using direct CLI calls §Great for: –server applications –servlets, where the web server and data on same i 5/OS 18 Driver. Manager. register. Driver(. . . ); Connection c = Driver. Manager. get. Connection(. . . ); Statement select = c. create. Statement(); Result. Set rs = select. execute. Query("SELECT * FROM. . . "); while (rs. next()) System. out. println(rs. get. String(column)); © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 Record-level database access Fast access to i 5/OS database files Provides access to database files: §Access records sequentially, by record number, or by key §Physical and logical file members are described by a Record. Format §Support for locking §Support for transactions §Familiar paradigm for RPG programmers §Limited System/36 SSP file capability, too! AS 400 system = new AS 400("my. System"); Sequential. File file = new Sequential. File(system, "/QSYS. LIB/MYLIB. LIB/MYFILE"); file. set. Record. Format(. . . ); file. open(. . . ); Record r = file. read. Next(); 19 © 2006 IBM Corporation
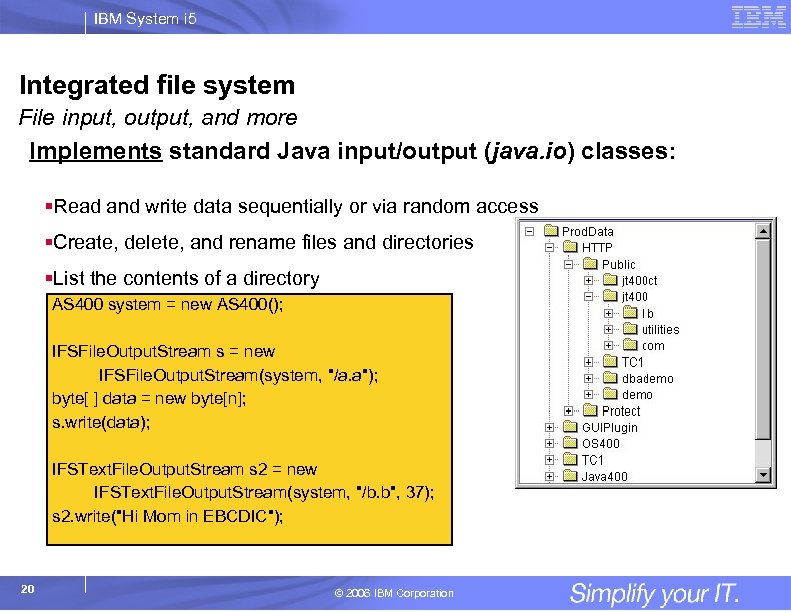
IBM System i 5 Integrated file system File input, output, and more Implements standard Java input/output (java. io) classes: §Read and write data sequentially or via random access §Create, delete, and rename files and directories §List the contents of a directory AS 400 system = new AS 400(); IFSFile. Output. Stream s = new IFSFile. Output. Stream(system, "/a. a"); byte[ ] data = new byte[n]; s. write(data); IFSText. File. Output. Stream s 2 = new IFSText. File. Output. Stream(system, "/b. b", 37); s 2. write("Hi Mom in EBCDIC"); 20 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Network print Access print objects and spooled files §List printers, output queues, writers and spooled files §Manage printers, output queues and writers §Read and write spooled files §Spooled file viewer 21 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Command call and program call Make use of legacy code and system APIs AS 400 system = new AS 400(); Command. Call cc = new Command. Call(system); cc. run("CRTLIB NEWLIB"); Java program Input parameters Output parameters and messages AS 400 system = new AS 400(); Program. Parameter[ ] parm. List = new Program. Parameter[n]; parm. List[0] = new Program. Parameter(data); . . . Program. Call pc = new Program. Call(system, "/QSYS. LIB/MYLIB. LIB/MYPGM. PGM", parm. List); pc. run(); 22 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Program Call Markup Language (PCML) Describe program calls using XML Automates program call parameter and structure definition Simplifies data description and conversion Java program Input parameters Output parameters and messages <pcml> <program name="rtvsts" path="/QSYS. lib/MYLIB. lib/RTVSTS. pgm"> <data name="custid" usage="input" type="int"> <data name="status" usage="output" type="char" length="20"> </program> </pcml> 23 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Interprogram Communication Data queues, Data areas, User spaces, . . . Transfer data between programs using: Java program §Data areas §Data queues (keyed or sequential) §User spaces Partner can be Java program, traditional i 5/OS program, on i 5/OS or another client AS 400 system = new AS 400(); User. Space us = new User. Space(system, "/QSYS. LIB/MYLIB. LIB/MYDATA. USRSPC"); byte[ ] data = new byte[1024]; us. read(data, 0); 24 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 RFML (Record Format Markup Language) Very similar to PCML (Program Call Markup Language) While PCML is designed only for Program Parameters, RFML is useful for parsing/composing: §Data queue entries §User spaces §Physical file records §Data buffers Specify record formats using XML; get/set field values Segregate the data layout from the program logic 25 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 RFML vs. Field. Description Example: Composing a customer record Without RFML: Using RFML: import com. ibm. as 400. access. AS 400 Text; import com. ibm. as 400. access. AS 400 Unsigned. Bin 2; import com. ibm. as 400. data. Record. Format. Document; import com. ibm. as 400. access. AS 400 Zoned. Decimal; Record. Format. Document rfml. Doc = new Record. Format. Document("customer"); import com. ibm. as 400. access. Binary. Field. Description; import com. ibm. as 400. access. Character. Field. Description; import com. ibm. as 400. access. Record. Format; ( In a separate file named "customer. rfml": ) import com. ibm. as 400. access. Zoned. Decimal. Field. Description; <rfml version="4. 0" ccsid="37"> <recordformat name="cusrec"> <data name="cusnum" type="int" length="2" precision="16"/> <data name="lstnam" type="char" length="8"/> <data name="baldue" type="zoned" length="6" precision="2"/> </recordformat> </rfml> Record. Format rec. Fmt = new Record. Format("cusrec"); AS 400 Unsigned. Bin 2 conv 1 = new AS 400 Unsigned. Bin 2(); Binary. Field. Description desc 1 = new Binary. Field. Description(conv 1, "cusnum"); rec. Fmt. add. Field. Description(desc 1); AS 400 Text conv 2 = new AS 400 Text(8, 37); Character. Field. Description desc 2 = new Character. Field. Description(conv 2, "lstnam"); rec. Fmt. add. Field. Description(desc 2); AS 400 Zoned. Decimal conv 3 = new AS 400 Zoned. Decimal(6, 2); Zoned. Decimal. Field. Description desc 3 = new Zoned. Decimal. Field. Description(conv 3, "baldue"); rec. Fmt. add. Field. Description(desc 3); 26 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Server Objects Jobs, Users, System Values, . . . §List i 5/OS jobs §List i 5/OS users and groups §Display and change system values §Manage message queues §Manage user permissions to objects AS 400 system = new AS 400(); System. Value sv = new System. Value(system, "QDATE"); System. out. println(sv. get. Value()); 27 © 2006 IBM Corporation
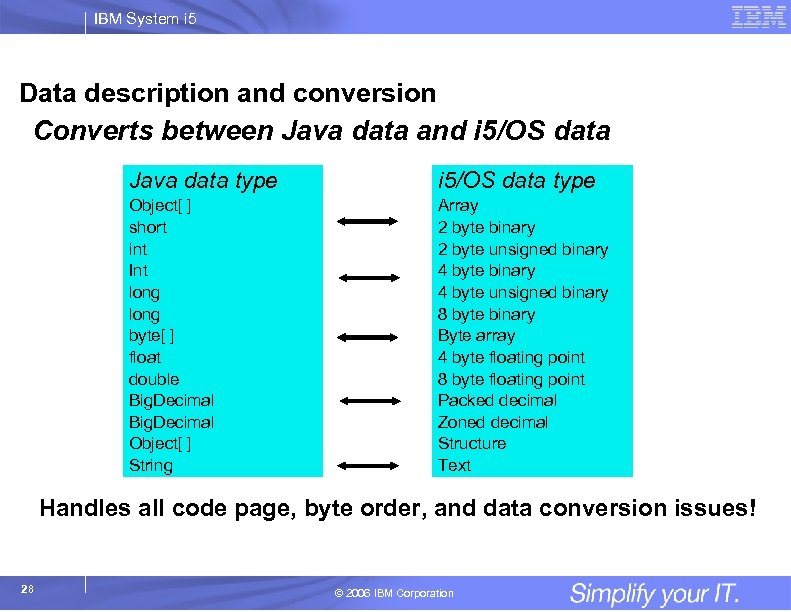
IBM System i 5 Data description and conversion Converts between Java data and i 5/OS data Java data type i 5/OS data type Object[ ] short int Int long byte[ ] float double Big. Decimal Object[ ] String Array 2 byte binary 2 byte unsigned binary 4 byte unsigned binary 8 byte binary Byte array 4 byte floating point 8 byte floating point Packed decimal Zoned decimal Structure Text Handles all code page, byte order, and data conversion issues! 28 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Data description and conversion Record formats Access data in the record by field name Convert data automatically for: §Program calls §Data queues §Record-level database access 29 Binary. Field. Description customer. Number = new Binary. Field. Description(new AS 400 Bin 4(), "CUSTOMER_ NUMBER"); Character. Field. Description customer. Name = new Character. Field. Description (new AS 400 Text(20, system), "CUSTOMER_NAME"); Record. Format record. Format = new Record. Format(); record. Format. add. Field. Description(customer. Number); record. Format. add. Field. Description(customer. Name); Record data = record. Format. get. New. Record(data. Queue. read(). get. Data()); Integer I = (INTEGER) data. get. Field("CUSTOMER_NUMBER"); String name = (String) data. get. Field("CUSTOMER_NAME"); © 2006 IBM Corporation
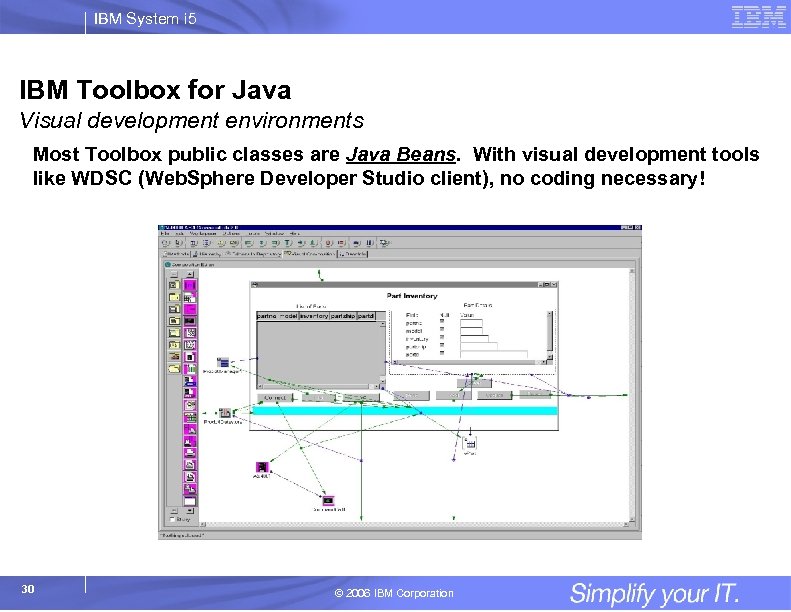
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Visual development environments Most Toolbox public classes are Java Beans. With visual development tools like WDSC (Web. Sphere Developer Studio client), no coding necessary! 30 © 2006 IBM Corporation
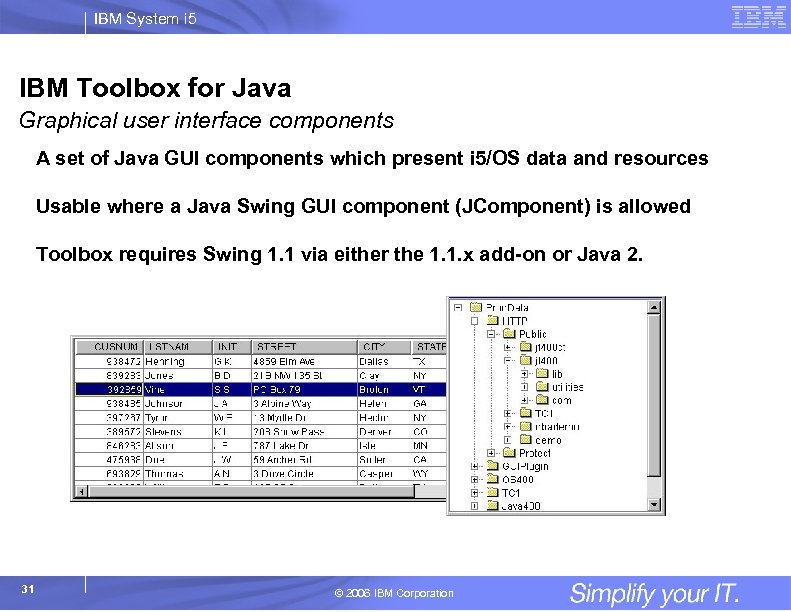
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java Graphical user interface components A set of Java GUI components which present i 5/OS data and resources Usable where a Java Swing GUI component (JComponent) is allowed Toolbox requires Swing 1. 1 via either the 1. 1. x add-on or Java 2. 31 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 HTML and Servlet classes Web components create tables and forms Provides access to database files: §Access database file with Record Level Access or SQL via JDBC §Includes Meta Data Provides classes to display data: §Display data in tables or forms §Toolbox provides converters that will produce HTML tables or forms based on the row data HTMLTable. Converter converter = new HTMLTable. Converter(); Result. Set result. Set = statement. get. Result. Set(); SQLResult. Set. Row. Data rowdata = new SQLResult. Set. Row. Data(result. Set); String[ ] html = converter. convert(rowdata); out. println(html[0]); 32 © 2006 IBM Corporation
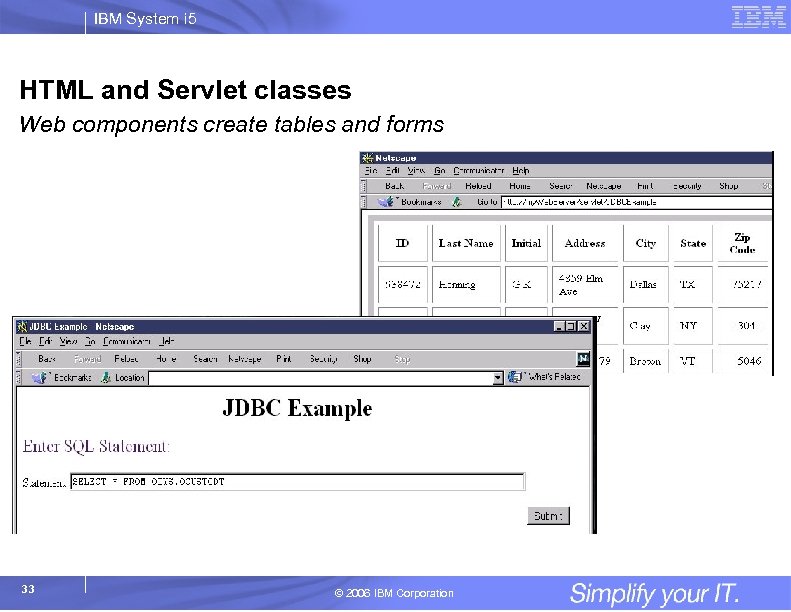
IBM System i 5 HTML and Servlet classes Web components create tables and forms 33 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 HTML and Servlet classes Web components create tree hierarchy Provides classes to display the Integrated File System: §Display contents of the Integrated File System §Toolbox provides classes to create and display a customized and traversable tree HTMLTree tree = new HTMLTree(HTTPrequest) IFSJava. File root = new IFSJava. File(system. Object, "/QIBM"); Dir. Filter filter = new Dir. Filter(); File[] dir. List = root. list. Files(filter); for (int i=0; i<dir. List. length; i++) { File. Tree. Element node = new File. Tree. Element(dir. List[i]); tree. add. Element(node); } 34 © 2006 IBM Corporation
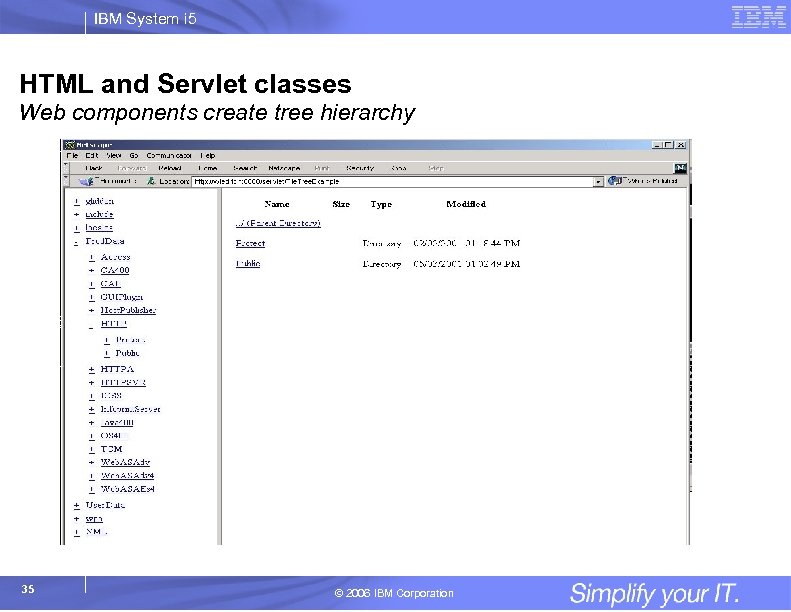
IBM System i 5 HTML and Servlet classes Web components create tree hierarchy 35 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Toolbox Micro Edition Terms What is Toolbox. ME? A subset of the Toolbox for Java classes which will provide access to i 5/OS data and resources from a Tier 0 device What is a Tier 0 device? §Tier 3: the i. Series server §Tier 2: the application or web server §Tier 1: the client desktop or laptop §Tier 0: refers to the next level down. Tier 0 devices are predominantly thought of as web-enabled cell phones and personal digital assistants (PDAs). 36 © 2006 IBM Corporation
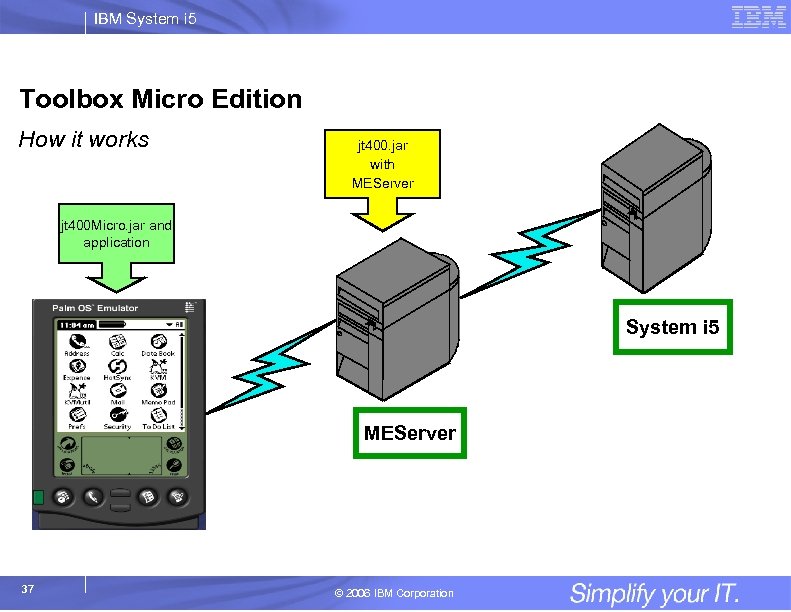
IBM System i 5 Toolbox Micro Edition How it works jt 400. jar with MEServer jt 400 Micro. jar and application System i 5 MEServer 37 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Toolbox Micro Edition Supported Components §AS 400 §Command Call §Program Call via PCML §Data Queues §Jdbc. Me 38 © 2006 IBM Corporation
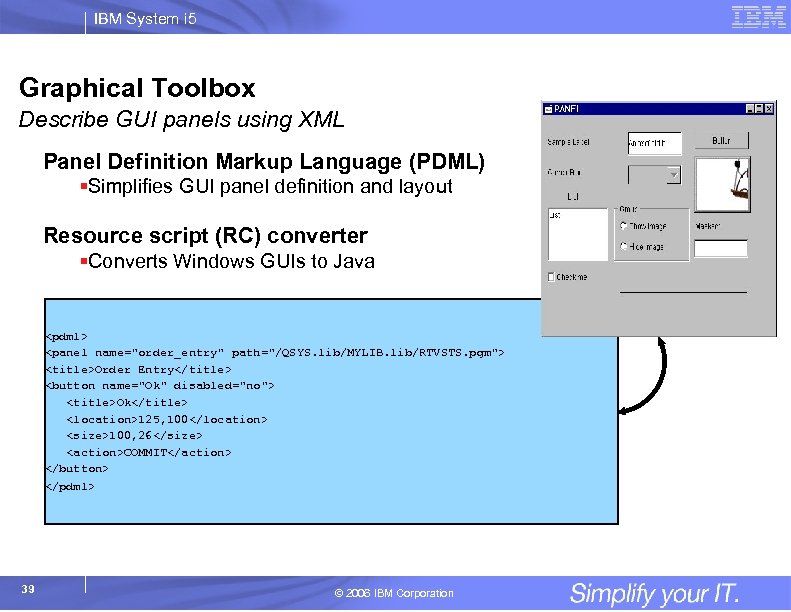
IBM System i 5 Graphical Toolbox Describe GUI panels using XML Panel Definition Markup Language (PDML) §Simplifies GUI panel definition and layout Resource script (RC) converter §Converts Windows GUIs to Java <pdml> <panel name="order_entry" path="/QSYS. lib/MYLIB. lib/RTVSTS. pgm"> <title>Order Entry</title> <button name="Ok" disabled="no"> <title>Ok</title> <location>125, 100</location> <size>100, 26</size> <action>COMMIT</action> </button> </pdml> 39 © 2006 IBM Corporation
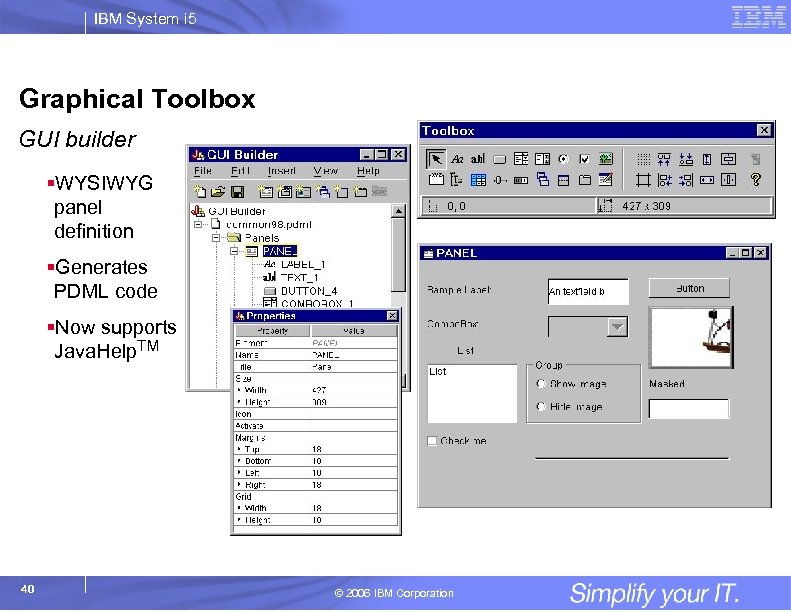
IBM System i 5 Graphical Toolbox GUI builder §WYSIWYG panel definition §Generates PDML code §Now supports Java. Help. TM 40 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Other components The list keeps growing! §Net. Server §Proxy Support §Jar. Maker §Save File §i 5/OS Messages §Report Writer §Message files §Servlets §System status §System Properties 41 © 2006 IBM Corporation
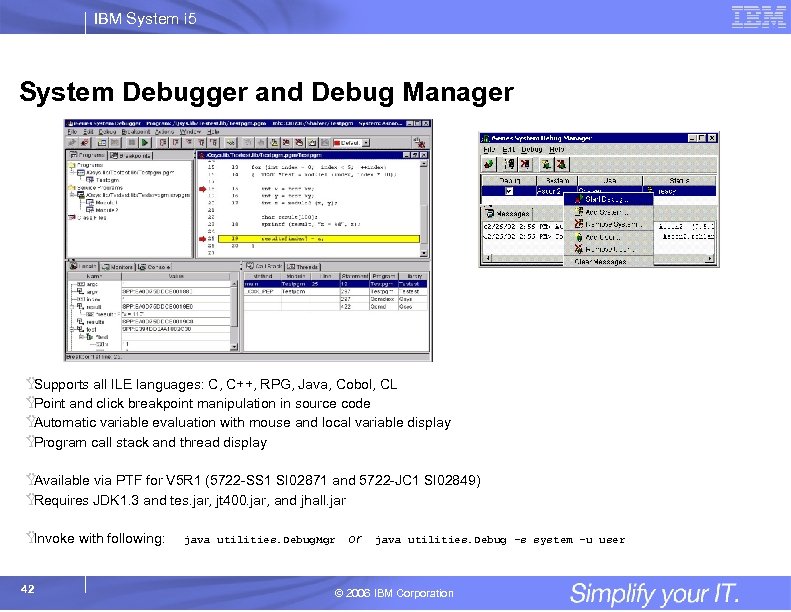
IBM System i 5 System Debugger and Debug Manager Ÿ Supports all ILE languages: C, C++, RPG, Java, Cobol, CL Ÿ Point and click breakpoint manipulation in source code Ÿ Automatic variable evaluation with mouse and local variable display Ÿ Program call stack and thread display Ÿ Available via PTF for V 5 R 1 (5722 -SS 1 SI 02871 and 5722 -JC 1 SI 02849) Ÿ Requires JDK 1. 3 and tes. jar, jt 400. jar, and jhall. jar Ÿ Invoke with following: 42 java utilities. Debug. Mgr or java utilities. Debug -s system -u user © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 New in JTOpen and V 5 R 4 Now available at http: //www. ibm. com/servers/eserver/iseries/toolbox/ Other new classes §JDBC enhancements §JDBC performance improvements §Self-managed JDBC Connection Pool §Bidi. Conversion. Properties §Call. Stack. Entry §Save File §IFSFile. System. View §Signon. Handler Plus §CL command documentation generator §Kerberos authentication is now supported through the use of JGSS §Performance improvements in list processing (users, jobs, etc. ) §Additional code pages (e. g. GB 18030) 43 © 2006 IBM Corporation NEW!
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java home page 44 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 IBM Toolbox for Java/JTOpen Forum 45 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Toolbox Programmer's Guide 46 © 2006 IBM Corporation
IBM System i 5 Javadoc 47 © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM System i 5 References Where can I get more information? http: //www. ibm. com/servers/eserver/iseries/toolbox/ §News, downloads, FAQs, service packs, articles, COMMON labs http: //jt 400. sourceforge. net/ §JTOpen - open source, bug reporting, feature requests http: //www. ibm. com/servers/eserver/support/iseries/index. html §System i 5 Technical Forums - including IBM Toolbox for Java/JTOpen Forum IBM Toolbox for Java Programmers Guide §Shipped with the IBM Toolbox for Java §Contains overview, full API documentation (javadoc), and code examples §Available in the i 5/OS Information Center §Link off of the Toolbox home page Building AS/400 Client/Server Applications with Java §Redbook SG 24 -2152 -02 48 © 2006 IBM Corporation
4781b27e4931351dbb714ac6933f05e1.ppt