28052b87bcc95140aaa12a29c1e77dfe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
MIS 710 Module 0 Database fundamentals Arijit Sengupta
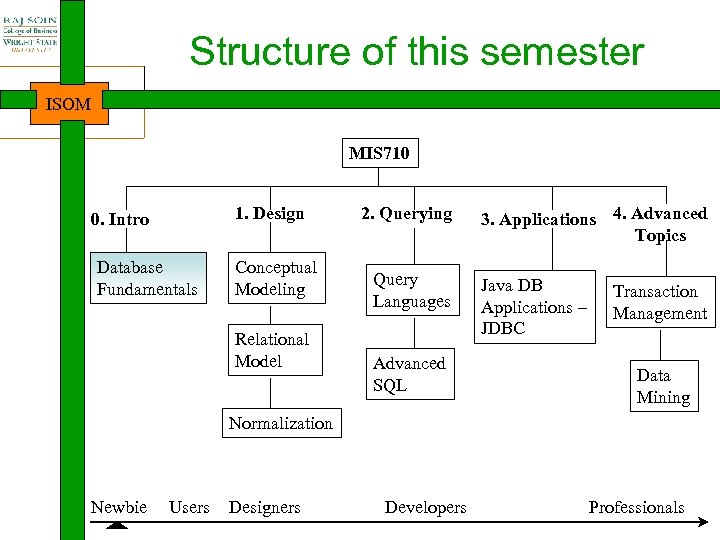
Structure of this semester ISOM MIS 710 1. Design 0. Intro Database Fundamentals Conceptual Modeling Relational Model 2. Querying Query Languages Advanced SQL 3. Applications 4. Advanced Topics Java DB Applications – JDBC Transaction Management Data Mining Normalization Newbie Users Designers Developers Professionals
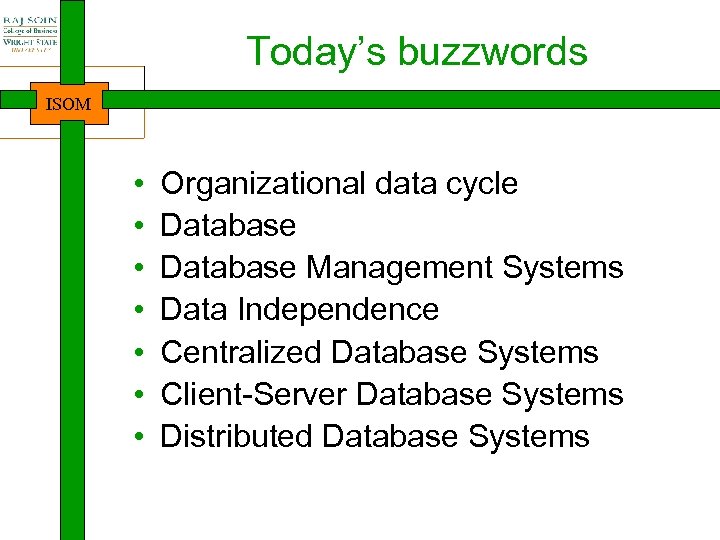
Today’s buzzwords ISOM • • Organizational data cycle Database Management Systems Data Independence Centralized Database Systems Client-Server Database Systems Distributed Database Systems
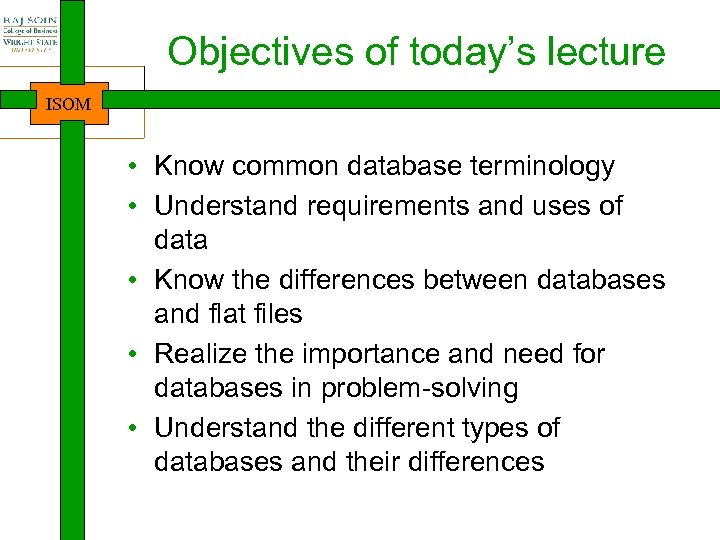
Objectives of today’s lecture ISOM • Know common database terminology • Understand requirements and uses of data • Know the differences between databases and flat files • Realize the importance and need for databases in problem-solving • Understand the different types of databases and their differences
Data: A Resource ISOM • The Success of an organization depends on efficient use of its resources: Ø Buildings, factories, equipment Ø Technical know-how Ø Human resources Ø Data • Data: An important organizational resource
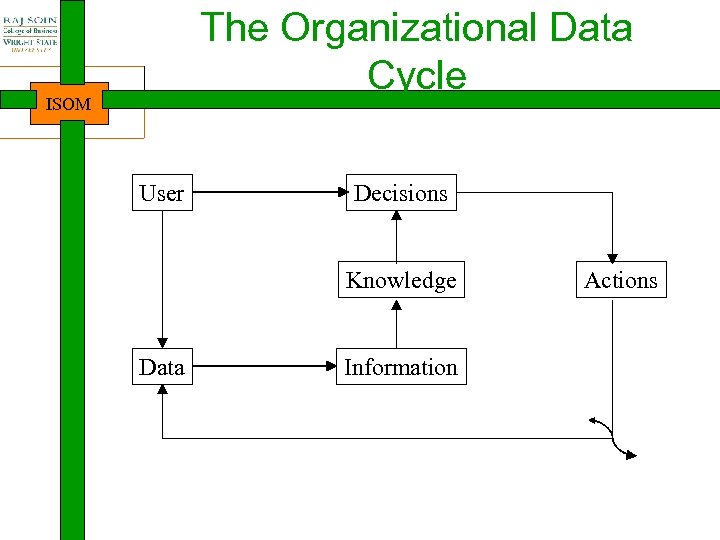
The Organizational Data Cycle ISOM User Decisions Knowledge Data Information Actions
Electronic Data ISOM • Why? ØLarge volume in a small space ØEase of sharing ØEase of use ØData analysis • How? ØFile-based system versus databases
Legacy (File-based) Systems ISOM • • Uncontrolled data redundancy, Data inconsistency Poor data sharing Difficult to keep up with changes Record format Vs. user requirements Programs Vs. record format Low productivity High maintenance cost
So what is a database? ISOM • According to Oxford English Dictionary: “A structured collection of data held in computer storage; esp. one that incorporates software to make it accessible in a variety of ways” • So does it make pretty much every collection of data a “database”?
The Database ISOM • The data itself PLUS The data definitions (metadata), applications, queries and visualizations
Database Approach ISOM • Non-redundant collection of logically related facts Ø representing some aspect of the real world Ø the data itself plus the data definitions • • • Permits sharing Consistent representation for each piece of data Avoids (minimizes) redundancy Allows different user views Users are isolated from most changes
Why Databases? ISOM • Independence from representation formats • Control redundancy and consistency • Ensure integrity/security • Better scalability • Allow ad hoc access • Better maintenance • Better concurrency
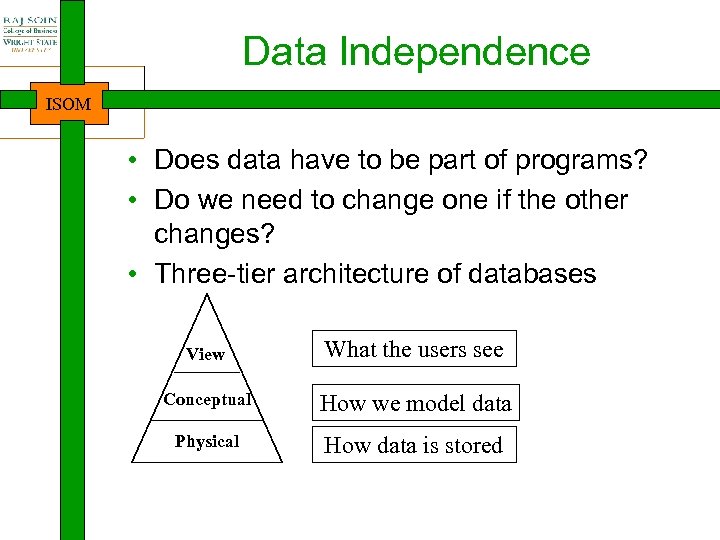
Data Independence ISOM • Does data have to be part of programs? • Do we need to change one if the other changes? • Three-tier architecture of databases View What the users see Conceptual How we model data Physical How data is stored
Access Flexibility ISOM • • • Easy to ask ad-hoc questions No need for separate codes User-friendly interface Command-based (e. g. , SQL) Graphical (e. g. , QBE)
Data Integrity ISOM • Ensures that the stored data are consistent and correct • Easy to define global rules Øcustomer_age > 21 years Ønumber_of_credits < 18 • Can allow multiple users to access data without compromising on data integrity
Data Security ISOM • Access definition ØGlobal ØLocal • Uniform access authorization
Data Redundancy ISOM • • • Data need not be replicated Less wastage of storage space Less data anomaly Reduced and controlled redundancy Tighter control of replicated data
Standardization ISOM • Everybody talks the same talk. ØLess chance of misunderstanding ØEasier to interpret other’s data • Easier to merge ØUseful when several organizations combine to form one.
ISOM Productivity and Maintenance • Increase in productivity Ø User-friendly interface Ø Independence from specific data structure • Easier maintenance Ø Less code to maintain • The DBMS is the bulk of the code. • Ad-hoc queries make it possible to make do with much less code. Ø The vendor makes revisions of the DBMS. • Economy of scale
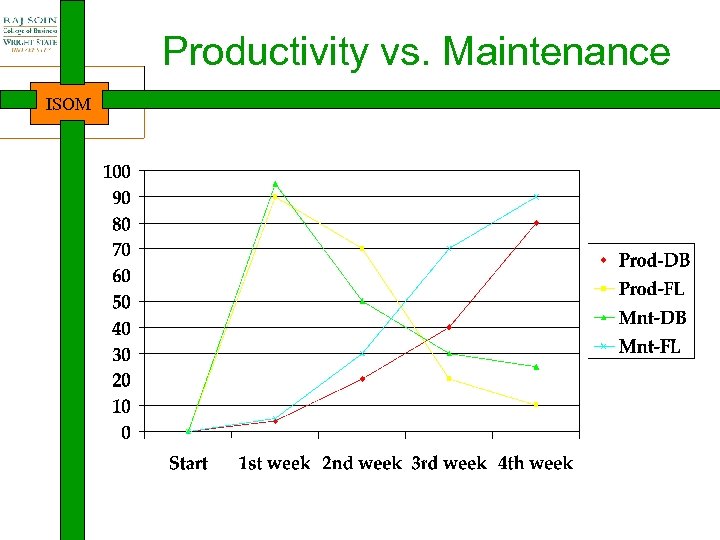
Productivity vs. Maintenance ISOM
Disadvantages of Databases ISOM • • • Software complexity Processing inefficiency Need for co-ordination Organizational impact Risk
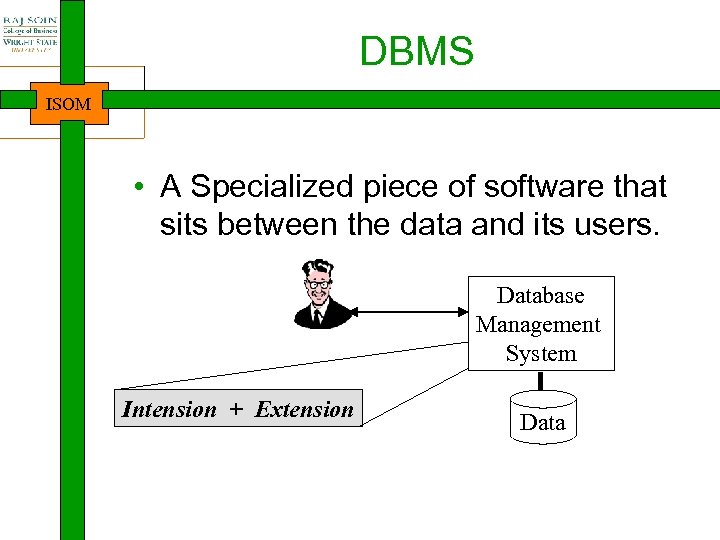
DBMS ISOM • A Specialized piece of software that sits between the data and its users. Database Management System Intension + Extension Data
DBMS Functions and Users ISOM • Four major uses of a DBMS package Ø Database Development, Interrogation, Maintenance, and Ø Application Development • Automated tools for design, query, and application development • Database users Ø Database administrators ( DBAs ) Ø Database designer Ø End Users
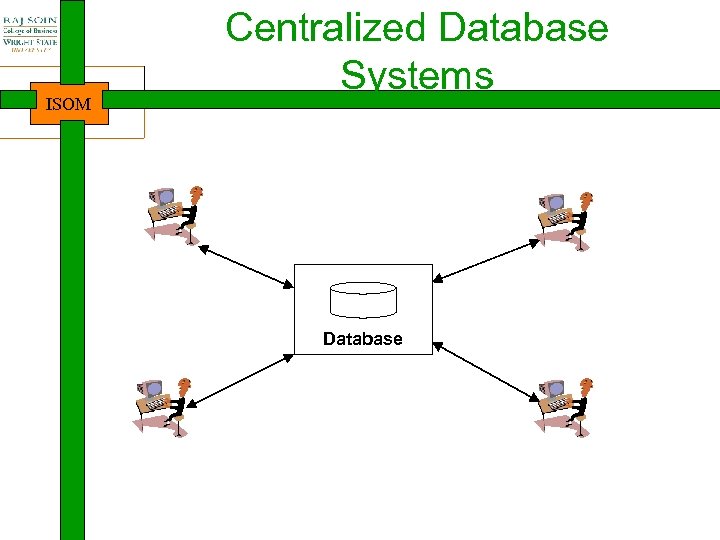
ISOM Centralized Database Systems Database
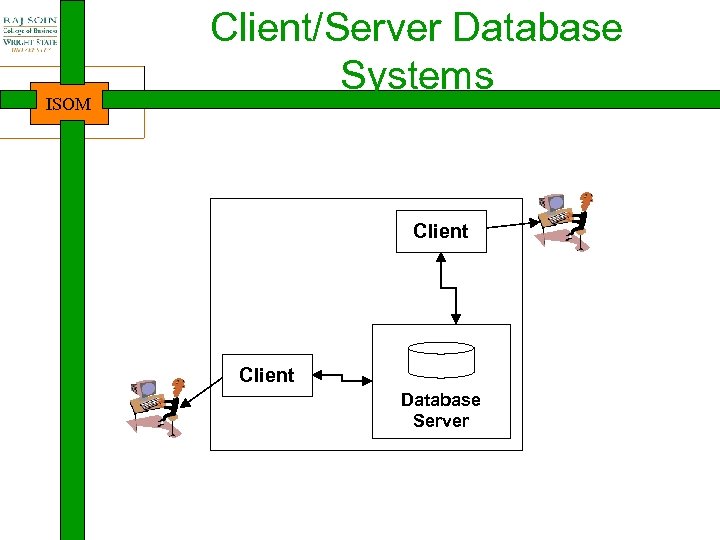
ISOM Client/Server Database Systems Client Database Server
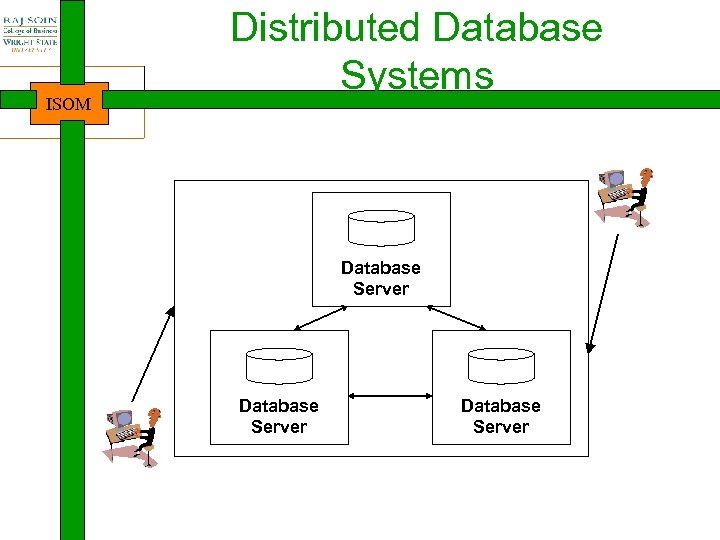
ISOM Distributed Database Systems Database Server
Summary ISOM • Data is essential for an organization • A Database is usually the most effective way of storing and organizing data • File-based Vs. database systems • Database system properties • Types of database systems
28052b87bcc95140aaa12a29c1e77dfe.ppt