45c4f3623aa2fd15ca881ac56b7064ce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 MINS 298 C SAP Configuration & Use: Security Copyright 1996, 1997, 1998 - James R. Mensching, Gail Corbitt Contents of this file are for the exclusive use of the special MINS 298 C class dealing with SAP software at CSU Chico for the Fall, 1998 semester. Any other use in either electronic or hardcopy form is prohibited without the express written permission of the author. This material is confidential. Do not share it with anyone not enrolled in the class. CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG Security Lecture SAP Security Lecture 1
MINS 298 C SAP Configuration & Use: Security Copyright 1996, 1997, 1998 - James R. Mensching, Gail Corbitt Contents of this file are for the exclusive use of the special MINS 298 C class dealing with SAP software at CSU Chico for the Fall, 1998 semester. Any other use in either electronic or hardcopy form is prohibited without the express written permission of the author. This material is confidential. Do not share it with anyone not enrolled in the class. CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG Security Lecture SAP Security Lecture 1
 SAP Security l Purpose of Security: n Assign users rights to perform job tasks that they need to do. n Prohibit users from doing tasks that they are not supposed to do. l Objectives of presentation n Define key security concepts n Examine relationship between user and security concepts n Apply concepts to real situations CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 2
SAP Security l Purpose of Security: n Assign users rights to perform job tasks that they need to do. n Prohibit users from doing tasks that they are not supposed to do. l Objectives of presentation n Define key security concepts n Examine relationship between user and security concepts n Apply concepts to real situations CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 2
 SAP Security l Security is performed at the object level n 30 + Object classes, such as Basis Administration, FI, MM Master Data (View Objects within classes by using SU 03) n About 500 + objects within the 30 + classes l SAP Security works on a pass-fail system. It checks constraints until if finds a failure. l Levels of Setting: n Authorization Object in the form of authorization (test on an object) n Profile (sets of authorizations) n User ID CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 3
SAP Security l Security is performed at the object level n 30 + Object classes, such as Basis Administration, FI, MM Master Data (View Objects within classes by using SU 03) n About 500 + objects within the 30 + classes l SAP Security works on a pass-fail system. It checks constraints until if finds a failure. l Levels of Setting: n Authorization Object in the form of authorization (test on an object) n Profile (sets of authorizations) n User ID CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 3
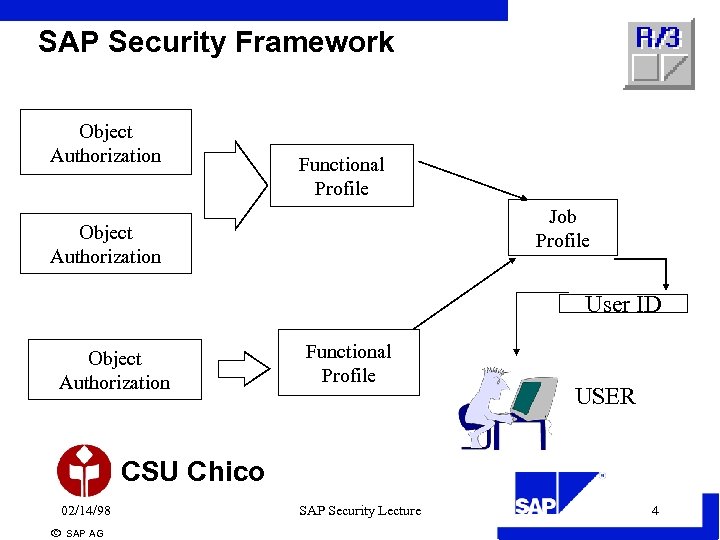 SAP Security Framework Object Authorization Functional Profile Job Profile Object Authorization User ID Object Authorization Functional Profile USER CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 4
SAP Security Framework Object Authorization Functional Profile Job Profile Object Authorization User ID Object Authorization Functional Profile USER CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 4
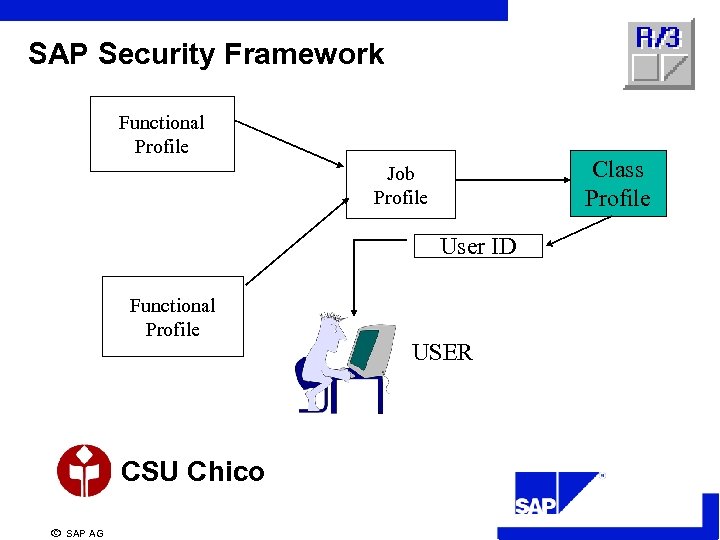 SAP Security Framework Functional Profile Class Profile Job Profile User ID Functional Profile CSU Chico ã SAP AG USER
SAP Security Framework Functional Profile Class Profile Job Profile User ID Functional Profile CSU Chico ã SAP AG USER
 SAP Security Components l Authorization Object: something in the system that potentially needs protecting (company code, document type, etc. ) l Fields: attributes that can be used to set protection (110 fields per object that vary with object) n Activity: such as create, update, delete, view. . n Authorization Group: Values that the object needs n IDOC Type l Profile (set of authorizations) l User Master Record (all profiles for that user) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 5
SAP Security Components l Authorization Object: something in the system that potentially needs protecting (company code, document type, etc. ) l Fields: attributes that can be used to set protection (110 fields per object that vary with object) n Activity: such as create, update, delete, view. . n Authorization Group: Values that the object needs n IDOC Type l Profile (set of authorizations) l User Master Record (all profiles for that user) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 5
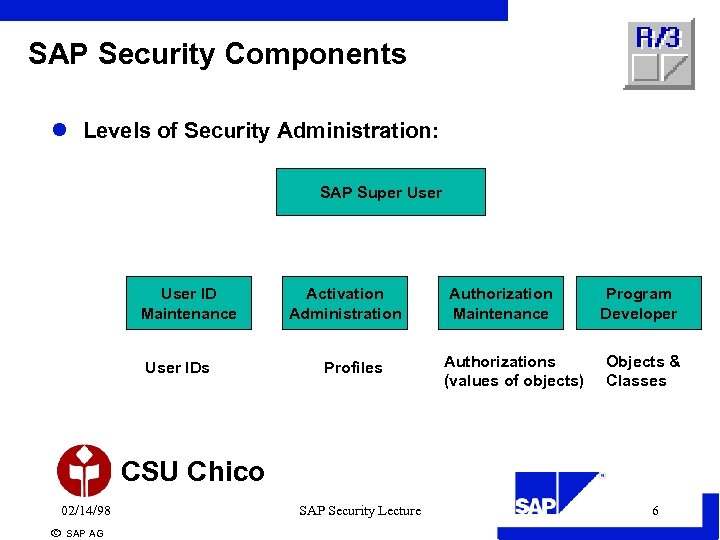 SAP Security Components l Levels of Security Administration: SAP Super User ID Maintenance User IDs Activation Administration Profiles Authorization Maintenance Authorizations (values of objects) Program Developer Objects & Classes CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 6
SAP Security Components l Levels of Security Administration: SAP Super User ID Maintenance User IDs Activation Administration Profiles Authorization Maintenance Authorizations (values of objects) Program Developer Objects & Classes CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 6
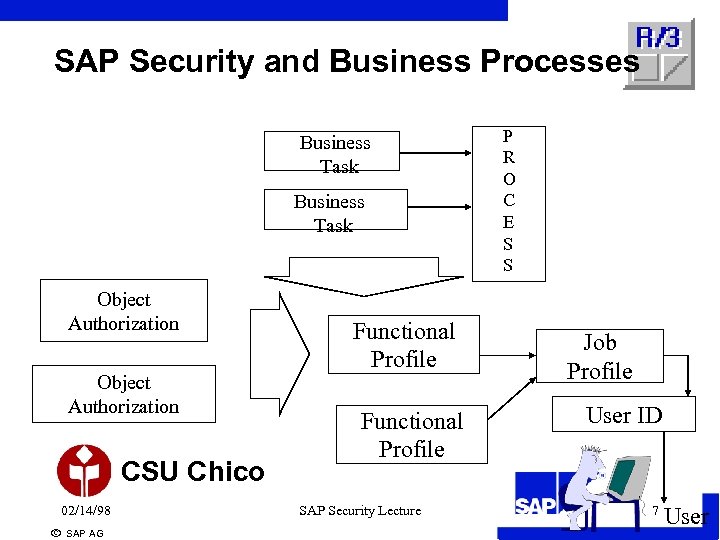 SAP Security and Business Processes Business Task Object Authorization CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG Functional Profile SAP Security Lecture P R O C E S S Job Profile User ID 7 User
SAP Security and Business Processes Business Task Object Authorization CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG Functional Profile SAP Security Lecture P R O C E S S Job Profile User ID 7 User
 SAP Security l Authorization: Set of specified values for fields in an Authorization Object = test conditions for the object l Standard Authorizations provided by SAP n Object: F_BKPF_BED: Customer Account n Activity: * n Account Group: * l Never Change or Delete an SAP authorization l Custom Authorizations (should start with Z) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 8
SAP Security l Authorization: Set of specified values for fields in an Authorization Object = test conditions for the object l Standard Authorizations provided by SAP n Object: F_BKPF_BED: Customer Account n Activity: * n Account Group: * l Never Change or Delete an SAP authorization l Custom Authorizations (should start with Z) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 8
 SAP Security Example l Object Class: Financial Accounting l Authorization: ZS_D 01 l Authorization Object: F_BKPF_BED: Customer Account l Activity: 01 -03, 10 (create, change, print, post) l Account Group: CALF, HAW l SAP programs perform AUTHORITY-CHECK on objects for values in fields CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 9
SAP Security Example l Object Class: Financial Accounting l Authorization: ZS_D 01 l Authorization Object: F_BKPF_BED: Customer Account l Activity: 01 -03, 10 (create, change, print, post) l Account Group: CALF, HAW l SAP programs perform AUTHORITY-CHECK on objects for values in fields CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 9
 SAP Security: Creating an Authorization l Create a name for the authorization n Start with the letter Z n Don’t use underscore as second character n Example: ZS_D 01 l Use SU 03 to create the authorization (Tools --> Administration -->Maintain Users) n Create (first icon: sheet of paper) n Maintain values sets the values you want n Save n Activate CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 10
SAP Security: Creating an Authorization l Create a name for the authorization n Start with the letter Z n Don’t use underscore as second character n Example: ZS_D 01 l Use SU 03 to create the authorization (Tools --> Administration -->Maintain Users) n Create (first icon: sheet of paper) n Maintain values sets the values you want n Save n Activate CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 10
 SAP Security l Profile: Set of Authorization Objects l Simple Profile: 1 Authorization Object l Composite Profile: more than one authorization object l Can have a composite made up of composites CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 11
SAP Security l Profile: Set of Authorization Objects l Simple Profile: 1 Authorization Object l Composite Profile: more than one authorization object l Can have a composite made up of composites CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 11
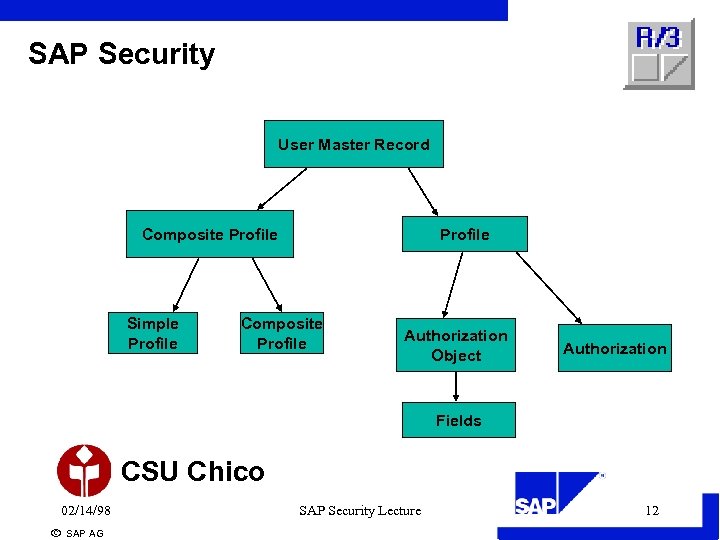 SAP Security User Master Record Composite Profile Simple Profile Composite Profile Authorization Object Authorization Fields CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 12
SAP Security User Master Record Composite Profile Simple Profile Composite Profile Authorization Object Authorization Fields CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 12
 SAP Security l SAP Standard Profile: F_BKPF_KANZ (Display vendor Accounts) l Custom Profile: AA: FIAR_M 01 l Create profile then activate l Copy from existing profile then rename l To look at, change or create profiles use SU 02 CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 13
SAP Security l SAP Standard Profile: F_BKPF_KANZ (Display vendor Accounts) l Custom Profile: AA: FIAR_M 01 l Create profile then activate l Copy from existing profile then rename l To look at, change or create profiles use SU 02 CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 13
 SAP Security l Standard Profiles common to all SAP installations n SAP_ALL (unlimited access to system) n SAP_NEW (allows older standard profiles to work in newer SAP releases) n S_A_SYSTEM: System Administrator n S_A_SHOW: Display authorizations only CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 14
SAP Security l Standard Profiles common to all SAP installations n SAP_ALL (unlimited access to system) n SAP_NEW (allows older standard profiles to work in newer SAP releases) n S_A_SYSTEM: System Administrator n S_A_SHOW: Display authorizations only CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 14
 SAP Security: Users l User Profiles assign profiles to specific user IDs l Users can belong to Group, I. e. ABAP Developers, C&I Admin l Can’t assign authorizations to groups only to individual users l User Group is a field in some authorization objects l Groups useful to separate responsibility, I. e. more than one security administrator, each responsible for a group of users CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 15
SAP Security: Users l User Profiles assign profiles to specific user IDs l Users can belong to Group, I. e. ABAP Developers, C&I Admin l Can’t assign authorizations to groups only to individual users l User Group is a field in some authorization objects l Groups useful to separate responsibility, I. e. more than one security administrator, each responsible for a group of users CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 15
 SAP Security: Users l Name the ID for the User l Set the password l Lock/unlock the account l Define time period for the ID l Set default printer and printing rights l Define PIDs (Parameters) l Define profiles CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 16
SAP Security: Users l Name the ID for the User l Set the password l Lock/unlock the account l Define time period for the ID l Set default printer and printing rights l Define PIDs (Parameters) l Define profiles CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 16
 SAP Security: Users l Rules for setting passwords: n Must be at least 3 characters n Can not begin with ! or ? n First 3 characters can not be a sequence of 3 characters in user ID. I. e. if by user id is gcorbitt, my password can not contain orb, or cor. n First 3 characters can not be the same, I. e. ccc n Can not use “pass” or “sap” CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 17
SAP Security: Users l Rules for setting passwords: n Must be at least 3 characters n Can not begin with ! or ? n First 3 characters can not be a sequence of 3 characters in user ID. I. e. if by user id is gcorbitt, my password can not contain orb, or cor. n First 3 characters can not be the same, I. e. ccc n Can not use “pass” or “sap” CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 17
 SAP Security: Users l PID : Parameter ID l Example of parameter: n default menu options, I. e. fast entry n default currency n posting period options CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 18
SAP Security: Users l PID : Parameter ID l Example of parameter: n default menu options, I. e. fast entry n default currency n posting period options CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 18
 SAP Security: Users l User types n Dialog n BDC: inbound interfaces (I. e. data coming in from a legacy system) n CPIC: machine to machine ID connect through UNIX (I. e. EDI inbound or outbound) n BDC and CPIC do not have expiration dates on the passwords CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 19
SAP Security: Users l User types n Dialog n BDC: inbound interfaces (I. e. data coming in from a legacy system) n CPIC: machine to machine ID connect through UNIX (I. e. EDI inbound or outbound) n BDC and CPIC do not have expiration dates on the passwords CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 19
 SAP Security: Transactions l SU 01: Creates and maintains users l SU 02: Creates and maintains profiles l SU 53: Displays LAST authorization failure l ST 01: Traces keystrokes l SU 03: Lists objects and classes l SM 04: Monitors user activity l SE 16: Looks at specific tables in SAP (T 003 = auth. group) l SA 38: Looks at programs (AUTHORITY-CHECK) l SU 12: Deletes all users (usually disabled) l SU 10: Adds or deletes a profile to all users CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 20
SAP Security: Transactions l SU 01: Creates and maintains users l SU 02: Creates and maintains profiles l SU 53: Displays LAST authorization failure l ST 01: Traces keystrokes l SU 03: Lists objects and classes l SM 04: Monitors user activity l SE 16: Looks at specific tables in SAP (T 003 = auth. group) l SA 38: Looks at programs (AUTHORITY-CHECK) l SU 12: Deletes all users (usually disabled) l SU 10: Adds or deletes a profile to all users CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 20
 SAP Security: Coming Attractions l SAP Profile Generator (31. G, R 4) n Makes it easier to track and maintain multiple profiles per user n Uses menu paths to create authorizations or profiles n Activity Groups similar to our functional profiles l Activity Group Maintenance (31. G) n Allows for profile updates, parameter settings by group instead of by individual user n Hopefully allows for resetting expiration, start dates, printer options, etc. by groups of users instead of one user at a time CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 21
SAP Security: Coming Attractions l SAP Profile Generator (31. G, R 4) n Makes it easier to track and maintain multiple profiles per user n Uses menu paths to create authorizations or profiles n Activity Groups similar to our functional profiles l Activity Group Maintenance (31. G) n Allows for profile updates, parameter settings by group instead of by individual user n Hopefully allows for resetting expiration, start dates, printer options, etc. by groups of users instead of one user at a time CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 21
 Application of SAP Security to Classroom Activity l Define what “jobs” or roles we want the students to have per class --functional profiles l Set up authorizations for each job or role - job profiles l Assign job profiles to users l Document existing authorizations for Display and Create Activities for each “application” object l Create authorizations for Display and Create where missing l Create a standard profile that any user could have (view only to all modules) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 22
Application of SAP Security to Classroom Activity l Define what “jobs” or roles we want the students to have per class --functional profiles l Set up authorizations for each job or role - job profiles l Assign job profiles to users l Document existing authorizations for Display and Create Activities for each “application” object l Create authorizations for Display and Create where missing l Create a standard profile that any user could have (view only to all modules) CSU Chico 02/14/98 ã SAP AG SAP Security Lecture 22


