62b2004c228a4e880f9dafa6dd52e0bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Ministry of Health, Malaysia Non-Communica Diseases in Malaysia Feisul Idzwan Mustapha MBBS, MPH, AM(M) Disease Control Division Ministry of Health, Malaysia Email: dr. feisul@moh. gov. my
Ministry of Health, Malaysia Non-Communica Diseases in Malaysia Feisul Idzwan Mustapha MBBS, MPH, AM(M) Disease Control Division Ministry of Health, Malaysia Email: dr. feisul@moh. gov. my
 MALAYSIA Total Population: ~28 million (2008) Life expectancy at birth (years) • Male 71. 7 • Female 76. 5 2
MALAYSIA Total Population: ~28 million (2008) Life expectancy at birth (years) • Male 71. 7 • Female 76. 5 2
 Who are Malaysians? n Malay q q n Malaysia's largest ethnic group, accounting for over 60% With the oldest indigenous people, they form a group called bumiputera, which translates as "sons" or "princes of the soil" Chinese About 26% of the population n Indian About 8% of the population 3
Who are Malaysians? n Malay q q n Malaysia's largest ethnic group, accounting for over 60% With the oldest indigenous people, they form a group called bumiputera, which translates as "sons" or "princes of the soil" Chinese About 26% of the population n Indian About 8% of the population 3
 Malaysian Health Care System at a glance n n n n Health care provided at nominal charge for all Malaysians (& even non-citizens) Total MOH Budget (RM 12. 9 billion); 7. 29% of total National Budget Total expenditure on health (% of GDP) 4. 70% MOH Health Clinics: 802 Private Medical Clinics: 6, 371 MOH Hospitals: 130 (33, 004 beds) Private Hospitals: 209 (11, 689 beds) Source: Health Informatics Centre, MOH (all figures for 2008, except % of GDP 2007) 4
Malaysian Health Care System at a glance n n n n Health care provided at nominal charge for all Malaysians (& even non-citizens) Total MOH Budget (RM 12. 9 billion); 7. 29% of total National Budget Total expenditure on health (% of GDP) 4. 70% MOH Health Clinics: 802 Private Medical Clinics: 6, 371 MOH Hospitals: 130 (33, 004 beds) Private Hospitals: 209 (11, 689 beds) Source: Health Informatics Centre, MOH (all figures for 2008, except % of GDP 2007) 4
 Burden of NCD in Malaysia n n Currently about 60 -70% of total health clinic attendances are related to NCD Excluding normal deliveries, NCD contributes to over 20% of total hospitalisation in MOH Hospitals NCD is also in the top five most common cause of death in MOH Hospitals in the past five years Most common cause of premature death (below 60 years of age) in Malaysia are due to cardiovascular diseases, followed by road traffic accidents Sources: Health Informatics Centre, MOH Malaysian Burden of Disease & Injury Study 2004 5
Burden of NCD in Malaysia n n Currently about 60 -70% of total health clinic attendances are related to NCD Excluding normal deliveries, NCD contributes to over 20% of total hospitalisation in MOH Hospitals NCD is also in the top five most common cause of death in MOH Hospitals in the past five years Most common cause of premature death (below 60 years of age) in Malaysia are due to cardiovascular diseases, followed by road traffic accidents Sources: Health Informatics Centre, MOH Malaysian Burden of Disease & Injury Study 2004 5
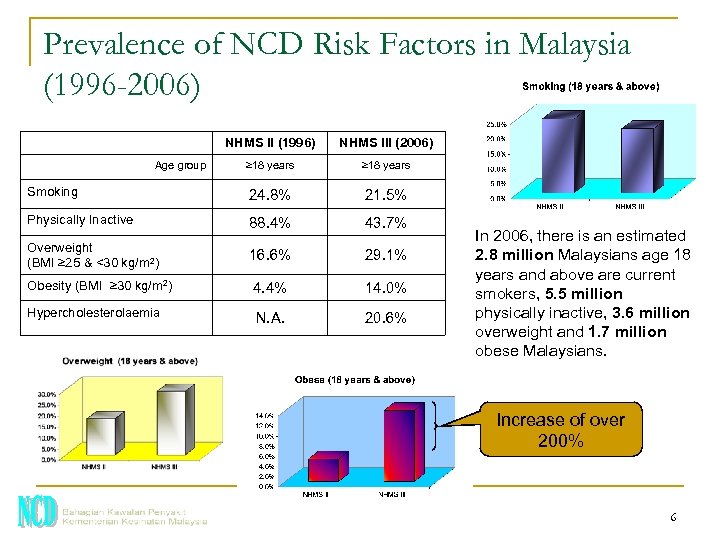 Prevalence of NCD Risk Factors in Malaysia (1996 -2006) NHMS II (1996) NHMS III (2006) ≥ 18 years Smoking 24. 8% 21. 5% Physically Inactive 88. 4% 43. 7% Overweight (BMI ≥ 25 & <30 kg/m 2) 16. 6% 29. 1% Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m 2) 4. 4% 14. 0% Hypercholesterolaemia N. A. 20. 6% Age group In 2006, there is an estimated 2. 8 million Malaysians age 18 years and above are current smokers, 5. 5 million physically inactive, 3. 6 million overweight and 1. 7 million obese Malaysians. Increase of over 200% 6
Prevalence of NCD Risk Factors in Malaysia (1996 -2006) NHMS II (1996) NHMS III (2006) ≥ 18 years Smoking 24. 8% 21. 5% Physically Inactive 88. 4% 43. 7% Overweight (BMI ≥ 25 & <30 kg/m 2) 16. 6% 29. 1% Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m 2) 4. 4% 14. 0% Hypercholesterolaemia N. A. 20. 6% Age group In 2006, there is an estimated 2. 8 million Malaysians age 18 years and above are current smokers, 5. 5 million physically inactive, 3. 6 million overweight and 1. 7 million obese Malaysians. Increase of over 200% 6
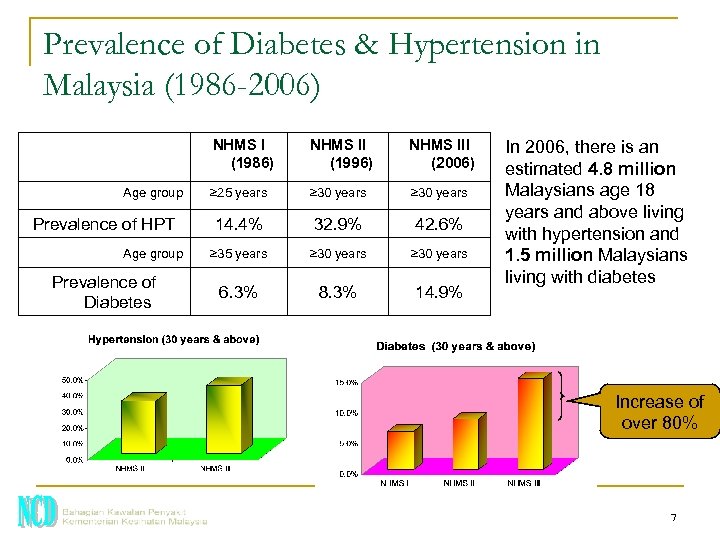 Prevalence of Diabetes & Hypertension in Malaysia (1986 -2006) NHMS I (1986) Age group Prevalence of HPT Age group Prevalence of Diabetes NHMS II (1996) NHMS III (2006) ≥ 25 years ≥ 30 years 14. 4% 32. 9% 42. 6% ≥ 35 years ≥ 30 years 6. 3% 8. 3% 14. 9% In 2006, there is an estimated 4. 8 million Malaysians age 18 years and above living with hypertension and 1. 5 million Malaysians living with diabetes Increase of over 80% 7
Prevalence of Diabetes & Hypertension in Malaysia (1986 -2006) NHMS I (1986) Age group Prevalence of HPT Age group Prevalence of Diabetes NHMS II (1996) NHMS III (2006) ≥ 25 years ≥ 30 years 14. 4% 32. 9% 42. 6% ≥ 35 years ≥ 30 years 6. 3% 8. 3% 14. 9% In 2006, there is an estimated 4. 8 million Malaysians age 18 years and above living with hypertension and 1. 5 million Malaysians living with diabetes Increase of over 80% 7
 Mapping of current health system activities of NCD in Malaysia n n n p p p Malaysia have fulfilled most indicators of the building blocks However current activities disjointed, not well coordinated, restricted to ‘health sector’ & not truly multi-sectoral Lack of strong civil society Stewardship: Government mandate for NCD policies Health financing: Government pays for bulk of primary care Heath workforce: Information & skills in NCD part of basic training Info & evidence: Availability of nationwide risk factor data Medicines & technology: First & second line drugs available Health services: Risk factor screening & intervention 8
Mapping of current health system activities of NCD in Malaysia n n n p p p Malaysia have fulfilled most indicators of the building blocks However current activities disjointed, not well coordinated, restricted to ‘health sector’ & not truly multi-sectoral Lack of strong civil society Stewardship: Government mandate for NCD policies Health financing: Government pays for bulk of primary care Heath workforce: Information & skills in NCD part of basic training Info & evidence: Availability of nationwide risk factor data Medicines & technology: First & second line drugs available Health services: Risk factor screening & intervention 8
 NSP-NCD: Seven Action Areas for Malaysia 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Prevention and Promotion Clinical Management Increasing Patient Compliance Action with NGOs, Professional Bodies & Other Stakeholders Monitoring, Research and Surveillance Capacity Building Policy and Regulatory interventions • NSP-NCD provides the framework for NCD prevention & control at the National level • Diabetes & Obesity selected as entry points • Action Areas in line with WHO recommendations 9
NSP-NCD: Seven Action Areas for Malaysia 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Prevention and Promotion Clinical Management Increasing Patient Compliance Action with NGOs, Professional Bodies & Other Stakeholders Monitoring, Research and Surveillance Capacity Building Policy and Regulatory interventions • NSP-NCD provides the framework for NCD prevention & control at the National level • Diabetes & Obesity selected as entry points • Action Areas in line with WHO recommendations 9
 Emotions Perception of the Public versus Reality 10
Emotions Perception of the Public versus Reality 10
 Politics 11
Politics 11
 Work in Progress… n Creation of a cabinet-level committee, chaired by the Deputy Primer Minister. Members from 9 other key ministries: q q q q q Education Information & Communication Rural Development Agriculture Youth & Sports Human Resource Domestic Trade & Consumerism Housing & Local Government Women, Family & Community 12
Work in Progress… n Creation of a cabinet-level committee, chaired by the Deputy Primer Minister. Members from 9 other key ministries: q q q q q Education Information & Communication Rural Development Agriculture Youth & Sports Human Resource Domestic Trade & Consumerism Housing & Local Government Women, Family & Community 12
 Work in Progress (2) n n Whole-of-government approach Policy & regulatory interventions q q n Regulation of salt & sugar in food/drinks Regulation on advertising Expansion of workplace-based, schoolbased, & community-based interventions 13
Work in Progress (2) n n Whole-of-government approach Policy & regulatory interventions q q n Regulation of salt & sugar in food/drinks Regulation on advertising Expansion of workplace-based, schoolbased, & community-based interventions 13
 Lessons learned n n Put the right people at the right place Have all of the materials and tools prepared – seize the chance when the opportunities come Seek out the “right” partners in other ministries & civil societies Facts may not actually work well in getting buy-in. Need to become a salesman 14
Lessons learned n n Put the right people at the right place Have all of the materials and tools prepared – seize the chance when the opportunities come Seek out the “right” partners in other ministries & civil societies Facts may not actually work well in getting buy-in. Need to become a salesman 14
 My Grand Challenge n n Raise the political priority of NCD Provide committed and effective leadership in NCD 15
My Grand Challenge n n Raise the political priority of NCD Provide committed and effective leadership in NCD 15
 16
16
 Terima Kasih 17
Terima Kasih 17


