6f091f4e6158a27faeca4ae82388ad87.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Mineral Resources Chapter 11 Section 1
Mineral Resources Chapter 11 Section 1
 2 Categories of Resources – Nonrenewable resources-their supply is limited and they cannot be replaced once they are used – Renewable resources- can be replaced within a human lifetime or as they are used • Ex: trees, air, water – Mineral resources- may be metals or nonmetals
2 Categories of Resources – Nonrenewable resources-their supply is limited and they cannot be replaced once they are used – Renewable resources- can be replaced within a human lifetime or as they are used • Ex: trees, air, water – Mineral resources- may be metals or nonmetals
 Formation of Ores Ore- deposits of minerals from which metals and nonmetals can be removed profitably • Examples: – Hematite & Magnetite are used to extract iron – Bauxite is an ore of aluminum – Halite- salt – Quartz- glass BAUXITE. Ohio State University Newark. Web. 15 Dec. 2011. http: //www 1. newark. ohiotate. edu/Professional/OSU/Faculty/jstjohn/Common%20 rocks/Bauxit. htm>. Bauxite
Formation of Ores Ore- deposits of minerals from which metals and nonmetals can be removed profitably • Examples: – Hematite & Magnetite are used to extract iron – Bauxite is an ore of aluminum – Halite- salt – Quartz- glass BAUXITE. Ohio State University Newark. Web. 15 Dec. 2011. http: //www 1. newark. ohiotate. edu/Professional/OSU/Faculty/jstjohn/Common%20 rocks/Bauxit. htm>. Bauxite
 – Ores and Cooling Magma • Heavy metals such as Chromium, Nickel and Lead will sink to the bottom of magma, forming a deposit – Ores and Contact Metamorphism • Lead, copper and zinc ores form from contact metamorphism – Contact metamorphism- when magma heats surrounding • Veins- hot mineral solutions spread through many small cracks and deposit valuable minerals • Lode- large number of thick mineral veins – “Mother Lode” Rocks in the Field. Oxford Earth Sciences Image Store, June 2004. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
– Ores and Cooling Magma • Heavy metals such as Chromium, Nickel and Lead will sink to the bottom of magma, forming a deposit – Ores and Contact Metamorphism • Lead, copper and zinc ores form from contact metamorphism – Contact metamorphism- when magma heats surrounding • Veins- hot mineral solutions spread through many small cracks and deposit valuable minerals • Lode- large number of thick mineral veins – “Mother Lode” Rocks in the Field. Oxford Earth Sciences Image Store, June 2004. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 – Ores and Moving Water • Fragments of native elements such as gold are released as rock breaks down due to weathering and erosion. Due to their high density, they get deposited in weak currents creating Placer deposits. • Water can also dissolve minerals which will later be precipitated out in veins
– Ores and Moving Water • Fragments of native elements such as gold are released as rock breaks down due to weathering and erosion. Due to their high density, they get deposited in weak currents creating Placer deposits. • Water can also dissolve minerals which will later be precipitated out in veins
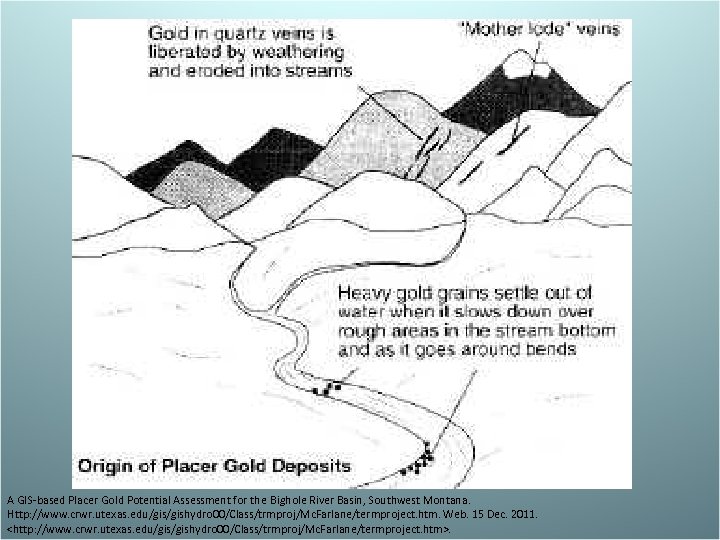 A GIS-based Placer Gold Potential Assessment for the Bighole River Basin, Southwest Montana. Http: //www. crwr. utexas. edu/gishydro 00/Class/trmproj/Mc. Farlane/termproject. htm. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
A GIS-based Placer Gold Potential Assessment for the Bighole River Basin, Southwest Montana. Http: //www. crwr. utexas. edu/gishydro 00/Class/trmproj/Mc. Farlane/termproject. htm. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 • Uses of Mineral Resources – Gemstones- rare mineral crystals that display extraordinary brilliance and color – Building materials- gypsum, calcite • Mineral Conservation – Minerals are being consumed at an alarming rate which is increasing each year. Eventually, we will run out Blue Zircon. Gemselect. com, 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
• Uses of Mineral Resources – Gemstones- rare mineral crystals that display extraordinary brilliance and color – Building materials- gypsum, calcite • Mineral Conservation – Minerals are being consumed at an alarming rate which is increasing each year. Eventually, we will run out Blue Zircon. Gemselect. com, 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Fossil Fuels – Natural resources • coal, petroleum, natural gas • form from the remains of living organisms • Fossil fuel- organic in origin (carbon) • Hydrocarbons- rich in compounds of carbon and hydrogen; contain energy obtained from sunlight by plants and animals that lived millions of years ago Refining Industry. The Way Inc. , 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Fossil Fuels – Natural resources • coal, petroleum, natural gas • form from the remains of living organisms • Fossil fuel- organic in origin (carbon) • Hydrocarbons- rich in compounds of carbon and hydrogen; contain energy obtained from sunlight by plants and animals that lived millions of years ago Refining Industry. The Way Inc. , 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Petroleum Engeneering. Missouri University of Science & Technology, 2008. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Petroleum Engeneering. Missouri University of Science & Technology, 2008. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
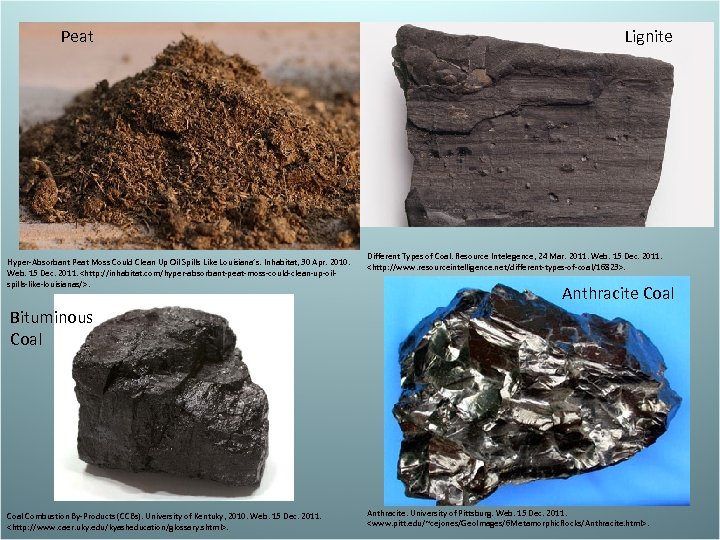
 Coal – Dark-colored organic rock • Form in swamps because there is little oxygen for microorganisms to decompose the dead organic material – Formation of coal • Coal forms from plants that have been carbonized • Carbonization- when bacteria partially decompose plants which releases methane and carbon dioxide. As an end result, only carbon remains – Types of coal • Peat- partially decomposed plants • Lignite- when peat becomes compacted forming brown coal • Bituminous coal- when lignite becomes compacted forming soft coal; most abundant • Anthracite coal- when bituminous coal is morphed (heat & pressure) forming the hardest coal
Coal – Dark-colored organic rock • Form in swamps because there is little oxygen for microorganisms to decompose the dead organic material – Formation of coal • Coal forms from plants that have been carbonized • Carbonization- when bacteria partially decompose plants which releases methane and carbon dioxide. As an end result, only carbon remains – Types of coal • Peat- partially decomposed plants • Lignite- when peat becomes compacted forming brown coal • Bituminous coal- when lignite becomes compacted forming soft coal; most abundant • Anthracite coal- when bituminous coal is morphed (heat & pressure) forming the hardest coal
 Peat Hyper-Absorbant Peat Moss Could Clean Up Oil Spills Like Louisiana’s. Inhabitat, 30 Apr. 2010. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Peat Hyper-Absorbant Peat Moss Could Clean Up Oil Spills Like Louisiana’s. Inhabitat, 30 Apr. 2010. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Petroleum and Natural Gas – Intro • Mixtures of hydrocarbons which are from microorganisms in the oceans millions of years ago • Petroleum- liquid • Natural gas- gas – Formation of Petroleum and Natural Gas • When oceanic microorganism die, they settle on the bottom or the ocean. Since there is little to no oxygen at the bottom, the remains do not get decomposed by bacteria. As they get buried, pressure increases turning them into liquid petroleum. If the heat and pressure become extreme, the petroleum will convert to natural gas. – Petroleum and Natural Gas Deposits • Petroleum and natural gas can seep through permeable rock but get trapped by impermeable rock
Petroleum and Natural Gas – Intro • Mixtures of hydrocarbons which are from microorganisms in the oceans millions of years ago • Petroleum- liquid • Natural gas- gas – Formation of Petroleum and Natural Gas • When oceanic microorganism die, they settle on the bottom or the ocean. Since there is little to no oxygen at the bottom, the remains do not get decomposed by bacteria. As they get buried, pressure increases turning them into liquid petroleum. If the heat and pressure become extreme, the petroleum will convert to natural gas. – Petroleum and Natural Gas Deposits • Petroleum and natural gas can seep through permeable rock but get trapped by impermeable rock
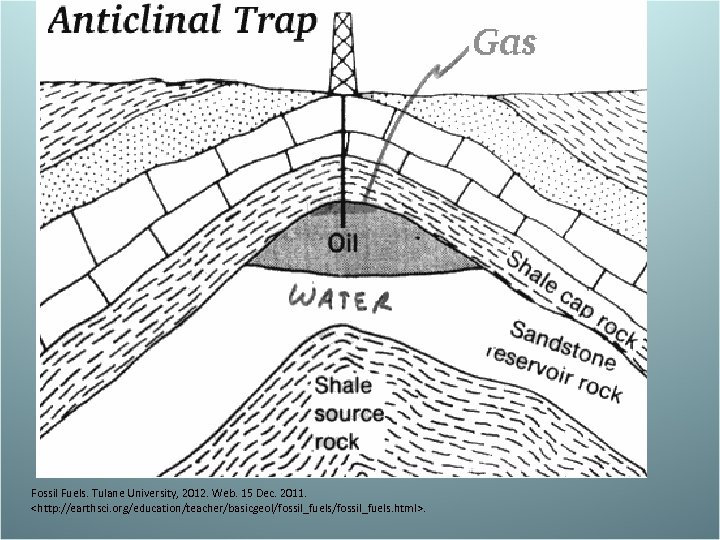 Fossil Fuels. Tulane University, 2012. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Fossil Fuels. Tulane University, 2012. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Uses of Fossil Fuels – Coal- 71% electricity, 13% coal exports, 8% industrial, 7% steel making – Petroleum- 38. 6% gasoline, 38% other fuels, 13. 6% heating oil and kerosene, 8. 4% lubricants, wax and asphalt – Crude oil- unrefined petroleum – Advantage- cheap, efficient – Disadvantage- environmental problems (acid rain, CO 2, SO 2, erosion) • Fossil Fuel Supplies – Nonrenewable resource – Coal is the most abundant but with our current consumption it will only last 200 years – Scientists estimate the U. S. discovered about 75% of its petroleum. The rest is under the ocean floor along the edges of North America
Uses of Fossil Fuels – Coal- 71% electricity, 13% coal exports, 8% industrial, 7% steel making – Petroleum- 38. 6% gasoline, 38% other fuels, 13. 6% heating oil and kerosene, 8. 4% lubricants, wax and asphalt – Crude oil- unrefined petroleum – Advantage- cheap, efficient – Disadvantage- environmental problems (acid rain, CO 2, SO 2, erosion) • Fossil Fuel Supplies – Nonrenewable resource – Coal is the most abundant but with our current consumption it will only last 200 years – Scientists estimate the U. S. discovered about 75% of its petroleum. The rest is under the ocean floor along the edges of North America
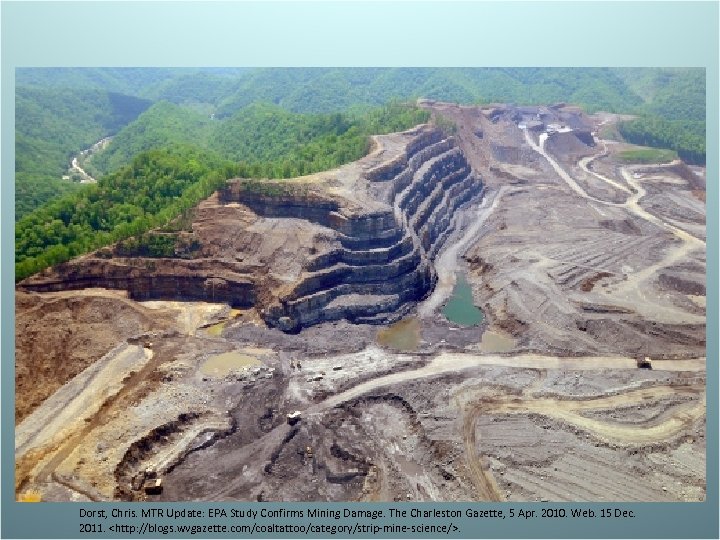
 • Fossil Fuels and the Environment – Strip mining coal- leaves deep ditches; source of acid run off • Rain water will dissolve acidic rocks and wash the acid into streams, lowering the p. H, causing aquatic life to be extinguished – Air pollution • Burning fossil fuels will emit carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) and sulfur dioxide (causes acid rain) – Oil spills
• Fossil Fuels and the Environment – Strip mining coal- leaves deep ditches; source of acid run off • Rain water will dissolve acidic rocks and wash the acid into streams, lowering the p. H, causing aquatic life to be extinguished – Air pollution • Burning fossil fuels will emit carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) and sulfur dioxide (causes acid rain) – Oil spills
 Dorst, Chris. MTR Update: EPA Study Confirms Mining Damage. The Charleston Gazette, 5 Apr. 2010. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Dorst, Chris. MTR Update: EPA Study Confirms Mining Damage. The Charleston Gazette, 5 Apr. 2010. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Nuclear Fission • Nuclear Fission – Nuclear fission- splitting of the nucleus of a large atom into two or more smaller nuclei emits energy which is used to generate electricity – Process: • Uranium 235 is the fuel we use (U-235) to create U-235 fuel rods • Inside the reactor (building) the rods are bombarded with neutrons, which split the nuclei. • Each nucleus will then release a neutron and energy. This generates a chain reaction • Water pumped around the fuel rods to absorb and carry away heat. This produces steam • The steam is used to turn turbines (magnet inside copper) which generates electricity by moving electrons – Disadvantage: • Radioactive waste- now is stored on site • If a meltdown were to occur, radioactive material would be released, harming anything in its path. – Advantage- expensive to build the reactor but the fuel is cheap. Not many casualties among workers, does not pollute
Nuclear Fission • Nuclear Fission – Nuclear fission- splitting of the nucleus of a large atom into two or more smaller nuclei emits energy which is used to generate electricity – Process: • Uranium 235 is the fuel we use (U-235) to create U-235 fuel rods • Inside the reactor (building) the rods are bombarded with neutrons, which split the nuclei. • Each nucleus will then release a neutron and energy. This generates a chain reaction • Water pumped around the fuel rods to absorb and carry away heat. This produces steam • The steam is used to turn turbines (magnet inside copper) which generates electricity by moving electrons – Disadvantage: • Radioactive waste- now is stored on site • If a meltdown were to occur, radioactive material would be released, harming anything in its path. – Advantage- expensive to build the reactor but the fuel is cheap. Not many casualties among workers, does not pollute
 Nuclear Fission Basics. Dummies. com, 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Nuclear Fission Basics. Dummies. com, 2011. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
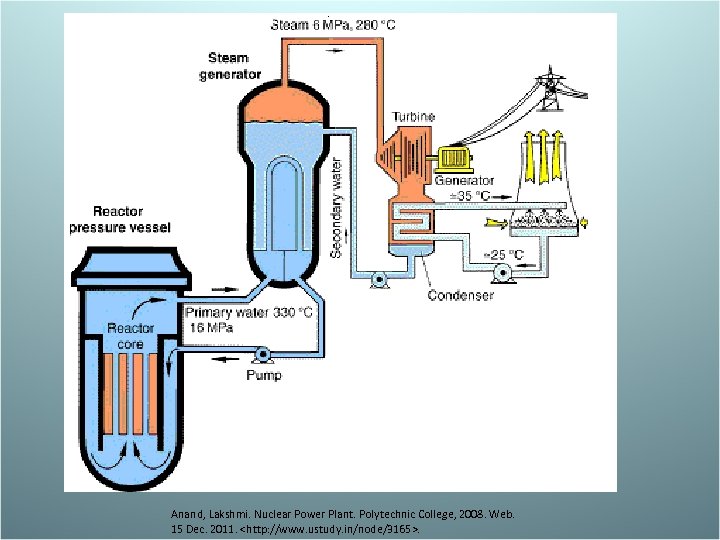 Anand, Lakshmi. Nuclear Power Plant. Polytechnic College, 2008. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Anand, Lakshmi. Nuclear Power Plant. Polytechnic College, 2008. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
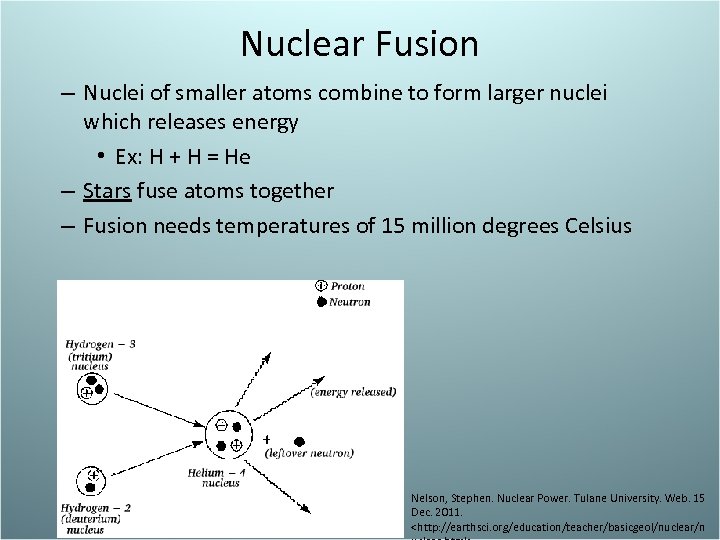 Nuclear Fusion – Nuclei of smaller atoms combine to form larger nuclei which releases energy • Ex: H + H = He – Stars fuse atoms together – Fusion needs temperatures of 15 million degrees Celsius Nelson, Stephen. Nuclear Power. Tulane University. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
Nuclear Fusion – Nuclei of smaller atoms combine to form larger nuclei which releases energy • Ex: H + H = He – Stars fuse atoms together – Fusion needs temperatures of 15 million degrees Celsius Nelson, Stephen. Nuclear Power. Tulane University. Web. 15 Dec. 2011.
 Solar Energy – Passive system- “greenhouse” sunlight can enter a room though glass, the energy is absorbed and released as infrared radiation. This infrared radiation is blocked by the glass. This system has no working parts. • Advantage- clean & cheep • Disadvantage- sun doesn’t always shine – Active- use solar collectors: a glass box is located on a roof. Pipes filled with water pass through the box, heating the water. The water is then circulated through the house. • Photovoltaic cells- converts sunlight directly to electricity. Works great for small devices. • Advantage- clean • Disadvantage- Not very efficient, needs sunlight, not good for high latitudes
Solar Energy – Passive system- “greenhouse” sunlight can enter a room though glass, the energy is absorbed and released as infrared radiation. This infrared radiation is blocked by the glass. This system has no working parts. • Advantage- clean & cheep • Disadvantage- sun doesn’t always shine – Active- use solar collectors: a glass box is located on a roof. Pipes filled with water pass through the box, heating the water. The water is then circulated through the house. • Photovoltaic cells- converts sunlight directly to electricity. Works great for small devices. • Advantage- clean • Disadvantage- Not very efficient, needs sunlight, not good for high latitudes
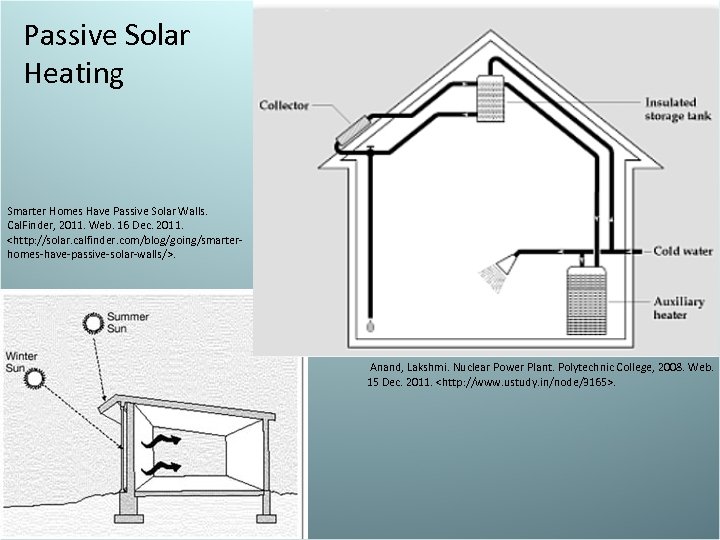 Passive Solar Heating Smarter Homes Have Passive Solar Walls. Cal. Finder, 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
Passive Solar Heating Smarter Homes Have Passive Solar Walls. Cal. Finder, 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
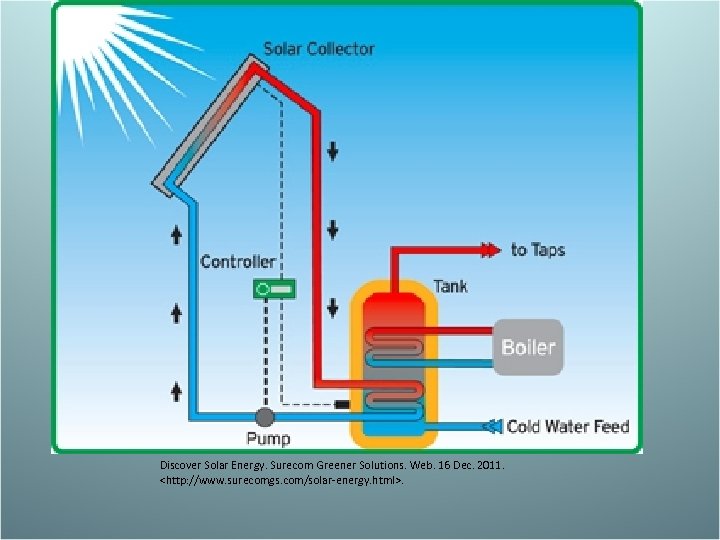 Discover Solar Energy. Surecom Greener Solutions. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
Discover Solar Energy. Surecom Greener Solutions. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
 Geothermal Energy – “energy from the heat of the earth’s interior. – Ground water that flows through cracks close enough to magma will heat up. We drill 2 wells into the ground. We pump cold water down the first well. The water flows through cracks, heating up. We then pump the hot water up a second well to use. – Advantage- clean – Disadvantage- expensive – http: //www 1. eere. energy. gov/geothermal/gpp_a nimation. html
Geothermal Energy – “energy from the heat of the earth’s interior. – Ground water that flows through cracks close enough to magma will heat up. We drill 2 wells into the ground. We pump cold water down the first well. The water flows through cracks, heating up. We then pump the hot water up a second well to use. – Advantage- clean – Disadvantage- expensive – http: //www 1. eere. energy. gov/geothermal/gpp_a nimation. html
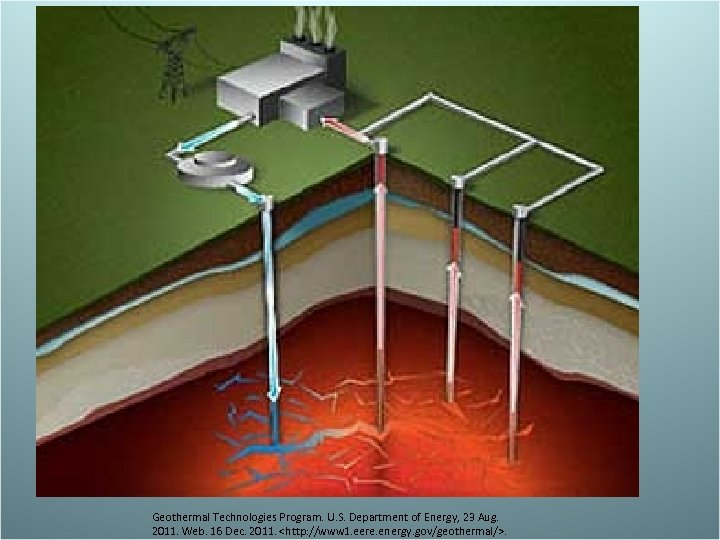 Geothermal Technologies Program. U. S. Department of Energy, 23 Aug. 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
Geothermal Technologies Program. U. S. Department of Energy, 23 Aug. 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
 Hydroelectricity • Hydroelectric energy- energy produced by running water • Dams hold back running water and channel it trough the plant. The water is forced through a turbine which produces electricity • A turbine is basically a magnet in copper wiring, which moves electrons. Electricity is moving electrons. • Advantage- clean, renewable • Disadvantages- you need a river, building a dam will flood upstream ecosystems and dry out downstream ecosystems, they are expensive to build
Hydroelectricity • Hydroelectric energy- energy produced by running water • Dams hold back running water and channel it trough the plant. The water is forced through a turbine which produces electricity • A turbine is basically a magnet in copper wiring, which moves electrons. Electricity is moving electrons. • Advantage- clean, renewable • Disadvantages- you need a river, building a dam will flood upstream ecosystems and dry out downstream ecosystems, they are expensive to build
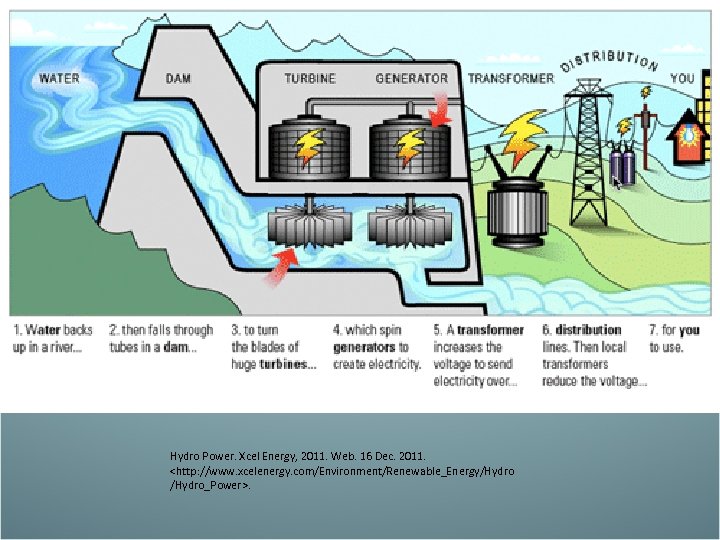 Hydro Power. Xcel Energy, 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
Hydro Power. Xcel Energy, 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
 Tidal Energy • Twice a day, oceans move towards then away from land. Dams are built to trap the water at high tide and release it at low tide. The water runs through turbines, producing electricity • Advantage- clean, renewable • Disadvantage- disrupt ecosystems, not all locations have strong tidal currents, can only supply electricity to towns near an ocean.
Tidal Energy • Twice a day, oceans move towards then away from land. Dams are built to trap the water at high tide and release it at low tide. The water runs through turbines, producing electricity • Advantage- clean, renewable • Disadvantage- disrupt ecosystems, not all locations have strong tidal currents, can only supply electricity to towns near an ocean.
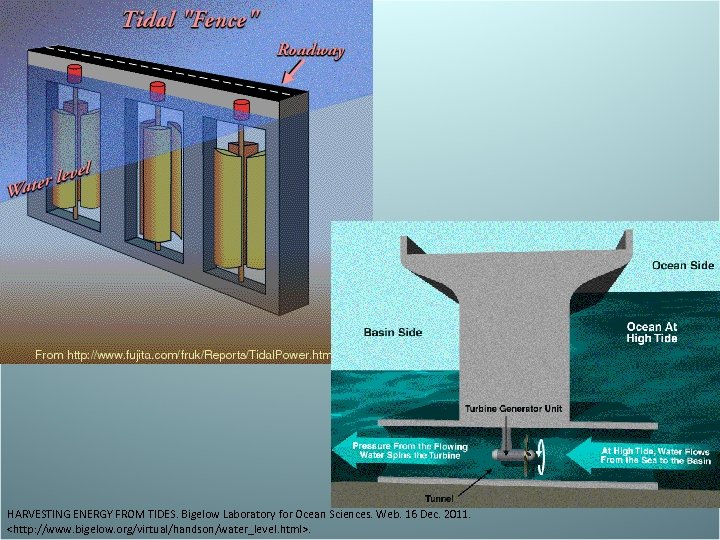 HARVESTING ENERGY FROM TIDES. Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
HARVESTING ENERGY FROM TIDES. Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
 Overview of Tidal Energy. Solar Power Notes. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
Overview of Tidal Energy. Solar Power Notes. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
 Wind Energy • Wind turns windmills, which turns a turbine. The turbine produces energy. • Advantage- relatively cheep, clean • Disadvantage- You need a windy location. The wind doesn’t always blow.
Wind Energy • Wind turns windmills, which turns a turbine. The turbine produces energy. • Advantage- relatively cheep, clean • Disadvantage- You need a windy location. The wind doesn’t always blow.
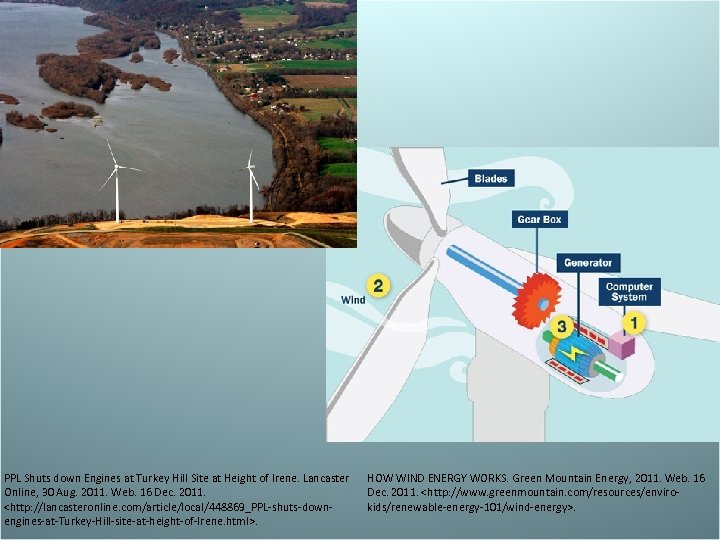 PPL Shuts down Engines at Turkey Hill Site at Height of Irene. Lancaster Online, 30 Aug. 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.
PPL Shuts down Engines at Turkey Hill Site at Height of Irene. Lancaster Online, 30 Aug. 2011. Web. 16 Dec. 2011.


