MINE WORKINGS.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 13
 MINE WORKINGS
MINE WORKINGS
 Mine working (excavation, driftage, mine roadway, drivage, entry, opening, road, tunnel, heading) – artificially made cavity in Earth’s crust that are formed due to mining operations and is used for deposits mining. A mine working is restricted by the surfaces: top – roof, lower – bottom, side – sides of the opening. Face (advance heading, mine face, breast, working face, bottomhole – скважины) – surface that restricting mine working and moving as a result of mining operations. Face in rocks is called drifting face Face in a mineral is called stoping face (longwall face, face). Part of a working’s area adjacent to a face is called face space (face area). Depending on deep angle, there are o horizontal o inclined o vertical openings
Mine working (excavation, driftage, mine roadway, drivage, entry, opening, road, tunnel, heading) – artificially made cavity in Earth’s crust that are formed due to mining operations and is used for deposits mining. A mine working is restricted by the surfaces: top – roof, lower – bottom, side – sides of the opening. Face (advance heading, mine face, breast, working face, bottomhole – скважины) – surface that restricting mine working and moving as a result of mining operations. Face in rocks is called drifting face Face in a mineral is called stoping face (longwall face, face). Part of a working’s area adjacent to a face is called face space (face area). Depending on deep angle, there are o horizontal o inclined o vertical openings
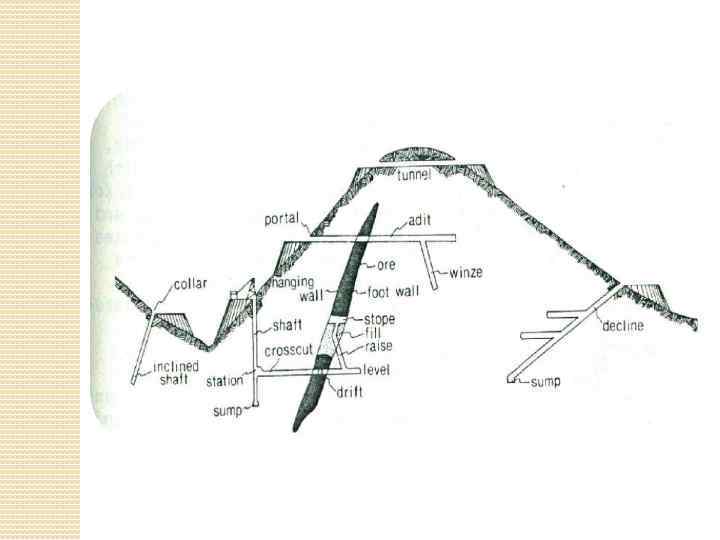
 HORIZONTAL OPENINGS Adit – horizontal or inclined opening that has an exit to the surface and usually is designed for extraction of minerals or service of mine workings. Adit is a basic main opening (вск. выработка) for deposits mining in mountainous areas. Drift (drive, roadway, coal heading, entry, gateway, gateroad, head) – underground mine working that does not have direct exit to the surface and serves for ventilation and transportation. Cross-cut (cross-entry, crossdrift, crossway, cross gallery, crosstunnel) - permanent working that does not have a direct exit to the surface and is driven along a host rock (more often perpendicular) to the ore body. It is designed for a mineral opening, transportation, also for people movement, ventilation, water sewage. Gain – орт (cross drift, ort, breakthrough, cross adit) – horizontal mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface and driven to the roof or to the bottom of a seam or from the roof to the bottom. It is designed for accumulation and transportation of extracted minerals to the main transport working.
HORIZONTAL OPENINGS Adit – horizontal or inclined opening that has an exit to the surface and usually is designed for extraction of minerals or service of mine workings. Adit is a basic main opening (вск. выработка) for deposits mining in mountainous areas. Drift (drive, roadway, coal heading, entry, gateway, gateroad, head) – underground mine working that does not have direct exit to the surface and serves for ventilation and transportation. Cross-cut (cross-entry, crossdrift, crossway, cross gallery, crosstunnel) - permanent working that does not have a direct exit to the surface and is driven along a host rock (more often perpendicular) to the ore body. It is designed for a mineral opening, transportation, also for people movement, ventilation, water sewage. Gain – орт (cross drift, ort, breakthrough, cross adit) – horizontal mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface and driven to the roof or to the bottom of a seam or from the roof to the bottom. It is designed for accumulation and transportation of extracted minerals to the main transport working.
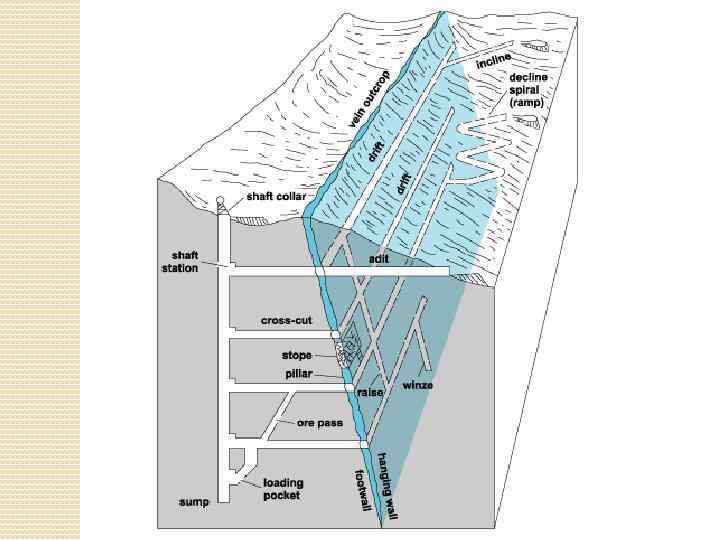
 VERTICAL OPENINGS Shaft – vertical main working that has direct exit on the surface and is designed for servicing of underground mining operations. Shafts are used for lowering and hoisting up the minerals, rock, materials, equipment, people and ventilation of the mine. Depending on the main purpose, mine shafts are divided into main and auxiliary. Main shaft is used for lifting the minerals to the surface. Auxiliary shaft – for lifting of the people, ventilation (incoming air stream). Top part of the shaft that exits on the surface is called a collar. Lowest part of the shaft is called sump (sunk basin, dibhole). Diameter of the shafts reaches 9 meters, depth – 3 -3. 5 meters (the world’s deepest mine in 3. 9 km long – in South Africa). Pit-hole (delve, exploratory shaft, prospecting shaft) – vertical (sometimes inclined) working that is driven from the surface for exploration of minerals, ventilation, dewatering (pumping), materials transportation, lifting of people and for other purposes. Blind shaft (way shaft, dummy shaft) - vertical mine working that does not have exit to the surface and is designed for transportation of minerals, people, loads from underlying levels to the above situated ones, also for ventilation. Winze – underground vertical or inclined mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface. It connects different levels in a mine. It is used for transportation of the mineral to the underlying level by its gravity weight, ventilation. Usually it is equipped with a stair case.
VERTICAL OPENINGS Shaft – vertical main working that has direct exit on the surface and is designed for servicing of underground mining operations. Shafts are used for lowering and hoisting up the minerals, rock, materials, equipment, people and ventilation of the mine. Depending on the main purpose, mine shafts are divided into main and auxiliary. Main shaft is used for lifting the minerals to the surface. Auxiliary shaft – for lifting of the people, ventilation (incoming air stream). Top part of the shaft that exits on the surface is called a collar. Lowest part of the shaft is called sump (sunk basin, dibhole). Diameter of the shafts reaches 9 meters, depth – 3 -3. 5 meters (the world’s deepest mine in 3. 9 km long – in South Africa). Pit-hole (delve, exploratory shaft, prospecting shaft) – vertical (sometimes inclined) working that is driven from the surface for exploration of minerals, ventilation, dewatering (pumping), materials transportation, lifting of people and for other purposes. Blind shaft (way shaft, dummy shaft) - vertical mine working that does not have exit to the surface and is designed for transportation of minerals, people, loads from underlying levels to the above situated ones, also for ventilation. Winze – underground vertical or inclined mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface. It connects different levels in a mine. It is used for transportation of the mineral to the underlying level by its gravity weight, ventilation. Usually it is equipped with a stair case.
 Winze
Winze
 INCLINED WORKINGS Incline (ramp, dipping drift, sloping tunnel) – inclined underground mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface, driven downdip of a mineral. During mineral extraction is used for lifting of the loads from lower to upper level. Inclined winze (drift) - бремсберг, (dukeway, rope incline, gravity incline, brake incline) – underground inclined mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface, as a rule is driven along the seam (along deep line) and serves for lowering of minerals in mine trolleys from overlying to underlying levels. If a gravity incline is driven along the rock it is called rock incline (полевой). Raise – an opening that does not have an exit to the surface and driven bottom-upwards at any angle. Inclined shaft – an inclined underground mine working that has a direct exit to the surface and has the same purposes as the vertical shaft. Usually it is driven along a seam, rarely along a rock. Usually equipped with rails, conveyors (depending on the incline angle), cable hoist.
INCLINED WORKINGS Incline (ramp, dipping drift, sloping tunnel) – inclined underground mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface, driven downdip of a mineral. During mineral extraction is used for lifting of the loads from lower to upper level. Inclined winze (drift) - бремсберг, (dukeway, rope incline, gravity incline, brake incline) – underground inclined mine working that does not have a direct exit to the surface, as a rule is driven along the seam (along deep line) and serves for lowering of minerals in mine trolleys from overlying to underlying levels. If a gravity incline is driven along the rock it is called rock incline (полевой). Raise – an opening that does not have an exit to the surface and driven bottom-upwards at any angle. Inclined shaft – an inclined underground mine working that has a direct exit to the surface and has the same purposes as the vertical shaft. Usually it is driven along a seam, rarely along a rock. Usually equipped with rails, conveyors (depending on the incline angle), cable hoist.
 Drop, chute, ramp, millhole, downward slope, descent – скат, - an inclined underground mine working that does not have a direct exit on the surface, driven along a seam or rock and designed for transportation of a mineral by its own weight. Manway (pass, traveling way) – mine working driven parallel to an inclined winze (бремсберг) or to an incline and used for people movement and transportation of loads, ventilation. Depending on its purpose, there are people and freight manways. rise entry, set-up entry, raise) – an inclined underground mine working driven along a seam and designed for coal, freight transportation, ventilation, people movement. Rise entry driven along a mineral between haulage and ventilation (air) drifts for a longwall development is called face entry (разрезная печь).
Drop, chute, ramp, millhole, downward slope, descent – скат, - an inclined underground mine working that does not have a direct exit on the surface, driven along a seam or rock and designed for transportation of a mineral by its own weight. Manway (pass, traveling way) – mine working driven parallel to an inclined winze (бремсберг) or to an incline and used for people movement and transportation of loads, ventilation. Depending on its purpose, there are people and freight manways. rise entry, set-up entry, raise) – an inclined underground mine working driven along a seam and designed for coal, freight transportation, ventilation, people movement. Rise entry driven along a mineral between haulage and ventilation (air) drifts for a longwall development is called face entry (разрезная печь).
 OTHER MINE WORKINGS Longwall (long face) – underground mine working of a significant length (up to hundreds of meters), one side of which is formed by a coal massif (longwall face) and the other one – by a backfill and caved rock of a goaf. It has exits on haulage and air drifts. Borehole – mine working of a circular shape, drilled from the surface or from an underground working without access of a man to the face, with diameter not bigger than 2 meters. Cross slit (connection) – underground mine working (horizontal or inclined), that connects two adjacent workings, for example, drifts. Chamber (room, stall) – mine working that is not very long (compared to its cross-section) and is designed for equipment and materials placement.
OTHER MINE WORKINGS Longwall (long face) – underground mine working of a significant length (up to hundreds of meters), one side of which is formed by a coal massif (longwall face) and the other one – by a backfill and caved rock of a goaf. It has exits on haulage and air drifts. Borehole – mine working of a circular shape, drilled from the surface or from an underground working without access of a man to the face, with diameter not bigger than 2 meters. Cross slit (connection) – underground mine working (horizontal or inclined), that connects two adjacent workings, for example, drifts. Chamber (room, stall) – mine working that is not very long (compared to its cross-section) and is designed for equipment and materials placement.
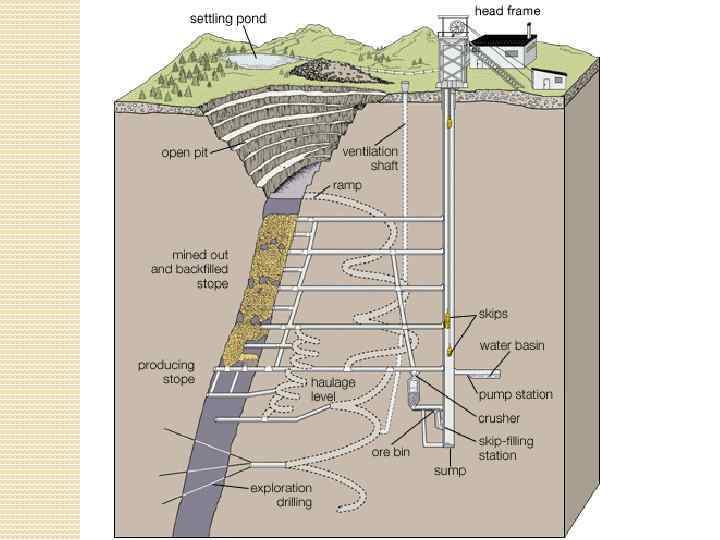
 Shaft bottom (pit bottom) – aggregate of openings serving for connection of the shaft with all the rest mine workings and for placement of some mine facilities (water sewage system, power substations, electric locomotive garage, storage of fire-prevention tools). Level: All of the horizontal openings which connect to a shaft at a specific point Ramp: An inclined rubber wheeled access opening between horizontal openings at different elevations. Sub-Level: A set of horizontal openings immediately above the main horizontal access openings. Sump: An excavation for the purpose of collecting water so that it may be transferred to a pump. This often is the bottom most portion of a shaft.
Shaft bottom (pit bottom) – aggregate of openings serving for connection of the shaft with all the rest mine workings and for placement of some mine facilities (water sewage system, power substations, electric locomotive garage, storage of fire-prevention tools). Level: All of the horizontal openings which connect to a shaft at a specific point Ramp: An inclined rubber wheeled access opening between horizontal openings at different elevations. Sub-Level: A set of horizontal openings immediately above the main horizontal access openings. Sump: An excavation for the purpose of collecting water so that it may be transferred to a pump. This often is the bottom most portion of a shaft.
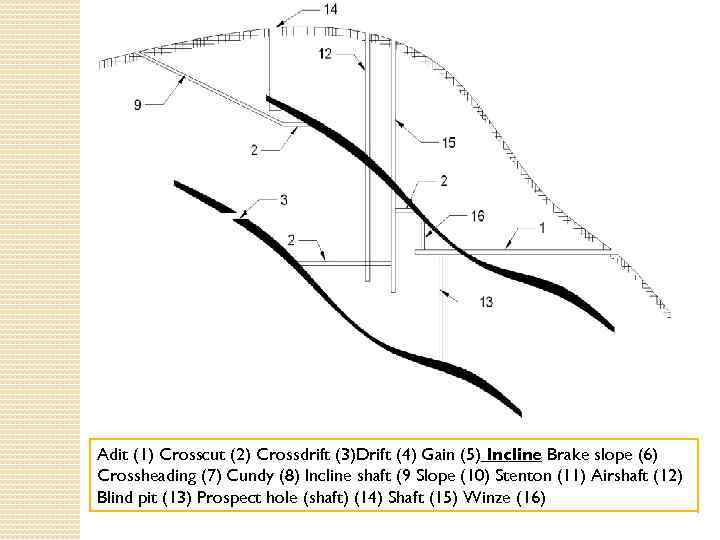 Adit (1) Crosscut (2) Crossdrift (3)Drift (4) Gain (5) Incline Brake slope (6) Crossheading (7) Cundy (8) Incline shaft (9 Slope (10) Stenton (11) Airshaft (12) Blind pit (13) Prospect hole (shaft) (14) Shaft (15) Winze (16)
Adit (1) Crosscut (2) Crossdrift (3)Drift (4) Gain (5) Incline Brake slope (6) Crossheading (7) Cundy (8) Incline shaft (9 Slope (10) Stenton (11) Airshaft (12) Blind pit (13) Prospect hole (shaft) (14) Shaft (15) Winze (16)


