6ccf7c0f11e194bae74a617cd9534867.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

MINE LIFE CYCLE, DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING, AND SUSTAINABILITY STAGE 1 - Exploration and Assessment STAGE 2 - Construction STAGE 3 - Operation STAGE 4 - Closure

MINE LIFE CYCLE, DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING, AND SUSTAINABILITY STAGE 1 - Exploration and Assessment (1 -10 years) • Exploration - Geophysics • Exploration - Drilling (1/10) • Geology - Analytical and Mineralogical Assessment • Economic Feasibility Assessment (1/10) • Orebody Modeling (1/10) • Mine Planning and Metallurgical Testwork

3 -D Orebody Model for Mine Planning • INCO's Research Mine at Sudbury, Ontario

Underground LHD Campbell Mine, Ontario

Remote-LHD Olympic Dam Mine, Australia

Mine Life Cycle (continued) STAGE 2 - Construction( 0. 5 -2 years ) • Mine – Shaft-sinking & tunnel/stope development (U/G) – Adit & tunnel/stope development (mountain-top) – Top soil removal, key-cut, haul road development (Open-Pit) • Plant – Site Preparation, Foundations, Construction of buildings – Procurement and Installation of Equipment • Waste and Tailing Disposal – Site Selection and Preparation – Construction of Initial Coffer Dam for tailing disposal

Open Pit Mine Bingham Canyon Mine

Open Pit Mining Shovel Loading - Porgera Mine, Papua New Guinea

Strip Mining Coal Mine Shovel-Truck Operation

200 T Haulage Truck

Open Pits are Colorful Florida Phosphate Mining

Diamond Pipe Deposit

Ekati Diamond Mine Kimberlite Pipe Deposit

What its all about at Ekati! Diamonds are forever!

Polar Diamond Certificate

Ekati's Polar Diamond

Mill Complex Bingham Canyon Mill
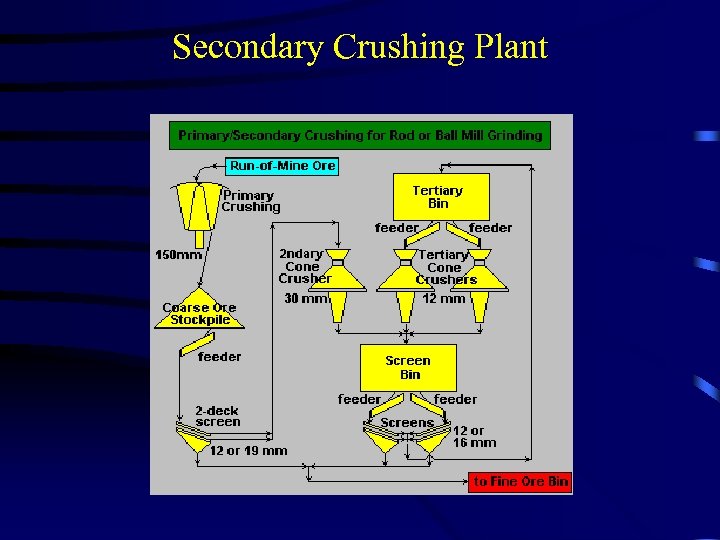
Secondary Crushing Plant

Grinding Mills Bingham Canyon Grinding Mills

Grinding Mills

Mill Control Room Carlin Mine, Nevada

Separation Circuit

Mine Life Cycle (continued) STAGE 3 - Operation ( 3 - 400 years ) • Mine – Blast, Load, Haul, Dump – Transport (hoist, convey, truck, rail), Stockpile – Safely Store Waste (on site or in-mine) • Mill – – Crush, Grind (comminution) Physical Separation (maybe chemical) (beneficiation) Thicken and Filter (dewater) Safely Store Tailing

Mine Life Cycle (continued) STAGE 3 - Operation ( 3 - 400 years ) • Waste Disposal – Dump – Contour, Spread top soil – Hydro-seed and plan for final drainage • Tailing Disposal – – Plan for Lifts as Tailing Dam builds Control Water Levels Recover water for recycle Revegetate dam walls

Revegetation Hydro-Seeding a Waste Dump

Tailing Dam Reclamation

Mine Life Cycle (continued) STAGE 4 - Closure( 1 - 20 years ) • Mine – Flood Pit – Seal Underground workings – Long-term Acid Rock Drainage plan for waste dumps • Mill – – Salvage Equipment Raze Buildings Contour and reseed site Long-term ARD plan for tailing dam

Mine/Mill Complex Musslewhite Mine, Ontario

Downstream Processing • Mine/mill complex – produces ore or concentrate or unrefined metal/product – product transported by airplane, rail, truck or ship to smelter or refinery – if leaching is used at mine/mill, unrefined metal or final product is produced • Smelting – pyrometallurgical processing (multi-stage) • • roasting to partially remove/control sulfur content melting to separate oxides from sulfides (flux and slag) oxidation to remove sulfur and iron need SO 2 control and slag disposal system

Downstream Processing • Leaching – hydrometallurgical processing – vat leach, agitation leach, heap leach, in-situ leach – Pressure Oxidation or Biological Leaching – solid/liquid separation or ion adsorption process – solution purification (solvent extraction/ion exchange) – need residue disposal method (dewatering/storage) • Refining – electrometallurgical processing • electrowinning to recover metals from solution • electrorefining to purify unrefined metal • treatment of slime deposits for PMs recovery
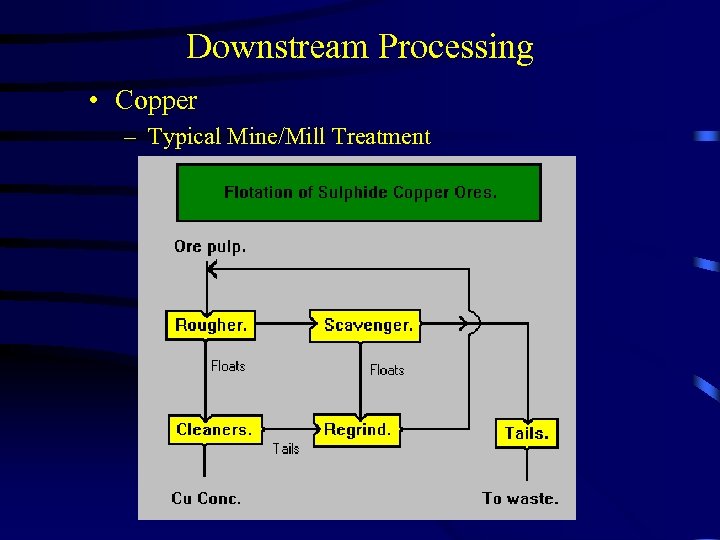
Downstream Processing • Copper – Typical Mine/Mill Treatment

Downstream Processing • Copper – Oxide copper treatment

Heap Leach Operation Installing a Plastic Membrane Liner
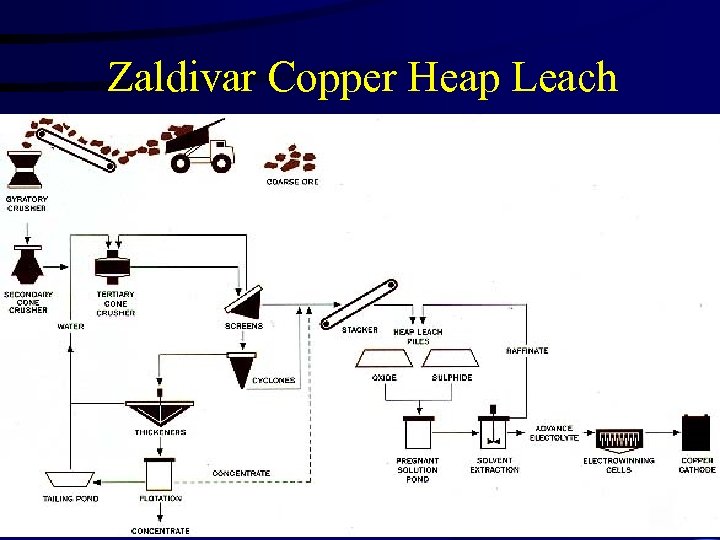
Zaldivar Copper Heap Leach
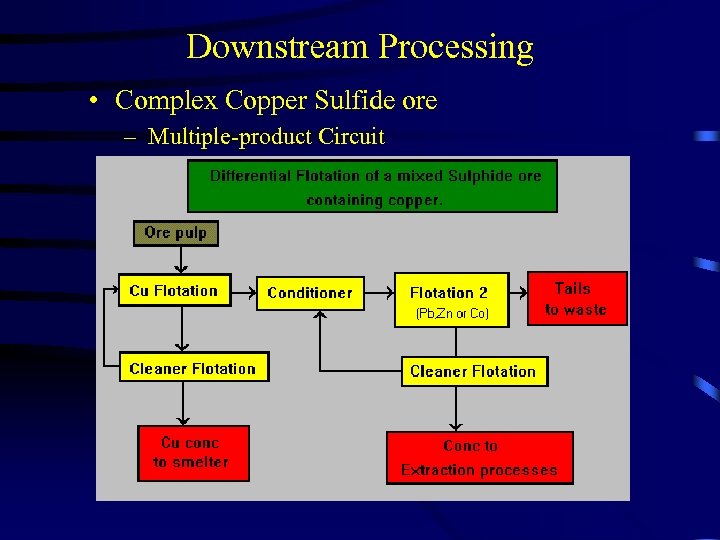
Downstream Processing • Complex Copper Sulfide ore – Multiple-product Circuit
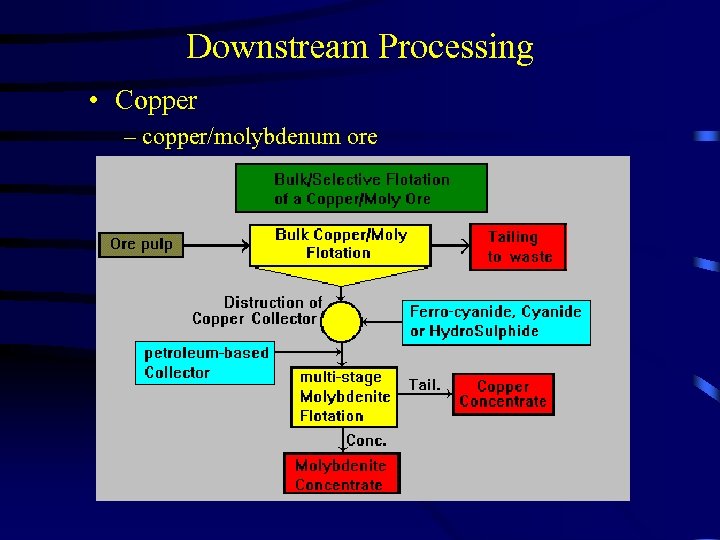
Downstream Processing • Copper – copper/molybdenum ore
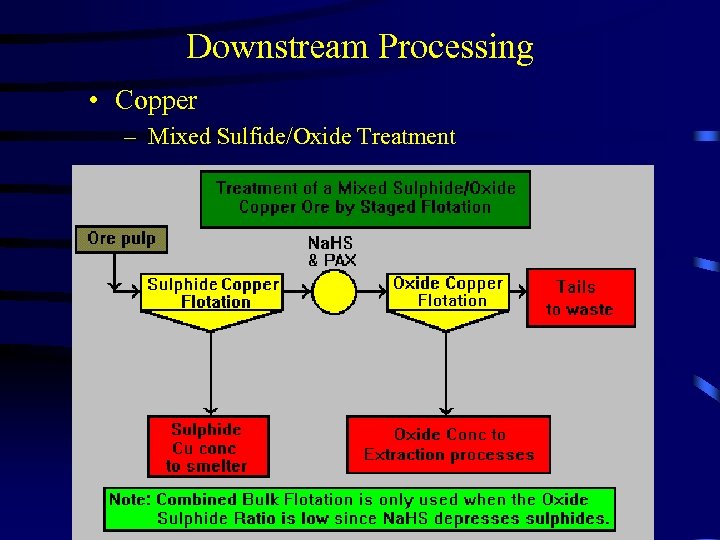
Downstream Processing • Copper – Mixed Sulfide/Oxide Treatment
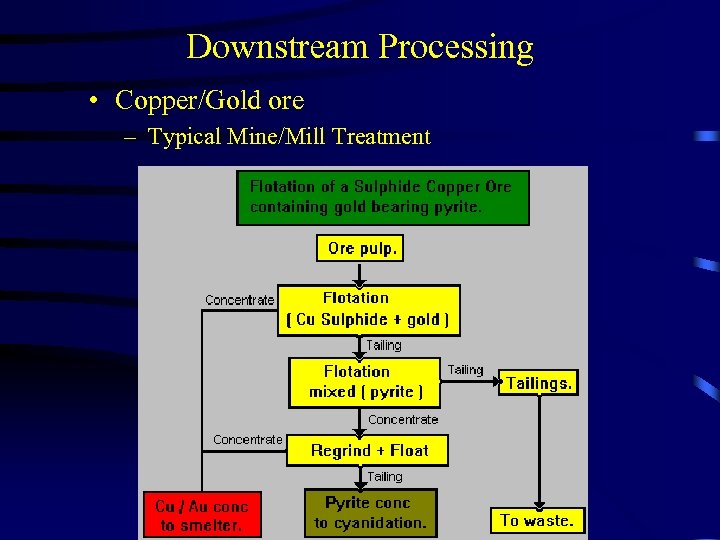
Downstream Processing • Copper/Gold ore – Typical Mine/Mill Treatment

Downstream Processing • Gold processing options

Downstream Processing • Copper – LPF Processing
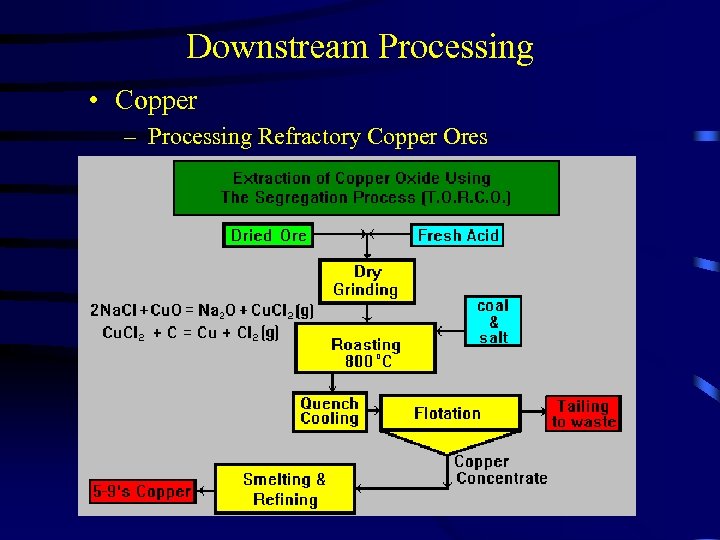
Downstream Processing • Copper – Processing Refractory Copper Ores
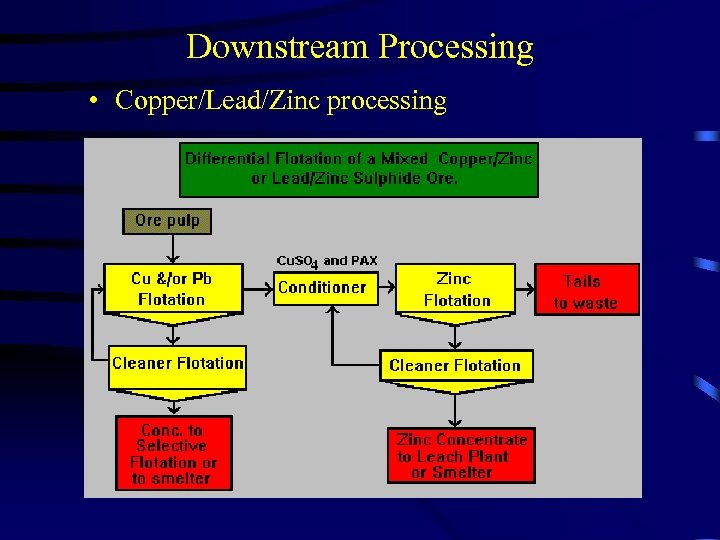
Downstream Processing • Copper/Lead/Zinc processing
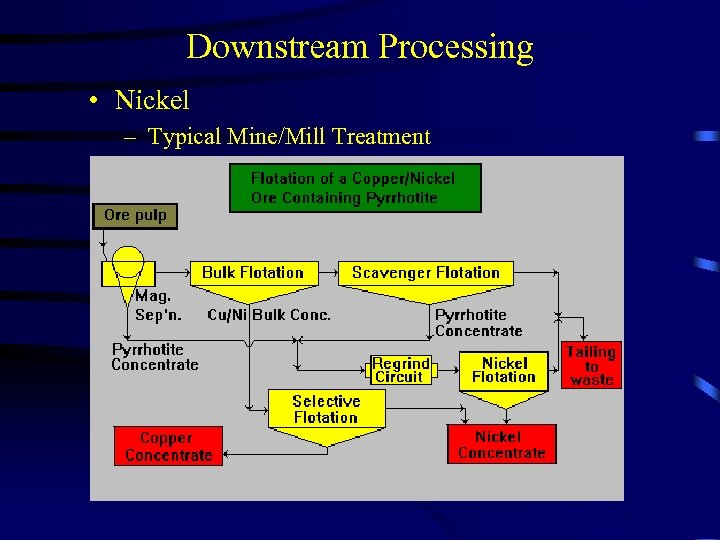
Downstream Processing • Nickel – Typical Mine/Mill Treatment
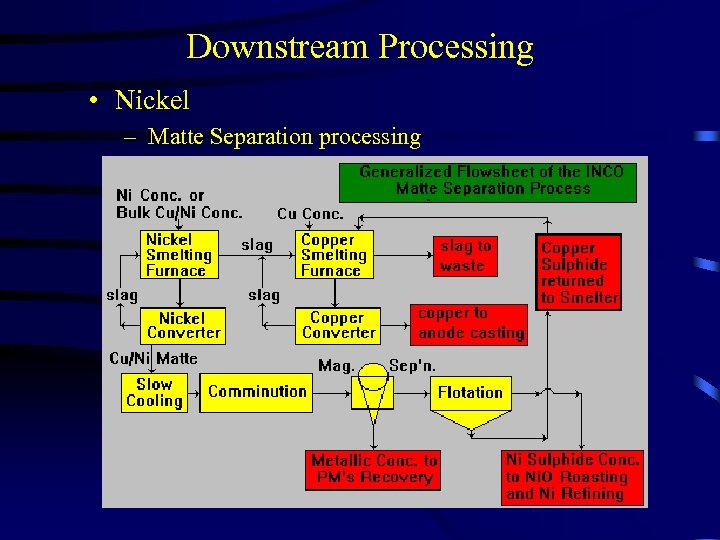
Downstream Processing • Nickel – Matte Separation processing

Chuquicamata Mine/Mill/Smelter

Copper Anode Casting Wheel
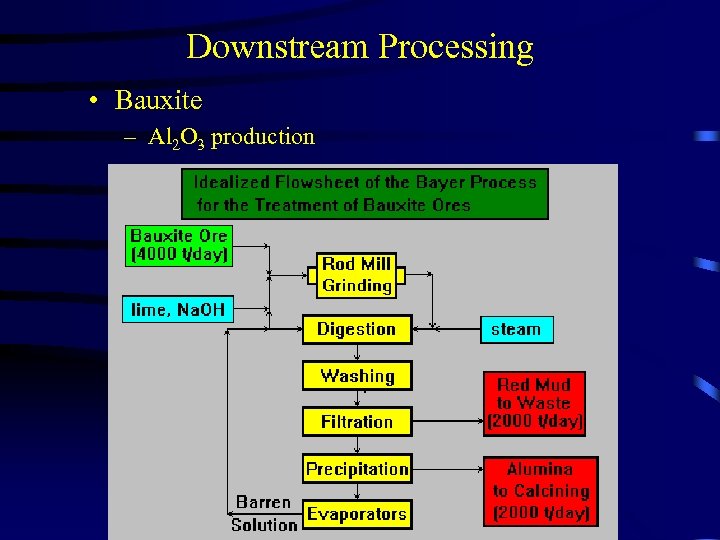
Downstream Processing • Bauxite – Al 2 O 3 production

Downstream Processing • Phosphate ore processing

Downstream Processing • Uranium Ore processing

Copper-Uranium Ore Olympic Dam Mine, Australia
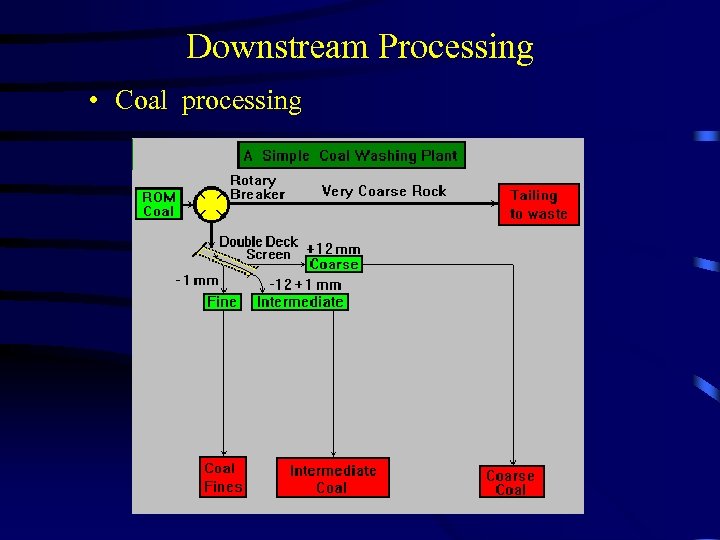
Downstream Processing • Coal processing

Downstream Processing • Coal processing

Downstream Processing • Coal processing

Downstream Processing • Coal processing
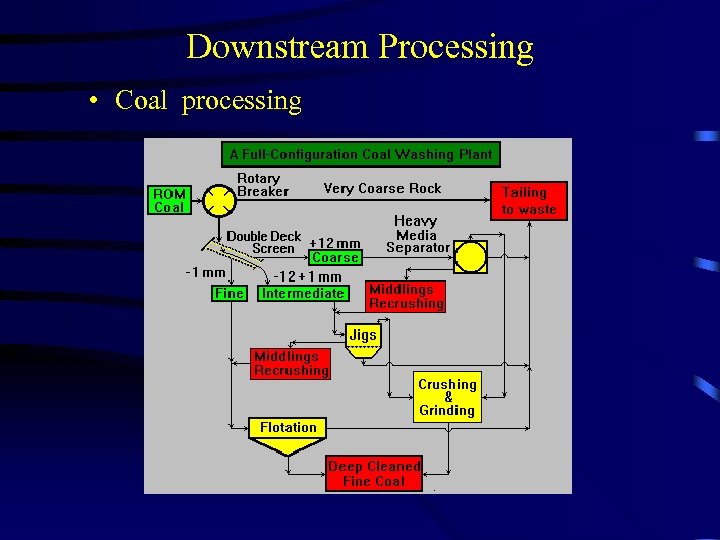
Downstream Processing • Coal processing

Sustainability • Important Factors – Technical – Economic – Social/Political – Environmental • Past mining activities focussed on only the first two • The latter two have now become equally, if not more important
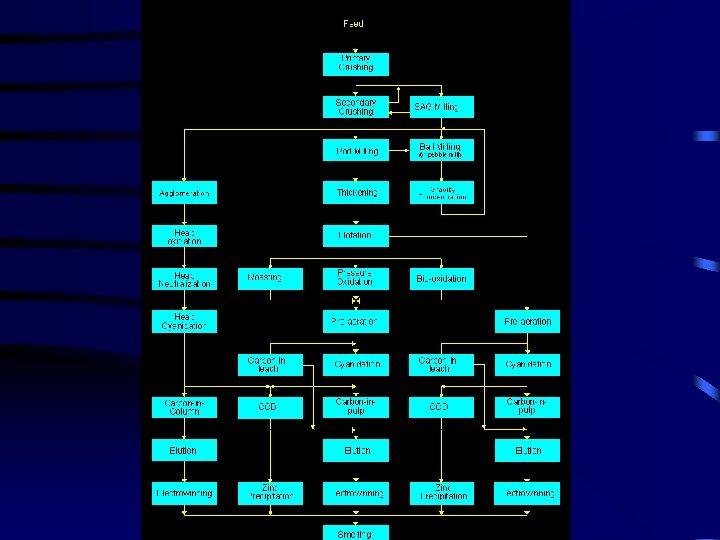
Gold Flakes

Gold Panning

Gold Flakes

Grinding and Cyanide Leaching Musslewhite Mine, Ontario

Smelting Gold Campbell Mine, Ontario

Pouring Slag Musslewhite Mine, Ontario

Pouring Gold Bullion Bars

What its all about! Gold Bullion

Samarco Iron Ore Flowsheet

Samarco Iron Ore Concentrator
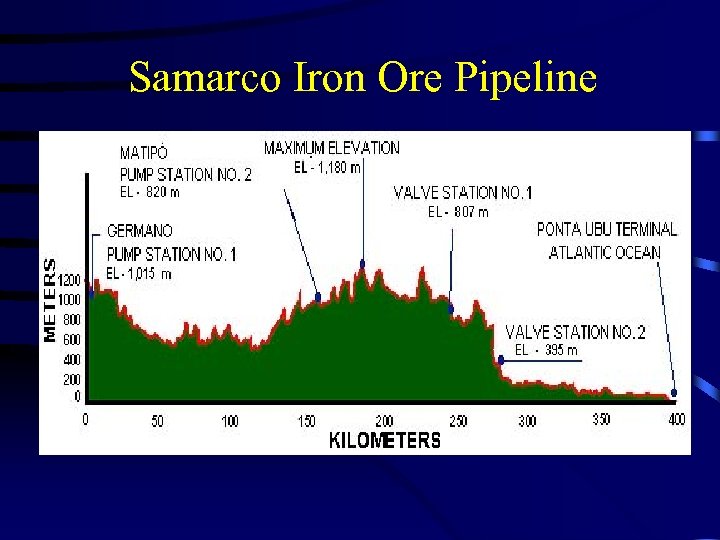
Samarco Iron Ore Pipeline

Iron Ore Pellets Malmberget, Norway

Sustainability • A Mine must plan for closure before it starts up • A mining company must always consider local communities in all parts of the world • As an industry, we must find ways to enhance our image and to influence government decision-making • Future methods must reduce the footprint of mining – no more open pits – waste returned to the mine – processing at the face – robotics and remote-mining systems

Sustainability • Social/Political Issues – Land Use – Government policies – The Influence of Activism – Environmental concerns – Aboriginal peoples and treaties – Need for jobs and a diversified economy • In BC, the Tatsenshini/Windy Craggy decision has had important long-term impact on Mining • Similarly, the Delgamuk decision and Nishka Treaty are important to the future of BC's mining industry

Sustainability • The BC Mining Industry must encourage its members to institute vertical integration policies • We need to invest in much more value-added processing (i. e. smelting and refining in BC) • Downstream manufacturing industries must be encouraged to develop in BC • This will provide the necessary systems to begin significant recycling of metals and other materials in the Pacific North-West
6ccf7c0f11e194bae74a617cd9534867.ppt