6f04fc708c166d9549a04a4861e19c57.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72

 Military Cryptographic Systems Information Assurance Module 3 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-2
Military Cryptographic Systems Information Assurance Module 3 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-2
 Objectives Students will learn about commonly used military cryptographic systems (ie. KG-84, KIV-7, KIV-19, STE, KG-75), including data rates, connection and fill requirements, and practical applications. Provide an Overview of the DOD Cryptographic Modernization Initiative with Focus on the Army CM Program. Be able to describe the EKMS/AKMS Programs. At the conclusion of this block, students will be able to choose a cryptographic device to encrypt a link given the data rate, terminal equipment and transmission medium. They will be able to explain the CM, EKMS and AKMS Programs. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-3
Objectives Students will learn about commonly used military cryptographic systems (ie. KG-84, KIV-7, KIV-19, STE, KG-75), including data rates, connection and fill requirements, and practical applications. Provide an Overview of the DOD Cryptographic Modernization Initiative with Focus on the Army CM Program. Be able to describe the EKMS/AKMS Programs. At the conclusion of this block, students will be able to choose a cryptographic device to encrypt a link given the data rate, terminal equipment and transmission medium. They will be able to explain the CM, EKMS and AKMS Programs. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-3
 Outline • • • Cryptographic Standards NSA Cryptographic Types Black/Red Signals Military Cryptographic Equipment (Layers 1 – 3) Telephony Cryptographic Equipment Fill Devices Key Generators Cryptographic Modernization Program Electronic/Army Key Management Systems FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-4
Outline • • • Cryptographic Standards NSA Cryptographic Types Black/Red Signals Military Cryptographic Equipment (Layers 1 – 3) Telephony Cryptographic Equipment Fill Devices Key Generators Cryptographic Modernization Program Electronic/Army Key Management Systems FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-4
 Cryptographic Standards (1 of 2) 1. National Security Agency (NSA) – Secret and above – Type 1 encryption required – Classified Algorithms 2. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – Set standards for Sensitive traffic – de facto standards organization for commercial businesses FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-5
Cryptographic Standards (1 of 2) 1. National Security Agency (NSA) – Secret and above – Type 1 encryption required – Classified Algorithms 2. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – Set standards for Sensitive traffic – de facto standards organization for commercial businesses FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-5
 Cryptographic Standards (2 of 2) 3. American National Standards Institute (ANSI) – Cryptographic standards organization for the U. S. – ANSI X 9 series closely mirrors NIST’s Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 4. International Organization of Standards (ISO) – X. 509 and Common Criteria FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-6
Cryptographic Standards (2 of 2) 3. American National Standards Institute (ANSI) – Cryptographic standards organization for the U. S. – ANSI X 9 series closely mirrors NIST’s Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 4. International Organization of Standards (ISO) – X. 509 and Common Criteria FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-6
 Approved Cryptosystems for the US Army are either: 1. Produced by NSA 2. Commercial Off the Shelf Systems approved by NSA for local purchase 3. Electronically generated and distributed using NSA approved key generating equipment and procedures IAW NAG 16 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-7
Approved Cryptosystems for the US Army are either: 1. Produced by NSA 2. Commercial Off the Shelf Systems approved by NSA for local purchase 3. Electronically generated and distributed using NSA approved key generating equipment and procedures IAW NAG 16 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-7
 NSA Cryptographic Types 1. Products – US government/military for Classified Info – Only approved commercial users are defense contractors for US classified projects 2. Products – US government for sensitive info – Requires US government agency sponsorship 3. Algorithms – Exportable only to US corporations abroad, and remain under the control of US citizen. 4. Algorithms – Exportable to any country and/or organization, except those prohibited by the US government FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-8
NSA Cryptographic Types 1. Products – US government/military for Classified Info – Only approved commercial users are defense contractors for US classified projects 2. Products – US government for sensitive info – Requires US government agency sponsorship 3. Algorithms – Exportable only to US corporations abroad, and remain under the control of US citizen. 4. Algorithms – Exportable to any country and/or organization, except those prohibited by the US government FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-8
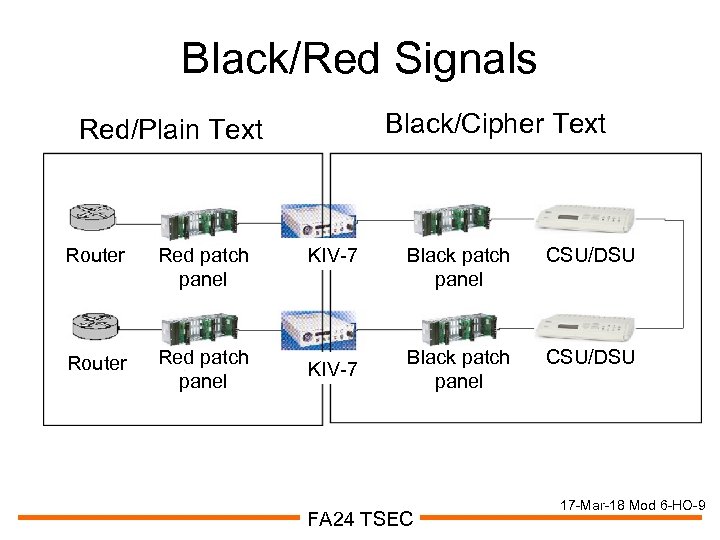 Black/Red Signals Black/Cipher Text Red/Plain Text Router Red patch panel KIV-7 Black patch panel CSU/DSU FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-9
Black/Red Signals Black/Cipher Text Red/Plain Text Router Red patch panel KIV-7 Black patch panel CSU/DSU FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-9
 Red/Black Installation (1 of 2) • Separation of 1 m b/w RED processor and: – BLACK equipment – BLACK wire lines that exit the inspectable space or are connected to an RF transmitter – BLACK power lines – Conductors that exit the inspectable space • Separation of 5 cm b/w RED wire line and: – BLACK wire lines that exit the inspectable space or are connected to an RF transmitter – BLACK power lines FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-10
Red/Black Installation (1 of 2) • Separation of 1 m b/w RED processor and: – BLACK equipment – BLACK wire lines that exit the inspectable space or are connected to an RF transmitter – BLACK power lines – Conductors that exit the inspectable space • Separation of 5 cm b/w RED wire line and: – BLACK wire lines that exit the inspectable space or are connected to an RF transmitter – BLACK power lines FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-10
 Red/Black Installation (2 of 2) • RED and BLACK wire lines will not use a common distribution vehicle unless the power lines exiting the space are equipped with powerline filters. • Patch Panels – Jack fields should have incompatible connectors to prevent inadvertent RED to BLACK patching – Separate RED and BLACK by 1 m • 1 m separation required b/w different classifications (i. e. SIPRNET and JWICS, SIPRNET and SECRET – Coalition) • SCIFs require separate red and black ground FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-11
Red/Black Installation (2 of 2) • RED and BLACK wire lines will not use a common distribution vehicle unless the power lines exiting the space are equipped with powerline filters. • Patch Panels – Jack fields should have incompatible connectors to prevent inadvertent RED to BLACK patching – Separate RED and BLACK by 1 m • 1 m separation required b/w different classifications (i. e. SIPRNET and JWICS, SIPRNET and SECRET – Coalition) • SCIFs require separate red and black ground FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-11
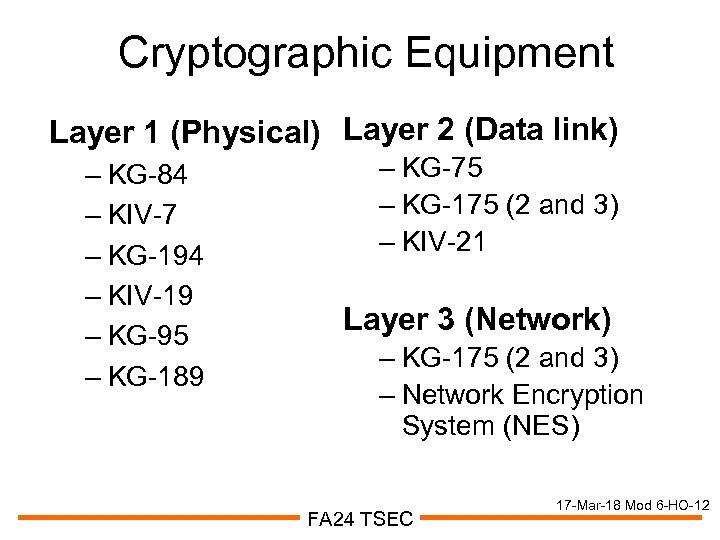 Cryptographic Equipment Layer 1 (Physical) Layer 2 (Data link) – KG-84 – KIV-7 – KG-194 – KIV-19 – KG-95 – KG-189 – KG-75 – KG-175 (2 and 3) – KIV-21 Layer 3 (Network) – KG-175 (2 and 3) – Network Encryption System (NES) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-12
Cryptographic Equipment Layer 1 (Physical) Layer 2 (Data link) – KG-84 – KIV-7 – KG-194 – KIV-19 – KG-95 – KG-189 – KG-75 – KG-175 (2 and 3) – KIV-21 Layer 3 (Network) – KG-175 (2 and 3) – Network Encryption System (NES) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-12
 KG-84 • • KG-84 A -- 256 kbps KG-84 C -- 64 kbps Military standard DS-101 fill plug Operates from 50 to 9600 Mbps asynchronous • Process up to 32 Kbps using internal clock • Built-in wireline modem FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-13
KG-84 • • KG-84 A -- 256 kbps KG-84 C -- 64 kbps Military standard DS-101 fill plug Operates from 50 to 9600 Mbps asynchronous • Process up to 32 Kbps using internal clock • Built-in wireline modem FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-13
 KIV-7 • Four models – KIV-7 HSA/B 512 Kbps 1. 544 Mbps 2. 048 Mbps • Interoperable with KG-84 • Serial Data Interfaces – EIA-530, EIA-449, EIA-232 • Removable CIK • No internal strappings • Optional Wireline Module for Tactical FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-14
KIV-7 • Four models – KIV-7 HSA/B 512 Kbps 1. 544 Mbps 2. 048 Mbps • Interoperable with KG-84 • Serial Data Interfaces – EIA-530, EIA-449, EIA-232 • Removable CIK • No internal strappings • Optional Wireline Module for Tactical FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-14
 KG-194 • • KG-94/94 A/194 A Operates from 9. 6 kbps to 13 Mbps Uses traditional or firefly key Two versions -- tactical and fixed plant FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-15
KG-194 • • KG-94/94 A/194 A Operates from 9. 6 kbps to 13 Mbps Uses traditional or firefly key Two versions -- tactical and fixed plant FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-15
 KIV-19 • • Operates from 9. 6 kbps to 13 Mbps Use traditional or firefly key Compatible with KG-194 Newest version KIV-19 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-16
KIV-19 • • Operates from 9. 6 kbps to 13 Mbps Use traditional or firefly key Compatible with KG-194 Newest version KIV-19 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-16
 KG-95 • DS 3 encryptor • Bulk Encryption • Three models: – KG-95 -1 operates from 10 -50 Mbs – KG-95 -2 operates only at DS-3 rate – KG-95 R two KG-95 -2 s together FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-17
KG-95 • DS 3 encryptor • Bulk Encryption • Three models: – KG-95 -1 operates from 10 -50 Mbs – KG-95 -2 operates only at DS-3 rate – KG-95 R two KG-95 -2 s together FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-17
 KG-189 • • • SONET Encryptor Operates at OC-3, OC-12 and OC-48 Type I encryption Firefly key DS-101/KSD-64 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-18
KG-189 • • • SONET Encryptor Operates at OC-3, OC-12 and OC-48 Type I encryption Firefly key DS-101/KSD-64 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-18
 KG-75 (FASTLANE) • • ATM encryptor KG-75 - up to OC-12 KG-75 A - up to OC-192 Supports up to 4094 simultaneous, cryptographically isolated ATM channels Supports DS 1, DS 3, OC 3 C and OC 12 C Supports PNNI 1. 0, UNI 4. 0 and SNMP Firefly and traditional key CYZ-10/DTD fill device FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-19
KG-75 (FASTLANE) • • ATM encryptor KG-75 - up to OC-12 KG-75 A - up to OC-192 Supports up to 4094 simultaneous, cryptographically isolated ATM channels Supports DS 1, DS 3, OC 3 C and OC 12 C Supports PNNI 1. 0, UNI 4. 0 and SNMP Firefly and traditional key CYZ-10/DTD fill device FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-19
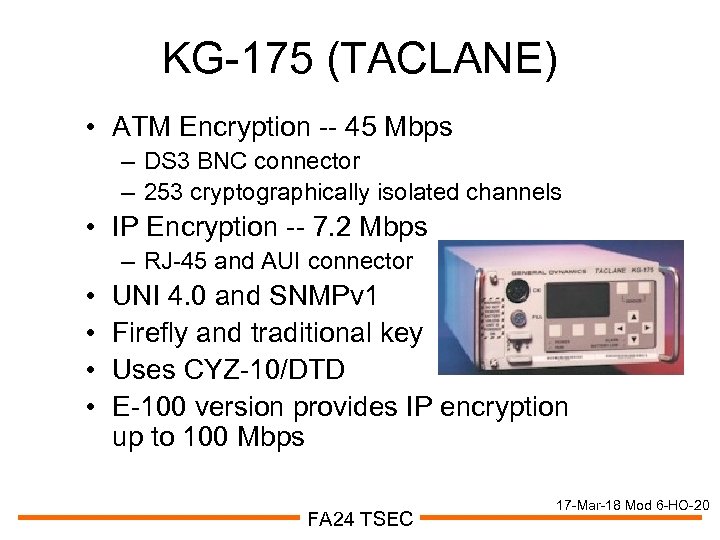 KG-175 (TACLANE) • ATM Encryption -- 45 Mbps – DS 3 BNC connector – 253 cryptographically isolated channels • IP Encryption -- 7. 2 Mbps – RJ-45 and AUI connector • • UNI 4. 0 and SNMPv 1 Firefly and traditional key Uses CYZ-10/DTD E-100 version provides IP encryption up to 100 Mbps FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-20
KG-175 (TACLANE) • ATM Encryption -- 45 Mbps – DS 3 BNC connector – 253 cryptographically isolated channels • IP Encryption -- 7. 2 Mbps – RJ-45 and AUI connector • • UNI 4. 0 and SNMPv 1 Firefly and traditional key Uses CYZ-10/DTD E-100 version provides IP encryption up to 100 Mbps FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-20
 KIV-21 • Converts black EIA-422, DB 37 HDLC into red IEEE 802. 3 ethernet • Replaces KIV-7/KG-84/KG-194 and CSU/DSU for a single site • Throughput - 8 Kbps to 3 Mbps • Frame relay FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-21
KIV-21 • Converts black EIA-422, DB 37 HDLC into red IEEE 802. 3 ethernet • Replaces KIV-7/KG-84/KG-194 and CSU/DSU for a single site • Throughput - 8 Kbps to 3 Mbps • Frame relay FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-21
 Network Encryption System (NES) • • • IP Encryption NES 4001 supports up to 3. 4 Mbps NES 4001 A throughput is 4. 3 Mbps Required black and red IP addresses FIREFLY key distribution FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-22
Network Encryption System (NES) • • • IP Encryption NES 4001 supports up to 3. 4 Mbps NES 4001 A throughput is 4. 3 Mbps Required black and red IP addresses FIREFLY key distribution FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-22
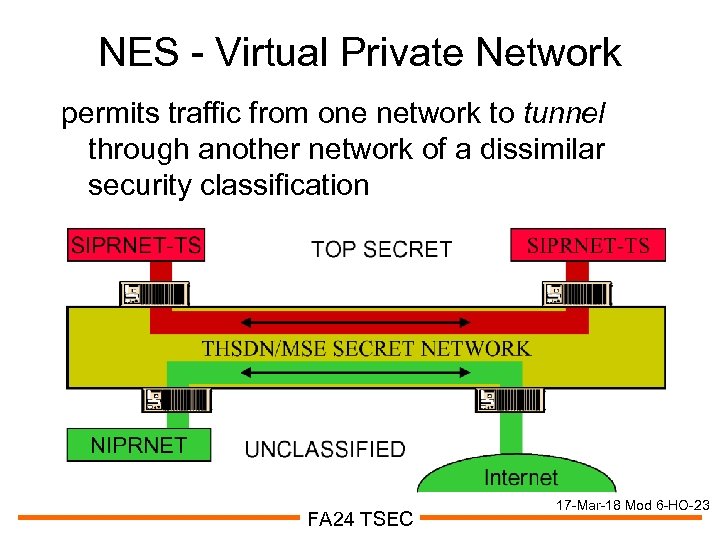 NES - Virtual Private Network permits traffic from one network to tunnel through another network of a dissimilar security classification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-23
NES - Virtual Private Network permits traffic from one network to tunnel through another network of a dissimilar security classification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-23
 Telephony Equipment • • • STU-III STE Omni Secure Cell Phones KY-68 FNBDT FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-24
Telephony Equipment • • • STU-III STE Omni Secure Cell Phones KY-68 FNBDT FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-24
 STU-III and SDD • Secure Data Device • Operate at 2. 4 or 4. 8 kbps code-excited line prediction (CELP) • Data transmitted at 2. 4, 4. 8 and 9. 6 kbps • Supports the ITU-T standards – V. 26 bit – V. 26 ter – V. 32 • KSD-64 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-25
STU-III and SDD • Secure Data Device • Operate at 2. 4 or 4. 8 kbps code-excited line prediction (CELP) • Data transmitted at 2. 4, 4. 8 and 9. 6 kbps • Supports the ITU-T standards – V. 26 bit – V. 26 ter – V. 32 • KSD-64 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-25
 STE • Replaces STU-III and KY-68 • Key is Fortezza Plus (KOV-14) • Interoperable with: – – STU-III DNVT ISDN: NI-1, NI-2, 5 ESS, DMS-100, DEFINITY Euro ISDN • Network Interface – – ISDN S/T BRI – 1 B+D or 2 B+D – RJ-45 PSTN – RJ-11 TRI-TAC/MSE – 4 wire line modem EIA-232/530 A • Host Interface – EIA-232/530 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-26
STE • Replaces STU-III and KY-68 • Key is Fortezza Plus (KOV-14) • Interoperable with: – – STU-III DNVT ISDN: NI-1, NI-2, 5 ESS, DMS-100, DEFINITY Euro ISDN • Network Interface – – ISDN S/T BRI – 1 B+D or 2 B+D – RJ-45 PSTN – RJ-11 TRI-TAC/MSE – 4 wire line modem EIA-232/530 A • Host Interface – EIA-232/530 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-26
 Omni • Secure Terminal provides Type-1 security for voice and data • Analog and Digital network • FNBDT compliant • Compatible with POTs and STU-III FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-27
Omni • Secure Terminal provides Type-1 security for voice and data • Analog and Digital network • FNBDT compliant • Compatible with POTs and STU-III FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-27
 Secure Cell Phones (1 of 2) Motorola Cipher-Tac 2000 • STU-III and STE compatible • Type 1 analog cellular security • sleeve slides between battery and phone to operate in secure mode Qualcomm Qsec 800 • Secure voice and data (CMDA) • Type 1 analog cellular security • requires no add-on module FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-28
Secure Cell Phones (1 of 2) Motorola Cipher-Tac 2000 • STU-III and STE compatible • Type 1 analog cellular security • sleeve slides between battery and phone to operate in secure mode Qualcomm Qsec 800 • Secure voice and data (CMDA) • Type 1 analog cellular security • requires no add-on module FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-28
 Secure Cell Phones (2 of 2) General Dynamics • Tri-band (GSM 900/1800/1900) • Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) • Clip-in security module • Type 1 security Motorola Satellite Series 9505 • satellite and cellular service • type 1 end-to-end security • Iridium security module attaches to it FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-29
Secure Cell Phones (2 of 2) General Dynamics • Tri-band (GSM 900/1800/1900) • Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) • Clip-in security module • Type 1 security Motorola Satellite Series 9505 • satellite and cellular service • type 1 end-to-end security • Iridium security module attaches to it FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-29
 KY-68 • TRI-TAC and MSE • Operates at 16/32 Kbps with CVSD (wideband) • Provides encryption of voice or data traffic on switched links to a circuit switch FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-30
KY-68 • TRI-TAC and MSE • Operates at 16/32 Kbps with CVSD (wideband) • Provides encryption of voice or data traffic on switched links to a circuit switch FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-30
 Future Narrow Band Digital Terminal (FNBDT) • Designed primarily for low-bandwidth, error prone networks such as cell phones • Secure global interoperability • FNBDT is an open standard • Satisfies both NATO and individual nation objectives • Uses MELP and Forward Error Correction FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-31
Future Narrow Band Digital Terminal (FNBDT) • Designed primarily for low-bandwidth, error prone networks such as cell phones • Secure global interoperability • FNBDT is an open standard • Satisfies both NATO and individual nation objectives • Uses MELP and Forward Error Correction FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-31
 Fill and Storage Devices • • • KYK-13 KOI-18 KYX-15 CYZ-10 KG-83 KGX-93 Fortezza Card KOV-14 KSD-64 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-32
Fill and Storage Devices • • • KYK-13 KOI-18 KYX-15 CYZ-10 KG-83 KGX-93 Fortezza Card KOV-14 KSD-64 A FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-32
 KYK-13 • Receive, store and load key in electronic form • Can hold six 128 bit keys • CCI is unclassified when empty -- takes on highest classification of key in memory FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-33
KYK-13 • Receive, store and load key in electronic form • Can hold six 128 bit keys • CCI is unclassified when empty -- takes on highest classification of key in memory FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-33
 KOI-18 • Used to read/transform paper key into electronic key • Can directly fill crypto equipment or load another fill device • Unclassified • No memory FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-34
KOI-18 • Used to read/transform paper key into electronic key • Can directly fill crypto equipment or load another fill device • Unclassified • No memory FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-34
 KYX-15 • Can store sixteen 128 bit keys • Unclassified when empty - takes on the highest classification of the key in memory • Used to perform OTAR • Can generate key locally when used with KG-84, KIV-7 or KY-68 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-35
KYX-15 • Can store sixteen 128 bit keys • Unclassified when empty - takes on the highest classification of the key in memory • Used to perform OTAR • Can generate key locally when used with KG-84, KIV-7 or KY-68 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-35
 AN/CYZ-10 • Data Transfer Device (DTD) can emulate other fill devices • Receives, audits and transfers 128 bit keys with identification information • CCI and is unclassified when empty or when the CIK is removed • Referred to as an ANCD FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-36
AN/CYZ-10 • Data Transfer Device (DTD) can emulate other fill devices • Receives, audits and transfers 128 bit keys with identification information • CCI and is unclassified when empty or when the CIK is removed • Referred to as an ANCD FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-36
 Simple Key Loader (SKL) Processor 32 -bit Intel® XScale™ CPU (400 MHz) O/S Win CE. NET (4. 1) RAM 128 MB of SDRAM ROM 64 MB of Flash Memory Graphics 2 -D Accelerator Size 7” x 3. 5” x 1. 8” Weight Approx 18 oz. 504 gms. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-37
Simple Key Loader (SKL) Processor 32 -bit Intel® XScale™ CPU (400 MHz) O/S Win CE. NET (4. 1) RAM 128 MB of SDRAM ROM 64 MB of Flash Memory Graphics 2 -D Accelerator Size 7” x 3. 5” x 1. 8” Weight Approx 18 oz. 504 gms. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-37
 Fortezza Card (1 of 2) • • • Used with DMS to encrypt/decrypt 1. 5 MBs processing rate Tamper proof/ultrasonically welded Exportable with State Department approval Includes RISC based processor FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-38
Fortezza Card (1 of 2) • • • Used with DMS to encrypt/decrypt 1. 5 MBs processing rate Tamper proof/ultrasonically welded Exportable with State Department approval Includes RISC based processor FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-38
 Fortezza Card (2 of 2) • Provides Cryptographic Functions – – – – Public Key Exchange Message Encryption Digital Signature Hashing Timestamp Password Certificate • Algorithms used – KEA, Skipjack, DSA, SHA-1 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-39
Fortezza Card (2 of 2) • Provides Cryptographic Functions – – – – Public Key Exchange Message Encryption Digital Signature Hashing Timestamp Password Certificate • Algorithms used – KEA, Skipjack, DSA, SHA-1 FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-39
 KOV-14 (Fortezza Plus) • Special PCMCIA card - provides encryption and other security services • Used to enable STE • Classified to level of keying material • Unclassified when separated from STE • Stays with COMSEC Material Control System (CMCS) until destroyed • With operational key – classified • With seed key -- unclassified FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-40
KOV-14 (Fortezza Plus) • Special PCMCIA card - provides encryption and other security services • Used to enable STE • Classified to level of keying material • Unclassified when separated from STE • Stays with COMSEC Material Control System (CMCS) until destroyed • With operational key – classified • With seed key -- unclassified FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-40
 KSD-64 A • Contains electronic fill info for STU-III • May contain classified operational key or unclassified seed key • Can operate in three modes FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-41
KSD-64 A • Contains electronic fill info for STU-III • May contain classified operational key or unclassified seed key • Can operate in three modes FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-41
 KSD-64 A Modes 1. Operational Key – Load STU-III to make direct secure calls to other STU-IIIs – Fill Device 2. Seed Key – Load STU-III to electronically obtain its operational key during a rekey phone call – Fill Device 3. Crypto Ignition Key (CIK) – Stores an electronic "password. " – CIK is used in STU-III that shares this password to unlock the terminal's secure transmission features FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-42
KSD-64 A Modes 1. Operational Key – Load STU-III to make direct secure calls to other STU-IIIs – Fill Device 2. Seed Key – Load STU-III to electronically obtain its operational key during a rekey phone call – Fill Device 3. Crypto Ignition Key (CIK) – Stores an electronic "password. " – CIK is used in STU-III that shares this password to unlock the terminal's secure transmission features FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-42
 Key Generators • KG-83 • KGX-93 • LMD/KP (KOK-22) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-43
Key Generators • KG-83 • KGX-93 • LMD/KP (KOK-22) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-43
 KG-83 • TRI-TAC and stand alone applications • Generates 128 bit TEK up to Top Secret • Compatible with most COMSEC equipment that accepts 128 bit keys • Requires initial/annual certification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-44
KG-83 • TRI-TAC and stand alone applications • Generates 128 bit TEK up to Top Secret • Compatible with most COMSEC equipment that accepts 128 bit keys • Requires initial/annual certification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-44
 KGX-93 • MSE and TRI-TAC switches • Generates 128 bit key up to Top Secret • Can also store key • Requires initial/annual certification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-45
KGX-93 • MSE and TRI-TAC switches • Generates 128 bit key up to Top Secret • Can also store key • Requires initial/annual certification FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-45
 Local Management Device/Key Processor (LMD/KP) • 128 bit key • Key Processor – KOK-22 A – Key Generation • Local key generation, distribution, auditing and reconciliation • Access to ACCOR • Tier 2 of EKMS • Can load 1000 keys at once FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-46
Local Management Device/Key Processor (LMD/KP) • 128 bit key • Key Processor – KOK-22 A – Key Generation • Local key generation, distribution, auditing and reconciliation • Access to ACCOR • Tier 2 of EKMS • Can load 1000 keys at once FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-46
 Cryptographic Modernization Program • Replacement of DOD’s aging Cryptographic Equipment Inventory to meet Current and Objective Capability Needs. • Intent is to achieve more robust security, network adaptability (Network. Centric) and performance enhanced equipment solutions. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-47
Cryptographic Modernization Program • Replacement of DOD’s aging Cryptographic Equipment Inventory to meet Current and Objective Capability Needs. • Intent is to achieve more robust security, network adaptability (Network. Centric) and performance enhanced equipment solutions. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-47
 Background (1 of 2) FY 99/00 MCEB and NSA Studies Concluded: • Technologically Obsolete 20 -30 years old • Cannot Support Network-Centric Architectures • Inventory Becoming Logistically Unsupportable Feb 01 ASD(C 3 I) Arthur Money memo directs: • Road Map for Crypto Systems Upgrade/Replacement/Retirement • Services Procure Modernized Crypto in FY 0309 POM FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-48
Background (1 of 2) FY 99/00 MCEB and NSA Studies Concluded: • Technologically Obsolete 20 -30 years old • Cannot Support Network-Centric Architectures • Inventory Becoming Logistically Unsupportable Feb 01 ASD(C 3 I) Arthur Money memo directs: • Road Map for Crypto Systems Upgrade/Replacement/Retirement • Services Procure Modernized Crypto in FY 0309 POM FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-48
 Background (2 of 2) Sep 02 JRB • 9 Crypto Systems as near term Modernization efforts • Approved Joint Forces Command as CRD Sponsor • Directed Joint Staffing of CM MNS and Completion of CM Implementation Plan Nov 03 SIGCEN • BG Hicks, signed the Charter establishing the CM ICT • ICT process serves to shorten the requirements determination event of the acquisition process by employing the team approach to requirements determination. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-49
Background (2 of 2) Sep 02 JRB • 9 Crypto Systems as near term Modernization efforts • Approved Joint Forces Command as CRD Sponsor • Directed Joint Staffing of CM MNS and Completion of CM Implementation Plan Nov 03 SIGCEN • BG Hicks, signed the Charter establishing the CM ICT • ICT process serves to shorten the requirements determination event of the acquisition process by employing the team approach to requirements determination. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-49
 Existing Deficiencies • Equipment Obsolescence • Incompatibilities with new architectures/technologies • Interoperability/Releasability problems • Restrictions on key management pose major challenges • Affects ability to support dynamic communications • Lack of programmability/flexibility • Incompatibility with modernized DOD KMI • Lack direct interfaces • Cryptographic equipment shortages • Readiness and surge capabilities affected FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-50
Existing Deficiencies • Equipment Obsolescence • Incompatibilities with new architectures/technologies • Interoperability/Releasability problems • Restrictions on key management pose major challenges • Affects ability to support dynamic communications • Lack of programmability/flexibility • Incompatibility with modernized DOD KMI • Lack direct interfaces • Cryptographic equipment shortages • Readiness and surge capabilities affected FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-50
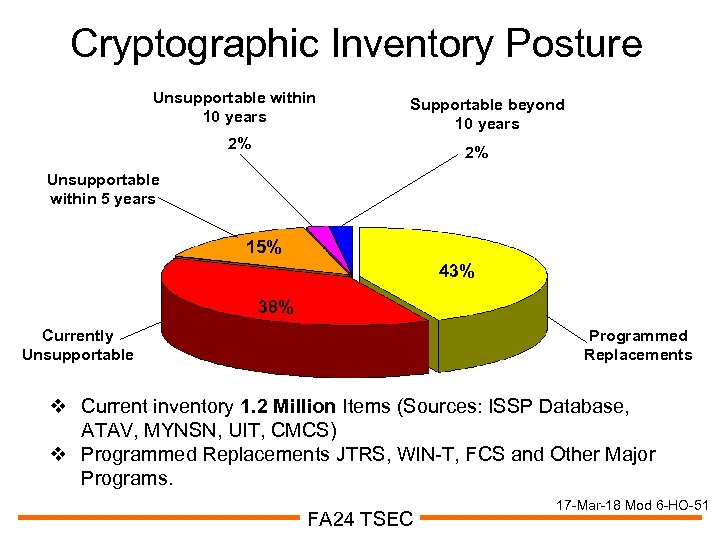 Cryptographic Inventory Posture Unsupportable within 10 years Supportable beyond 10 years 2% 2% Unsupportable within 5 years 15% 43% 38% Currently Unsupportable Programmed Replacements v Current inventory 1. 2 Million Items (Sources: ISSP Database, ATAV, MYNSN, UIT, CMCS) v Programmed Replacements JTRS, WIN-T, FCS and Other Major Programs. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-51
Cryptographic Inventory Posture Unsupportable within 10 years Supportable beyond 10 years 2% 2% Unsupportable within 5 years 15% 43% 38% Currently Unsupportable Programmed Replacements v Current inventory 1. 2 Million Items (Sources: ISSP Database, ATAV, MYNSN, UIT, CMCS) v Programmed Replacements JTRS, WIN-T, FCS and Other Major Programs. FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-51
 Threat Continuing trends reflect significantly increased risks of C 4 ISR, IT, and weapons systems to attacks on cryptography • • • Increases in computing power Increasing reliance upon COTS systems Service/Allied/Coalition use Availability of Electronic Warfare Systems Widespread distribution of Computer Network Attack (CNA) and Computer Network Exploitation (CNE) Tools FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-52
Threat Continuing trends reflect significantly increased risks of C 4 ISR, IT, and weapons systems to attacks on cryptography • • • Increases in computing power Increasing reliance upon COTS systems Service/Allied/Coalition use Availability of Electronic Warfare Systems Widespread distribution of Computer Network Attack (CNA) and Computer Network Exploitation (CNE) Tools FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-52
 CM Concept • Leverage Latest Technology • Develop Multi-Functional Components that Replace Entire Families of Crypto Equipment • NSA Partnership with Services on Program Development NSA will: - Retain Crypto Certification Approval - Fund Services for Program Development R&D Services will: - Program Funding for Procurement and Fielding - Conduct Program Development Process - Develop Equipment Shortage/Supportability Lists - Prepare Fielding and Transition Plans FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-53
CM Concept • Leverage Latest Technology • Develop Multi-Functional Components that Replace Entire Families of Crypto Equipment • NSA Partnership with Services on Program Development NSA will: - Retain Crypto Certification Approval - Fund Services for Program Development R&D Services will: - Program Funding for Procurement and Fielding - Conduct Program Development Process - Develop Equipment Shortage/Supportability Lists - Prepare Fielding and Transition Plans FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-53
 CM Core Capabilities • Programmable/Reprogrammable Algorithms • Capable of Receiving an Algorithm • Scalable Components • Embedded Modules (Whenever Possible) • EKMS/KMI Compliant/Capable • Network-Centric Functionality • Assured control of DOD networks • Interoperability • Physical - Form and Fit FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-54
CM Core Capabilities • Programmable/Reprogrammable Algorithms • Capable of Receiving an Algorithm • Scalable Components • Embedded Modules (Whenever Possible) • EKMS/KMI Compliant/Capable • Network-Centric Functionality • Assured control of DOD networks • Interoperability • Physical - Form and Fit FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-54
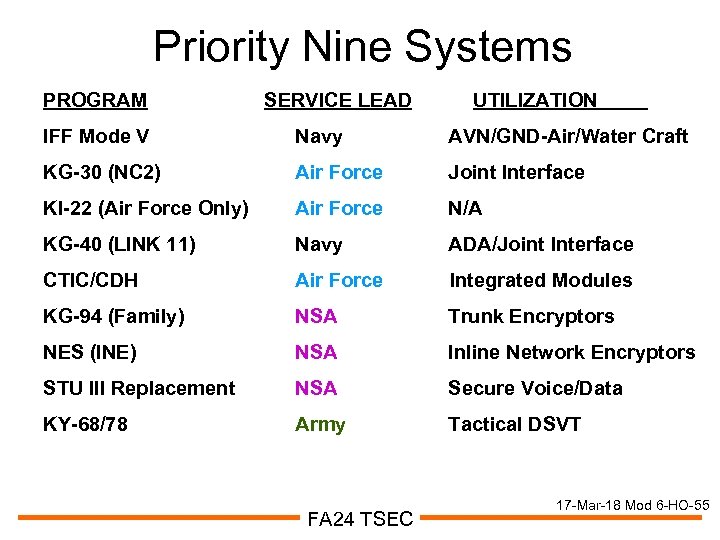 Priority Nine Systems PROGRAM SERVICE LEAD UTILIZATION IFF Mode V Navy AVN/GND-Air/Water Craft KG-30 (NC 2) Air Force Joint Interface KI-22 (Air Force Only) Air Force N/A KG-40 (LINK 11) Navy ADA/Joint Interface CTIC/CDH Air Force Integrated Modules KG-94 (Family) NSA Trunk Encryptors NES (INE) NSA Inline Network Encryptors STU III Replacement NSA Secure Voice/Data KY-68/78 Army Tactical DSVT FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-55
Priority Nine Systems PROGRAM SERVICE LEAD UTILIZATION IFF Mode V Navy AVN/GND-Air/Water Craft KG-30 (NC 2) Air Force Joint Interface KI-22 (Air Force Only) Air Force N/A KG-40 (LINK 11) Navy ADA/Joint Interface CTIC/CDH Air Force Integrated Modules KG-94 (Family) NSA Trunk Encryptors NES (INE) NSA Inline Network Encryptors STU III Replacement NSA Secure Voice/Data KY-68/78 Army Tactical DSVT FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-55
 EKMS and AKMS • EKMS Architecture and Concepts • AKMS Description and Operational Concepts • Doctrinal Impacts • Roles/Responsibilities • Issues FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-56
EKMS and AKMS • EKMS Architecture and Concepts • AKMS Description and Operational Concepts • Doctrinal Impacts • Roles/Responsibilities • Issues FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-56
 Electronic Key Mgt System • DOD initiative to modernize management/distribution of COMSEC to support the warfighter and non-military government users. • Replaces slow cumbersome paper and manpower intensive processes of management and distribution of COMSEC material. • Increase security of key management processes • Increase responsiveness to user needs • Provide for interoperability FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-57
Electronic Key Mgt System • DOD initiative to modernize management/distribution of COMSEC to support the warfighter and non-military government users. • Replaces slow cumbersome paper and manpower intensive processes of management and distribution of COMSEC material. • Increase security of key management processes • Increase responsiveness to user needs • Provide for interoperability FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-57
 EKMS Tier Levels 0. National Security Agency (NSA) 1. Central Office of Record (COR) 2. LCMS COMSEC User Accounts 3. Common Fill Devices FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-58
EKMS Tier Levels 0. National Security Agency (NSA) 1. Central Office of Record (COR) 2. LCMS COMSEC User Accounts 3. Common Fill Devices FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-58
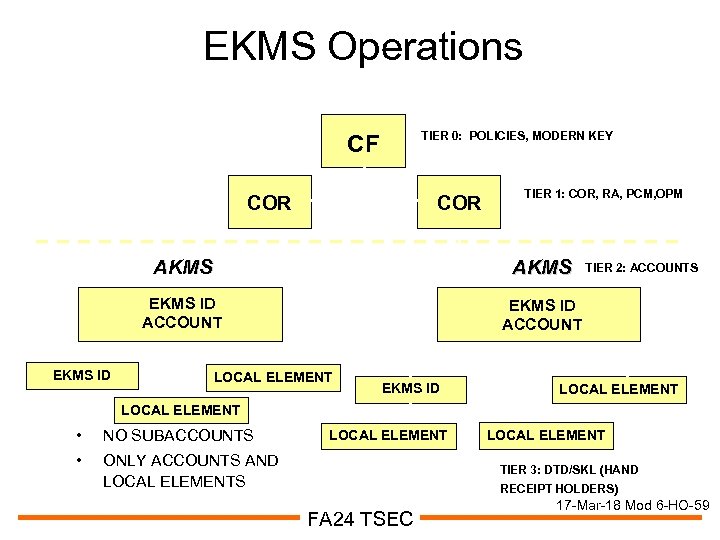 EKMS Operations TIER 0: POLICIES, MODERN KEY CF COR TIER 1: COR, RA, PCM, OPM AKMS EKMS ID ACCOUNT EKMS ID AKMS EKMS ID ACCOUNT LOCAL ELEMENT EKMS ID TIER 2: ACCOUNTS LOCAL ELEMENT • NO SUBACCOUNTS • ONLY ACCOUNTS AND LOCAL ELEMENTS LOCAL ELEMENT TIER 3: DTD/SKL (HAND RECEIPT HOLDERS) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-59
EKMS Operations TIER 0: POLICIES, MODERN KEY CF COR TIER 1: COR, RA, PCM, OPM AKMS EKMS ID ACCOUNT EKMS ID AKMS EKMS ID ACCOUNT LOCAL ELEMENT EKMS ID TIER 2: ACCOUNTS LOCAL ELEMENT • NO SUBACCOUNTS • ONLY ACCOUNTS AND LOCAL ELEMENTS LOCAL ELEMENT TIER 3: DTD/SKL (HAND RECEIPT HOLDERS) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-59
 Tier 0 – NSA Central Facility Provides for production, management, and distribution of specialized electronic cryptographic key and associated materials. MODEM key National Security Agency (NSA) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-60
Tier 0 – NSA Central Facility Provides for production, management, and distribution of specialized electronic cryptographic key and associated materials. MODEM key National Security Agency (NSA) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-60
 Tier 1 - Central Office of Record • CORs are focal points for production, management, auditing, and distribution of Service. Unique electronic cryptographic key and materials • Supports joint operations at theater and strategic levels • Act as alternates to the other in cases of degraded operations, activity, and geographic location • Major functional areas: – Central Office of Record (COR) – Registration Authority (RA) – Privilege Certificate Manager (PCM) – Ordering Privilege Manager (OPM) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-61
Tier 1 - Central Office of Record • CORs are focal points for production, management, auditing, and distribution of Service. Unique electronic cryptographic key and materials • Supports joint operations at theater and strategic levels • Act as alternates to the other in cases of degraded operations, activity, and geographic location • Major functional areas: – Central Office of Record (COR) – Registration Authority (RA) – Privilege Certificate Manager (PCM) – Ordering Privilege Manager (OPM) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-61
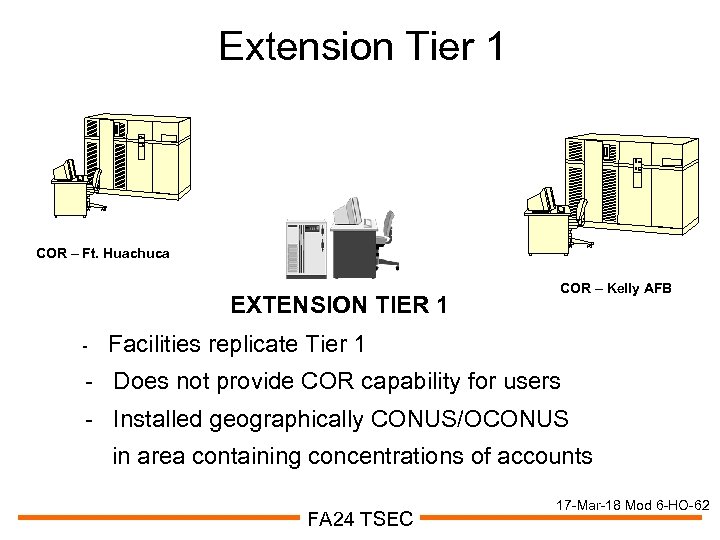 Extension Tier 1 COR – Ft. Huachuca EXTENSION TIER 1 - COR – Kelly AFB Facilities replicate Tier 1 - Does not provide COR capability for users - Installed geographically CONUS/OCONUS in area containing concentrations of accounts FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-62
Extension Tier 1 COR – Ft. Huachuca EXTENSION TIER 1 - COR – Kelly AFB Facilities replicate Tier 1 - Does not provide COR capability for users - Installed geographically CONUS/OCONUS in area containing concentrations of accounts FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-62
 Tier 2 – LCMS User Accounts • Represents individual EKMS user accounts • Developed by NSA • Used by all services • Individual service policies and procedures • AKMS – Army Tier 2 outlines Army policies and procedures FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-63
Tier 2 – LCMS User Accounts • Represents individual EKMS user accounts • Developed by NSA • Used by all services • Individual service policies and procedures • AKMS – Army Tier 2 outlines Army policies and procedures FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-63
 AKMS • • Replaces slow, cumbersome paper and manpower intensive processes Provides a reliable, responsive and secure system Implements an electronic key strategy w/in the Army Provides Tier 0 and Tier 1 electronic interoperability Provides COMSEC and communications planning capabilities Provides real time key generation and distribution To make AKMS work as a system, all three components (LCMS, ACES, DTD) are required FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-64
AKMS • • Replaces slow, cumbersome paper and manpower intensive processes Provides a reliable, responsive and secure system Implements an electronic key strategy w/in the Army Provides Tier 0 and Tier 1 electronic interoperability Provides COMSEC and communications planning capabilities Provides real time key generation and distribution To make AKMS work as a system, all three components (LCMS, ACES, DTD) are required FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-64
 LCMS Workstation • NSA and Army produced and distributed • Automated account management • Local key generation, distribution, auditing, reconciliation • Access to CF and COR FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-65
LCMS Workstation • NSA and Army produced and distributed • Automated account management • Local key generation, distribution, auditing, reconciliation • Access to CF and COR FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-65
 ACES Workstation • Army produced and distributed • Designed for Cryptonet planning and management • Includes SOI/ EP planning and management • Employs ACES-specific application functions FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-66
ACES Workstation • Army produced and distributed • Designed for Cryptonet planning and management • Includes SOI/ EP planning and management • Employs ACES-specific application functions FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-66
 Fill Device DTD • Receive, distribute, store, and manage key • Receive, transfer, and display SOI SKL • Perform Audit FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-67
Fill Device DTD • Receive, distribute, store, and manage key • Receive, transfer, and display SOI SKL • Perform Audit FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-67
 ACES Scenario U. S. MILITARY IS NEEDED SOMEWHERE ACES COMMUNICATIONS PLAN AN KEY REQUIREMENTS DA TA LCMS OPERATOR (TIER 2) PL S-3 ACES OPERATOR SHORT TITLE INFORMATION TRIBU DIS KEYS EDED S NE TED A DTD/SKL (TIER 3) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-68
ACES Scenario U. S. MILITARY IS NEEDED SOMEWHERE ACES COMMUNICATIONS PLAN AN KEY REQUIREMENTS DA TA LCMS OPERATOR (TIER 2) PL S-3 ACES OPERATOR SHORT TITLE INFORMATION TRIBU DIS KEYS EDED S NE TED A DTD/SKL (TIER 3) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-68
 Doctrinal Impacts • • Accounts no longer manual Acclaims no longer in effect Sub-accounts no longer authorized Key produced locally and distribution process streamlined • Electronic key transfer increased; physical key transfer decreased • Modern key ordering incorporated to mainstream FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-69
Doctrinal Impacts • • Accounts no longer manual Acclaims no longer in effect Sub-accounts no longer authorized Key produced locally and distribution process streamlined • Electronic key transfer increased; physical key transfer decreased • Modern key ordering incorporated to mainstream FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-69
 Roles/Responsibilities • CIO/G-6: EKMS/AKMS oversight; IA system integrator • G-2: COMSEC Policy • G-8: Program Funding • PEO C 3 T: Responsible PEO; DAA • PM TRCS: PM for LCMS, ACES, and DTD, under PM WIN-T • CSLA: Primary service authority role; primary Tier 1 segment (COR); EKMS subject matter experts and support to IA directorate • CECOM: Tier 1 software support activity; Tier 2 lifecycle support (minus SW) • SIGCEN: AKMS requirements and operational concepts; sustainment training FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-70
Roles/Responsibilities • CIO/G-6: EKMS/AKMS oversight; IA system integrator • G-2: COMSEC Policy • G-8: Program Funding • PEO C 3 T: Responsible PEO; DAA • PM TRCS: PM for LCMS, ACES, and DTD, under PM WIN-T • CSLA: Primary service authority role; primary Tier 1 segment (COR); EKMS subject matter experts and support to IA directorate • CECOM: Tier 1 software support activity; Tier 2 lifecycle support (minus SW) • SIGCEN: AKMS requirements and operational concepts; sustainment training FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-70
 IA Directorate (DCD) Role • Provides EKMS/AKMS oversight • Provides representation to: – KMI Committee (KMI EC) – Joint Key Management Infrastructure Working Group EKMS Transition Team (ETT) – Tier 1 System Management Board (TSMB) – Other working groups and boards • Chairs AKM Infrastructure Working Group (AKMIWG) • Facilitates exchange of info/coordination among Army Orgs (G-8, G-2, CIO/G-6, SIGCEN, CSLA, PM WIN-T) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-71
IA Directorate (DCD) Role • Provides EKMS/AKMS oversight • Provides representation to: – KMI Committee (KMI EC) – Joint Key Management Infrastructure Working Group EKMS Transition Team (ETT) – Tier 1 System Management Board (TSMB) – Other working groups and boards • Chairs AKM Infrastructure Working Group (AKMIWG) • Facilitates exchange of info/coordination among Army Orgs (G-8, G-2, CIO/G-6, SIGCEN, CSLA, PM WIN-T) FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-71
 E/AKMS Issues • Simple Key Loader (SKL) Testing • Tier 1 & Tier 2 phase 4 certification and accreditation • Software Support Activity (SSA) • merging of EKMS, KMI, and COMSEC modernization programs • ACES Fielding FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-72
E/AKMS Issues • Simple Key Loader (SKL) Testing • Tier 1 & Tier 2 phase 4 certification and accreditation • Software Support Activity (SSA) • merging of EKMS, KMI, and COMSEC modernization programs • ACES Fielding FA 24 TSEC 17 -Mar-18 Mod 6 -HO-72


