7d1467cb6b404944cfb8e60848794e82.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

MIGRATION

Movement Mobility ranging from local to global and daily to once a lifetime n Movement is a good example of the spatial process (spatial interaction; diffusion; distribution; patterns). n

What is activity space? n n n The great majority of people have a daily routine that takes them through a sequence of short moves that geographers call activity space. America is the world’s most mobile society. Why? Technology has greatly expanded activity space, particularly in wealthier, more developed countries.

Types of movement n Cyclic movement n Periodic movement n Migration

Types of Movement n n CYCLIC MOVEMENT: movement that has a closed route Examples n n Commuting: Home to work and back home Seasonal: “Sunbelt” States Nomadism: Movement over territory for survival repeated time and again Daily classes

Types of Movement PERIODIC MOVEMENT: movement away from home for a longer period. n Examples n Migrant labor: moving across borders for work n Transhumance: moving livestock to pastures based on season (rain, temperature) n Military service n College attendance n

What is Migration? n Definition: the long-term relocation of an individual, household, or group to a new location outside the community of origin; a purposeful movement involving a change of permanent residence

Migration is a complex phenomenon that raises many questions. n Why do people move? n All migration is a combination of push and pull factors.

What are push factors of migration? n n Defined: unfavorable characteristics of a locale that contribute to the dissatisfaction of its residents and impel their emigration Examples: widespread unemployment; poverty; discrimination; political unrest; war; famine and/or drought; land shortage; overpopulation
What are pull factors of migration? n n n Defined: characteristics of a locale that act as attractive forces, drawing migrants from other places Examples: employment opportunities; political and/or personal freedoms (speech; religion, right to vote, etc. ); land; amenities (e. g. retirement) Important note: Many people to move based on excessively positive images and expectations (not always accurate).

Most people migrate for economic reasons. Search for better paying jobs n To find new jobs/employment n To escape poverty or low standards of living n

Catalysts of Migration: What causes it to happen? n Economic conditions n n n Poverty (push factors) Perceived opportunities in destinations (pull factors) Technological advances n n Modern transportation makes migration easier Allows people to migrate where jobs are available

Other reasons/catalysts for migration… n Armed conflict and civil war n n n Three million people drive from their homes in the former Yugoslavia Civil war in Rwanda (Hutu and Tutsis) Political circumstances n n n Oppressive regimes Cuba Vietnam’s “boat people”

Reasons continued… n Environmental Conditions n n n Potato Famine in Ireland (1840 s) Major earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or hurricanes (Gulf Coast of U. S. — 2005) Culture and Tradition n n Muslims migrated from India when it was partitioned Jews left the former Soviet Union for Israel

Voluntary Migration n Occurs when people choose to migrate Remember: the # 1 reason people migrate: ECONOMIC! Any voluntary migration flow represents the numbers going from the source to the destination minus those returning to the source. Forced Migration n n Also referred to as involuntary migration Examples: n n n The Transatlantic Slave Trade: largest number of slaves were brought to plantations in the Caribbean and eastern South America; black population was one million in U. S. in 1800 Convicts shipped from Britain to Australia beginning in 1788 1800 s: Native Americans in U. S. forced to live on reservations

E. G. RAVENSTEIN (1834— 1913) British sociologist n LAWS OF MIGRATION: 1. Most migrants go only a short distance. 2. Longer distance migration favors big city destinations. In other words, people will travel farther if they are migrating to a city. 3. Most migration proceeds step-by-step. 4. Most migration is rural to urban. 5. Each migration flow produces a counterflow. 6. Most migrants are adults; families are less likely to make international moves. 7. Most international migrants are young males.

About Ravenstein’s laws: 1. He concluded that most move short distances and that the frequency of moves declines with distance (distance decay). 2. Step Migration – When a migrant follows a path of a series of stages, or steps toward a final destination. * intervening opportunity –at one of the steps along the path, pull factors encourage the migrant to settle there. 3. Urban residents are less migratory than inhabitants of rural areas. 4. Chain migration also needs to be considered. n Defined: a process by which people are given preference for migrating to another country because a relative was previously admitted. Asians are know to be the most effective users of chain migration. 5. Less valid today than when first proposed. In reality, women and girls now comprise between 40 -60% of all international migrants worldwide.

INTERNAL MIGRATIONS n n Migration that occurs within a single countries borders n Example: African-Americans moved northward during World War I; n most migrants came from rural areas; n 1970 s—more were leaving the North and returning to the South because of changing civil rights conditions Varies depending on mobility of country (USA = high mobility) n US: Urban to Suburban n Peru: Rural to Urban
INTERNAL MIGRATIONS Two Types: 1. Intraregional 2. Interregional

Intraregional Migration n Intraregional migrations--people moving or being moved within one geographic realm (region) of a country n Current examples: n Rural to urban: n increases with development, ¾ of core countries population in urban areas n Urban to suburban: n lifestyle changes n Metropolitan to nonmetropolitan areas: n called counterurbanization, increased technology allows people to work outside of the city

Interregional Migrations n. Definition-people moving or being moved from one geographic realm (region) to another within a country From South n Current USA examples: n n n Movement North to South, and East to West refugees/evacuees from the Gulf Coast region to other parts of the United States, rural to urban areas to find jobs

Interregional Migrations n Current World examples: n To Brazil’s interior: Brasilia n to North in Italy, and North to South in the UK for Jobs n Islands of development are cities with foreign investment and jobs n n West African coast European colonies in SE Asia attracted Chinese

External Migration n Movement across country borders n n Emigrant: one who migrates out of a country n n Also called International migration Subtracts from total population Immigrant: one who migrates into a country n Adds to total population
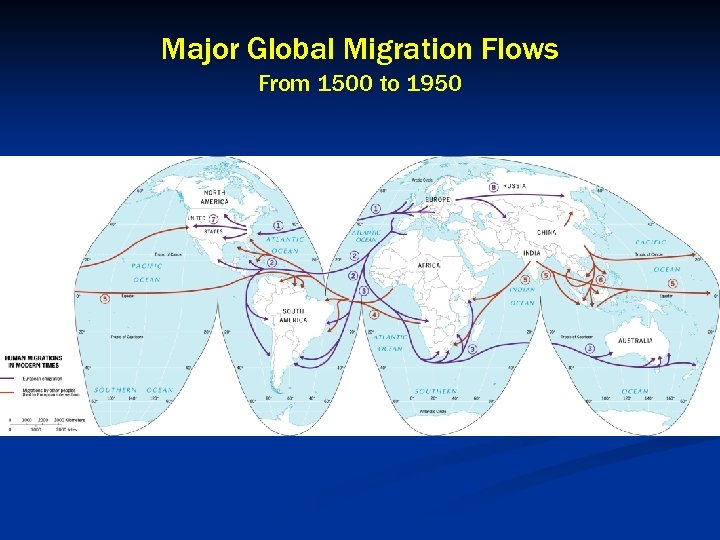
Major Global Migration Flows From 1500 to 1950

Global Migration Patterns From less-developed Stage 2 countries into moredeveloped Stage 4/5 countries n 3 largest migration flows n Asia and Africa to Europe n Asia to North America n Latin America to North America n Net In Migration: North America, Europe, Oceania n Net Out Migration: Asia, Latin America, Africa n

US Immigration Patterns n Three main waves 1. Colonial America: 1607 -1840 1. European settlement- 2 million, mostly British 2. African slaves – 800, 000

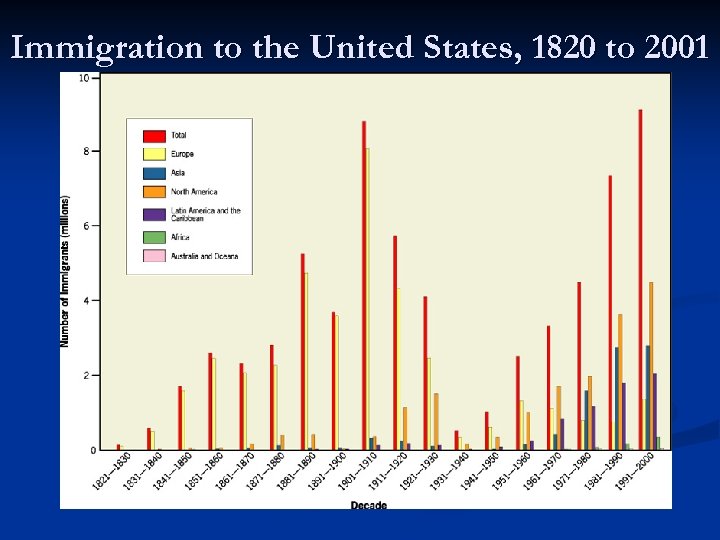
Immigration to the United States, 1820 to 2001

US Immigration Patterns 2. 19 th century (1840 -1910) 3 European Peaks 1. 1840 s and 1850 s: -Northern and Western Europe (Ireland, Germany) 2. 1880 s: -Northern and Western Europe (Ireland, Germany, Norway, Sweden) 3. 1900 -1910: -Southern and Eastern Europe [Italy, Russia, Austria-Hungary (Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Czech Republic, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Ukraine) ]
Immigration to the United States, 1820 to 2001

US Immigration Patterns 3. Second-half of 20 th century (1950 -2008) Less developed regions 1. Latin America: Mexico, Dominican Republic, El Salvador 2. Asia: China, Philippines, India, Vietnam
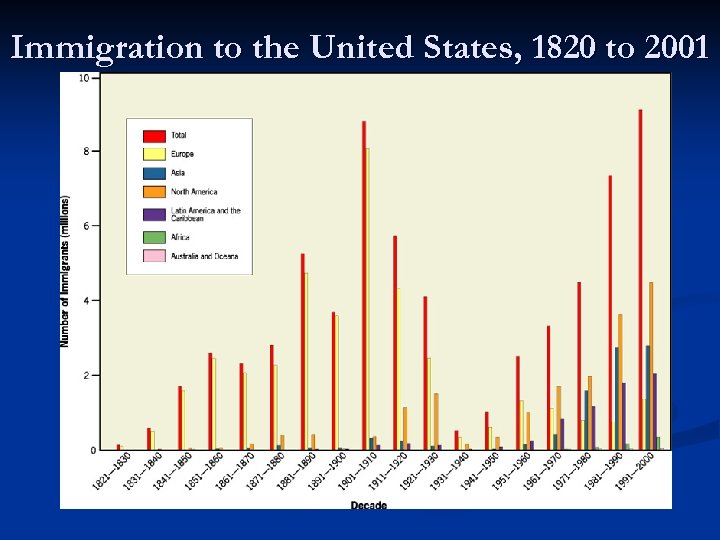
Immigration to the United States, 1820 to 2001
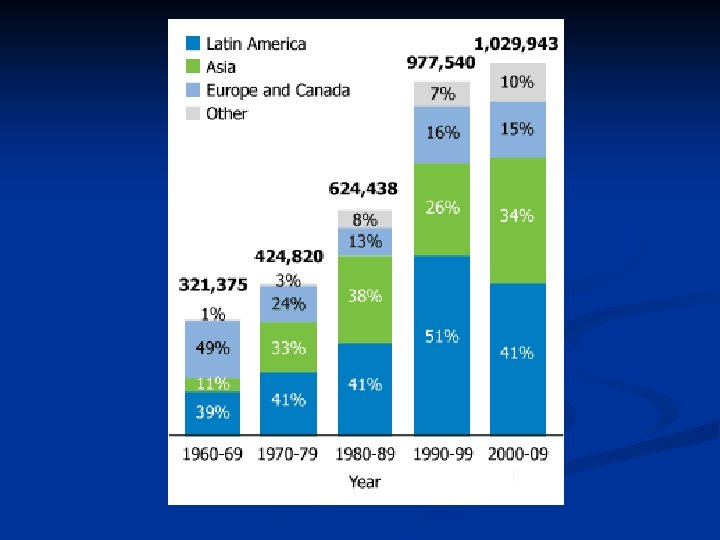
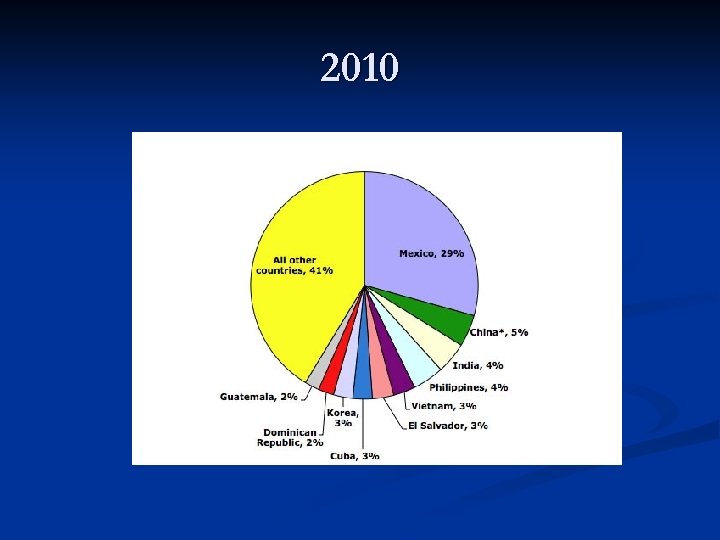
2010

Immigration Policies n USA Quota Laws Quota Act of 1921 and Origins Act of 1924: 2% of 1910 population n Immigration Act of 1965 n n 1968: Hemisphere quotas n 1978: Global Quotas n Currently: Global Quota of 620, 000 with no more than 7% from each country n Major Exceptions: family reunification, employment, talented, lottery, refugees

Immigration Policies Brain Drain: large-scale emigration by talented people n Guest Workers: To Europe from Middle East and North Africa n n n Example: 750, 000 Turks employed in Germany Time-Contract workers: South and East Asian workers to Southeast Asia

What about refugees? n UN definition n A person who has well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political group. n UN reports around 20 million refugees worldwide

What about refugees? UN definitions n International refugees: n Those who have crossed one or more international borders and are encamped in a country other than their own n Intranational refugees: n Those who abandoned homes but not homeland have their

It is difficult to identify refugees. n n n No mention of natural/enviromental disaster UN must distinguish between refugees and voluntary migrants before granting asylum. Three general characteristics, individual or aggregate (collectively): n n n 1) Most refugees move without any more tangible property than they can carry or transport with them. 2) Most refugees make their first “step” on foot, by bicycle, wagon, or open boat. 3) Refugees move without the official documents that accompany channeled migrations.
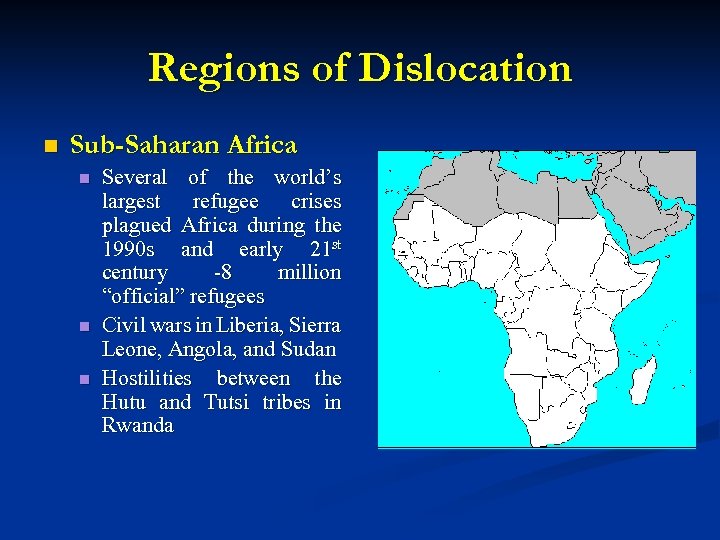
Regions of Dislocation n Sub-Saharan Africa n n n Several of the world’s largest refugee crises plagued Africa during the 1990 s and early 21 st century -8 million “official” refugees Civil wars in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Angola, and Sudan Hostilities between the Hutu and Tutsi tribes in Rwanda
Other regions of dislocation… n North Africa and Southwest Asia n n n Israel and the displaced Arab populations that surround it Exhibits qualities that are likely to generate additional refugee flow in the future The Kurdish population following the Gulf War (1991) Taliban rule in Afghanistan after the Soviet invasion during the 1980 s

Regions of dislocation continued… n South Asia n n Pakistan accommodated forced emigrants from Afghanistan Major refugee problem stems from a civil war in Sri Lanka

Regions of dislocation continued… n Southeast Asia n n n “Boat people” who fled communist rule in Vietnam In the early 1990 s, Cambodia generated the region’s largest refugee flow Today--largest number of refugees come from Myanmar (Burma)
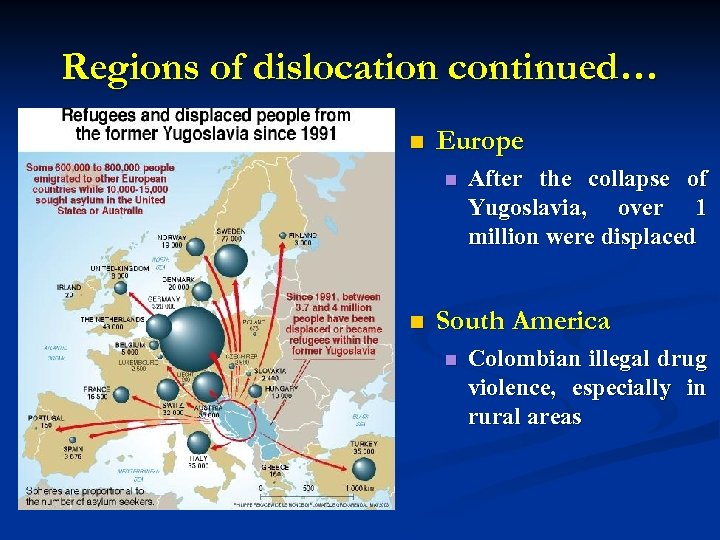
Regions of dislocation continued… n Europe n n After the collapse of Yugoslavia, over 1 million were displaced South America n Colombian illegal drug violence, especially in rural areas
7d1467cb6b404944cfb8e60848794e82.ppt