6bc69104e4ee5aaf3a2d9fa2dad98d14.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITES IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC (THE DELPHI SURVEY) Dušan Drbohlav Lenka Lachmanová Charles University in Prague Faculty of Science Department of Social Geography and Regional Development drbohlav@natur. cuni. cz

Results based on: The research project done for The Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs of the Czech Republic: „International Migration and Migrants´ Illegal/Irregular Activities: The Czech Republic in a Broader European Context“ see: www. geography. cz/illegal. htm and The research programme No. MSM 0021620831 of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sport of the Czech Republic

THE DELPHI METHOD l l l „A procedure to obtain the most reliable consensus of opinion of a group of experts … by a series of intensive questionnaires interspersed with controlled opinion feedback“ Anonymity and no direct contact between respondents Forms of the Delphi method: a) Conventional Delphi - basic principles + statistical presentation of answers, used for predicting future development, based on a consensus among experts b) Policy Delphi - to analyse policy problems, focus upon policy or strategical measures l a) b) c) Conditions that support applying the Delphi: Complexity of the research problem (different policy fields involved) When objective data are lacking When designing a common future scenario

THE DELPHI SURVEY 2005 - 2006 l l Small-scale research of two rounds (n=32, 23) Conventional + Policy Delphi methods l FIRST ROUND (November-February 2005/2006) – 32 respondents (62 were contacted) l SECOND ROUND (May-June 2006) - 23 respondents l Respondents´ professional background: l 13 academic sphere l 7 GOs l 7 NGOs l 2 representatives of international organizations (IOM, UNHCR) l 1 politician l 1 entrepreneur l 1 representative of Trade Unions

THE DELPHI SURVEY 2005 - 2006 SELECTED RESEARCH QUESTIONS l What forms of migrants´ illegal economic activities do we have in l l l Why do we have them? Who are illegal immigrants? How many illegal immigrants stay in the Czech Republic? How l What impacts do migrants´ illegal economic activities have on l What important measures should be applied to eliminate l Future development? the Czech Republic? many of them may come in the future? the country of destination, the employer, the immigrant himself/herself and the country of origin? (to successfully combat) illegal/irregular immigration?
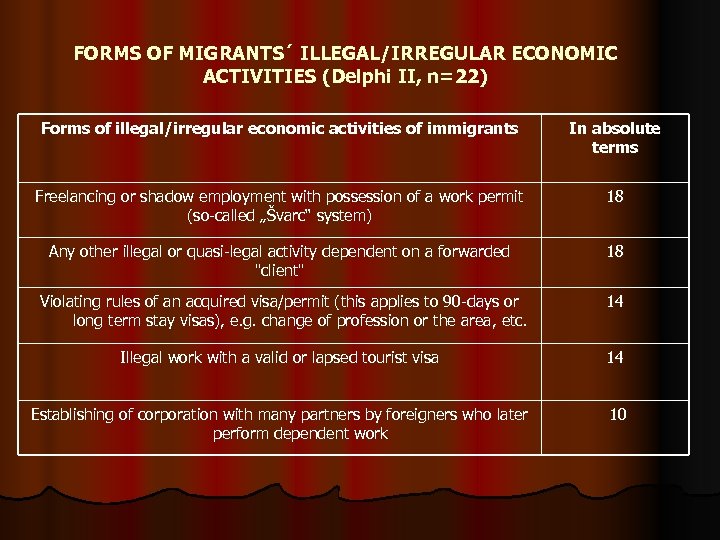
FORMS OF MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES (Delphi II, n=22) Forms of illegal/irregular economic activities of immigrants In absolute terms Freelancing or shadow employment with possession of a work permit (so-called „Švarc“ system) 18 Any other illegal or quasi-legal activity dependent on a forwarded "client" 18 Violating rules of an acquired visa/permit (this applies to 90 -days or long term stay visas), e. g. change of profession or the area, etc. 14 Illegal work with a valid or lapsed tourist visa 14 Establishing of corporation with many partners by foreigners who later perform dependent work 10

REASONS FOR MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES (Delphi II, n=23) Scale from 1 to 5 (1 = for key reason, . . . , 5 = for unimportant reason) Most important reasons Importance Established system of middlemen (clientage) 1. 70 Strong demand on illegal (cheap and flexible) foreign labour, especially in manual works (e. g. construction) 1. 78 Illegal employment (even of natives) is a widespread phenomenon 1. 82 Too much bureaucracy in acquiring and applying for a work/residence permit 2. 00 Unimportant reasons The Czech Republic serving as a temporary stop during immigrants´ passage to countries of Western Europe 3. 52 Labour migration to the Czech Republic is a traditional activity, especially for the Ukrainians from the western part of Ukraine 3. 29 Entering the Czech Republic is very simple 3. 00
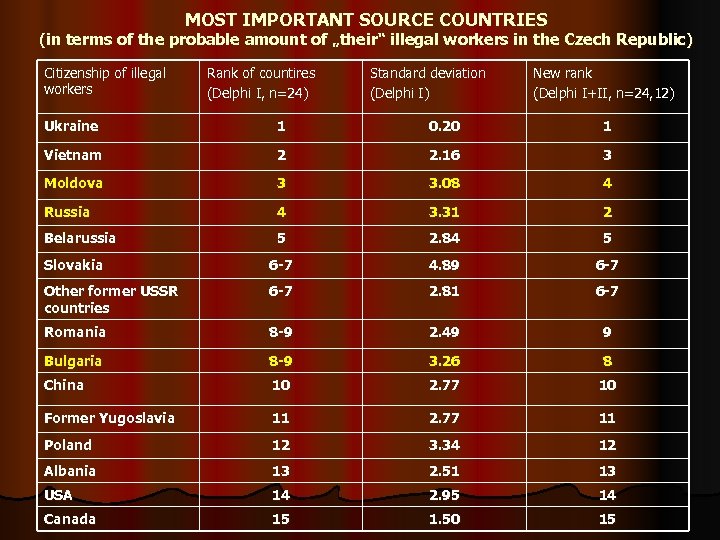
MOST IMPORTANT SOURCE COUNTRIES (in terms of the probable amount of „their“ illegal workers in the Czech Republic) Citizenship of illegal workers Rank of countires (Delphi I, n=24) Standard deviation (Delphi I) New rank (Delphi I+II, n=24, 12) Ukraine 1 0. 20 1 Vietnam 2 2. 16 3 Moldova 3 3. 08 4 Russia 4 3. 31 2 Belarussia 5 2. 84 5 Slovakia 6 -7 4. 89 6 -7 Other former USSR countries 6 -7 2. 81 6 -7 Romania 8 -9 2. 49 9 Bulgaria 8 -9 3. 26 8 China 10 2. 77 10 Former Yugoslavia 11 2. 77 11 Poland 12 3. 34 12 Albania 13 2. 51 13 USA 14 2. 95 14 Canada 15 1. 50 15

SECTORIAL STRUCUTRE OF FOREIGN ILLEGAL LABOUR (Delphi II, n=20) Economic sector Share of „truly illegal“ immigrants working in the economic sector (in %) Construction 41 Hotels and restaurants 13 Household services (housekeeping, caring etc. ) 12 Agriculture 11 Retail/Wholesale 11 Textile industry 9 Food industry 8 Other important sectors: Translating, Foreign languages teaching, Journalism
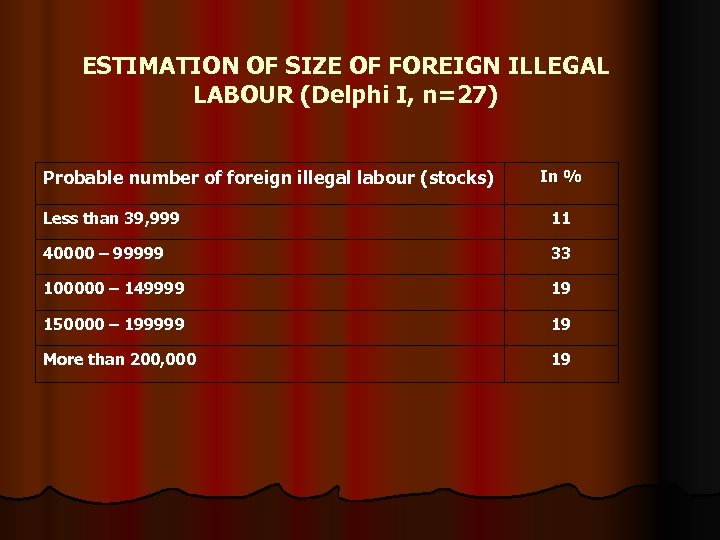
ESTIMATION OF SIZE OF FOREIGN ILLEGAL LABOUR (Delphi I, n=27) Probable number of foreign illegal labour (stocks) In % Less than 39, 999 11 40000 – 99999 33 100000 – 149999 19 150000 – 199999 19 More than 200, 000 19

MOST SIGINIFICANT POSITIVE IMPACTS OF MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES ON THE CZECH REPUBLIC (Delphi II) Postive impacts In absolute terms Fitting unattractive and low paid working positions 18 Cheap and flexible labour improves the economic growth 16 Development of some economic subject and branches (e. g. construction) 15 Individual households profit from presence of illegal workers (cheaper houseworks, cheaper services or reconstruction, etc. ) 12 Price reduction of some services or economic activities 10 Growth of competition among companies emlpoying illegal working labour x Increased competitive advantage of employers who use illegal work force 9
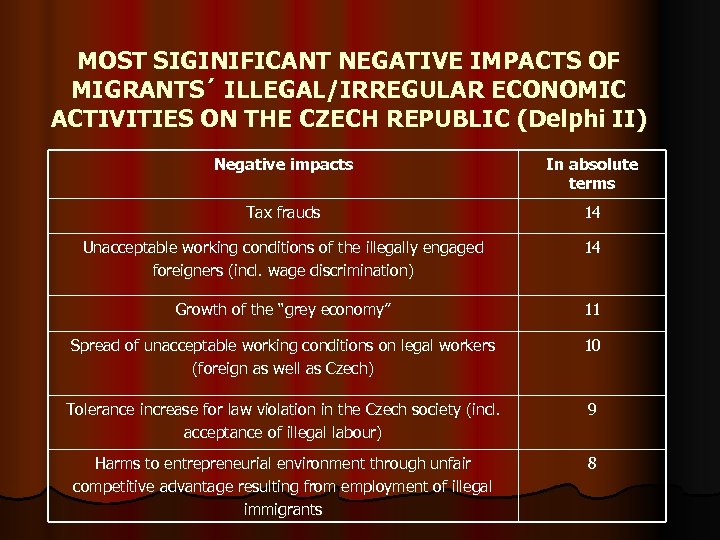
MOST SIGINIFICANT NEGATIVE IMPACTS OF MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES ON THE CZECH REPUBLIC (Delphi II) Negative impacts In absolute terms Tax frauds 14 Unacceptable working conditions of the illegally engaged foreigners (incl. wage discrimination) 14 Growth of the “grey economy” 11 Spread of unacceptable working conditions on legal workers (foreign as well as Czech) 10 Tolerance increase for law violation in the Czech society (incl. acceptance of illegal labour) 9 Harms to entrepreneurial environment through unfair competitive advantage resulting from employment of illegal immigrants 8
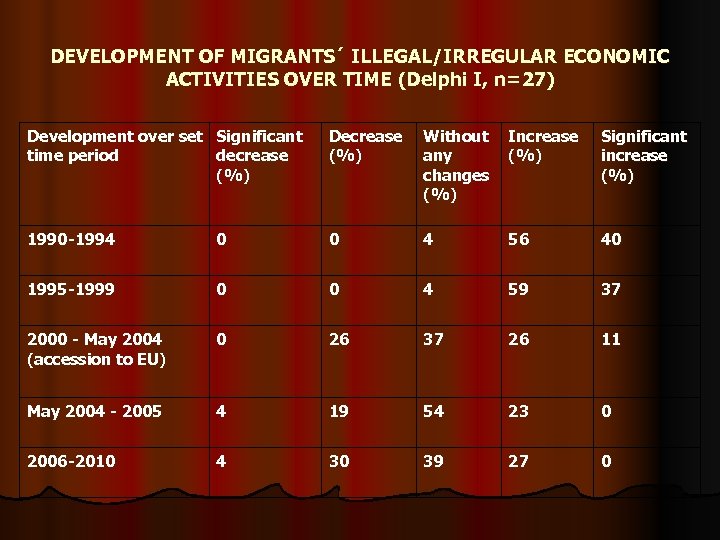
DEVELOPMENT OF MIGRANTS´ ILLEGAL/IRREGULAR ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES OVER TIME (Delphi I, n=27) Development over set Significant time period decrease (%) Decrease (%) Without any changes (%) Increase (%) Significant increase (%) 1990 -1994 0 0 4 56 40 1995 -1999 0 0 4 59 37 2000 - May 2004 (accession to EU) 0 26 37 26 11 May 2004 - 2005 4 19 54 23 0 2006 -2010 4 30 39 27 0
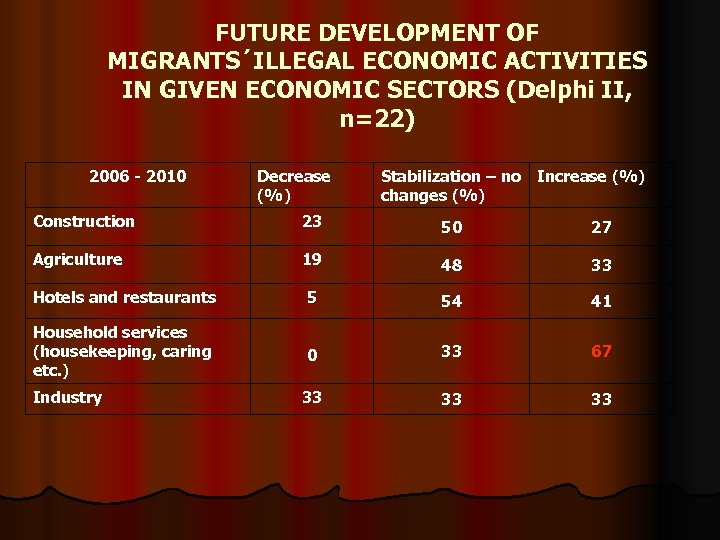
FUTURE DEVELOPMENT OF MIGRANTS´ILLEGAL ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES IN GIVEN ECONOMIC SECTORS (Delphi II, n=22) 2006 - 2010 Decrease (%) Stabilization – no Increase (%) changes (%) Construction 23 50 27 Agriculture 19 48 33 Hotels and restaurants 5 54 41 Household services (housekeeping, caring etc. ) 0 33 67 33 33 33 Industry

POLICY GOALS TO BE ACHIEVED (Delphi II, n=23) - in terms of their desirability Rating of 47 goals in terms of their desirability l Scale from 1 = very desirable to 5 = very undesirable l Goals Desirability Fight against corruption of the Czech Police 1. 35 Increase awareness about legal employment in the source countries and in the Czech Republic (e. g. about opportunities, procedures, advantages) 1. 52 Extend flexibility of acquired work permit 1. 57 Increase the quality of the information system about legal labour immigration to the Czech Republic 1. 57 Stronger protection of witnesses during processes concerning white slavery 1. 57

POLICY GOALS TO BE ACHIEVED (Delphi II, n=23) - in terms of their feasibility Rating of 47 goals in terms of their feasibility l Scale from 1 = easily feasible to 5 = strongly unfeasible l Goals Feasibility Increase awareness about legal employment in the source countries and in the Czech Republic (e. g. about opportunities, procedures, advantages) 1. 87 Increase the quality of the information system about legal labour immigration to the Czech Republic 1. 91 Extend flexibility of acquired work permit 2. 09 Specification of legal measures concerning controls and sanctions 2. 17 More flexible deportations of illegal foreigners 2. 17

POLICY GOALS TO BE ACHIEVED (Delphi II) - important goals to apply l The most desirable goals which are easily feasible Goals D F (D-F) Increase awareness about legal employment in the source countries and in the Czech Republic (e. g. about opportunities, procedures, advantages) 1. 52 1. 87 -0. 35 Increase the quality of the information system about legal labour immigration to the Czech Republic 1. 57 1. 91 -0. 34 Extend flexibility of acquired work permit 1. 57 2. 09 -0. 52 Stronger protection of witnesses during processes concerning white slavery 1. 57 2. 22 -0. 65
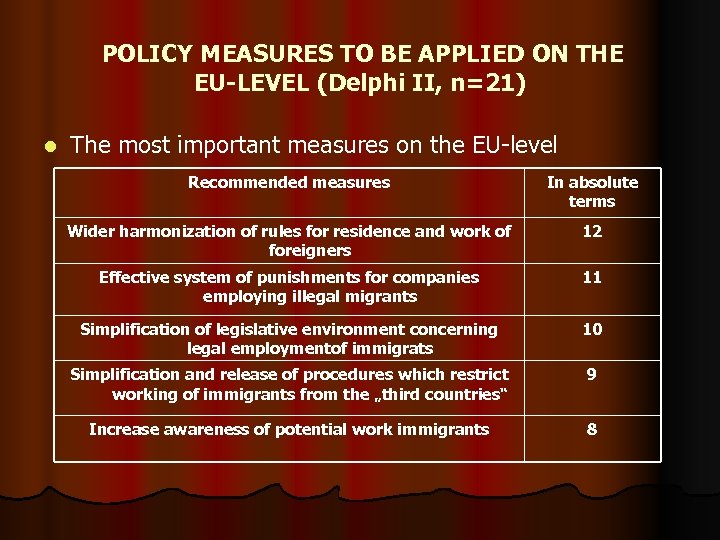
POLICY MEASURES TO BE APPLIED ON THE EU-LEVEL (Delphi II, n=21) l The most important measures on the EU-level Recommended measures In absolute terms Wider harmonization of rules for residence and work of foreigners 12 Effective system of punishments for companies employing illegal migrants 11 Simplification of legislative environment concerning legal employmentof immigrats 10 Simplification and release of procedures which restrict working of immigrants from the „third countries“ 9 Increase awareness of potential work immigrants 8

CONCLUSIONS I Small consensus among experts in assessing amount, structure and future development of illegal immigration in the Czech Republic l Convergence in opinions: l Assessing negative as well as positive impacts of illegal economic activities of foreigners l „Dominance“ of Ukrainians l Significant presence of illegal immigrants in construction l Increase of the volume of illegal immigrants working in the household services in the near future l Criticising labour market restrictions imposed by “old” EU countries concerning workers from the „new“ EUcountries l

CONCLUSIONS II l Convergence in desirable solution of illegal economic activities of immigrants: More harmonization l More information l More flexible and simple legislation l Harder controls and sanctions (for corruption, illegality etc. ) l l An effective policy is thus based on spreading information, increasing flexibility, simplifying legislation and stricter sanctions…
6bc69104e4ee5aaf3a2d9fa2dad98d14.ppt