977861344e9de98a3aa3f7848f2ca908.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Midteram Overview SY DE 142 Midterm: n Date: June 14, 2004 Time: 1: 30 - 3: 30 pm n Room: DC 1350 n Aids Allowed: n Text book: Wickens and Set Phasers on Stun l Calculator l n Solutions must be written in pen, not in pencil.
Midteram Overview SY DE 142 Midterm: n Date: June 14, 2004 Time: 1: 30 - 3: 30 pm n Room: DC 1350 n Aids Allowed: n Text book: Wickens and Set Phasers on Stun l Calculator l n Solutions must be written in pen, not in pencil.
 Case Studies w. Business in Bhopal w. Silent Warning w. In Search of the Lost Cord w. An Act of God w. The Wizards of Wall Street w. Set Phasers on Stun
Case Studies w. Business in Bhopal w. Silent Warning w. In Search of the Lost Cord w. An Act of God w. The Wizards of Wall Street w. Set Phasers on Stun
 Films w. Death on the Job w. Bhopal, a Lingering Tragedy w. Why Planes Crash w. Broken Bus
Films w. Death on the Job w. Bhopal, a Lingering Tragedy w. Why Planes Crash w. Broken Bus
 Course Material Outline w Accident Analysis and Fault Trees w Mappings and Affordances w Gulfs of Execution and Evaluation w Human Action Cycle w Information Processing w Human Decision Making w Human Error - Mistakes w w w Human Error- slips Human machine model Displays Control Human-Computer Interaction w Usability Testing w Automation w More details on slides and in book.
Course Material Outline w Accident Analysis and Fault Trees w Mappings and Affordances w Gulfs of Execution and Evaluation w Human Action Cycle w Information Processing w Human Decision Making w Human Error - Mistakes w w w Human Error- slips Human machine model Displays Control Human-Computer Interaction w Usability Testing w Automation w More details on slides and in book.
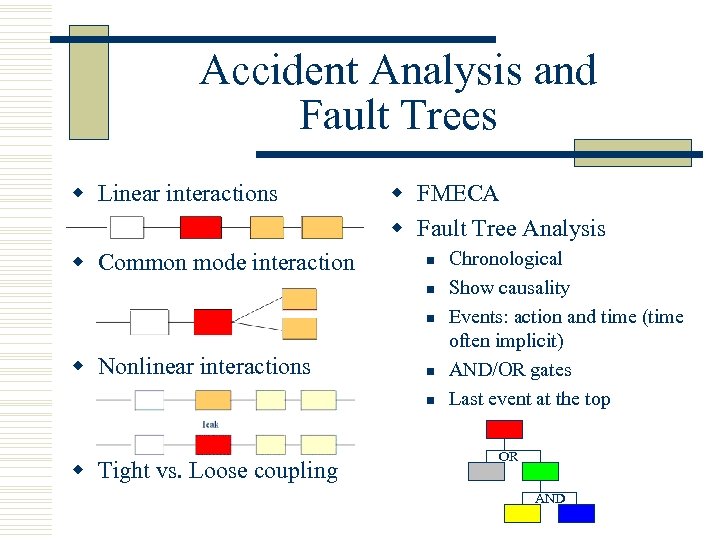 Accident Analysis and Fault Trees w Linear interactions w Common mode interaction w FMECA w Fault Tree Analysis n n n w Nonlinear interactions n n w Tight vs. Loose coupling Chronological Show causality Events: action and time (time often implicit) AND/OR gates Last event at the top OR AND
Accident Analysis and Fault Trees w Linear interactions w Common mode interaction w FMECA w Fault Tree Analysis n n n w Nonlinear interactions n n w Tight vs. Loose coupling Chronological Show causality Events: action and time (time often implicit) AND/OR gates Last event at the top OR AND
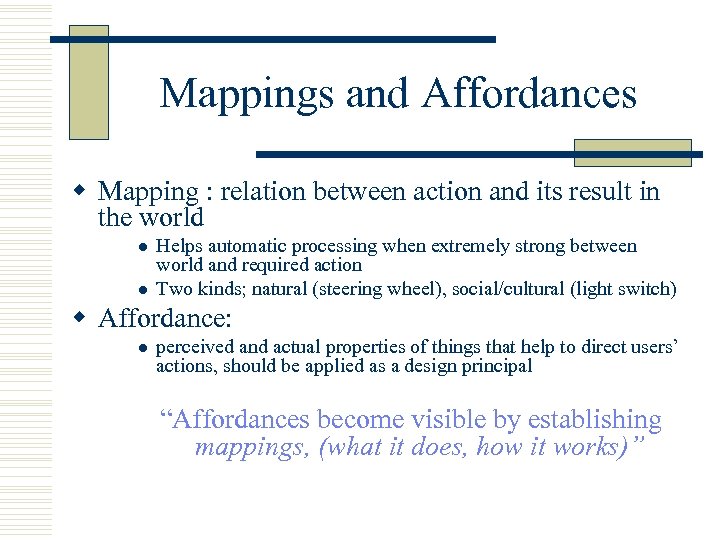 Mappings and Affordances w Mapping : relation between action and its result in the world l l Helps automatic processing when extremely strong between world and required action Two kinds; natural (steering wheel), social/cultural (light switch) w Affordance: l perceived and actual properties of things that help to direct users’ actions, should be applied as a design principal “Affordances become visible by establishing mappings, (what it does, how it works)”
Mappings and Affordances w Mapping : relation between action and its result in the world l l Helps automatic processing when extremely strong between world and required action Two kinds; natural (steering wheel), social/cultural (light switch) w Affordance: l perceived and actual properties of things that help to direct users’ actions, should be applied as a design principal “Affordances become visible by establishing mappings, (what it does, how it works)”
 Gulfs of Execution and Evaluation (and HAC) w Gulfs: n n Execution: have an intention but can’t figure out action (difference in seq of action & action in the Human Action Cycle) Evaluation: Can’t figure out whether the goal has been achieved
Gulfs of Execution and Evaluation (and HAC) w Gulfs: n n Execution: have an intention but can’t figure out action (difference in seq of action & action in the Human Action Cycle) Evaluation: Can’t figure out whether the goal has been achieved
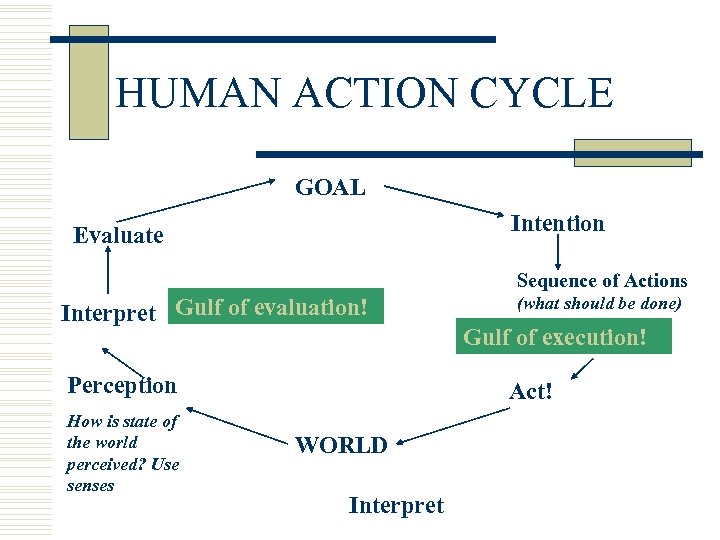 HUMAN ACTION CYCLE GOAL Intention Evaluate Interpret Gulf of evaluation! Act Perception How is state of the world perceived? Use senses Sequence of Actions (what should be done) Gulf of execution! Act! WORLD Interpret
HUMAN ACTION CYCLE GOAL Intention Evaluate Interpret Gulf of evaluation! Act Perception How is state of the world perceived? Use senses Sequence of Actions (what should be done) Gulf of execution! Act! WORLD Interpret
 Information Processing “How we Think” w Memory n Short term, long term , how to improve, knowledge in head vs. knowledge in world w Perception n Feature analysis (bottom-up processing), unitization, top down processing ----design implications w Attention n n Selective, divided ---- design implications Resource model, Multiple resource model
Information Processing “How we Think” w Memory n Short term, long term , how to improve, knowledge in head vs. knowledge in world w Perception n Feature analysis (bottom-up processing), unitization, top down processing ----design implications w Attention n n Selective, divided ---- design implications Resource model, Multiple resource model
 More Information Processing “How we Think” w Situation awareness (SA): being aware of meanings of dynamic changes in the environment n n 3 stages: Perceive, understand, predict Measuring SA: by SA Global Assessment technique (SAGAT) w Decision making n n Normative model (methods: multi-attribute utility theory, expected value theory, SEUT) Descriptive model (methods: satisfaction not optimal, heuristics, and biases to create easier ways of thinking)
More Information Processing “How we Think” w Situation awareness (SA): being aware of meanings of dynamic changes in the environment n n 3 stages: Perceive, understand, predict Measuring SA: by SA Global Assessment technique (SAGAT) w Decision making n n Normative model (methods: multi-attribute utility theory, expected value theory, SEUT) Descriptive model (methods: satisfaction not optimal, heuristics, and biases to create easier ways of thinking)
 Human Decision Making w Heuristics and Biases in Human decision making (look at updated lecture notes) n could happen in any of the following stages: 1. Getting information input (input or cue biases) 2. Generating hypotheses and selection ( 6 biases). 3. Plan generation and action choice (4 biases). w SRK Framework n n n Skill based decisions (automated) Rule Based decisions (procedural) Knowledge based decisions
Human Decision Making w Heuristics and Biases in Human decision making (look at updated lecture notes) n could happen in any of the following stages: 1. Getting information input (input or cue biases) 2. Generating hypotheses and selection ( 6 biases). 3. Plan generation and action choice (4 biases). w SRK Framework n n n Skill based decisions (automated) Rule Based decisions (procedural) Knowledge based decisions
 Human Error -- mistake w Mistake: wrong goal and intention but right action n n Why it happens? Types of mistaken similarity, l misjudged probability, l rationalizing small events, l social pressures/cultural factors and $ l w Forcing Functions
Human Error -- mistake w Mistake: wrong goal and intention but right action n n Why it happens? Types of mistaken similarity, l misjudged probability, l rationalizing small events, l social pressures/cultural factors and $ l w Forcing Functions
 Human Error -- slips w Slip: right goal and intention but wrong action, Mostly occurs with skilled behavior (WHY? ) n Mode Error: right action in wrong mode (therefore the action becomes WRONG) n
Human Error -- slips w Slip: right goal and intention but wrong action, Mostly occurs with skilled behavior (WHY? ) n Mode Error: right action in wrong mode (therefore the action becomes WRONG) n
 Information Displays Human-Machine Model w Human machine system model : n user Elements: Interface w Feedback: (4 feedbacks) n n machine World n n begins with Action : l l l Operator acts on the interface. Interface sends a control signal to the machine. Machine acts on the world. n State of world to interface Action of machine to interface Indication of control signal (machine to interface) Information from interface to operator w Any missing item may cause an accident
Information Displays Human-Machine Model w Human machine system model : n user Elements: Interface w Feedback: (4 feedbacks) n n machine World n n begins with Action : l l l Operator acts on the interface. Interface sends a control signal to the machine. Machine acts on the world. n State of world to interface Action of machine to interface Indication of control signal (machine to interface) Information from interface to operator w Any missing item may cause an accident
 Display contents w should permit evaluation and execution w Display principles: n n Perceptual (legible, give reference, redundancy, design for distinctive features) Mental model (pictorial, moving part, ecological) Attention (multi-resource, proximity compatibility, information access cost) Memory (predictive aids, knowledge in the world, consistency
Display contents w should permit evaluation and execution w Display principles: n n Perceptual (legible, give reference, redundancy, design for distinctive features) Mental model (pictorial, moving part, ecological) Attention (multi-resource, proximity compatibility, information access cost) Memory (predictive aids, knowledge in the world, consistency
 Display forms w Digital vs. Analog (precision vs. change) w Configural displays n n Rankine cycle Polar star display w Heads-up w Ecological displays
Display forms w Digital vs. Analog (precision vs. change) w Configural displays n n Rankine cycle Polar star display w Heads-up w Ecological displays
 Control w Control vs. display : control is same as display till user interacts with system through display w Very important in design same guidelines as displays. w Laws and principals: n n Hick-Hyman law for Reaction Time Fitts law for Movement Time w Control Types : zero order (mouse), first order (steering wheel) and second order (thrust of shuttle)
Control w Control vs. display : control is same as display till user interacts with system through display w Very important in design same guidelines as displays. w Laws and principals: n n Hick-Hyman law for Reaction Time Fitts law for Movement Time w Control Types : zero order (mouse), first order (steering wheel) and second order (thrust of shuttle)
 Human-Computer Interaction w What your focus is as a designer: n User group: l n who is using your system (novice, infrequent, frequent expert) and what should you know about these users. Interaction styles: l how will the user (based on expertise) interact with the system (eg. Menu, form, QA, command language, function keys, direct manipulation, natural language, …. )
Human-Computer Interaction w What your focus is as a designer: n User group: l n who is using your system (novice, infrequent, frequent expert) and what should you know about these users. Interaction styles: l how will the user (based on expertise) interact with the system (eg. Menu, form, QA, command language, function keys, direct manipulation, natural language, …. )
 Usability and user testing n Usability Approaches (4) w Cognitive walkthrough w Heuristic evaluation (Neilson’s usability principals) w Performance measurement w Field study l Tasks l Usability measures (satisfaction, learnability, errors)
Usability and user testing n Usability Approaches (4) w Cognitive walkthrough w Heuristic evaluation (Neilson’s usability principals) w Performance measurement w Field study l Tasks l Usability measures (satisfaction, learnability, errors)
 Automation w When and why use automation w Classes of automation l Information acquisition (warnings, filters) l Information integration (pattern recognition, expert systems) l Action selection (TCAS) l Action execution and control (autopilots, cruise control)
Automation w When and why use automation w Classes of automation l Information acquisition (warnings, filters) l Information integration (pattern recognition, expert systems) l Action selection (TCAS) l Action execution and control (autopilots, cruise control)
 Automation w Levels of automation w Reliability Issues: n n n complacency (over trust), mistrust, dumb and dutiful effect. w Best form is Human Centered Automation
Automation w Levels of automation w Reliability Issues: n n n complacency (over trust), mistrust, dumb and dutiful effect. w Best form is Human Centered Automation
 Good luck
Good luck


