38a0790cfda16227b54a717d66cb3f1d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107
 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102: Mapping Out Your Strategy Internet 2 Spring Meeting 6 May 2002 EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
Middleware Planning and Deployment 102: Mapping Out Your Strategy Internet 2 Spring Meeting 6 May 2002 EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
 Panelists – Tom Barton, University of Memphis/Internet 2 – Renee Woodten Frost University of Michigan/Internet 2 – Jack Suess, University of Maryland, Baltimore County – Ann West, EDUCAUSE/Internet 2/Michigan Tech EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 2
Panelists – Tom Barton, University of Memphis/Internet 2 – Renee Woodten Frost University of Michigan/Internet 2 – Jack Suess, University of Maryland, Baltimore County – Ann West, EDUCAUSE/Internet 2/Michigan Tech EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 2
 Agenda • • • Introductions and Overview Two factors for success: Environment and Leadership Case Study: U of Maryland, Baltimore County Discussion Break Third factor for success: Implementation Case Study: U of Memphis Discussion Research, Resources, and Wrap up EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 3
Agenda • • • Introductions and Overview Two factors for success: Environment and Leadership Case Study: U of Maryland, Baltimore County Discussion Break Third factor for success: Implementation Case Study: U of Memphis Discussion Research, Resources, and Wrap up EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 3
 A Bit About Middleware makes “transparent use” happen, providing consistency, security, privacy and capability • Identity - unique markers of who you (person, machine, service, group) are • Authentication - how you prove or establish that you are that identity • Authorization - what an identity is permitted to do • Directories - where an identity’s basic characteristics are kept EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 4
A Bit About Middleware makes “transparent use” happen, providing consistency, security, privacy and capability • Identity - unique markers of who you (person, machine, service, group) are • Authentication - how you prove or establish that you are that identity • Authorization - what an identity is permitted to do • Directories - where an identity’s basic characteristics are kept EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 4
 Map of Middleware Land EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 5
Map of Middleware Land EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 5
 Topics Not Covered • Business Case • Long-term Value • Technology details EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 6
Topics Not Covered • Business Case • Long-term Value • Technology details EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 6
 Themes • Middleware is not just a technology project • Implementation challenges are a reflection of the –Institutional culture and needs –Installed technology, requirements, and available resources –Leadership EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 7
Themes • Middleware is not just a technology project • Implementation challenges are a reflection of the –Institutional culture and needs –Installed technology, requirements, and available resources –Leadership EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 7
 Contributors to Success Institutional Culture and Environment Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Leadership Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 8
Contributors to Success Institutional Culture and Environment Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Leadership Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 8
 Institutional Environment EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 9
Institutional Environment EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 9
 Institutional Environment • • Public vs. Private Institutions Institutional Vision vs. Local Control Change Readiness Strategic vs. Tactical Planning Role of IT Policy & Legal Constraints Resource Determination/Allocation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 10
Institutional Environment • • Public vs. Private Institutions Institutional Vision vs. Local Control Change Readiness Strategic vs. Tactical Planning Role of IT Policy & Legal Constraints Resource Determination/Allocation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 10
 Institutional Environment: Public vs. Private Institutions Public and private institutions will be subjected to different governance pressures that may impact how Middleware might be developed and deployed. • Legal • Financial • Organizational Politics • Governance Structure EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 11
Institutional Environment: Public vs. Private Institutions Public and private institutions will be subjected to different governance pressures that may impact how Middleware might be developed and deployed. • Legal • Financial • Organizational Politics • Governance Structure EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 11
 Institutional Environment: Vision vs. Local Control • Effective middleware development will require participation from all quarters –Is there a strategic vision for the institution or is business done an a day-to-day, year-to-year basis? –Are business practices and applications wellcoordinated? –How “hardened” are your silos? • Development in a culture of cooperation and information sharing is less effort EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 12
Institutional Environment: Vision vs. Local Control • Effective middleware development will require participation from all quarters –Is there a strategic vision for the institution or is business done an a day-to-day, year-to-year basis? –Are business practices and applications wellcoordinated? –How “hardened” are your silos? • Development in a culture of cooperation and information sharing is less effort EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 12
 Institutional Environment: Change Readiness • Changes the way we do business – Shifts control of services and/or applications – Relies on unfamiliar technologies – Requires additional communication • Change is tough – Free agents can be used to innovate – Command-control required to ensure stability – Need both. Think about incentives. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 13
Institutional Environment: Change Readiness • Changes the way we do business – Shifts control of services and/or applications – Relies on unfamiliar technologies – Requires additional communication • Change is tough – Free agents can be used to innovate – Command-control required to ensure stability – Need both. Think about incentives. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 13
 Institutional Environment: Strategic vs. Tactical Planning Middleware development and deployment will require both approaches. –Strategic planning to define the implementation “road map, ” ensure long-term success and ongoing alignment with the institutional mission –Tactical planning and project management to ensure implementation stays on time and on budget EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 14
Institutional Environment: Strategic vs. Tactical Planning Middleware development and deployment will require both approaches. –Strategic planning to define the implementation “road map, ” ensure long-term success and ongoing alignment with the institutional mission –Tactical planning and project management to ensure implementation stays on time and on budget EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 14
 Institutional Environment: Role of IT • Perceived Value of Central IT –Is Central IT seen as adding value, or as a barrier to progress? –Will it accepted in a coordinating role or will a surrogate be required? • Strategic Resource vs. Tactical Tool –Are strategic decisions made with IT in mind, or is IT a bolt-on after the fact? –Are funding decisions made with IT input? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 15
Institutional Environment: Role of IT • Perceived Value of Central IT –Is Central IT seen as adding value, or as a barrier to progress? –Will it accepted in a coordinating role or will a surrogate be required? • Strategic Resource vs. Tactical Tool –Are strategic decisions made with IT in mind, or is IT a bolt-on after the fact? –Are funding decisions made with IT input? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 15
 Institutional Environment: Policy & Legal Constraints • Ownership of Data –Is data stewardship well-defined? –Is it centralized or distributed? • Access to Data –Formally or loosely governed? –Access authority centralized or distributed? • Data Administration –Centrally managed or distributed? –HIPPA and FERPA compliant? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 16
Institutional Environment: Policy & Legal Constraints • Ownership of Data –Is data stewardship well-defined? –Is it centralized or distributed? • Access to Data –Formally or loosely governed? –Access authority centralized or distributed? • Data Administration –Centrally managed or distributed? –HIPPA and FERPA compliant? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 16
 Institutional Environment: Resource Determination/Allocation • Financial Resources –Centrally managed or distributed? –Multi-year or annual budgets? • Human Resources –Centrally managed or distributed? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 17
Institutional Environment: Resource Determination/Allocation • Financial Resources –Centrally managed or distributed? –Multi-year or annual budgets? • Human Resources –Centrally managed or distributed? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 17
 Leadership EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 18
Leadership EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 18
 Leadership Requirements Developing an Enterprise Directory is akin to implementing an ERP project. • Executive leadership • Developing campus support • Change management • Managing expectations EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 19
Leadership Requirements Developing an Enterprise Directory is akin to implementing an ERP project. • Executive leadership • Developing campus support • Change management • Managing expectations EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 19
 Leadership: Executive Role • Unlike ERP, a CIO can’t expect other executives to “sponsor” middleware • A CIO must make the case, meaning justifying the ROI, of middleware • Identify the tangible benefits from middleware that matter to your campus • Make certain you treat this as a major project with a well-defined system development life cycle (SDLC) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 20
Leadership: Executive Role • Unlike ERP, a CIO can’t expect other executives to “sponsor” middleware • A CIO must make the case, meaning justifying the ROI, of middleware • Identify the tangible benefits from middleware that matter to your campus • Make certain you treat this as a major project with a well-defined system development life cycle (SDLC) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 20
 Leadership: Developing Campus Support Laying the groundwork • Meet privately with key leaders and explain middleware and discuss what it means to their unit. Include faculty leaders in this • Use all opportunities to discuss the project with faculty, staff, and executives • Don’t forget to build consensus in your internal IT organization EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 21
Leadership: Developing Campus Support Laying the groundwork • Meet privately with key leaders and explain middleware and discuss what it means to their unit. Include faculty leaders in this • Use all opportunities to discuss the project with faculty, staff, and executives • Don’t forget to build consensus in your internal IT organization EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 21
 Leadership: Change Management • Like ERP, middleware cuts across divisions and requires broad support • Create a sense of urgency to the project, why is it important? • It isn’t possible to over-communicate • Identify ways to involve stakeholders in the decision making process • Make certain you develop some quick wins EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 22
Leadership: Change Management • Like ERP, middleware cuts across divisions and requires broad support • Create a sense of urgency to the project, why is it important? • It isn’t possible to over-communicate • Identify ways to involve stakeholders in the decision making process • Make certain you develop some quick wins EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 22
 Leadership: Managing Expectations and Budget • Like ERP, middleware development is an on-going process: • A well-written project plan with quick wins defined at appropriate intervals is key to managing expectations and budget • Life-cycle budgeting needs to be identified • Middleware’s benefit is often found in productivity gains or through self-service. Identify ways to measure this ahead of time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 23
Leadership: Managing Expectations and Budget • Like ERP, middleware development is an on-going process: • A well-written project plan with quick wins defined at appropriate intervals is key to managing expectations and budget • Life-cycle budgeting needs to be identified • Middleware’s benefit is often found in productivity gains or through self-service. Identify ways to measure this ahead of time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 23
 Leadership: Final Comments • IT is responsible for campus technology architecture, of which, middleware is a fundamental component. No one else will do this for you. • Every campus has leaders that must be brought on board for major projects. Seek them out. • Make certain you develop formal plans, identify quick wins, and communicate the benefits and successes • Success enables more success. Make sure you can accommodate later requests quickly. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 24
Leadership: Final Comments • IT is responsible for campus technology architecture, of which, middleware is a fundamental component. No one else will do this for you. • Every campus has leaders that must be brought on board for major projects. Seek them out. • Make certain you develop formal plans, identify quick wins, and communicate the benefits and successes • Success enables more success. Make sure you can accommodate later requests quickly. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 24
 Case Study #1: Enterprise Directory Project Planning at University of Maryland, Baltimore County Jack Suess, CIO jack@umbc. edu http: //umbc. edu/~jack/sac 2002 EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
Case Study #1: Enterprise Directory Project Planning at University of Maryland, Baltimore County Jack Suess, CIO jack@umbc. edu http: //umbc. edu/~jack/sac 2002 EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
 What I Will Discuss –The business factors driving this initiative –The directory development team and process – Development and deployment of new applications using the directory service –Creation of a single sign on web authenticator –Future directory plans at UMBC –Applying the lessons learned - how to jumpstart a directory project –Questions EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 26
What I Will Discuss –The business factors driving this initiative –The directory development team and process – Development and deployment of new applications using the directory service –Creation of a single sign on web authenticator –Future directory plans at UMBC –Applying the lessons learned - how to jumpstart a directory project –Questions EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 26
 Business Factors UMBC Needed to Address - Fall 1999 –Finishing up with Y 2 K. –UMBC decided we would begin discussions to replace our SIS, HR and Finance systems. –UMBC started two online graduate programs and began planning for a third program. We needed to add more web-based self-service applications, especially account generation. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 27
Business Factors UMBC Needed to Address - Fall 1999 –Finishing up with Y 2 K. –UMBC decided we would begin discussions to replace our SIS, HR and Finance systems. –UMBC started two online graduate programs and began planning for a third program. We needed to add more web-based self-service applications, especially account generation. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 27
 Business Factors - Continued Fall 1999 –We had successfully deployed our web portal, my. UMBC and were getting requests to extend it to alumni, parents, and prospective students. –Fall 1999, we saw Web. CT usage plateau, discussions with faculty pointed at need to make it “easier” to use course tools. • Eliminate faculty handling of student account problems • Make it easier to “enroll” students • Eliminate the need to know HTML EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 28
Business Factors - Continued Fall 1999 –We had successfully deployed our web portal, my. UMBC and were getting requests to extend it to alumni, parents, and prospective students. –Fall 1999, we saw Web. CT usage plateau, discussions with faculty pointed at need to make it “easier” to use course tools. • Eliminate faculty handling of student account problems • Make it easier to “enroll” students • Eliminate the need to know HTML EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 28
 Business Requirements – Applications needed 7 x 24 access –The indecision over our SIS/HR plans made using those systems directly a mistake. –We needed to reduce transactions on our overloaded administrative systems. –We had reorganized support services and made our Helpdesk the focal point. We needed to empower them with ability to manage basic account functions. –To support alumni we needed to expand authentication services beyond solely using Kerberos EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 29
Business Requirements – Applications needed 7 x 24 access –The indecision over our SIS/HR plans made using those systems directly a mistake. –We needed to reduce transactions on our overloaded administrative systems. –We had reorganized support services and made our Helpdesk the focal point. We needed to empower them with ability to manage basic account functions. –To support alumni we needed to expand authentication services beyond solely using Kerberos EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 29
 Why Deploy an Enterprise Directory • Hype- Directories were hot technologies in 1999, though not necessarily mature. • UMBC has a large Unix infrastructure and significant Unix development experience • We didn’t want the complexity or cost associated with using a DBMS • We wanted to solve this in a way that would allow us to collaborate with other schools. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 30
Why Deploy an Enterprise Directory • Hype- Directories were hot technologies in 1999, though not necessarily mature. • UMBC has a large Unix infrastructure and significant Unix development experience • We didn’t want the complexity or cost associated with using a DBMS • We wanted to solve this in a way that would allow us to collaborate with other schools. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 30
 Getting Started January 2000 –I 2 was beginning to focus on the problem of middleware, I saw this as an opportunity for UMBC to be engaged in I 2. –I 2 was soliciting schools to participate in an Early Adopters program and UMBC applied. –I was the initial project sponsor for middleware at UMBC. –January 2000 we created our middleware project team EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 31
Getting Started January 2000 –I 2 was beginning to focus on the problem of middleware, I saw this as an opportunity for UMBC to be engaged in I 2. –I 2 was soliciting schools to participate in an Early Adopters program and UMBC applied. –I was the initial project sponsor for middleware at UMBC. –January 2000 we created our middleware project team EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 31
 Directory Project Team –A technical lead was identified and the project team created. • Members represented all areas of IT • I needed to get the team understanding what was meant by directory services • Sharp differences on team over what directory platform to use • I 2 middleware group was very helpful in framing issues for consideration EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 32
Directory Project Team –A technical lead was identified and the project team created. • Members represented all areas of IT • I needed to get the team understanding what was meant by directory services • Sharp differences on team over what directory platform to use • I 2 middleware group was very helpful in framing issues for consideration EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 32
 Directory Development Engaging Non-IT Staff –I met privately with our Vice Provost for Academic Affairs and CFO to discuss the project and get their support –I worked through our IT Steering committee and discussed the project in terms of the business factors, not technology. –In hindsight we should of done a better job broadly communicating this to the campus. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 33
Directory Development Engaging Non-IT Staff –I met privately with our Vice Provost for Academic Affairs and CFO to discuss the project and get their support –I worked through our IT Steering committee and discussed the project in terms of the business factors, not technology. –In hindsight we should of done a better job broadly communicating this to the campus. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 33
 Selecting a Directory Product –This became contentious - we looked at NDS, AD, Innosoft, i. Planet and Oracle –Our process looked at initial cost, cost per entry, API, scalability, and availability. –We had concerns about directory products tied too closely to network LAN products. –i. Planet had the best product but cost was a concern. Opportunity struck - we purchased Innosoft - i. Planet then bought company and transitioned customers over to i. Planet : -) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 34
Selecting a Directory Product –This became contentious - we looked at NDS, AD, Innosoft, i. Planet and Oracle –Our process looked at initial cost, cost per entry, API, scalability, and availability. –We had concerns about directory products tied too closely to network LAN products. –i. Planet had the best product but cost was a concern. Opportunity struck - we purchased Innosoft - i. Planet then bought company and transitioned customers over to i. Planet : -) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 34
 Defining Data Access Strategy –We initially focused on data needed for whitepages and account management. –We negotiated read access to SIS and HR. – Updates to demographic data would be done through our portal, my. UMBC. –Where duplicate data exists in HR/SIS we used most recent entry as “current” –Broad IT support was critical here, we needed input from our analysts and DBA’s to fully understand what data was needed and get database triggers defined. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 35
Defining Data Access Strategy –We initially focused on data needed for whitepages and account management. –We negotiated read access to SIS and HR. – Updates to demographic data would be done through our portal, my. UMBC. –Where duplicate data exists in HR/SIS we used most recent entry as “current” –Broad IT support was critical here, we needed input from our analysts and DBA’s to fully understand what data was needed and get database triggers defined. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 35
 Defining Data Update Strategy –Goal for account generation was that a PT student could register that day and get an account within 30 minutes. –We discussed merits of real-time, near real-time, and batch updates of directory. • Realtime - triggers between DBMS tables • Near realtime - triggers generate a changelog queue • Batch - extract and update periodically –Selected near realtime to meet our goal for account generation but lessen dependencies. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 36
Defining Data Update Strategy –Goal for account generation was that a PT student could register that day and get an account within 30 minutes. –We discussed merits of real-time, near real-time, and batch updates of directory. • Realtime - triggers between DBMS tables • Near realtime - triggers generate a changelog queue • Batch - extract and update periodically –Selected near realtime to meet our goal for account generation but lessen dependencies. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 36
 Directory Development Team March 2000 • 1 full-time directory architect • 1 directory programmer (. 75) • PT access to an Oracle DBA (<. 25) • PT access to SIS and HR analysts (<. 25) • Allocated $75, 000 in startup funding EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 37
Directory Development Team March 2000 • 1 full-time directory architect • 1 directory programmer (. 75) • PT access to an Oracle DBA (<. 25) • PT access to SIS and HR analysts (<. 25) • Allocated $75, 000 in startup funding EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 37
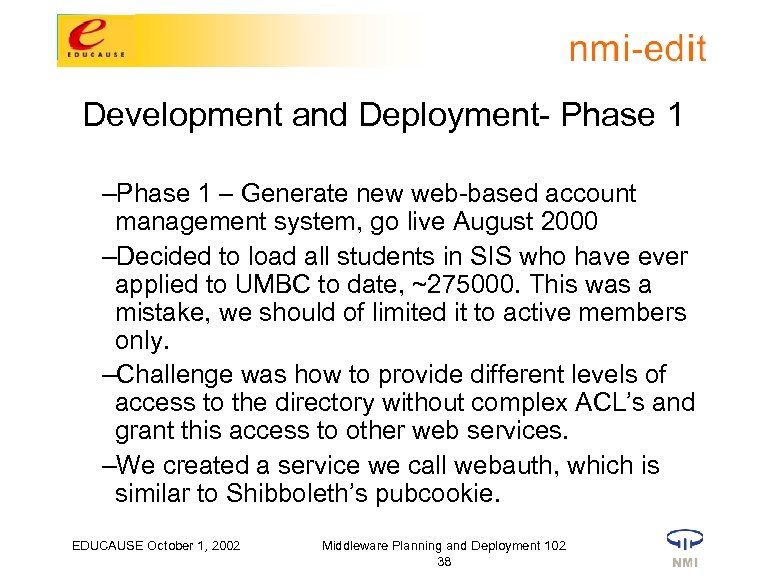 Development and Deployment- Phase 1 – Generate new web-based account management system, go live August 2000 –Decided to load all students in SIS who have ever applied to UMBC to date, ~275000. This was a mistake, we should of limited it to active members only. –Challenge was how to provide different levels of access to the directory without complex ACL’s and grant this access to other web services. –We created a service we call webauth, which is similar to Shibboleth’s pubcookie. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 38
Development and Deployment- Phase 1 – Generate new web-based account management system, go live August 2000 –Decided to load all students in SIS who have ever applied to UMBC to date, ~275000. This was a mistake, we should of limited it to active members only. –Challenge was how to provide different levels of access to the directory without complex ACL’s and grant this access to other web services. –We created a service we call webauth, which is similar to Shibboleth’s pubcookie. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 38
 Development of Webauth –Goal was to provide a web-based single sign on (Web. ISO) that can authenticate across any webbased application. • In summer 2000, nothing had been released that did this. We modeled our approach on Kerberos and each web service has a unique service ticket • Created apache module • Created Java and Perl interfaces –Available upon request but I would strongly suggest you consider I 2’s Pubcookie. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 39
Development of Webauth –Goal was to provide a web-based single sign on (Web. ISO) that can authenticate across any webbased application. • In summer 2000, nothing had been released that did this. We modeled our approach on Kerberos and each web service has a unique service ticket • Created apache module • Created Java and Perl interfaces –Available upon request but I would strongly suggest you consider I 2’s Pubcookie. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 39
 UMBC Directory Applications • Webadmin –web-based tool to enable delegated authority of dir updates • Course management system – accounts and course auto-enroll • Windows 2000 migration - supporting Active Directory • Remedy ticketing system – feed client info • Webauth extended to third parties • VPN access EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 40
UMBC Directory Applications • Webadmin –web-based tool to enable delegated authority of dir updates • Course management system – accounts and course auto-enroll • Windows 2000 migration - supporting Active Directory • Remedy ticketing system – feed client info • Webauth extended to third parties • VPN access EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 40
 UMBC Directory Applications - Webadmin • Created Webadmin, a web-based tool for accessing the directory, released 8/2000 –Allows delegation of control over different functions to groups or people based on roles and needs. Helpdesk group can now reset passwords and quotas. –Self-service - students can now select username and password, create email aliases, and forward mail without coming onto campus –Mistake - the user interface could have been better EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 41
UMBC Directory Applications - Webadmin • Created Webadmin, a web-based tool for accessing the directory, released 8/2000 –Allows delegation of control over different functions to groups or people based on roles and needs. Helpdesk group can now reset passwords and quotas. –Self-service - students can now select username and password, create email aliases, and forward mail without coming onto campus –Mistake - the user interface could have been better EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 41
 Delegating Authority Fall 2000 Goal - Let Helpdesk immediately handle basic account tasks on behalf of users without root access –Store user preferences in LDAP as attributes, wrote LDAP interface to Unix systems –Users must use Webadmin to update account –Helpdesk can reset passwords, quota, set forwarding address, and Unix preferences. –Fall 2000, delegation horror story. Helpdesk student stole class project from another student EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 42
Delegating Authority Fall 2000 Goal - Let Helpdesk immediately handle basic account tasks on behalf of users without root access –Store user preferences in LDAP as attributes, wrote LDAP interface to Unix systems –Users must use Webadmin to update account –Helpdesk can reset passwords, quota, set forwarding address, and Unix preferences. –Fall 2000, delegation horror story. Helpdesk student stole class project from another student EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 42
 Integrating Course Management Tools with the Directory • One of our initial goals was to simplify the faculty effort when utilizing course management tools. –Eliminate account management problems –Simplify enrollment of students into a course • Purchased Blackboard Level 3 license, paid them to accept our Webauth credentials solving account management issue, 1/2001 • We developed code for Web. CT 3. 1 to accept our webauth credentials but decided to drop Web. CT EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 43
Integrating Course Management Tools with the Directory • One of our initial goals was to simplify the faculty effort when utilizing course management tools. –Eliminate account management problems –Simplify enrollment of students into a course • Purchased Blackboard Level 3 license, paid them to accept our Webauth credentials solving account management issue, 1/2001 • We developed code for Web. CT 3. 1 to accept our webauth credentials but decided to drop Web. CT EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 43
 Supporting Windows 2000 Spring 2001 • Goal - Migrate our public labs from Windows NT to Windows 2000. All our labs provided common file access (AFS) and used our Kerberos authentication. • Problem - Windows 2000 requires AD, how do we get our account information now stored in i. Planet into AD? • Spring 2001, tested AD against existing Kerberos environment and got this working EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 44
Supporting Windows 2000 Spring 2001 • Goal - Migrate our public labs from Windows NT to Windows 2000. All our labs provided common file access (AFS) and used our Kerberos authentication. • Problem - Windows 2000 requires AD, how do we get our account information now stored in i. Planet into AD? • Spring 2001, tested AD against existing Kerberos environment and got this working EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 44
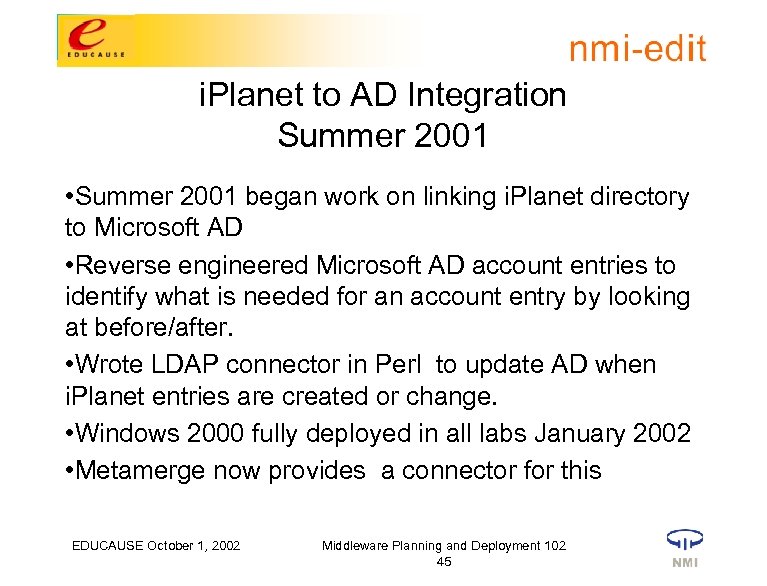 i. Planet to AD Integration Summer 2001 • Summer 2001 began work on linking i. Planet directory to Microsoft AD • Reverse engineered Microsoft AD account entries to identify what is needed for an account entry by looking at before/after. • Wrote LDAP connector in Perl to update AD when i. Planet entries are created or change. • Windows 2000 fully deployed in all labs January 2002 • Metamerge now provides a connector for this EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 45
i. Planet to AD Integration Summer 2001 • Summer 2001 began work on linking i. Planet directory to Microsoft AD • Reverse engineered Microsoft AD account entries to identify what is needed for an account entry by looking at before/after. • Wrote LDAP connector in Perl to update AD when i. Planet entries are created or change. • Windows 2000 fully deployed in all labs January 2002 • Metamerge now provides a connector for this EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 45
 Remedy Integration Summer 2001 • Goal - Keep client information (phone, office, email) up to date in Remedy • Developed a connector between LDAP and Remedy (Oracle DBMS) that updates Remedy whenever certain data elements are updated in LDAP. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 46
Remedy Integration Summer 2001 • Goal - Keep client information (phone, office, email) up to date in Remedy • Developed a connector between LDAP and Remedy (Oracle DBMS) that updates Remedy whenever certain data elements are updated in LDAP. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 46
 Extending Webauth to 3 rd Parties Spring 2002 –Spring 2002 - provided linkage to one-card vendor (Die. Bold/JSA) for e. Commerce. We provide a link from our portal to our JSA. –We provided JSA with a webauth service ticket for their server and webauth client code to request validated campus-id when presenting a webauth cookie. –I’d love to do with other 3 rd Parties such as Sallie Mae Solutions EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 47
Extending Webauth to 3 rd Parties Spring 2002 –Spring 2002 - provided linkage to one-card vendor (Die. Bold/JSA) for e. Commerce. We provide a link from our portal to our JSA. –We provided JSA with a webauth service ticket for their server and webauth client code to request validated campus-id when presenting a webauth cookie. –I’d love to do with other 3 rd Parties such as Sallie Mae Solutions EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 47
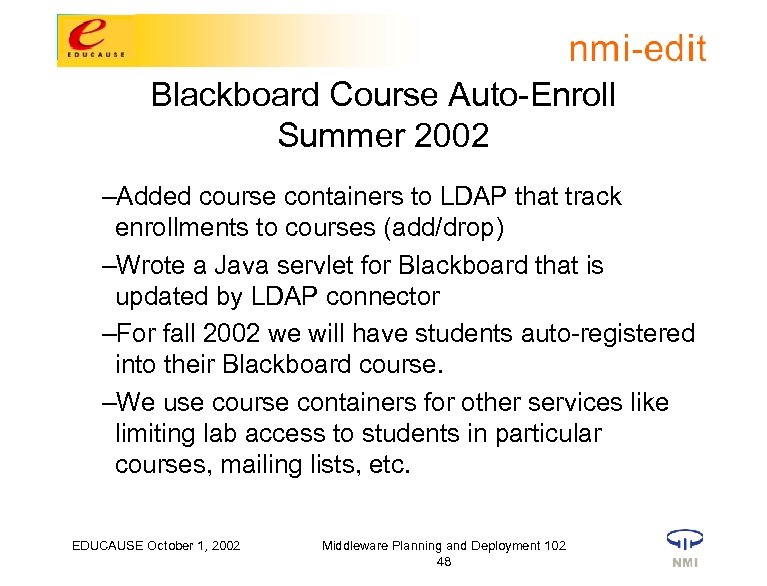 Blackboard Course Auto-Enroll Summer 2002 –Added course containers to LDAP that track enrollments to courses (add/drop) –Wrote a Java servlet for Blackboard that is updated by LDAP connector –For fall 2002 we will have students auto-registered into their Blackboard course. –We use course containers for other services like limiting lab access to students in particular courses, mailing lists, etc. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 48
Blackboard Course Auto-Enroll Summer 2002 –Added course containers to LDAP that track enrollments to courses (add/drop) –Wrote a Java servlet for Blackboard that is updated by LDAP connector –For fall 2002 we will have students auto-registered into their Blackboard course. –We use course containers for other services like limiting lab access to students in particular courses, mailing lists, etc. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 48
 VPN Access • Fall 2002 Goal - Rollout VPN services in fall to secure wireless and provide remote access to administrative applications • Driven through LDAP group membership –Due to limitations in VPN users can only be in one group, we had to be creative in how we defined groups to meet needs of different users. –Most users automatically defined into a group but some people have to be managed manually EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 49
VPN Access • Fall 2002 Goal - Rollout VPN services in fall to secure wireless and provide remote access to administrative applications • Driven through LDAP group membership –Due to limitations in VPN users can only be in one group, we had to be creative in how we defined groups to meet needs of different users. –Most users automatically defined into a group but some people have to be managed manually EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 49
 Short Term Plans AY 2002 -2003 • The following are project proposals under consideration –Peoplesoft 8. 0 integration with LDAP –Automated account deletion/deactivation –OS/X Netinfo and Novell 6 integration –Shibboleth –Alumni access EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 50
Short Term Plans AY 2002 -2003 • The following are project proposals under consideration –Peoplesoft 8. 0 integration with LDAP –Automated account deletion/deactivation –OS/X Netinfo and Novell 6 integration –Shibboleth –Alumni access EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 50
 Peoplesoft Plans • Goal - Use LDAP to manage access to Peoplesoft. • Bringing Finance 8. 4, HR 8, EPM 8. 3 in July 2003. SA development will then start with deployment done by 8/2005 • Recently begun testing of using LDAP for authentication and managing user profiles in Peoplesoft 8 with good results. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 51
Peoplesoft Plans • Goal - Use LDAP to manage access to Peoplesoft. • Bringing Finance 8. 4, HR 8, EPM 8. 3 in July 2003. SA development will then start with deployment done by 8/2005 • Recently begun testing of using LDAP for authentication and managing user profiles in Peoplesoft 8 with good results. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 51
 Automated Account Deletion • Currently we have the ability to quickly deactivate an account via LDAP with the exception of Novell. • We are working with our IT Steering committee to get deletion procedures defined. • Approach will be to deactivate accounts, then based on the group the user belongs to delete accounts at some point in the future. • I 2 has recently put up a discussion paper on account management and deletion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 52
Automated Account Deletion • Currently we have the ability to quickly deactivate an account via LDAP with the exception of Novell. • We are working with our IT Steering committee to get deletion procedures defined. • Approach will be to deactivate accounts, then based on the group the user belongs to delete accounts at some point in the future. • I 2 has recently put up a discussion paper on account management and deletion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 52
 OS/X Netinfo and Novell 6 Integration • Transitioning to Novell 6 this summer, goal is to look at integrating Novell 6 and i. Planet so we can manage accounts through i. Planet • Goal is to transition Macintosh labs to OS/X over summer 2003. We would like to utilize LDAP and Kerberos for managing OS/X in the labs. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 53
OS/X Netinfo and Novell 6 Integration • Transitioning to Novell 6 this summer, goal is to look at integrating Novell 6 and i. Planet so we can manage accounts through i. Planet • Goal is to transition Macintosh labs to OS/X over summer 2003. We would like to utilize LDAP and Kerberos for managing OS/X in the labs. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 53
 Shibboleth • Shibboleth provides inter-institutional authorization service where the person controls what information is released to whom. • We will be demonstrating this to our USM library directors in the fall as a possible solution for intercampus (USM) access to library databases. • We hope to have webauth working with Shibboleth sometime this fall EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 54
Shibboleth • Shibboleth provides inter-institutional authorization service where the person controls what information is released to whom. • We will be demonstrating this to our USM library directors in the fall as a possible solution for intercampus (USM) access to library databases. • We hope to have webauth working with Shibboleth sometime this fall EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 54
 Alumni Access to our Portal • An original goal of the directory project was opening our portal to alumni. • To support this we developed an authentication routine that supports both Kerberos and LDAP. Members will use Kerberos and affiliates use LDAP. • We’re working with our Alumni group on whether to release this now or when we complete our new Portal next summer. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 55
Alumni Access to our Portal • An original goal of the directory project was opening our portal to alumni. • To support this we developed an authentication routine that supports both Kerberos and LDAP. Members will use Kerberos and affiliates use LDAP. • We’re working with our Alumni group on whether to release this now or when we complete our new Portal next summer. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 55
 Results –After Kerberos and DNS, the directory service has been our most reliable service, at least 99. 99% uptime. –These self-service applications have revamped the way we support users and the services we provide. –Automated Blackboard connections were well received by faculty. –Using a directory allowed us to utilize our institutional data in an academic context. The staff that did this would never be able to directly access and update our legacy SIS tables. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 56
Results –After Kerberos and DNS, the directory service has been our most reliable service, at least 99. 99% uptime. –These self-service applications have revamped the way we support users and the services we provide. –Automated Blackboard connections were well received by faculty. –Using a directory allowed us to utilize our institutional data in an academic context. The staff that did this would never be able to directly access and update our legacy SIS tables. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 56
 Lessons Learned 1. CIO leadership is important 2. Building support for the project inside and outside of IT is critical 3. This will be a new service that must be continually supported. 4. Managing expectations is important 5. The benefits exceed the costs 6. Don’t reinvent the wheel EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 57
Lessons Learned 1. CIO leadership is important 2. Building support for the project inside and outside of IT is critical 3. This will be a new service that must be continually supported. 4. Managing expectations is important 5. The benefits exceed the costs 6. Don’t reinvent the wheel EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 57
 Lessons Learned: CIO Leadership • Unlike ERP, a CIO can’t expect other executives to “sponsor” middleware. • A CIO must make the business case for middleware and find the money • Identify the tangible benefits from middleware that matter to your campus • Look at Middleware Business Case on the CD, it identifies 24 possible applications EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 58
Lessons Learned: CIO Leadership • Unlike ERP, a CIO can’t expect other executives to “sponsor” middleware. • A CIO must make the business case for middleware and find the money • Identify the tangible benefits from middleware that matter to your campus • Look at Middleware Business Case on the CD, it identifies 24 possible applications EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 58
 Lessons Learned: Developing Campus Support • Laying the groundwork: • Meet privately with key leaders and explain middleware and discuss what it means to their unit. Include faculty leaders in this • Use the opportunities a CIO has to discuss the project with faculty, staff, and executives • Don’t forget to build consensus inside your IT organization for the project. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 59
Lessons Learned: Developing Campus Support • Laying the groundwork: • Meet privately with key leaders and explain middleware and discuss what it means to their unit. Include faculty leaders in this • Use the opportunities a CIO has to discuss the project with faculty, staff, and executives • Don’t forget to build consensus inside your IT organization for the project. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 59
 Lessons Learned: Planning For Support • Treat this as a formal application development project • Don’t skimp on hardware or redundancy • Be prepared to redefine responsibilities of people as workload changes • Initial development team might not be the best to support this once it is in production • Look for ways to make IT services easier and better as a way to build internal support EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 60
Lessons Learned: Planning For Support • Treat this as a formal application development project • Don’t skimp on hardware or redundancy • Be prepared to redefine responsibilities of people as workload changes • Initial development team might not be the best to support this once it is in production • Look for ways to make IT services easier and better as a way to build internal support EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 60
 Lessons Learned: Managing Expectations is Important • Middleware development is an on-going process: • A well-written project plan with quick wins defined at appropriate intervals is key to managing expectations and budget • Life-cycle funding needs to be identified • Middleware’s benefit is often found in productivity gains or through self-service. Identify ways to measure this ahead of time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 61
Lessons Learned: Managing Expectations is Important • Middleware development is an on-going process: • A well-written project plan with quick wins defined at appropriate intervals is key to managing expectations and budget • Life-cycle funding needs to be identified • Middleware’s benefit is often found in productivity gains or through self-service. Identify ways to measure this ahead of time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 61
 Lessons Learned: The Benefits Exceed the Cost • Problems related to accounts - account generation, forgotten passwords, and disk quota represented 1/3 of our helpdesk requests, we can now handle 90% of these over the phone. This essentially freed 1. 5 sysadmin positions. • Infrastructure projects by their nature usually provide many unintended benefits. In our case we never expected to use this system for our one-card or VPN. I’m sure over the next few years we will find many other benefits EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 62
Lessons Learned: The Benefits Exceed the Cost • Problems related to accounts - account generation, forgotten passwords, and disk quota represented 1/3 of our helpdesk requests, we can now handle 90% of these over the phone. This essentially freed 1. 5 sysadmin positions. • Infrastructure projects by their nature usually provide many unintended benefits. In our case we never expected to use this system for our one-card or VPN. I’m sure over the next few years we will find many other benefits EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 62
 Lessons Learned: Don’t Reinvent the Wheel –UMBC started this process 2. 5 years ago. Many of the technical issues we found difficult now have solutions - Web. ISO, Blackboard, and AD. –I 2, NMI, and Educause now have a wide array of material on their web sites that will help you get started. –NMI is running middleware camps, my suggestion is for any campus considering this to take their team to the camp, learn from others, and plan your strategy EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 63
Lessons Learned: Don’t Reinvent the Wheel –UMBC started this process 2. 5 years ago. Many of the technical issues we found difficult now have solutions - Web. ISO, Blackboard, and AD. –I 2, NMI, and Educause now have a wide array of material on their web sites that will help you get started. –NMI is running middleware camps, my suggestion is for any campus considering this to take their team to the camp, learn from others, and plan your strategy EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 63
 Discussion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 64
Discussion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 64
 Contributors to Success Institutional Culture and Environment Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Leadership Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 65
Contributors to Success Institutional Culture and Environment Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Leadership Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 65
 Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 66
Implementation EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 66
 Implementation • Issues, factors and choices that determine how IT does the implementation. • Previous section examined the institutional environment and how it will influence your middleware implementation. Now the rubber starts to hit the road… EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 67
Implementation • Issues, factors and choices that determine how IT does the implementation. • Previous section examined the institutional environment and how it will influence your middleware implementation. Now the rubber starts to hit the road… EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 67
 Implementation: Organization Culture & Structure • Number of IT departments outside central IT –MW is integrative infrastructure –If existing services are compartmentalized • slower progress • more effort is need for organizational engineering • Consolidate organizational functions or separate reporting structure –Build or reinforce communication/coordination channels –Find “wormholes. ” EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 68
Implementation: Organization Culture & Structure • Number of IT departments outside central IT –MW is integrative infrastructure –If existing services are compartmentalized • slower progress • more effort is need for organizational engineering • Consolidate organizational functions or separate reporting structure –Build or reinforce communication/coordination channels –Find “wormholes. ” EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 68
 Implementation: Organizational Culture & Structure • Competitive or collaborative –Challenges “ownership” –Can feel disenfranchised –Anticipate clear needs and keep everyone on the same page • Willingness to change –Technical infrastructure –Formally or informally, organizational structure must change too EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 69
Implementation: Organizational Culture & Structure • Competitive or collaborative –Challenges “ownership” –Can feel disenfranchised –Anticipate clear needs and keep everyone on the same page • Willingness to change –Technical infrastructure –Formally or informally, organizational structure must change too EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 69
 Implementation: Skill Sets & Roles • Technical architecture planning Grasps the breadth of databases, applications, security, and their interrelationships. Understands organizational needs and values and can map those into functional and security requirements for MW. • Project management This person needs to have a level of influence equal to being near the top of the central IT org chart. Might be the same as the technical architect. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 70
Implementation: Skill Sets & Roles • Technical architecture planning Grasps the breadth of databases, applications, security, and their interrelationships. Understands organizational needs and values and can map those into functional and security requirements for MW. • Project management This person needs to have a level of influence equal to being near the top of the central IT org chart. Might be the same as the technical architect. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 70
 Implementation: Skill Sets & Roles • Systems analysis & interpersonal communications Interacting with data stewards. Ensuring that detailed designs mesh with real practices in business & academic offices. • Systems, database & application development People who can implement the selected technologies and who understand the details of how they must be integrated into the existing infrastructure. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 71
Implementation: Skill Sets & Roles • Systems analysis & interpersonal communications Interacting with data stewards. Ensuring that detailed designs mesh with real practices in business & academic offices. • Systems, database & application development People who can implement the selected technologies and who understand the details of how they must be integrated into the existing infrastructure. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 71
 Implementation: Staff Resources • FTE required Head. Count/10000 + number. Platform. Types/3 + number. Apps/4 + number. CBSs/2 Increase for shorter implementation time or for complex policy requirements. It depends…. • Ongoing staffing >= initial level Anticipate success. More MW services will be built to integrate more apps over time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 72
Implementation: Staff Resources • FTE required Head. Count/10000 + number. Platform. Types/3 + number. Apps/4 + number. CBSs/2 Increase for shorter implementation time or for complex policy requirements. It depends…. • Ongoing staffing >= initial level Anticipate success. More MW services will be built to integrate more apps over time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 72
 Implementation: Staff Resources • Train staff-in-residence, hire new staff, use consultants… – Creative management – Acceptability of outsourcing • Sharing the vision –Key technical people must understand the strategic value of the project • Providing the middleware-architect skill may determine how a project is done or whether it requires new money • Offering incentives to other staff EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 73
Implementation: Staff Resources • Train staff-in-residence, hire new staff, use consultants… – Creative management – Acceptability of outsourcing • Sharing the vision –Key technical people must understand the strategic value of the project • Providing the middleware-architect skill may determine how a project is done or whether it requires new money • Offering incentives to other staff EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 73
 Implementation: Project Resources - Summary • “Assimilate” or fund a “New Activity” – For assimilation, must have sufficient • Skills • Time • Money – For new activity, must lack • Skills, staffing time, a natural “home” within your existing organizational structure • Nothing, but you can get more by asking for it EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 74
Implementation: Project Resources - Summary • “Assimilate” or fund a “New Activity” – For assimilation, must have sufficient • Skills • Time • Money – For new activity, must lack • Skills, staffing time, a natural “home” within your existing organizational structure • Nothing, but you can get more by asking for it EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 74
 Implementation: Communication Plan • Champion – Must share the vision at meetings/presentations and be supported from the top – Tailor the message; financial officer, data owners, IT stakeholders, techies – Emphasize ROI, identity management, security, applications – Use Public Affairs, PR offices if available • Website and personal touch – Consistent message – Continual flow of info for a diverse audience – Personal visits tailor the message for the specific audience EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 75
Implementation: Communication Plan • Champion – Must share the vision at meetings/presentations and be supported from the top – Tailor the message; financial officer, data owners, IT stakeholders, techies – Emphasize ROI, identity management, security, applications – Use Public Affairs, PR offices if available • Website and personal touch – Consistent message – Continual flow of info for a diverse audience – Personal visits tailor the message for the specific audience EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 75
 Implementation: Middleware and its Role • Middleware Must Be Defined –Do the stakeholders understand what it is? –Have the components and their relationships been defined? • Benefits of Middleware Described –Do program managers understand how middleware can help improve/increase service? –Do end-users understand how it will affect their activities? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 76
Implementation: Middleware and its Role • Middleware Must Be Defined –Do the stakeholders understand what it is? –Have the components and their relationships been defined? • Benefits of Middleware Described –Do program managers understand how middleware can help improve/increase service? –Do end-users understand how it will affect their activities? EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 76
 Implementation: Middleware and its Role • Business & Academic Drivers Defined –Internal drivers: • Transactions between members of campus community • Transactions between members and institution –External drivers: • Transactions between institutions • Mapping Benefits Against Drivers –Match priority applications against the appropriate middleware components EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 77
Implementation: Middleware and its Role • Business & Academic Drivers Defined –Internal drivers: • Transactions between members of campus community • Transactions between members and institution –External drivers: • Transactions between institutions • Mapping Benefits Against Drivers –Match priority applications against the appropriate middleware components EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 77
 Implementation: Technology • New vendors or technologies needed? –Plan up front for time to assess what you have –See how that meshes with the proposed technical architecture • Metadirectory processing –Expect your technical architecture to include a “metadirectory”. –Spend some time to carefully consider its design and component technologies – you will have to live with this for a long time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 78
Implementation: Technology • New vendors or technologies needed? –Plan up front for time to assess what you have –See how that meshes with the proposed technical architecture • Metadirectory processing –Expect your technical architecture to include a “metadirectory”. –Spend some time to carefully consider its design and component technologies – you will have to live with this for a long time. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 78
 Implementation: Technology • New hardware needed? Plan on it –Meet performance & functional requirements –Avoid side-effects occurring with multiple services –Provision for scalability, it will payoff • Solid network infrastructure –Network must work flawlessly –Remediate before you start –Relies completely on the integrity and performance of the network EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 79
Implementation: Technology • New hardware needed? Plan on it –Meet performance & functional requirements –Avoid side-effects occurring with multiple services –Provision for scalability, it will payoff • Solid network infrastructure –Network must work flawlessly –Remediate before you start –Relies completely on the integrity and performance of the network EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 79
 Case Study #2: A Decade of Directory Services at The University of Memphis ~~~~~ in 30 minutes! ~~~~~ Dr. Tom Barton tbarton@umemphis. edu EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
Case Study #2: A Decade of Directory Services at The University of Memphis ~~~~~ in 30 minutes! ~~~~~ Dr. Tom Barton tbarton@umemphis. edu EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
 Three Phases of Middleware I. Initial Integration First community wide services. II. Common IT Platform Common identifiers, authentication, authorization, & messaging services, and account provisioning reduce complexity for users and for IT staff. III. Rational Identity Management BPR & architectural changes to have an authoritative database for identity, enable earlier & remote engagement of constituents. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 81
Three Phases of Middleware I. Initial Integration First community wide services. II. Common IT Platform Common identifiers, authentication, authorization, & messaging services, and account provisioning reduce complexity for users and for IT staff. III. Rational Identity Management BPR & architectural changes to have an authoritative database for identity, enable earlier & remote engagement of constituents. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 81
 I. Initial Integration • What – Initial SIS & HRS “feeds” integrated for CSO Nameservice (aka Ph) – Dialup authentication & authorization – Email routing for @memphis. edu – White pages • Drivers – Inadequate dialup service – Frustration with central IT • How – Stealth, 1 FTE. Central IT management not involved!! EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 82
I. Initial Integration • What – Initial SIS & HRS “feeds” integrated for CSO Nameservice (aka Ph) – Dialup authentication & authorization – Email routing for @memphis. edu – White pages • Drivers – Inadequate dialup service – Frustration with central IT • How – Stealth, 1 FTE. Central IT management not involved!! EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 82
 I. Initial Integration • Organizational interactions – Heretical idea to use data for other than original purpose – Adversarial relationship between central IT & business offices – Circumstantial solution: academic proponent (a noncombatant!) with gloss of executive blessing • Demonstrated values & lessons – Possible to provide popular services with little staff overhead – Beginning of an organizational learning curve for central IT management and key business offices – Data integrated across core business systems is the foundation for community wide applications EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 83
I. Initial Integration • Organizational interactions – Heretical idea to use data for other than original purpose – Adversarial relationship between central IT & business offices – Circumstantial solution: academic proponent (a noncombatant!) with gloss of executive blessing • Demonstrated values & lessons – Possible to provide popular services with little staff overhead – Beginning of an organizational learning curve for central IT management and key business offices – Data integrated across core business systems is the foundation for community wide applications EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 83
 II. Common IT Platform: Continuous Improvement Cycle What – Common username for all basic services – Password synchronization across several authentication services – Integration of suite of basic services with directory services for authentication & authorization: mailbox, many COTS & custom web applications, CMS, calendar, dialup & wireless, group messaging, authenticated email, computer labs, shell accounts, network registration, guest registration, card swipes, … – Automated resource lifecycle management EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 84
II. Common IT Platform: Continuous Improvement Cycle What – Common username for all basic services – Password synchronization across several authentication services – Integration of suite of basic services with directory services for authentication & authorization: mailbox, many COTS & custom web applications, CMS, calendar, dialup & wireless, group messaging, authenticated email, computer labs, shell accounts, network registration, guest registration, card swipes, … – Automated resource lifecycle management EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 84
 II. Common IT Platform • Drivers – Avoid requiring users to know where in the network they are as our services become more complex – Provide competitive level of service within severe resource constraints • Simplicity of operational management • Delegation of selected authorization management to appropriate departments • Self serve account maintenance • Automation or avoidance of otherwise manual tasks commonly left for central IT EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 85
II. Common IT Platform • Drivers – Avoid requiring users to know where in the network they are as our services become more complex – Provide competitive level of service within severe resource constraints • Simplicity of operational management • Delegation of selected authorization management to appropriate departments • Self serve account maintenance • Automation or avoidance of otherwise manual tasks commonly left for central IT EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 85
 II. Common IT Platform • How – Earlier additions stealthy, some later ones declared projects. – 1. 5 FTE ongoing – No additional funding – assign normal resources according to priority • Organizational interactions – Earlier: wormholes between traditionally siloed groups in central IT. – Later: absorbed into basic function of several standing teams – IT leadership that promoted Learning Organization principles and a more flexible approach to organizational structure – Institutional IT governance & strategic planning processes EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 86
II. Common IT Platform • How – Earlier additions stealthy, some later ones declared projects. – 1. 5 FTE ongoing – No additional funding – assign normal resources according to priority • Organizational interactions – Earlier: wormholes between traditionally siloed groups in central IT. – Later: absorbed into basic function of several standing teams – IT leadership that promoted Learning Organization principles and a more flexible approach to organizational structure – Institutional IT governance & strategic planning processes EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 86
 II. Common IT Platform Demonstrated values & lessons – “Middleware Business Case” values drawn from our experience & vetted by other Internet 2 Early Adopters. – Additional funding & dedicated project teams are nice, but might not be a necessity. – Effective institutional IT governance processes and a flexible central IT organizational structure can alleviate organizational pain with middleware implementations. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 87
II. Common IT Platform Demonstrated values & lessons – “Middleware Business Case” values drawn from our experience & vetted by other Internet 2 Early Adopters. – Additional funding & dedicated project teams are nice, but might not be a necessity. – Effective institutional IT governance processes and a flexible central IT organizational structure can alleviate organizational pain with middleware implementations. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 87
 III. Rational Identity Management What – A single authoritative source for identity related data which is made to appear wherever else it needs to be – Business process tinkering so that business offices actually maintain identity data in the identity database and not directly (or solely) in their own system. – Further tinkering so that self-serve online processes are used with new affiliations, enabling the constituent’s ID info to be automatically populated by reference to their online account. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 88
III. Rational Identity Management What – A single authoritative source for identity related data which is made to appear wherever else it needs to be – Business process tinkering so that business offices actually maintain identity data in the identity database and not directly (or solely) in their own system. – Further tinkering so that self-serve online processes are used with new affiliations, enabling the constituent’s ID info to be automatically populated by reference to their online account. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 88
 III. Rational Identity Management: A Scenario 1. Prospective student X uses http: //i. AM. memphis. edu to get account with self-asserted, unvalidated ID info. Being foreign, a bogus SSN is generated for X in case it is needed. 2. X uses account to apply for admission online. This creates a record in SIS with unvalidated ID info. ID database now also has SIS identifier for X. 3. Admissions Office validates X’s ID info as they deem appropriate & admits, conditionally updating ID database. 4. X enrolls. Campus ID card office updates ID database with correct birthdate from driver’s license. Correction flows back to SIS as well. 5. Becoming a student worker, X gives HR a real SSN. HR updates ID database with real SSN, enabling HRS and SIS updates pertaining to X to be integrated by the metadirectory. SIS receives updated SSN. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 89
III. Rational Identity Management: A Scenario 1. Prospective student X uses http: //i. AM. memphis. edu to get account with self-asserted, unvalidated ID info. Being foreign, a bogus SSN is generated for X in case it is needed. 2. X uses account to apply for admission online. This creates a record in SIS with unvalidated ID info. ID database now also has SIS identifier for X. 3. Admissions Office validates X’s ID info as they deem appropriate & admits, conditionally updating ID database. 4. X enrolls. Campus ID card office updates ID database with correct birthdate from driver’s license. Correction flows back to SIS as well. 5. Becoming a student worker, X gives HR a real SSN. HR updates ID database with real SSN, enabling HRS and SIS updates pertaining to X to be integrated by the metadirectory. SIS receives updated SSN. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 89
 III. Rational Identity Management How – Initial phase will supply ID database query & update tools to supplement existing record creation and maintenance processes. – Determine per-affiliation ID data validation requirements & solutions. – Determine online affiliation engagement processes. – Remote account initialization for those following existing affiliation engagement processes. – Later, automate the record creation & maintenance processes for identity data in major ERP systems. – 1. 5 – 3. 0 expected FTE during each of several 2 month conversion periods, drawn from Systems, Developers, and Business Offices. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 90
III. Rational Identity Management How – Initial phase will supply ID database query & update tools to supplement existing record creation and maintenance processes. – Determine per-affiliation ID data validation requirements & solutions. – Determine online affiliation engagement processes. – Remote account initialization for those following existing affiliation engagement processes. – Later, automate the record creation & maintenance processes for identity data in major ERP systems. – 1. 5 – 3. 0 expected FTE during each of several 2 month conversion periods, drawn from Systems, Developers, and Business Offices. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 90
 III. Rational Identity Management • Organizational interactions – Idea viewed as helpful but heretical by most data stewards. – Executive officers have bought in, on the promise of enabling online services to reach a broader constituency, and thus improvement to the bottom line. – Piggyback on all of the BPR that will attend an upcoming ERP conversion project. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 91
III. Rational Identity Management • Organizational interactions – Idea viewed as helpful but heretical by most data stewards. – Executive officers have bought in, on the promise of enabling online services to reach a broader constituency, and thus improvement to the bottom line. – Piggyback on all of the BPR that will attend an upcoming ERP conversion project. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 91
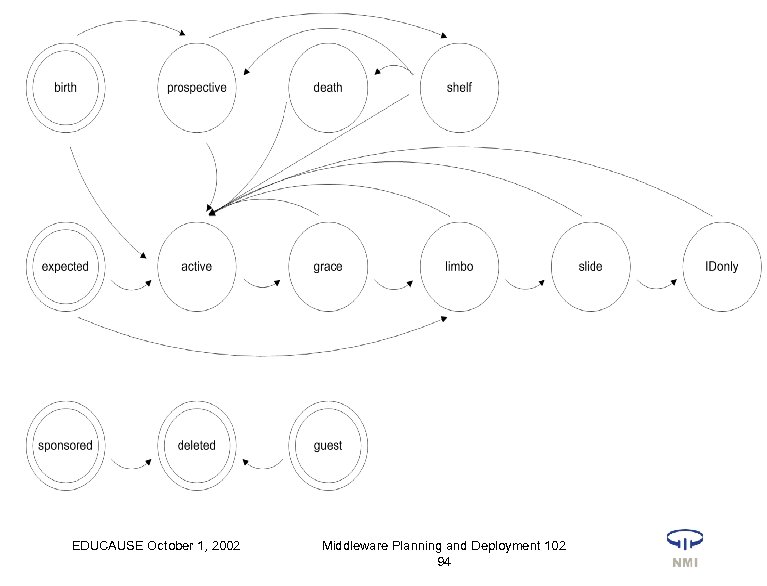
 Metadirectory Extension Project What – Add new major affiliations of “admitted student”, “registered student”, “faculty” (as opposed to “staff”), “alum” to existing affiliations of “enrolled student”, “staff”. – Remote account initialization. – Provision resources to enable limited access to “prospective” members of community, and to support outsourced services for alums. – Example of “continous improvement cycle” to the “common IT platform”. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 92
Metadirectory Extension Project What – Add new major affiliations of “admitted student”, “registered student”, “faculty” (as opposed to “staff”), “alum” to existing affiliations of “enrolled student”, “staff”. – Remote account initialization. – Provision resources to enable limited access to “prospective” members of community, and to support outsourced services for alums. – Example of “continous improvement cycle” to the “common IT platform”. EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 92
 Metadirectory Extension Project • Drivers – – – Online post-admission process Improve service to new faculty Job search & email redirection services for alums Email communication with new constituencies Improve “class e-mail” • How – 2. 5 FTE among 7 members of a project team – no new funding – Extend existing provisioning state machine; augment http: //i. AM. memphis. edu website EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 93
Metadirectory Extension Project • Drivers – – – Online post-admission process Improve service to new faculty Job search & email redirection services for alums Email communication with new constituencies Improve “class e-mail” • How – 2. 5 FTE among 7 members of a project team – no new funding – Extend existing provisioning state machine; augment http: //i. AM. memphis. edu website EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 93
 EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 94
EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 94
 Metadirectory Extension Project • Organizational interactions – Requests from Provost, Registrar, & Student Services handled cooperatively. – Administrative systems developers now reasonably aware of metadirectory and its value. – This has become business as usual. • Demonstrated values & lessons – Check back same time next year!! EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 95
Metadirectory Extension Project • Organizational interactions – Requests from Provost, Registrar, & Student Services handled cooperatively. – Administrative systems developers now reasonably aware of metadirectory and its value. – This has become business as usual. • Demonstrated values & lessons – Check back same time next year!! EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 95
 Discussion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 96
Discussion EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 96
 Research and Resources EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
Research and Resources EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
 Research Community • Expert, diverse leadership and collaborators • Broad participation and review –MACE and related working groups –NSF catalytic grants –Early Adopters –Higher Education Partners • campuses, CNI, CREN, GRIDS, NACUBO, NACUA… –Government Partners • NSF, NIH, NIST, f. PKI TWG… –Corporate Partners • IBM/Metamerge, Liberty Alliance, Radvision, Sun… –International communities –Standards bodies EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 98
Research Community • Expert, diverse leadership and collaborators • Broad participation and review –MACE and related working groups –NSF catalytic grants –Early Adopters –Higher Education Partners • campuses, CNI, CREN, GRIDS, NACUBO, NACUA… –Government Partners • NSF, NIH, NIST, f. PKI TWG… –Corporate Partners • IBM/Metamerge, Liberty Alliance, Radvision, Sun… –International communities –Standards bodies EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 98
 NSF Middleware Initiative • NSF award for middleware integrators to – GRIDS Center • Globus (NCSA, UCSD, University of Chicago, USC/ ISI, and University of Wisconsin) – NMI-EDIT Consortium • Internet 2, EDUCAUSE, and SURA • Separate awards to academic pure research components • Build on the successes of the Globus project and Internet 2/MACE initiative • Multi-year effort • A practical (deployment) activity that necessitates some research • Releases occur every six months, roughly May and October EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 99
NSF Middleware Initiative • NSF award for middleware integrators to – GRIDS Center • Globus (NCSA, UCSD, University of Chicago, USC/ ISI, and University of Wisconsin) – NMI-EDIT Consortium • Internet 2, EDUCAUSE, and SURA • Separate awards to academic pure research components • Build on the successes of the Globus project and Internet 2/MACE initiative • Multi-year effort • A practical (deployment) activity that necessitates some research • Releases occur every six months, roughly May and October EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 99
 Research Working Groups/Projects • Directories – LDAP Analyzer – Practice Papers – Object Classes • • • Shibboleth - Inter-institution web access PKI – HEPKI-TAG & PAG, S/MIME, PKI Labs Middleware for Video – VC, Vo. D Digital Rights Management Medical Middleware Implementation Roadmap EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 100
Research Working Groups/Projects • Directories – LDAP Analyzer – Practice Papers – Object Classes • • • Shibboleth - Inter-institution web access PKI – HEPKI-TAG & PAG, S/MIME, PKI Labs Middleware for Video – VC, Vo. D Digital Rights Management Medical Middleware Implementation Roadmap EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 100
 Enterprise Middleware Resources Available • NMI-EDIT Release Components Software Directory Object Classes Conventions and Practices Recommended Practices White Papers Policies Services Works in progress: White Papers EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 101
Enterprise Middleware Resources Available • NMI-EDIT Release Components Software Directory Object Classes Conventions and Practices Recommended Practices White Papers Policies Services Works in progress: White Papers EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 101
 Enterprise Middleware Educational Opportunities • Workshops – Pre-conference Seminars at EDUCAUSE Regional Meetings – Campus Architectural Middleware Planning Workshops • Base CAMP (Orientation) – Feb 5 -7, 2003 – CIO and Technical staff – Getting started topics • Advanced CAMP– July 2003 – Highly technical – Research topics EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
Enterprise Middleware Educational Opportunities • Workshops – Pre-conference Seminars at EDUCAUSE Regional Meetings – Campus Architectural Middleware Planning Workshops • Base CAMP (Orientation) – Feb 5 -7, 2003 – CIO and Technical staff – Getting started topics • Advanced CAMP– July 2003 – Highly technical – Research topics EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102
 On-line Resources Available • Introductory Documents – Sample Middleware Business Case and corresponding Writer’s Guide – Identifiers, Authentication, and Directories: Best Practices for Higher Education – Identifier Mapping Template and Campus Examples • See handouts EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 103
On-line Resources Available • Introductory Documents – Sample Middleware Business Case and corresponding Writer’s Guide – Identifiers, Authentication, and Directories: Best Practices for Higher Education – Identifier Mapping Template and Campus Examples • See handouts EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 103
 Websites and Discussion Lists • Websites http: //middleware. internet 2. edu http: //www. nsf-middleware. org http: //www. nmi-edit. org http: //www. grids-center. org • Middleware information and discussion lists http: //mw-announce@internet 2. edu http: //mw-discuss@internet 2. edu NMI lists (see websites) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 104
Websites and Discussion Lists • Websites http: //middleware. internet 2. edu http: //www. nsf-middleware. org http: //www. nmi-edit. org http: //www. grids-center. org • Middleware information and discussion lists http: //mw-announce@internet 2. edu http: //mw-discuss@internet 2. edu NMI lists (see websites) EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 104
 CDROM Materials Contents • Presentations • Practice papers • Tools • Software EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 105
CDROM Materials Contents • Presentations • Practice papers • Tools • Software EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 105
 Session Wrap-up • Middleware is: – A strategic infrastructure – 50% technical and 100% political • Don’t reinvent the wheel – Each implementation is different – Big picture process and requirements are the same – There are resources that can help • Assess strengths and weaknesses and plan accordingly • Communication and relationship management is key EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 106
Session Wrap-up • Middleware is: – A strategic infrastructure – 50% technical and 100% political • Don’t reinvent the wheel – Each implementation is different – Big picture process and requirements are the same – There are resources that can help • Assess strengths and weaknesses and plan accordingly • Communication and relationship management is key EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 106
 Questions and Comments? – Tom Barton, tbarton@memphis. edu – Renee Frost, rwfrost@internet 2. edu – Jack Suess, jack@umbc. edu – Ann West, awest@educause. edu EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 107
Questions and Comments? – Tom Barton, tbarton@memphis. edu – Renee Frost, rwfrost@internet 2. edu – Jack Suess, jack@umbc. edu – Ann West, awest@educause. edu EDUCAUSE October 1, 2002 Middleware Planning and Deployment 102 107


