2d42a3f8346af597b6593f0cd38322e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 Microsoft Virtualization: Today and Tomorrow Kevin Sangwell Infrastructure Architect Microsoft Europe, Middle East & Africa kevin. sangwell@microsoft. com
Microsoft Virtualization: Today and Tomorrow Kevin Sangwell Infrastructure Architect Microsoft Europe, Middle East & Africa kevin. sangwell@microsoft. com
 Agenda 09: 00 – 09: 45 Welcome 09: 45 – 11: 00 Microsoft Virtualization Today and Tomorrow 11: 00 – 11: 15 Break 11: 15 – 12: 30 Managing a Mixed Virtual/Physical Environment: Tools and Techniques 12: 30 – 13: 30 Lunch 13: 30 – 14: 45 Windows Server Virtualization Deep Dive 14: 45 – 15: 00 Break 15: 00 – 16: 00 Virtual Server notes from the field 16: 00 – 16: 20 Panel Questions and Answers 16: 20 – 16: 30 Event Closure and Zune “raffle”
Agenda 09: 00 – 09: 45 Welcome 09: 45 – 11: 00 Microsoft Virtualization Today and Tomorrow 11: 00 – 11: 15 Break 11: 15 – 12: 30 Managing a Mixed Virtual/Physical Environment: Tools and Techniques 12: 30 – 13: 30 Lunch 13: 30 – 14: 45 Windows Server Virtualization Deep Dive 14: 45 – 15: 00 Break 15: 00 – 16: 00 Virtual Server notes from the field 16: 00 – 16: 20 Panel Questions and Answers 16: 20 – 16: 30 Event Closure and Zune “raffle”
 What is Virtualization? “a technique for hiding the physical characteristics of computing resources from the way in which other systems, applications, or end users interact with those resources” • Abstraction and Emulation • Virtual IP Address, Virtual Directory, SAN
What is Virtualization? “a technique for hiding the physical characteristics of computing resources from the way in which other systems, applications, or end users interact with those resources” • Abstraction and Emulation • Virtual IP Address, Virtual Directory, SAN
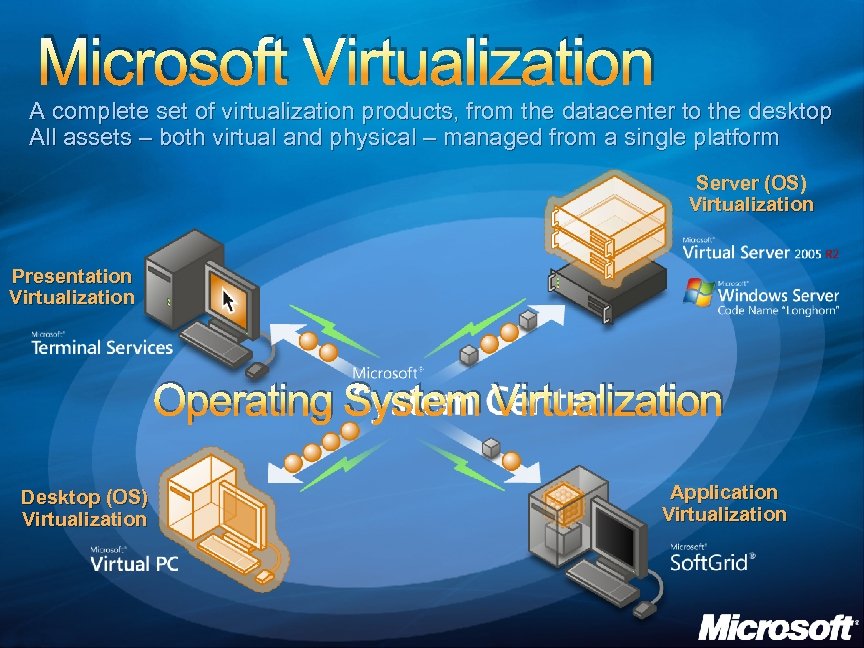 Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Operating System Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Operating System Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
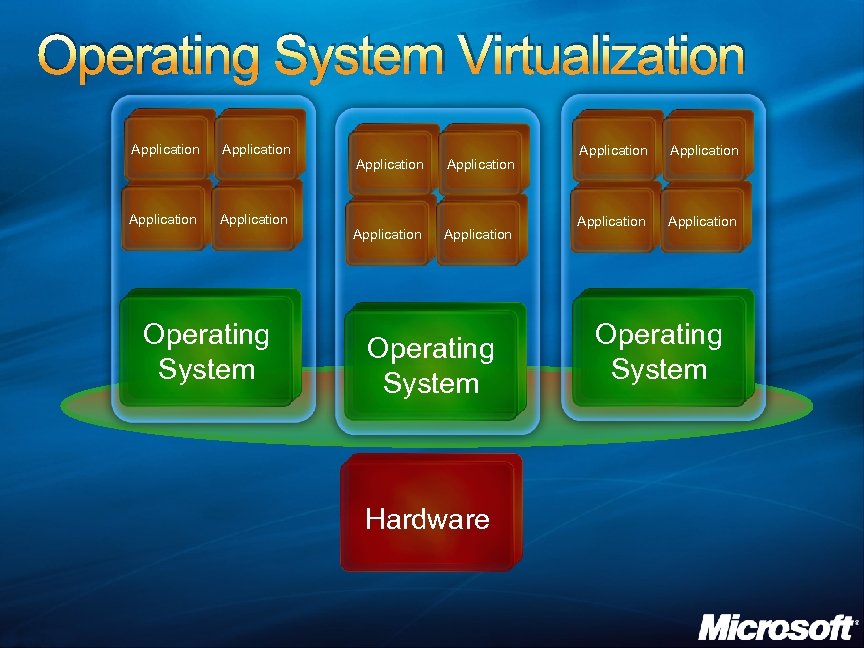 Operating System Virtualization Application Application Operating System Hardware Application Operating System
Operating System Virtualization Application Application Operating System Hardware Application Operating System
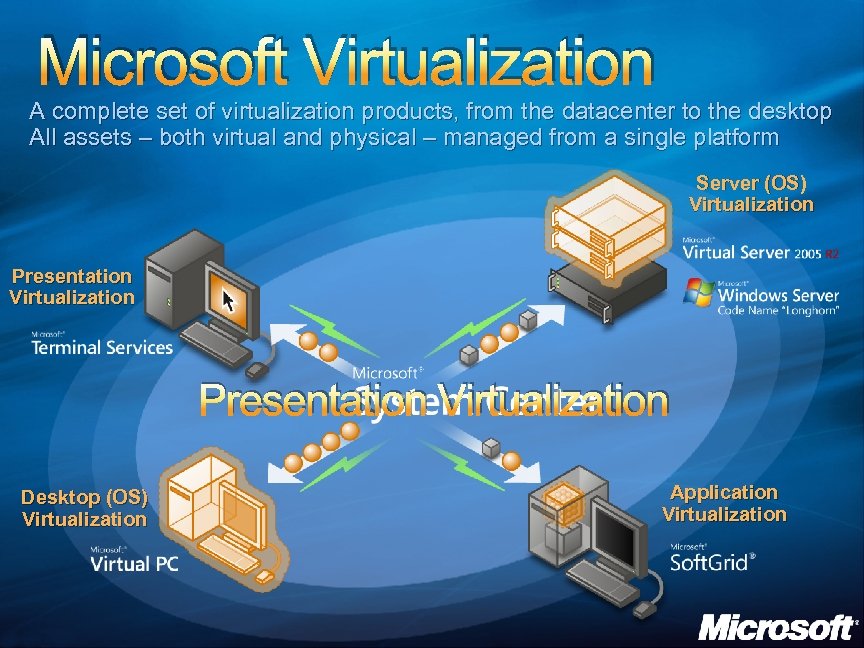 Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
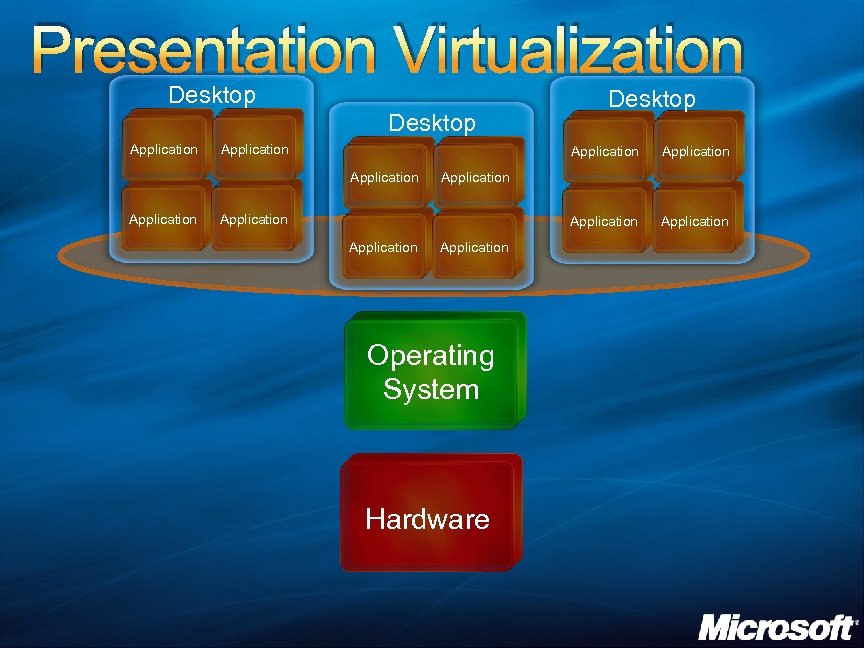 Presentation Virtualization Desktop Application Application Application Desktop Application Operating System Hardware
Presentation Virtualization Desktop Application Application Application Desktop Application Operating System Hardware
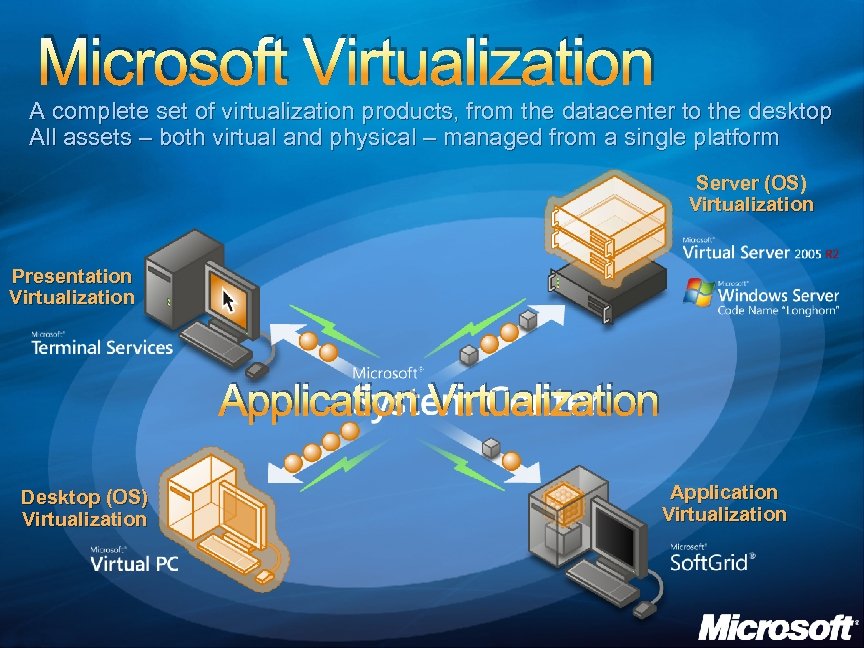 Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Application Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
Microsoft Virtualization A complete set of virtualization products, from the datacenter to the desktop All assets – both virtual and physical – managed from a single platform Server (OS) Virtualization Presentation Virtualization Application Virtualization Desktop (OS) Virtualization Application Virtualization
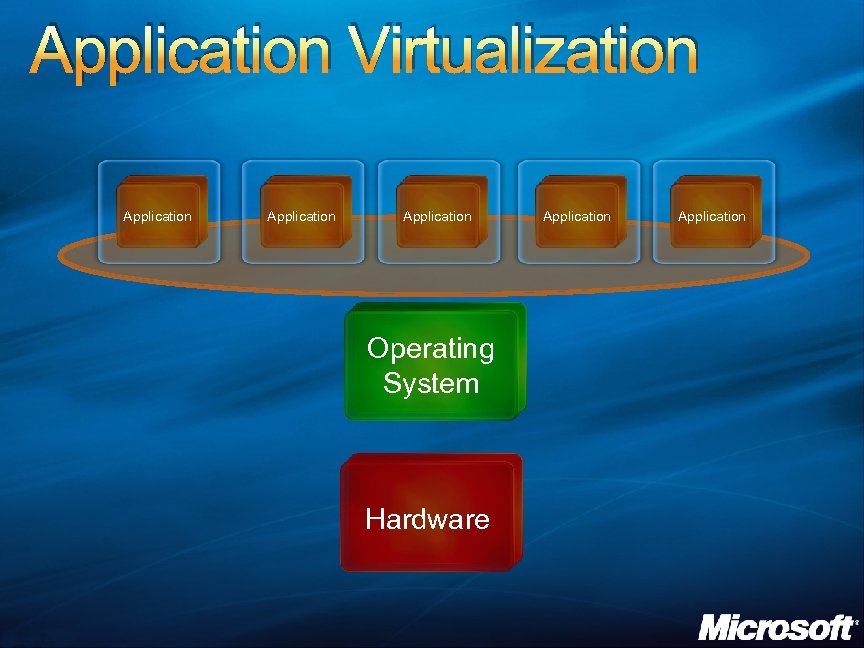 Application Virtualization Application Operating System Hardware Application
Application Virtualization Application Operating System Hardware Application
 OS VIRTUALIZATION: VIRTUAL SERVER 2005 R 2
OS VIRTUALIZATION: VIRTUAL SERVER 2005 R 2
 Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 R 2 A cost-effective and well supported server virtualization technology for the Windows Server System™ platform. Focused on key customer scenarios Consolidate server workloads Automate and consolidate software test and development environments Disaster recovery Reduce costs and improve IT responsiveness Reduce hardware costs by at least 50% Reduce provisioning times by 50 -95% Increase administrator productivity
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 R 2 A cost-effective and well supported server virtualization technology for the Windows Server System™ platform. Focused on key customer scenarios Consolidate server workloads Automate and consolidate software test and development environments Disaster recovery Reduce costs and improve IT responsiveness Reduce hardware costs by at least 50% Reduce provisioning times by 50 -95% Increase administrator productivity
 Virtual Server R 2: Overview Kernel-mode Virtual Machine Monitor for Windows service with a Web interface Designed for remote administration Fully documented COM API for scripting and ISVs Virtualizes most of an x 86 system Provides virtual disks (VHD), virtual networking and virtual video
Virtual Server R 2: Overview Kernel-mode Virtual Machine Monitor for Windows service with a Web interface Designed for remote administration Fully documented COM API for scripting and ISVs Virtualizes most of an x 86 system Provides virtual disks (VHD), virtual networking and virtual video
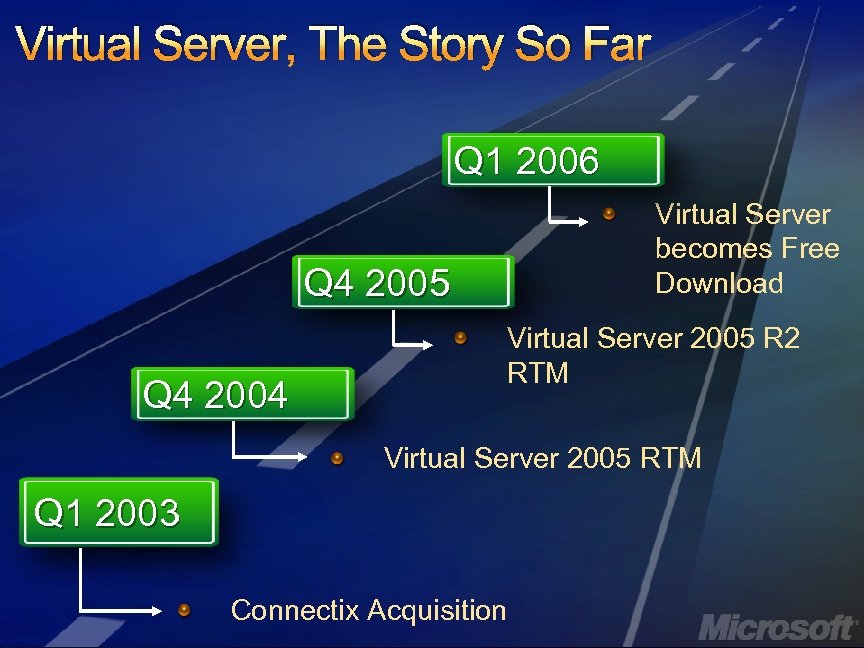 Virtual Server, The Story So Far Q 1 2006 Virtual Server becomes Free Download Q 4 2005 Q 4 2004 Virtual Server 2005 R 2 RTM Virtual Server 2005 RTM Q 1 2003 Connectix Acquisition
Virtual Server, The Story So Far Q 1 2006 Virtual Server becomes Free Download Q 4 2005 Q 4 2004 Virtual Server 2005 R 2 RTM Virtual Server 2005 RTM Q 1 2003 Connectix Acquisition
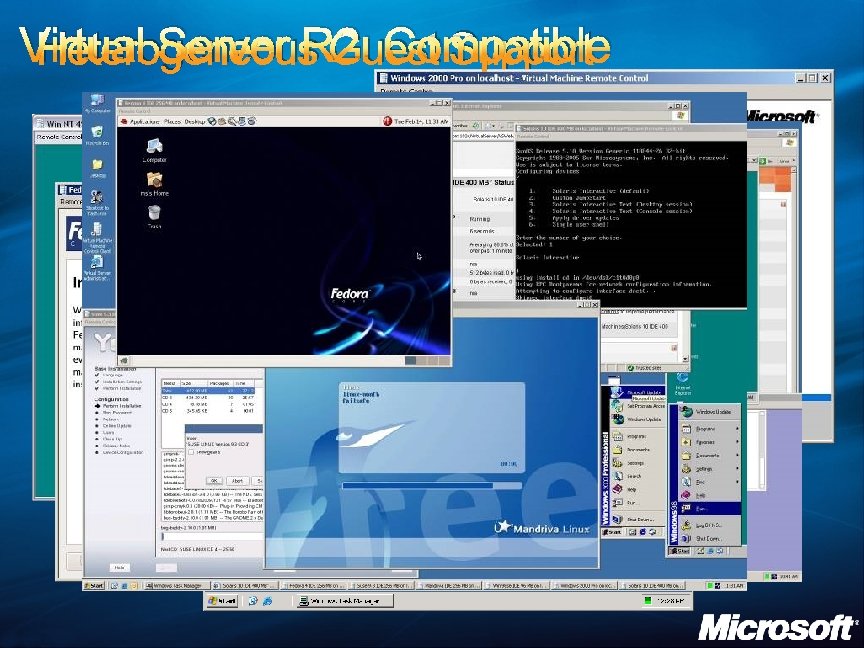 Virtual Server R 2: Compatible Heterogeneous Guest Support
Virtual Server R 2: Compatible Heterogeneous Guest Support
 Virtual Server R 2: Compatible Microsoft: Compatible means: “it just works” Compatible guest operating systems DOS Windows Client: Every version, 1. x, 3. 1, 95, 98, ME, XP Window Server: Every version, NT, 2000, 2003 (all editions except Datacenter, which requires a minimum of 8 processors) Linux Red Hat, Suse, Mandrake, Mandriva, Ubuntu, Fedora, etc. Others: OS/2, Cho-Kanji >1000 OSs “just work”: http: //vpc. visualwin. com/
Virtual Server R 2: Compatible Microsoft: Compatible means: “it just works” Compatible guest operating systems DOS Windows Client: Every version, 1. x, 3. 1, 95, 98, ME, XP Window Server: Every version, NT, 2000, 2003 (all editions except Datacenter, which requires a minimum of 8 processors) Linux Red Hat, Suse, Mandrake, Mandriva, Ubuntu, Fedora, etc. Others: OS/2, Cho-Kanji >1000 OSs “just work”: http: //vpc. visualwin. com/
 Virtual Server R 2: Key Features High Availability Virtual Server R 2 Host Cluster support Guest operating system-agnostic Up to 64 guests / host x 64 hosts (32 -bit guests) 64 -bit port of Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) and service Better scaling from larger kernel address space Linux Guest Support VMs compatible with Virtual PC
Virtual Server R 2: Key Features High Availability Virtual Server R 2 Host Cluster support Guest operating system-agnostic Up to 64 guests / host x 64 hosts (32 -bit guests) 64 -bit port of Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) and service Better scaling from larger kernel address space Linux Guest Support VMs compatible with Virtual PC
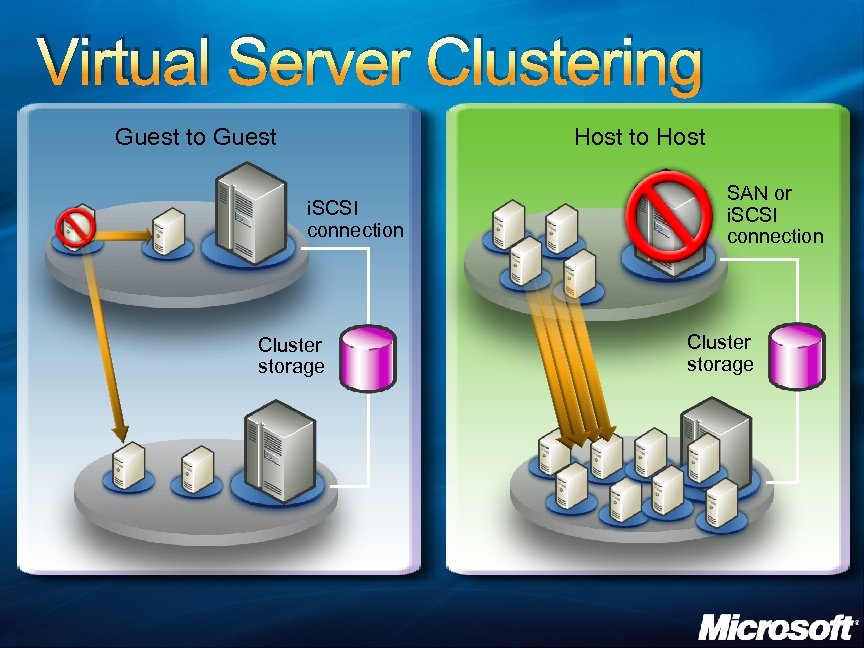 Virtual Server Clustering Guest to Guest Host to Host i. SCSI connection Cluster storage SAN or i. SCSI connection Cluster storage
Virtual Server Clustering Guest to Guest Host to Host i. SCSI connection Cluster storage SAN or i. SCSI connection Cluster storage
 SELF MANAGED DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
SELF MANAGED DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
 Where and why its being deployed Test and Development Rapid provisioning & reset of dev/test environment Server Consolidation SQL Server, File & Print Low utilization servers (e. g. NT 4. 0 Lo. B) Datacenter Reduce space, power, cooling requirements Increase flexibility Disaster Recovery Clone live datacenter
Where and why its being deployed Test and Development Rapid provisioning & reset of dev/test environment Server Consolidation SQL Server, File & Print Low utilization servers (e. g. NT 4. 0 Lo. B) Datacenter Reduce space, power, cooling requirements Increase flexibility Disaster Recovery Clone live datacenter
 The Future Windows Server 2005 R 2 SP 1 Support >64 guest machines on x 64 hosts Support for Intel-VT and AMD-V assists Improved backup through integrated VSS support Q 1 CY 07 (public beta now) VHD Mounting Windows Server Virtualization Longhorn Timeframe (2 H CY 07) Hypervisor Based Longhorn Server Core
The Future Windows Server 2005 R 2 SP 1 Support >64 guest machines on x 64 hosts Support for Intel-VT and AMD-V assists Improved backup through integrated VSS support Q 1 CY 07 (public beta now) VHD Mounting Windows Server Virtualization Longhorn Timeframe (2 H CY 07) Hypervisor Based Longhorn Server Core
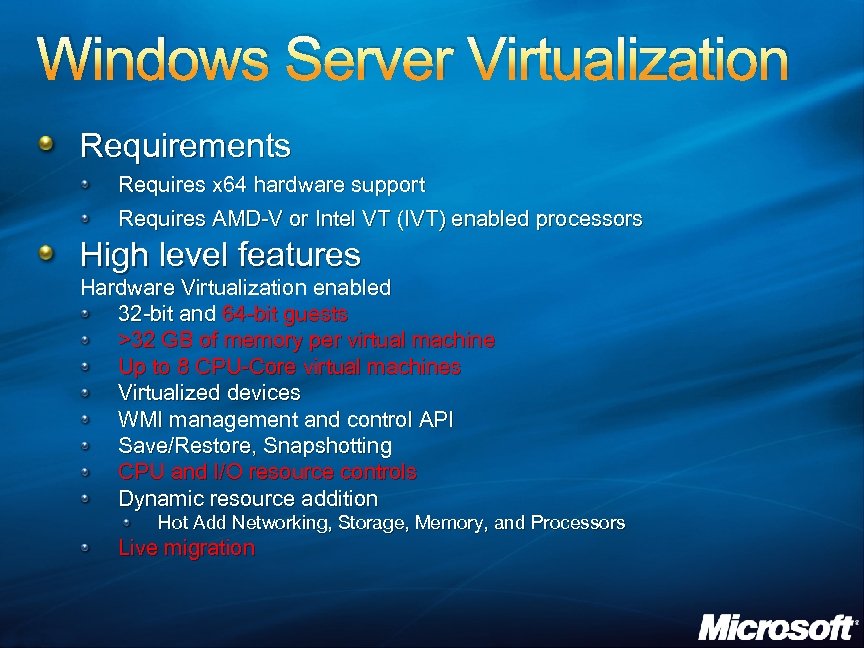 Windows Server Virtualization Requirements Requires x 64 hardware support Requires AMD-V or Intel VT (IVT) enabled processors High level features Hardware Virtualization enabled 32 -bit and 64 -bit guests >32 GB of memory per virtual machine Up to 8 CPU-Core virtual machines Virtualized devices WMI management and control API Save/Restore, Snapshotting CPU and I/O resource controls Dynamic resource addition Hot Add Networking, Storage, Memory, and Processors Live migration
Windows Server Virtualization Requirements Requires x 64 hardware support Requires AMD-V or Intel VT (IVT) enabled processors High level features Hardware Virtualization enabled 32 -bit and 64 -bit guests >32 GB of memory per virtual machine Up to 8 CPU-Core virtual machines Virtualized devices WMI management and control API Save/Restore, Snapshotting CPU and I/O resource controls Dynamic resource addition Hot Add Networking, Storage, Memory, and Processors Live migration
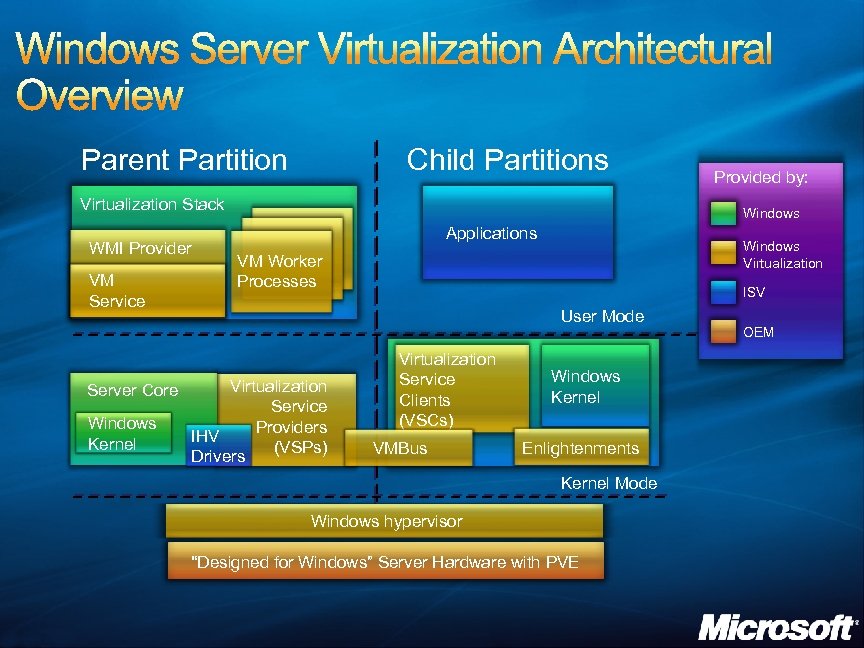 Parent Partition Child Partitions Virtualization Stack WMI Provider VM Service Server Core Windows Kernel Provided by: Windows Applications Windows Virtualization VM Worker Processes ISV User Mode Virtualization Service Providers IHV (VSPs) Drivers Virtualization Service Clients (VSCs) VMBus Windows Kernel Enlightenments Kernel Mode Windows hypervisor “Designed for Windows” Server Hardware with PVE OEM
Parent Partition Child Partitions Virtualization Stack WMI Provider VM Service Server Core Windows Kernel Provided by: Windows Applications Windows Virtualization VM Worker Processes ISV User Mode Virtualization Service Providers IHV (VSPs) Drivers Virtualization Service Clients (VSCs) VMBus Windows Kernel Enlightenments Kernel Mode Windows hypervisor “Designed for Windows” Server Hardware with PVE OEM
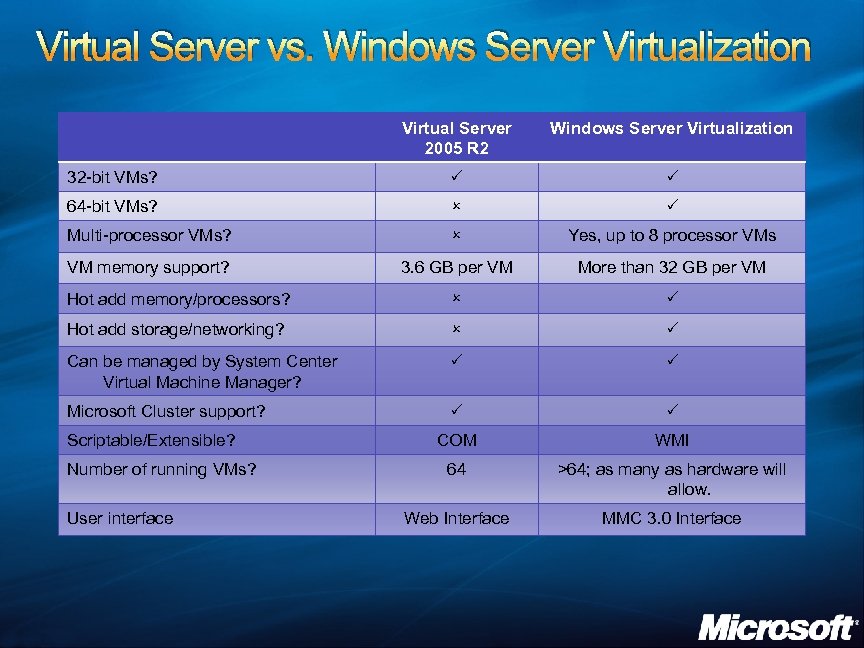 Virtual Server vs. Windows Server Virtualization Virtual Server 2005 R 2 Windows Server Virtualization 32 -bit VMs? P P 64 -bit VMs? O P Multi-processor VMs? O Yes, up to 8 processor VMs VM memory support? 3. 6 GB per VM More than 32 GB per VM Hot add memory/processors? O P Hot add storage/networking? O P Can be managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager? P P Microsoft Cluster support? P P COM WMI 64 >64; as many as hardware will allow. Web Interface MMC 3. 0 Interface Scriptable/Extensible? Number of running VMs? User interface
Virtual Server vs. Windows Server Virtualization Virtual Server 2005 R 2 Windows Server Virtualization 32 -bit VMs? P P 64 -bit VMs? O P Multi-processor VMs? O Yes, up to 8 processor VMs VM memory support? 3. 6 GB per VM More than 32 GB per VM Hot add memory/processors? O P Hot add storage/networking? O P Can be managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager? P P Microsoft Cluster support? P P COM WMI 64 >64; as many as hardware will allow. Web Interface MMC 3. 0 Interface Scriptable/Extensible? Number of running VMs? User interface
 DESKTOP/SESSION VIRTUALIZATION
DESKTOP/SESSION VIRTUALIZATION
 Aren’t Desktop and Application Virtualization the same? Desktop Virtualization Execution occurs on the server No application client deployment: just UI is displayed on the client (RDP) Multiple isolated users per server Excellent for: Branch Office High Volume data applications Centralized desktop management Application Virtualization Execution occurs on the client Application still needs deployment to client Multiple isolated applications per client Excellent for: Reducing test matrix Concurrently running multiple versions of the same application Reducing application management
Aren’t Desktop and Application Virtualization the same? Desktop Virtualization Execution occurs on the server No application client deployment: just UI is displayed on the client (RDP) Multiple isolated users per server Excellent for: Branch Office High Volume data applications Centralized desktop management Application Virtualization Execution occurs on the client Application still needs deployment to client Multiple isolated applications per client Excellent for: Reducing test matrix Concurrently running multiple versions of the same application Reducing application management
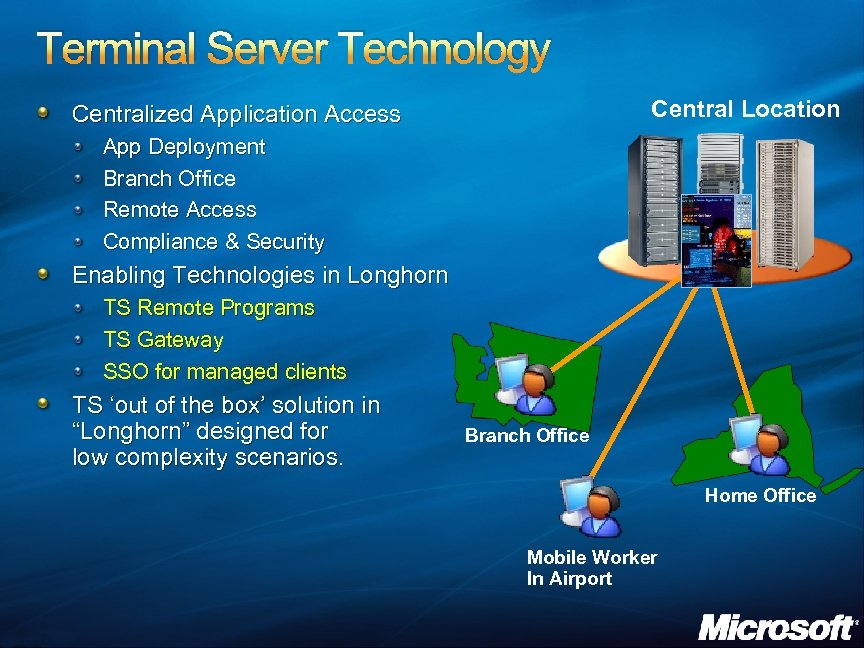 Terminal Server Technology Central Location Centralized Application Access App Deployment Branch Office Remote Access Compliance & Security Enabling Technologies in Longhorn TS Remote Programs TS Gateway SSO for managed clients TS ‘out of the box’ solution in “Longhorn” designed for low complexity scenarios. Branch Office Home Office Mobile Worker In Airport
Terminal Server Technology Central Location Centralized Application Access App Deployment Branch Office Remote Access Compliance & Security Enabling Technologies in Longhorn TS Remote Programs TS Gateway SSO for managed clients TS ‘out of the box’ solution in “Longhorn” designed for low complexity scenarios. Branch Office Home Office Mobile Worker In Airport
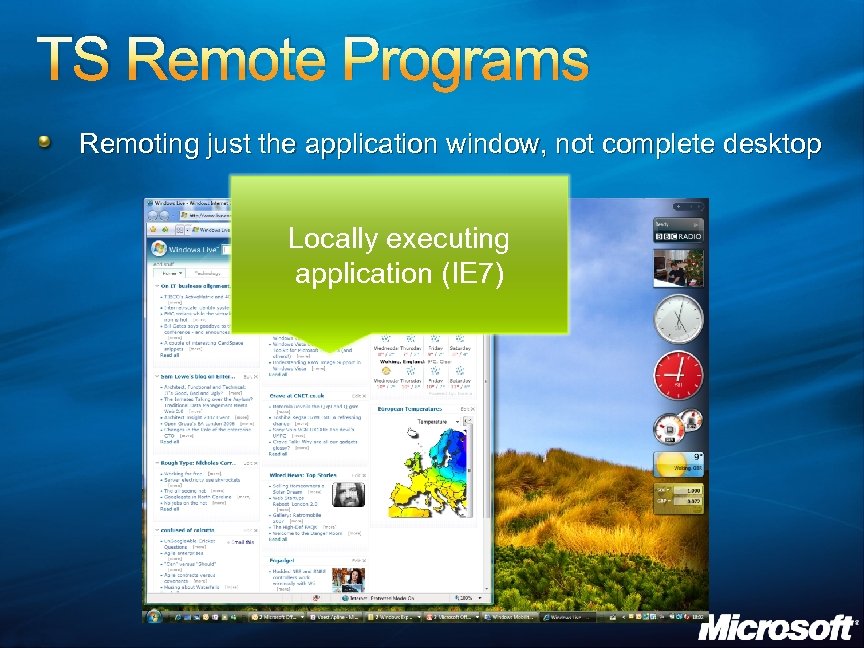 TS Remote Programs Remoting just the application window, not complete desktop Locally executing application (IE 7)
TS Remote Programs Remoting just the application window, not complete desktop Locally executing application (IE 7)
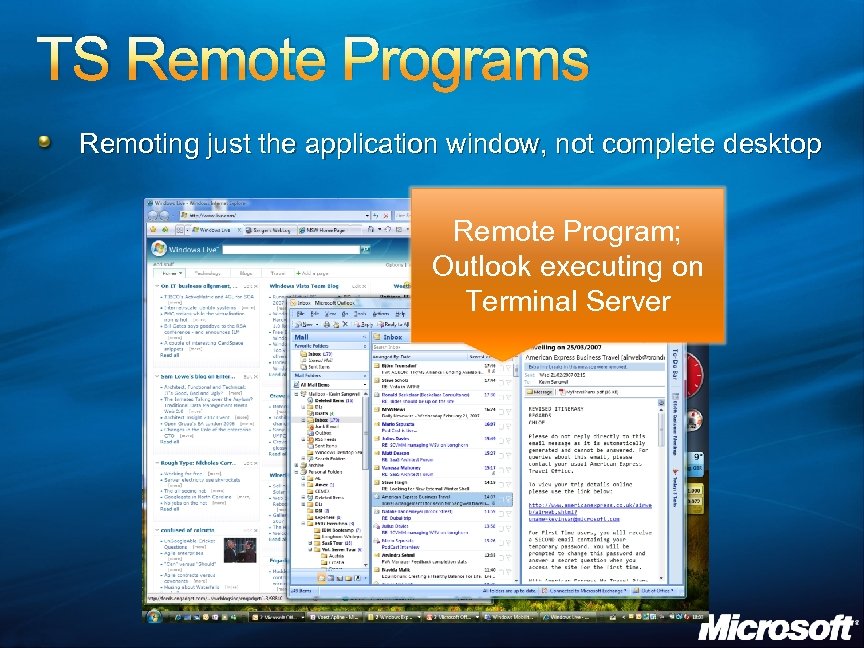 TS Remote Programs Remoting just the application window, not complete desktop Remote Program; Outlook executing on Terminal Server
TS Remote Programs Remoting just the application window, not complete desktop Remote Program; Outlook executing on Terminal Server
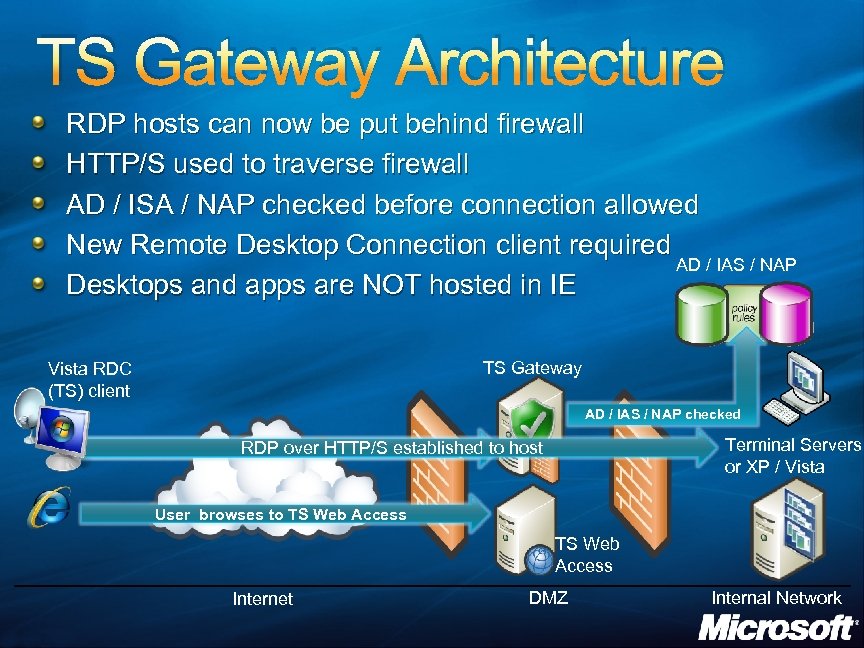 TS Gateway Architecture RDP hosts can now be put behind firewall HTTP/S used to traverse firewall AD / ISA / NAP checked before connection allowed New Remote Desktop Connection client required AD / IAS / NAP Desktops and apps are NOT hosted in IE TS Gateway Vista RDC (TS) client AD / IAS / NAP checked Terminal Servers or XP / Vista RDP over HTTP/S established User initiates HTTP/S connection to TS Gateway to host User browses to TS Web Access Internet DMZ Internal Network
TS Gateway Architecture RDP hosts can now be put behind firewall HTTP/S used to traverse firewall AD / ISA / NAP checked before connection allowed New Remote Desktop Connection client required AD / IAS / NAP Desktops and apps are NOT hosted in IE TS Gateway Vista RDC (TS) client AD / IAS / NAP checked Terminal Servers or XP / Vista RDP over HTTP/S established User initiates HTTP/S connection to TS Gateway to host User browses to TS Web Access Internet DMZ Internal Network
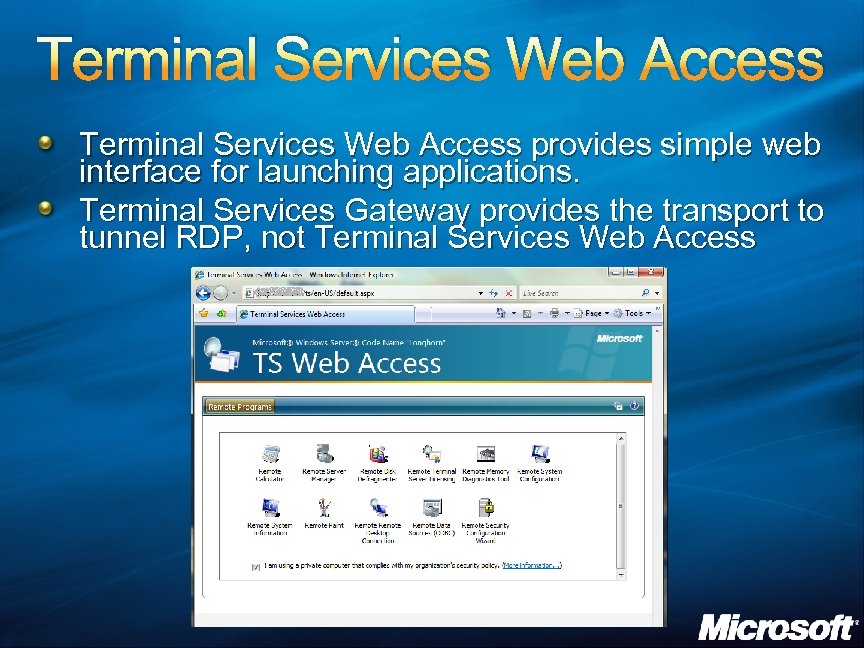 Terminal Services Web Access provides simple web interface for launching applications. Terminal Services Gateway provides the transport to tunnel RDP, not Terminal Services Web Access
Terminal Services Web Access provides simple web interface for launching applications. Terminal Services Gateway provides the transport to tunnel RDP, not Terminal Services Web Access
 APPLICATION VIRTUALIZATION
APPLICATION VIRTUALIZATION
 Application Virtualization Most software is not designed to operate in a utility model State is “mixed-in” Reconfiguration is costly More and more software leads to unreliable desktops and massive test matrix Application Virtualization enables software to be managed independently and transformed without the need for source code
Application Virtualization Most software is not designed to operate in a utility model State is “mixed-in” Reconfiguration is costly More and more software leads to unreliable desktops and massive test matrix Application Virtualization enables software to be managed independently and transformed without the need for source code
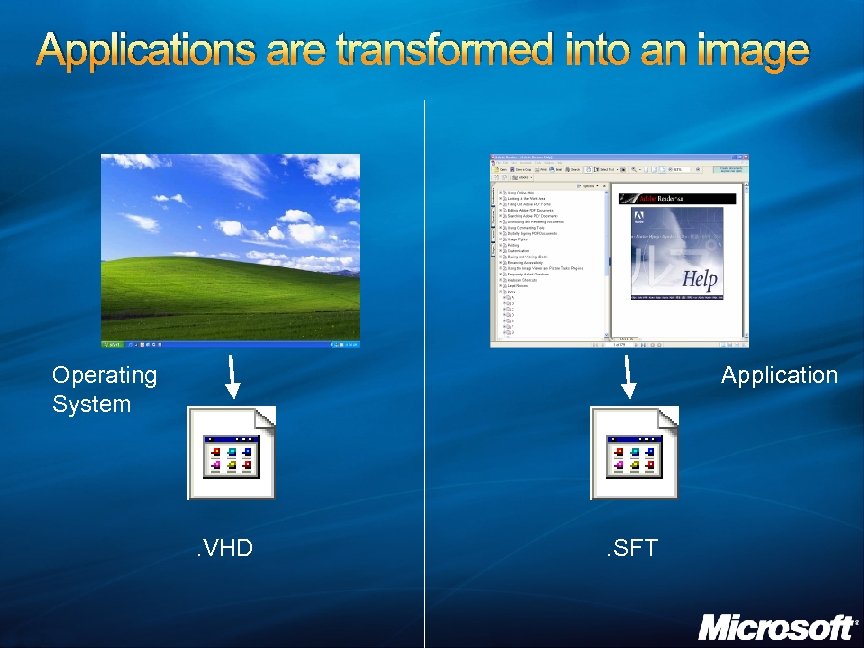 Applications are transformed into an image Operating System Application . VHD . SFT
Applications are transformed into an image Operating System Application . VHD . SFT
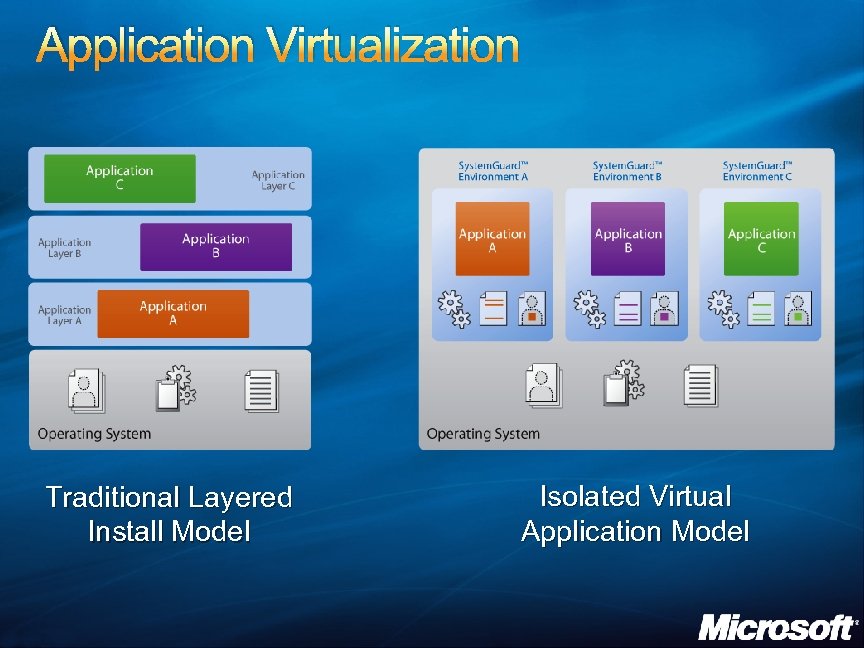 Application Virtualization Traditional Layered Install Model Isolated Virtual Application Model
Application Virtualization Traditional Layered Install Model Isolated Virtual Application Model
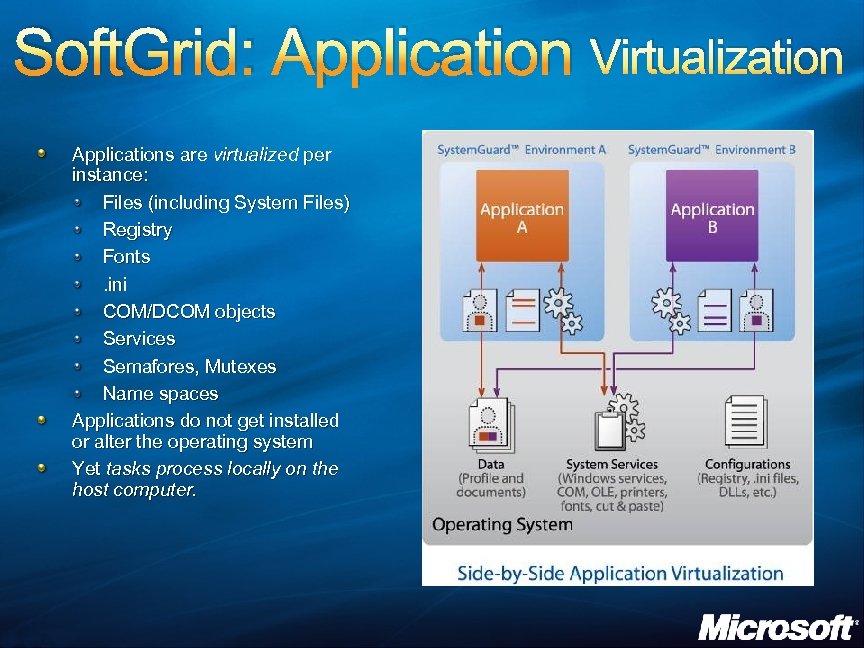 Soft. Grid: Application Virtualization Applications are virtualized per instance: Files (including System Files) Registry Fonts. ini COM/DCOM objects Services Semafores, Mutexes Name spaces Applications do not get installed or alter the operating system Yet tasks process locally on the host computer.
Soft. Grid: Application Virtualization Applications are virtualized per instance: Files (including System Files) Registry Fonts. ini COM/DCOM objects Services Semafores, Mutexes Name spaces Applications do not get installed or alter the operating system Yet tasks process locally on the host computer.
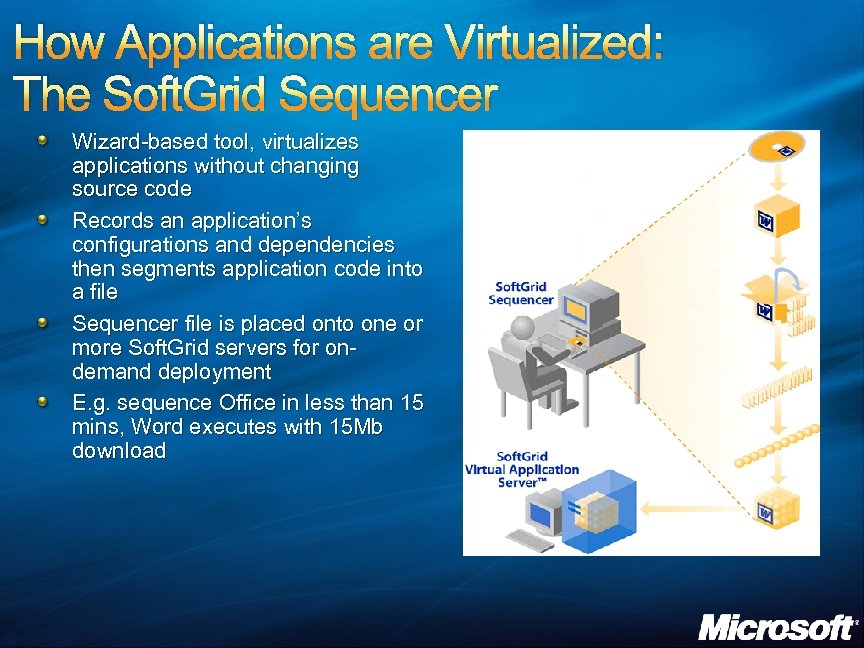 How Applications are Virtualized: The Soft. Grid Sequencer Wizard-based tool, virtualizes applications without changing source code Records an application’s configurations and dependencies then segments application code into a file Sequencer file is placed onto one or more Soft. Grid servers for ondemand deployment E. g. sequence Office in less than 15 mins, Word executes with 15 Mb download
How Applications are Virtualized: The Soft. Grid Sequencer Wizard-based tool, virtualizes applications without changing source code Records an application’s configurations and dependencies then segments application code into a file Sequencer file is placed onto one or more Soft. Grid servers for ondemand deployment E. g. sequence Office in less than 15 mins, Word executes with 15 Mb download
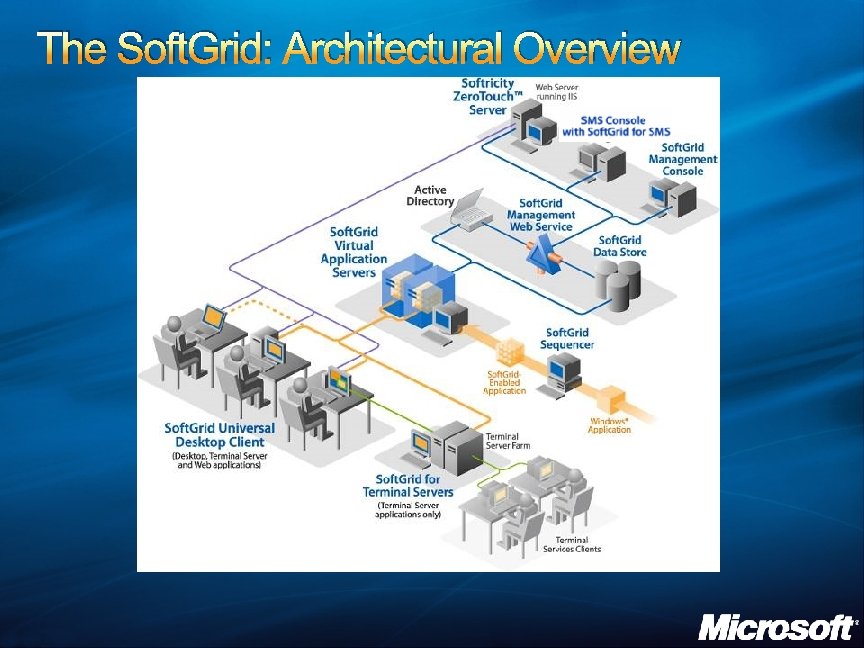 The Soft. Grid: Architectural Overview
The Soft. Grid: Architectural Overview
 Microsoft Soft. Grid Availability Microsoft Soft. Grid 4. 1 for Windows Desktops • Available as a component of Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack for SA • Select, Open, EA Licensing • Does not include Soft. Grid CAL for Terminal Services Soft. Grid Application Virtualization for Terminal Services • • Available in same channels as Terminal Services CAL Soft. Grid for Terminal Services licensed as CAL Terminal Services CAL still required Does not include Soft. Grid for Desktops • Can be used in conjunction with Soft. Grid for Desktops; both share infrastructure)
Microsoft Soft. Grid Availability Microsoft Soft. Grid 4. 1 for Windows Desktops • Available as a component of Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack for SA • Select, Open, EA Licensing • Does not include Soft. Grid CAL for Terminal Services Soft. Grid Application Virtualization for Terminal Services • • Available in same channels as Terminal Services CAL Soft. Grid for Terminal Services licensed as CAL Terminal Services CAL still required Does not include Soft. Grid for Desktops • Can be used in conjunction with Soft. Grid for Desktops; both share infrastructure)
 VIRTUAL MACHINE MANAGEMENT AND TOOLS
VIRTUAL MACHINE MANAGEMENT AND TOOLS
 System Center Virtual Machine Manager Physical resource optimization Simple identification of consolidation candidates Fast and reliable Physical to Virtual migration (P 2 V) Uses Volume Shadow Services Intelligent placement Placement is at the crux of maximizing the utilization of physical assets Centralized resource optimization Optimizing workloads for: Maximum number of virtual machines per servers Maximum dispersion across multiple servers
System Center Virtual Machine Manager Physical resource optimization Simple identification of consolidation candidates Fast and reliable Physical to Virtual migration (P 2 V) Uses Volume Shadow Services Intelligent placement Placement is at the crux of maximizing the utilization of physical assets Centralized resource optimization Optimizing workloads for: Maximum number of virtual machines per servers Maximum dispersion across multiple servers
 Virtual Machine Manager Rapid provisioning of new workloads Central library Self-service provisioning Industry standard storage architecture Employs distributed storage architecture on industry standard hardware and network infrastructure to use resources with optimal locality Host provisioning
Virtual Machine Manager Rapid provisioning of new workloads Central library Self-service provisioning Industry standard storage architecture Employs distributed storage architecture on industry standard hardware and network infrastructure to use resources with optimal locality Host provisioning
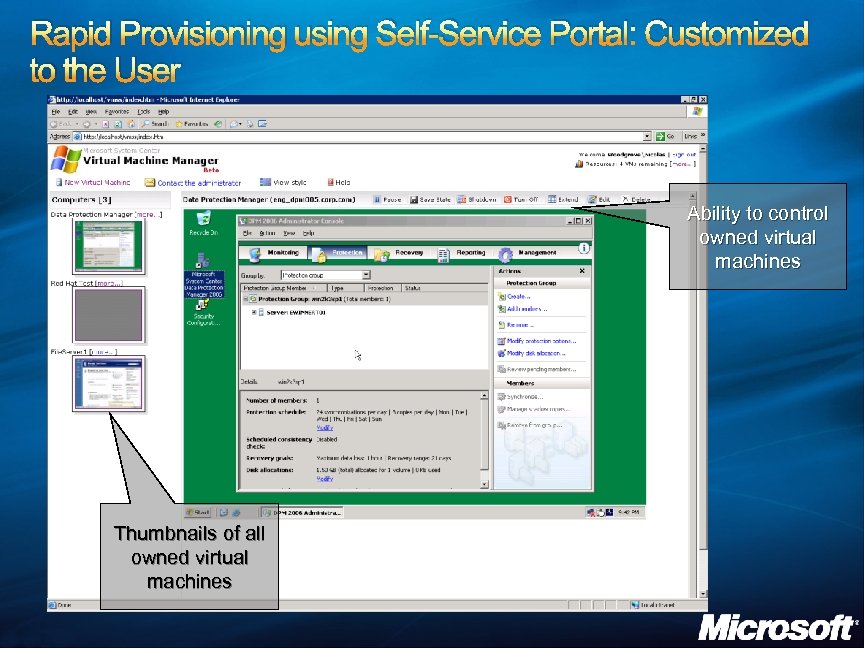 Rapid Provisioning using Self-Service Portal: Customized to the User Ability to control owned virtual machines Thumbnails of all owned virtual machines
Rapid Provisioning using Self-Service Portal: Customized to the User Ability to control owned virtual machines Thumbnails of all owned virtual machines
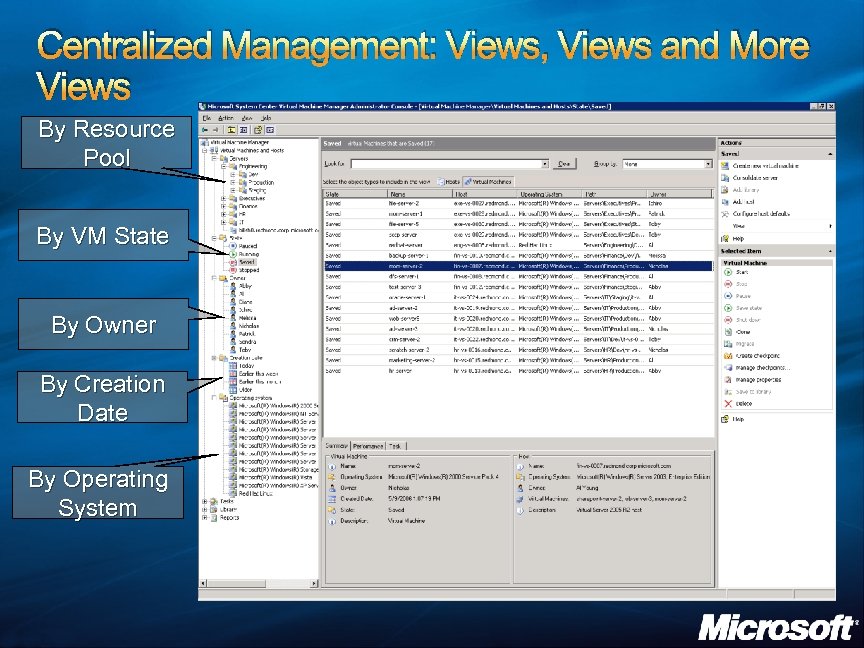 Centralized Management: Views, Views and More Views By Resource Pool By VM State By Owner By Creation Date By Operating System
Centralized Management: Views, Views and More Views By Resource Pool By VM State By Owner By Creation Date By Operating System
 IMPACT ON THE FACE OF IT
IMPACT ON THE FACE OF IT
 Skillset Technology Politics Architects Operating Systems Storage Networking Security Server Hardware Principals: P vs V Performance vs Flexibility Single points of failure Vendor Support Loss of ownership and control Shared resources Budgeting Operations Backup Patching Clustering disciplines Performance Monitoring Optimisation
Skillset Technology Politics Architects Operating Systems Storage Networking Security Server Hardware Principals: P vs V Performance vs Flexibility Single points of failure Vendor Support Loss of ownership and control Shared resources Budgeting Operations Backup Patching Clustering disciplines Performance Monitoring Optimisation
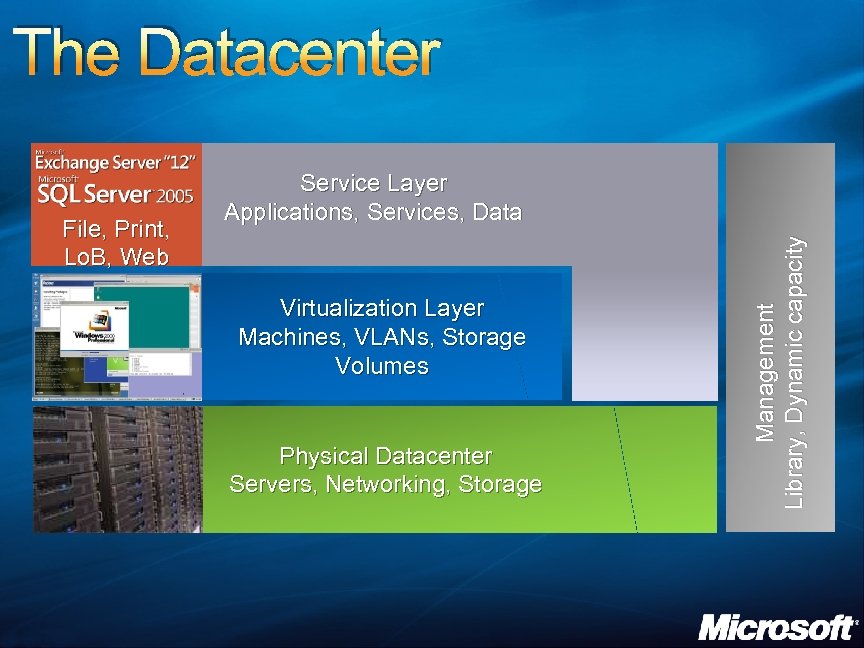 The Datacenter Virtualization Layer Machines, VLANs, Storage Volumes Physical Datacenter Servers, Networking, Storage Management Library, Dynamic capacity File, Print, Lo. B, Web Service Layer Applications, Services, Data
The Datacenter Virtualization Layer Machines, VLANs, Storage Volumes Physical Datacenter Servers, Networking, Storage Management Library, Dynamic capacity File, Print, Lo. B, Web Service Layer Applications, Services, Data
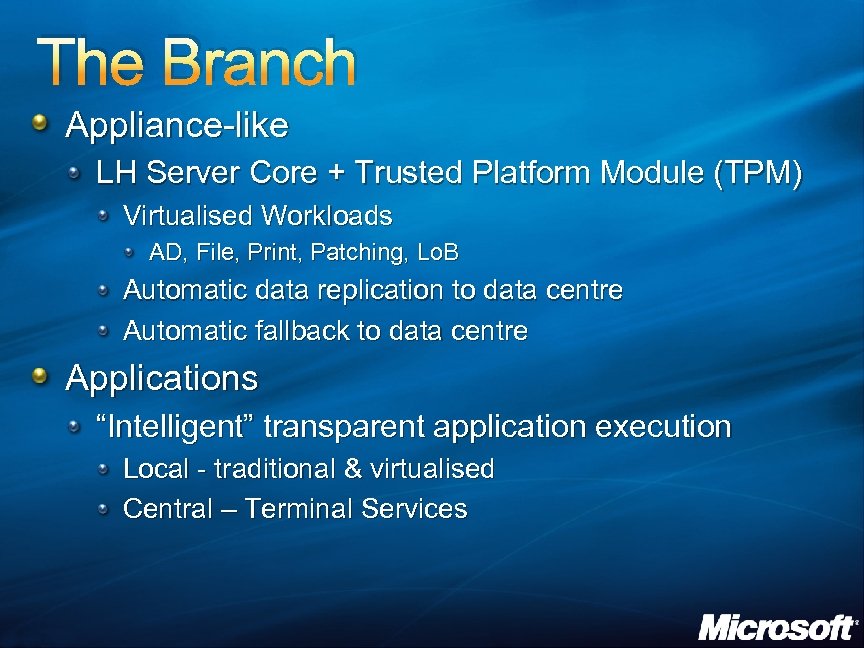 The Branch Appliance-like LH Server Core + Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Virtualised Workloads AD, File, Print, Patching, Lo. B Automatic data replication to data centre Automatic fallback to data centre Applications “Intelligent” transparent application execution Local - traditional & virtualised Central – Terminal Services
The Branch Appliance-like LH Server Core + Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Virtualised Workloads AD, File, Print, Patching, Lo. B Automatic data replication to data centre Automatic fallback to data centre Applications “Intelligent” transparent application execution Local - traditional & virtualised Central – Terminal Services
 Licensing the virtual. . . Windows licensed per physical processor socket (not core) Windows Server 2003 R 2 EE Includes license for 4 x Win 2 K 3 VMs Windows Server 2003 R 2 Datacenter Includes license for unlimited Win 2 K 3 VMs Server Products licensed per running virtual processor Vista Enterprise with Software Assurance License for 4 Instances in Virtual. PC 2007 http: //www. microsoft. com/licensing/highlights/virtualization. mspx
Licensing the virtual. . . Windows licensed per physical processor socket (not core) Windows Server 2003 R 2 EE Includes license for 4 x Win 2 K 3 VMs Windows Server 2003 R 2 Datacenter Includes license for unlimited Win 2 K 3 VMs Server Products licensed per running virtual processor Vista Enterprise with Software Assurance License for 4 Instances in Virtual. PC 2007 http: //www. microsoft. com/licensing/highlights/virtualization. mspx
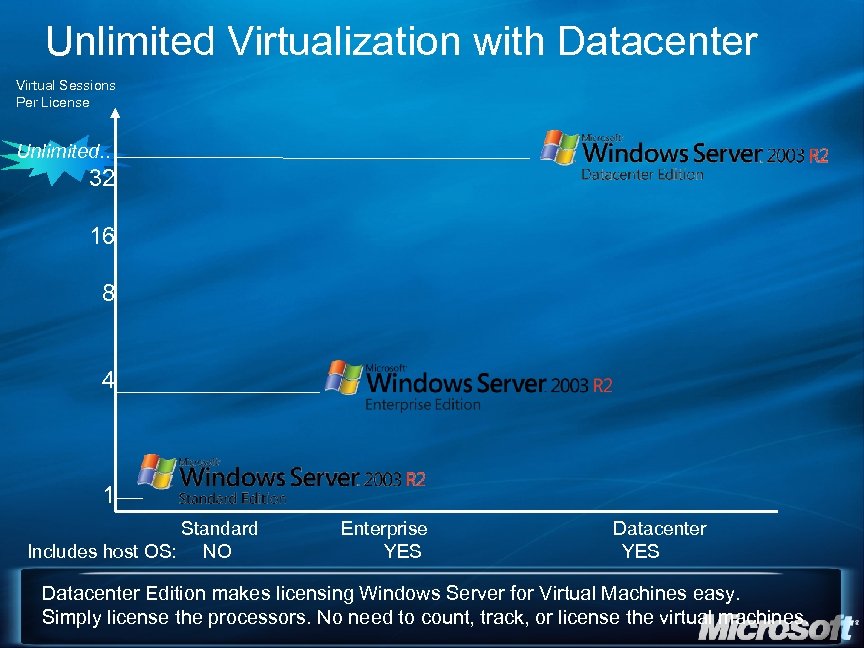 Unlimited Virtualization with Datacenter Virtual Sessions Per License Unlimited. . 32 16 8 4 1 Standard Includes host OS: NO Enterprise YES Datacenter Edition makes licensing Windows Server for Virtual Machines easy. Simply license the processors. No need to count, track, or license the virtual machines.
Unlimited Virtualization with Datacenter Virtual Sessions Per License Unlimited. . 32 16 8 4 1 Standard Includes host OS: NO Enterprise YES Datacenter Edition makes licensing Windows Server for Virtual Machines easy. Simply license the processors. No need to count, track, or license the virtual machines.
 Summary Virtual Server 2005 R 2 – Shipping today Released Q 4 2004 Well received in the industry Used for production server consolidation Remote management of virtual machine operations Great perf gains and functionality enhancement in SP 1 64 -bit host support, PXE support, and others
Summary Virtual Server 2005 R 2 – Shipping today Released Q 4 2004 Well received in the industry Used for production server consolidation Remote management of virtual machine operations Great perf gains and functionality enhancement in SP 1 64 -bit host support, PXE support, and others
 Summary WSV Windows Server codename Longhorn will have integrated virtualization support Hypercall interfaces can be used to support foreign operating systems Remote management thru robust WMI I/F’s Currently targeting H 1/2007 for public beta, RTM within 180 days of Longhorn Server Systems with processor virtualization extensions widely available from OEM’s today will be required.
Summary WSV Windows Server codename Longhorn will have integrated virtualization support Hypercall interfaces can be used to support foreign operating systems Remote management thru robust WMI I/F’s Currently targeting H 1/2007 for public beta, RTM within 180 days of Longhorn Server Systems with processor virtualization extensions widely available from OEM’s today will be required.
 Resources Virtual Server 2003 R 2 Free Download http: //www. microsoft. com/windowsserversystem/virtualserver/software/defa ult. mspx Virtual Server 2005 R 2 SP 1 Public Beta http: //connect. microsoft. com Guidance: Building a Virtual Test Lab http: //go. microsoft. com/fwlink/? Link. Id=50491 Lo. B Consolidation Guidance http: //www. microsoft. com/technet/itsolutions/ucs/ lob/lobsaovw. mspx Clustering Virtual Server & Scripting Virtual Server http: //www. microsoft. com/technet/prodtechnol/virtualserver/default. mspx
Resources Virtual Server 2003 R 2 Free Download http: //www. microsoft. com/windowsserversystem/virtualserver/software/defa ult. mspx Virtual Server 2005 R 2 SP 1 Public Beta http: //connect. microsoft. com Guidance: Building a Virtual Test Lab http: //go. microsoft. com/fwlink/? Link. Id=50491 Lo. B Consolidation Guidance http: //www. microsoft. com/technet/itsolutions/ucs/ lob/lobsaovw. mspx Clustering Virtual Server & Scripting Virtual Server http: //www. microsoft. com/technet/prodtechnol/virtualserver/default. mspx
 Complete your evaluation… And enter a prize draw for a 30 GB White: ZUNE Terms and conditions available on request
Complete your evaluation… And enter a prize draw for a 30 GB White: ZUNE Terms and conditions available on request
 Agenda 09: 00 – 09: 45 Welcome 09: 45 – 11: 00 Microsoft Virtualization Today and Tomorrow 11: 00 – 11: 15 Break 11: 15 – 12: 30 Managing a Mixed Virtual/Physical Environment: Tools and Techniques 12: 30 – 13: 30 Lunch 13: 30 – 14: 45 Windows Server Virtualization Deep Dive 14: 45 – 15: 00 Break 15: 00 – 16: 00 Virtual Server notes from the field 16: 00 – 16: 20 Panel Questions and Answers 16: 20 – 16: 30 Event Closure and Zune “raffle”
Agenda 09: 00 – 09: 45 Welcome 09: 45 – 11: 00 Microsoft Virtualization Today and Tomorrow 11: 00 – 11: 15 Break 11: 15 – 12: 30 Managing a Mixed Virtual/Physical Environment: Tools and Techniques 12: 30 – 13: 30 Lunch 13: 30 – 14: 45 Windows Server Virtualization Deep Dive 14: 45 – 15: 00 Break 15: 00 – 16: 00 Virtual Server notes from the field 16: 00 – 16: 20 Panel Questions and Answers 16: 20 – 16: 30 Event Closure and Zune “raffle”
 © 2007 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Windows Vista and other product names are or may be registered trademarks and/or trademarks in the U. S. and/or other countries. The information herein is for informational purposes only and represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation as of the date of this presentation. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information provided after the date of this presentation. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, AS TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PRESENTATION.
© 2007 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Windows Vista and other product names are or may be registered trademarks and/or trademarks in the U. S. and/or other countries. The information herein is for informational purposes only and represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation as of the date of this presentation. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information provided after the date of this presentation. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, AS TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PRESENTATION.


