0d019e6e98d08cc9158a8ff17038d535.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Microsoft HPC Server 2008 A brief overview with emphasis on cluster performance Eric Lantz (elantz@microsoft. com) Lead Program Manager , HPC Team Microsoft Corp. Fab Tillier (ftillier@microsoft. com ) Developer, HPC Team Microsoft Corp.

HPC Server 2008 A Brief Overview of this second release from Microsoft’s HPC team.
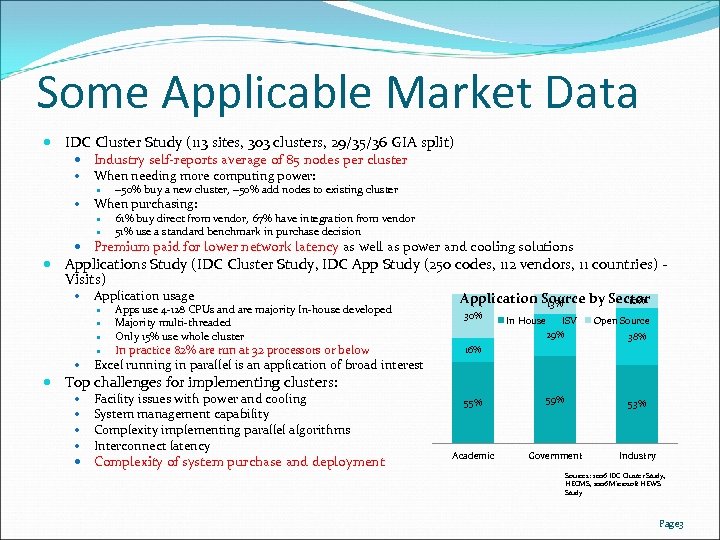
Some Applicable Market Data IDC Cluster Study (113 sites, 303 clusters, 29/35/36 GIA split) Industry self-reports average of 85 nodes per cluster When needing more computing power: When purchasing: ~50% buy a new cluster, ~50% add nodes to existing cluster 61% buy direct from vendor, 67% have integration from vendor 51% use a standard benchmark in purchase decision Premium paid for lower network latency as well as power and cooling solutions Applications Study (IDC Cluster Study, IDC App Study (250 codes, 112 vendors, 11 countries) Visits) Application usage Apps use 4 -128 CPUs and are majority In-house developed Majority multi-threaded Only 15% use whole cluster In practice 82% are run at 32 processors or below Application Source by Sector 10% 13% 30% In House ISV 29% Open Source 38% 16% Excel running in parallel is an application of broad interest Top challenges for implementing clusters: Facility issues with power and cooling System management capability Complexity implementing parallel algorithms Interconnect latency Complexity of system purchase and deployment 55% 59% 53% Academic Government Industry Sources: 2006 IDC Cluster Study, HECMS, 2006 Microsoft HEWS Study Page 3
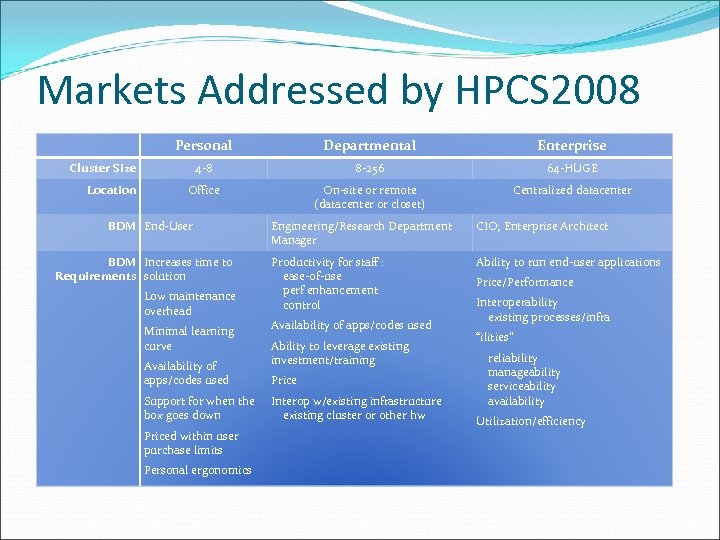
Markets Addressed by HPCS 2008 Personal Departmental Enterprise 4 -8 8 -256 64 -HUGE Office On-site or remote (datacenter or closet) Centralized datacenter Cluster Size Location BDM End-User BDM Increases time to Requirements solution Low maintenance overhead Minimal learning curve Availability of apps/codes used Support for when the box goes down Priced within user purchase limits Personal ergonomics Engineering/Research Department Manager CIO; Enterprise Architect Productivity for staff : ease-of-use perf enhancement control Ability to run end-user applications Availability of apps/codes used Ability to leverage existing investment/training Price Interop w/existing infrastructure existing cluster or other hw Price/Performance Interoperability existing processes/infra “ilities” reliability manageability serviceability availability Utilization/efficiency
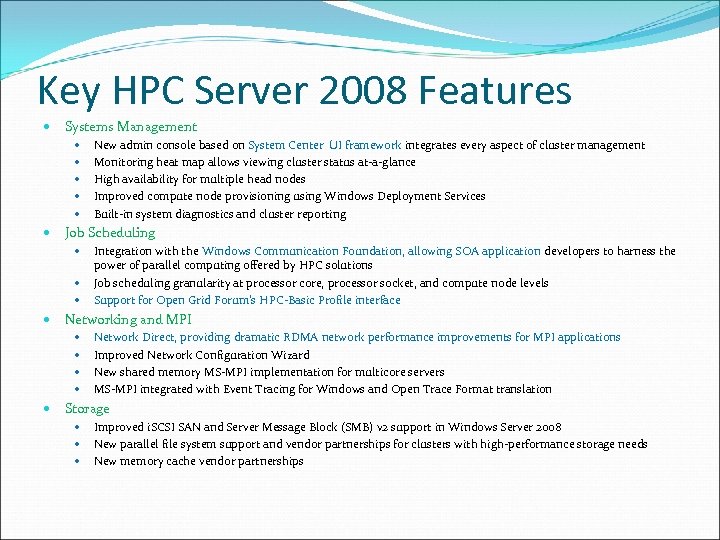
Key HPC Server 2008 Features Systems Management Job Scheduling Integration with the Windows Communication Foundation, allowing SOA application developers to harness the power of parallel computing offered by HPC solutions Job scheduling granularity at processor core, processor socket, and compute node levels Support for Open Grid Forum’s HPC-Basic Profile interface Networking and MPI New admin console based on System Center UI framework integrates every aspect of cluster management Monitoring heat map allows viewing cluster status at-a-glance High availability for multiple head nodes Improved compute node provisioning using Windows Deployment Services Built-in system diagnostics and cluster reporting Network Direct, providing dramatic RDMA network performance improvements for MPI applications Improved Network Configuration Wizard New shared memory MS-MPI implementation for multicore servers MS-MPI integrated with Event Tracing for Windows and Open Trace Format translation Storage Improved i. SCSI SAN and Server Message Block (SMB) v 2 support in Windows Server 2008 New parallel file system support and vendor partnerships for clusters with high-performance storage needs New memory cache vendor partnerships
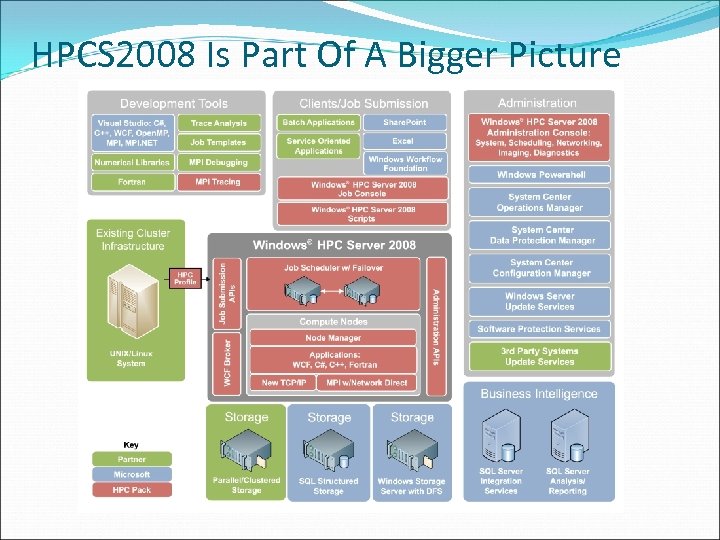
HPCS 2008 Is Part Of A Bigger Picture

HPC Server 2008 Push for Performance 8
End-To-End Approach To Performance Multi-Core is Key Big improvements in MS-MPI shared memory communications Network. Direct A new RDMA networking interface built for speed and stability Devs can't tune what they can't see MS-MPI integrated with Event Tracing for Windows Perf takes a village Partnering for perf Regular Top 500 runs Performed by the HPCS 2008 product team on a permanent, scale- testing cluster 9
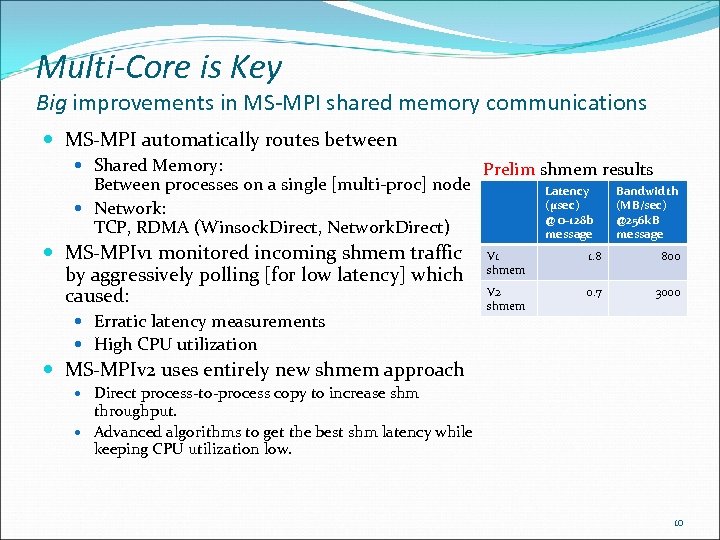
Multi-Core is Key Big improvements in MS-MPI shared memory communications MS-MPI automatically routes between Shared Memory: Between processes on a single [multi-proc] node Network: TCP, RDMA (Winsock. Direct, Network. Direct) MS-MPIv 1 monitored incoming shmem traffic by aggressively polling [for low latency] which caused: Erratic latency measurements Prelim shmem results Latency (µsec) @ 0 -128 b message Bandwidth (MB/sec) @256 k. B message V 1 shmem 1. 8 800 V 2 shmem 0. 7 3000 High CPU utilization MS-MPIv 2 uses entirely new shmem approach Direct process-to-process copy to increase shm throughput. Advanced algorithms to get the best shm latency while keeping CPU utilization low. 10
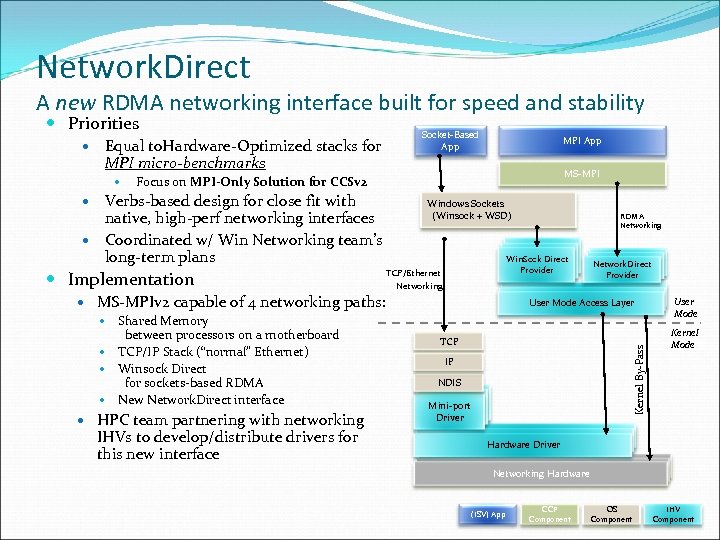
Network. Direct A new RDMA networking interface built for speed and stability Priorities Equal to. Hardware-Optimized stacks for MPI micro-benchmarks Socket-Based App MPI App MS-MPI Focus on MPI-Only Solution for CCSv 2 Verbs-based design for close fit with native, high-perf networking interfaces Coordinated w/ Win Networking team’s long-term plans Implementation Windows Sockets (Winsock + WSD) Networking Win. Sock Direct Hardware Provider TCP/Ethernet Networking HPC team partnering with networking IHVs to develop/distribute drivers for this new interface TCP Kernel By-Pass Shared Memory between processors on a motherboard TCP/IP Stack (“normal” Ethernet) Winsock Direct for sockets-based RDMA New Network. Direct interface Networking Network. Direct Hardware Provider Networking Hardware User Mode Access Layer MS-MPIv 2 capable of 4 networking paths: RDMA Networking IP NDIS Networking Mini-port Hardware Driver User Mode Kernel Mode Networking Hardware Driver Networking Hardware (ISV) App CCP Component OS Component IHV Component
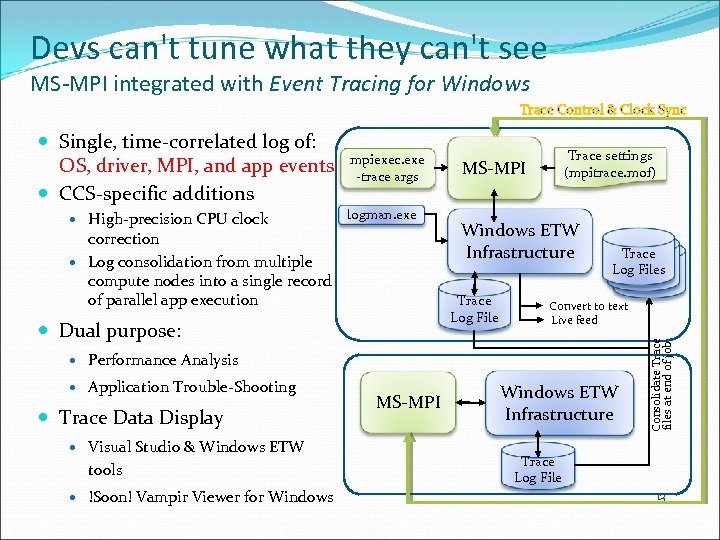
Devs can't tune what they can't see MS-MPI integrated with Event Tracing for Windows Trace Control & Clock Sync High-precision CPU clock mpiexec. exe -trace args logman. exe correction Log consolidation from multiple compute nodes into a single record of parallel app execution Windows ETW Infrastructure Trace Log File Dual purpose: Trace settings (mpitrace. mof) MS-MPI Trace Log. Files Convert to text Live feed Performance Analysis Application Trouble-Shooting Trace Data Display Visual Studio & Windows ETW tools !Soon! Vampir Viewer for Windows MS-MPI Windows ETW Infrastructure Consolidate Trace files at end of job Single, time-correlated log of: OS, driver, MPI, and app events CCS-specific additions Trace Log File 13

Perf takes a village (Partnering for perf) Networking Hardware vendors Network. Direct design review Network. Direct & Winsock. Direct provider development Windows Core Networking Team Commercial Software Vendors Win 64 best practices MPI usage patterns Collaborative performance tuning 3 ISVs and counting 4 benchmarking centers online IBM, HP, Dell, SGI 14
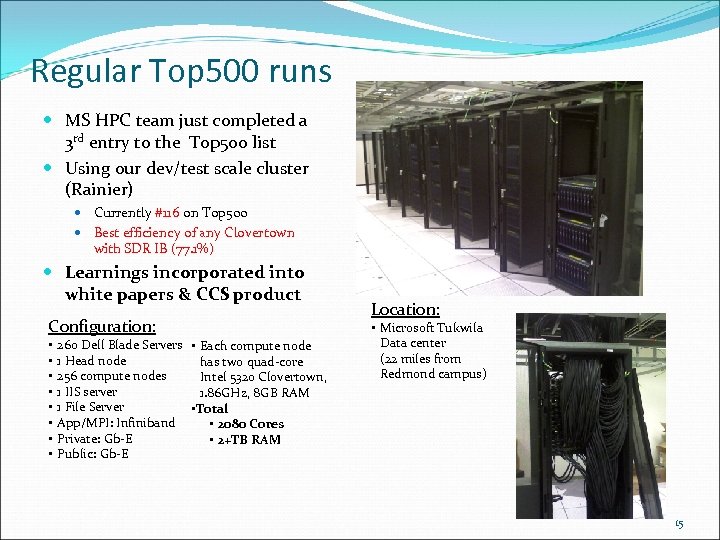
Regular Top 500 runs MS HPC team just completed a 3 rd entry to the Top 500 list Using our dev/test scale cluster (Rainier) Currently #116 on Top 500 Best efficiency of any Clovertown with SDR IB (77. 1%) Learnings incorporated into white papers & CCS product Configuration: • • 260 Dell Blade Servers • Each compute node 1 Head node has two quad-core 256 compute nodes Intel 5320 Clovertown, 1 IIS server 1. 86 GHz, 8 GB RAM 1 File Server • Total App/MPI: Infiniband • 2080 Cores Private: Gb-E • 2+TB RAM Public: Gb-E Location: • Microsoft Tukwila Data center (22 miles from Redmond campus) 15

Network. Direct Details

What is Network Direct? What Verbs should look like for Windows: Service Provider Interface (SPI) Verbs Specifications are not APIs! Aligned with industry-standard Verbs Some changes for simplicity Some changes for convergence of IB and i. WARP Windows-centric design Leverage Windows asynchronous I/O capabilities
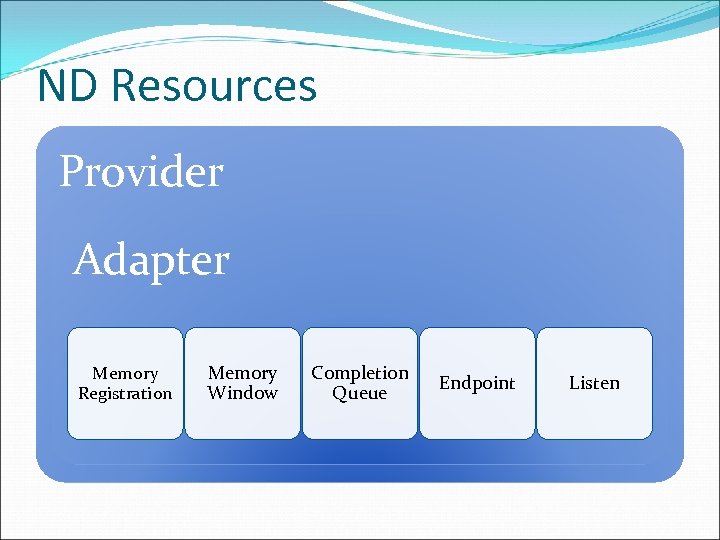
ND Resources Provider Adapter Memory Registration Memory Window Completion Queue Endpoint Listen
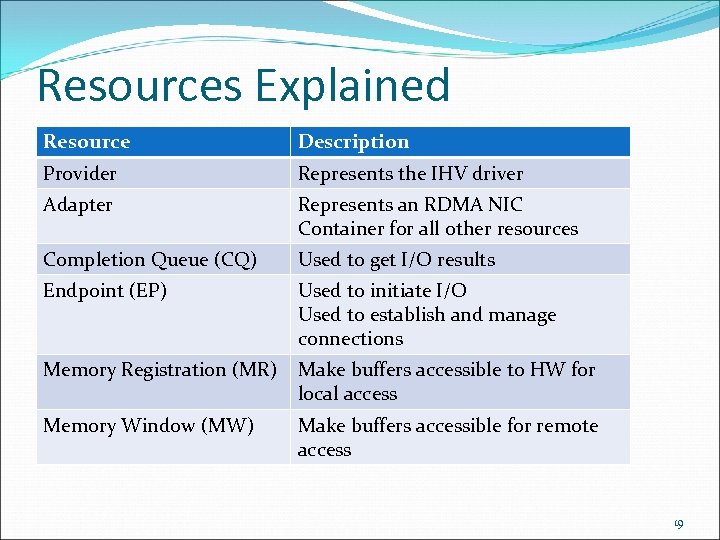
Resources Explained Resource Description Provider Represents the IHV driver Adapter Represents an RDMA NIC Container for all other resources Completion Queue (CQ) Used to get I/O results Endpoint (EP) Used to initiate I/O Used to establish and manage connections Memory Registration (MR) Make buffers accessible to HW for local access Memory Window (MW) Make buffers accessible for remote access 19
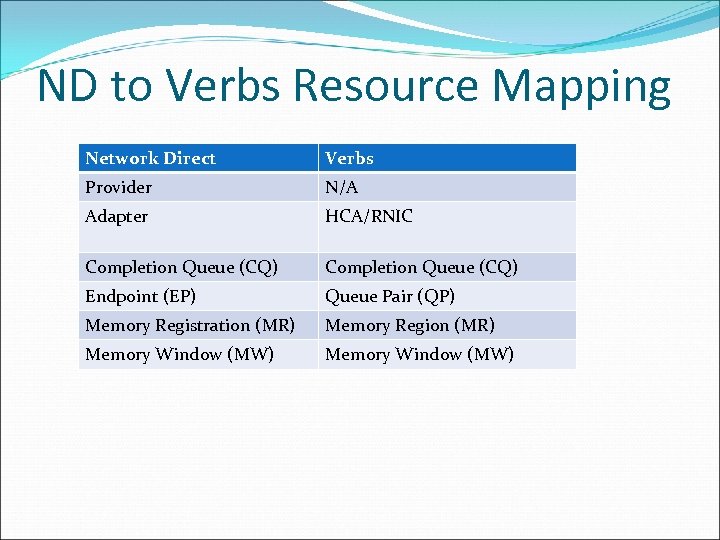
ND to Verbs Resource Mapping Network Direct Verbs Provider N/A Adapter HCA/RNIC Completion Queue (CQ) Endpoint (EP) Queue Pair (QP) Memory Registration (MR) Memory Region (MR) Memory Window (MW)

ND SPI Traits Explicit resource management Application manages memory registrations Applications manages CQ to Endpoint bindings Only asynchronous data transfers Initiate requests on an Endpoint Get request results from the associated CQ Application can use event driven and/or polling I/O model Leverage Win 32 asynchronous I/O for event driven operation No kernel transitions for polling mode “Simple” Memory Management Model Memory Registrations are used for local access Memory Windows are used for remote access IP Addressing No proprietary address management required 21
ND SPI Model Collection of COM interfaces No COM runtime dependency Use the interface model only Follows model adopted by the UMDF Thread-less providers No callbacks Aligned with industry standard Verbs Facilitates IHV adoption

Why COM Interfaces? Well understood programming model Easily extensible via IUnknown: : Query. Interface Allows retrieving any interface supported by an object Object oriented C/C++ language independent Callers and providers can be independently implemented in C or C++ without impact on one another Interfaces support native code syntax - no wrappers

Asynchronous Operations Win 32 Overlapped operations used for: Memory Registration CQ Notification Connection Management Client controls threading and completion mechanism I/O Completion Port or Get. Overlapped. Result Simpler for kernel drivers to support Io. Complete. Request – I/O manager handles the rest.

References Microsoft HPC web site - HPC Server 2008 (beta) Available Now!! http: //www. microsoft. com/hpc Network Direct SPI documentation, header and test executables In the HPC Server 2008 (beta) SDK http: //www. microsoft. com/hpc Microsoft HPC Community Site http: //windowshpc. net/default. aspx Argonne National Lab’s MPI website http: //www-unix. mcs. anl. gov/mpi/ CCS 2003 Performance Tuning Whitepaper http: //www. microsoft. com/downloads/details. aspx? Family. ID=40 cd 8 152 -f 89 d-4 abf-ab 1 c-a 467 e 180 cce 4&Display. Lang=en Or go to http: //www. microsoft. com/downloads and search for CCS Performance

Backup Slides
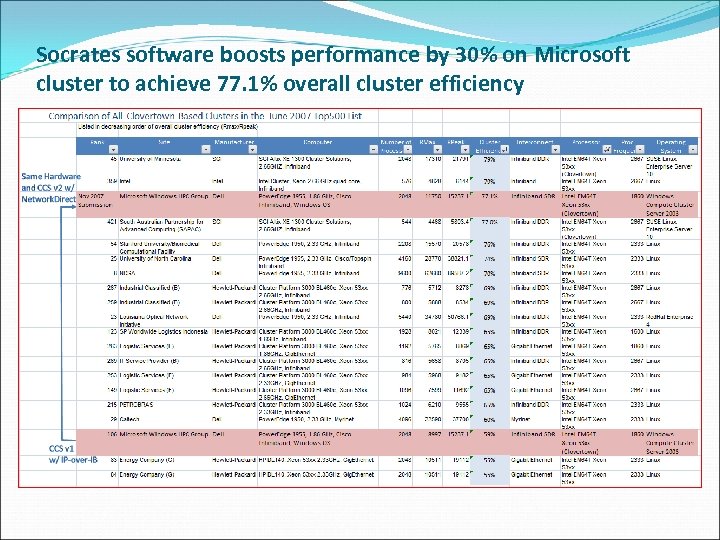
Socrates software boosts performance by 30% on Microsoft cluster to achieve 77. 1% overall cluster efficiency
Performance improvement was demonstrated with exactly the same hardware and is attributed to : Improved networking performance of MS-MPI’s Network. Direct interface Entirely new MS-MPI implementation for shared memory communications Tools and scripts to optimize process placement and tune the Linpack parameters for this 256 -node, 2048 -processor cluster Windows Server 2008 improvements in querying completion port status Use of Visual Studio’s Profile Guided Optimization (POGO) on the Linpack, MS-MPI, and the ND provider binaries
0d019e6e98d08cc9158a8ff17038d535.ppt