0f05270b39dfa90bdd6ce685ac2ff5e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Microsoft Biz. Talk Server Basics

Introduction • Biz. Talk belongs to the Microsoft Server family • Connects disparate systems together • Communication among systems are established through messages • All messages inside Biztalk are XML data • Since XML can be interpreted in any system, Biz. Talk helps in connectivity

Need for communication • An organisation may follow a software with different configuration for a process and another software with entirely different configuration to take care of another process • Both processes may depend on each other’s data • For example a company’s attendance system need to be connected with payroll system • Or a purchase order need to be communicated to invoice generating system

History of Biz. Talk Server • 2000 – Microsoft Released the first Version of Biz. Talk – Editor – Writing XML Data – Mapper – Translate data from source format to destination format – Management Desk – Tracking data – Protocols supported – EDI, HTTPS, MSMQ, SMTP, FTP

History (contd. . . ) • 2002 – Next version. Not much change • 2004 – Added Human Workflow Services (HWS) and Business Activity Services – Supported by. Net framework 1. 0 – Integrated VS 2003 support for editor and mapper • 2006 – Business Activity Monitor (BAM) was added. Also Health and Activity Tracking component for tracking the server status was added. –. Net framework 2. 0 support – Integrated VS 2005 support

History (Contd. . . ) • 2007 – Also called as 2006 R 2 (Release 2). – Rich UI administration was incorporated. –. Net Framework 3. 0 (WCF, WF) support • 2009 – Recent version. – RFID support – Separate RFID Server)
Overview of Basic Configuration • Basic configuration does not allow remote SQL server. To use remote SQL server use custom configuration • The following need to be configured: – Enterprise SSO (Single Sign On) • This is used for managing credentials of users who can log on the server. • Enterprise SSO Secret Back. Up – This keeps the password that can be used for taking a back up of credentials in case of any system crash. • After configuring this component a database SSODB is created in MS SQL server

Basic Configuration Contd. . • Group – Collection of settings that govern the way Biz. Talk server behaves and the data store it uses – After this step the following databases – Biz. Talk. Mgmt. Db, Biz. Talk. Msg. Box. Db, Biz. Talk. DTADb are created • Biz. Talk Runtime – This is to manage the routing capabilities

Basic Configuration Contd. . • MSMQ – Microsoft Message Queue. This is to manage messages that are transferred to and from the server • Business Rules Engine – This configuration takes care of business rules necessary for the server. – The configurations are stored in Biz. Talk. Rule. Engine. Db. – Service used is Rule Engine update service. – Initiates action based on evaluation

Basic Configuration Contd. . • HWS – Human Workflow Services – Two components • HWS Runtime • HWS Webservice – encapsulates the functionality of client applications like sharepoint to provide workflow capabilities to information workers – DB – Hws. Db – Service – HWS Runtime Account and HWS Webservice Account – This dynamically composes workflow
Basic Configuration Contd. . • BAM – Business Activity Monitor – BAM Tools – Provides business users a set of monitoring tools • BAM Alerts – Notification services are provided based on subscription – Uses DB like BAMAlerts. NSMain. Application • BAMPrimary. Import, BAMStar. Schema, BAMArchieve, BAMAnalysis are the other databases used – BAM Portal – Service used is Biz. Talk EDI/AS 2 Runtime. Messages are sent and received using EDI/AS 2 Protocol

Biz. Talk Editor - Overview • Editor is used for generating Schema. • Biz. Talk generates XDS (XML Schema Definition) as the application communicates through XML • Editor comes as a part of Visual Studio IDE. • In VS IDE, create a biztalk project and add a schema file to create a schema.

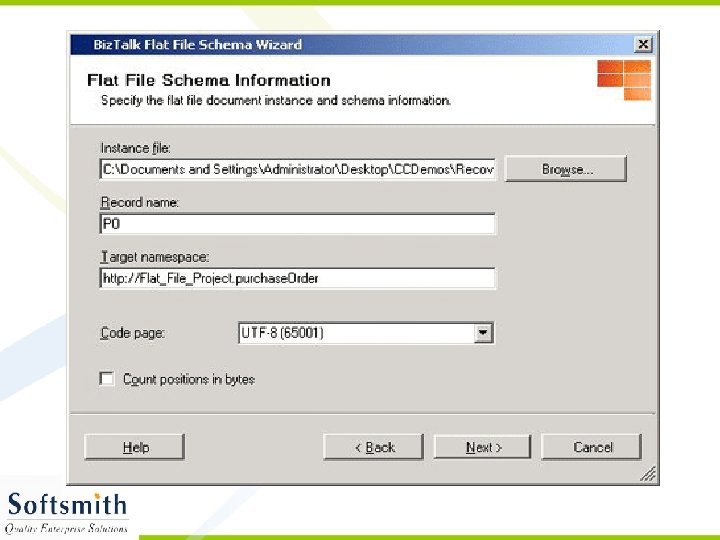
Creating XSD • Open Visual Studio 2005 (if you are using Biz. Talk 2006 and higher version) • Click on File -> New Project • Select Biz. Talk Projects and click on Empty Biz. Talk Application • Give a name and click OK • In the solution explorer, right click on the project and select Add -> New Item • Select Schema Files on the left pane and select Flat File Schema Wizard. • Refer to the screen shots for further processes.
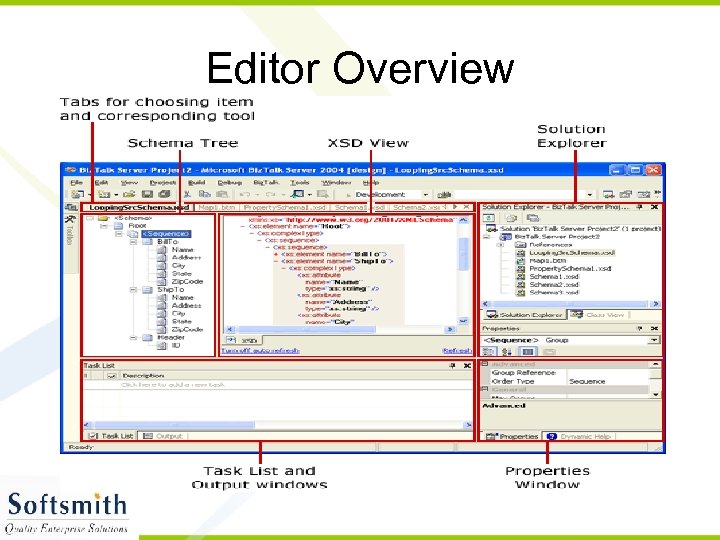
Editor Overview

Flat File Schema Wizard • Refer to notes page for explanation
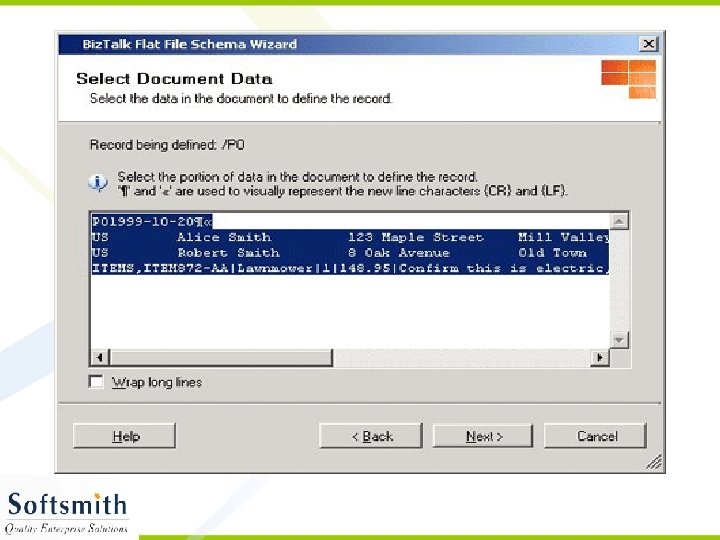
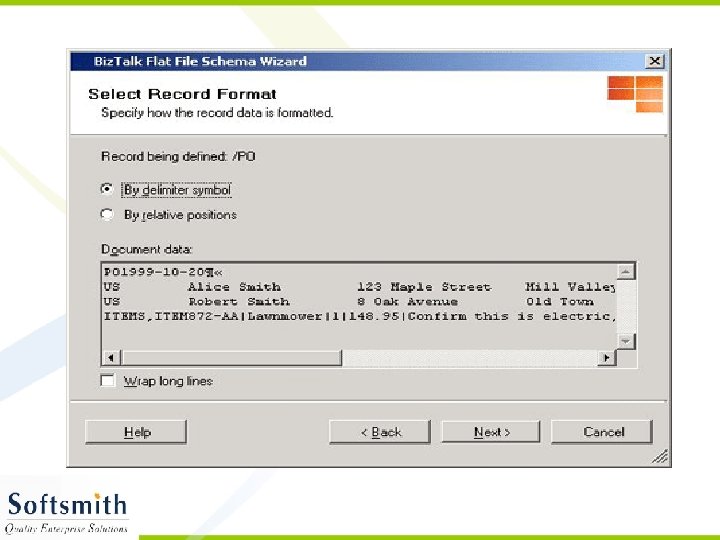
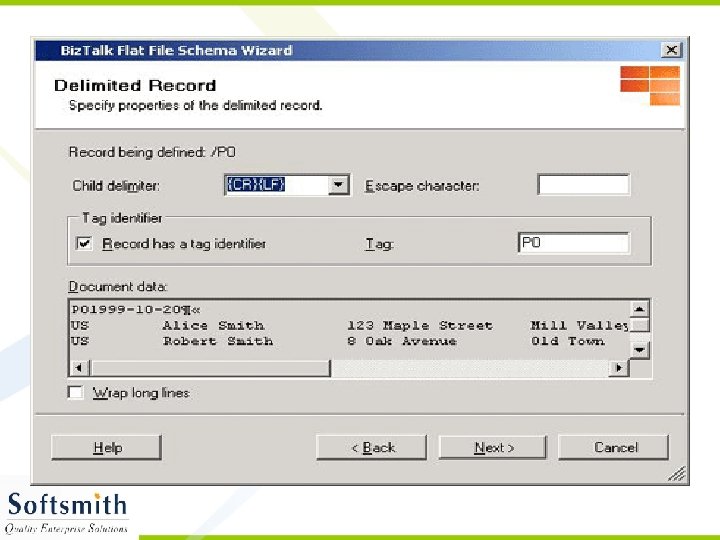
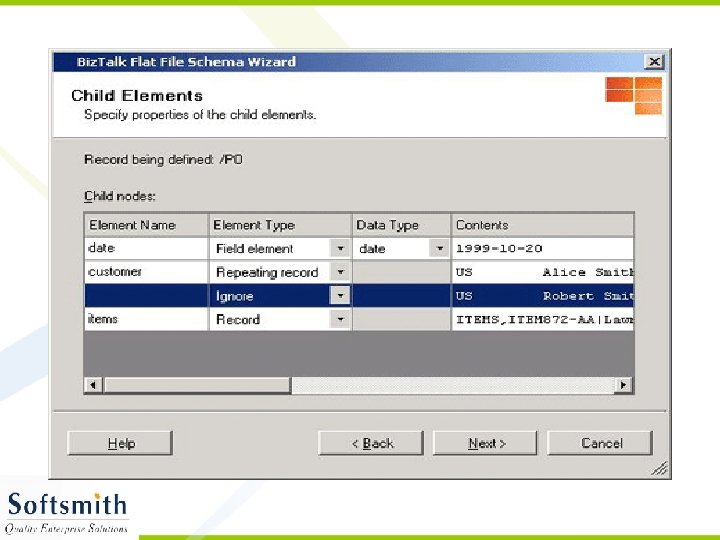
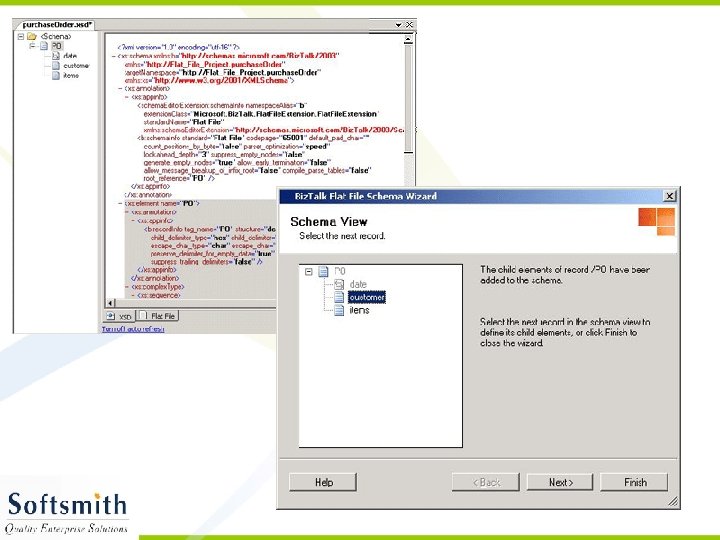
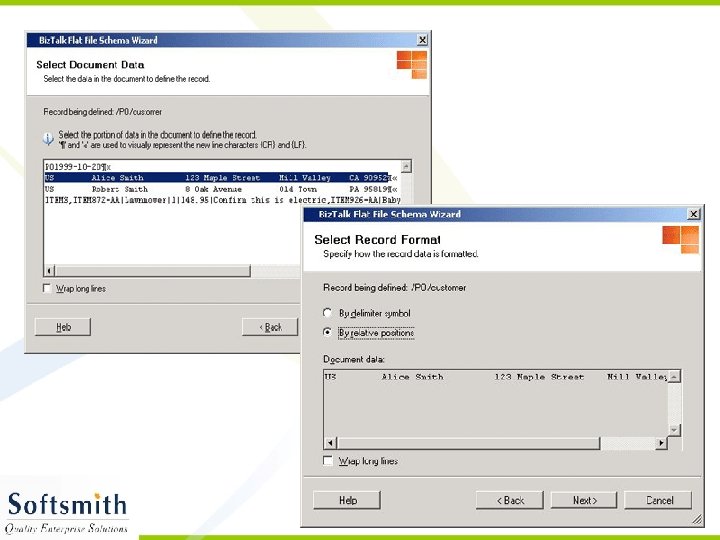
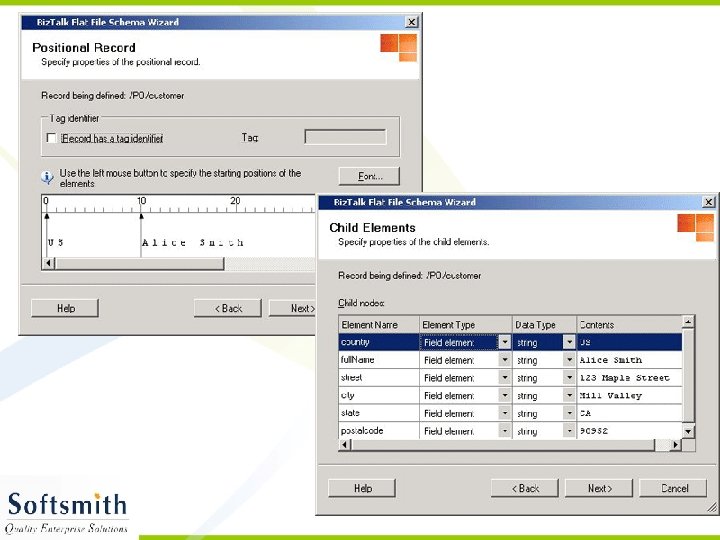
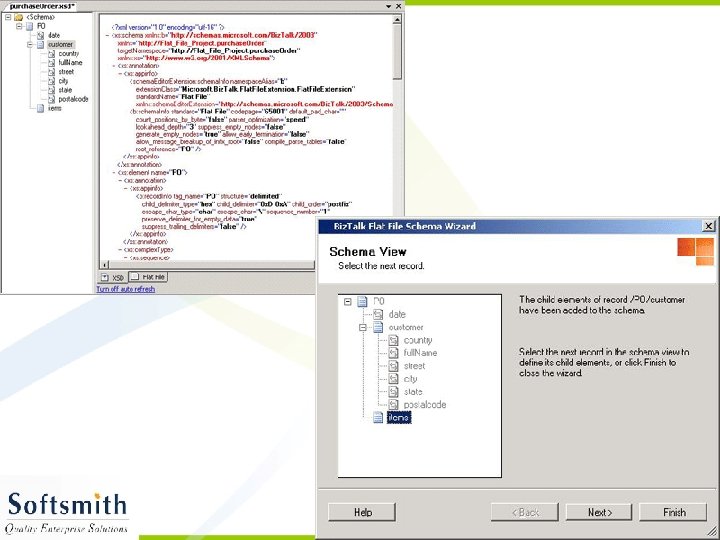
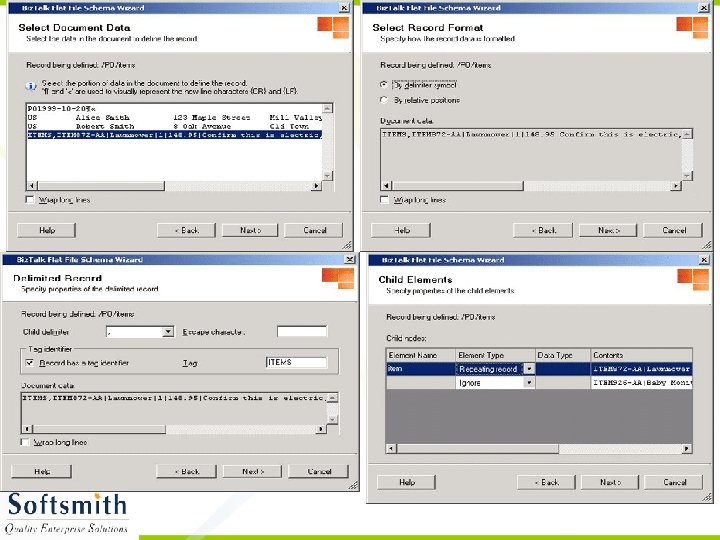
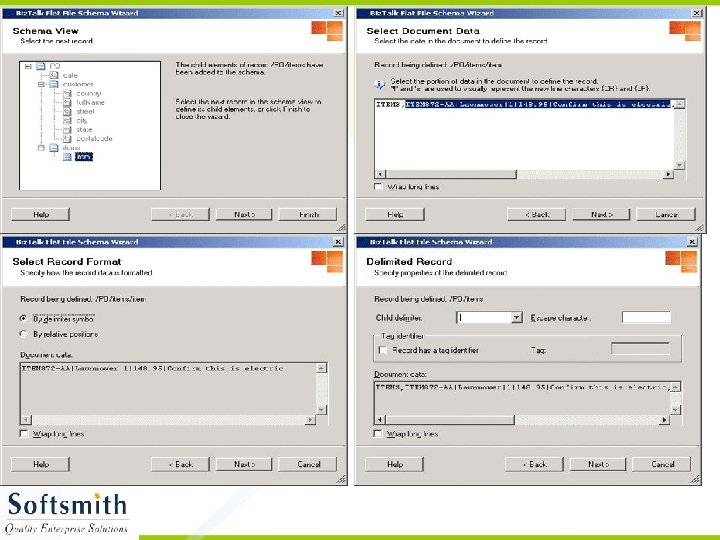
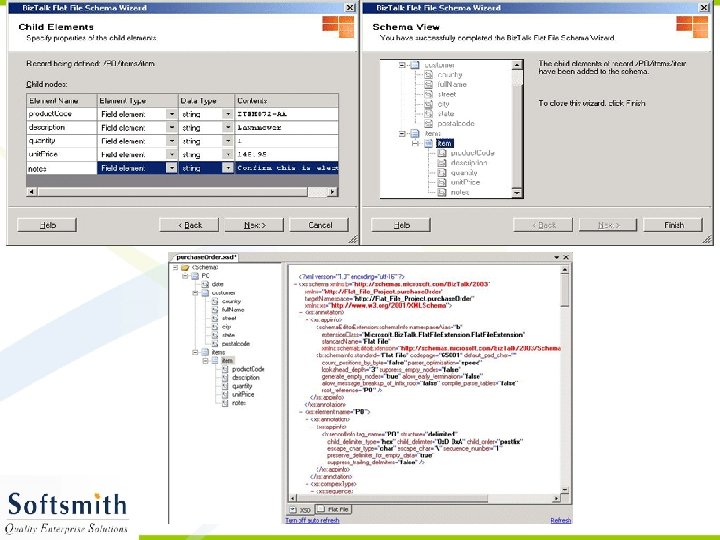

Generating XML from the XSD • Right click on the Project and select Validate Schema • Once the validation is over, click on Generate Instance Message. • An empty XML file with sample data entry in accordance to the schema will be generated. • This XML file can be modified and used with any application that supports XML.

Biz. Talk Mapper - Overview • Mapper is a tool that is used for mapping data • The source data is mapped with the destination data • Since Biz. Talk involves with connecting disparate systems, the source data need to be transformed to another format acceptable by the destination. • Hence Mapper plays a vital role. • Mapper too comes integrated with VS IDE.

Creating Maps • Open Biz. Talk Project containing the XSDs • Right click on the project and select Add -> New Item. • Select Maps in the left pane and Empty Map in the right pane • Give a name for the map and click OK • It will open a GUI where we can select the source and the destination schema and map accordingly. • Refer to the screen shots for more details.
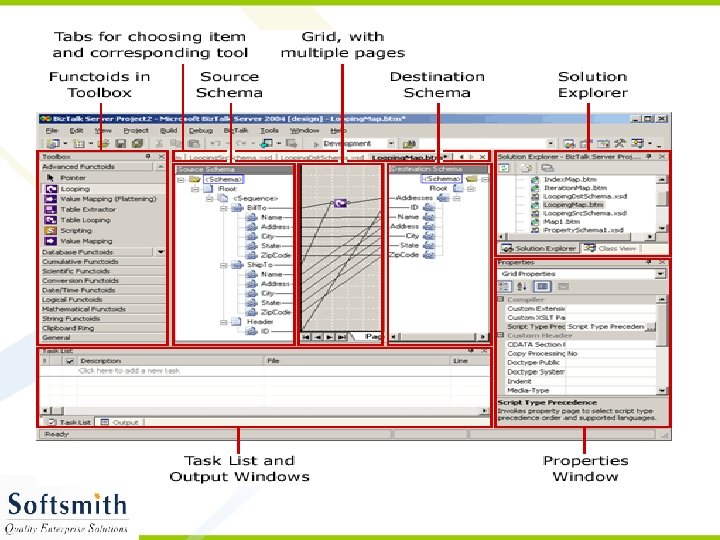
Functoids • Functoids are functions that can be used with mapper. • The source data can be applied with functoids and transformed to destination friendly data. • Many functions for manipulating strings (concat, uppercase conversion etc), numbers (add, multiply etc), scientific functions (log, exponent etc), database are available. • Refer to the tool bar, the violet color box in the grid in the previous picture.

Biz. Talk Administration Console • Administration console is used for performing administrative tasks like – Starting and stopping an application – Taking reports concerned with messages transferred, application usage etc – Configuring send and receiving ports – Adding resources to the application – Managing Orchestration, Maps, Schemas, Pipelines for the application

Biz. Talk Application • Feature of biz talk server that helps in deployment, management, trouble shooting of biz talk server solutions • Logical grouping of artifacts – – – Biztalk and. Net assemblies Send ports, groups Receive ports, locations Policies Certificates, scripts, COM Components Biz. Talk specific resources (schema, map, orchestration, pipeline)

Orchestrations • To add orchestration for a biz talk project, right click on the project and select Add -> New Item • Select Orchestration from the left pane and empty orchestration from the right pane • Give a name for the orchestration and click OK • A new orchestration designer with a file extension odx is opened. • Use the tool bar to add components that we want.

Pipelines • To add pipelines for a biz talk project, right click on the project and select Add -> New Item • Select Pipelines from the left pane and either send pipeline or receive pipeline from the right pane • Give a name for the pipeline selected and click OK • A new pipeline designer is opened. • Use the tool bar to add components that we want.
Receive Pipeline • This is for transforming data at the receiving end • It has – Decoder – to decode the incoming data (MIME decoder) – Disassembler – to convert data (flat file or any) to XML – Validator – to validate the generated XML against a schema (XSD) – Party Resolver – To determine identity of party from who the message is received.

Send Pipeline • This is present at the sending end for transforming the outgoing message • It has – Pre assembler – optional component containing custom tools – Assembler – Converting XML data to destination data – Encoder – To encode the outgoing data

Human Workflow Services • This is for dynamically configuring workflow • We can define constraints and lot of other condtions and design the workflow. • Hws. Db stores details about workflow. • Refer to screen shots in the following slides for more details about Human Workflow Services

Business Rule Composer • This is used for composing business rules • We can set an action to be performed upon an occurrence of an event • Actions are evaluated based on the facts (rules) • We can compose vocabulary (definitions) or policy (logical grouping of rules) using business rule composer.
0f05270b39dfa90bdd6ce685ac2ff5e8.ppt