3a92219a534f36ac7f49d9cc85f5b845.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Microsoft AREC TAM Internship SQL Server Performance Tuning(I) -- SQL Server 2000 Haijun Yang AREC SQL Support Team mailto: hjyang@microsoft. com Feb, 2001
Microsoft AREC TAM Internship SQL Server Performance Tuning(I) -- SQL Server 2000 Haijun Yang AREC SQL Support Team mailto: hjyang@microsoft. com Feb, 2001
 Agenda n n n Introduction to Optimizing Queries Index Strategies Query Plan Analysis 2
Agenda n n n Introduction to Optimizing Queries Index Strategies Query Plan Analysis 2
 Overview n n Introduction to the Query Optimizer Obtaining Query Plan Information Indexing Fundamentals Introduction to Statistics 3
Overview n n Introduction to the Query Optimizer Obtaining Query Plan Information Indexing Fundamentals Introduction to Statistics 3
 Function of the Query Optimizer n Determines the Most Efficient Query Plan n n n Determining whether indexes exist and evaluating their usefulness Determining which indexes or columns can be used Determining how to process joins Using cost-based evaluation Creating column statistics Produces a Query Plan Uses Available Information 4
Function of the Query Optimizer n Determines the Most Efficient Query Plan n n n Determining whether indexes exist and evaluating their usefulness Determining which indexes or columns can be used Determining how to process joins Using cost-based evaluation Creating column statistics Produces a Query Plan Uses Available Information 4
 How the Query Optimizer Uses Cost-Based Optimization n Limits the Number of Optimization Plans n n Cost is estimated in terms of I/O and CPU cost Determines Query Processing Time n n Use of physical operators and sequence of operations Use of parallel and serial processing 5
How the Query Optimizer Uses Cost-Based Optimization n Limits the Number of Optimization Plans n n Cost is estimated in terms of I/O and CPU cost Determines Query Processing Time n n Use of physical operators and sequence of operations Use of parallel and serial processing 5
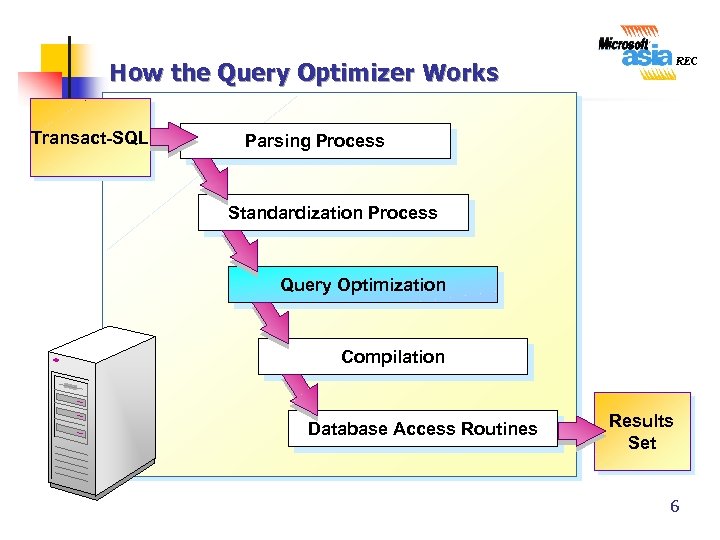 How the Query Optimizer Works Transact-SQL Parsing Process Standardization Process Query Optimization Compilation Database Access Routines Results Set 6
How the Query Optimizer Works Transact-SQL Parsing Process Standardization Process Query Optimization Compilation Database Access Routines Results Set 6
 Query Optimization Phases n Query Analysis n n Index Selection n Identifies the search and join criteria of the query Determines whether an index or indexes exist Assesses the usefulness of the index or indexes Join Selection n Evaluates which join strategy to use 7
Query Optimization Phases n Query Analysis n n Index Selection n Identifies the search and join criteria of the query Determines whether an index or indexes exist Assesses the usefulness of the index or indexes Join Selection n Evaluates which join strategy to use 7
 Caching Query Plan n Storing a Query Plan in Memory n n n Using an Execution Context n n n One copy for all serial executions Another copy for all parallel executions An existing query plan is reused, if one exists A new query plan is generated, if one does not exist Recompiling Query Plans n Changes in database cause query plan to be inefficient or invalid 8
Caching Query Plan n Storing a Query Plan in Memory n n n Using an Execution Context n n n One copy for all serial executions Another copy for all parallel executions An existing query plan is reused, if one exists A new query plan is generated, if one does not exist Recompiling Query Plans n Changes in database cause query plan to be inefficient or invalid 8
 • Obtaining Query Plan Information n n Querying the sysindexes Table Viewing STATISTIC Statements Output Viewing SHOWPLAN_ALL and SHOWPLAN_TEXT Output Viewing Graphical Showplan 9
• Obtaining Query Plan Information n n Querying the sysindexes Table Viewing STATISTIC Statements Output Viewing SHOWPLAN_ALL and SHOWPLAN_TEXT Output Viewing Graphical Showplan 9
 Querying the sysindexes Table n Stores Table and Index Information n n Type of index (indid) Space used (dpages, reserved, and used) Fill factor (Orig. Fill. Factor) Stores Statistics for Each Index 10
Querying the sysindexes Table n Stores Table and Index Information n n Type of index (indid) Space used (dpages, reserved, and used) Fill factor (Orig. Fill. Factor) Stores Statistics for Each Index 10
 Viewing SHOWPLAN_ALL and SHOWPLAN_TEXT Output n Structure of the SHOWPLAN Statement Output n n n Returns information as a set of rows Forms a hierarchical tree Represents steps taken by the query optimizer Shows estimated values of how a query was optimized, not the actual query plan Details of the Execution Steps Difference Between SHOWPLAN_TEXT and SHOWPLAN_ALL Output 11
Viewing SHOWPLAN_ALL and SHOWPLAN_TEXT Output n Structure of the SHOWPLAN Statement Output n n n Returns information as a set of rows Forms a hierarchical tree Represents steps taken by the query optimizer Shows estimated values of how a query was optimized, not the actual query plan Details of the Execution Steps Difference Between SHOWPLAN_TEXT and SHOWPLAN_ALL Output 11
 • Viewing Graphical Showplan n n Elements of Graphical Showplan Reading Graphical Query Plan Output 12
• Viewing Graphical Showplan n n Elements of Graphical Showplan Reading Graphical Query Plan Output 12
 Elements of Graphical Showplan n n Steps Are Units of Work to Process a Query Sequence of Steps Is the Order in Which the Steps Are Processed Logical Operators Describe Relational Algebraic Operation Used to Process a Statement Physical Operators Describe Physical Implementation Algorithm Used to Process a Statement 13
Elements of Graphical Showplan n n Steps Are Units of Work to Process a Query Sequence of Steps Is the Order in Which the Steps Are Processed Logical Operators Describe Relational Algebraic Operation Used to Process a Statement Physical Operators Describe Physical Implementation Algorithm Used to Process a Statement 13
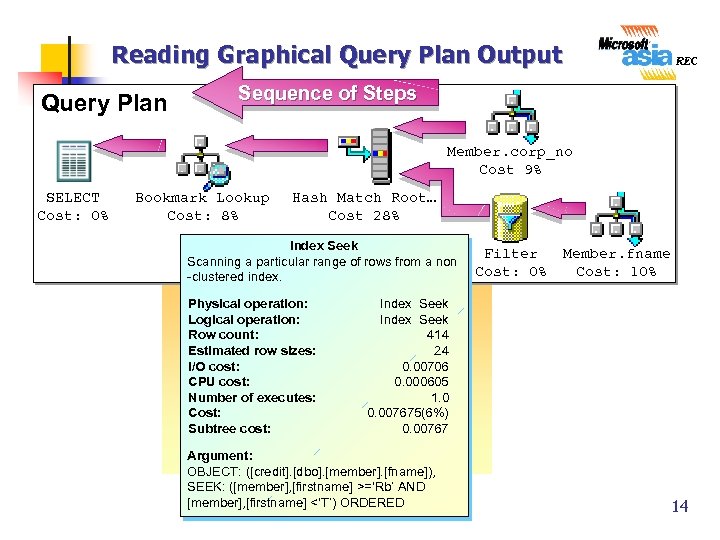 Reading Graphical Query Plan Output Query Plan Sequence of Steps Member. corp_no Cost 9% SELECT Cost: 0% Bookmark Lookup Cost: 8% Hash Match Root… Cost 28% Index Seek Scanning a particular range of rows from a non -clustered index. Physical operation: Logical operation: Row count: Estimated row sizes: I/O cost: CPU cost: Number of executes: Cost: Subtree cost: Filter Cost: 0% Member. fname Cost: 10% Index Seek 414 24 0. 00706 0. 000605 1. 0 0. 007675(6%) 0. 00767 Argument: OBJECT: ([credit]. [dbo]. [member]. [fname]), SEEK: ([member], [firstname] >=‘Rb’ AND [member], [firstname] <‘T’) ORDERED 14
Reading Graphical Query Plan Output Query Plan Sequence of Steps Member. corp_no Cost 9% SELECT Cost: 0% Bookmark Lookup Cost: 8% Hash Match Root… Cost 28% Index Seek Scanning a particular range of rows from a non -clustered index. Physical operation: Logical operation: Row count: Estimated row sizes: I/O cost: CPU cost: Number of executes: Cost: Subtree cost: Filter Cost: 0% Member. fname Cost: 10% Index Seek 414 24 0. 00706 0. 000605 1. 0 0. 007675(6%) 0. 00767 Argument: OBJECT: ([credit]. [dbo]. [member]. [fname]), SEEK: ([member], [firstname] >=‘Rb’ AND [member], [firstname] <‘T’) ORDERED 14
 • Indexing Fundamentals n n n Understanding the Data Limiting a Search Determining Selectivity Determining Density Determining Distribution of Data 15
• Indexing Fundamentals n n n Understanding the Data Limiting a Search Determining Selectivity Determining Density Determining Distribution of Data 15
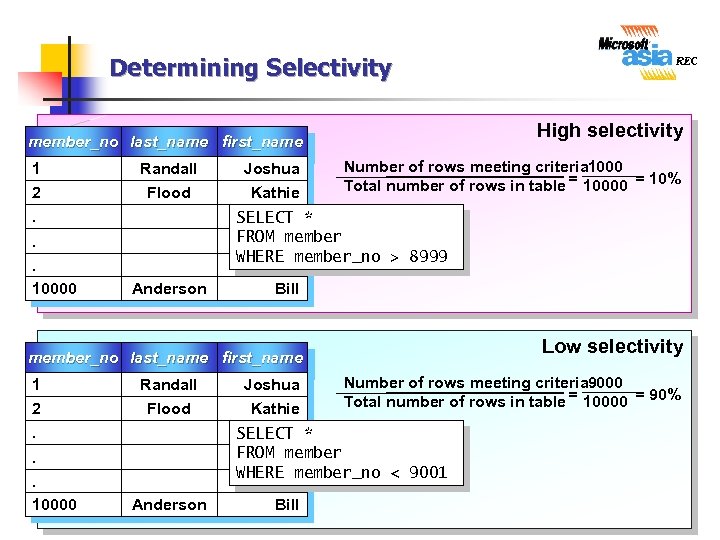 Determining Selectivity High selectivity member_no last_name first_name 1 2. Randall Flood Number of rows meeting criteria 1000 Total number of rows in table = 10000 = 10% SELECT * FROM member WHERE member_no > 8999 . . 10000 Joshua Kathie Anderson Bill Low selectivity member_no last_name first_name 1 2. Randall Flood Number of rows meeting criteria 9000 Total number of rows in table = 10000 = 90% SELECT * FROM member WHERE member_no < 9001 . . 10000 Joshua Kathie Anderson Bill 16
Determining Selectivity High selectivity member_no last_name first_name 1 2. Randall Flood Number of rows meeting criteria 1000 Total number of rows in table = 10000 = 10% SELECT * FROM member WHERE member_no > 8999 . . 10000 Joshua Kathie Anderson Bill Low selectivity member_no last_name first_name 1 2. Randall Flood Number of rows meeting criteria 9000 Total number of rows in table = 10000 = 90% SELECT * FROM member WHERE member_no < 9001 . . 10000 Joshua Kathie Anderson Bill 16
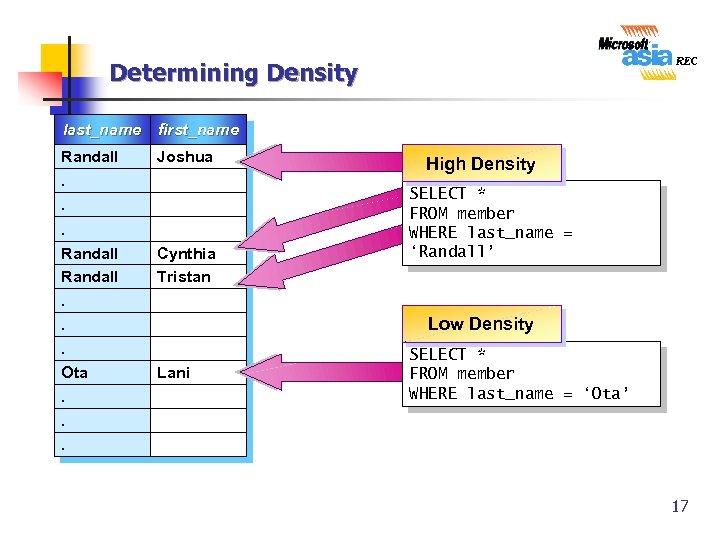 Determining Density last_name first_name Randall Joshua . . . Randall. . . Ota. . Cynthia Tristan High Density SELECT * FROM member WHERE last_name = ‘Randall’ Low Density Lani SELECT * FROM member WHERE last_name = ‘Ota’ . 17
Determining Density last_name first_name Randall Joshua . . . Randall. . . Ota. . Cynthia Tristan High Density SELECT * FROM member WHERE last_name = ‘Randall’ Low Density Lani SELECT * FROM member WHERE last_name = ‘Ota’ . 17
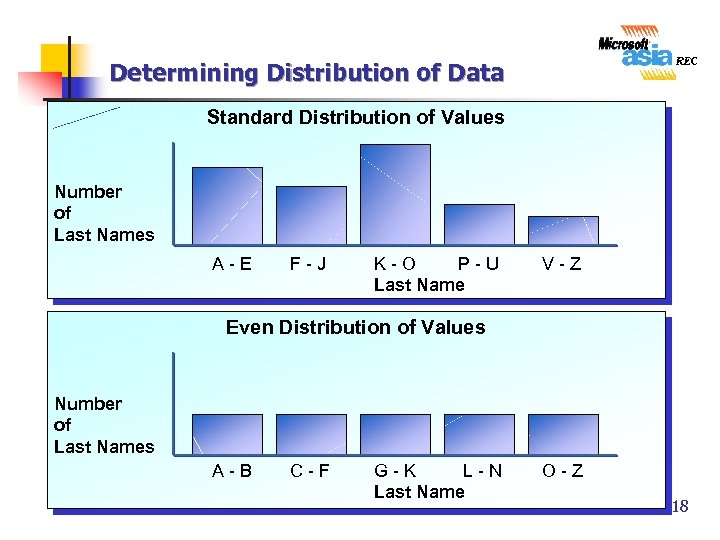 Determining Distribution of Data Standard Distribution of Values Number of Last Names A-E F-J K-O P-U Last Name V-Z Even Distribution of Values Number of Last Names A-B C-F G-K L-N Last Name O-Z 18
Determining Distribution of Data Standard Distribution of Values Number of Last Names A-E F-J K-O P-U Last Name V-Z Even Distribution of Values Number of Last Names A-B C-F G-K L-N Last Name O-Z 18
 Updating Statistics n n n Frequency of Updating Statistics Automatically Updating Statistics Manually Updating Statistics n n n If you created an index before any data was put into the table If a table is truncated If you added many rows to a table that contained minimal or no data, and you plan to immediately query against that table 19
Updating Statistics n n n Frequency of Updating Statistics Automatically Updating Statistics Manually Updating Statistics n n n If you created an index before any data was put into the table If a table is truncated If you added many rows to a table that contained minimal or no data, and you plan to immediately query against that table 19
 Viewing Statistics SQL Server Returns Information on: n The Time When the Statistics Were Last Updated n The Number of Rows Sampled to Produce the Histogram n Density Information n Average Key Length n Contents of the statsblob Column DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS 20
Viewing Statistics SQL Server Returns Information on: n The Time When the Statistics Were Last Updated n The Number of Rows Sampled to Produce the Histogram n Density Information n Average Key Length n Contents of the statsblob Column DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS 20
 Overview n n Accessing Data Using an Index to Cover a Query Using Index Tuning Tools to Improve Query Performance Indexing Strategies 21
Overview n n Accessing Data Using an Index to Cover a Query Using Index Tuning Tools to Improve Query Performance Indexing Strategies 21
 • Accessing Data n n n Table Scans and Indexes Index Architecture and Navigation Using Row Identifiers to Access Data 22
• Accessing Data n n n Table Scans and Indexes Index Architecture and Navigation Using Row Identifiers to Access Data 22
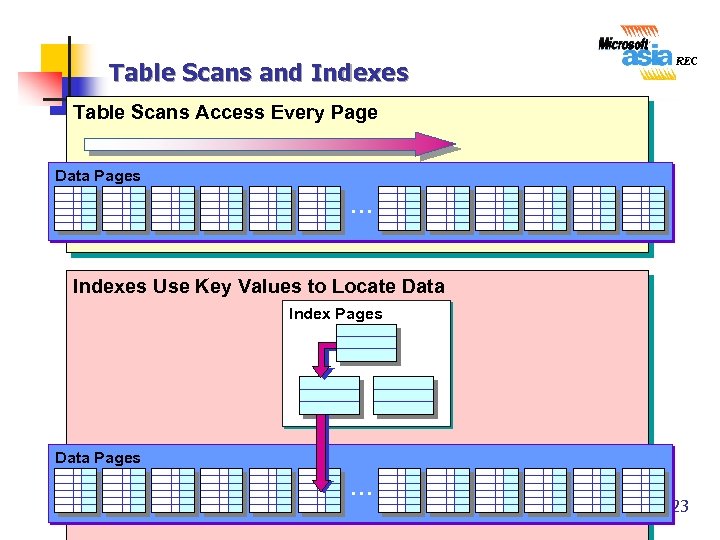 Table Scans and Indexes Table Scans Access Every Page Data Pages … Indexes Use Key Values to Locate Data Index Pages Data Pages … 23
Table Scans and Indexes Table Scans Access Every Page Data Pages … Indexes Use Key Values to Locate Data Index Pages Data Pages … 23
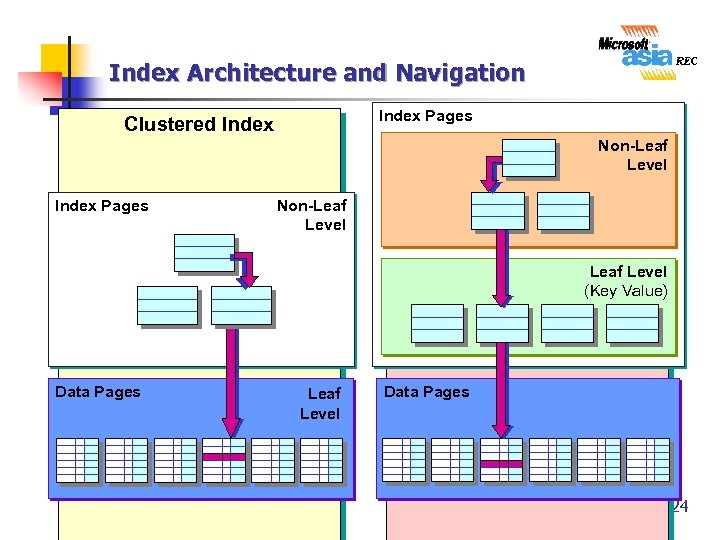 Index Architecture and Navigation Index Pages Clustered Index Nonclustered Index Non-Leaf Level Index Pages Non-Leaf Level (Key Value) Data Pages Leaf Level Data Pages 24
Index Architecture and Navigation Index Pages Clustered Index Nonclustered Index Non-Leaf Level Index Pages Non-Leaf Level (Key Value) Data Pages Leaf Level Data Pages 24
 Using Row Identifiers to Access Data n Creation and Storage of a RID n n n Consists of the file number, page number, and slot number, which identify the exact location of a row Is an internal value RID Is Used to Retrieve Rows n n Accessing the nonclustered index Performing a Bookmark Lookup operation 25
Using Row Identifiers to Access Data n Creation and Storage of a RID n n n Consists of the file number, page number, and slot number, which identify the exact location of a row Is an internal value RID Is Used to Retrieve Rows n n Accessing the nonclustered index Performing a Bookmark Lookup operation 25
 • Using an Index to Cover a Query n n n Introduction to Indexes That Cover a Query Locating Data by Using Indexes That Cover a Query Identifying Whether an Index Can Be Used to Cover a Query Determining Whether an Index Is Used to Cover a Query Guidelines to Creating Indexes That Can Cover a Query 26
• Using an Index to Cover a Query n n n Introduction to Indexes That Cover a Query Locating Data by Using Indexes That Cover a Query Identifying Whether an Index Can Be Used to Cover a Query Determining Whether an Index Is Used to Cover a Query Guidelines to Creating Indexes That Can Cover a Query 26
 Locating Data by Using Indexes That Cover a Query n n n Example of Single Page Navigation Example of Partial Scan Navigation Example of Full Scan Navigation 27
Locating Data by Using Indexes That Cover a Query n n n Example of Single Page Navigation Example of Partial Scan Navigation Example of Full Scan Navigation 27
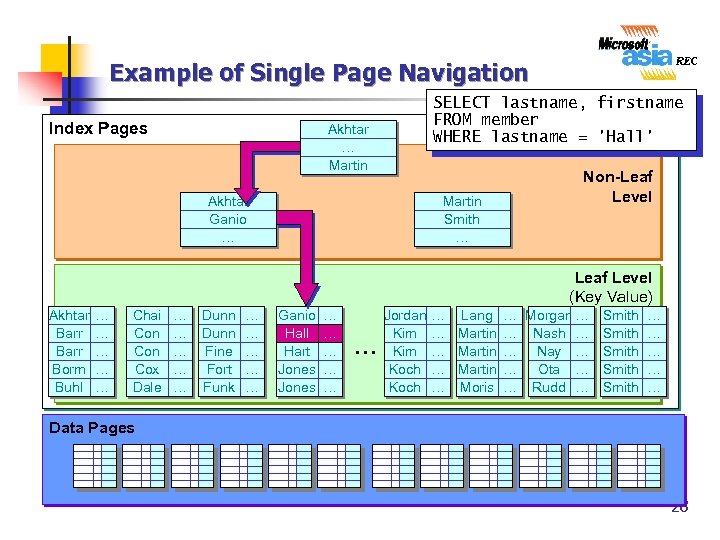 Example of Single Page Navigation Index Pages SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member WHERE lastname = 'Hall' Akhtar … Martin Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Non-Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim Koch … Lang … Morgan … … Martin … Nash … … Martin … Nay … … Martin … Ota … … Moris … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 28
Example of Single Page Navigation Index Pages SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member WHERE lastname = 'Hall' Akhtar … Martin Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Non-Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim Koch … Lang … Morgan … … Martin … Nash … … Martin … Nay … … Martin … Ota … … Moris … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 28
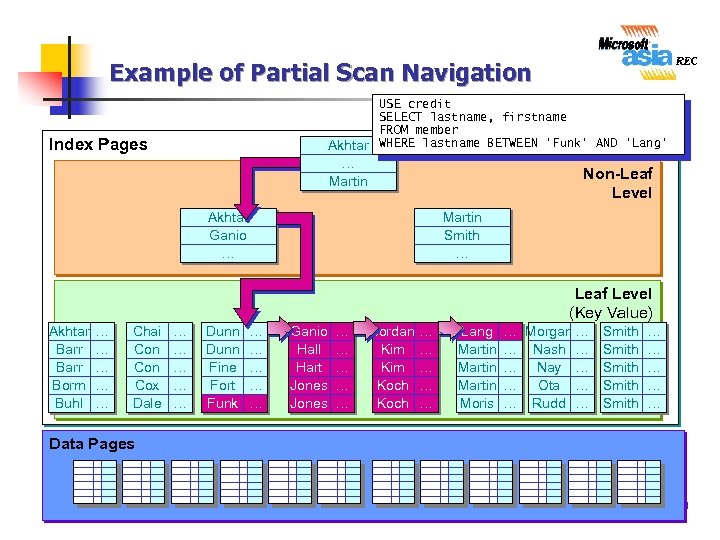 Example of Partial Scan Navigation USE credit SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member Akhtar WHERE lastname BETWEEN 'Funk' AND 'Lang' Index Pages … Martin Non-Leaf Level Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim Koch … … … Lang Martin Moris … Morgan … … Nash … … Nay … … Ota … … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 29
Example of Partial Scan Navigation USE credit SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member Akhtar WHERE lastname BETWEEN 'Funk' AND 'Lang' Index Pages … Martin Non-Leaf Level Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim Koch … … … Lang Martin Moris … Morgan … … Nash … … Nay … … Ota … … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 29
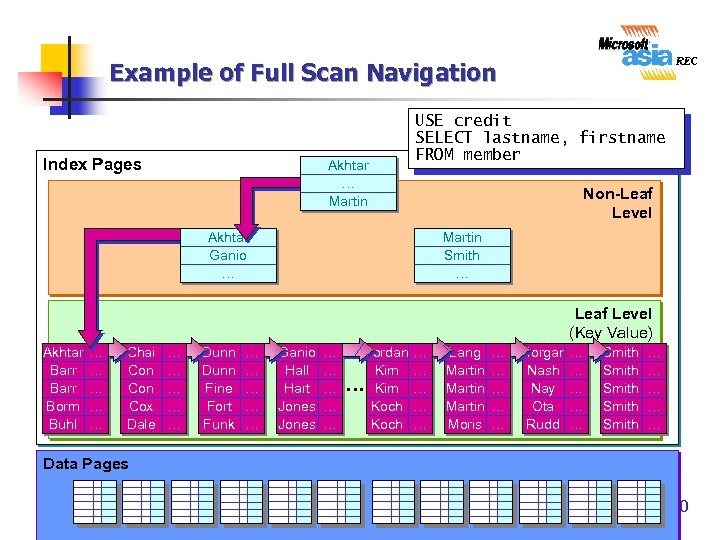 Example of Full Scan Navigation Index Pages Akhtar … Martin USE credit SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member Non-Leaf Level Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim … Kim Koch … … … Lang Martin Moris … … … Morgan … Nash … Nay … Ota … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 30
Example of Full Scan Navigation Index Pages Akhtar … Martin USE credit SELECT lastname, firstname FROM member Non-Leaf Level Akhtar Ganio … Martin Smith … Leaf Level (Key Value) Akhtar Barr Borm Buhl … … … Chai Con Cox Dale … … … Dunn Fine Fort Funk … … … Ganio Hall Hart Jones … … … Jordan Kim … Kim Koch … … … Lang Martin Moris … … … Morgan … Nash … Nay … Ota … Rudd … Smith Smith … … … Data Pages 30
 Identifying Whether an Index Can Be Used to Cover a Query n n n All Data Can Be Found in the Index First Column of a Composite Index Is Not Referenced in the WHERE Clause A WHERE Clause Does Not Exist There Is a Clustered Index on a Column Referenced in the WHERE Clause, and Selectivity Requires More I/O to Use the Clustered Index Join Operations Exist 31
Identifying Whether an Index Can Be Used to Cover a Query n n n All Data Can Be Found in the Index First Column of a Composite Index Is Not Referenced in the WHERE Clause A WHERE Clause Does Not Exist There Is a Clustered Index on a Column Referenced in the WHERE Clause, and Selectivity Requires More I/O to Use the Clustered Index Join Operations Exist 31
 Determining Whether an Index Is Used to Cover a Query n Observing the Query Plan Output n n Displays the phrase “Scanning a nonclustered index entirely or only a range” Comparing I/O n Nonclustered index Total n n number of of levels in the non–leaf level pages that make up the leaf level rows per leaf-level page rows per data page Total Number of pages that make up the table 32
Determining Whether an Index Is Used to Cover a Query n Observing the Query Plan Output n n Displays the phrase “Scanning a nonclustered index entirely or only a range” Comparing I/O n Nonclustered index Total n n number of of levels in the non–leaf level pages that make up the leaf level rows per leaf-level page rows per data page Total Number of pages that make up the table 32
 Guidelines to Creating Indexes That Can Cover a Query n n n Adding Columns to Indexes Limiting Index Key Size Maintaining Row-to-Key Size Ratio 33
Guidelines to Creating Indexes That Can Cover a Query n n n Adding Columns to Indexes Limiting Index Key Size Maintaining Row-to-Key Size Ratio 33
 Demo: Analyzing How Queries Are Covered By Different Types of Indexes 34
Demo: Analyzing How Queries Are Covered By Different Types of Indexes 34
 Using Index Tuning Tools to Improve Query Performance n Using the Index Tuning Wizard n n n Recommends or verifies optimal index configuration Provides cost analysis reports Recommends ways to tune the database Specifies criteria when a workload is evaluated Using the Index Analysis Tool n Recommends optimal set of indexes to support a given query or batch 35
Using Index Tuning Tools to Improve Query Performance n Using the Index Tuning Wizard n n n Recommends or verifies optimal index configuration Provides cost analysis reports Recommends ways to tune the database Specifies criteria when a workload is evaluated Using the Index Analysis Tool n Recommends optimal set of indexes to support a given query or batch 35
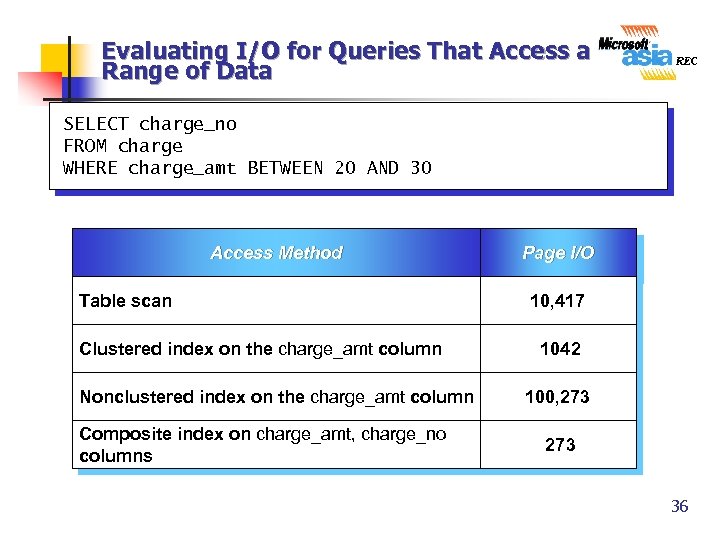 Evaluating I/O for Queries That Access a Range of Data SELECT charge_no FROM charge WHERE charge_amt BETWEEN 20 AND 30 Access Method Table scan Clustered index on the charge_amt column Nonclustered index on the charge_amt column Composite index on charge_amt, charge_no columns Page I/O 10, 417 1042 100, 273 36
Evaluating I/O for Queries That Access a Range of Data SELECT charge_no FROM charge WHERE charge_amt BETWEEN 20 AND 30 Access Method Table scan Clustered index on the charge_amt column Nonclustered index on the charge_amt column Composite index on charge_amt, charge_no columns Page I/O 10, 417 1042 100, 273 36
 Demo : Analyzing Queries That Use the AND and OR Operators 37
Demo : Analyzing Queries That Use the AND and OR Operators 37
 Microsoft AREC TAM Internship go ? WHERE DO YOU WANT TO TODAY Microsoft
Microsoft AREC TAM Internship go ? WHERE DO YOU WANT TO TODAY Microsoft


