1_Magnification.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Microscopy and Magnification
Microscopy and Magnification
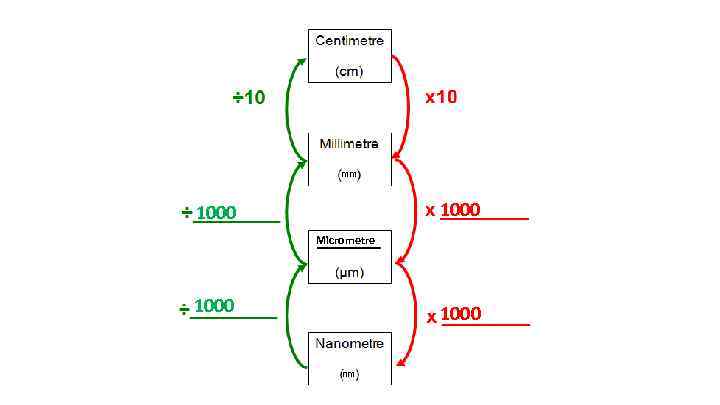 mm 1000 Micrometre 1000 nm
mm 1000 Micrometre 1000 nm
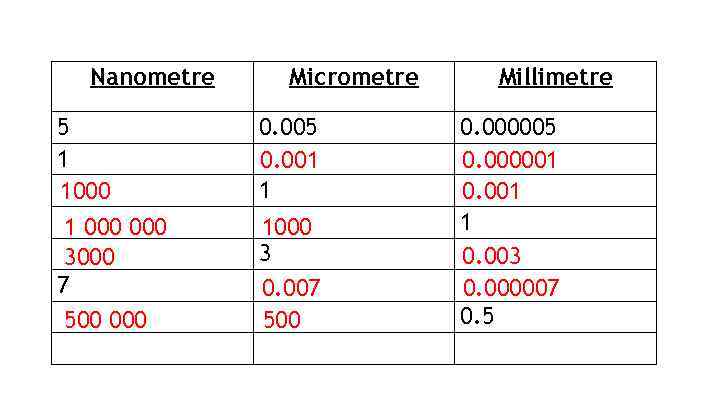 Nanometre 5 1 1000 1 000 3000 7 500 000 Micrometre 0. 005 0. 001 1 1000 3 0. 007 500 Millimetre 0. 000005 0. 000001 0. 001 1 0. 003 0. 000007 0. 5
Nanometre 5 1 1000 1 000 3000 7 500 000 Micrometre 0. 005 0. 001 1 1000 3 0. 007 500 Millimetre 0. 000005 0. 000001 0. 001 1 0. 003 0. 000007 0. 5
 The difference between magnification and resolution. • Magnification is the degree to which the size of an image is larger than the image itself. • Resolution is the degree to which it is possible to distinguish between two objects that are very close together.
The difference between magnification and resolution. • Magnification is the degree to which the size of an image is larger than the image itself. • Resolution is the degree to which it is possible to distinguish between two objects that are very close together.
 How do we find the overall magnification of a light microscope? Eyepiece Objective lens Eyepiece Magnification Objective Magnification Overall Magnification X 10 X 4 X 10 X 40 X 100 400 1000
How do we find the overall magnification of a light microscope? Eyepiece Objective lens Eyepiece Magnification Objective Magnification Overall Magnification X 10 X 4 X 10 X 40 X 100 400 1000
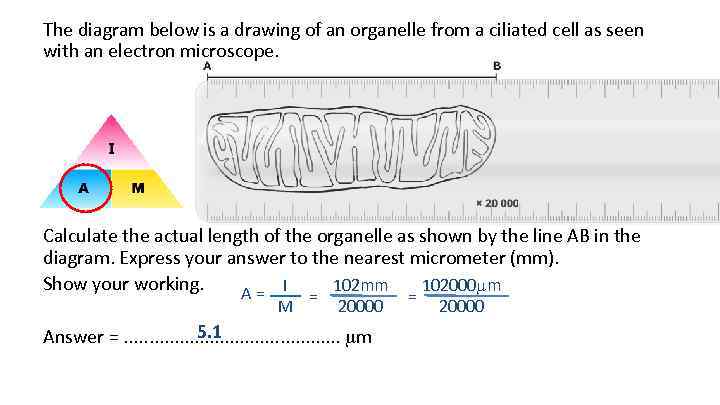 The diagram below is a drawing of an organelle from a ciliated cell as seen with an electron microscope. Calculate the actual length of the organelle as shown by the line AB in the diagram. Express your answer to the nearest micrometer (mm). Show your working. A = I = 102 mm = 102000 m M 20000 5. 1 Answer =. . . m
The diagram below is a drawing of an organelle from a ciliated cell as seen with an electron microscope. Calculate the actual length of the organelle as shown by the line AB in the diagram. Express your answer to the nearest micrometer (mm). Show your working. A = I = 102 mm = 102000 m M 20000 5. 1 Answer =. . . m
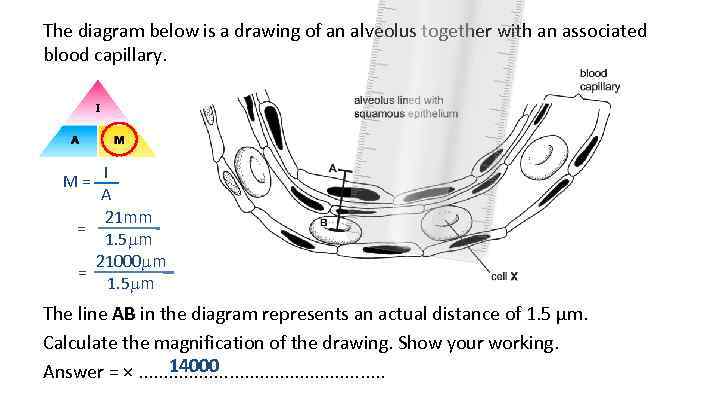 The diagram below is a drawing of an alveolus together with an associated blood capillary. M = I A 21 mm = 1. 5 m 21000 m = 1. 5 m The line AB in the diagram represents an actual distance of 1. 5 µm. Calculate the magnification of the drawing. Show your working. 14000 Answer = ×. . .
The diagram below is a drawing of an alveolus together with an associated blood capillary. M = I A 21 mm = 1. 5 m 21000 m = 1. 5 m The line AB in the diagram represents an actual distance of 1. 5 µm. Calculate the magnification of the drawing. Show your working. 14000 Answer = ×. . .
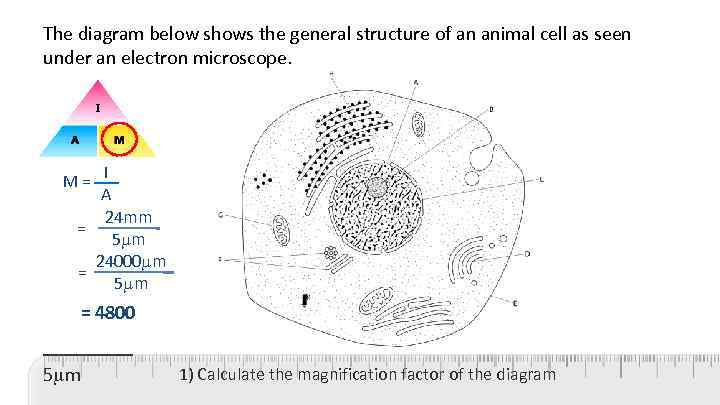 The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. M = I A 24 mm = 5 m 24000 m = 5 m = 4800 _____ 5 m 1) Calculate the magnification factor of the diagram
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. M = I A 24 mm = 5 m 24000 m = 5 m = 4800 _____ 5 m 1) Calculate the magnification factor of the diagram
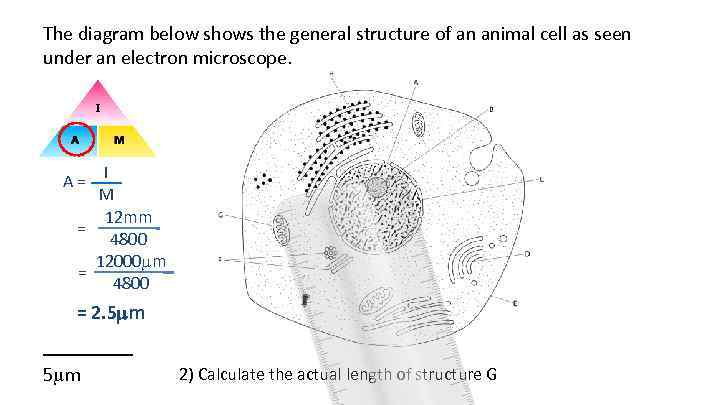 The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 12 mm = 4800 12000 m = 4800 = 2. 5 mm _____ 5 m 2) Calculate the actual length of structure G
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 12 mm = 4800 12000 m = 4800 = 2. 5 mm _____ 5 m 2) Calculate the actual length of structure G
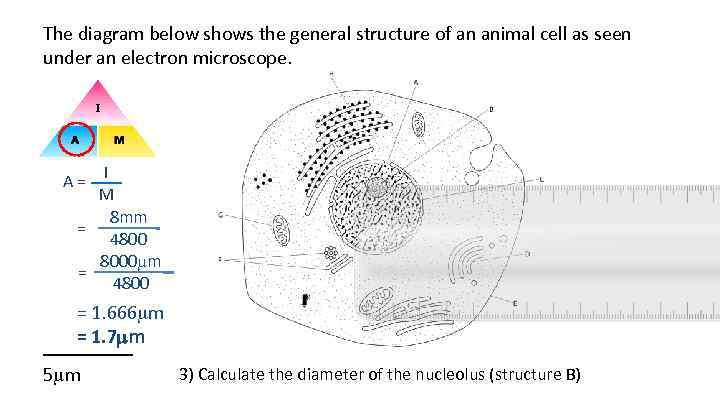 The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 8 mm = 4800 8000 m = 4800 = 1. 666 m = 1. 7 mm _____ 5 m 3) Calculate the diameter of the nucleolus (structure B)
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 8 mm = 4800 8000 m = 4800 = 1. 666 m = 1. 7 mm _____ 5 m 3) Calculate the diameter of the nucleolus (structure B)
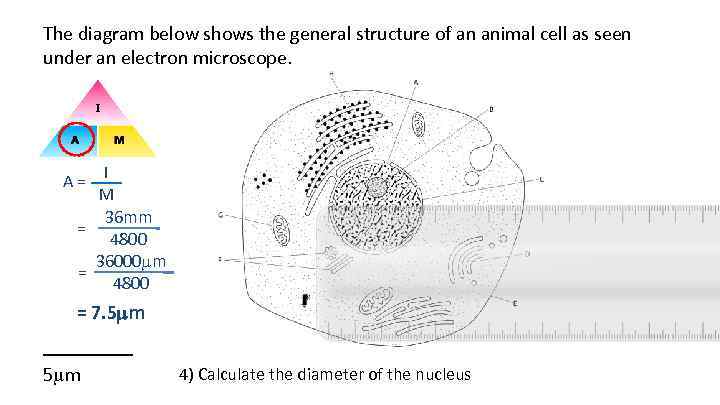 The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 36 mm = 4800 36000 m = 4800 = 7. 5 mm _____ 5 m 4) Calculate the diameter of the nucleus
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 36 mm = 4800 36000 m = 4800 = 7. 5 mm _____ 5 m 4) Calculate the diameter of the nucleus
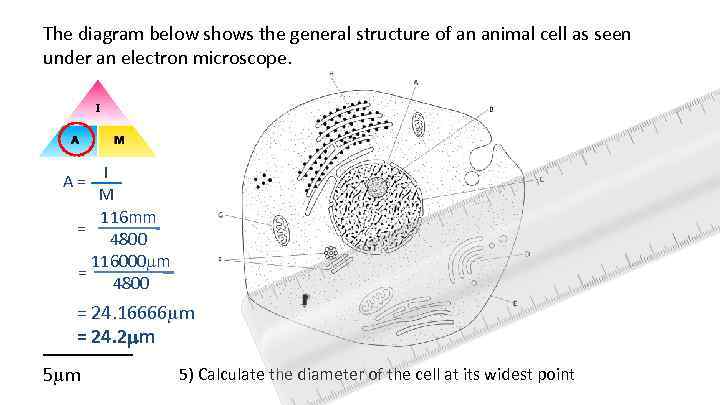 The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 116 mm = 4800 116000 m = 4800 = 24. 16666 m = 24. 2 mm _____ 5 m 5) Calculate the diameter of the cell at its widest point
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. A = I M 116 mm = 4800 116000 m = 4800 = 24. 16666 m = 24. 2 mm _____ 5 m 5) Calculate the diameter of the cell at its widest point
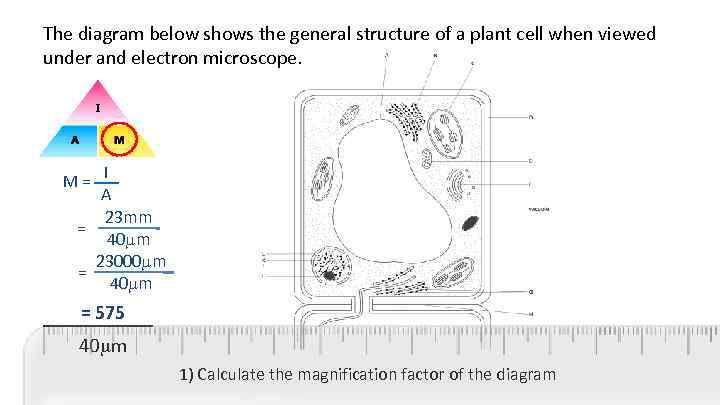 The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. M = I A 23 mm = 40 m 23000 m = 40 m = 575 ______ 40 m 1) Calculate the magnification factor of the diagram
The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. M = I A 23 mm = 40 m 23000 m = 40 m = 575 ______ 40 m 1) Calculate the magnification factor of the diagram
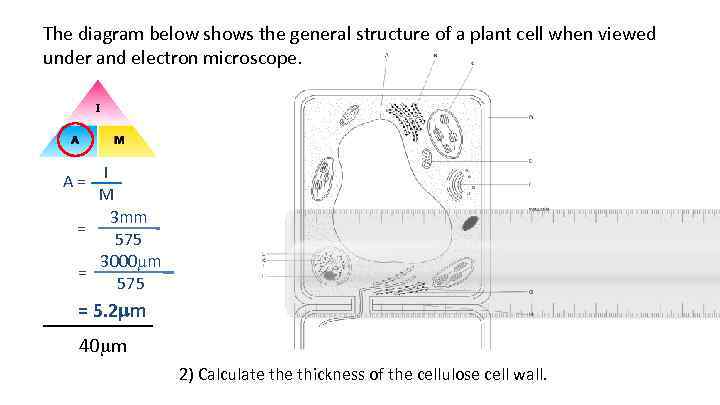 The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 3 mm = 575 3000 m = 575 = 5. 2 mm ______ 40 m 2) Calculate thickness of the cellulose cell wall.
The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 3 mm = 575 3000 m = 575 = 5. 2 mm ______ 40 m 2) Calculate thickness of the cellulose cell wall.
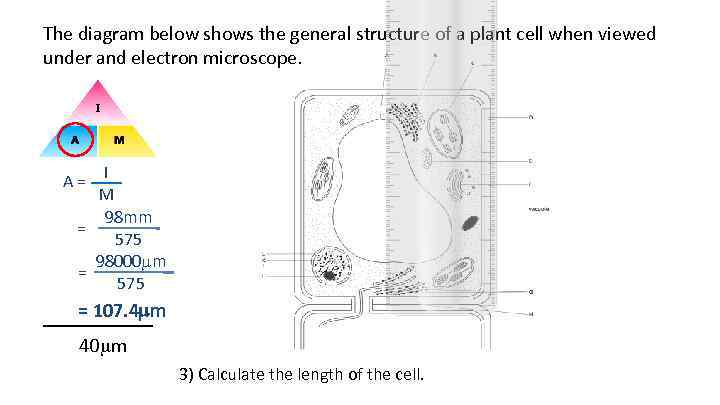 The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 98 mm = 575 98000 m = 575 = 107. 4 mm ______ 40 m 3) Calculate the length of the cell.
The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 98 mm = 575 98000 m = 575 = 107. 4 mm ______ 40 m 3) Calculate the length of the cell.
 The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 24 mm = 575 24000 m = 575 = 41. 7 mm ______ 40 m 4) Calculate the length of structure C.
The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 24 mm = 575 24000 m = 575 = 41. 7 mm ______ 40 m 4) Calculate the length of structure C.
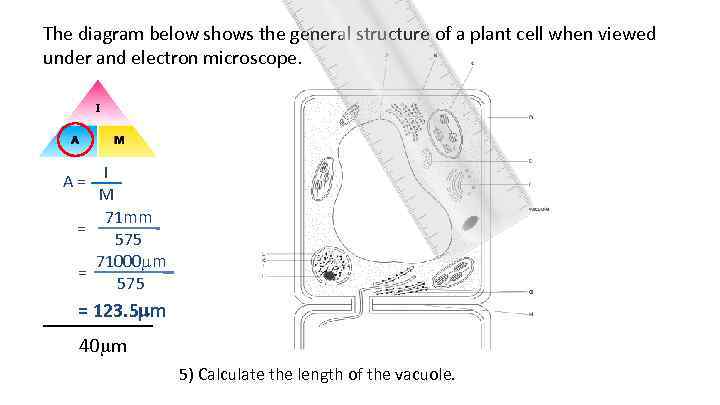 The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 71 mm = 575 71000 m = 575 = 123. 5 mm ______ 40 m 5) Calculate the length of the vacuole.
The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. A = I M 71 mm = 575 71000 m = 575 = 123. 5 mm ______ 40 m 5) Calculate the length of the vacuole.
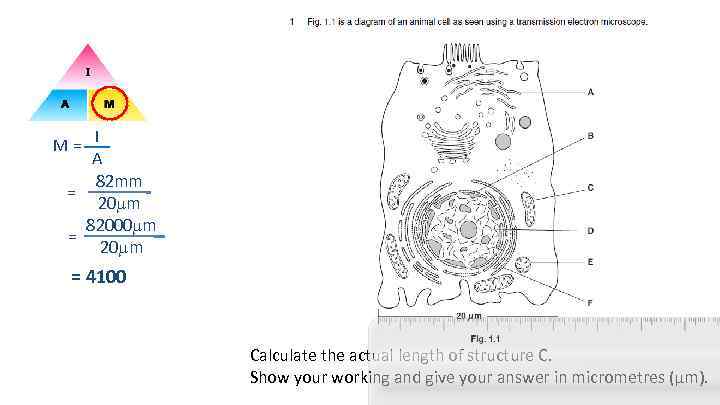 M = I A 82 mm = 20 m 82000 m = 20 m = 4100 Calculate the actual length of structure C. Show your working and give your answer in micrometres (μm).
M = I A 82 mm = 20 m 82000 m = 20 m = 4100 Calculate the actual length of structure C. Show your working and give your answer in micrometres (μm).
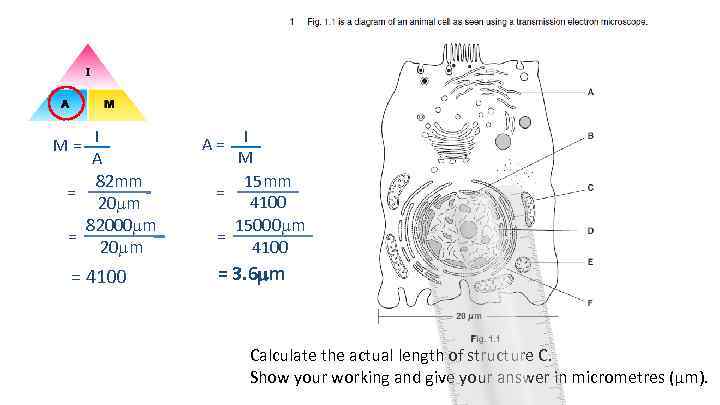 M = I A 82 mm = 20 m 82000 m = 20 m = 4100 A = I M 15 mm = 4100 15000 m = 4100 = 3. 6 mm Calculate the actual length of structure C. Show your working and give your answer in micrometres (μm).
M = I A 82 mm = 20 m 82000 m = 20 m = 4100 A = I M 15 mm = 4100 15000 m = 4100 = 3. 6 mm Calculate the actual length of structure C. Show your working and give your answer in micrometres (μm).
 • Take a calculator and a clear ruler into Biology exams • Always show the working out • Make sure correct units are added
• Take a calculator and a clear ruler into Biology exams • Always show the working out • Make sure correct units are added


