8497e4e25917a83300e22c77102ebcdc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Microeconomics ECONOMICS
Microeconomics ECONOMICS
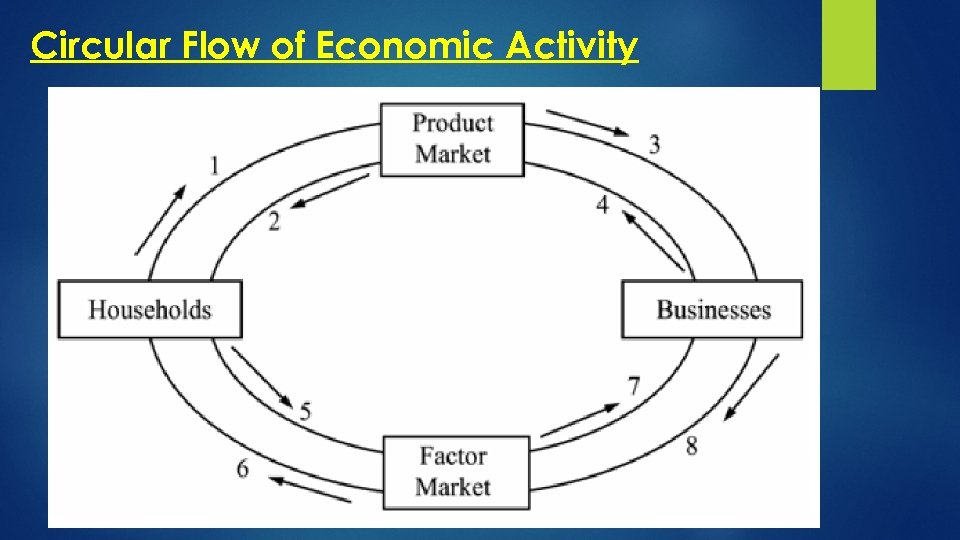 Circular Flow of Economic Activity
Circular Flow of Economic Activity
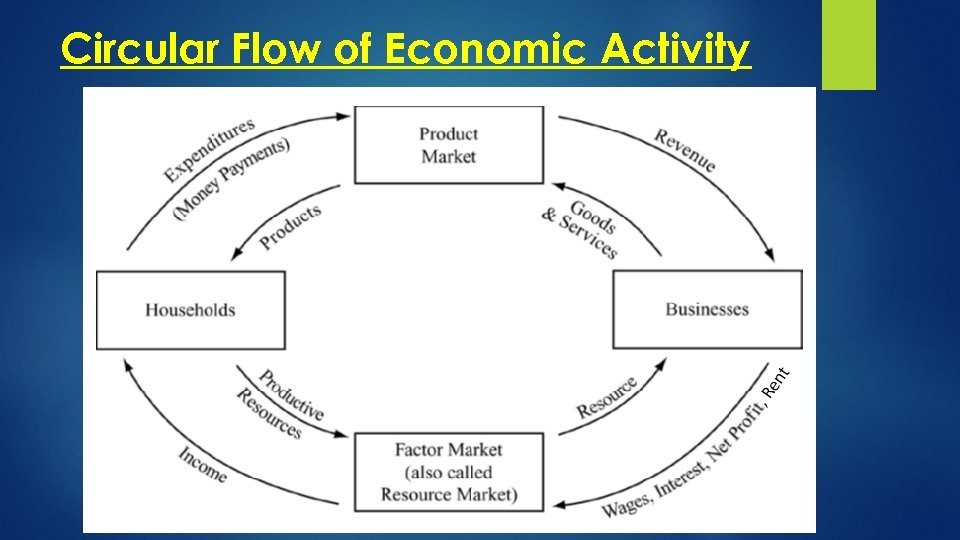 Circular Flow of Economic Activity
Circular Flow of Economic Activity
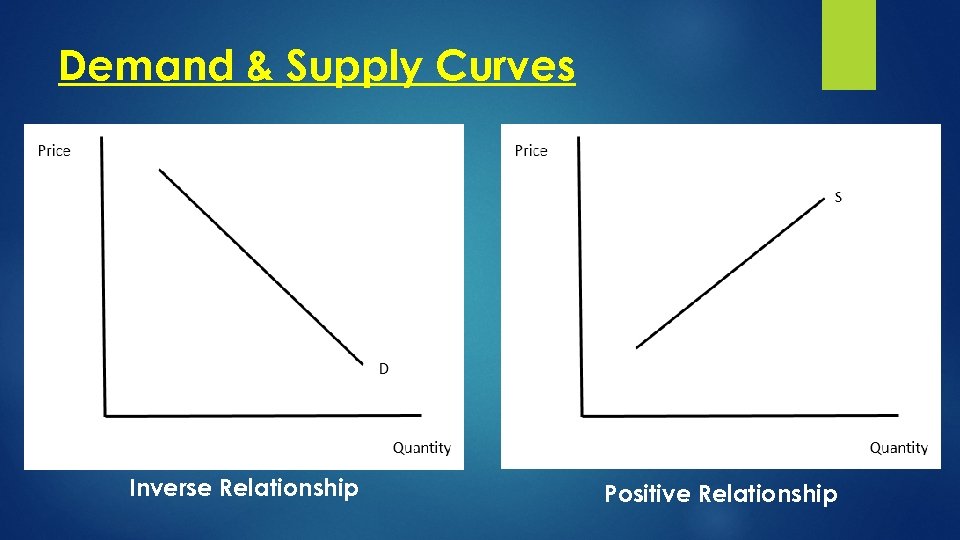 Demand & Supply Curves Inverse Relationship Positive Relationship
Demand & Supply Curves Inverse Relationship Positive Relationship
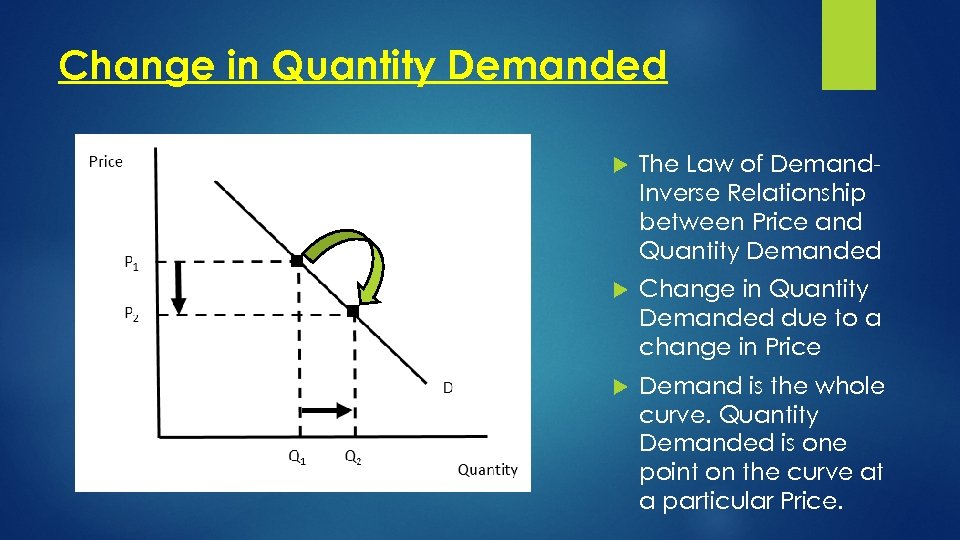 Change in Quantity Demanded The Law of Demand. Inverse Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded Change in Quantity Demanded due to a change in Price Demand is the whole curve. Quantity Demanded is one point on the curve at a particular Price.
Change in Quantity Demanded The Law of Demand. Inverse Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded Change in Quantity Demanded due to a change in Price Demand is the whole curve. Quantity Demanded is one point on the curve at a particular Price.
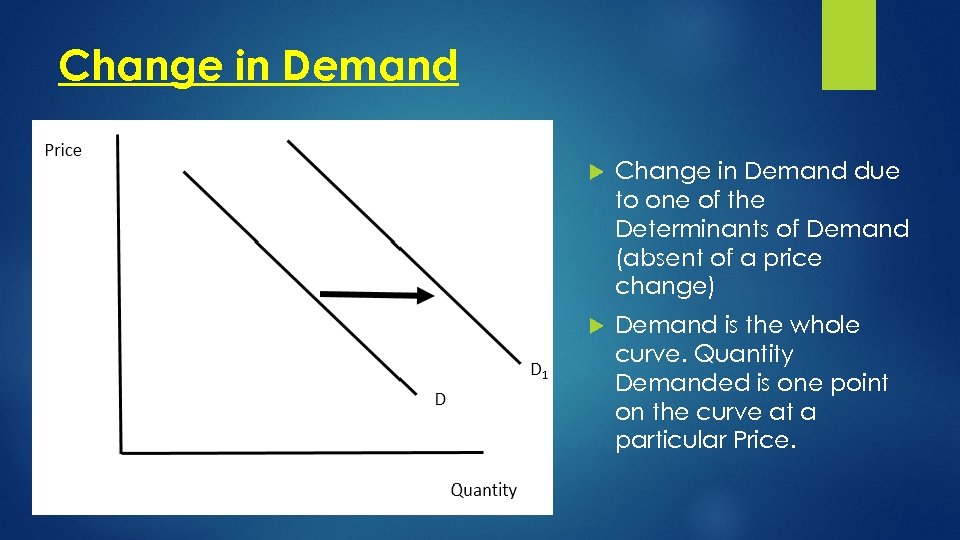 Change in Demand due to one of the Determinants of Demand (absent of a price change) Demand is the whole curve. Quantity Demanded is one point on the curve at a particular Price.
Change in Demand due to one of the Determinants of Demand (absent of a price change) Demand is the whole curve. Quantity Demanded is one point on the curve at a particular Price.
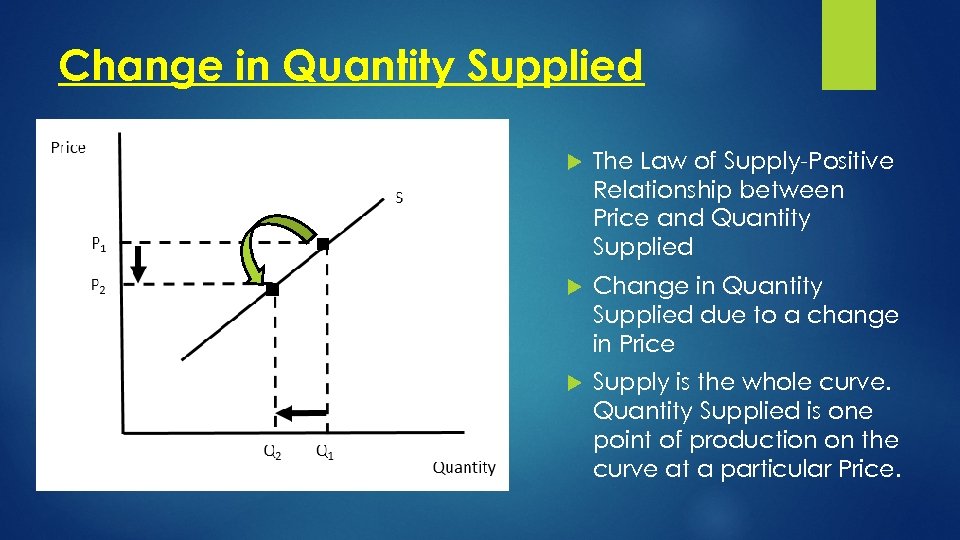 Change in Quantity Supplied The Law of Supply-Positive Relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied Change in Quantity Supplied due to a change in Price Supply is the whole curve. Quantity Supplied is one point of production on the curve at a particular Price.
Change in Quantity Supplied The Law of Supply-Positive Relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied Change in Quantity Supplied due to a change in Price Supply is the whole curve. Quantity Supplied is one point of production on the curve at a particular Price.
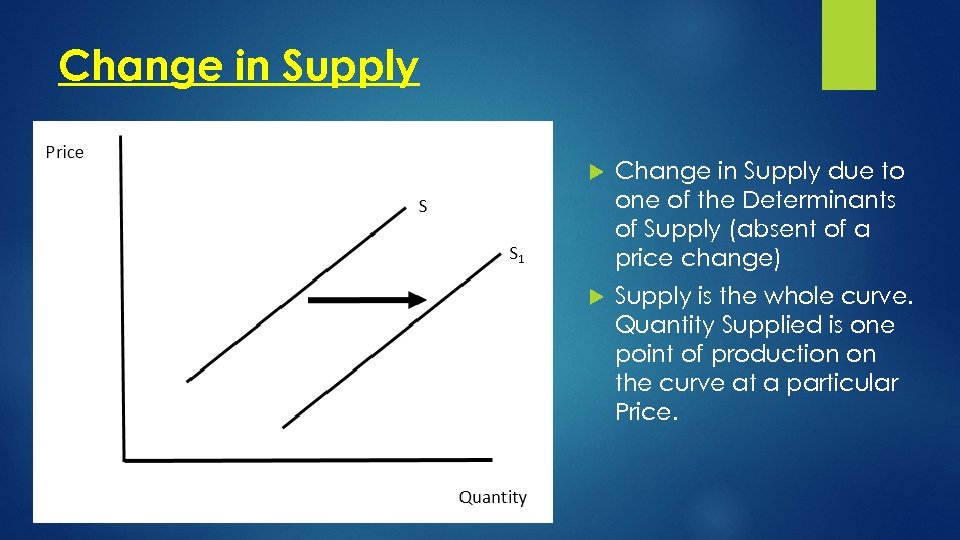 Change in Supply due to one of the Determinants of Supply (absent of a price change) Supply is the whole curve. Quantity Supplied is one point of production on the curve at a particular Price.
Change in Supply due to one of the Determinants of Supply (absent of a price change) Supply is the whole curve. Quantity Supplied is one point of production on the curve at a particular Price.
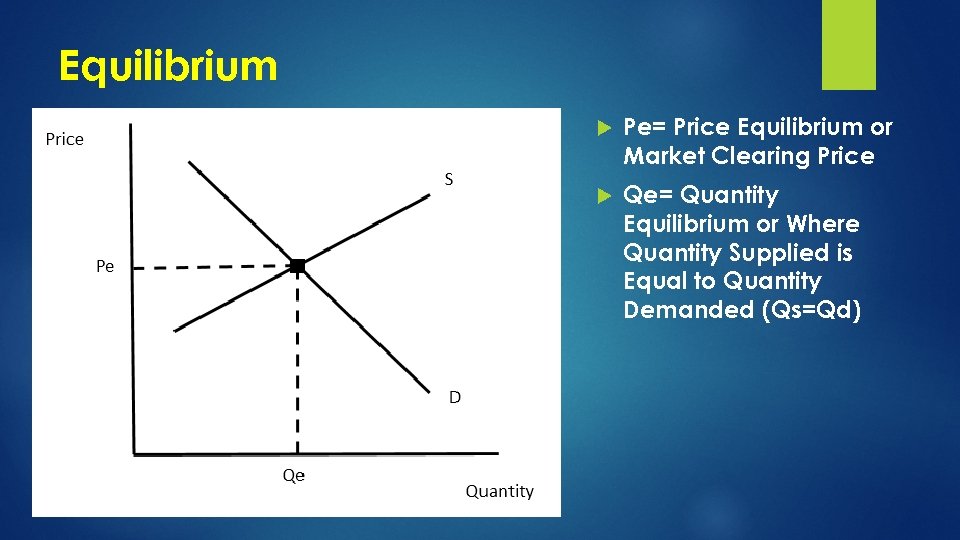 Equilibrium Pe= Price Equilibrium or Market Clearing Price Qe= Quantity Equilibrium or Where Quantity Supplied is Equal to Quantity Demanded (Qs=Qd)
Equilibrium Pe= Price Equilibrium or Market Clearing Price Qe= Quantity Equilibrium or Where Quantity Supplied is Equal to Quantity Demanded (Qs=Qd)
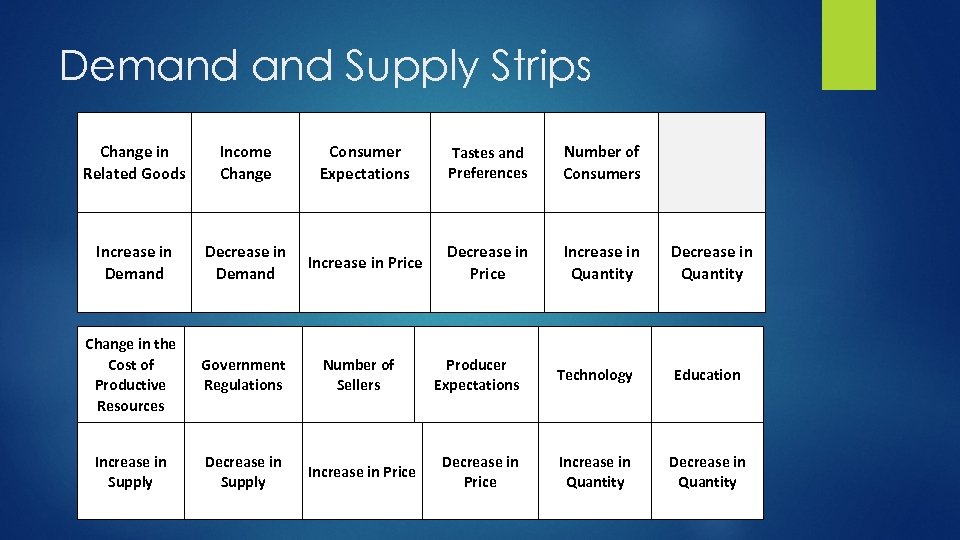 Demand Supply Strips Change in Related Goods Income Change Consumer Expectations Tastes and Preferences Number of Consumers Increase in Demand Decrease in Demand Increase in Price Decrease in Price Increase in Quantity Decrease in Quantity Change in the Cost of Productive Resources Government Regulations Number of Sellers Increase in Supply Decrease in Supply Increase in Price Producer Expectations Technology Education Decrease in Price Increase in Quantity Decrease in Quantity
Demand Supply Strips Change in Related Goods Income Change Consumer Expectations Tastes and Preferences Number of Consumers Increase in Demand Decrease in Demand Increase in Price Decrease in Price Increase in Quantity Decrease in Quantity Change in the Cost of Productive Resources Government Regulations Number of Sellers Increase in Supply Decrease in Supply Increase in Price Producer Expectations Technology Education Decrease in Price Increase in Quantity Decrease in Quantity
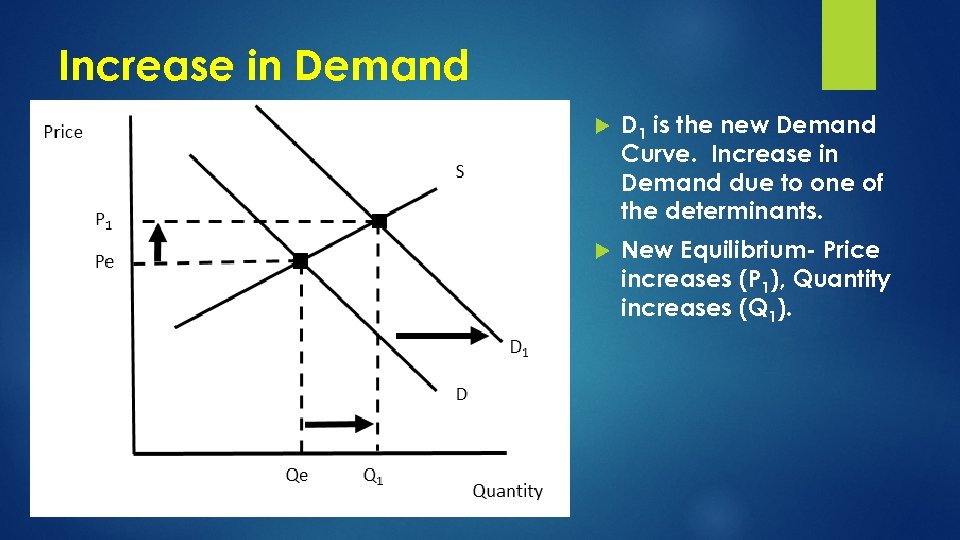 Increase in Demand D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Increase in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price increases (P 1), Quantity increases (Q 1).
Increase in Demand D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Increase in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price increases (P 1), Quantity increases (Q 1).
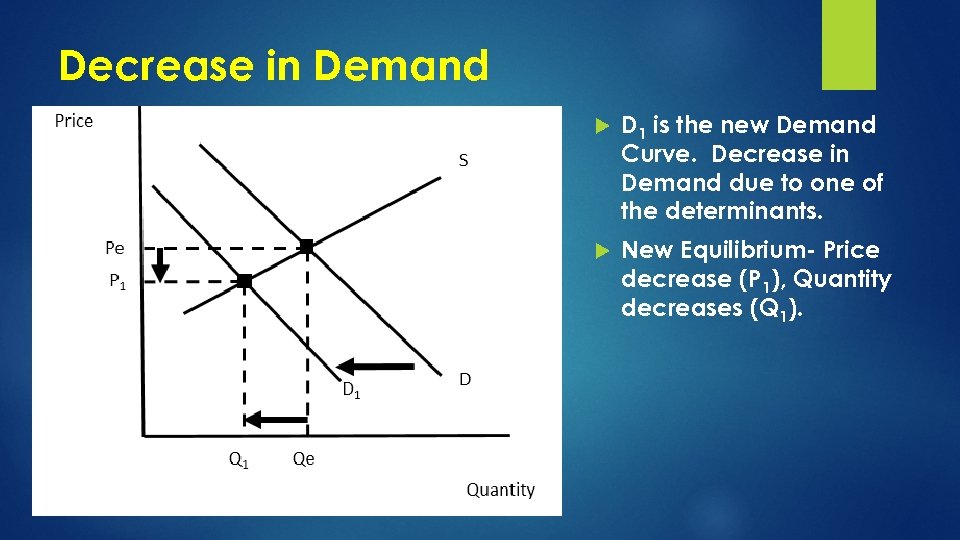 Decrease in Demand D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Decrease in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price decrease (P 1), Quantity decreases (Q 1).
Decrease in Demand D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Decrease in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price decrease (P 1), Quantity decreases (Q 1).
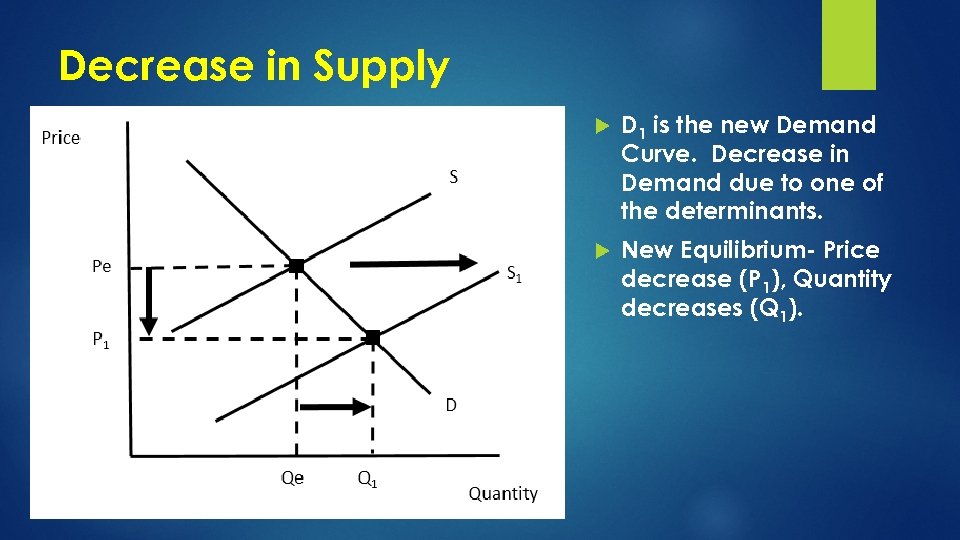 Decrease in Supply D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Decrease in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price decrease (P 1), Quantity decreases (Q 1).
Decrease in Supply D 1 is the new Demand Curve. Decrease in Demand due to one of the determinants. New Equilibrium- Price decrease (P 1), Quantity decreases (Q 1).
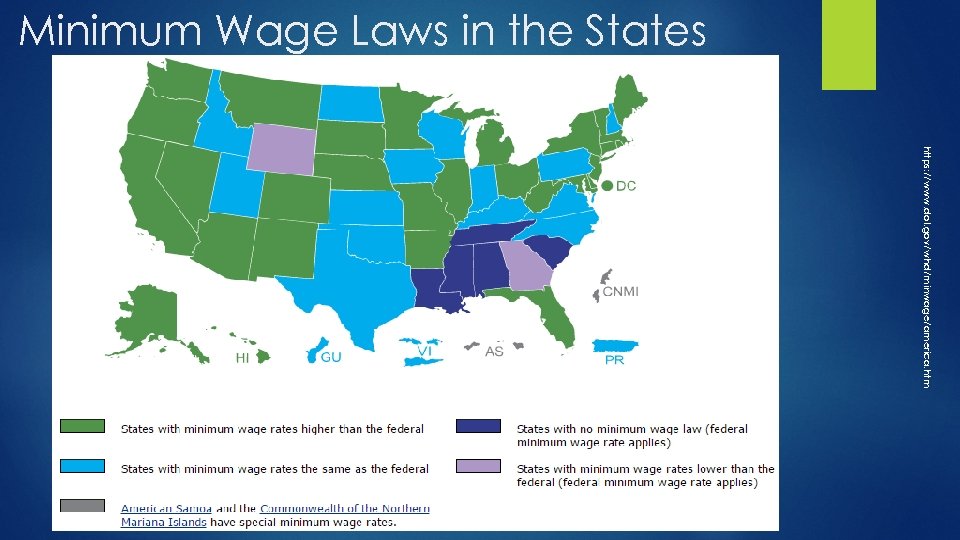 Minimum Wage Laws in the States https: //www. dol. gov/whd/minwage/america. htm
Minimum Wage Laws in the States https: //www. dol. gov/whd/minwage/america. htm
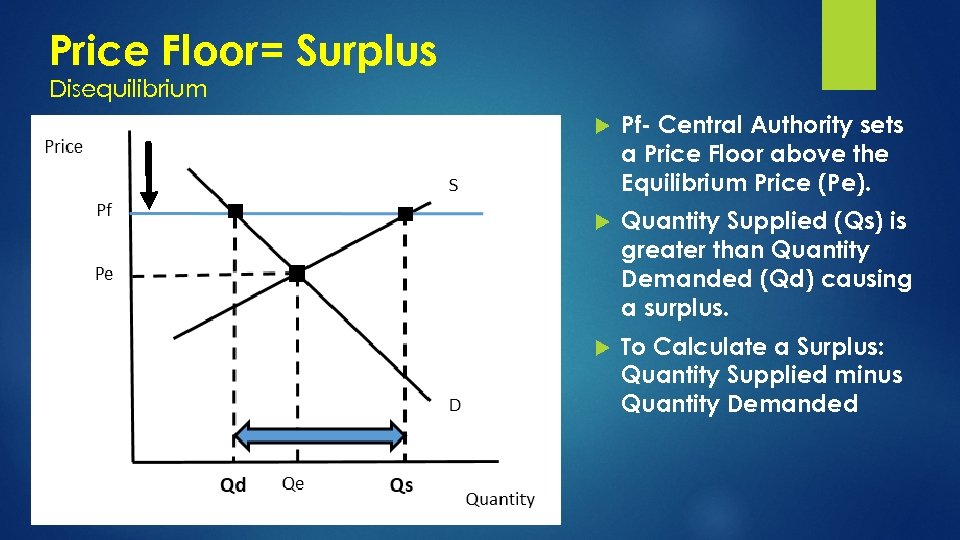 Price Floor= Surplus Disequilibrium Pf- Central Authority sets a Price Floor above the Equilibrium Price (Pe). Quantity Supplied (Qs) is greater than Quantity Demanded (Qd) causing a surplus. To Calculate a Surplus: Quantity Supplied minus Quantity Demanded
Price Floor= Surplus Disequilibrium Pf- Central Authority sets a Price Floor above the Equilibrium Price (Pe). Quantity Supplied (Qs) is greater than Quantity Demanded (Qd) causing a surplus. To Calculate a Surplus: Quantity Supplied minus Quantity Demanded
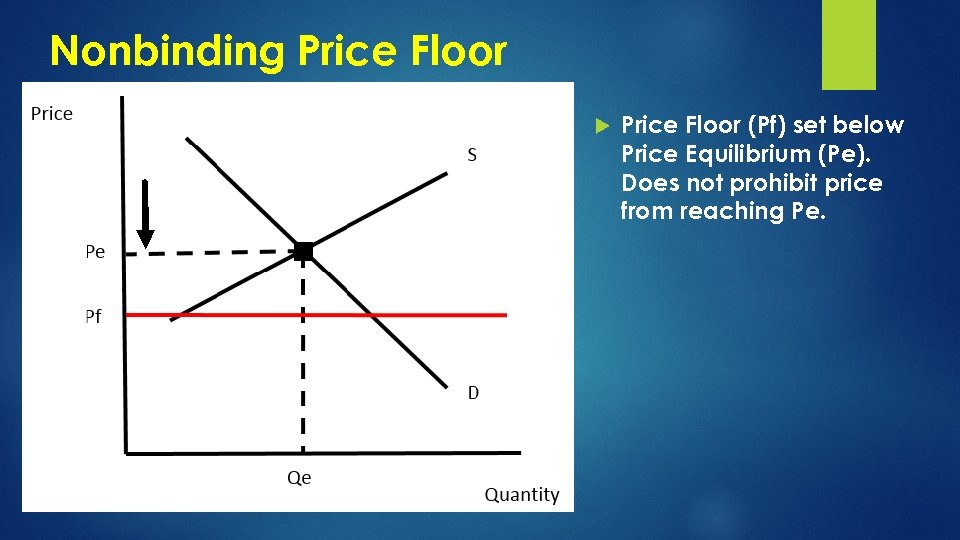 Nonbinding Price Floor (Pf) set below Price Equilibrium (Pe). Does not prohibit price from reaching Pe.
Nonbinding Price Floor (Pf) set below Price Equilibrium (Pe). Does not prohibit price from reaching Pe.
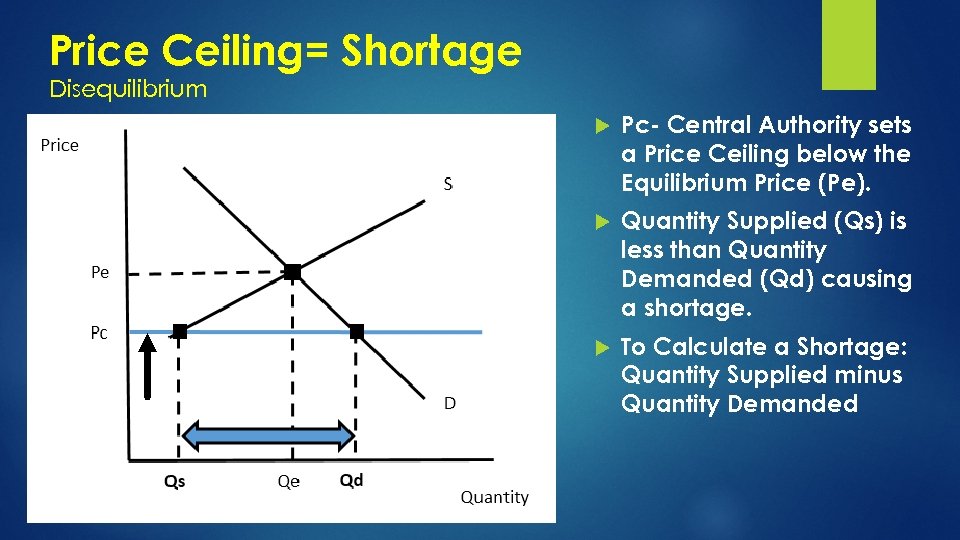 Price Ceiling= Shortage Disequilibrium Pc- Central Authority sets a Price Ceiling below the Equilibrium Price (Pe). Quantity Supplied (Qs) is less than Quantity Demanded (Qd) causing a shortage. To Calculate a Shortage: Quantity Supplied minus Quantity Demanded
Price Ceiling= Shortage Disequilibrium Pc- Central Authority sets a Price Ceiling below the Equilibrium Price (Pe). Quantity Supplied (Qs) is less than Quantity Demanded (Qd) causing a shortage. To Calculate a Shortage: Quantity Supplied minus Quantity Demanded
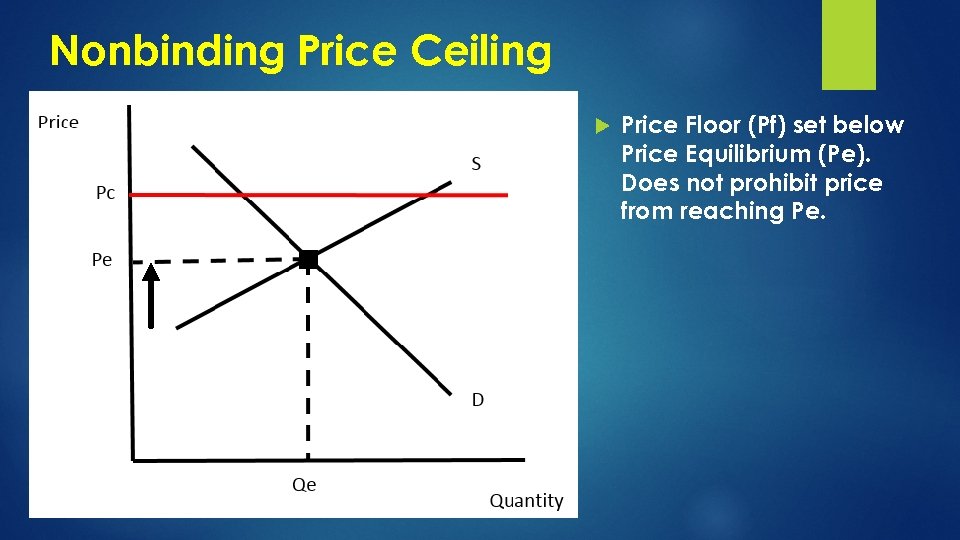 Nonbinding Price Ceiling Price Floor (Pf) set below Price Equilibrium (Pe). Does not prohibit price from reaching Pe.
Nonbinding Price Ceiling Price Floor (Pf) set below Price Equilibrium (Pe). Does not prohibit price from reaching Pe.
 Business Organizations ship tor prie Pro Sole Both Partn ershi p
Business Organizations ship tor prie Pro Sole Both Partn ershi p
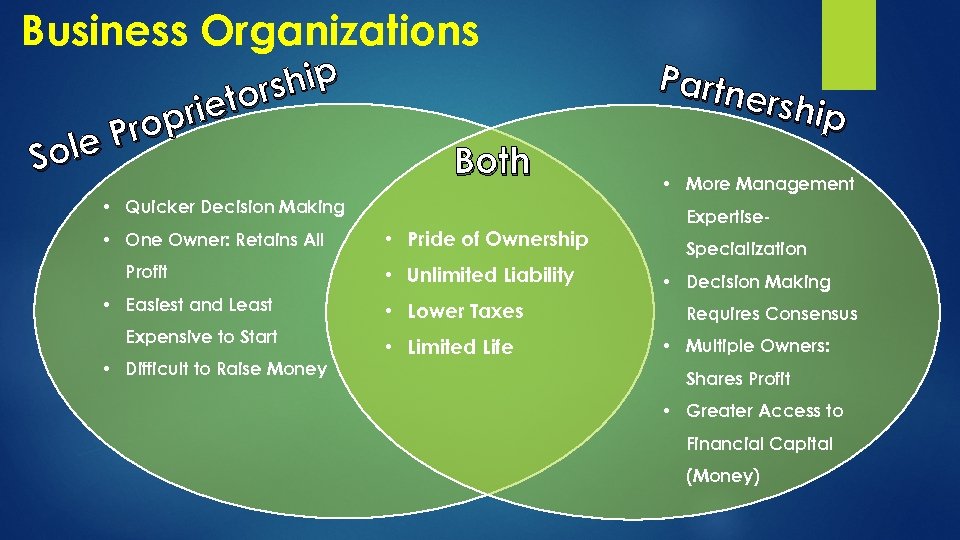 Business Organizations ship tor rie Prop Sole Both • Quicker Decision Making • One Owner: Retains All Profit • Easiest and Least Expensive to Start • Difficult to Raise Money • Pride of Ownership • Unlimited Liability • Lower Taxes • Limited Life Partn ershi p • More Management Expertise. Specialization • Decision Making Requires Consensus • Multiple Owners: Shares Profit • Greater Access to Financial Capital (Money)
Business Organizations ship tor rie Prop Sole Both • Quicker Decision Making • One Owner: Retains All Profit • Easiest and Least Expensive to Start • Difficult to Raise Money • Pride of Ownership • Unlimited Liability • Lower Taxes • Limited Life Partn ershi p • More Management Expertise. Specialization • Decision Making Requires Consensus • Multiple Owners: Shares Profit • Greater Access to Financial Capital (Money)
 Business Organizations
Business Organizations
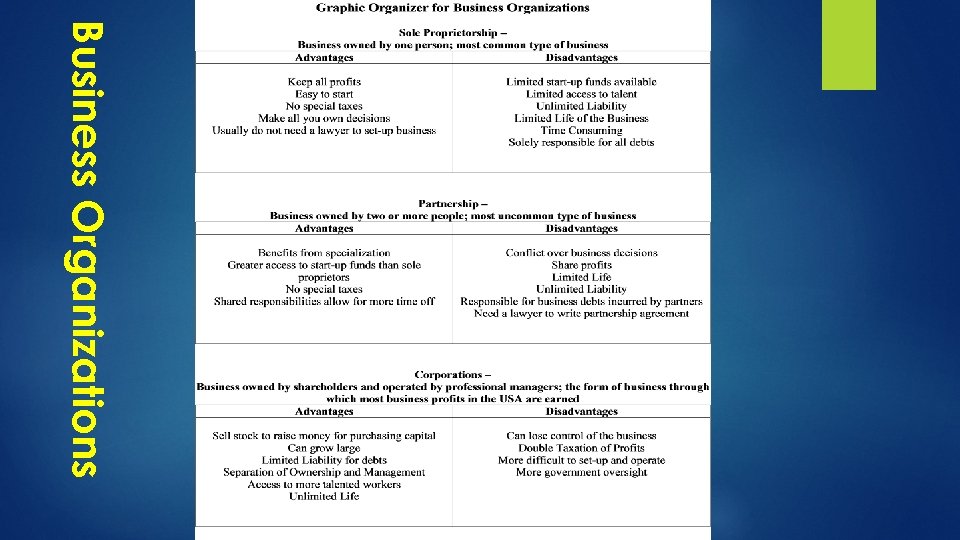 Business Organizations
Business Organizations
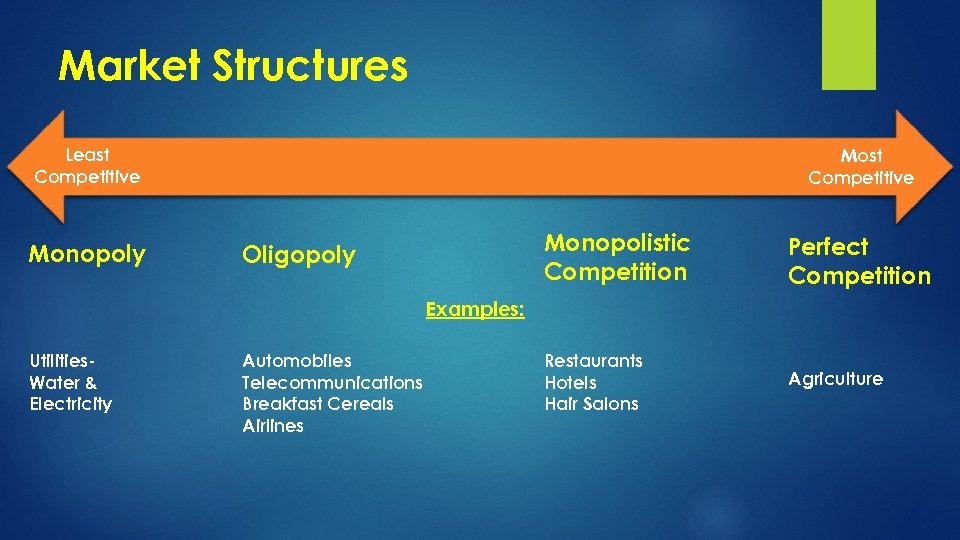 Market Structures Least Competitive Monopoly Most Competitive Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Perfect Competition Restaurants Hotels Hair Salons Agriculture Examples: Utilities. Water & Electricity Automobiles Telecommunications Breakfast Cereals Airlines
Market Structures Least Competitive Monopoly Most Competitive Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Perfect Competition Restaurants Hotels Hair Salons Agriculture Examples: Utilities. Water & Electricity Automobiles Telecommunications Breakfast Cereals Airlines
 Market Structures
Market Structures
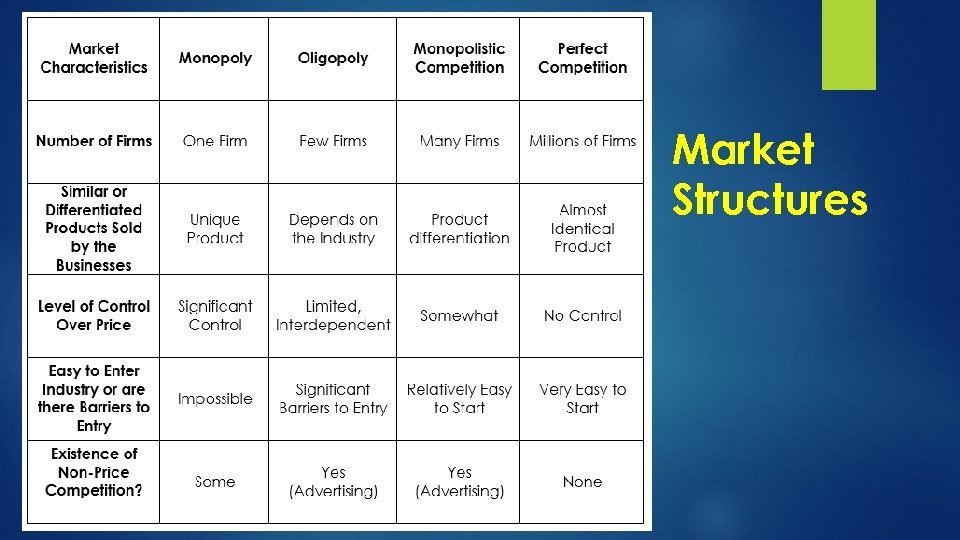 Market Structures
Market Structures


