7efad544b55f89cbe46a8cafec198a47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Microecon – Unit 2 Part 3
Microecon – Unit 2 Part 3
 You have a group of average consumers. Let’s say they all have a favorite gum… which normally costs 50¢. Would most of these consumers still buy the gum if the price rose to 75¢?
You have a group of average consumers. Let’s say they all have a favorite gum… which normally costs 50¢. Would most of these consumers still buy the gum if the price rose to 75¢?
 Same group of consumers. Some years they go on their favorite vacation with their wives… . . . which normally costs $1, 000. Would most of these consumers still go if the price rose to $1500?
Same group of consumers. Some years they go on their favorite vacation with their wives… . . . which normally costs $1, 000. Would most of these consumers still go if the price rose to $1500?
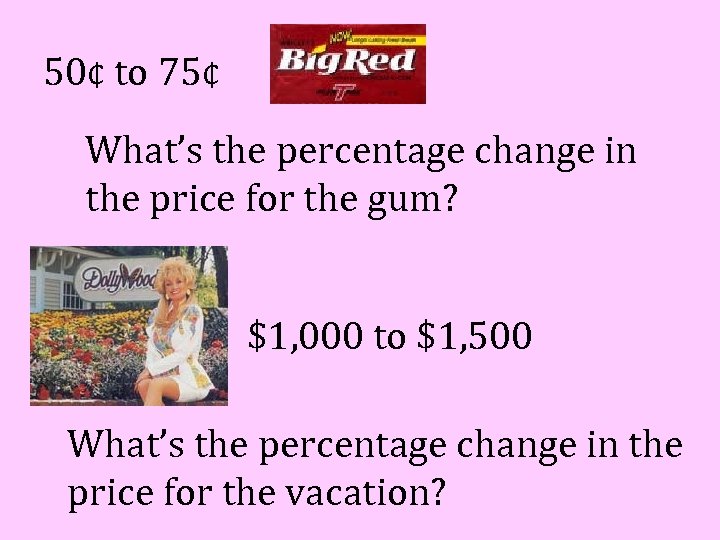 50¢ to 75¢ What’s the percentage change in the price for the gum? $1, 000 to $1, 500 What’s the percentage change in the price for the vacation?
50¢ to 75¢ What’s the percentage change in the price for the gum? $1, 000 to $1, 500 What’s the percentage change in the price for the vacation?
 Economists examine this idea…. How will the demand for an item/service change when the price is changed? If the price goes up… will consumers buy the same amount? will consumers buy less or none at all?
Economists examine this idea…. How will the demand for an item/service change when the price is changed? If the price goes up… will consumers buy the same amount? will consumers buy less or none at all?
 This is called…. Elasticity is the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable, ceteris parabis (other things equal). Elasticity examines…. will the quantity consumed change if the price goes up…or if the price goes down?
This is called…. Elasticity is the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable, ceteris parabis (other things equal). Elasticity examines…. will the quantity consumed change if the price goes up…or if the price goes down?
 If the quantity demanded does not change we call the demand inelastic. P If the quantity demanded changes we call the demand elastic. INELASTIC P ELASTIC $300 $3 $2 $200 $1 $100 D 10 m Q D 100 200 500 Q
If the quantity demanded does not change we call the demand inelastic. P If the quantity demanded changes we call the demand elastic. INELASTIC P ELASTIC $300 $3 $2 $200 $1 $100 D 10 m Q D 100 200 500 Q
 There are characteristics of goods/services that can make their demand tend to be more elastic or more inelastic. Use your intuition to decide if each makes the demand more elastic or inelastic. Copy this chart into your notes.
There are characteristics of goods/services that can make their demand tend to be more elastic or more inelastic. Use your intuition to decide if each makes the demand more elastic or inelastic. Copy this chart into your notes.
 Elastic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Inelastic
Elastic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Inelastic
 Elastic Inelastic few substitutes many substitutes Will a change in the price of Dasani bottled water make a difference in the quantity demanded?
Elastic Inelastic few substitutes many substitutes Will a change in the price of Dasani bottled water make a difference in the quantity demanded?
 Elastic 1. many substitutes 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Inelastic few substitutes
Elastic 1. many substitutes 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Inelastic few substitutes
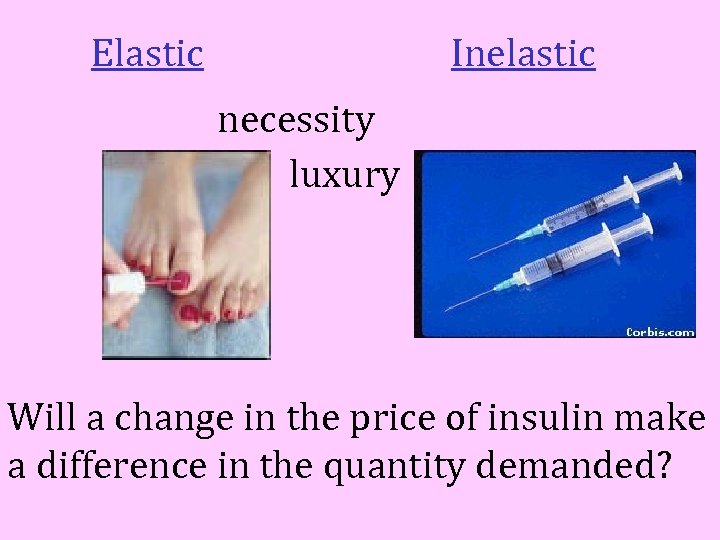 Elastic Inelastic necessity luxury Will a change in the price of insulin make a difference in the quantity demanded?
Elastic Inelastic necessity luxury Will a change in the price of insulin make a difference in the quantity demanded?
 Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. 4. 5. 6.
Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. 4. 5. 6.
 Elastic Inelastic inexpensive Will a change in the price of pens make a difference in the quantity demanded?
Elastic Inelastic inexpensive Will a change in the price of pens make a difference in the quantity demanded?
 Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. 5. 6.
Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. 5. 6.
 Elastic Inelastic habit-forming non-habit forming Will a change in the price of coffee make a difference in the quantity demanded?
Elastic Inelastic habit-forming non-habit forming Will a change in the price of coffee make a difference in the quantity demanded?
 Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. 6.
Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. 6.
 Elastic Inelastic shorter time period longer time period Let’s say your refrig broke…would a change in the price of refrigs make a difference in the quantity demanded?
Elastic Inelastic shorter time period longer time period Let’s say your refrig broke…would a change in the price of refrigs make a difference in the quantity demanded?
 Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. longer time period shorter time period 6.
Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. longer time period shorter time period 6.
 In addition to characteristics of products that tend to make demand for them be more elastic or inelastic… There is also the Total Revenue Test which will tell you if demand is elastic or inelastic. Total Revenue = price x quantity
In addition to characteristics of products that tend to make demand for them be more elastic or inelastic… There is also the Total Revenue Test which will tell you if demand is elastic or inelastic. Total Revenue = price x quantity
 Let’s say there’s only one nail salon… in town where you could adorn your nails with this lovely design… . . or the very popular French nail manicure…
Let’s say there’s only one nail salon… in town where you could adorn your nails with this lovely design… . . or the very popular French nail manicure…
 Let’s say the nail salon changed the price of its manicures and found the following: price quantity $10 15 5 1 $15 $30 To apply the total revenue test, we see what happened to TR when P .
Let’s say the nail salon changed the price of its manicures and found the following: price quantity $10 15 5 1 $15 $30 To apply the total revenue test, we see what happened to TR when P .
 So what is total revenue? Total Revenue = price x quantity $150 $75 $10 15 $30 $30 5 1 With manicures, when the price went up the TR went down. So was the demand for manicures elastic (responsive) or inelastic?
So what is total revenue? Total Revenue = price x quantity $150 $75 $10 15 $30 $30 5 1 With manicures, when the price went up the TR went down. So was the demand for manicures elastic (responsive) or inelastic?
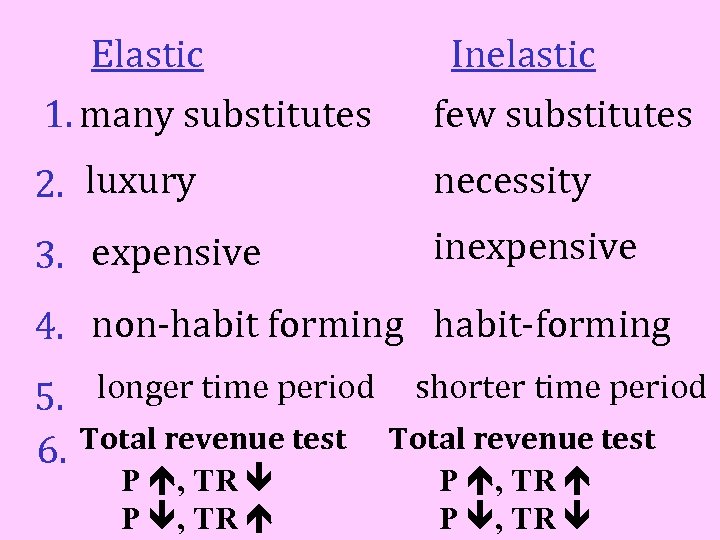 Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. longer time period shorter time period 6. Total revenue test P , TR
Elastic 1. many substitutes Inelastic few substitutes 2. luxury necessity 3. expensive inexpensive 4. non-habit forming habit-forming 5. longer time period shorter time period 6. Total revenue test P , TR
 Give 2 or 3 reasons to explain why demand for these products / services is more elastic or inelastic.
Give 2 or 3 reasons to explain why demand for these products / services is more elastic or inelastic.
 P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q So why does it matter if demand is more elastic or more inelastic? Which demand is relatively more inelastic?
P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q So why does it matter if demand is more elastic or more inelastic? Which demand is relatively more inelastic?
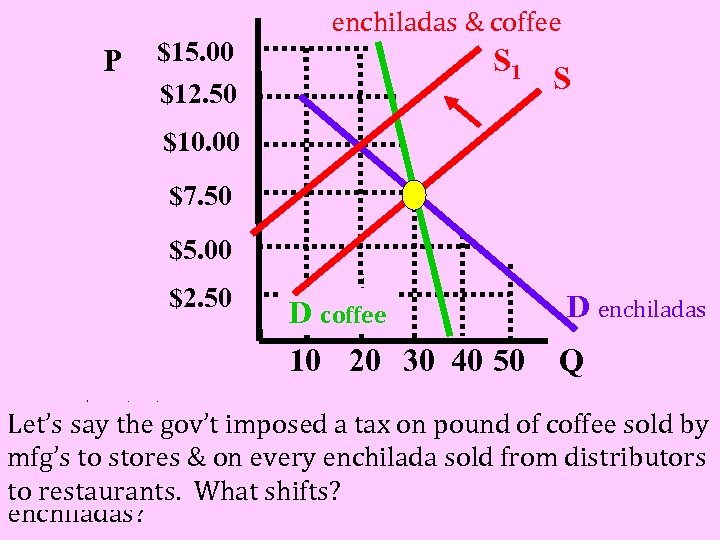 P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q at P =say thehow many Let’s $7. 50 gov’t imposed a tax on pound of coffee sold by cups of coffee areon every enchilada sold from distributors mfg’s to stores & demanded? how many to restaurants. What shifts? enchiladas?
P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q at P =say thehow many Let’s $7. 50 gov’t imposed a tax on pound of coffee sold by cups of coffee areon every enchilada sold from distributors mfg’s to stores & demanded? how many to restaurants. What shifts? enchiladas?
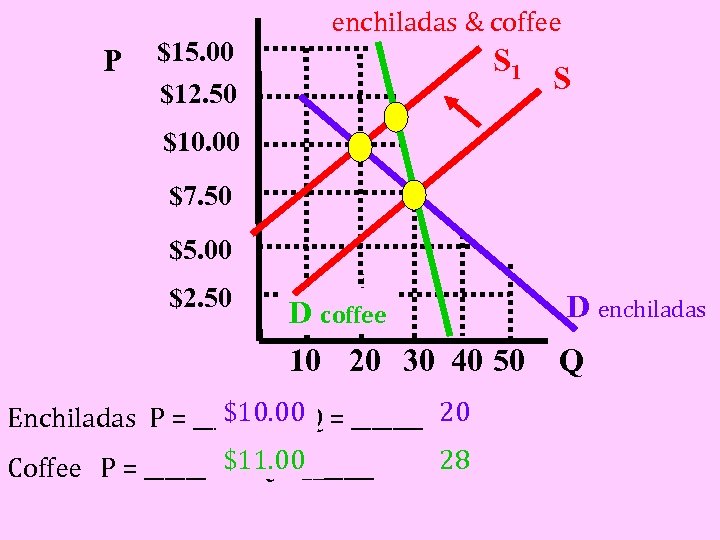 P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 $10. 00 Enchiladas P = ______ & Q = _______ 20 28 Coffee P = ______ $11. 00_______ & Q= D enchiladas Q
P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 $10. 00 Enchiladas P = ______ & Q = _______ 20 28 Coffee P = ______ $11. 00_______ & Q= D enchiladas Q
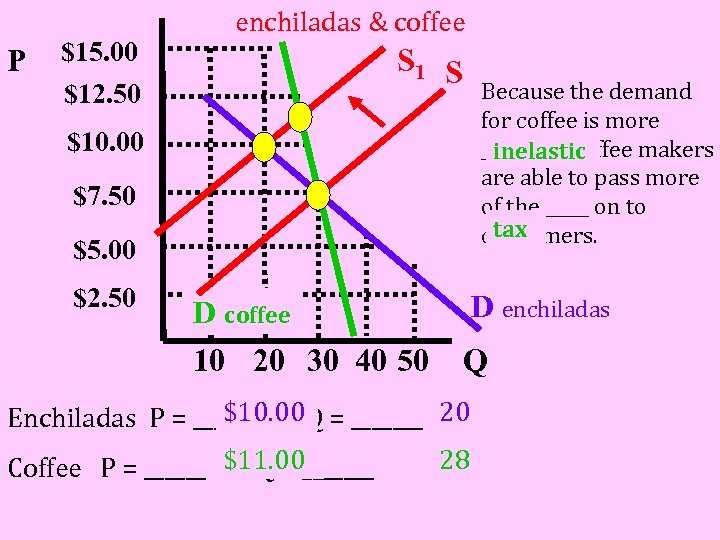 P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S Because the demand for coffee is more _____, coffee makers inelastic are able to pass more of the _____ on to tax consumers. $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q $10. 00 Enchiladas P = ______ & Q = _______ 20 28 Coffee P = ______ $11. 00_______ & Q=
P $15. 00 $12. 50 enchiladas & coffee S 1 S Because the demand for coffee is more _____, coffee makers inelastic are able to pass more of the _____ on to tax consumers. $10. 00 $7. 50 $5. 00 $2. 50 D coffee 10 20 30 40 50 D enchiladas Q $10. 00 Enchiladas P = ______ & Q = _______ 20 28 Coffee P = ______ $11. 00_______ & Q=


