9ef848983c86fb609d14e658facbd9b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 101
 Micro. Solve Commercial Edgar Clodfelter APAS, LLC Chris Miele NEMRC 1
Micro. Solve Commercial Edgar Clodfelter APAS, LLC Chris Miele NEMRC 1
 Micro. Solve Commercial Workshop Aims to Give some Practical Understanding -Not a class on using MVS Commercial system. • Commercial System is a Black Box from M&S -Installation and setup is important -Simple and easy to use -Keep it simple -Approach is similar to calculator method 2
Micro. Solve Commercial Workshop Aims to Give some Practical Understanding -Not a class on using MVS Commercial system. • Commercial System is a Black Box from M&S -Installation and setup is important -Simple and easy to use -Keep it simple -Approach is similar to calculator method 2
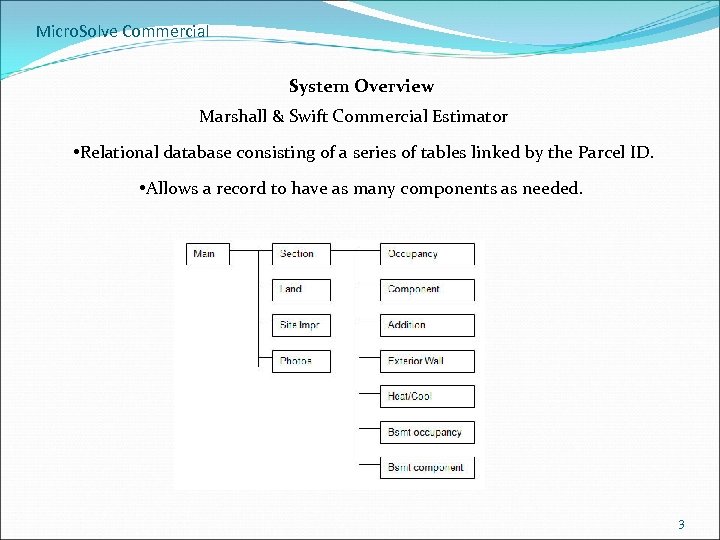 Micro. Solve Commercial System Overview Marshall & Swift Commercial Estimator • Relational database consisting of a series of tables linked by the Parcel ID. • Allows a record to have as many components as needed. 3
Micro. Solve Commercial System Overview Marshall & Swift Commercial Estimator • Relational database consisting of a series of tables linked by the Parcel ID. • Allows a record to have as many components as needed. 3
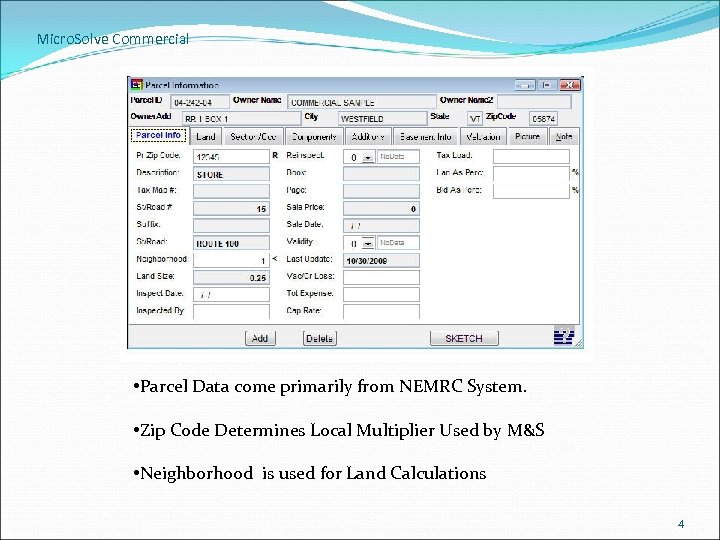 Micro. Solve Commercial • Parcel Data come primarily from NEMRC System. • Zip Code Determines Local Multiplier Used by M&S • Neighborhood is used for Land Calculations 4
Micro. Solve Commercial • Parcel Data come primarily from NEMRC System. • Zip Code Determines Local Multiplier Used by M&S • Neighborhood is used for Land Calculations 4
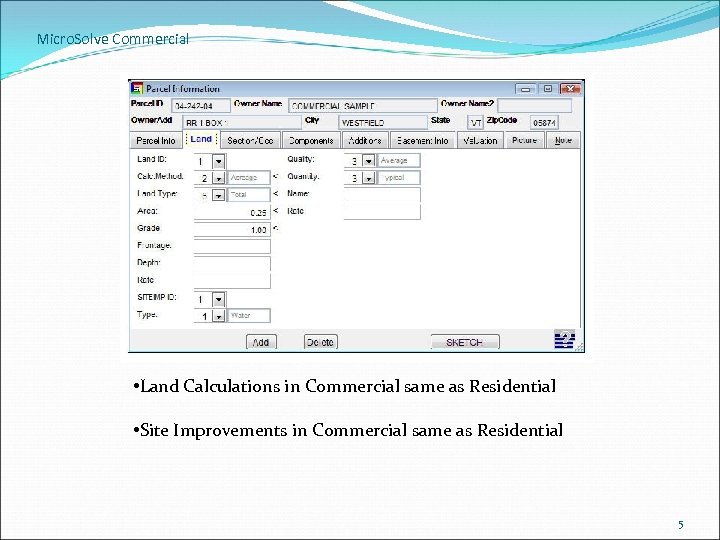 Micro. Solve Commercial • Land Calculations in Commercial same as Residential • Site Improvements in Commercial same as Residential 5
Micro. Solve Commercial • Land Calculations in Commercial same as Residential • Site Improvements in Commercial same as Residential 5
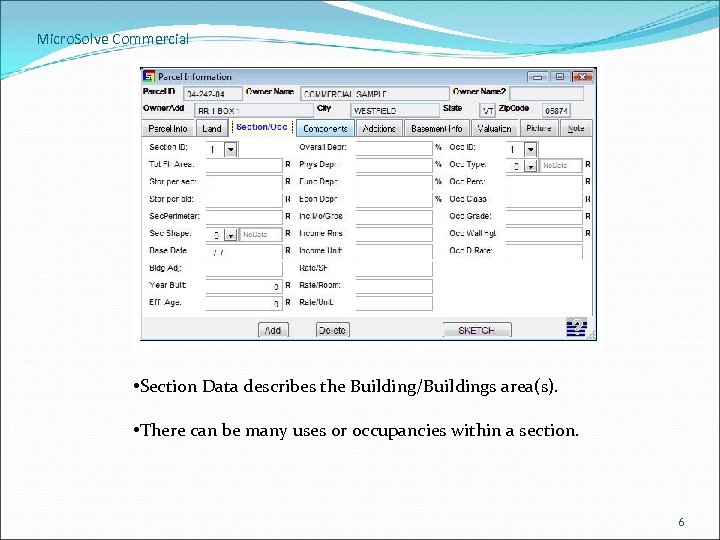 Micro. Solve Commercial • Section Data describes the Building/Buildings area(s). • There can be many uses or occupancies within a section. 6
Micro. Solve Commercial • Section Data describes the Building/Buildings area(s). • There can be many uses or occupancies within a section. 6
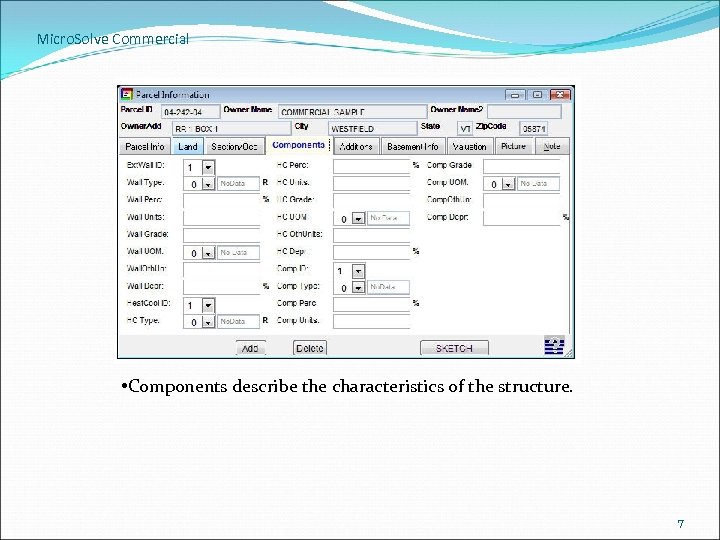 Micro. Solve Commercial • Components describe the characteristics of the structure. 7
Micro. Solve Commercial • Components describe the characteristics of the structure. 7
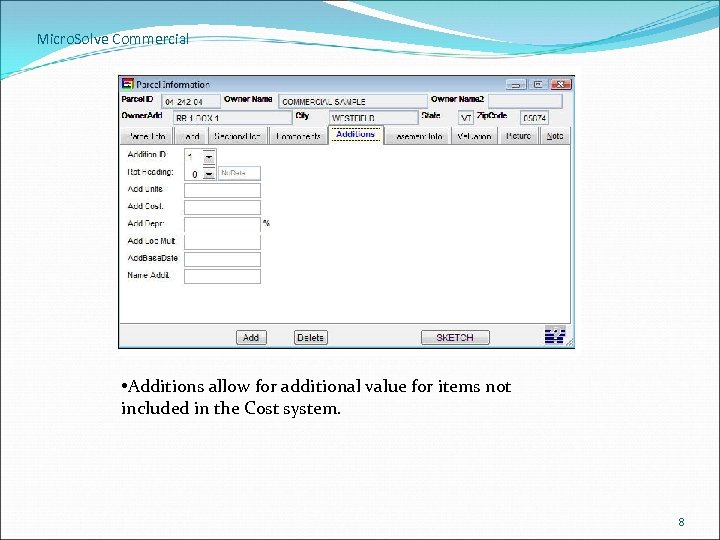 Micro. Solve Commercial • Additions allow for additional value for items not included in the Cost system. 8
Micro. Solve Commercial • Additions allow for additional value for items not included in the Cost system. 8
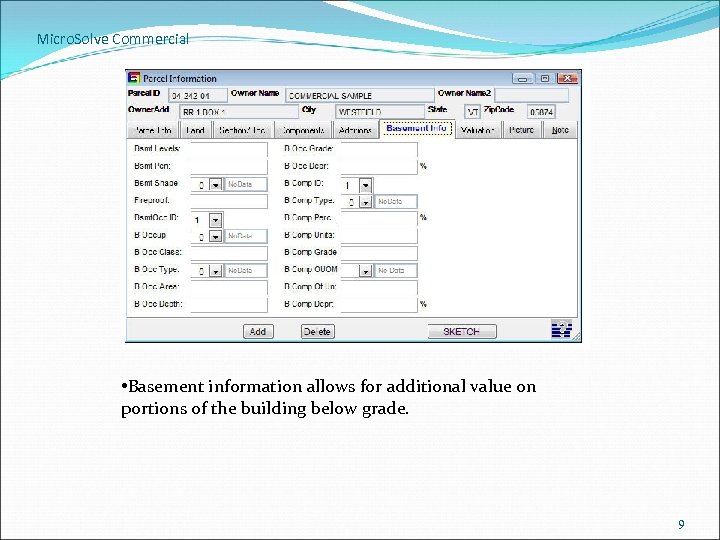 Micro. Solve Commercial • Basement information allows for additional value on portions of the building below grade. 9
Micro. Solve Commercial • Basement information allows for additional value on portions of the building below grade. 9
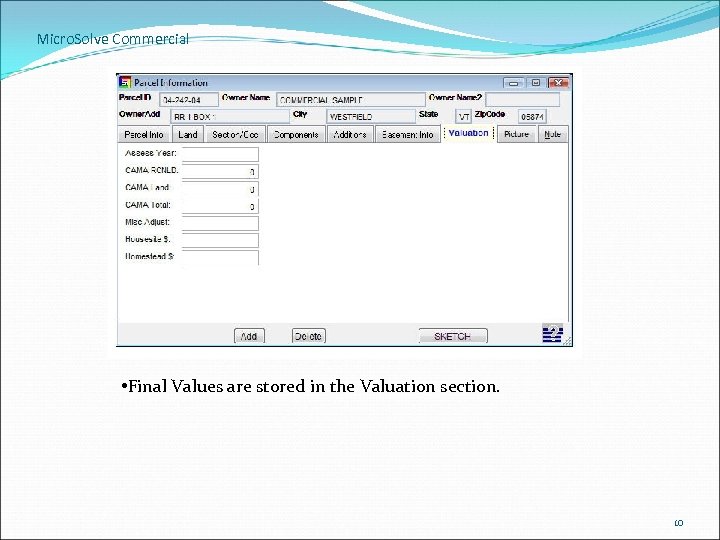 Micro. Solve Commercial • Final Values are stored in the Valuation section. 10
Micro. Solve Commercial • Final Values are stored in the Valuation section. 10
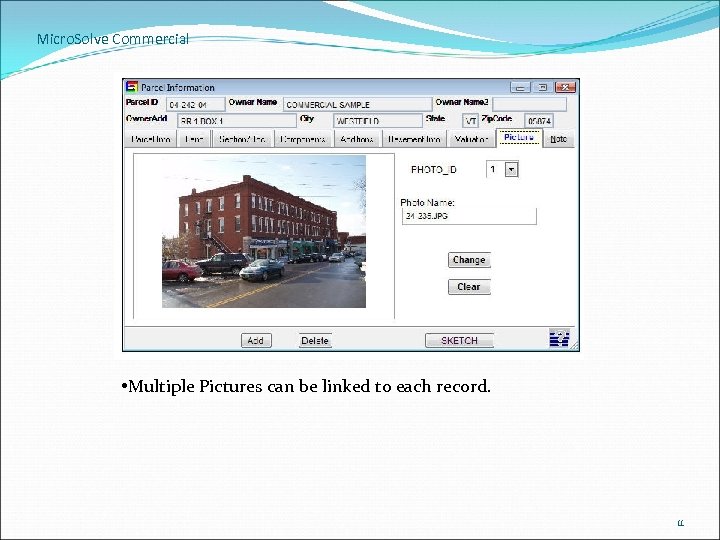 Micro. Solve Commercial • Multiple Pictures can be linked to each record. 11
Micro. Solve Commercial • Multiple Pictures can be linked to each record. 11
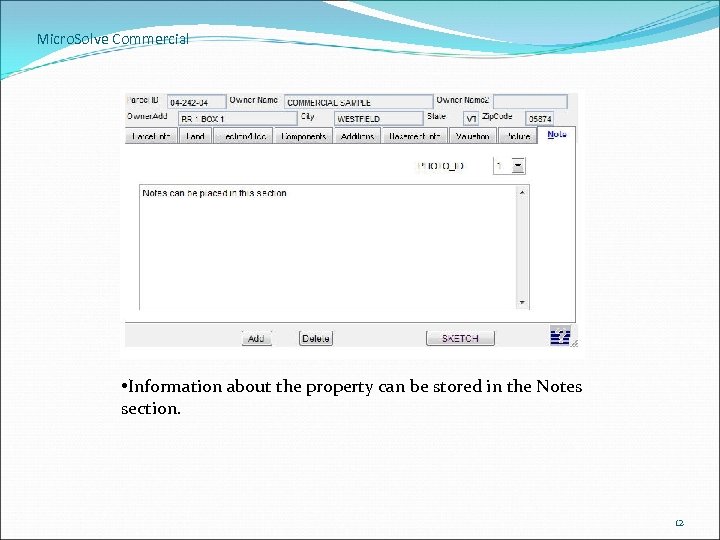 Micro. Solve Commercial • Information about the property can be stored in the Notes section. 12
Micro. Solve Commercial • Information about the property can be stored in the Notes section. 12
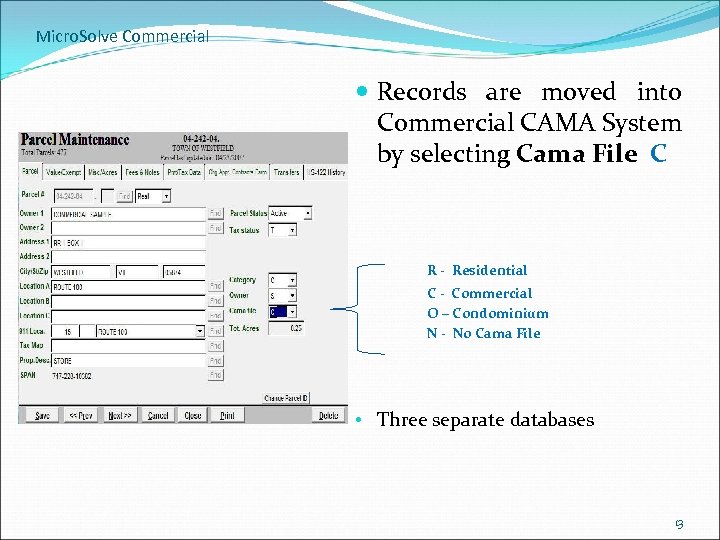 Micro. Solve Commercial Records are moved into Commercial CAMA System by selecting Cama File C R - Residential C - Commercial O – Condominium N - No Cama File • Three separate databases 13
Micro. Solve Commercial Records are moved into Commercial CAMA System by selecting Cama File C R - Residential C - Commercial O – Condominium N - No Cama File • Three separate databases 13
 Micro. Solve Commercial Caution: Just because a property is classified or categorized as commercial does not mean it should be valued in the commercial system. 14
Micro. Solve Commercial Caution: Just because a property is classified or categorized as commercial does not mean it should be valued in the commercial system. 14
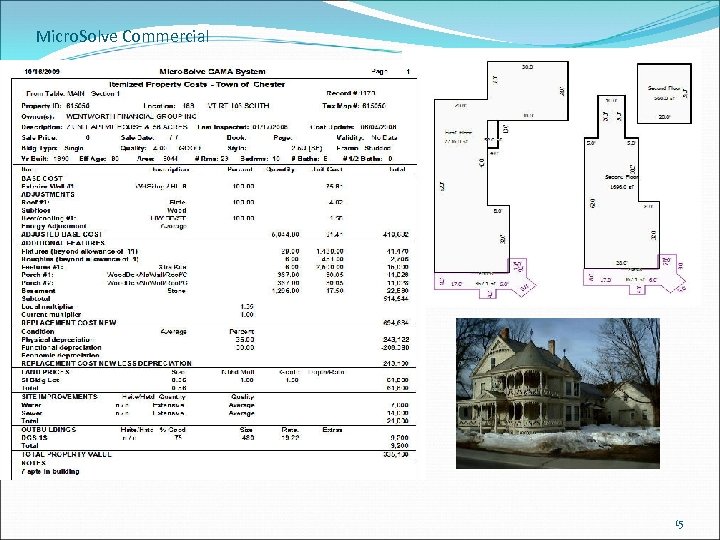 Micro. Solve Commercial 15
Micro. Solve Commercial 15
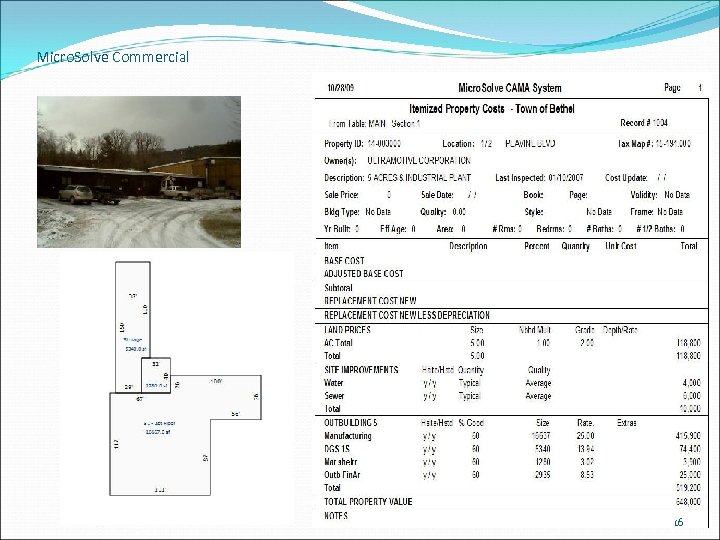 Micro. Solve Commercial 16
Micro. Solve Commercial 16
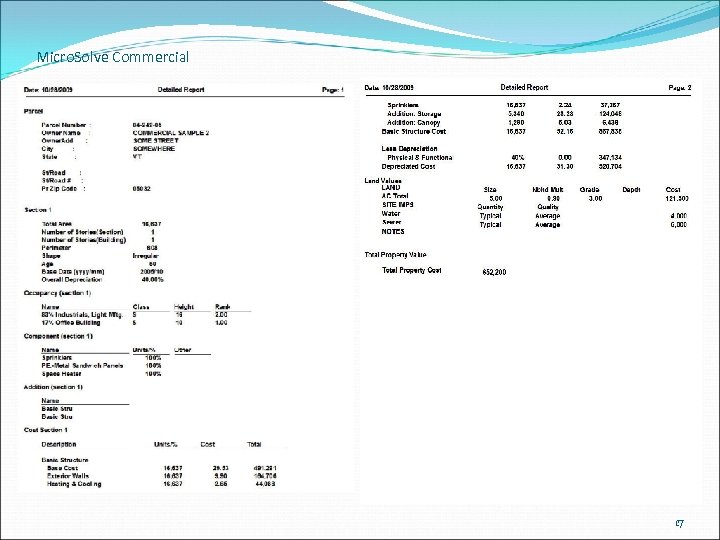 Micro. Solve Commercial 17
Micro. Solve Commercial 17
 Micro. Solve Commercial Need to decide if building is really a commercial style. Houses converted to Offices Garages Low quality steel buildings Are there considerations making a building suited to residential database? Outbuildings - garages, sheds Concerns about excessive value Need for greater control of value Multiple dwellings/buildings 18
Micro. Solve Commercial Need to decide if building is really a commercial style. Houses converted to Offices Garages Low quality steel buildings Are there considerations making a building suited to residential database? Outbuildings - garages, sheds Concerns about excessive value Need for greater control of value Multiple dwellings/buildings 18
 Micro. Solve Commercial Three Approaches to Value 1. Cost Approach • • Indication of value that is the sum of estimated land value and estimated depreciated cost of the building and other improvements. V = LV + IV (CN – D) 2. Market Approach • Valuation procedure based on prices paid in actual market transactions used to determine most probable sale price of property being appraised. 3. Income Approach • Converts anticipated benefits (dollars) to be derived from ownership into a value estimate. 19
Micro. Solve Commercial Three Approaches to Value 1. Cost Approach • • Indication of value that is the sum of estimated land value and estimated depreciated cost of the building and other improvements. V = LV + IV (CN – D) 2. Market Approach • Valuation procedure based on prices paid in actual market transactions used to determine most probable sale price of property being appraised. 3. Income Approach • Converts anticipated benefits (dollars) to be derived from ownership into a value estimate. 19
 Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value 1. Replacement Cost • Total cost of building construction required to: a. b. c. Replace the subject building. Substitute with like or equal utility. Using current standards of materials and design 2. Reproduction Cost • Total cost of building construction to replace with actual replica of salient characteristics or components. a. b. c. Newer buildings replacement approximates reproduction. Use segregated cost method for older buildings Actual replacement may not be available or desirable. 3. Principle of Substitution • Economic principle that the price of a commodity tends to be no higher than the price of a substitute having equal utility without undue delay. 20
Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value 1. Replacement Cost • Total cost of building construction required to: a. b. c. Replace the subject building. Substitute with like or equal utility. Using current standards of materials and design 2. Reproduction Cost • Total cost of building construction to replace with actual replica of salient characteristics or components. a. b. c. Newer buildings replacement approximates reproduction. Use segregated cost method for older buildings Actual replacement may not be available or desirable. 3. Principle of Substitution • Economic principle that the price of a commodity tends to be no higher than the price of a substitute having equal utility without undue delay. 20
 Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value • Marshall and Swift Cost Approach is based on end costs of buildings to the buyer or owner. • Costs are averages of detailed estimates of actual costs breakdowns and total end costs of actual construction projects. – Completed from surveys of construction jobs. • Elements of cost include: a. b. c. Direct Costs (labor, materials, equipment, fees and charges) Indirect Costs (overhead, permits, financing, selling expenses) Profit. 21
Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value • Marshall and Swift Cost Approach is based on end costs of buildings to the buyer or owner. • Costs are averages of detailed estimates of actual costs breakdowns and total end costs of actual construction projects. – Completed from surveys of construction jobs. • Elements of cost include: a. b. c. Direct Costs (labor, materials, equipment, fees and charges) Indirect Costs (overhead, permits, financing, selling expenses) Profit. 21
 Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value • Cost Approach Based on cost of production. 2. Applicable for new or proposed construction. 3. Applicable for unique or special purpose properties. 4. Represents the highest and best use of the site. 1. • Cost is an avenue to market value. • The goal is not Cost, but Market 22
Micro. Solve Commercial Cost Approach and Value • Cost Approach Based on cost of production. 2. Applicable for new or proposed construction. 3. Applicable for unique or special purpose properties. 4. Represents the highest and best use of the site. 1. • Cost is an avenue to market value. • The goal is not Cost, but Market 22
 Micro. Solve Commercial Marshall and Swift Concepts 23
Micro. Solve Commercial Marshall and Swift Concepts 23
 Micro. Solve Commercial Marshall and Swift Methods and Terms Calculator Method – (Used with commercial estimator) 1. a. b. c. Based on concept of cost per increment of floor area. Areas or buildings are defined by a section or multiple sections. Sections are defined by the use of the building, or occupancy. Example – Restaurant, Health Club, Bank, Office, Service Station. d. Within each occupancy are sqft refinements or components. Example – Exterior Wall, Heating/Cooling, Elevator, Mezzanine. Buildings are classified by Occupancy, and grouped into Sections. Segregated Method – (Not used with commercial estimator) 2. a. b. Computes total cost by successively adding the costs of all components of the building. The method is specific and detailed. 24
Micro. Solve Commercial Marshall and Swift Methods and Terms Calculator Method – (Used with commercial estimator) 1. a. b. c. Based on concept of cost per increment of floor area. Areas or buildings are defined by a section or multiple sections. Sections are defined by the use of the building, or occupancy. Example – Restaurant, Health Club, Bank, Office, Service Station. d. Within each occupancy are sqft refinements or components. Example – Exterior Wall, Heating/Cooling, Elevator, Mezzanine. Buildings are classified by Occupancy, and grouped into Sections. Segregated Method – (Not used with commercial estimator) 2. a. b. Computes total cost by successively adding the costs of all components of the building. The method is specific and detailed. 24
 Micro. Solve Commercial Section Information 25
Micro. Solve Commercial Section Information 25
 Micro. Solve Commercial SECTION: BUILDING DATA • Building Data consists of: • Size and shape data, including the total floor area, number of stories and perimeter or shape. • Age data, including effective age, base date and a special age adjustment value. • Depreciation data. • Occupancy data, including the building's occupancy (use), class of construction, story height and cost rank (quality). The following factors are included: Total Floor Area (sq. ft. ) * Stories per Section * Stories per Building Perimeter (linear feet) Shape * -Use either Perimeter or Shape. Base Date – Base date of cost tables Building Adj. A dollar amount reflecting unusual conditions. Fireproof A logical field: enter T or F. Year Built Effective Age (years) * Use either YB or Effective Age. Depreciation % Physical Functional Economic * Required Field 26
Micro. Solve Commercial SECTION: BUILDING DATA • Building Data consists of: • Size and shape data, including the total floor area, number of stories and perimeter or shape. • Age data, including effective age, base date and a special age adjustment value. • Depreciation data. • Occupancy data, including the building's occupancy (use), class of construction, story height and cost rank (quality). The following factors are included: Total Floor Area (sq. ft. ) * Stories per Section * Stories per Building Perimeter (linear feet) Shape * -Use either Perimeter or Shape. Base Date – Base date of cost tables Building Adj. A dollar amount reflecting unusual conditions. Fireproof A logical field: enter T or F. Year Built Effective Age (years) * Use either YB or Effective Age. Depreciation % Physical Functional Economic * Required Field 26
 Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Single Section: Can be one building with one section. Example: 27
Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Single Section: Can be one building with one section. Example: 27
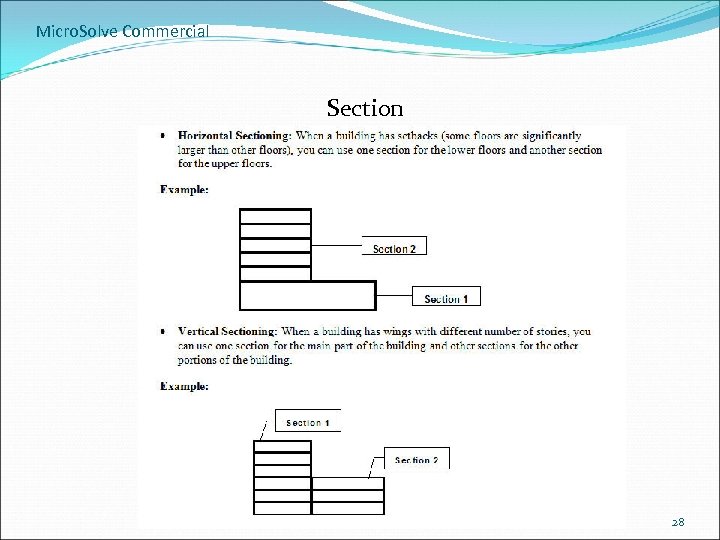 Micro. Solve Commercial Section 28
Micro. Solve Commercial Section 28
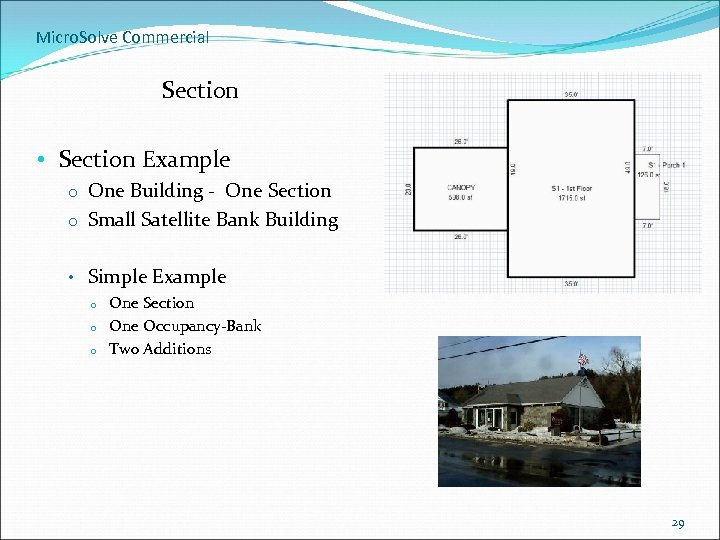 Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Section Example o One Building - One Section o Small Satellite Bank Building • Simple Example o o o One Section One Occupancy-Bank Two Additions 29
Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Section Example o One Building - One Section o Small Satellite Bank Building • Simple Example o o o One Section One Occupancy-Bank Two Additions 29
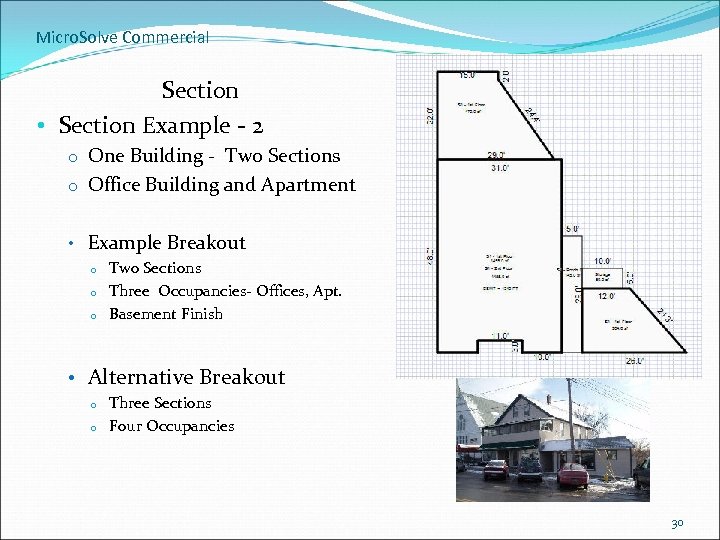 Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Section Example - 2 o One Building - Two Sections o Office Building and Apartment • Example Breakout o o o Two Sections Three Occupancies- Offices, Apt. Basement Finish • Alternative Breakout o o Three Sections Four Occupancies 30
Micro. Solve Commercial Section • Section Example - 2 o One Building - Two Sections o Office Building and Apartment • Example Breakout o o o Two Sections Three Occupancies- Offices, Apt. Basement Finish • Alternative Breakout o o Three Sections Four Occupancies 30
 Micro. Solve Commercial Section Example - 3 o Two Buildings – Two Sections on same Property o Manufacturing Building o Restaurant Building with Retail and apartment. • More Complex Example o o o Two Sections, Two Buildings Section 1 - 2 Occupancies Section 2 – 3 Occupancies 31
Micro. Solve Commercial Section Example - 3 o Two Buildings – Two Sections on same Property o Manufacturing Building o Restaurant Building with Retail and apartment. • More Complex Example o o o Two Sections, Two Buildings Section 1 - 2 Occupancies Section 2 – 3 Occupancies 31
 Micro. Solve Commercial Section Fields Total Floor Area (Required) The total floor area of a section is the total area on all floors based on the building's exterior dimensions. Example: The entry for 24, 525 square feet is: Total Floor Area (sq. ft. ) 24525 No Commas 32
Micro. Solve Commercial Section Fields Total Floor Area (Required) The total floor area of a section is the total area on all floors based on the building's exterior dimensions. Example: The entry for 24, 525 square feet is: Total Floor Area (sq. ft. ) 24525 No Commas 32
 Micro. Solve Commercial Section Fields Number of Stories Estimate with One Section: If estimate has only one section, enter its number of stories in “Number of Stories: Section” only. Example: The entry for a building with 3 stories, entered as a single section, is: Number of Stories: Section _3___ Building ____ 33
Micro. Solve Commercial Section Fields Number of Stories Estimate with One Section: If estimate has only one section, enter its number of stories in “Number of Stories: Section” only. Example: The entry for a building with 3 stories, entered as a single section, is: Number of Stories: Section _3___ Building ____ 33
 Micro. Solve Commercial Vertically Sectioned Building: The entries for this building are: If you vertically section a building, enter the number of Section 1 stories in each section under Story/Section __6__ Building ____ “Number of Stories: Section. ” Section 2: Example: A building that is part Story/Section __3__ Building ____ 6 stories and part 3 stories can be vertically sectioned as follows: 34
Micro. Solve Commercial Vertically Sectioned Building: The entries for this building are: If you vertically section a building, enter the number of Section 1 stories in each section under Story/Section __6__ Building ____ “Number of Stories: Section. ” Section 2: Example: A building that is part Story/Section __3__ Building ____ 6 stories and part 3 stories can be vertically sectioned as follows: 34
 Micro. Solve Commercial Horizontally Section Buildings: If you horizontally section a building, enter the number of stories in each section under “Number of Stories: Section, ” and the total number of stories in the building under “Number of Stories: Building. ” Example: A building that has a onestory bank on the first floor (20' story height), and five stories of offices on the second through sixth stories (10' story height), is sectioned horizontally as follows: The entries for the Building are: Section 1: Stories/Section __1__ Building __6__ Section 2: Stories/ Section __5__Building __6__ 35
Micro. Solve Commercial Horizontally Section Buildings: If you horizontally section a building, enter the number of stories in each section under “Number of Stories: Section, ” and the total number of stories in the building under “Number of Stories: Building. ” Example: A building that has a onestory bank on the first floor (20' story height), and five stories of offices on the second through sixth stories (10' story height), is sectioned horizontally as follows: The entries for the Building are: Section 1: Stories/Section __1__ Building __6__ Section 2: Stories/ Section __5__Building __6__ 35
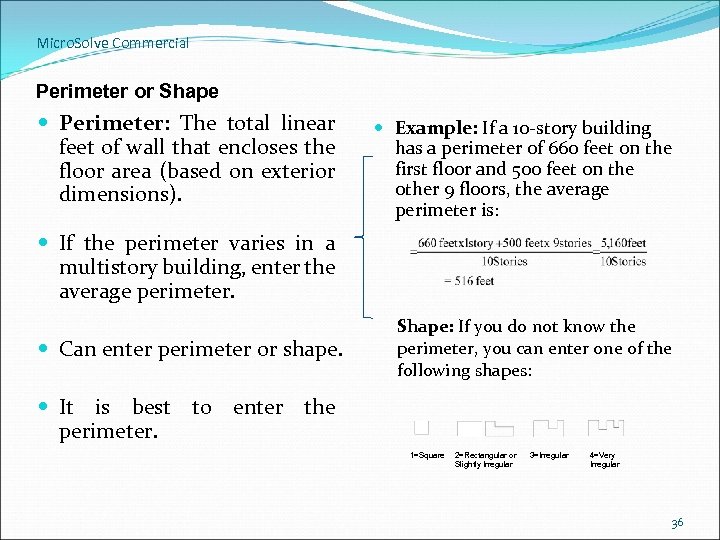 Micro. Solve Commercial Perimeter or Shape Perimeter: The total linear feet of wall that encloses the floor area (based on exterior dimensions). Example: If a 10 -story building has a perimeter of 660 feet on the first floor and 500 feet on the other 9 floors, the average perimeter is: If the perimeter varies in a multistory building, enter the average perimeter. Can enter perimeter or shape. Shape: If you do not know the perimeter, you can enter one of the following shapes: It is best to enter the perimeter. 1=Square 2=Rectangular or Slightly Irregular 3=Irregular 4=Very Irregular 36
Micro. Solve Commercial Perimeter or Shape Perimeter: The total linear feet of wall that encloses the floor area (based on exterior dimensions). Example: If a 10 -story building has a perimeter of 660 feet on the first floor and 500 feet on the other 9 floors, the average perimeter is: If the perimeter varies in a multistory building, enter the average perimeter. Can enter perimeter or shape. Shape: If you do not know the perimeter, you can enter one of the following shapes: It is best to enter the perimeter. 1=Square 2=Rectangular or Slightly Irregular 3=Irregular 4=Very Irregular 36
 Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation (determined by the system) is calculated based on age or effective age, rank, occupancy and class. There is no field for Condition. This calculation does not include either abnormal or excessive functional depreciation, or any external obsolescence. System documentation regarding base date and effective age has changed. o Base date is now the base date of the cost tables in use. Definitions Depreciation is loss in value due to any cause. Depreciation is divided into three general categories, as discussed below. 1. Physical depreciation is loss in value due to physical deterioration. Curable – Short lived items (Flooring, Paint) Incurable – Long lived items, require major construction to replace (Foundations, Heating systems) 2. Functional obsolescence is loss in value due to lack of utility or desirability of part or all of the property. - Many older buildings suffer from functional obsolescence. - Lack of Elevators, Adequate Wiring 3. External, locational or economic obsolescence is loss in value due to causes outside the property and independent of it. 37
Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation (determined by the system) is calculated based on age or effective age, rank, occupancy and class. There is no field for Condition. This calculation does not include either abnormal or excessive functional depreciation, or any external obsolescence. System documentation regarding base date and effective age has changed. o Base date is now the base date of the cost tables in use. Definitions Depreciation is loss in value due to any cause. Depreciation is divided into three general categories, as discussed below. 1. Physical depreciation is loss in value due to physical deterioration. Curable – Short lived items (Flooring, Paint) Incurable – Long lived items, require major construction to replace (Foundations, Heating systems) 2. Functional obsolescence is loss in value due to lack of utility or desirability of part or all of the property. - Many older buildings suffer from functional obsolescence. - Lack of Elevators, Adequate Wiring 3. External, locational or economic obsolescence is loss in value due to causes outside the property and independent of it. 37
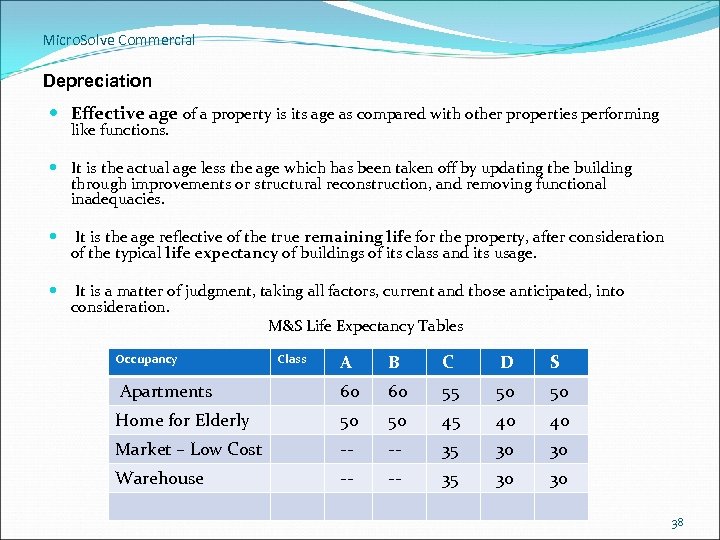 Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Effective age of a property is its age as compared with other properties performing like functions. It is the actual age less the age which has been taken off by updating the building through improvements or structural reconstruction, and removing functional inadequacies. It is the age reflective of the true remaining life for the property, after consideration of the typical life expectancy of buildings of its class and its usage. It is a matter of judgment, taking all factors, current and those anticipated, into consideration. M&S Life Expectancy Tables A B C D S Apartments 60 55 50 Home for Elderly 50 45 40 Market – Low Cost -- 35 30 Warehouse -- 35 30 Occupancy Class 38
Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Effective age of a property is its age as compared with other properties performing like functions. It is the actual age less the age which has been taken off by updating the building through improvements or structural reconstruction, and removing functional inadequacies. It is the age reflective of the true remaining life for the property, after consideration of the typical life expectancy of buildings of its class and its usage. It is a matter of judgment, taking all factors, current and those anticipated, into consideration. M&S Life Expectancy Tables A B C D S Apartments 60 55 50 Home for Elderly 50 45 40 Market – Low Cost -- 35 30 Warehouse -- 35 30 Occupancy Class 38
 Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Example Retail/Office Building o Class C , Average Quality o Typical Life = 50 Years Ø Electrical System Replaced 10 Yrs. Ago Ø Heating system replaced 5 Yrs. Ago Ø Roof repaired 8 Yrs. Ago Ø Interior renovations 10 Yrs. Ago. Ø Estimated Remaining Life = 40 Yrs Typical Building Life = 50 Years Estimated Remaining = 40 Years Effective Age = 10 Years v What other form of obsolescence is associated with this building? v Compare the two buildings Utility. 39
Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Example Retail/Office Building o Class C , Average Quality o Typical Life = 50 Years Ø Electrical System Replaced 10 Yrs. Ago Ø Heating system replaced 5 Yrs. Ago Ø Roof repaired 8 Yrs. Ago Ø Interior renovations 10 Yrs. Ago. Ø Estimated Remaining Life = 40 Yrs Typical Building Life = 50 Years Estimated Remaining = 40 Years Effective Age = 10 Years v What other form of obsolescence is associated with this building? v Compare the two buildings Utility. 39
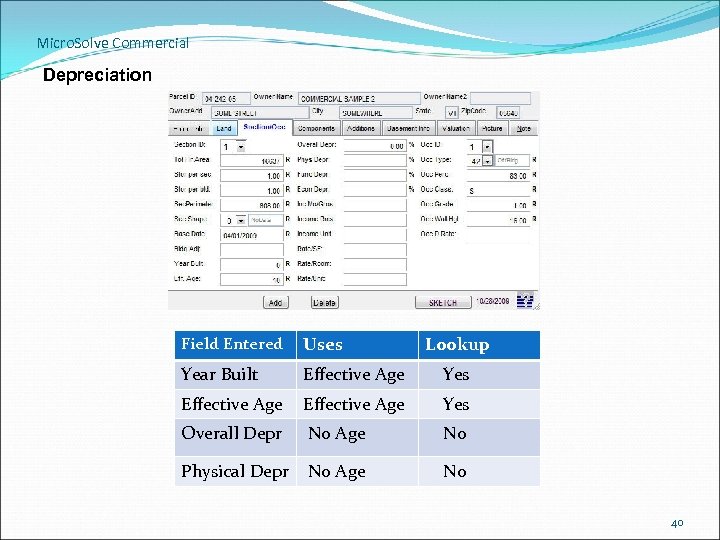 Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Field Entered Uses Lookup Year Built Effective Age Yes Overall Depr No Age No Physical Depr No Age No 40
Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Field Entered Uses Lookup Year Built Effective Age Yes Overall Depr No Age No Physical Depr No Age No 40
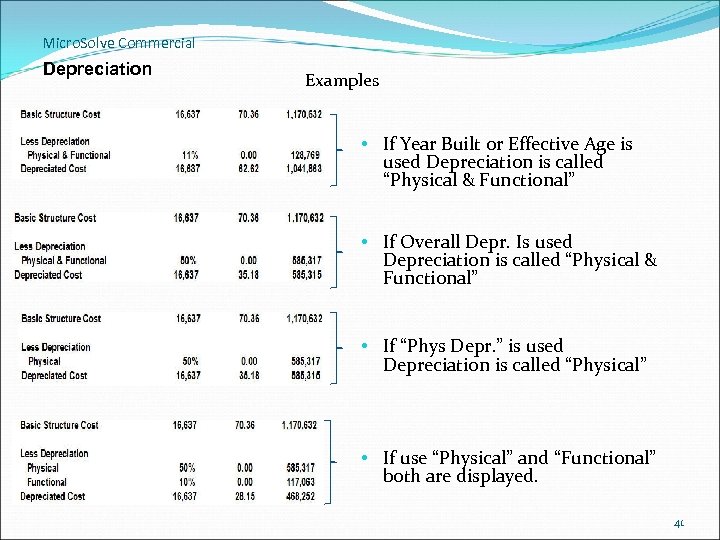 Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Examples • If Year Built or Effective Age is used Depreciation is called “Physical & Functional” • If Overall Depr. Is used Depreciation is called “Physical & Functional” • If “Phys Depr. ” is used Depreciation is called “Physical” • If use “Physical” and “Functional” both are displayed. 41
Micro. Solve Commercial Depreciation Examples • If Year Built or Effective Age is used Depreciation is called “Physical & Functional” • If Overall Depr. Is used Depreciation is called “Physical & Functional” • If “Phys Depr. ” is used Depreciation is called “Physical” • If use “Physical” and “Functional” both are displayed. 41
 Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy Information 42
Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy Information 42
 Micro. Solve Commercial OCCUPANCY • Occupancy, or building use : identifies the use or uses of the building as it was originally designed. • For a building without an exact occupancy description choose the most similar type. • If the designed use and the actual use differ, the design generally determines the cost used in calculating the basic replacement cost. Therefore, use the occupancy of the designed use to determine costs. • Example – Curves (health clubs/exercise facility) are frequently located in converted retail space. 43
Micro. Solve Commercial OCCUPANCY • Occupancy, or building use : identifies the use or uses of the building as it was originally designed. • For a building without an exact occupancy description choose the most similar type. • If the designed use and the actual use differ, the design generally determines the cost used in calculating the basic replacement cost. Therefore, use the occupancy of the designed use to determine costs. • Example – Curves (health clubs/exercise facility) are frequently located in converted retail space. 43
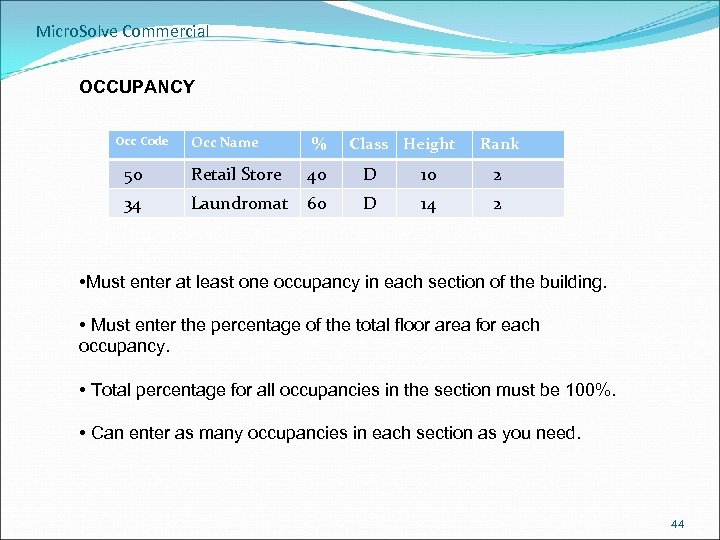 Micro. Solve Commercial OCCUPANCY Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Must enter at least one occupancy in each section of the building. • Must enter the percentage of the total floor area for each occupancy. • Total percentage for all occupancies in the section must be 100%. • Can enter as many occupancies in each section as you need. 44
Micro. Solve Commercial OCCUPANCY Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Must enter at least one occupancy in each section of the building. • Must enter the percentage of the total floor area for each occupancy. • Total percentage for all occupancies in the section must be 100%. • Can enter as many occupancies in each section as you need. 44
 Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy-related factors: (all required): Occupancy Type Select from the categorical list. Occupancy Percent Total of all occupancies in a section must be 100% Occupancy Class A, B, C, D, S Occupancy Rank Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. Occupancy Story Ht In feet. 45
Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy-related factors: (all required): Occupancy Type Select from the categorical list. Occupancy Percent Total of all occupancies in a section must be 100% Occupancy Class A, B, C, D, S Occupancy Rank Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. Occupancy Story Ht In feet. 45
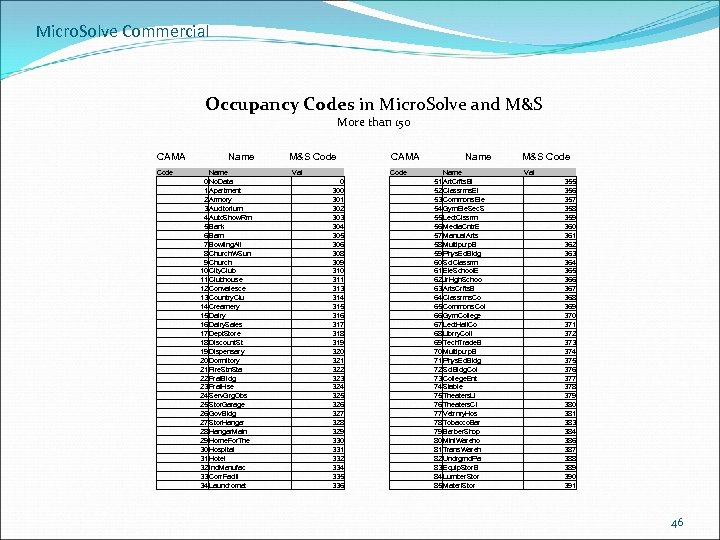 Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy Codes in Micro. Solve and M&S More than 150 CAMA Code Name M&S Code Name 0 No. Data 1 Apartment 2 Armory 3 Auditorium 4 Auto. Show. Rm 5 Bank 6 Barn 7 Bowling. All 8 Church. WSun 9 Church 10 City. Club 11 Clubhouse 12 Convalesce 13 Country. Clu 14 Creamery 15 Dairy 16 Dairy. Sales 17 Dept. Store 18 Discount. St 19 Dispensary 20 Dormitory 21 Fire. Stn. Sta 22 Frat. Bldg 23 Frat. Hse 24 Serv. Grg. Obs 25 Stor. Garage 26 Gov. Bldg 27 Stor. Hangar 28 Hangar. Main 29 Home. For. The 30 Hospital 31 Hotel 32 Ind. Manufac 33 Corr. Facili 34 Laundromat Val CAMA Code 0 301 302 303 304 305 306 308 309 310 311 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 334 335 336 Name 51 Art. Crfts. Bl 52 Classrms. El 53 Commons. Ele 54 Gym. Ele. Sec. S 55 Lect. Clssrm 56 Media. Cntr. E 57 Manual. Arts 58 Multipurp. B 59 Phys. Ed. Bldg 60 Sci. Classrm 61 Ele. School. E 62 Jr. Hgh. Schoo 63 Arts. Crfts. B 64 Classrms. Co 65 Commons. Col 66 Gym. College 67 Lect. Hall. Co 68 Librry. Coll 69 Tech. Trade. B 70 Multipurp. B 71 Phys. Ed. Bldg 72 Sci. Bldg. Col 73 College. Ent 74 Stable 75 Theaters. Li 76 Theaters. Ci 77 Vetrnry. Hos 78 Tobacco. Bar 79 Barber. Shop 80 Mini. Wareho 81 Trans. Wareh 82 Undrgrnd. Pa 83 Equip. Stor. B 84 Lumber. Stor 85 Materl. Stor M&S Code Val 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 383 384 386 387 388 389 390 391 46
Micro. Solve Commercial Occupancy Codes in Micro. Solve and M&S More than 150 CAMA Code Name M&S Code Name 0 No. Data 1 Apartment 2 Armory 3 Auditorium 4 Auto. Show. Rm 5 Bank 6 Barn 7 Bowling. All 8 Church. WSun 9 Church 10 City. Club 11 Clubhouse 12 Convalesce 13 Country. Clu 14 Creamery 15 Dairy 16 Dairy. Sales 17 Dept. Store 18 Discount. St 19 Dispensary 20 Dormitory 21 Fire. Stn. Sta 22 Frat. Bldg 23 Frat. Hse 24 Serv. Grg. Obs 25 Stor. Garage 26 Gov. Bldg 27 Stor. Hangar 28 Hangar. Main 29 Home. For. The 30 Hospital 31 Hotel 32 Ind. Manufac 33 Corr. Facili 34 Laundromat Val CAMA Code 0 301 302 303 304 305 306 308 309 310 311 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 334 335 336 Name 51 Art. Crfts. Bl 52 Classrms. El 53 Commons. Ele 54 Gym. Ele. Sec. S 55 Lect. Clssrm 56 Media. Cntr. E 57 Manual. Arts 58 Multipurp. B 59 Phys. Ed. Bldg 60 Sci. Classrm 61 Ele. School. E 62 Jr. Hgh. Schoo 63 Arts. Crfts. B 64 Classrms. Co 65 Commons. Col 66 Gym. College 67 Lect. Hall. Co 68 Librry. Coll 69 Tech. Trade. B 70 Multipurp. B 71 Phys. Ed. Bldg 72 Sci. Bldg. Col 73 College. Ent 74 Stable 75 Theaters. Li 76 Theaters. Ci 77 Vetrnry. Hos 78 Tobacco. Bar 79 Barber. Shop 80 Mini. Wareho 81 Trans. Wareh 82 Undrgrnd. Pa 83 Equip. Stor. B 84 Lumber. Stor 85 Materl. Stor M&S Code Val 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 383 384 386 387 388 389 390 391 46
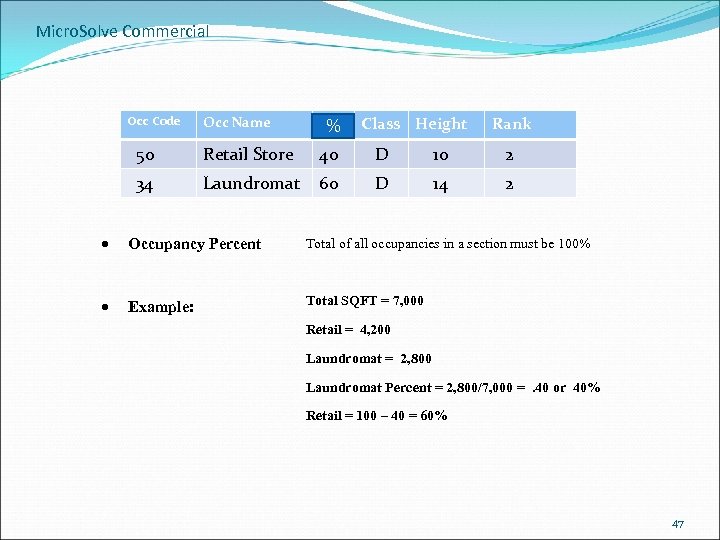 Micro. Solve Commercial Occ Code Occ Name % % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 Occupancy Percent Total of all occupancies in a section must be 100% Example: Total SQFT = 7, 000 Retail = 4, 200 Laundromat = 2, 800 Laundromat Percent = 2, 800/7, 000 =. 40 or 40% Retail = 100 – 40 = 60% 47
Micro. Solve Commercial Occ Code Occ Name % % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 Occupancy Percent Total of all occupancies in a section must be 100% Example: Total SQFT = 7, 000 Retail = 4, 200 Laundromat = 2, 800 Laundromat Percent = 2, 800/7, 000 =. 40 or 40% Retail = 100 – 40 = 60% 47
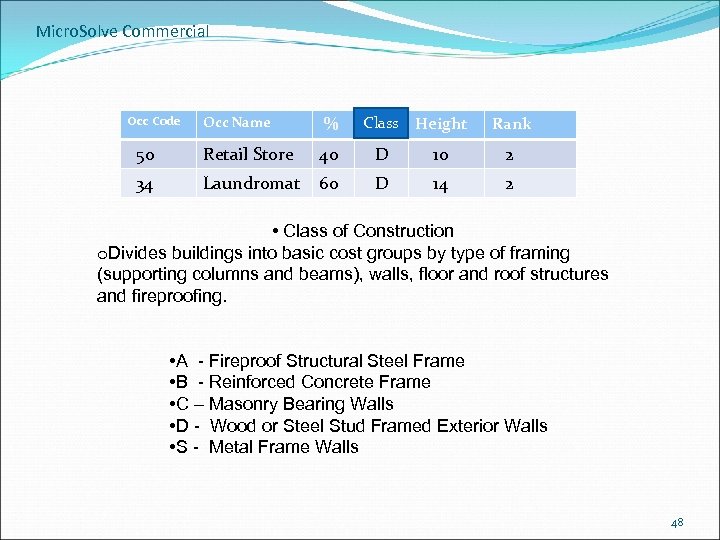 Micro. Solve Commercial Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Class of Construction o. Divides buildings into basic cost groups by type of framing (supporting columns and beams), walls, floor and roof structures and fireproofing. • A - Fireproof Structural Steel Frame • B - Reinforced Concrete Frame • C – Masonry Bearing Walls • D - Wood or Steel Stud Framed Exterior Walls • S - Metal Frame Walls 48
Micro. Solve Commercial Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Class of Construction o. Divides buildings into basic cost groups by type of framing (supporting columns and beams), walls, floor and roof structures and fireproofing. • A - Fireproof Structural Steel Frame • B - Reinforced Concrete Frame • C – Masonry Bearing Walls • D - Wood or Steel Stud Framed Exterior Walls • S - Metal Frame Walls 48
 Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS A: FIREPROOF STRUCTURAL STEEL FRAME • Fireproofed structural steel frame, which may be welded, bolted or riveted together. • The fireproofing may be masonry, poured concrete, plaster, sprayed fiber or any other method, which gives a high fire-resistance rating. • Floor and roof are normally reinforced concrete on steel decking or formed slabs resting on the frame or poured to become integral with it. • Exterior walls are curtain walls of masonry, concrete, steel studs and stucco, or one of the many types of panels of metal, glass, masonry or concrete. • Interior partitions frequently are of masonry or gypsum block, although many movable and lightweight steel partitions are used. 49
Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS A: FIREPROOF STRUCTURAL STEEL FRAME • Fireproofed structural steel frame, which may be welded, bolted or riveted together. • The fireproofing may be masonry, poured concrete, plaster, sprayed fiber or any other method, which gives a high fire-resistance rating. • Floor and roof are normally reinforced concrete on steel decking or formed slabs resting on the frame or poured to become integral with it. • Exterior walls are curtain walls of masonry, concrete, steel studs and stucco, or one of the many types of panels of metal, glass, masonry or concrete. • Interior partitions frequently are of masonry or gypsum block, although many movable and lightweight steel partitions are used. 49
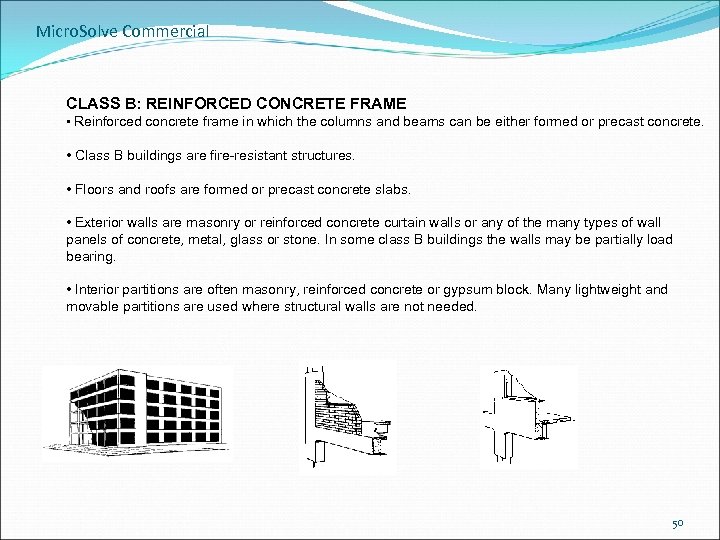 Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS B: REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME • Reinforced concrete frame in which the columns and beams can be either formed or precast concrete. • Class B buildings are fire-resistant structures. • Floors and roofs are formed or precast concrete slabs. • Exterior walls are masonry or reinforced concrete curtain walls or any of the many types of wall panels of concrete, metal, glass or stone. In some class B buildings the walls may be partially load bearing. • Interior partitions are often masonry, reinforced concrete or gypsum block. Many lightweight and movable partitions are used where structural walls are not needed. 50
Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS B: REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME • Reinforced concrete frame in which the columns and beams can be either formed or precast concrete. • Class B buildings are fire-resistant structures. • Floors and roofs are formed or precast concrete slabs. • Exterior walls are masonry or reinforced concrete curtain walls or any of the many types of wall panels of concrete, metal, glass or stone. In some class B buildings the walls may be partially load bearing. • Interior partitions are often masonry, reinforced concrete or gypsum block. Many lightweight and movable partitions are used where structural walls are not needed. 50
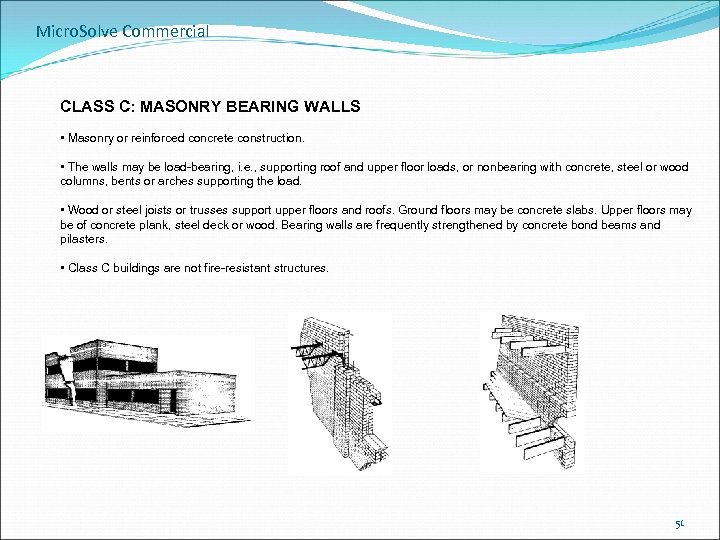 Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS C: MASONRY BEARING WALLS • Masonry or reinforced concrete construction. • The walls may be load-bearing, i. e. , supporting roof and upper floor loads, or nonbearing with concrete, steel or wood columns, bents or arches supporting the load. • Wood or steel joists or trusses support upper floors and roofs. Ground floors may be concrete slabs. Upper floors may be of concrete plank, steel deck or wood. Bearing walls are frequently strengthened by concrete bond beams and pilasters. • Class C buildings are not fire-resistant structures. 51
Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS C: MASONRY BEARING WALLS • Masonry or reinforced concrete construction. • The walls may be load-bearing, i. e. , supporting roof and upper floor loads, or nonbearing with concrete, steel or wood columns, bents or arches supporting the load. • Wood or steel joists or trusses support upper floors and roofs. Ground floors may be concrete slabs. Upper floors may be of concrete plank, steel deck or wood. Bearing walls are frequently strengthened by concrete bond beams and pilasters. • Class C buildings are not fire-resistant structures. 51
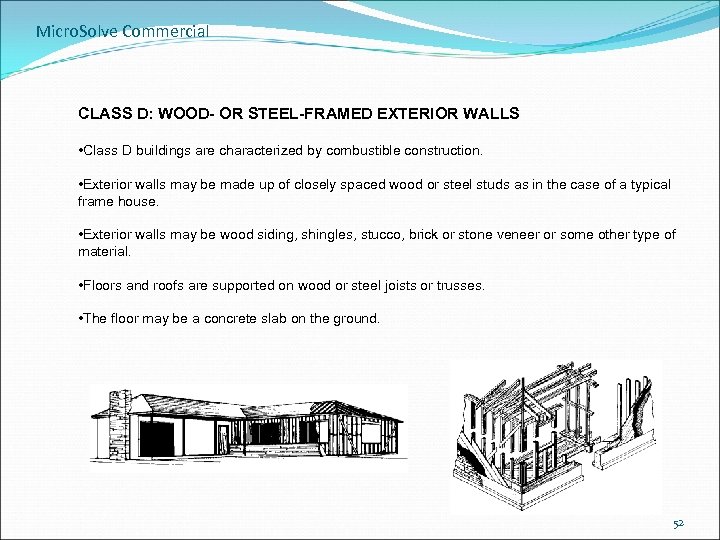 Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS D: WOOD- OR STEEL-FRAMED EXTERIOR WALLS • Class D buildings are characterized by combustible construction. • Exterior walls may be made up of closely spaced wood or steel studs as in the case of a typical frame house. • Exterior walls may be wood siding, shingles, stucco, brick or stone veneer or some other type of material. • Floors and roofs are supported on wood or steel joists or trusses. • The floor may be a concrete slab on the ground. 52
Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS D: WOOD- OR STEEL-FRAMED EXTERIOR WALLS • Class D buildings are characterized by combustible construction. • Exterior walls may be made up of closely spaced wood or steel studs as in the case of a typical frame house. • Exterior walls may be wood siding, shingles, stucco, brick or stone veneer or some other type of material. • Floors and roofs are supported on wood or steel joists or trusses. • The floor may be a concrete slab on the ground. 52
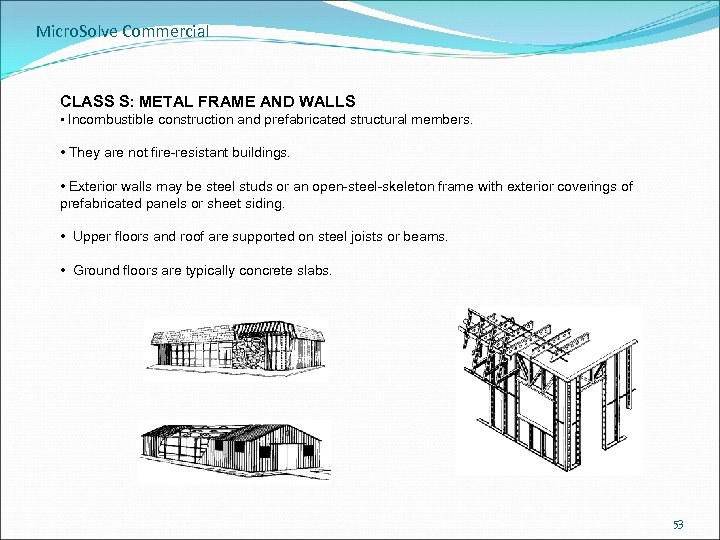 Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS S: METAL FRAME AND WALLS • Incombustible construction and prefabricated structural members. • They are not fire-resistant buildings. • Exterior walls may be steel studs or an open-steel-skeleton frame with exterior coverings of prefabricated panels or sheet siding. • Upper floors and roof are supported on steel joists or beams. • Ground floors are typically concrete slabs. 53
Micro. Solve Commercial CLASS S: METAL FRAME AND WALLS • Incombustible construction and prefabricated structural members. • They are not fire-resistant buildings. • Exterior walls may be steel studs or an open-steel-skeleton frame with exterior coverings of prefabricated panels or sheet siding. • Upper floors and roof are supported on steel joists or beams. • Ground floors are typically concrete slabs. 53
 Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Occ Code Occ Name % Height Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Story height is the vertical distance from the top of one floor to the top of the next floor. • In a one-story building, measure story height from the floor surface to the roof eave. (Do not include parapets (extensions of the wall above the roofline) in story height. ) • Must enter a story height for each occupancy. (Different from manual) 54
Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Occ Code Occ Name % Height Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 2 • Story height is the vertical distance from the top of one floor to the top of the next floor. • In a one-story building, measure story height from the floor surface to the roof eave. (Do not include parapets (extensions of the wall above the roofline) in story height. ) • Must enter a story height for each occupancy. (Different from manual) 54
 Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples When using a single section, if the story heights vary in a multistory building, you can do any of the following: Example 1: One section – Two Occupancies – Different Heights Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 44 Post Office 33 D 18 2 5 Bank 67 D 10 2 55
Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples When using a single section, if the story heights vary in a multistory building, you can do any of the following: Example 1: One section – Two Occupancies – Different Heights Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 44 Post Office 33 D 18 2 5 Bank 67 D 10 2 55
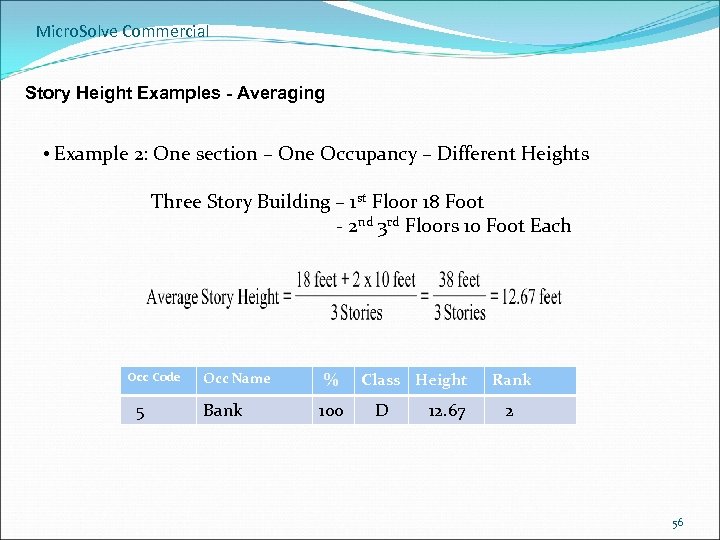 Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples - Averaging • Example 2: One section – One Occupancy – Different Heights Three Story Building – 1 st Floor 18 Foot - 2 nd 3 rd Floors 10 Foot Each Occ Code Occ Name % 5 Bank 100 D Class Height 12. 67 Rank 2 56
Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples - Averaging • Example 2: One section – One Occupancy – Different Heights Three Story Building – 1 st Floor 18 Foot - 2 nd 3 rd Floors 10 Foot Each Occ Code Occ Name % 5 Bank 100 D Class Height 12. 67 Rank 2 56
 Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples • Example 3: One section – One Occupancy – Different Heights • For unfinished attics, include half of the increased height of the attic area when computing average story height. Two Story Building – 10 Foot each Floor - 8 Foot Attic Area 57
Micro. Solve Commercial Story Height Examples • Example 3: One section – One Occupancy – Different Heights • For unfinished attics, include half of the increased height of the attic area when computing average story height. Two Story Building – 10 Foot each Floor - 8 Foot Attic Area 57
 Micro. Solve Commercial Rank Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 1. 5 Rank refers to Quality. The quality scales against which most buildings and their parts must be rated are: Rank 1 - LOW COST Rank 2 – AVERAGE Rank 3 – GOOD Rank 4 – EXCELLENT Split grades are allowed 58
Micro. Solve Commercial Rank Occ Code Occ Name % Class Height Rank 50 Retail Store 40 D 10 2 34 Laundromat 60 D 14 1. 5 Rank refers to Quality. The quality scales against which most buildings and their parts must be rated are: Rank 1 - LOW COST Rank 2 – AVERAGE Rank 3 – GOOD Rank 4 – EXCELLENT Split grades are allowed 58
 Micro. Solve Commercial Rank Low (Rank 1) - These tend to be very plain buildings that conform to minimum building code requirements. Interiors are plain with little attention given to detail or finish. Typically, there are minimum mechanical and low-cost finishes throughout. Average (Rank 2) - These buildings are the most commonly found and meet building code requirements. There is some ornamentation on the exterior with interiors having some trim items. Lighting and plumbing are adequate to service the occupants of the building. Good (Rank 3) - These are generally well designed buildings. Exterior walls usually have a mix of ornamental finishes. Interior walls are nicely finished and there are good quality floor covers. Lighting and plumbing include better quality fixtures. Excellent (Rank 4) - Usually, these buildings are specially designed, have high-cost materials and exhibit excellent workmanship. Both exteriors and interiors have custom and ornamental features. Lighting and plumbing include high-cost fixtures. 59
Micro. Solve Commercial Rank Low (Rank 1) - These tend to be very plain buildings that conform to minimum building code requirements. Interiors are plain with little attention given to detail or finish. Typically, there are minimum mechanical and low-cost finishes throughout. Average (Rank 2) - These buildings are the most commonly found and meet building code requirements. There is some ornamentation on the exterior with interiors having some trim items. Lighting and plumbing are adequate to service the occupants of the building. Good (Rank 3) - These are generally well designed buildings. Exterior walls usually have a mix of ornamental finishes. Interior walls are nicely finished and there are good quality floor covers. Lighting and plumbing include better quality fixtures. Excellent (Rank 4) - Usually, these buildings are specially designed, have high-cost materials and exhibit excellent workmanship. Both exteriors and interiors have custom and ornamental features. Lighting and plumbing include high-cost fixtures. 59
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Using MVS Commercial Manual 60
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Using MVS Commercial Manual 60
 Micro. Solve Commercial Components 61
Micro. Solve Commercial Components 61
 Micro. Solve Commercial Components • Building components include exterior walls, heating and cooling, elevators, sprinkler systems, fire alarms, mezzanines, balconies. • In Marshall & Swift tables, many types of buildings (or occupancies) are assumed to have such components, and their cost is already included in the square foot rate. • It is not necessary to enter components unless greater control, accuracy, or description is necessary. • However, it is a good idea to break down components: • Demonstrates a proper inspection was completed. • Gives greater control for complex buildings. • Underlying assumptions knowledge is limited. 62
Micro. Solve Commercial Components • Building components include exterior walls, heating and cooling, elevators, sprinkler systems, fire alarms, mezzanines, balconies. • In Marshall & Swift tables, many types of buildings (or occupancies) are assumed to have such components, and their cost is already included in the square foot rate. • It is not necessary to enter components unless greater control, accuracy, or description is necessary. • However, it is a good idea to break down components: • Demonstrates a proper inspection was completed. • Gives greater control for complex buildings. • Underlying assumptions knowledge is limited. 62
 Micro. Solve Commercial Components Wall Type Wall Percent Wall Units Wall Rank Wall Units of Measure Wall Other Units Wall Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. Heat/Cool Type Heat/Cool Percent Heat/Cool Units Heat/Cool Rank Heat/Cool UOM Heat/Cool Other Units Heat/Cool Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. Component Type Component Percent Component Units Component Rank Component UOM Component Other Units Component Deprec Select from the categorical list. See details in Part 2. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet or count. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage if desired. 63
Micro. Solve Commercial Components Wall Type Wall Percent Wall Units Wall Rank Wall Units of Measure Wall Other Units Wall Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. Heat/Cool Type Heat/Cool Percent Heat/Cool Units Heat/Cool Rank Heat/Cool UOM Heat/Cool Other Units Heat/Cool Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. Component Type Component Percent Component Units Component Rank Component UOM Component Other Units Component Deprec Select from the categorical list. See details in Part 2. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet or count. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage if desired. 63
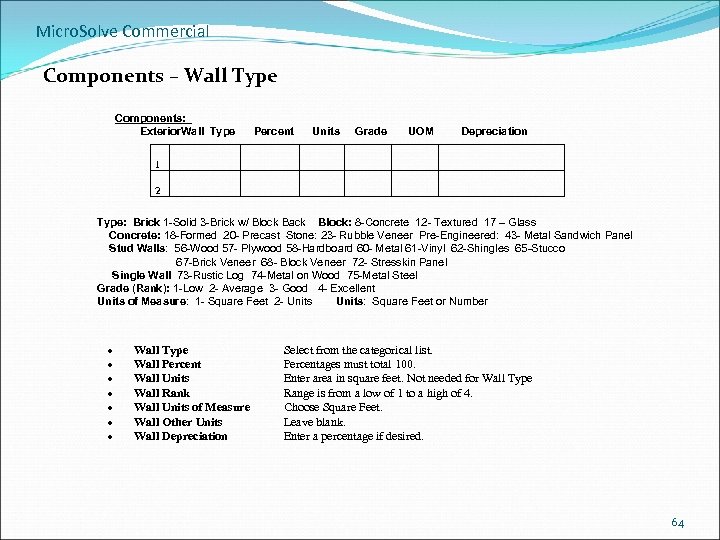 Micro. Solve Commercial Components – Wall Type Components: Exterior. Wall Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 Type: Brick 1 -Solid 3 -Brick w/ Block Back Block: 8 -Concrete 12 - Textured 17 – Glass Concrete: 18 -Formed 20 - Precast Stone: 23 - Rubble Veneer Pre-Engineered: 43 - Metal Sandwich Panel Stud Walls: 56 -Wood 57 - Plywood 58 -Hardboard 60 - Metal 61 -Vinyl 62 -Shingles 65 -Stucco 67 -Brick Veneer 68 - Block Veneer 72 - Stresskin Panel Single Wall 73 -Rustic Log 74 -Metal on Wood 75 -Metal Steel Grade (Rank): 1 -Low 2 - Average 3 - Good 4 - Excellent Units of Measure: 1 - Square Feet 2 - Units: Square Feet or Number Wall Type Wall Percent Wall Units Wall Rank Wall Units of Measure Wall Other Units Wall Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Not needed for Wall Type Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. 64
Micro. Solve Commercial Components – Wall Type Components: Exterior. Wall Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 Type: Brick 1 -Solid 3 -Brick w/ Block Back Block: 8 -Concrete 12 - Textured 17 – Glass Concrete: 18 -Formed 20 - Precast Stone: 23 - Rubble Veneer Pre-Engineered: 43 - Metal Sandwich Panel Stud Walls: 56 -Wood 57 - Plywood 58 -Hardboard 60 - Metal 61 -Vinyl 62 -Shingles 65 -Stucco 67 -Brick Veneer 68 - Block Veneer 72 - Stresskin Panel Single Wall 73 -Rustic Log 74 -Metal on Wood 75 -Metal Steel Grade (Rank): 1 -Low 2 - Average 3 - Good 4 - Excellent Units of Measure: 1 - Square Feet 2 - Units: Square Feet or Number Wall Type Wall Percent Wall Units Wall Rank Wall Units of Measure Wall Other Units Wall Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet. Not needed for Wall Type Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. 64
 Micro. Solve Commercial Wall Definitions Descriptions for exterior walls: (See back section of manual) MASONRY WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code MN (M&S Codes 801 -826) These walls are constructed entirely of masonry units (or concrete) which are bonded together with mortar or some other type of cementing material. CURTAIN WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code CW (M&S Codes 840 -855) These are non-bearing exterior walls supported by the structural frame of the building. These walls carry no load other than their own weight. The primary function of these walls is to protect the interior of the building from the weather. PRE‑ENGINEERED WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code PE (M&S Codes 860 -872) These walls are pre‑fabricated panels constructed with two sheets or “skins” (interior and exterior) bonded to a core material. STUD WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code SW (M&S Codes 880 -891) These walls are of wood or steel stud bearing wall construction. - When stresskin sandwich panel replaces the stud framing, use additive component Number 891. SINGLE WALL CONSTRUCTION – CAMA Pre-Code SN (M&S Codes 910 -929) Refers to a wall enclosure that is typically applied over an open skeleton prefabricated metal or wood pole framed building. 65
Micro. Solve Commercial Wall Definitions Descriptions for exterior walls: (See back section of manual) MASONRY WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code MN (M&S Codes 801 -826) These walls are constructed entirely of masonry units (or concrete) which are bonded together with mortar or some other type of cementing material. CURTAIN WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code CW (M&S Codes 840 -855) These are non-bearing exterior walls supported by the structural frame of the building. These walls carry no load other than their own weight. The primary function of these walls is to protect the interior of the building from the weather. PRE‑ENGINEERED WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code PE (M&S Codes 860 -872) These walls are pre‑fabricated panels constructed with two sheets or “skins” (interior and exterior) bonded to a core material. STUD WALLS – CAMA Pre-Code SW (M&S Codes 880 -891) These walls are of wood or steel stud bearing wall construction. - When stresskin sandwich panel replaces the stud framing, use additive component Number 891. SINGLE WALL CONSTRUCTION – CAMA Pre-Code SN (M&S Codes 910 -929) Refers to a wall enclosure that is typically applied over an open skeleton prefabricated metal or wood pole framed building. 65
 Micro. Solve Commercial Components - Heating/Cooling Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 Type: 1 -Electric 2 -Elec. Wall 3 -Forced Air 4 -Hot Water 5 -Hot Water Rad. 6 -Space Heat 7 -Steam 8 -Steam No Boiler 9 -Ventilation 10 -Wall Furnace 11 -Package Unit 12 -Warm Cool Air 13 -Hot Chill Water 14 -Heat Pump 15 -Floor Furnace 16 -Ind Thru Wall 17 -Complete HVAC 18 - Evap. Cool 19 -Refrig Cool 20 - No HVAC Heat/Cool Type Heat/Cool Percent Heat/Cool Units Heat/Cool Rank Heat/Cool UOM Heat/Cool Other Units Heat/Cool Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. * Enter area in square feet. * Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. *Enter Units in SQFT OR Percent of Heating Area • The commercial manual has a good description of each type. 66
Micro. Solve Commercial Components - Heating/Cooling Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 Type: 1 -Electric 2 -Elec. Wall 3 -Forced Air 4 -Hot Water 5 -Hot Water Rad. 6 -Space Heat 7 -Steam 8 -Steam No Boiler 9 -Ventilation 10 -Wall Furnace 11 -Package Unit 12 -Warm Cool Air 13 -Hot Chill Water 14 -Heat Pump 15 -Floor Furnace 16 -Ind Thru Wall 17 -Complete HVAC 18 - Evap. Cool 19 -Refrig Cool 20 - No HVAC Heat/Cool Type Heat/Cool Percent Heat/Cool Units Heat/Cool Rank Heat/Cool UOM Heat/Cool Other Units Heat/Cool Depreciation Select from the categorical list. Percentages must total 100. * Enter area in square feet. * Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet. Leave blank. Enter a percentage if desired. *Enter Units in SQFT OR Percent of Heating Area • The commercial manual has a good description of each type. 66
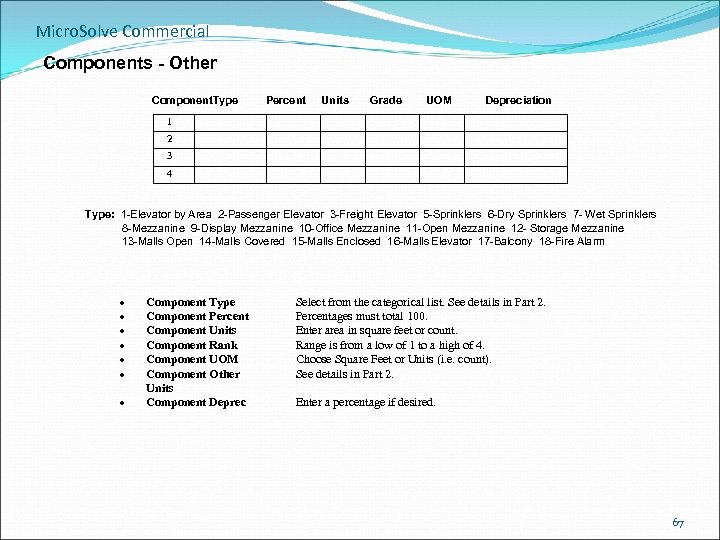 Micro. Solve Commercial Components - Other Component. Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 3 4 Type: 1 -Elevator by Area 2 -Passenger Elevator 3 -Freight Elevator 5 -Sprinklers 6 -Dry Sprinklers 7 - Wet Sprinklers 8 -Mezzanine 9 -Display Mezzanine 10 -Office Mezzanine 11 -Open Mezzanine 12 - Storage Mezzanine 13 -Malls Open 14 -Malls Covered 15 -Malls Enclosed 16 -Malls Elevator 17 -Balcony 18 -Fire Alarm Component Type Component Percent Component Units Component Rank Component UOM Component Other Units Component Deprec Select from the categorical list. See details in Part 2. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet or count. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage if desired. 67
Micro. Solve Commercial Components - Other Component. Type Percent Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 3 4 Type: 1 -Elevator by Area 2 -Passenger Elevator 3 -Freight Elevator 5 -Sprinklers 6 -Dry Sprinklers 7 - Wet Sprinklers 8 -Mezzanine 9 -Display Mezzanine 10 -Office Mezzanine 11 -Open Mezzanine 12 - Storage Mezzanine 13 -Malls Open 14 -Malls Covered 15 -Malls Enclosed 16 -Malls Elevator 17 -Balcony 18 -Fire Alarm Component Type Component Percent Component Units Component Rank Component UOM Component Other Units Component Deprec Select from the categorical list. See details in Part 2. Percentages must total 100. Enter area in square feet or count. Range is from a low of 1 to a high of 4. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage if desired. 67
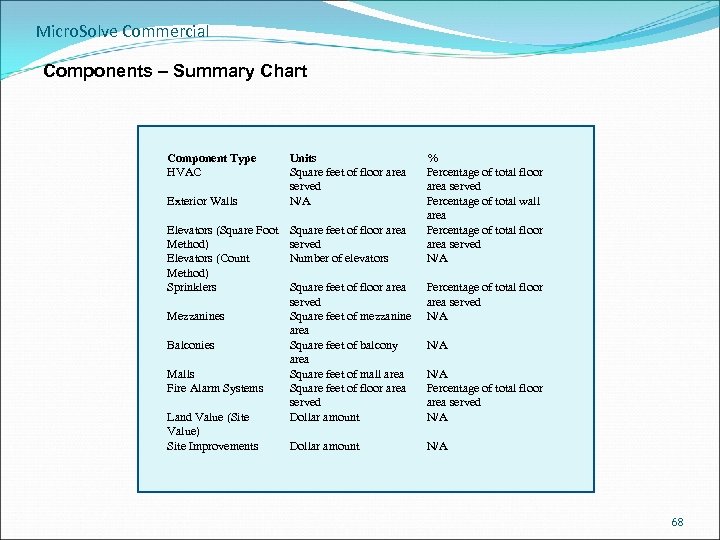 Micro. Solve Commercial Components – Summary Chart Component Type HVAC Exterior Walls Elevators (Square Foot Method) Elevators (Count Method) Sprinklers Mezzanines Balconies Malls Fire Alarm Systems Land Value (Site Value) Site Improvements Units Square feet of floor area served N/A Square feet of floor area served Number of elevators % Percentage of total floor area served Percentage of total wall area Percentage of total floor area served N/A Square feet of floor area served Square feet of mezzanine area Square feet of balcony area Square feet of mall area Square feet of floor area served Dollar amount Percentage of total floor area served N/A Dollar amount N/A N/A Percentage of total floor area served N/A 68
Micro. Solve Commercial Components – Summary Chart Component Type HVAC Exterior Walls Elevators (Square Foot Method) Elevators (Count Method) Sprinklers Mezzanines Balconies Malls Fire Alarm Systems Land Value (Site Value) Site Improvements Units Square feet of floor area served N/A Square feet of floor area served Number of elevators % Percentage of total floor area served Percentage of total wall area Percentage of total floor area served N/A Square feet of floor area served Square feet of mezzanine area Square feet of balcony area Square feet of mall area Square feet of floor area served Dollar amount Percentage of total floor area served N/A Dollar amount N/A N/A Percentage of total floor area served N/A 68
 Micro. Solve Commercial Additions allow the inclusion of items to the report that are not available in the M&S CAMA program. 69
Micro. Solve Commercial Additions allow the inclusion of items to the report that are not available in the M&S CAMA program. 69
 Micro. Solve Commercial Additions Report Headings indicates where to print the addition in the report, using one of the following codes: Basic Super Bsmnt Extra Depr Tot Bldg Basic Structure Cost - Depreciated Superstructure Cost - Depreciated Basement Cost Extras Depreciation (prints as negative) Total Value Added to Building – Not Depreciated Examples: • Porches or Decks • Tanks • Canopy • Storage Buildings 70
Micro. Solve Commercial Additions Report Headings indicates where to print the addition in the report, using one of the following codes: Basic Super Bsmnt Extra Depr Tot Bldg Basic Structure Cost - Depreciated Superstructure Cost - Depreciated Basement Cost Extras Depreciation (prints as negative) Total Value Added to Building – Not Depreciated Examples: • Porches or Decks • Tanks • Canopy • Storage Buildings 70
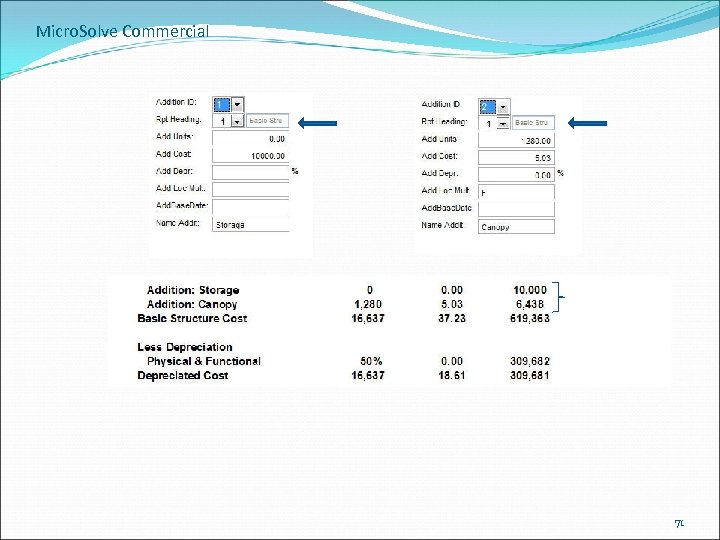 Micro. Solve Commercial 71
Micro. Solve Commercial 71
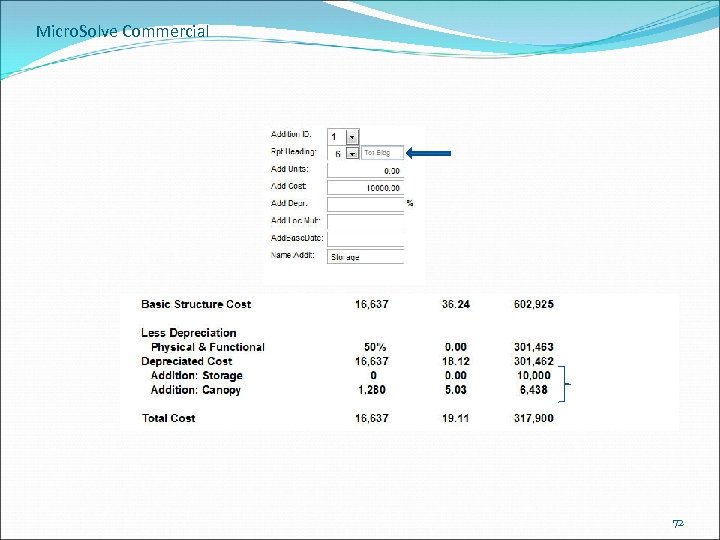 Micro. Solve Commercial 72
Micro. Solve Commercial 72
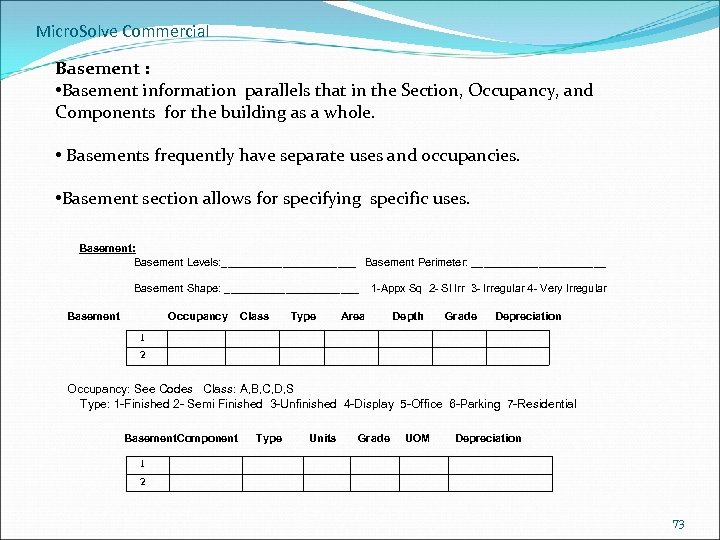 Micro. Solve Commercial Basement : • Basement information parallels that in the Section, Occupancy, and Components for the building as a whole. • Basements frequently have separate uses and occupancies. • Basement section allows for specifying specific uses. Basement: Basement Levels: ___________ Basement Perimeter: ___________ Basement Shape: ___________ 1 -Appx Sq 2 - Sl Irr 3 - Irregular 4 - Very Irregular Basement Occupancy Class Type Area Depth Grade Depreciation 1 2 Occupancy: See Codes Class: A, B, C, D, S Type: 1 -Finished 2 - Semi Finished 3 -Unfinished 4 -Display 5 -Office 6 -Parking 7 -Residential Basement. Component Type Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 73
Micro. Solve Commercial Basement : • Basement information parallels that in the Section, Occupancy, and Components for the building as a whole. • Basements frequently have separate uses and occupancies. • Basement section allows for specifying specific uses. Basement: Basement Levels: ___________ Basement Perimeter: ___________ Basement Shape: ___________ 1 -Appx Sq 2 - Sl Irr 3 - Irregular 4 - Very Irregular Basement Occupancy Class Type Area Depth Grade Depreciation 1 2 Occupancy: See Codes Class: A, B, C, D, S Type: 1 -Finished 2 - Semi Finished 3 -Unfinished 4 -Display 5 -Office 6 -Parking 7 -Residential Basement. Component Type Units Grade UOM Depreciation 1 2 73
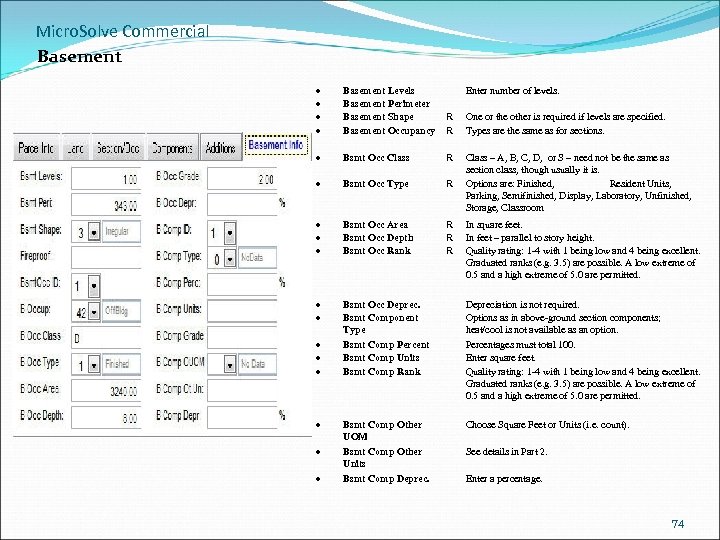 Micro. Solve Commercial Basement Levels Basement Perimeter Basement Shape Basement Occupancy R R One or the other is required if levels are specified. Types are the same as for sections. Bsmt Occ Class R Bsmt Occ Type R Class – A, B, C, D, or S – need not be the same as section class, though usually it is. Options are: Finished, Resident Units, Parking, Semifinished, Display, Laboratory, Unfinished, Storage, Classroom Bsmt Occ Area Bsmt Occ Depth Bsmt Occ Rank R R R Bsmt Occ Deprec. Bsmt Component Type Bsmt Comp Percent Bsmt Comp Units Bsmt Comp Rank Depreciation is not required. Options as in above-ground section components; heat/cool is not available as an option. Percentages must total 100. Enter square feet. Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. Bsmt Comp Other UOM Bsmt Comp Other Units Bsmt Comp Deprec. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). Enter number of levels. In square feet. In feet – parallel to story height. Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage. 74
Micro. Solve Commercial Basement Levels Basement Perimeter Basement Shape Basement Occupancy R R One or the other is required if levels are specified. Types are the same as for sections. Bsmt Occ Class R Bsmt Occ Type R Class – A, B, C, D, or S – need not be the same as section class, though usually it is. Options are: Finished, Resident Units, Parking, Semifinished, Display, Laboratory, Unfinished, Storage, Classroom Bsmt Occ Area Bsmt Occ Depth Bsmt Occ Rank R R R Bsmt Occ Deprec. Bsmt Component Type Bsmt Comp Percent Bsmt Comp Units Bsmt Comp Rank Depreciation is not required. Options as in above-ground section components; heat/cool is not available as an option. Percentages must total 100. Enter square feet. Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. Bsmt Comp Other UOM Bsmt Comp Other Units Bsmt Comp Deprec. Choose Square Feet or Units (i. e. count). Enter number of levels. In square feet. In feet – parallel to story height. Quality rating: 1 -4 with 1 being low and 4 being excellent. Graduated ranks (e. g. 3. 5) are possible. A low extreme of 0. 5 and a high extreme of 5. 0 are permitted. See details in Part 2. Enter a percentage. 74
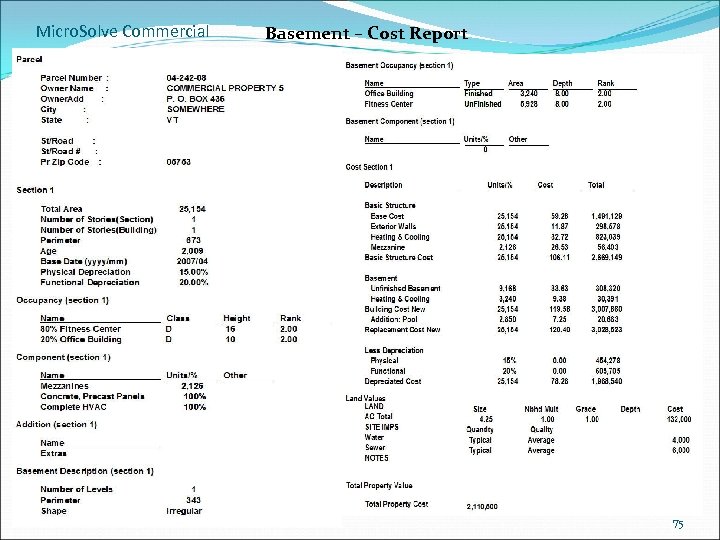 Micro. Solve Commercial Basement – Cost Report 75
Micro. Solve Commercial Basement – Cost Report 75
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples 76
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples 76
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -1 04 -242 -04 Retail/Apartments - 3 Story Brick Building 1 Section – 2 Occupancies – Unfinished Basement 10, 557 SQFT 77
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -1 04 -242 -04 Retail/Apartments - 3 Story Brick Building 1 Section – 2 Occupancies – Unfinished Basement 10, 557 SQFT 77
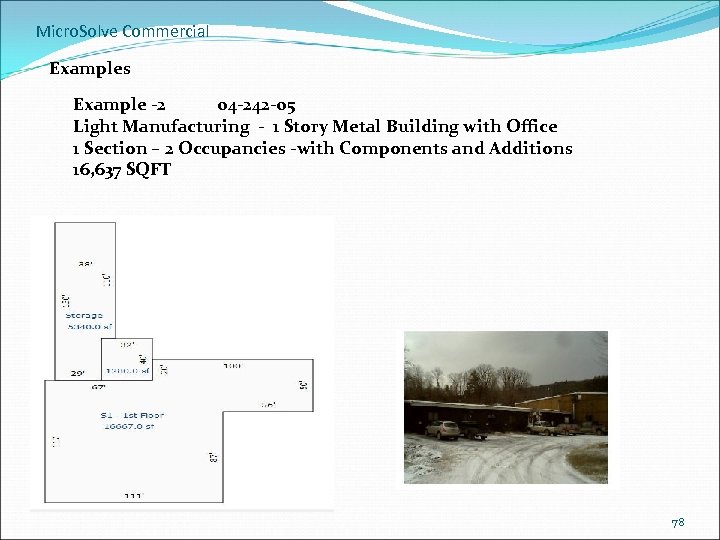 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -2 04 -242 -05 Light Manufacturing - 1 Story Metal Building with Office 1 Section – 2 Occupancies -with Components and Additions 16, 637 SQFT 78
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -2 04 -242 -05 Light Manufacturing - 1 Story Metal Building with Office 1 Section – 2 Occupancies -with Components and Additions 16, 637 SQFT 78
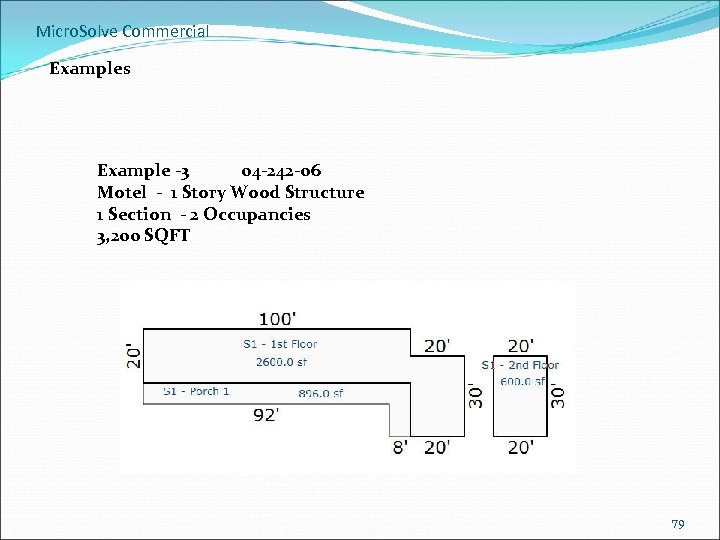 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -3 04 -242 -06 Motel - 1 Story Wood Structure 1 Section - 2 Occupancies 3, 200 SQFT 79
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -3 04 -242 -06 Motel - 1 Story Wood Structure 1 Section - 2 Occupancies 3, 200 SQFT 79
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -4 04 -242 -07 New Office Building - 2 Story Brick Building 1 Section – 1 Occupancy – Elevator and Sprinklers 52, 824 SQFT 80
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -4 04 -242 -07 New Office Building - 2 Story Brick Building 1 Section – 1 Occupancy – Elevator and Sprinklers 52, 824 SQFT 80
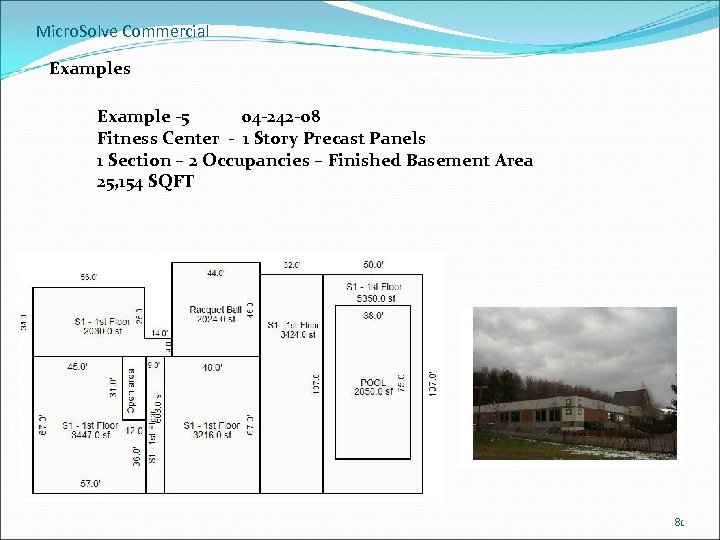 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -5 04 -242 -08 Fitness Center - 1 Story Precast Panels 1 Section – 2 Occupancies – Finished Basement Area 25, 154 SQFT 81
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -5 04 -242 -08 Fitness Center - 1 Story Precast Panels 1 Section – 2 Occupancies – Finished Basement Area 25, 154 SQFT 81
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -6 04 -242 -09 Warehouse Building with Office - 1 Story 1 Section – 1 Occupancy – Runs Income System 18, 512 SQFT 82
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -6 04 -242 -09 Warehouse Building with Office - 1 Story 1 Section – 1 Occupancy – Runs Income System 18, 512 SQFT 82
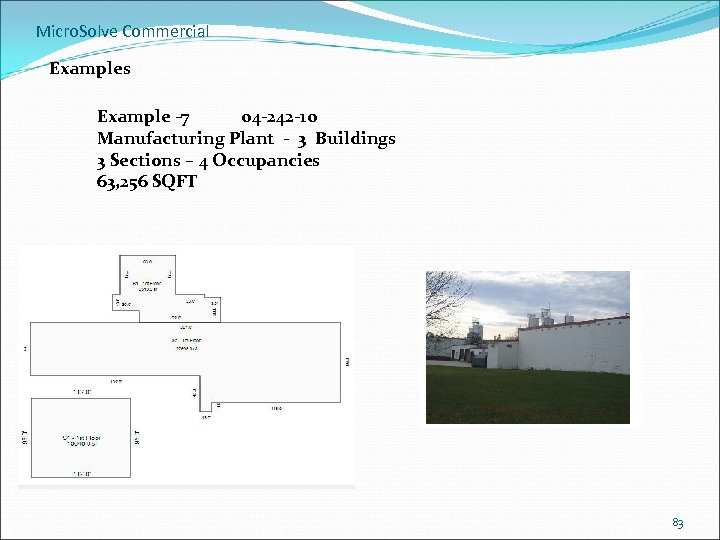 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -7 04 -242 -10 Manufacturing Plant - 3 Buildings 3 Sections – 4 Occupancies 63, 256 SQFT 83
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -7 04 -242 -10 Manufacturing Plant - 3 Buildings 3 Sections – 4 Occupancies 63, 256 SQFT 83
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -8 04 -242 -11 Lumber Yard - 2 Main Buildings with 7 Lumber Sheds 3 Sections - 11 Occupancies - 56, 642 SQFT 84
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -8 04 -242 -11 Lumber Yard - 2 Main Buildings with 7 Lumber Sheds 3 Sections - 11 Occupancies - 56, 642 SQFT 84
 Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -9 04 -242 -12 Marriott Hotel - 1 House 1 Sections – 1 Occupancy – 3 Additions 51 -191 SQFT 85
Micro. Solve Commercial Examples Example -9 04 -242 -12 Marriott Hotel - 1 House 1 Sections – 1 Occupancy – 3 Additions 51 -191 SQFT 85
 Micro. Solve Commercial Record to Enter – 04 -242 -13 and 14 16 ‘ Height – Equip. Shed Office SQFT = 2, 250 – 26% Full Basement Partial FNA Garage SQFT = 6, 300 – 74% Total SQFT = 8, 550 Class S - Stud Metal Siding EFF Age – 30 Porch Addition = 200 Sqft 10 ‘ Height – Office 20 ‘ Height – Service Repair Garage Equip Bldg SQFT 2 = 3, 200 Class D - Stud Wood Siding EFF Age - 20 86
Micro. Solve Commercial Record to Enter – 04 -242 -13 and 14 16 ‘ Height – Equip. Shed Office SQFT = 2, 250 – 26% Full Basement Partial FNA Garage SQFT = 6, 300 – 74% Total SQFT = 8, 550 Class S - Stud Metal Siding EFF Age – 30 Porch Addition = 200 Sqft 10 ‘ Height – Office 20 ‘ Height – Service Repair Garage Equip Bldg SQFT 2 = 3, 200 Class D - Stud Wood Siding EFF Age - 20 86
 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Errors 87
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Errors 87
 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Errors • Commercial CAMA system produces Calculation Errors for missing data that is required for completion of cost calculation. • The key is to be organized in your layout of the record, especially if multiple sections, occupancies , and components are involved. 88
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Errors • Commercial CAMA system produces Calculation Errors for missing data that is required for completion of cost calculation. • The key is to be organized in your layout of the record, especially if multiple sections, occupancies , and components are involved. 88
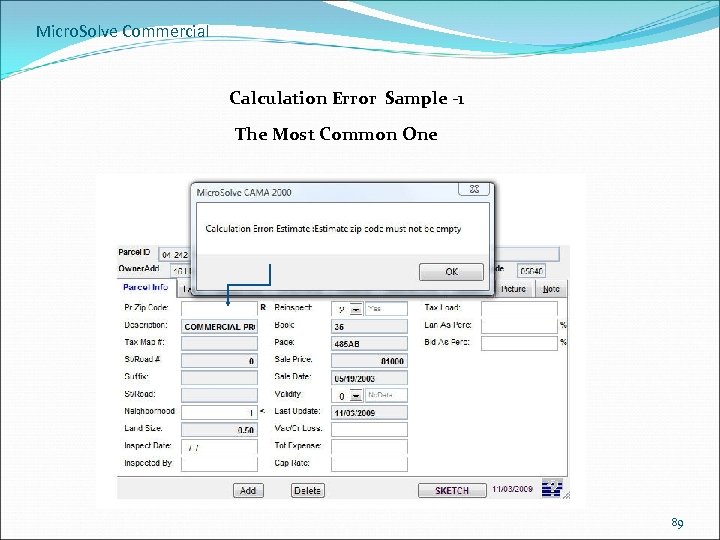 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -1 The Most Common One 89
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -1 The Most Common One 89
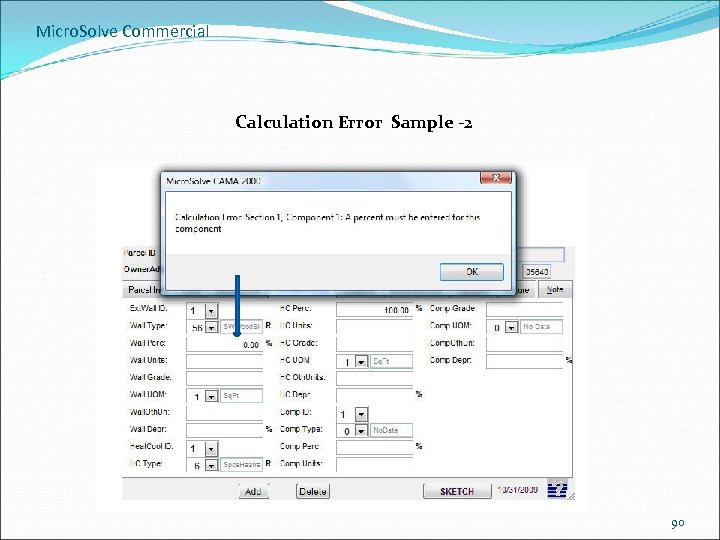 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -2 90
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -2 90
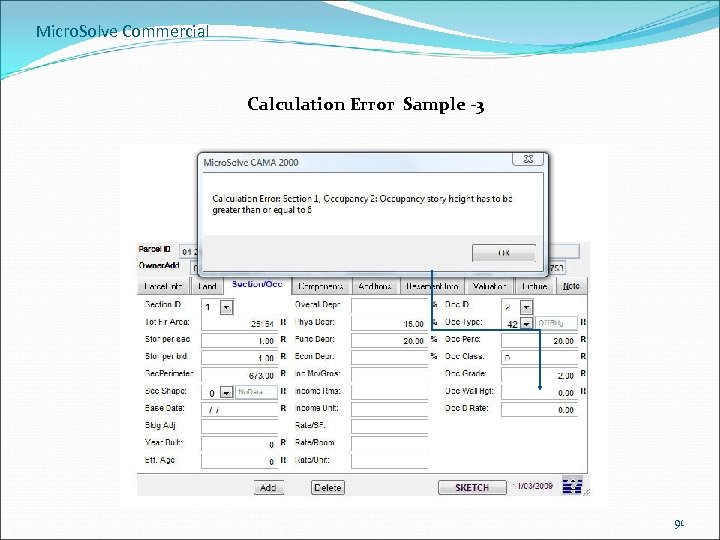 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -3 91
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -3 91
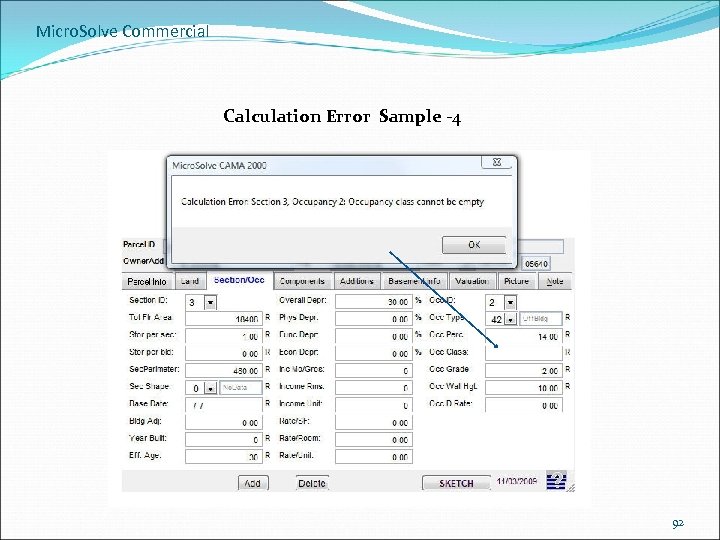 Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -4 92
Micro. Solve Commercial Calculation Error Sample -4 92
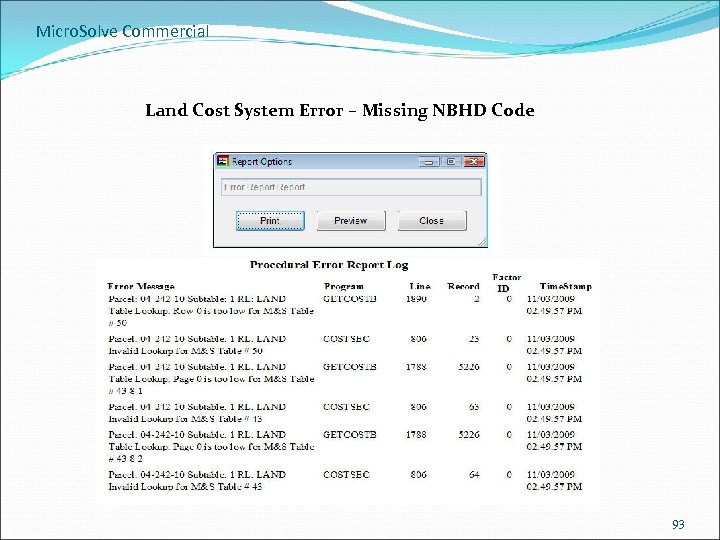 Micro. Solve Commercial Land Cost System Error – Missing NBHD Code 93
Micro. Solve Commercial Land Cost System Error – Missing NBHD Code 93
 Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach 94
Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach 94
 Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach • Income producing properties should be valued using the income approach to substantiate value. • Use the commercial cost approach to approximate the income approach value. • Income approach does not have to be elaborate. Must be able to “talk the talk. ” • Example of industrial plant in Ludlow. 95
Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach • Income producing properties should be valued using the income approach to substantiate value. • Use the commercial cost approach to approximate the income approach value. • Income approach does not have to be elaborate. Must be able to “talk the talk. ” • Example of industrial plant in Ludlow. 95
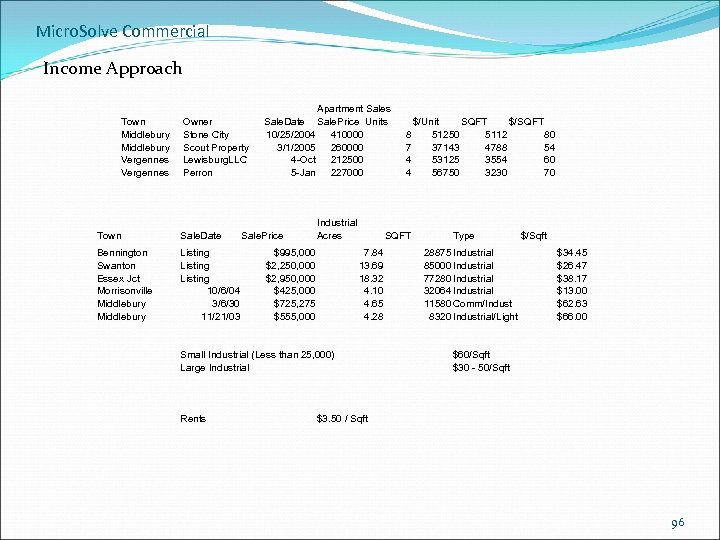 Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach Town Middlebury Vergennes Owner Stone City Scout Property Lewisburg. LLC Perron Town Sale. Date Bennington Swanton Essex Jct Morrisonville Middlebury Listing 10/6/04 3/6/30 11/21/03 Apartment Sales Sale. Date Sale. Price Units 10/25/2004 410000 3/1/2005 260000 4 -Oct 212500 5 -Jan 227000 Sale. Price Industrial Acres $995, 000 $2, 250, 000 $2, 950, 000 $425, 000 $725, 275 $555, 000 SQFT 7. 84 13. 69 18. 32 4. 10 4. 65 4. 28 Small Industrial (Less than 25, 000) Large Industrial Rents 8 7 4 4 $/Unit SQFT $/SQFT 51250 5112 80 37143 4788 54 53125 3554 60 56750 3230 70 Type 28875 Industrial 85000 Industrial 77280 Industrial 32064 Industrial 11580 Comm/Indust 8320 Industrial/Light $/Sqft $34. 45 $26. 47 $38. 17 $13. 00 $62. 63 $66. 00 $60/Sqft $30 - 50/Sqft $3. 50 / Sqft 96
Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach Town Middlebury Vergennes Owner Stone City Scout Property Lewisburg. LLC Perron Town Sale. Date Bennington Swanton Essex Jct Morrisonville Middlebury Listing 10/6/04 3/6/30 11/21/03 Apartment Sales Sale. Date Sale. Price Units 10/25/2004 410000 3/1/2005 260000 4 -Oct 212500 5 -Jan 227000 Sale. Price Industrial Acres $995, 000 $2, 250, 000 $2, 950, 000 $425, 000 $725, 275 $555, 000 SQFT 7. 84 13. 69 18. 32 4. 10 4. 65 4. 28 Small Industrial (Less than 25, 000) Large Industrial Rents 8 7 4 4 $/Unit SQFT $/SQFT 51250 5112 80 37143 4788 54 53125 3554 60 56750 3230 70 Type 28875 Industrial 85000 Industrial 77280 Industrial 32064 Industrial 11580 Comm/Indust 8320 Industrial/Light $/Sqft $34. 45 $26. 47 $38. 17 $13. 00 $62. 63 $66. 00 $60/Sqft $30 - 50/Sqft $3. 50 / Sqft 96
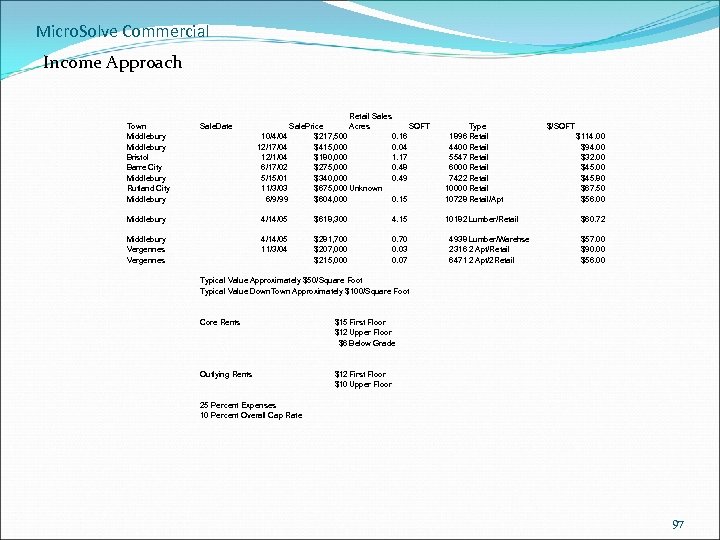 Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach Town Middlebury Bristol Barre City Middlebury Rutland City Middlebury Sale. Date Retail Sales Sale. Price Acres SQFT 10/4/04 $217, 500 0. 16 12/17/04 $415, 000 0. 04 12/1/04 $180, 000 1. 17 6/17/02 $275, 000 0. 48 5/15/01 $340, 000 0. 49 11/3/03 $675, 000 Unknown 6/9/99 $604, 000 0. 15 Middlebury 4/14/05 $618, 300 4. 15 Middlebury Vergennes 4/14/05 11/3/04 $281, 700 $207, 000 $215, 000 0. 70 0. 03 0. 07 Type 1896 Retail 4400 Retail 5547 Retail 6000 Retail 7422 Retail 10000 Retail 10728 Retail/Apt 10182 Lumber/Retail 4938 Lumber/Warehse 2316 2 Apt/Retail 6471 2 Apt/2 Retail $/SQFT $114. 00 $94. 00 $32. 00 $45. 80 $67. 50 $56. 00 $60. 72 $57. 00 $90. 00 $56. 00 Typical Value Approximately $50/Square Foot Typical Value Down. Town Approximately $100/Square Foot Core Rents $15 First Floor $12 Upper Floor $6 Below Grade Outlying Rents $12 First Floor $10 Upper Floor 25 Percent Expenses 10 Percent Overall Cap Rate 97
Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach Town Middlebury Bristol Barre City Middlebury Rutland City Middlebury Sale. Date Retail Sales Sale. Price Acres SQFT 10/4/04 $217, 500 0. 16 12/17/04 $415, 000 0. 04 12/1/04 $180, 000 1. 17 6/17/02 $275, 000 0. 48 5/15/01 $340, 000 0. 49 11/3/03 $675, 000 Unknown 6/9/99 $604, 000 0. 15 Middlebury 4/14/05 $618, 300 4. 15 Middlebury Vergennes 4/14/05 11/3/04 $281, 700 $207, 000 $215, 000 0. 70 0. 03 0. 07 Type 1896 Retail 4400 Retail 5547 Retail 6000 Retail 7422 Retail 10000 Retail 10728 Retail/Apt 10182 Lumber/Retail 4938 Lumber/Warehse 2316 2 Apt/Retail 6471 2 Apt/2 Retail $/SQFT $114. 00 $94. 00 $32. 00 $45. 80 $67. 50 $56. 00 $60. 72 $57. 00 $90. 00 $56. 00 Typical Value Approximately $50/Square Foot Typical Value Down. Town Approximately $100/Square Foot Core Rents $15 First Floor $12 Upper Floor $6 Below Grade Outlying Rents $12 First Floor $10 Upper Floor 25 Percent Expenses 10 Percent Overall Cap Rate 97
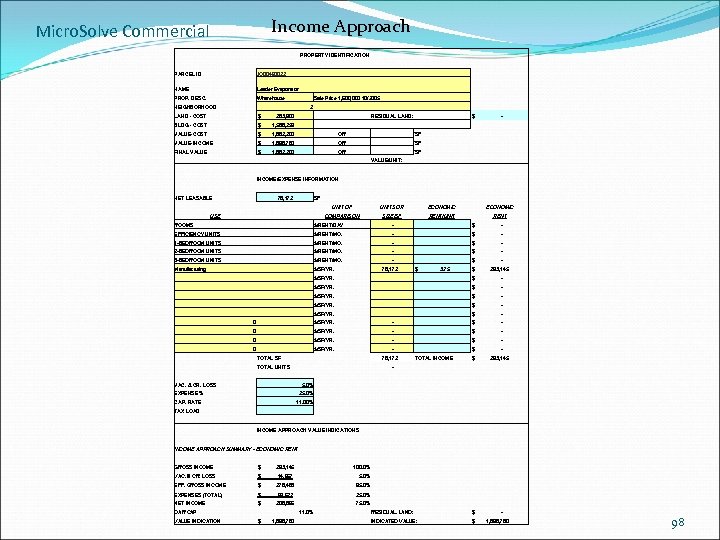 Income Approach Micro. Solve Commercial PROPERTY IDENTIFICATION PARCEL ID JO 00490022 NAME Leader Evaporator PROP. DESC. Wharehouse Sale Price 1, 600, 000 10/2005 NEIGHBORHOOD 2 LAND - COST $ 283, 900 RESIDUAL LAND: BLDG - COST $ 1, 588, 259 VALUE-COST $ 1, 882, 200 OR /SF VALUE-INCOME $ 1, 898, 780 OR /SF FINAL VALUE $ 1, 882, 200 OR /SF $ - VALUE/UNIT: INCOME/EXPENSE INFORMATION NET LEASABLE 78, 172 SF UNIT OF ECONOMIC COMPARISON USE UNITS OR SIZE/SF RENT/UNIT ECONOMIC RENT ROOMS $/RENT/DAY - $ - EFFICIENCY UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 1 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 2 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 3 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - Manufacturing $/SF/YR. 78, 172 $ 3. 75 $ 293, 145 $/SF/YR. $ - 0 $/SF/YR. - $ - TOTAL INCOME $ 293, 145 TOTAL SF 78, 172 TOTAL UNITS - VAC. & CR. LOSS 5. 0% EXPENSE % 25. 0% CAP. RATE 11. 00% TAX LOAD INCOME APPROACH VALUE INDICATIONS INCOME APPROACH SUMMARY - ECONOMIC RENT GROSS INCOME $ 293, 145 100. 0% VAC. & CR. LOSS $ 14, 657 5. 0% EFF. GROSS INCOME $ 278, 488 95. 0% EXPENSES (TOTAL) $ 69, 622 25. 0% NET INCOME $ 208, 866 75. 0% OAR CAP VALUE INDICATION 11. 0% $ 1, 898, 780 RESIDUAL. LAND: $ - INDICATED VALUE: $ 1, 898, 780 98
Income Approach Micro. Solve Commercial PROPERTY IDENTIFICATION PARCEL ID JO 00490022 NAME Leader Evaporator PROP. DESC. Wharehouse Sale Price 1, 600, 000 10/2005 NEIGHBORHOOD 2 LAND - COST $ 283, 900 RESIDUAL LAND: BLDG - COST $ 1, 588, 259 VALUE-COST $ 1, 882, 200 OR /SF VALUE-INCOME $ 1, 898, 780 OR /SF FINAL VALUE $ 1, 882, 200 OR /SF $ - VALUE/UNIT: INCOME/EXPENSE INFORMATION NET LEASABLE 78, 172 SF UNIT OF ECONOMIC COMPARISON USE UNITS OR SIZE/SF RENT/UNIT ECONOMIC RENT ROOMS $/RENT/DAY - $ - EFFICIENCY UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 1 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 2 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - 3 -BEDROOM UNITS $/RENT/MO. - $ - Manufacturing $/SF/YR. 78, 172 $ 3. 75 $ 293, 145 $/SF/YR. $ - 0 $/SF/YR. - $ - TOTAL INCOME $ 293, 145 TOTAL SF 78, 172 TOTAL UNITS - VAC. & CR. LOSS 5. 0% EXPENSE % 25. 0% CAP. RATE 11. 00% TAX LOAD INCOME APPROACH VALUE INDICATIONS INCOME APPROACH SUMMARY - ECONOMIC RENT GROSS INCOME $ 293, 145 100. 0% VAC. & CR. LOSS $ 14, 657 5. 0% EFF. GROSS INCOME $ 278, 488 95. 0% EXPENSES (TOTAL) $ 69, 622 25. 0% NET INCOME $ 208, 866 75. 0% OAR CAP VALUE INDICATION 11. 0% $ 1, 898, 780 RESIDUAL. LAND: $ - INDICATED VALUE: $ 1, 898, 780 98
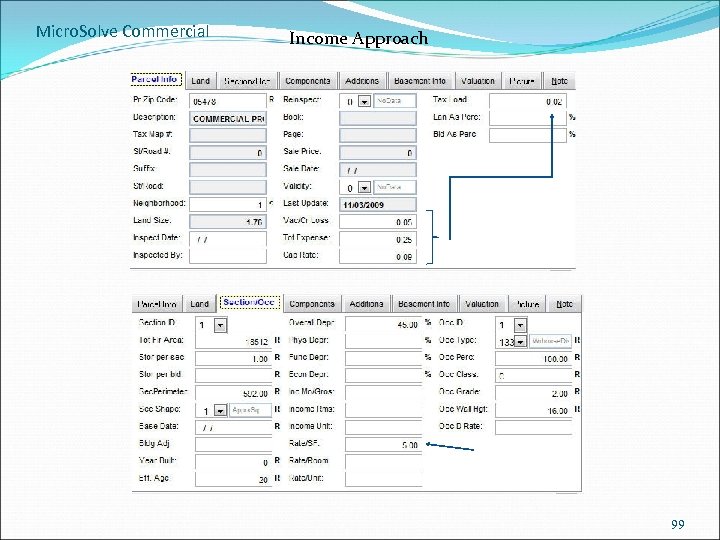 Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach 99
Micro. Solve Commercial Income Approach 99
 Micro. Solve Commercial Conclusions and Summary 100
Micro. Solve Commercial Conclusions and Summary 100
 Micro. Solve Commercial • NEMRC/Micro. Solve Commercial System has made improvements. • Still multiple versions in existence across the State. • It is simple to use, but can value complex properties. • There is no cookbook to appraising property. • Must understand the market and market conditions to value commercial property. • Cost is a means to MARKET VALUE. 101
Micro. Solve Commercial • NEMRC/Micro. Solve Commercial System has made improvements. • Still multiple versions in existence across the State. • It is simple to use, but can value complex properties. • There is no cookbook to appraising property. • Must understand the market and market conditions to value commercial property. • Cost is a means to MARKET VALUE. 101


