 Michael Elad The Computer Science Department The Technion, Israel
Michael Elad The Computer Science Department The Technion, Israel
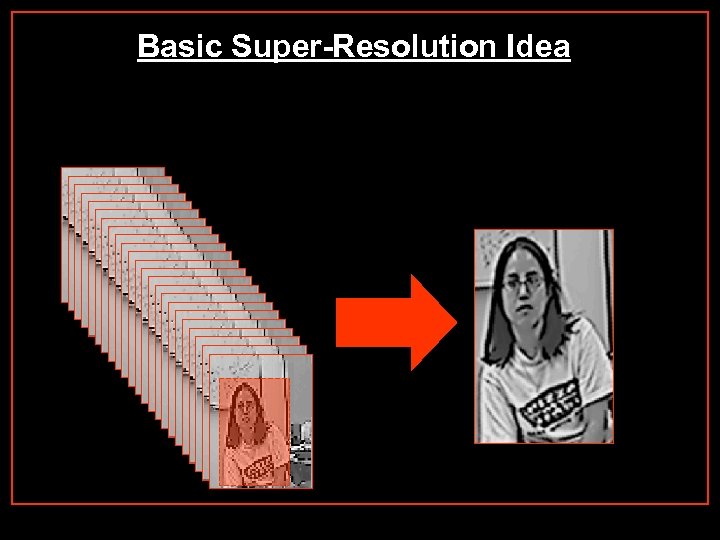 Basic Super-Resolution Idea
Basic Super-Resolution Idea
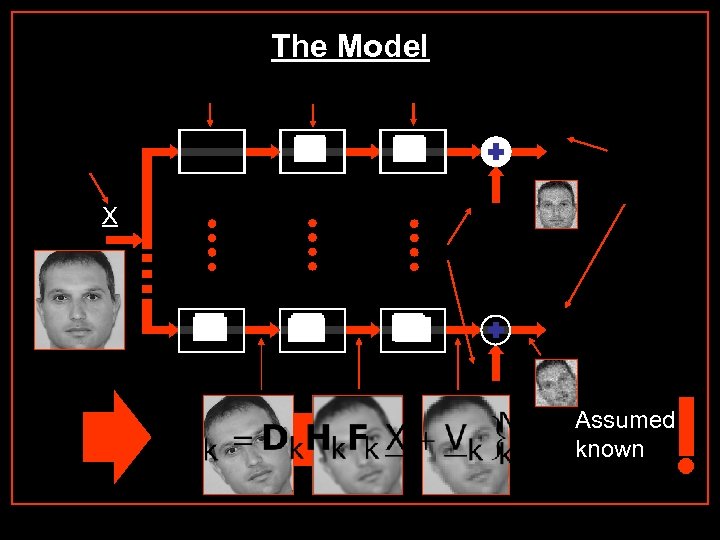 The Model X Assumed known
The Model X Assumed known
 The Model as One Equation
The Model as One Equation
 A Thumb Rule
A Thumb Rule
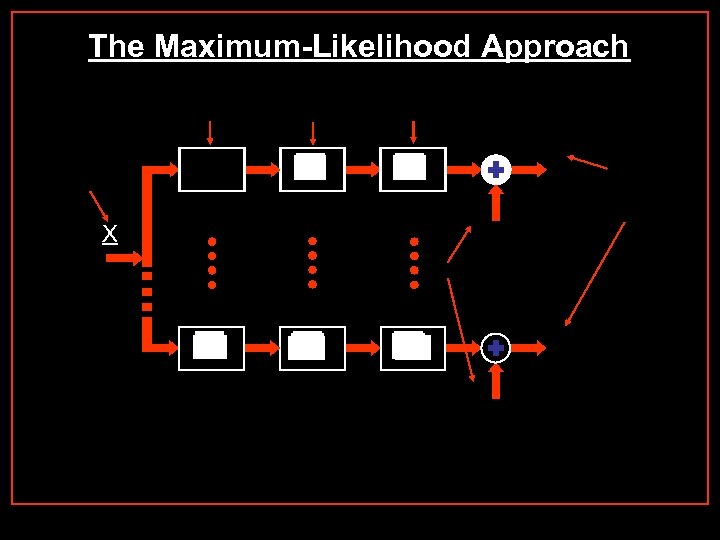 The Maximum-Likelihood Approach X
The Maximum-Likelihood Approach X
 ML Reconstruction
ML Reconstruction
 A Numerical Solution
A Numerical Solution
 The Model – A Statistical View
The Model – A Statistical View
 Maximum-Likelihood … Again The ML estimator is given by which means: Find the image X such that the measurements are the most likely to have happened. In our case this leads to what we have seen before
Maximum-Likelihood … Again The ML estimator is given by which means: Find the image X such that the measurements are the most likely to have happened. In our case this leads to what we have seen before
 ML Often Sucks !!! For Example … For the image denoising problem we get We got that the best ML estimate for a noisy image is … the noisy image itself.
ML Often Sucks !!! For Example … For the image denoising problem we get We got that the best ML estimate for a noisy image is … the noisy image itself.
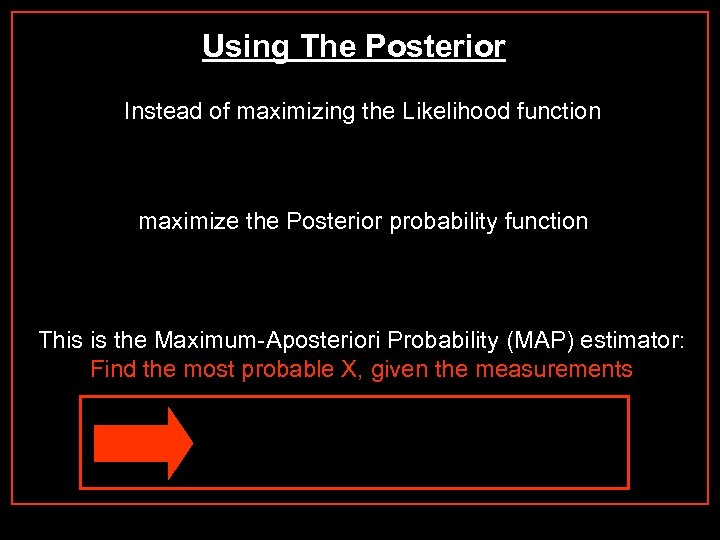 Using The Posterior Instead of maximizing the Likelihood function maximize the Posterior probability function This is the Maximum-Aposteriori Probability (MAP) estimator: Find the most probable X, given the measurements
Using The Posterior Instead of maximizing the Likelihood function maximize the Posterior probability function This is the Maximum-Aposteriori Probability (MAP) estimator: Find the most probable X, given the measurements
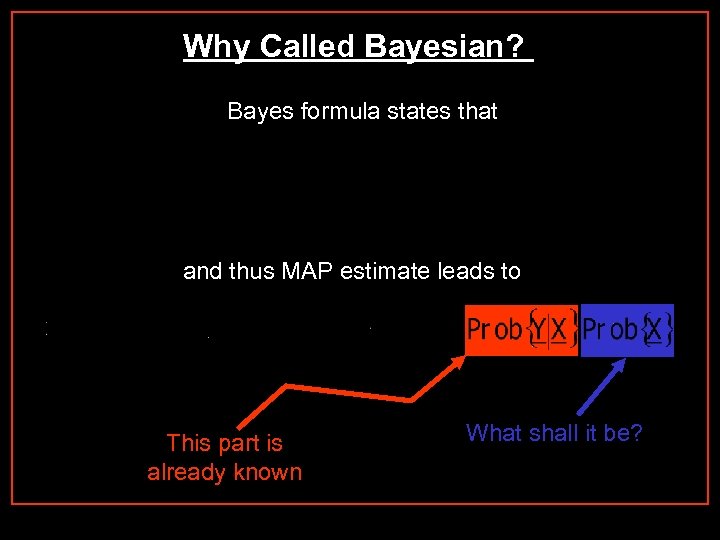 Why Called Bayesian? Bayes formula states that and thus MAP estimate leads to This part is already known What shall it be?
Why Called Bayesian? Bayes formula states that and thus MAP estimate leads to This part is already known What shall it be?
 Image Priors?
Image Priors?
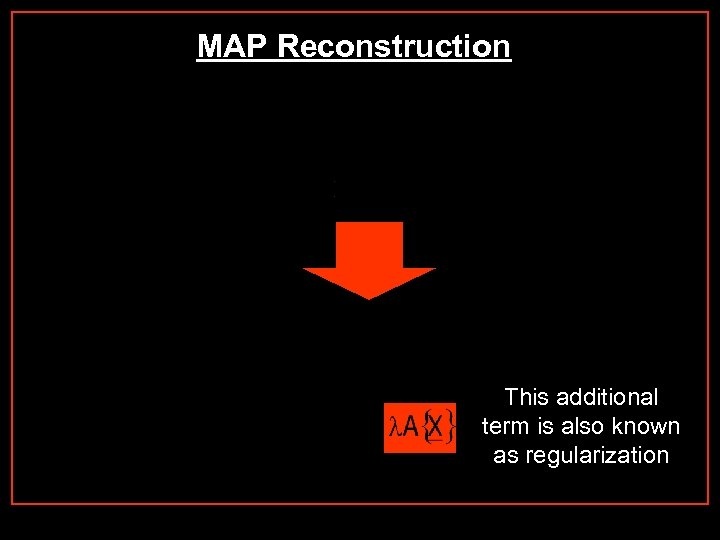 MAP Reconstruction This additional term is also known as regularization
MAP Reconstruction This additional term is also known as regularization
 Choice of Regularization Possible Prior functions - Examples:
Choice of Regularization Possible Prior functions - Examples:
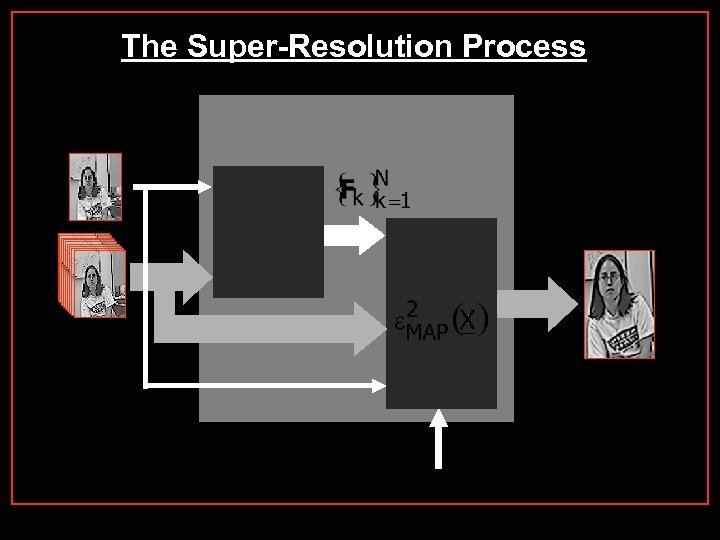 The Super-Resolution Process
The Super-Resolution Process
 Example 0 – Sanity Check
Example 0 – Sanity Check
 Example 1 – SR for Scanners
Example 1 – SR for Scanners
 Example 2 – SR for IR Imaging
Example 2 – SR for IR Imaging
 Example 3 – Surveillance
Example 3 – Surveillance
 Robust SR
Robust SR
 Example 4 – Robust SR
Example 4 – Robust SR
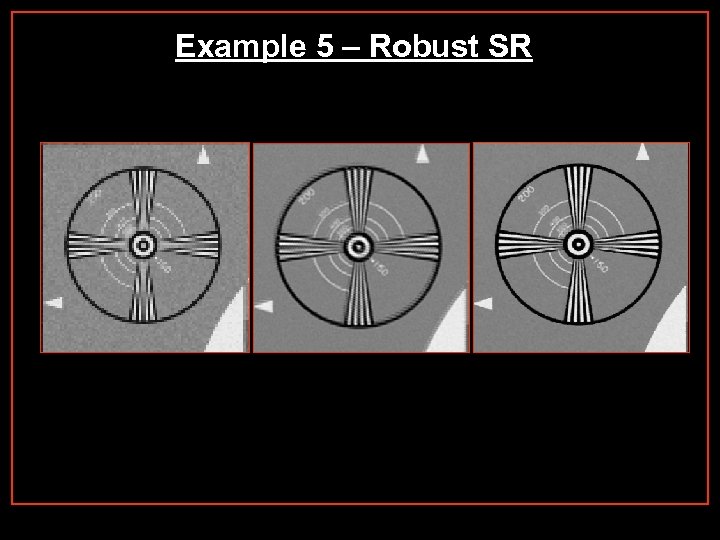 Example 5 – Robust SR
Example 5 – Robust SR
 Handling Color in SR
Handling Color in SR
 Example 6 – SR for Full Color
Example 6 – SR for Full Color
 Example 7 – SR+Demoaicing
Example 7 – SR+Demoaicing
 To Conclude
To Conclude
 Our Work in this Field All, including these slides) are found in http: //www. cs. technion. ac. il/~elad For our Matlab toolbox on Super-Resolution, see
Our Work in this Field All, including these slides) are found in http: //www. cs. technion. ac. il/~elad For our Matlab toolbox on Super-Resolution, see