c0f94892cd5f3374ae579221d7e73c23.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-23
MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-23
 Summary of Lecture-22
Summary of Lecture-22
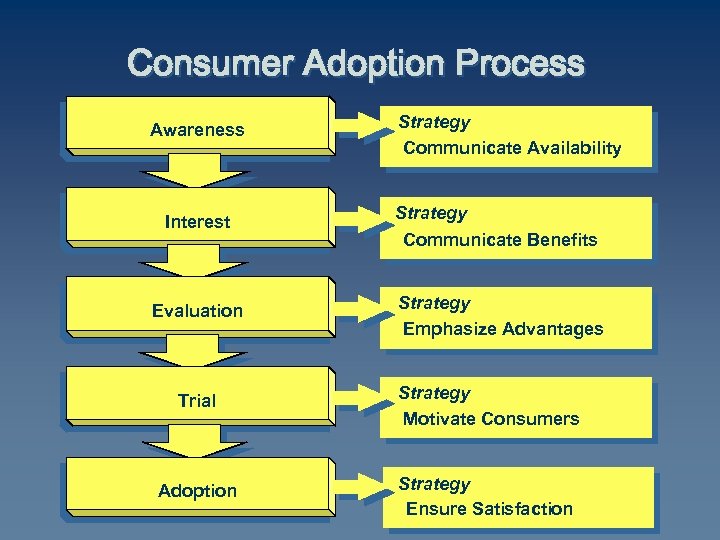 Consumer Adoption Process Awareness Strategy Communicate Availability Interest Strategy Communicate Benefits Evaluation Strategy Emphasize Advantages Trial Strategy Motivate Consumers Adoption Strategy Ensure Satisfaction
Consumer Adoption Process Awareness Strategy Communicate Availability Interest Strategy Communicate Benefits Evaluation Strategy Emphasize Advantages Trial Strategy Motivate Consumers Adoption Strategy Ensure Satisfaction
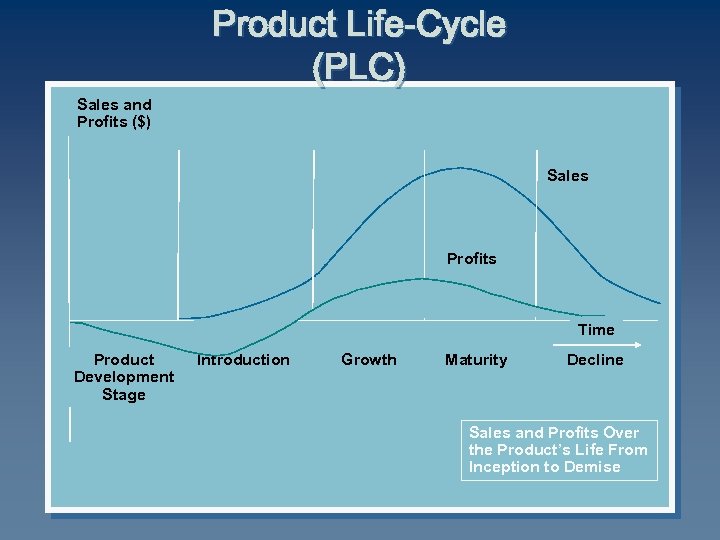 Product Life-Cycle (PLC) Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Product Life-Cycle (PLC) Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
 Today’s Topics Product
Today’s Topics Product
 Value-Driven Marketing Value – A customer’s subjective assessment of benefits relative to the costs in determining the worth of a product u. Customer value = customer benefits – customer costs – Customer benefits u. Anything desired by the customer that is received in an exchange – Customer costs u. Anything a customer gives up in an exchange for benefits –Monetary price of the benefit –Search costs (time and effort) to locate the product –Risks associated with the exchange
Value-Driven Marketing Value – A customer’s subjective assessment of benefits relative to the costs in determining the worth of a product u. Customer value = customer benefits – customer costs – Customer benefits u. Anything desired by the customer that is received in an exchange – Customer costs u. Anything a customer gives up in an exchange for benefits –Monetary price of the benefit –Search costs (time and effort) to locate the product –Risks associated with the exchange
 Benefits C Consumers don’t buy products; they buy benefits Functional benefits: relating to the practical purpose a product serves Psychological benefits: relating to how a product makes one feel
Benefits C Consumers don’t buy products; they buy benefits Functional benefits: relating to the practical purpose a product serves Psychological benefits: relating to how a product makes one feel
 Segmentation
Segmentation
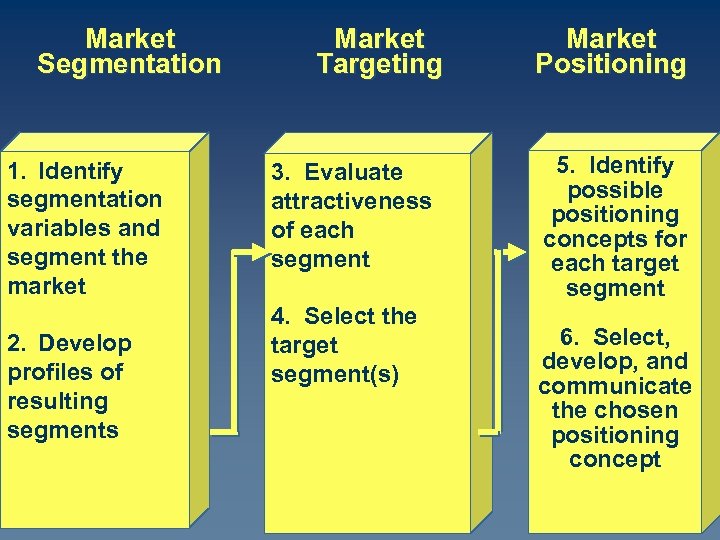 Market Segmentation 1. Identify segmentation variables and segment the market 2. Develop profiles of resulting segments Market Targeting 3. Evaluate attractiveness of each segment 4. Select the target segment(s) Market Positioning 5. Identify possible positioning concepts for each target segment 6. Select, develop, and communicate the chosen positioning concept
Market Segmentation 1. Identify segmentation variables and segment the market 2. Develop profiles of resulting segments Market Targeting 3. Evaluate attractiveness of each segment 4. Select the target segment(s) Market Positioning 5. Identify possible positioning concepts for each target segment 6. Select, develop, and communicate the chosen positioning concept
 Question: Why do you buy a product?
Question: Why do you buy a product?
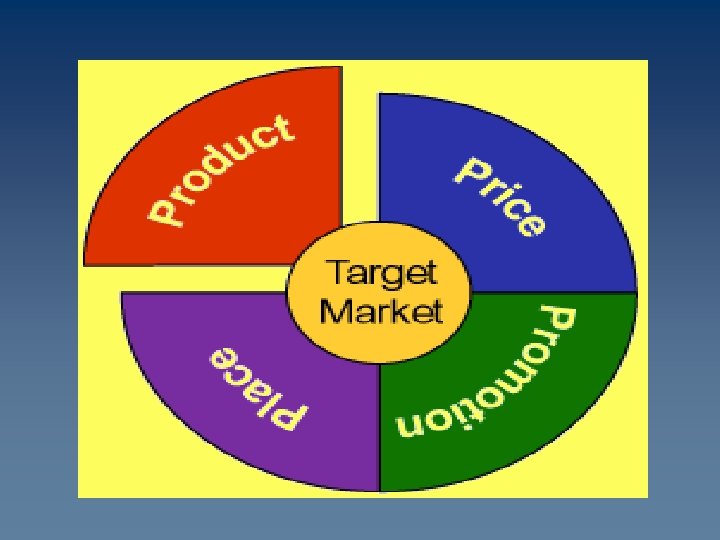
 Marketing Mix 4 Ps
Marketing Mix 4 Ps
 Marketing is the involved process of determining the 4 P’s of the Marketing Mix Product Price Promotion Place (Distribution)
Marketing is the involved process of determining the 4 P’s of the Marketing Mix Product Price Promotion Place (Distribution)
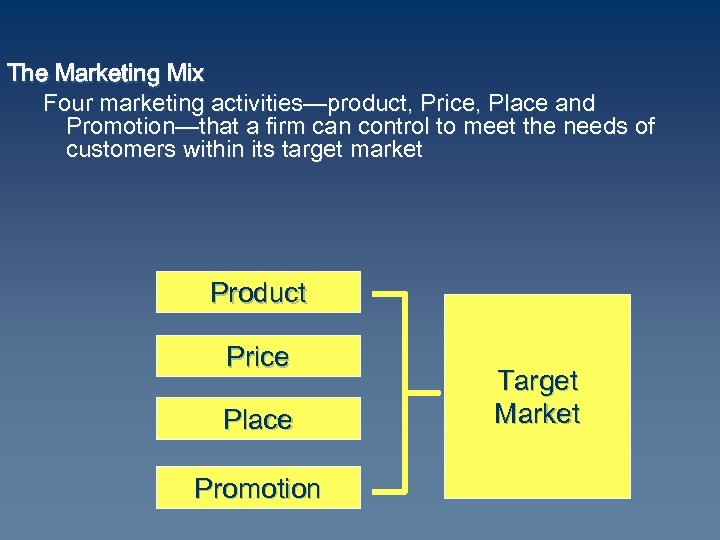 The Marketing Mix Four marketing activities—product, Price, Place and Promotion—that a firm can control to meet the needs of customers within its target market Product Price Place Promotion Target Market
The Marketing Mix Four marketing activities—product, Price, Place and Promotion—that a firm can control to meet the needs of customers within its target market Product Price Place Promotion Target Market
 Definitions Product Anything offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need or want. Service Any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in ownership of anything.
Definitions Product Anything offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need or want. Service Any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in ownership of anything.
 Goods Services
Goods Services
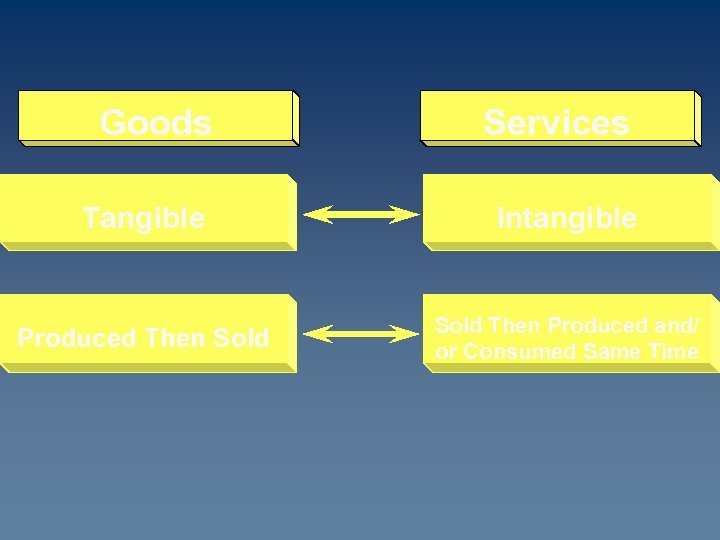 Goods Services Tangible Intangible Produced Then Sold Then Produced and/ or Consumed Same Time
Goods Services Tangible Intangible Produced Then Sold Then Produced and/ or Consumed Same Time
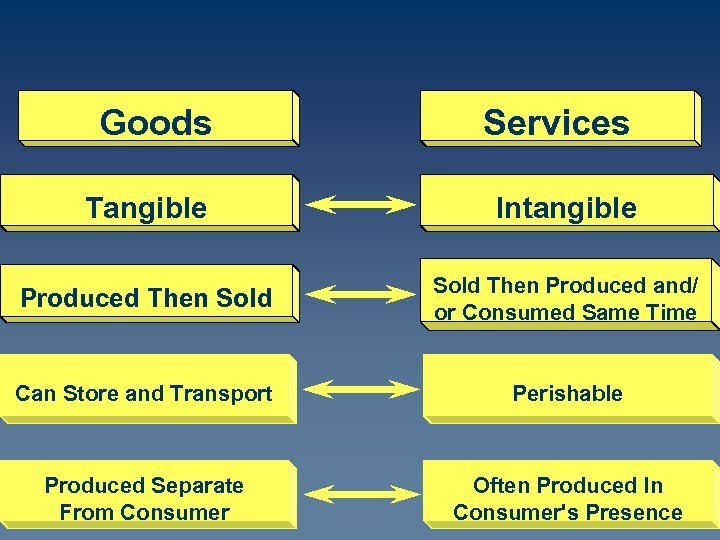 Goods Services Tangible Intangible Produced Then Sold Then Produced and/ or Consumed Same Time Can Store and Transport Perishable Produced Separate From Consumer Often Produced In Consumer's Presence
Goods Services Tangible Intangible Produced Then Sold Then Produced and/ or Consumed Same Time Can Store and Transport Perishable Produced Separate From Consumer Often Produced In Consumer's Presence
 Levels of Products
Levels of Products
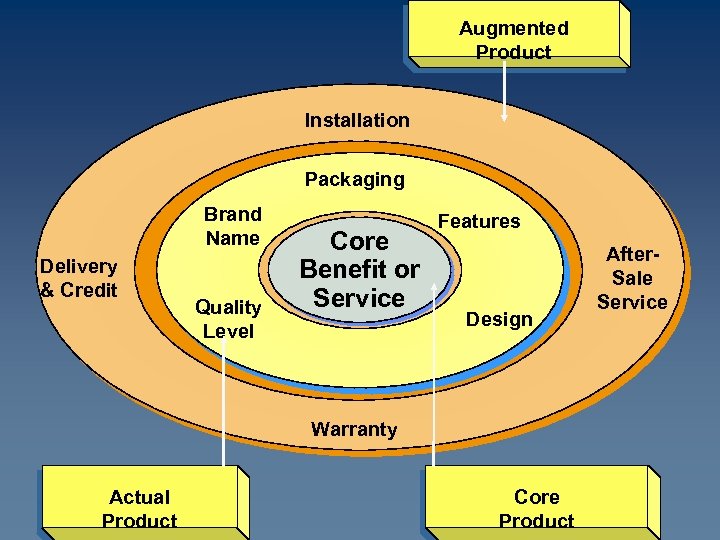 Augmented Product Installation Packaging Brand Name Delivery & Credit Quality Level Core Benefit or Service Features Design Warranty Actual Product Core Product After. Sale Service
Augmented Product Installation Packaging Brand Name Delivery & Credit Quality Level Core Benefit or Service Features Design Warranty Actual Product Core Product After. Sale Service
 Product Classifications
Product Classifications
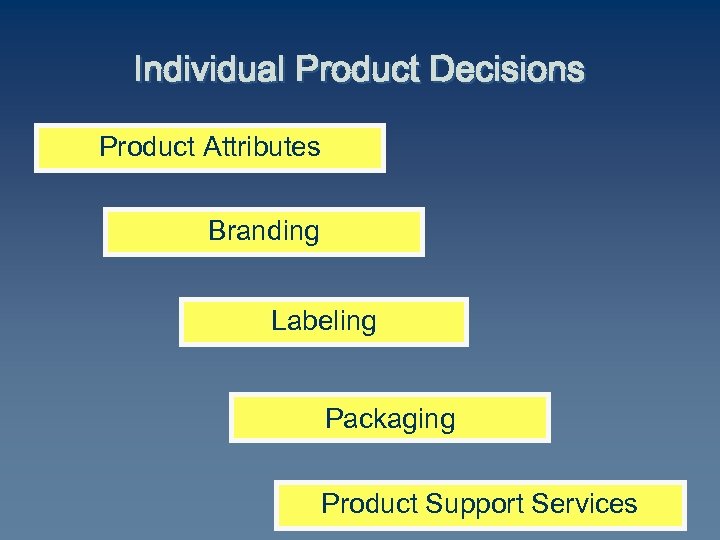 Individual Product Decisions Product Attributes Branding Labeling Packaging Product Support Services
Individual Product Decisions Product Attributes Branding Labeling Packaging Product Support Services
 Product Attributes Developing a Product or Service Involves Defining the Benefits that it Will Offer
Product Attributes Developing a Product or Service Involves Defining the Benefits that it Will Offer
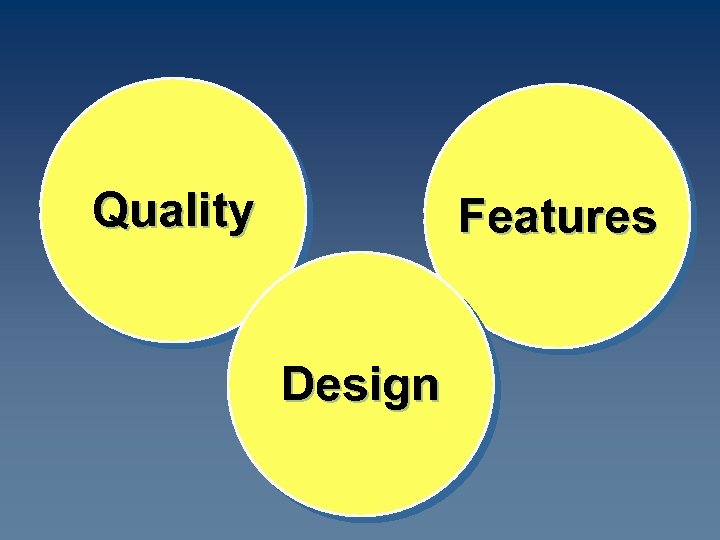 Quality Features Design
Quality Features Design
 Branding
Branding
 Brand A name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of these, intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those competitors
Brand A name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of these, intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those competitors
 To Brand or Not to Brand? Why Incur the Cost & Efforts to Brand?
To Brand or Not to Brand? Why Incur the Cost & Efforts to Brand?
 Brand Name Selection A Good Brand Name Is. . . • • Short and simple Suggestive of product benefits Legally available No negative imagery Easy to spell, read, and pronounce Adaptable for international markets Adaptable to packaging/labeling needs Adaptable to any advertising medium
Brand Name Selection A Good Brand Name Is. . . • • Short and simple Suggestive of product benefits Legally available No negative imagery Easy to spell, read, and pronounce Adaptable for international markets Adaptable to packaging/labeling needs Adaptable to any advertising medium
 Brand Development
Brand Development
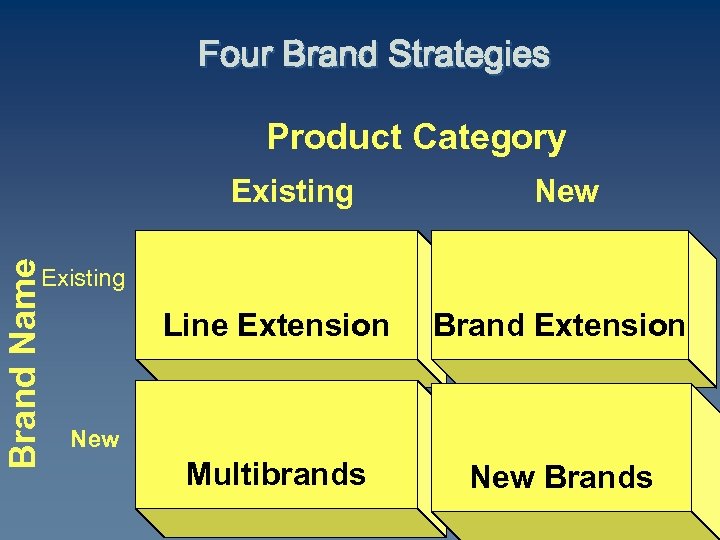 Four Brand Strategies Product Category Brand Name Existing New Existing Line Extension Brand Extension Multibrands New Brands New
Four Brand Strategies Product Category Brand Name Existing New Existing Line Extension Brand Extension Multibrands New Brands New
 Packaging
Packaging
 Goals of Packaging Protection against damage, spoilage, tampering etc. Assistance in marketing the product Cost effectiveness (and good for the environment)
Goals of Packaging Protection against damage, spoilage, tampering etc. Assistance in marketing the product Cost effectiveness (and good for the environment)
 Labeling
Labeling
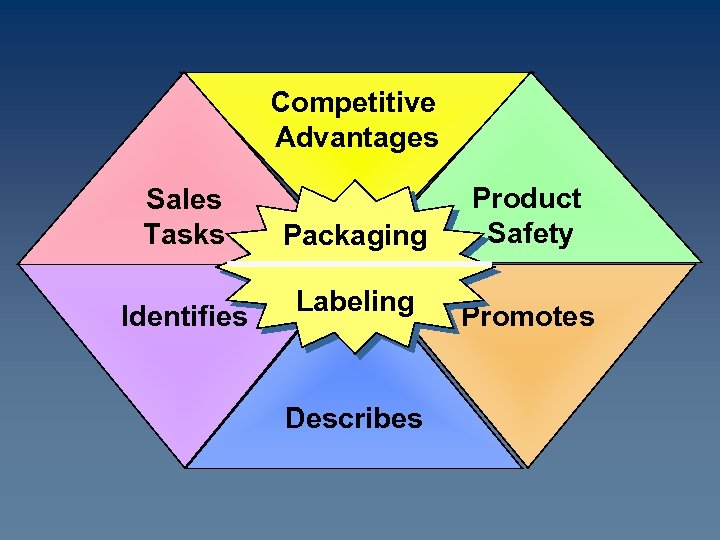 Competitive Advantages Sales Tasks Identifies Packaging Labeling Describes Product Safety Promotes
Competitive Advantages Sales Tasks Identifies Packaging Labeling Describes Product Safety Promotes
 Universal Product Code (UPC) C C A bar code on a product’s package that provides information read by optical scanners. UPC codes provide several advantages: labor saving, improve inventory control, and help with marketing research. 79400 80740
Universal Product Code (UPC) C C A bar code on a product’s package that provides information read by optical scanners. UPC codes provide several advantages: labor saving, improve inventory control, and help with marketing research. 79400 80740
 Product - Support Services
Product - Support Services
 Product Line Strategies
Product Line Strategies
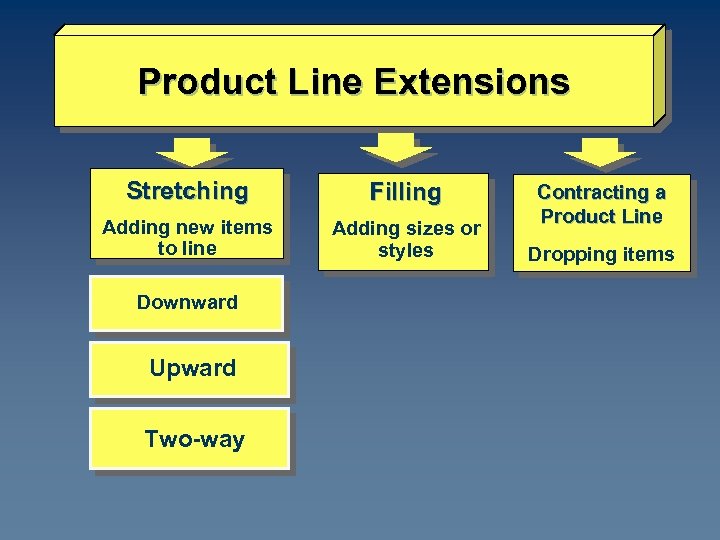 Product Line Extensions Stretching Filling Adding new items to line Adding sizes or styles Downward Upward Two-way Contracting a Product Line Dropping items
Product Line Extensions Stretching Filling Adding new items to line Adding sizes or styles Downward Upward Two-way Contracting a Product Line Dropping items
 New Product Development
New Product Development
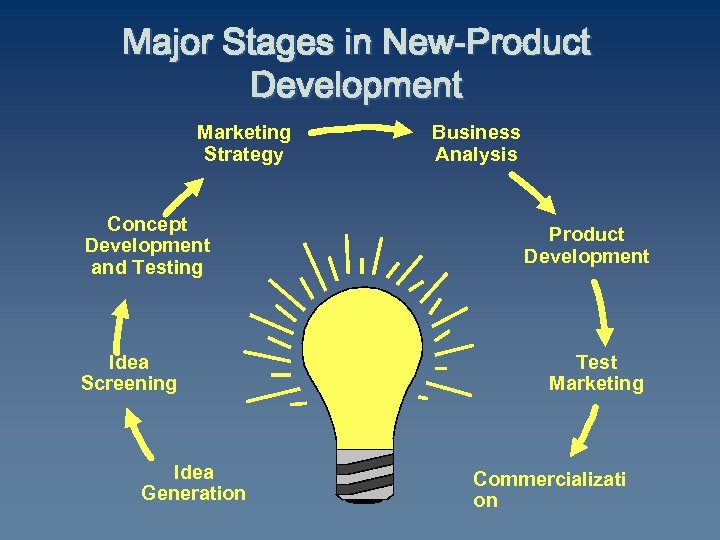 Major Stages in New-Product Development Marketing Strategy Concept Development and Testing Idea Screening Idea Generation Business Analysis Product Development Test Marketing Commercializati on
Major Stages in New-Product Development Marketing Strategy Concept Development and Testing Idea Screening Idea Generation Business Analysis Product Development Test Marketing Commercializati on
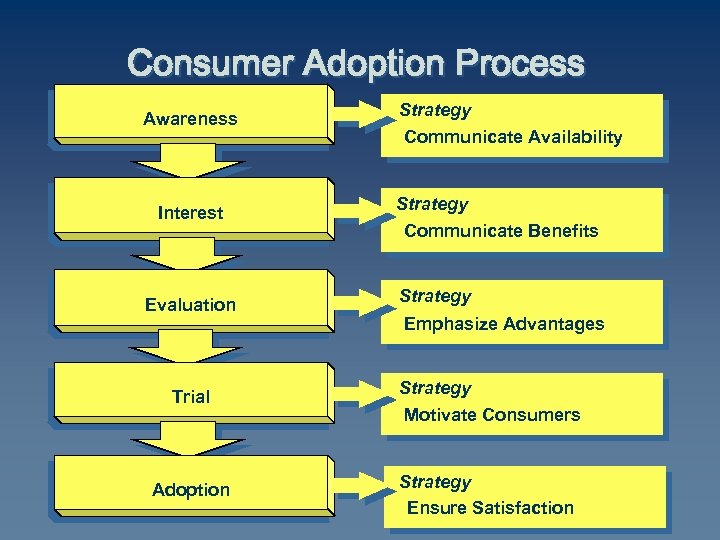 Consumer Adoption Process Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Adoption Strategy Communicate Availability Strategy Communicate Benefits Strategy Emphasize Advantages Strategy Motivate Consumers Strategy Ensure Satisfaction
Consumer Adoption Process Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Adoption Strategy Communicate Availability Strategy Communicate Benefits Strategy Emphasize Advantages Strategy Motivate Consumers Strategy Ensure Satisfaction
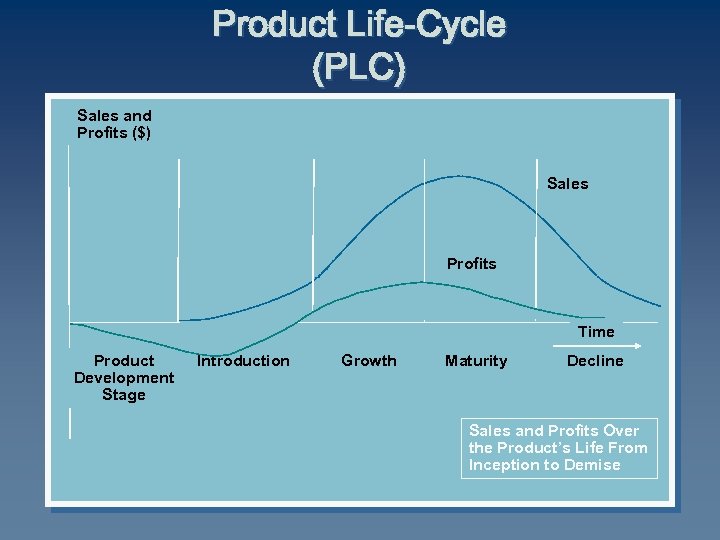 Product Life-Cycle (PLC) Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Product Life-Cycle (PLC) Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
 Product Life-Cycle Strategies
Product Life-Cycle Strategies
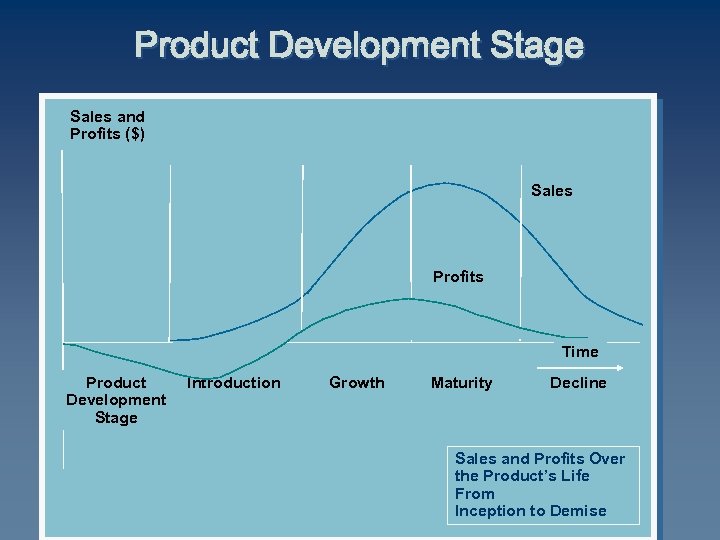 Product Development Stage Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Product Development Stage Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
 PLC Stages C ü Product development Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Begins when the company develops a new-product idea C Sales are zero C Investment costs are high C Profits are negative
PLC Stages C ü Product development Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Begins when the company develops a new-product idea C Sales are zero C Investment costs are high C Profits are negative
 Introduction Stage
Introduction Stage
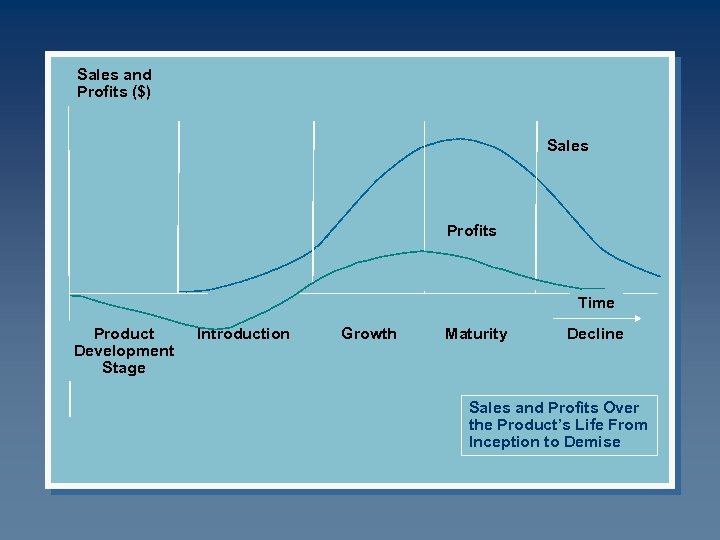 Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
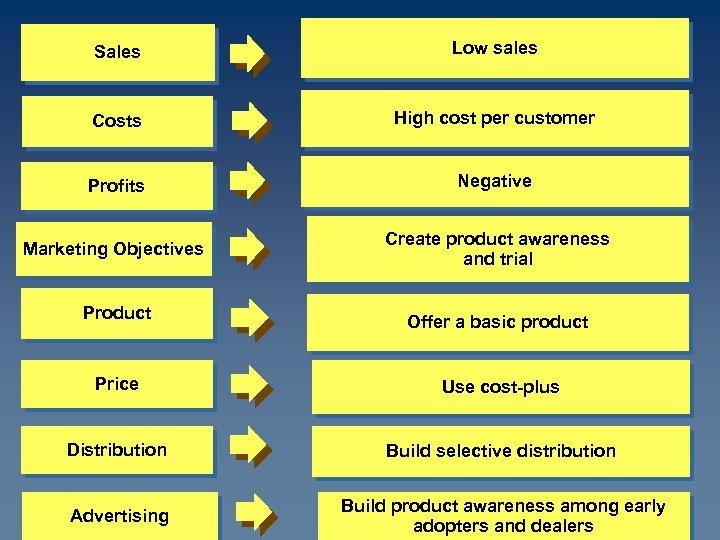 Sales Low sales Costs High cost per customer Profits Negative Marketing Objectives Create product awareness and trial Product Offer a basic product Price Use cost-plus Distribution Build selective distribution Advertising Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers
Sales Low sales Costs High cost per customer Profits Negative Marketing Objectives Create product awareness and trial Product Offer a basic product Price Use cost-plus Distribution Build selective distribution Advertising Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers
 Growth Stage
Growth Stage
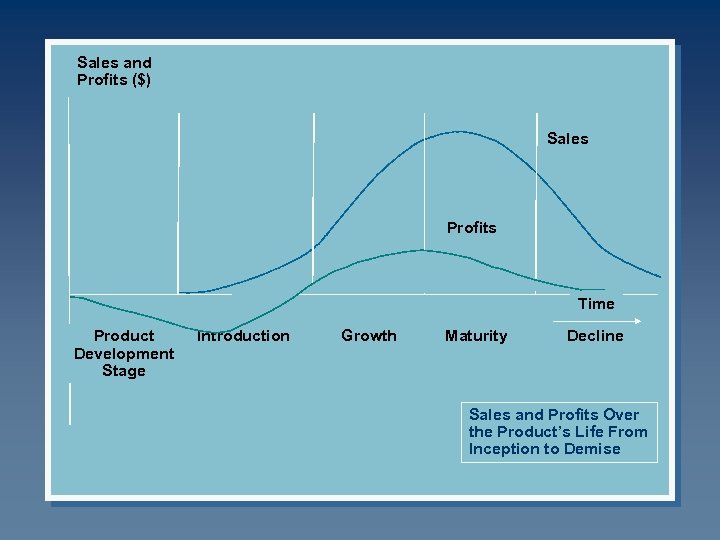 Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
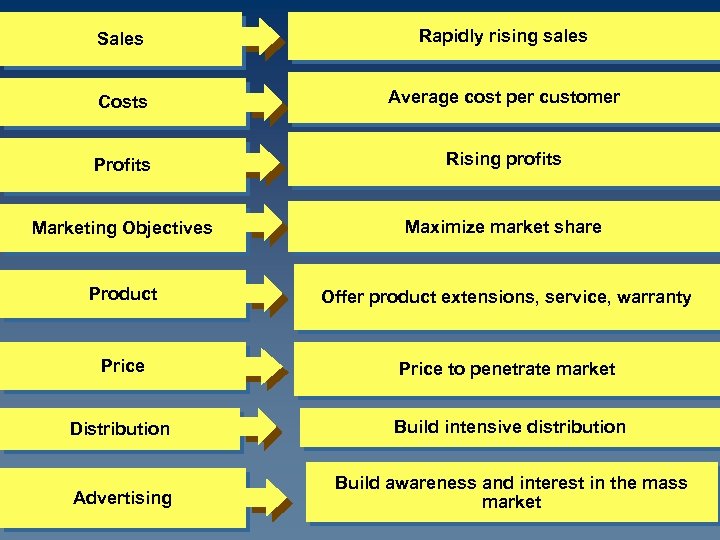 Sales Rapidly rising sales Costs Average cost per customer Profits Rising profits Marketing Objectives Maximize market share Product Offer product extensions, service, warranty Price to penetrate market Distribution Build intensive distribution Advertising Build awareness and interest in the mass market
Sales Rapidly rising sales Costs Average cost per customer Profits Rising profits Marketing Objectives Maximize market share Product Offer product extensions, service, warranty Price to penetrate market Distribution Build intensive distribution Advertising Build awareness and interest in the mass market
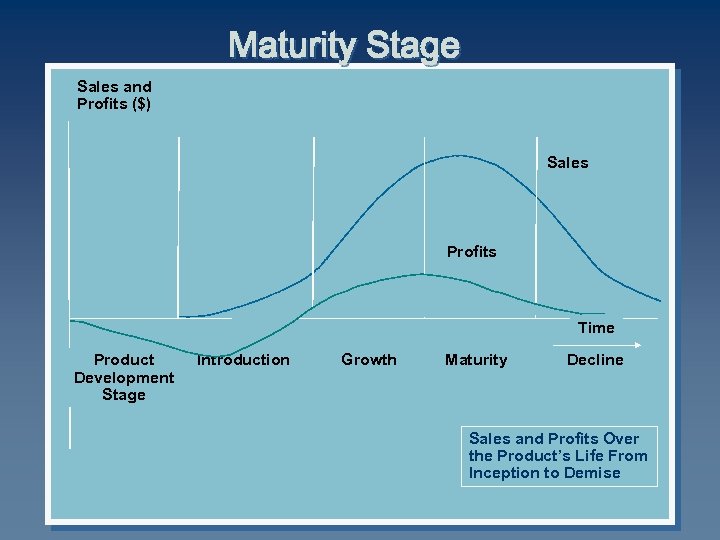 Maturity Stage Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Maturity Stage Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
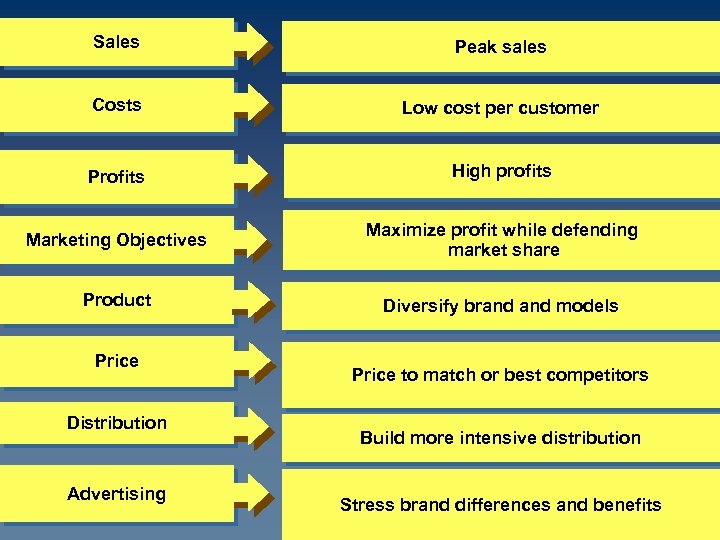 Sales Peak sales Costs Low cost per customer Profits High profits Marketing Objectives Maximize profit while defending market share Product Diversify brand models Price Distribution Advertising Price to match or best competitors Build more intensive distribution Stress brand differences and benefits
Sales Peak sales Costs Low cost per customer Profits High profits Marketing Objectives Maximize profit while defending market share Product Diversify brand models Price Distribution Advertising Price to match or best competitors Build more intensive distribution Stress brand differences and benefits
 Decline Stage
Decline Stage
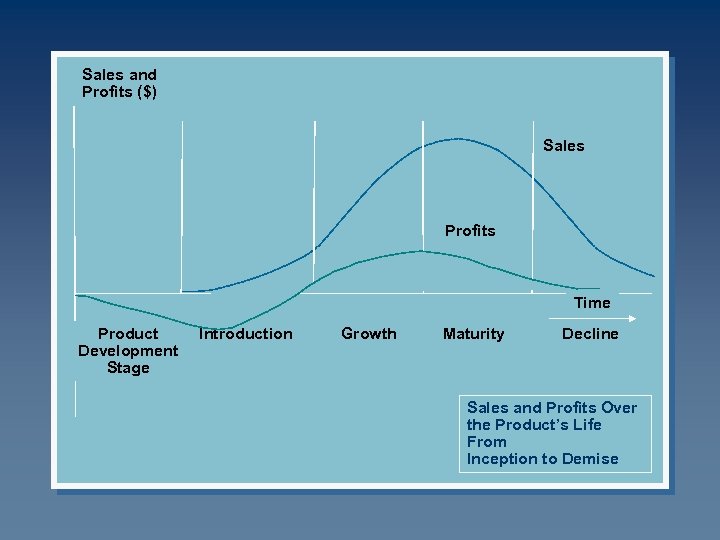 Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Stage Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise
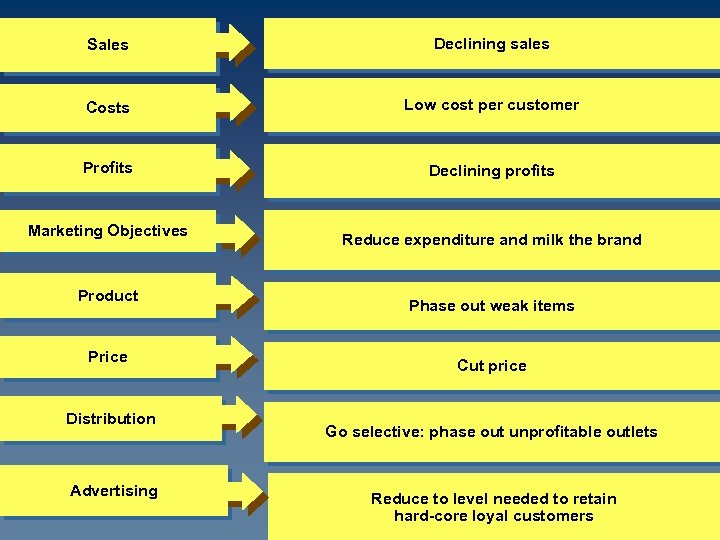 Sales Declining sales Costs Low cost per customer Profits Declining profits Marketing Objectives Product Price Distribution Advertising Reduce expenditure and milk the brand Phase out weak items Cut price Go selective: phase out unprofitable outlets Reduce to level needed to retain hard-core loyal customers
Sales Declining sales Costs Low cost per customer Profits Declining profits Marketing Objectives Product Price Distribution Advertising Reduce expenditure and milk the brand Phase out weak items Cut price Go selective: phase out unprofitable outlets Reduce to level needed to retain hard-core loyal customers
 Extending the Product Life Cycle
Extending the Product Life Cycle
 To prevent the product going into decline you modify the product C Adding new features, variations, model varieties will change the consumer reaction - create more demand therefore you attract more users
To prevent the product going into decline you modify the product C Adding new features, variations, model varieties will change the consumer reaction - create more demand therefore you attract more users
 Enough for today. . .
Enough for today. . .
 Summary Product
Summary Product
 Next…. 4 -P’s price
Next…. 4 -P’s price
 MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-23
MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-23


