Международная экономическая интеграция.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Международная экономическая интеграция International economic integration
Международная экономическая интеграция International economic integration
 Definition Economic integration The establishment of transnational rules and regulations that enhance economic trade and cooperation among countries
Definition Economic integration The establishment of transnational rules and regulations that enhance economic trade and cooperation among countries
 A number of regional economic efforts have been undertaken over the last 30 years to promote varying degrees of economic integration. The most successful has been the EU, although less developed countries (LDCs) have also made integration efforts.
A number of regional economic efforts have been undertaken over the last 30 years to promote varying degrees of economic integration. The most successful has been the EU, although less developed countries (LDCs) have also made integration efforts.
 Trade creation occurs when members of an economic integration group begin focusing their efforts on those goods and services for which they have a comparative advantage and start trading more extensively with each other. For example, the United States and Mexico have an agreement that allows cars to be assembled in Mexico and shipped into the United States. As a result, Mexico, a low-cost producer, supplies a large number of vehicles sold in America, and both countries prosper as a result.
Trade creation occurs when members of an economic integration group begin focusing their efforts on those goods and services for which they have a comparative advantage and start trading more extensively with each other. For example, the United States and Mexico have an agreement that allows cars to be assembled in Mexico and shipped into the United States. As a result, Mexico, a low-cost producer, supplies a large number of vehicles sold in America, and both countries prosper as a result.
 Trade diversion occurs when members of an economic integration group decrease their trade with non-member countries in favor of trade with each other. One common reason is that the removal of trade barriers among member countries makes it less expensive to buy from companies within the group, and the continuation of trade barriers with nonmember countries makes it more difficult for the latter to compete.
Trade diversion occurs when members of an economic integration group decrease their trade with non-member countries in favor of trade with each other. One common reason is that the removal of trade barriers among member countries makes it less expensive to buy from companies within the group, and the continuation of trade barriers with nonmember countries makes it more difficult for the latter to compete.
 The creation of economic integration groups is beneficial only if trade creation exceeds trade diversion
The creation of economic integration groups is beneficial only if trade creation exceeds trade diversion
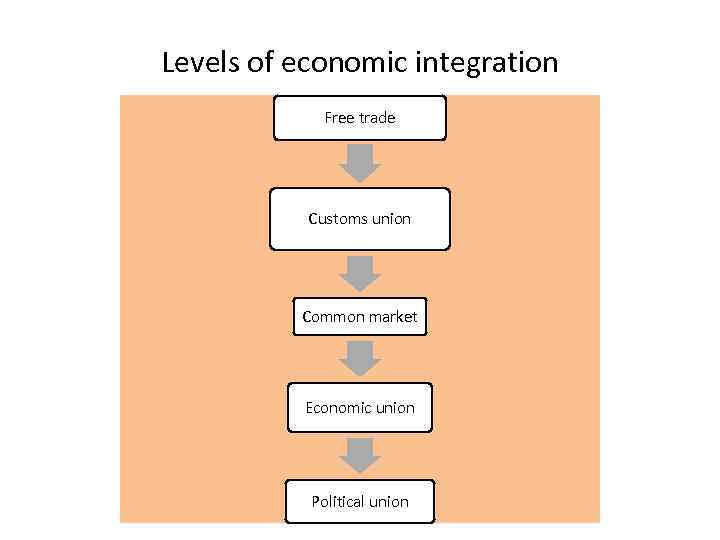 Levels of economic integration Free trade Customs union Common market Economic union Political union
Levels of economic integration Free trade Customs union Common market Economic union Political union
 Definitions Free trade area An economic integration arrangement in which barriers to trade (such as tariffs) among member countries are removed. North America Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) A regional free trade agreement among Canada, the United States, and Mexico
Definitions Free trade area An economic integration arrangement in which barriers to trade (such as tariffs) among member countries are removed. North America Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) A regional free trade agreement among Canada, the United States, and Mexico
 Definitions Customs union A form of economic integration in which all tariffs between member countries are eliminated and a common trade policy toward non-member countries is established. The Andean Community
Definitions Customs union A form of economic integration in which all tariffs between member countries are eliminated and a common trade policy toward non-member countries is established. The Andean Community
 Definitions Common market A form of economic integration characterized by the elimination of trade barriers among member nations, a common external trade policy, and mobility of factors of production among member countries. Previously EU
Definitions Common market A form of economic integration characterized by the elimination of trade barriers among member nations, a common external trade policy, and mobility of factors of production among member countries. Previously EU
 Definitions Political union An economic union in which there is full economic integration, unification of economic policies, and a single government
Definitions Political union An economic union in which there is full economic integration, unification of economic policies, and a single government
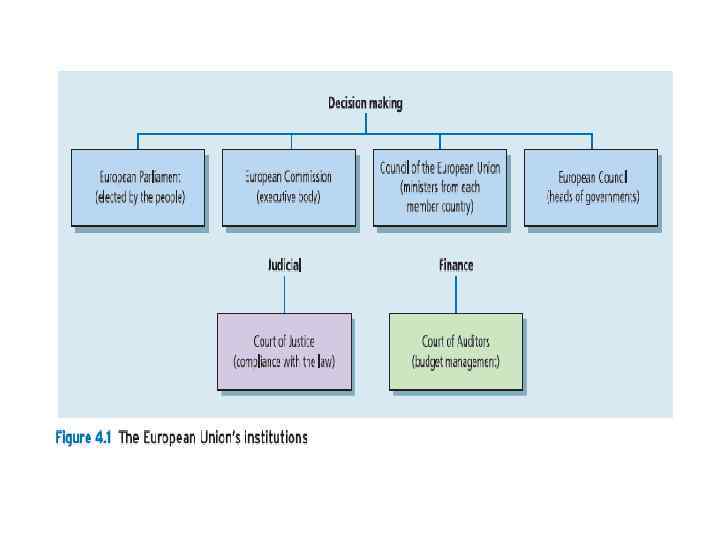
 European Union (EU) A treaty-based institutional framework that manages economic and political cooperation among its 25 member states: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the UK
European Union (EU) A treaty-based institutional framework that manages economic and political cooperation among its 25 member states: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the UK
 Andean Community The Andean Community is a customs union that was formed in 1969 with the signing of the Andean Pact by Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Today, Venezuela is a member, and Chile has withdrawn.
Andean Community The Andean Community is a customs union that was formed in 1969 with the signing of the Andean Pact by Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Today, Venezuela is a member, and Chile has withdrawn.
 Mercosur is a free trade group that was formed by Argentina and Brazil in 1988 to promote economic cooperation. Today the group has been expanded to include Paraguay and Uruguay, with Chile, Bolivia, and Peru as associate members.
Mercosur is a free trade group that was formed by Argentina and Brazil in 1988 to promote economic cooperation. Today the group has been expanded to include Paraguay and Uruguay, with Chile, Bolivia, and Peru as associate members.
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) An economic union founded in 1967 that includes Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand Vietnam; this economic bloc focuses not on reducing trade barriers among members but, rather, on promoting exports to other nations
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) An economic union founded in 1967 that includes Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand Vietnam; this economic bloc focuses not on reducing trade barriers among members but, rather, on promoting exports to other nations
 Мировая валютная система. International exchange system.
Мировая валютная система. International exchange system.
 The price of one currency in terms of another is called an exchange rate. You need 1. 3018 dollars to buy one unit of the European currency, the euro, so the dollar’s exchange rate against the euro was $1. 3018 per euro.
The price of one currency in terms of another is called an exchange rate. You need 1. 3018 dollars to buy one unit of the European currency, the euro, so the dollar’s exchange rate against the euro was $1. 3018 per euro.
 An exchange rate can be quoted in two ways: as the price of the foreign currency in terms of dollars (for example, $0. 01194 per yen) It is direct quotation
An exchange rate can be quoted in two ways: as the price of the foreign currency in terms of dollars (for example, $0. 01194 per yen) It is direct quotation
 as the price of dollars in terms of the foreign currency (for example, 83. 77 yen per dollar). Indirect quotation
as the price of dollars in terms of the foreign currency (for example, 83. 77 yen per dollar). Indirect quotation

 The market in which international currency trades take place is called the foreign exchange market.
The market in which international currency trades take place is called the foreign exchange market.
 The major participants in the foreign exchange market are commercial banks, corporations that engage in international trade, nonbank financial institutions such as asset-management firms and insurance companies, and central banks.
The major participants in the foreign exchange market are commercial banks, corporations that engage in international trade, nonbank financial institutions such as asset-management firms and insurance companies, and central banks.
 Foreign currency trading among banks —called interbank trading—accounts for much of the activity in the foreign exchange market.
Foreign currency trading among banks —called interbank trading—accounts for much of the activity in the foreign exchange market.
 Foreign exchange trading takes place in many financial centers, with the largest volumes of trade occurring in such major cities as London (the largest market), New York, Tokyo, Frankfurt, and Singapore
Foreign exchange trading takes place in many financial centers, with the largest volumes of trade occurring in such major cities as London (the largest market), New York, Tokyo, Frankfurt, and Singapore
 Two parties agree to an exchange of bank deposits and execute the deal immediately. Exchange rates governing such “on-the-spot” trading are called spot exchange rates, and the deal is called a spot transaction.
Two parties agree to an exchange of bank deposits and execute the deal immediately. Exchange rates governing such “on-the-spot” trading are called spot exchange rates, and the deal is called a spot transaction.
 Foreign exchange deals sometimes specify a future transaction date—one that may be 30 days, 90 days, 180 days, or even several years away. The exchange rates quoted in such transactions are called forward exchange rates
Foreign exchange deals sometimes specify a future transaction date—one that may be 30 days, 90 days, 180 days, or even several years away. The exchange rates quoted in such transactions are called forward exchange rates


