6b58886b93a288e2512ec976fdcecf7a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Metric System International System of Units (SI)
Metric System International System of Units (SI)
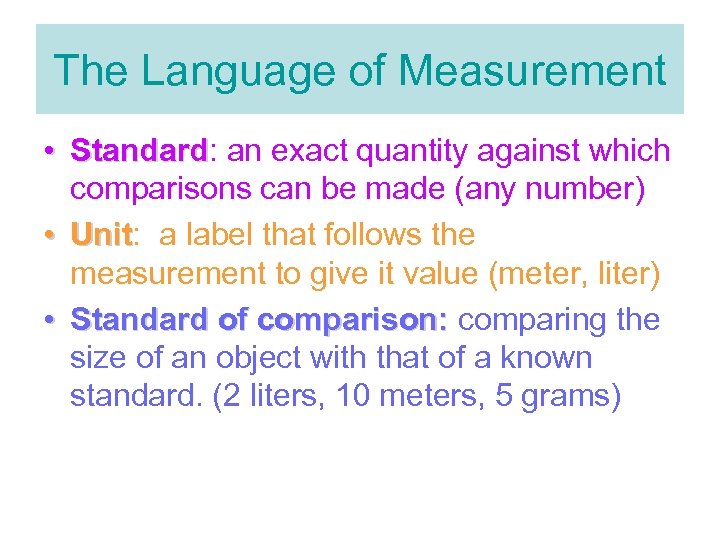 The Language of Measurement • Standard: an exact quantity against which Standard comparisons can be made (any number) • Unit: a label that follows the Unit measurement to give it value (meter, liter) • Standard of comparison: comparing the size of an object with that of a known standard. (2 liters, 10 meters, 5 grams)
The Language of Measurement • Standard: an exact quantity against which Standard comparisons can be made (any number) • Unit: a label that follows the Unit measurement to give it value (meter, liter) • Standard of comparison: comparing the size of an object with that of a known standard. (2 liters, 10 meters, 5 grams)
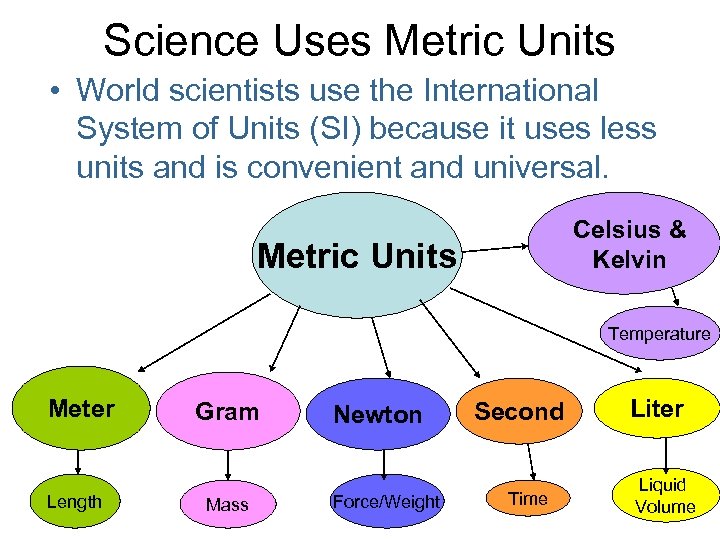 Science Uses Metric Units • World scientists use the International System of Units (SI) because it uses less units and is convenient and universal. Celsius & Kelvin Metric Units Temperature Meter Length Gram Mass Newton Force/Weight Second Time Liter Liquid Volume
Science Uses Metric Units • World scientists use the International System of Units (SI) because it uses less units and is convenient and universal. Celsius & Kelvin Metric Units Temperature Meter Length Gram Mass Newton Force/Weight Second Time Liter Liquid Volume
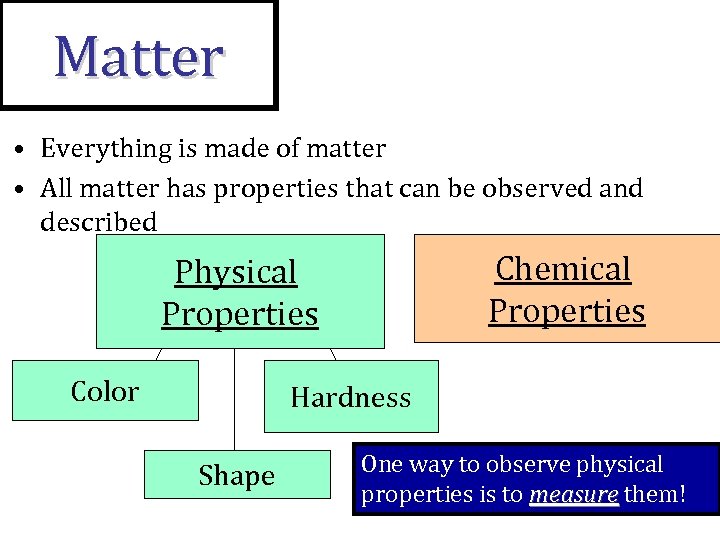 Matter • Everything is made of matter • All matter has properties that can be observed and described Chemical Properties Physical Properties Color Hardness Shape One way to observe physical properties is to measure them!
Matter • Everything is made of matter • All matter has properties that can be observed and described Chemical Properties Physical Properties Color Hardness Shape One way to observe physical properties is to measure them!
 ØMeasured using a meter ruler or meter stick ØBasic unit for length: meter - m Length - 26 cm
ØMeasured using a meter ruler or meter stick ØBasic unit for length: meter - m Length - 26 cm
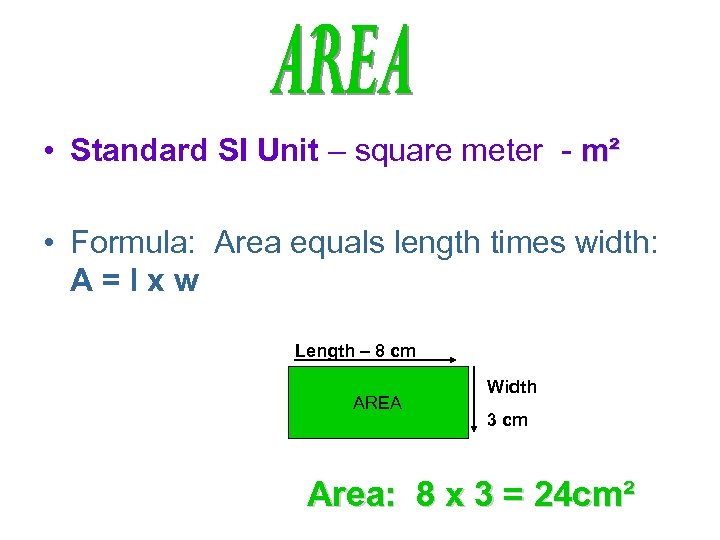 • Standard SI Unit – square meter - m² • Formula: Area equals length times width: A=lxw Length – 8 cm AREA Width 3 cm Area: 8 x 3 = 24 cm²
• Standard SI Unit – square meter - m² • Formula: Area equals length times width: A=lxw Length – 8 cm AREA Width 3 cm Area: 8 x 3 = 24 cm²
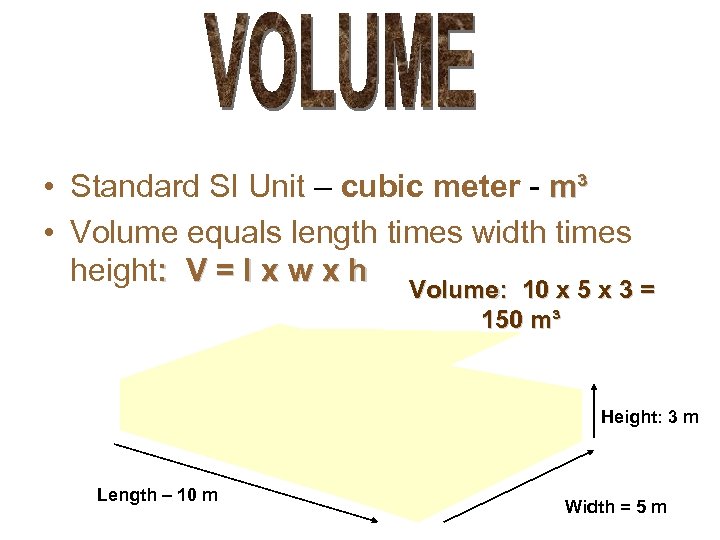 • Standard SI Unit – cubic meter - m³ • Volume equals length times width times height: V = l x w x h Volume: 10 x 5 x 3 = 150 m³ Height: 3 m Length – 10 m Width = 5 m
• Standard SI Unit – cubic meter - m³ • Volume equals length times width times height: V = l x w x h Volume: 10 x 5 x 3 = 150 m³ Height: 3 m Length – 10 m Width = 5 m
 Usually measured in Liters (L) Tools: Beakers Graduated Cylinder
Usually measured in Liters (L) Tools: Beakers Graduated Cylinder
 Amount of matter in an object Standard SI Unit: kilogram and gram Tool: Triple Beam Balance
Amount of matter in an object Standard SI Unit: kilogram and gram Tool: Triple Beam Balance
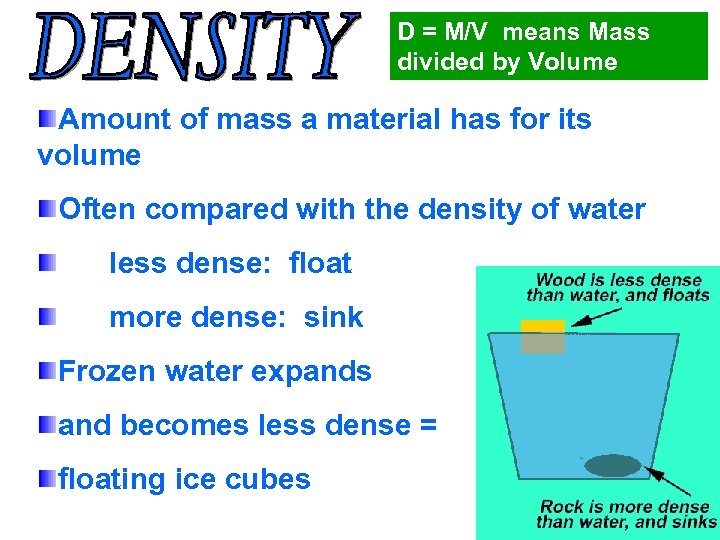 D = M/V means Mass divided by Volume Amount of mass a material has for its volume Often compared with the density of water less dense: float more dense: sink Frozen water expands and becomes less dense = floating ice cubes
D = M/V means Mass divided by Volume Amount of mass a material has for its volume Often compared with the density of water less dense: float more dense: sink Frozen water expands and becomes less dense = floating ice cubes
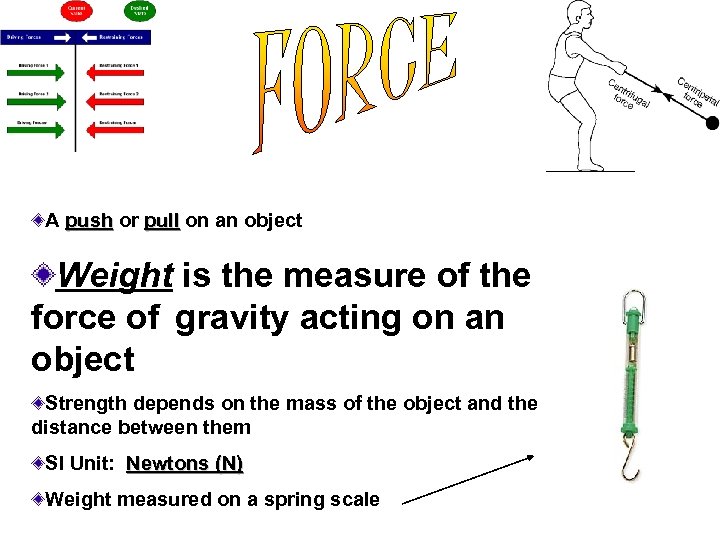 A push or pull on an object Weight is the measure of the force of gravity acting on an object Strength depends on the mass of the object and the distance between them SI Unit: Newtons (N) Weight measured on a spring scale
A push or pull on an object Weight is the measure of the force of gravity acting on an object Strength depends on the mass of the object and the distance between them SI Unit: Newtons (N) Weight measured on a spring scale
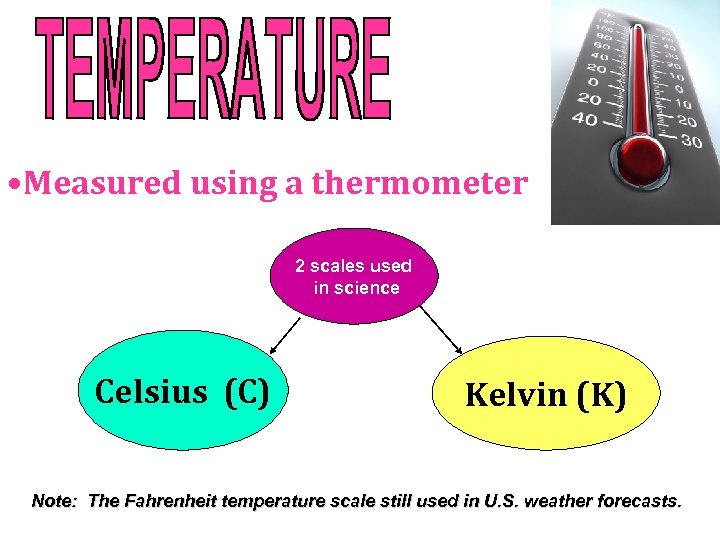 • Measured using a thermometer 2 scales used in science Celsius (C) Kelvin (K) Note: The Fahrenheit temperature scale still used in U. S. weather forecasts.
• Measured using a thermometer 2 scales used in science Celsius (C) Kelvin (K) Note: The Fahrenheit temperature scale still used in U. S. weather forecasts.
 A measurement of the period between two events. Not a property of matter SI Unit: Second In one second, light can travel about 7 ½ times around the earth at the Equator. Speed of light: 186, 300 per second Most accurate: atomic clock at the National Bureau of Standards in Washington, DC
A measurement of the period between two events. Not a property of matter SI Unit: Second In one second, light can travel about 7 ½ times around the earth at the Equator. Speed of light: 186, 300 per second Most accurate: atomic clock at the National Bureau of Standards in Washington, DC
 “WHY DO I NEED TO KNOW THE METRIC SYSTEM? ” All countries in the world use the Metric System… except Burma (Myanmar) and the United States National Bureau of Standards in Washington, DC sets accurate measurement standards for science, industry and commerce Industries that sell or buy goods in other countries must use SI units to compete in those countries.
“WHY DO I NEED TO KNOW THE METRIC SYSTEM? ” All countries in the world use the Metric System… except Burma (Myanmar) and the United States National Bureau of Standards in Washington, DC sets accurate measurement standards for science, industry and commerce Industries that sell or buy goods in other countries must use SI units to compete in those countries.
 Accuracy, Estimation, and Precision • ACCURACY: depends on how close your value is to the actual or accepted value • ESTIMATION: a valuable skill that saves time! – It can be improved with practice. • PRECISION: the degree of exactness with which the object is measured. – – Depends on the measuring instrument. Can’t improve with practice. Can only be as precise as the measurement instrument. Does not guarantee accuracy!
Accuracy, Estimation, and Precision • ACCURACY: depends on how close your value is to the actual or accepted value • ESTIMATION: a valuable skill that saves time! – It can be improved with practice. • PRECISION: the degree of exactness with which the object is measured. – – Depends on the measuring instrument. Can’t improve with practice. Can only be as precise as the measurement instrument. Does not guarantee accuracy!



