06ba34d406fd134de80bd64f36e0024a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Methodology for Estimating the Doses to Members of the Public from Contaminated Land W B Oatway and S F Mobbs NRPB, UK 7 th ALARA network, Arnhem 2003 ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Introduction • Overview of an assessment approach to contaminated land • Description of the general methodology – description of the contamination distribution – description of the exposure scenarios – description of the exposure pathways • Details of the radionuclides considered in the general methodology • Overview of the outputs given in the report describing the general methodology ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Overview of the general approach to dealing with contaminated land • Desk study – review all documents/reports relating to the site – identify the scope of the contamination and what the contamination consists of • Site survey – walk-over and laboratory analysis to determine activity concentrations present and the physical scope of the contamination • Dose assessment – determine the doses and risks to site users – compare results with dose criteria ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

The general contaminated land methodology • Developed by the NRPB to model exposure to members of the public from radionuclides present in the soil • Report describing the model published as NRPB report W 36 • The methodology calculates the dose per unit contamination using: – 6 contamination distributions – 7 exposure scenarios – 8 exposure pathways ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Contamination distributions • • • Exposed, uniform Buried, uniform Disturbed buried, uniform Exposed, patchy Buried, patchy Disturbed buried, patchy ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Exposure scenarios • Use of the land for agriculture – exposure whilst tending fields (including ploughing) – exposure from consuming crops grown on the contaminated land • Recreational use of the land – exposure to a general park user (walking dogs etc) – exposure from the use of a lake/river for swimming/fishing – exposure to a park worker involved in limited ground maintenance • Construction on the land of buildings – exposure during manual and mechanical disturbance of the ground ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Exposure scenarios • Use of the land for a school – exposure whilst inside a classroom – exposure whilst playing sports on a field • Use of the land for industrial offices – exposure whilst working at a desk in a ground floor office – exposure whilst using a small outside grass area • Use of the land for housing – exposure whilst inside a house – exposure whilst using/tending a garden – exposure from consuming foods grown in the garden • Use of the land for car parks or concrete play areas ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency
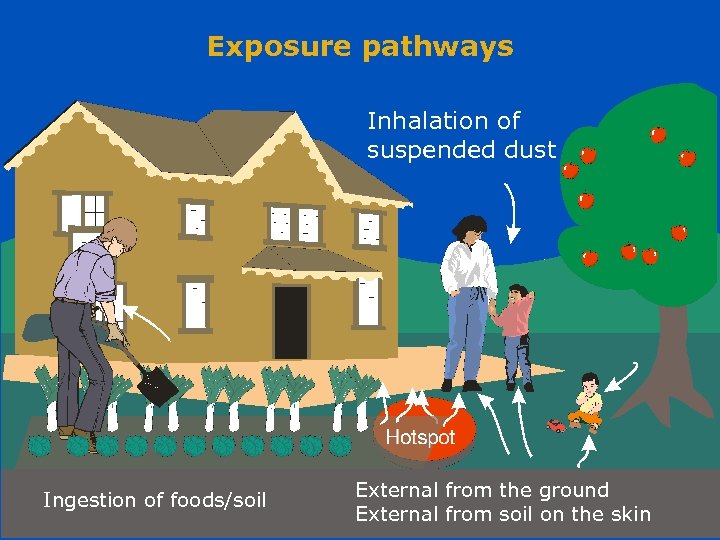
Exposure pathways Inhalation of suspended dust External from the ground Working in partnership with External from soil on the skin the Health Protection Agency Ingestion of foods/soil ©NRPB

What radionuclides to consider? Sources of Contamination in the UK • Radium luminising • Extracting and handling thorium and thorium compounds • Industries disposing of materials containing enhanced levels of naturals • Contamination on sites used for nuclear power production ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Radionuclides included in the general contaminated land methodology • Represent those radionuclides assessed in previous assessments for contaminated land • Includes other radionuclides likely to be present in contaminated land in the UK given likely sources of radionuclides • 36 radionuclides considered explicitly – 13 radionuclides considered with ingrowth of short-lived daughters ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency
Methodology outputs • Set of doses expressed in units of Sv/y per Bq/g • Calculations performed for 1 year olds, 10 year olds and adults • Doses given for all scenarios and contamination profiles • Maximum doses given for all land uses (maximum dose from all the exposure scenarios) ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Example results for soil contaminated with Ra+226 ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency

Conclusions • A general assessment methodology for exposure to contaminated land is described • Dose per unit activity given for exposure to 36 radionuclides for a variety of land uses • Results can be scaled to measured activity concentrations for site-specific assessments • Results can be used to derive clean-up levels • http: //www. nrpb. org/publications/ w_series_reports/2003/nrpb_w 36. htm ©NRPB Working in partnership with the Health Protection Agency
06ba34d406fd134de80bd64f36e0024a.ppt