bd4eeb49bb8e952592b13a9af56d88e9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Methodologies evaluation Agentlink III AOSE TFG Budapest, 17 sep. 2005

Evaluation framework for AOSEM n n n AOSE TFG Towards an evaluation framework for AOSEM Previous approaches Questionnaire results Review Outline and plan for document on AOSEM evaluation framework Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 2
An evaluation framework for AOSEM n Context n Diverse scope of application of methodologies • Several aspects: analysis, design, implementation, deployment, validation, verification, etc. • Several application domains: from closed systems to open systems, web support, etc. n Tool support • Tools for modelling and code generation • Some methodologies have no tool support at all (or in a very experimental state) n n n Development process not always defined Different notations Different agent concepts Standardization efforts Several approaches for integration: • A common standard agent specification language: which one? • Fragments: method engineering AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 3

An evaluation framework for AOSEM n Evaluation of AOSEM can help towards the success of AOSE n n AOSE TFG Clarification of concepts => towards some standardization Integration of fragments Definition of AOSE processes: heavy to light approaches Promotion of tools Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 4

Inputs for AOSEM evaluation n n AOSE TFG A. Sturm, O. Shehory, D. Dori (2004). Evaluation of Agent-Oriented Methodologies. In: AL 3 TF 1 -AOSE TFG Q. N. Tran, G. Low (2005). Comparison of ten agent-oriented methodologies. In: Henderson-Sellers, B. and Giorgini, P. , editors (2005). Agent-Oriented Methodologies. Idea Group Publishing. Chapter XII, pp. 341 -367. C. Bernon, et al. (2004). A Study of some Multi-Agent Meta-Models. Proc. AOSE 2004 (to appear in LNCS, Springer-Verlag). L. Cernuzzi, G. Rossi (2004). On the evaluation of agent oriented methodologies. In: Proc. of the OOPSLA 2002 Workshop on Agent. Oriented Methodologies. L. Cernuzzi, M. Cossentino, F. Zambonelli (2005). Process Models for Agent-Based Development. International Journal on Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence (EAAI). Elsevier. (in edition? ) Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 5

Questionnaire n n Originally from Mickael Winikoff and modified by Massimo Cossentino Aim: assess an AOSE methodology against a range of criteria. The criteria fall into a number of areas. n n AOSE TFG Concepts/properties: The ideas that the methodology deals with, basically the ontology Modelling: The models that are constructed and the notations used to express the models. Process: The phases and steps that are followed as part of the methodology. Pragmatics: Practical issues that are concerns when adopting a methodology (e. g. , the availability of training materials and courses, the existence and cost of tools, etc. ) Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 6

Questionnaire n Answers from: n n n n ADELFE (Carole Bernon/creator) INGENIAS (Jorge Gómez-Sanz & Juan Pavón/creators) OPEN Process Framework (OPF) (Brian Henderson. Sellers/creator) Prometheus-ROADMAP (Lin Padgham/creator) Gaia (Giancarlo Fortino/Alfredo Garro: users!!!) PASSI (M. Cossentino: creator, L. Sabatucci, V. Seidita/Ph. D Students: users/doing research on it, 8 graduating students: users) TROPOS (3 students) • Others are always welcome!!! • Answers from users (not creators) can provide a better critical view of methodologies AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 7

Questionnaire n Looking at the results of the questionnaire n It can be useful to consider changes in the questionnaire n n n AOSE TFG Subjective interpretation of questions and answers Not applicable Missing questions Useful? Clarifying? Identification of methodology challenges Let’s see what are the results and discuss… Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 8
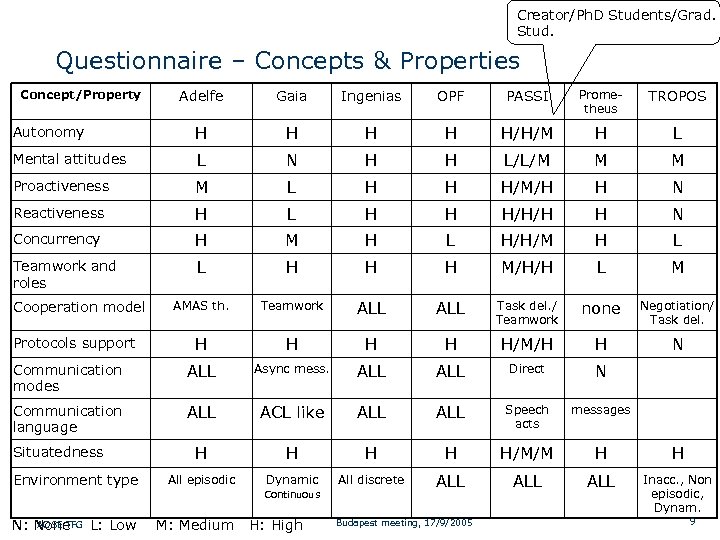
Creator/Ph. D Students/Grad. Stud. Questionnaire – Concepts & Properties Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus TROPOS Autonomy H H H/H/M H L Mental attitudes L N H H L/L/M M M Proactiveness M L H H H/M/H H N Reactiveness H L H H H/H/H H N Concurrency H M H L H/H/M H L Teamwork and roles L H H H M/H/H L M AMAS th. Teamwork ALL Task del. / Teamwork none Negotiation/ Task del. Protocols support H H H/M/H H N Communication modes ALL Async mess. ALL Direct N Communication language ALL ACL like ALL Speech acts messages H H H/M/M H H All episodic Dynamic All discrete ALL ALL Inacc. , Non episodic, Dynam. Concept/Property Cooperation model Situatedness Environment type Continuous AOSE TFG N: None L: Low M: Medium H: High Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 9
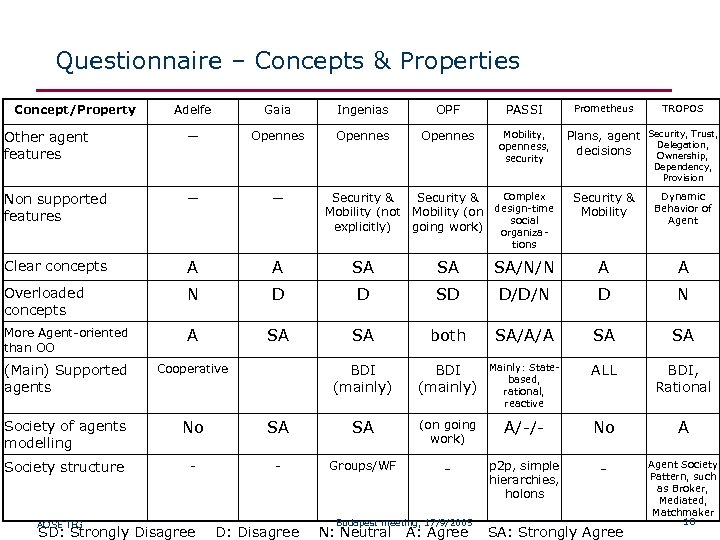
Questionnaire – Concepts & Properties Concept/Property Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Other agent features — Opennes Mobility, openness, security Non supported features — — Complex Security & design-time Mobility (not Mobility (on social explicitly) going work) organiza- Prometheus TROPOS Plans, agent Security, Trust, Delegation, decisions Ownership, Dependency, Provision Security & Mobility Dynamic Behavior of Agent tions Clear concepts A A SA SA SA/N/N A A Overloaded concepts N D D SD D/D/N D N More Agent-oriented than OO A SA SA both SA/A/A SA SA (Main) Supported agents Cooperative BDI (mainly) Mainly: Statebased, rational, reactive ALL BDI, Rational Society of agents modelling No SA SA (on going work) A/-/- No A Society structure - - Groups/WF - p 2 p, simple hierarchies, holons - Agent Society Pattern, such as Broker, Mediated, Matchmaker 10 AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 SD: Strongly Disagree D: Disagree N: Neutral A: Agree SA: Strongly Agree
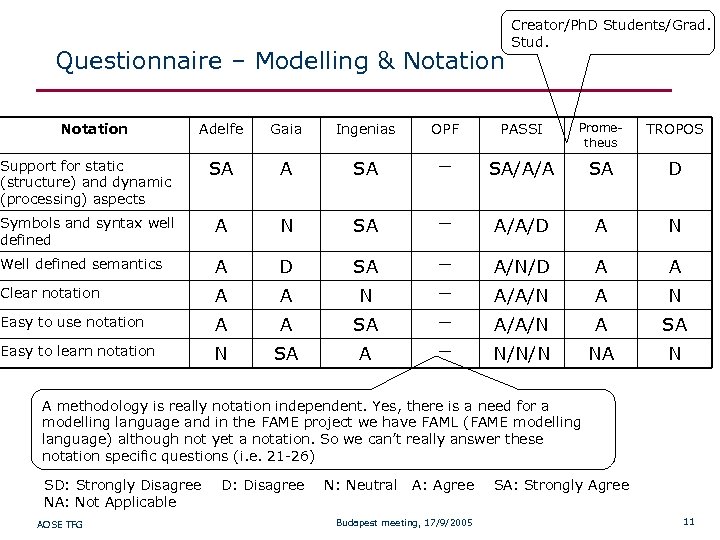
Questionnaire – Modelling & Notation Creator/Ph. D Students/Grad. Stud. Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus TROPOS Support for static (structure) and dynamic (processing) aspects SA A SA — SA/A/A SA D Symbols and syntax well defined A N SA — A/A/D A N Well defined semantics A D SA — A/N/D A A Clear notation A A N — A/A/N A N Easy to use notation A A SA — A/A/N A SA Easy to learn notation N SA A — N/N/N NA N A methodology is really notation independent. Yes, there is a need for a modelling language and in the FAME project we have FAML (FAME modelling language) although not yet a notation. So we can’t really answer these notation specific questions (i. e. 21 -26) SD: Strongly Disagree D: Disagree N: Neutral A: Agree SA: Strongly Agree NA: Not Applicable AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 11
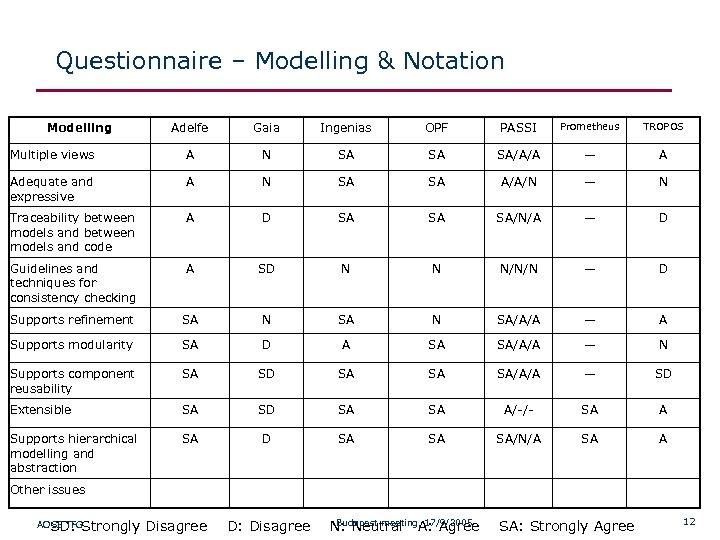
Questionnaire – Modelling & Notation Modelling Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus TROPOS Multiple views A N SA SA SA/A/A — A Adequate and expressive A N SA SA A/A/N — N Traceability between models and code A D SA SA SA/N/A — D Guidelines and techniques for consistency checking A SD N N N/N/N — D Supports refinement SA N SA/A/A — A Supports modularity SA D A SA SA/A/A — N Supports component reusability SA SD SA SA SA/A/A — SD Extensible SA SD SA SA A/-/- SA A Supports hierarchical modelling and abstraction SA D SA SA SA/N/A SA A Other issues Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 AOSE TFG SD: Strongly Disagree D: Disagree N: Neutral A: Agree SA: Strongly Agree 12
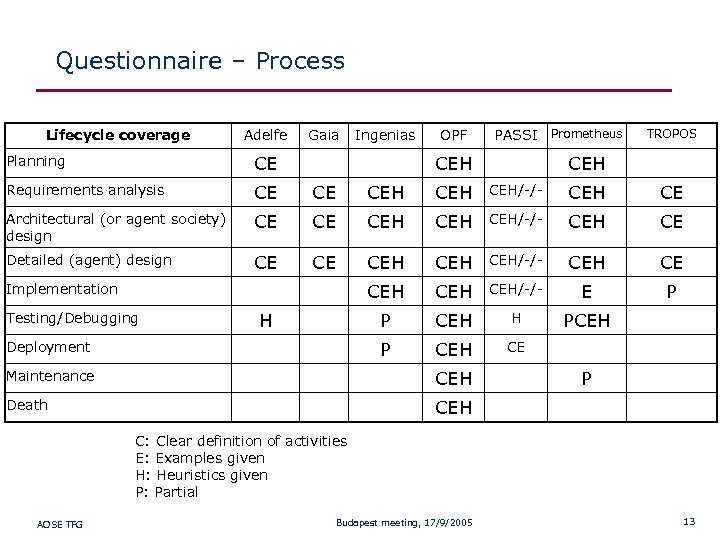
Questionnaire – Process Lifecycle coverage Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus CEH TROPOS Planning CE Requirements analysis CE CE CEH CEH/-/- CEH CE Architectural (or agent society) design CE CE CEH CEH/-/- CEH CE Detailed (agent) design CE CE CEH CEH/-/- CEH CEH CEH/-/- E P P CEH H PCEH P CEH CE Implementation Testing/Debugging H Deployment Maintenance CEH Death CEH P CEH C: Clear definition of activities E: Examples given H: Heuristics given P: Partial AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 13
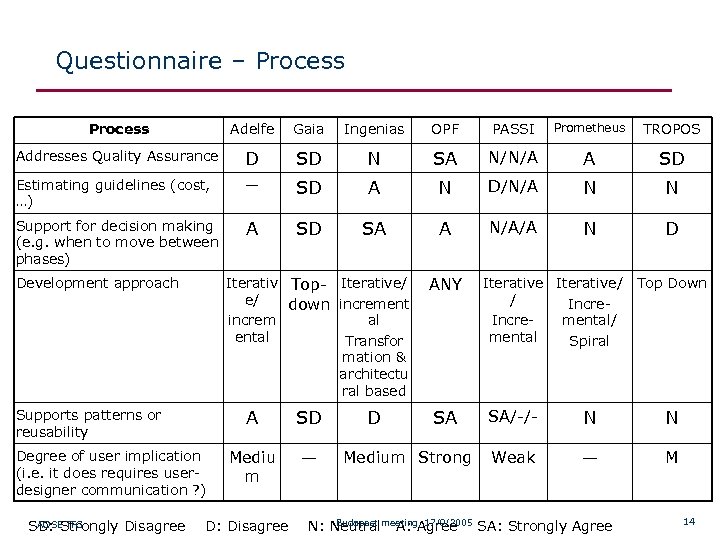
Questionnaire – Process Adelfe Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus TROPOS Addresses Quality Assurance D SD N SA N/N/A A SD Estimating guidelines (cost, …) — SD A N D/N/A N N Support for decision making (e. g. when to move between phases) A SD SA A N/A/A N D Development approach Supports patterns or reusability Degree of user implication (i. e. it does requires userdesigner communication ? ) Iterativ Top- Iterative/ e/ down increment increm al ental Transfor mation & architectu ral based A SD Mediu m — D ANY SA Medium Strong Iterative/ Top Down / Incremental/ mental Spiral SA/-/- N N Weak — M Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 AOSE TFG SD: Strongly Disagree D: Disagree N: Neutral A: Agree SA: Strongly Agree 14
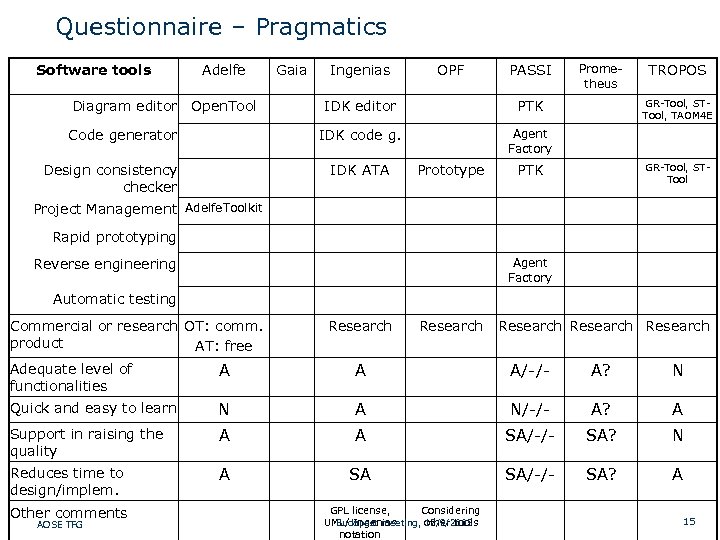
Questionnaire – Pragmatics Software tools Adelfe Diagram editor Open. Tool Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Design consistency checker PTK IDK code g. Code generator IDK editor Prome- theus TROPOS Agent Factory IDK ATA Prototype GR-Tool, STTool, TAOM 4 E PTK GR-Tool, STTool Project Management Adelfe. Toolkit Rapid prototyping Reverse engineering Agent Factory Automatic testing Commercial or research OT: comm. product AT: free Research Research Adequate level of functionalities A A A/-/- A? N Quick and easy to learn N A N/-/- A? A Support in raising the quality A A SA/-/- SA? N Reduces time to design/implem. A SA SA/-/- SA? A GPL license, Considering Other comments Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 UML/ Ingenias other tools AOSE TFG SD: Strongly Disagree D: Disagree N: Neutral A: Agree SA: Strongly Agree notation 15
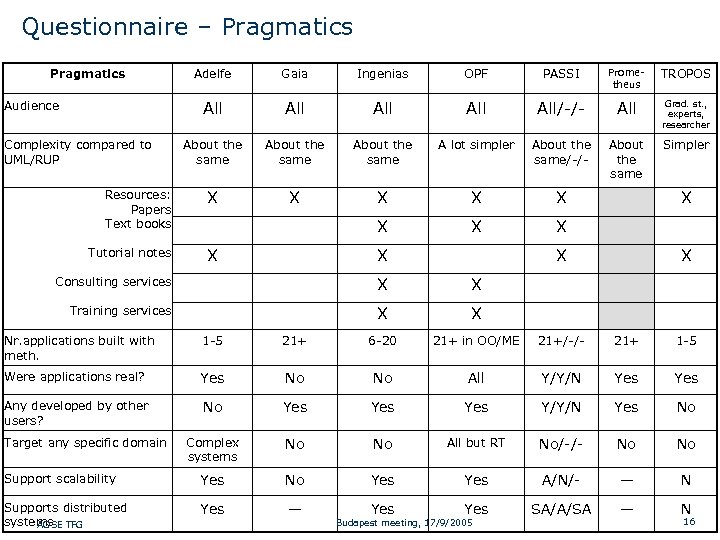
Questionnaire – Pragmatics Complexity compared to UML/RUP Gaia Ingenias OPF PASSI Prometheus TROPOS All Audience Adelfe All All/-/- All Grad. st. , experts, researcher About the same A lot simpler About the same/-/- About the same Simpler X X X Resources: X Papers Text books Tutorial notes X X X Consulting services X X Training services X X X Nr. applications built with meth. 1 -5 21+ 6 -20 21+ in OO/ME 21+/-/- 21+ 1 -5 Were applications real? Yes No No All Y/Y/N Yes Any developed by other users? No Yes Yes Y/Y/N Yes No Complex systems No No All but RT No/-/- No No Support scalability Yes No Yes A/N/- — N Supports distributed systems AOSE TFG Yes — Yes SA/A/SA — N Target any specific domain Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 16

Evaluation framework revisited n Taking the experience of this questionnaire n n Review evaluation framework criteria and their organization Review method for evaluation: questionnaire, case studies development, . . . • Refine questionnaire • Define case studies n Review metrics • How to avoid subjectivity AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 17
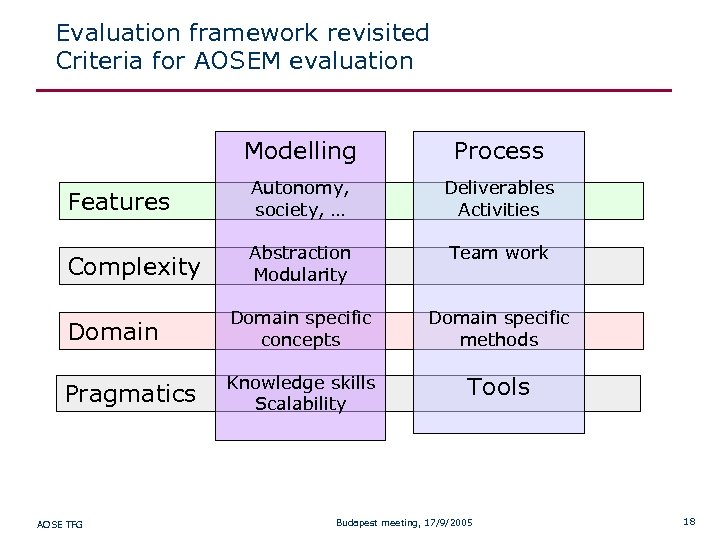
Evaluation framework revisited Criteria for AOSEM evaluation Modelling Process Features Autonomy, society, … Deliverables Activities Complexity Abstraction Modularity Team work Domain specific concepts Domain specific methods Pragmatics Knowledge skills Scalability Tools AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 18
Towards an AOSEM evaluation framework n The evaluation framework should allow: n n Criteria refinement and extensions Criteria metrics depending on the domain • E. g. agents in a web service or in robotics n Definition of standard case studies for evaluation • Evaluation of documentation and filling questionnaires is not enough n AOSE TFG … Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 19

Towards an AOSEM evaluation framework n The framework can be based on the definition and use of evaluation models n n Case studies for putting the methodologies to work Organized by criteria • For each criteria, define metrics • Criteria can be refined to get more insight or being more specific • For instance, agent behaviour, depending on whether BDI, neural network, CBR, reactive, or whatever model is used • New criteria can be added • Some criteria may be considered non applicable • Associate criteria to case studies AOSE TFG Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 20

Outline and plan for document on AOSEM evaluation framework n n n AOSE TFG Outline Participants Plan Budapest meeting, 17/9/2005 21
bd4eeb49bb8e952592b13a9af56d88e9.ppt