 Meteorology is the study and forecasting of weather changes resulting from large scale atmospheric circulation
Meteorology is the study and forecasting of weather changes resulting from large scale atmospheric circulation
 Introduction
Introduction
 Air Pollutant Cycle
Air Pollutant Cycle
 Transport
Transport
 Concentration & Dispersion
Concentration & Dispersion
 Prediction
Prediction
 Dispersion
Dispersion
 Atmosphere
Atmosphere
 Atmosphere
Atmosphere
 Atmosphere
Atmosphere
 Solar Radiation
Solar Radiation
 Insolation
Insolation
 Solar Incidence Angle
Solar Incidence Angle
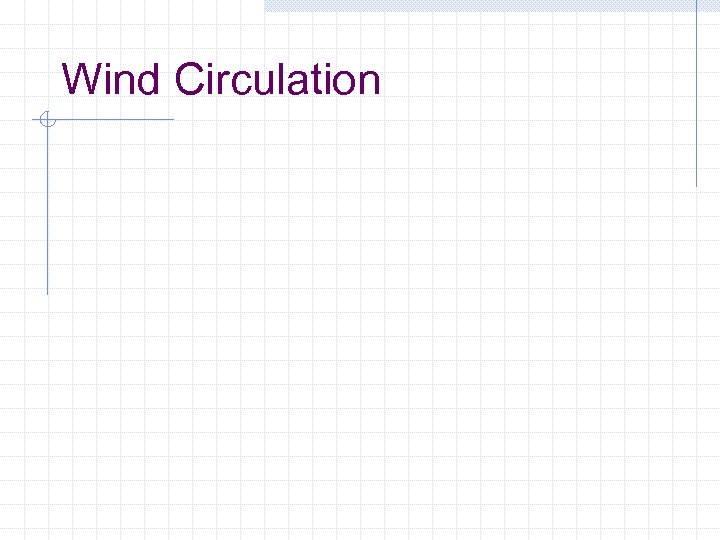 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
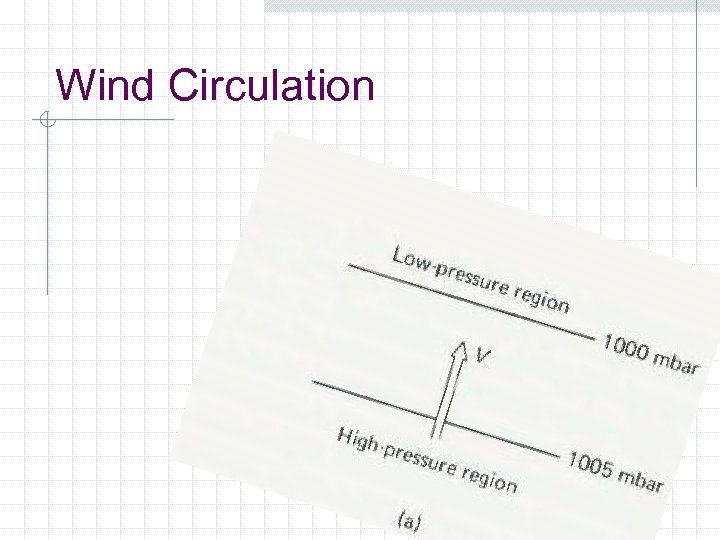 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
 Wind Circulation
Wind Circulation
 Rotation
Rotation
 Low-pressure system
Low-pressure system
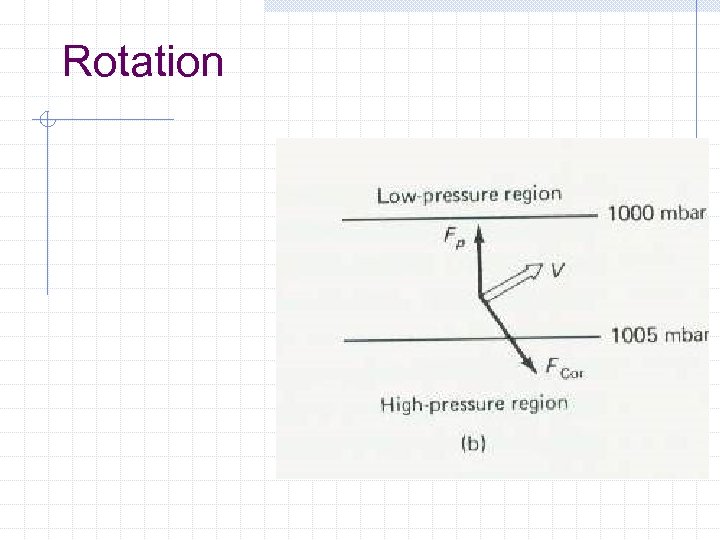 Rotation
Rotation
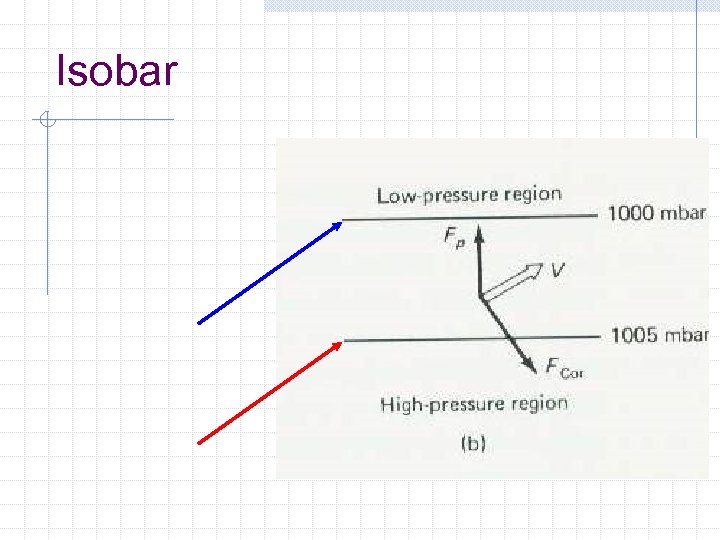 Isobar
Isobar
 Frictional Force
Frictional Force
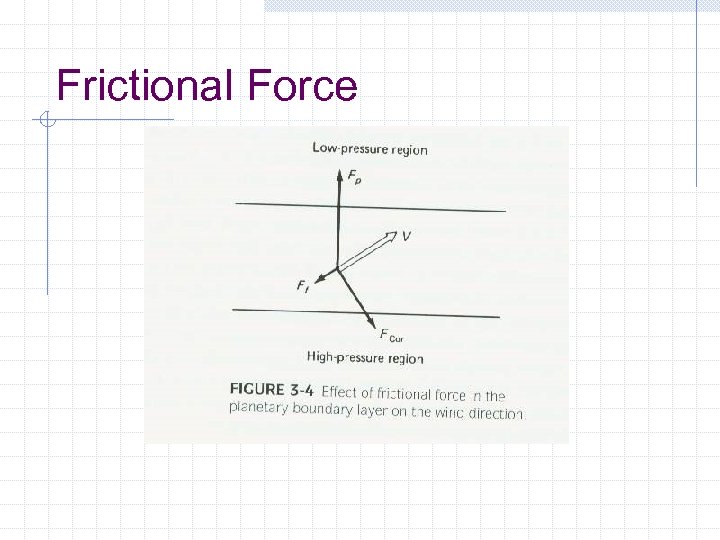 Frictional Force
Frictional Force
 Influence of Ground & Sea
Influence of Ground & Sea
 Influence of Ground & Sea
Influence of Ground & Sea
 Vertical Motion
Vertical Motion
 Properties of Gases
Properties of Gases
 Lapse Rate
Lapse Rate
 Adiabatic expansion
Adiabatic expansion
 Adiabatic expansion
Adiabatic expansion
 Adiabatic expansion
Adiabatic expansion
 Lapse rate
Lapse rate
 Lapse rate
Lapse rate
 International lapse rate
International lapse rate
 International Lapse Rate
International Lapse Rate
 Temperature change due to atmospheric height
Temperature change due to atmospheric height
 Atmospheric Stability
Atmospheric Stability
 Inversions
Inversions
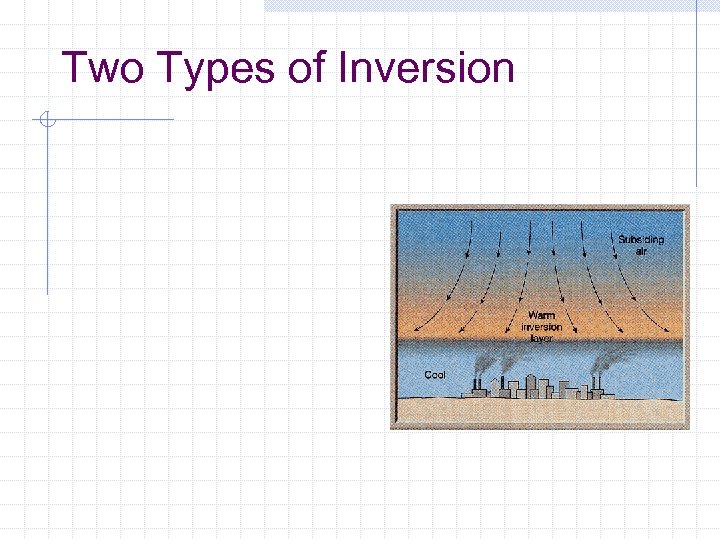 Two Types of Inversion
Two Types of Inversion
 Two more Types of Inversion
Two more Types of Inversion
 Stability Classes
Stability Classes
 Wind Velocity Profile
Wind Velocity Profile
 Wind Velocity Profile
Wind Velocity Profile
 Wind Velocity Profile
Wind Velocity Profile
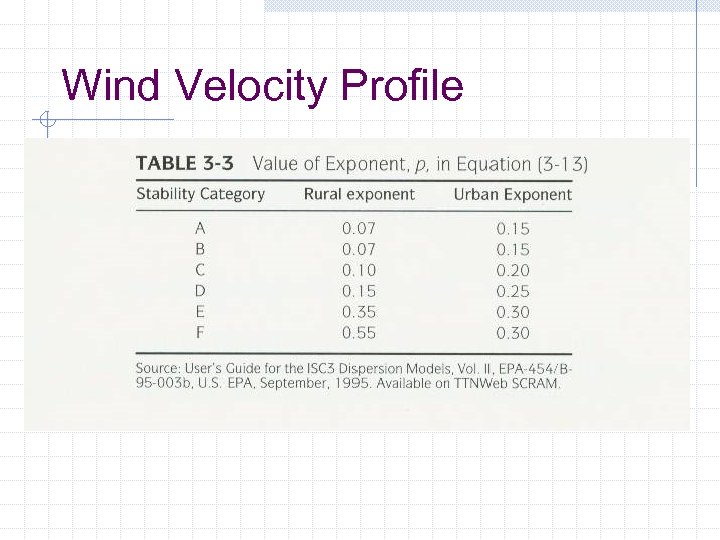 Wind Velocity Profile
Wind Velocity Profile
 Wind Direction
Wind Direction
 Predicting Wind Direction
Predicting Wind Direction
 Mixing Height
Mixing Height
 Mixing Height
Mixing Height
 Mixing Height
Mixing Height
 Mechanics of Mixing Height Parcel heated by solar radiation at earth’s surface Rises until temperature T’ = T T’ = particle’s temp T = atmospheric temp Achieves neutral equilibrium, no tendency for further upward motion
Mechanics of Mixing Height Parcel heated by solar radiation at earth’s surface Rises until temperature T’ = T T’ = particle’s temp T = atmospheric temp Achieves neutral equilibrium, no tendency for further upward motion
 Turbulence
Turbulence
 General Characteristics of Stack Plumes
General Characteristics of Stack Plumes
 Six Classes of Plume Behavior
Six Classes of Plume Behavior
 Six Classes of Plume Behavior
Six Classes of Plume Behavior
 Six Classes of Plume Behavior
Six Classes of Plume Behavior
 Six Classes of Plume Behavior
Six Classes of Plume Behavior
 Six Classes of Plume Behavior
Six Classes of Plume Behavior
 Assignment 3
Assignment 3