db400c560b4ae4afe7632081d8e79a09.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 98

Meta. Frame XP Presented by Rick Dehlinger Senior Systems Engineer Citrix Systems, Inc.

What are we going to cover today? Intro to Meta. Frame XP n What is Meta. Frame XP? n What’s new in Meta. Frame XP? n How is Meta. Frame XP Packaged? New Terms and Architectural Concepts Meta. Frame XP Features (technically speaking) Intro to Management Tools in Meta. Frame XP Time permitting: n Migrating to Meta. Frame XP n Useful XP Command Line Utilities

How do I stay on top of stuff like this? Participate in the Citrix. NW Yahoo! group n n n Self maintaining ‘newsletter’ style list Used to communicate pertinent technical/training info to Citrix users/integrators in Northwest Sign up at http: //groups. yahoo. com/group/citrixnw Participate in Multi events and Web Conferences n n Web Conferences every Thursday See http: //groups. yahoo. com/calendar/citrixnw for schedule and participation instructions Don’t worry about writing EVERYTHING down today n Download this presentation from http: //groups. yahoo. com/files/citrixnw “RD Face to Face Version x. zip”

Intro Meta. Frame XP
What is Meta. Frame XP? § The next generation of Citrix’s application deployment PLATFORM. § The product of a ground up reassessment by our engineers coupled with your input on what enterprise class server based computing should be. § Built to eliminate current and future obstacles to speed, performance and control while maintaining backward compatibility for ease of migration. § Everything you have seen in 1. 8/FR 1 and MORE.

What’s new in Meta. Frame XP? § Citrix Management Console § Application-based load management § § System monitoring and analysis § § ‘Resource Manager’ in XPe Application packaging and delivery § § ‘Load Management’ in XPa and XPe ‘Installation Manager’ in XPe Network management § ‘Network Manager’ in XPe § Printer management § Shadowing enhancements § Client time zone support § Enhanced scalability
What’s new in Meta. Frame XP? § Reduced IT administration § Reduced network traffic § Centralized license management § Enterprise-wide license pooling § Enhanced license availability § Active directory support § NFuse ready (turnkey NFuse) § ICA client extensibility § Meta. Frame and Win. Frame interoperability § ‘Mixed’ or ‘Interoperability’ mode

How is it Packaged? Meta. Frame XPs Meta. Frame XPa XPs plus: n Load Management Meta. Frame XPs plus: n n Load Management Resource Management Installation Management Network Management Licensed per Connection! n Deploy as many servers as you need…

New Terms and Architectural Concepts

New Terms § IMA: Independent Management Architecture § Data Store: Central configuration database § LHC: Local Host Cache. Persistent data cache that exists on each server. § Data Collector: Manages dynamic data and client enumeration/resolution (replaces ICA Master Browser). § Zone: Deliberate grouping of XP servers, each with it’s own Data Collector. § CMC: Citrix Management Console (replaces MF 1. 8 administration tools).
What is IMA? Why is it important? IMA… § § § Is a TCP based, event driven messaging bus, used by Meta. Frame servers and management tools communication. Is a modular and easily extensible subsystem capable of supporting current and future Meta. Frame products and tools. Overcomes the scalability constraints of the Meta. Frame 1. 8 Platform, allowing us to scale environments to new levels. Allows us to administer any farm from a central tool (CMC) that doesn’t have to run on a Meta. Frame server. Will allow Citrix to add functionality to the Platform independent of the base server.
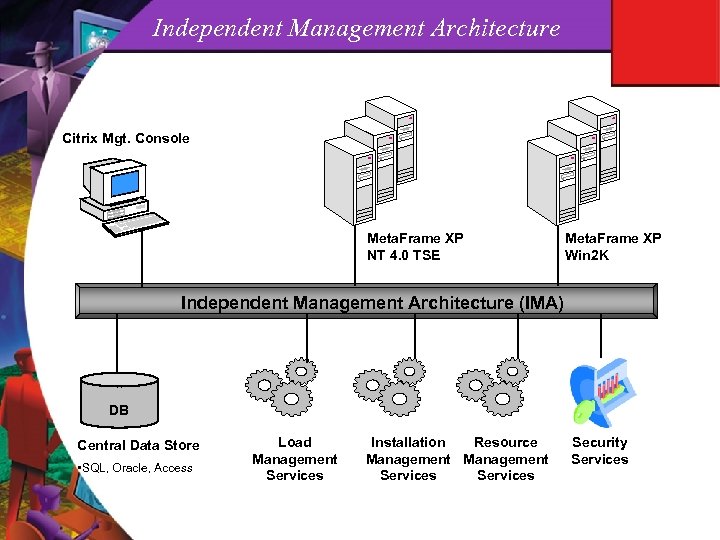
Independent Management Architecture Citrix Mgt. Console Meta. Frame XP NT 4. 0 TSE Meta. Frame XP Win 2 K Independent Management Architecture (IMA) DB Central Data Store • SQL, Oracle, Access Load Management Services Installation Resource Management Services Security Services
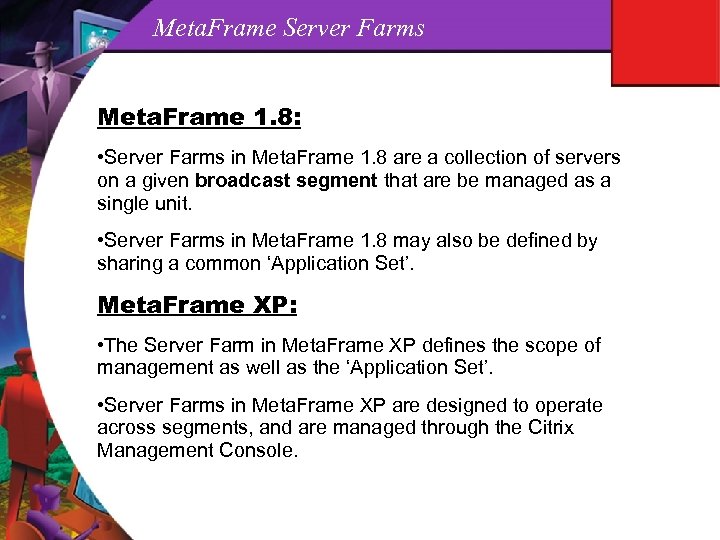
Meta. Frame Server Farms Meta. Frame 1. 8: • Server Farms in Meta. Frame 1. 8 are a collection of servers on a given broadcast segment that are be managed as a single unit. • Server Farms in Meta. Frame 1. 8 may also be defined by sharing a common ‘Application Set’. Meta. Frame XP: • The Server Farm in Meta. Frame XP defines the scope of management as well as the ‘Application Set’. • Server Farms in Meta. Frame XP are designed to operate across segments, and are managed through the Citrix Management Console.
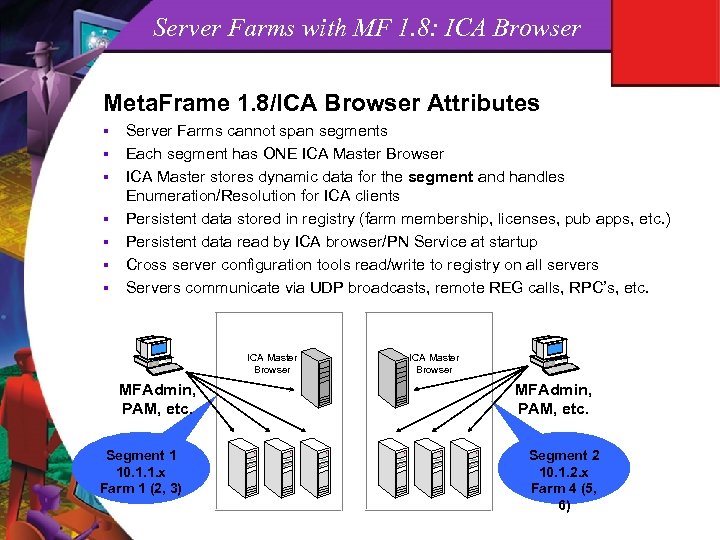
Server Farms with MF 1. 8: ICA Browser Meta. Frame 1. 8/ICA Browser Attributes § § § § Server Farms cannot span segments Each segment has ONE ICA Master Browser ICA Master stores dynamic data for the segment and handles Enumeration/Resolution for ICA clients Persistent data stored in registry (farm membership, licenses, pub apps, etc. ) Persistent data read by ICA browser/PN Service at startup Cross server configuration tools read/write to registry on all servers Servers communicate via UDP broadcasts, remote REG calls, RPC’s, etc. ICA Master Browser MFAdmin, PAM, etc. Segment 1 10. 1. 1. x Farm 1 (2, 3) ICA Master Browser MFAdmin, PAM, etc. Segment 2 10. 1. 2. x Farm 4 (5, 6)
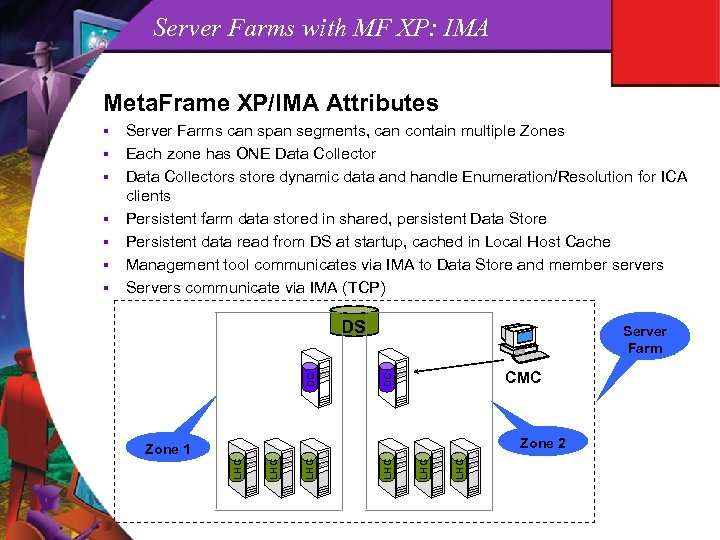
Server Farms with MF XP: IMA Meta. Frame XP/IMA Attributes DS Server Farm CMC Zone 2 LHC Zone 1 LHC § DC § LHC § Server Farms can span segments, can contain multiple Zones Each zone has ONE Data Collectors store dynamic data and handle Enumeration/Resolution for ICA clients Persistent farm data stored in shared, persistent Data Store Persistent data read from DS at startup, cached in Local Host Cache Management tool communicates via IMA to Data Store and member servers Servers communicate via IMA (TCP) LHC §
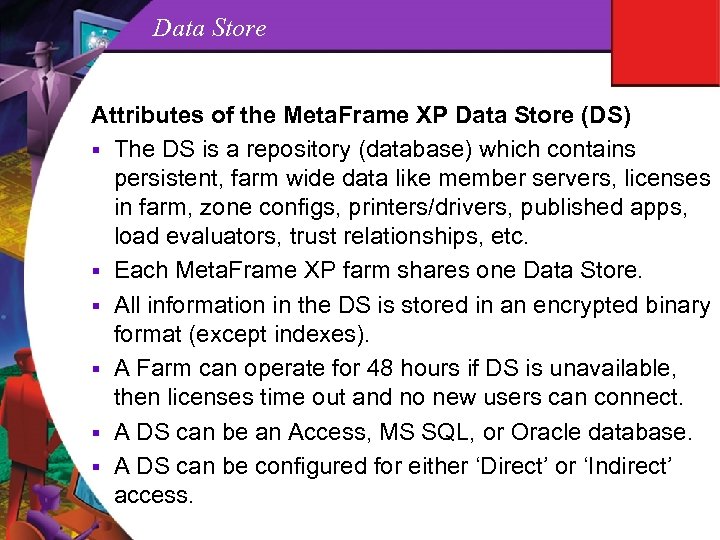
Data Store Attributes of the Meta. Frame XP Data Store (DS) § The DS is a repository (database) which contains persistent, farm wide data like member servers, licenses in farm, zone configs, printers/drivers, published apps, load evaluators, trust relationships, etc. § Each Meta. Frame XP farm shares one Data Store. § All information in the DS is stored in an encrypted binary format (except indexes). § A Farm can operate for 48 hours if DS is unavailable, then licenses time out and no new users can connect. § A DS can be an Access, MS SQL, or Oracle database. § A DS can be configured for either ‘Direct’ or ‘Indirect’ access.
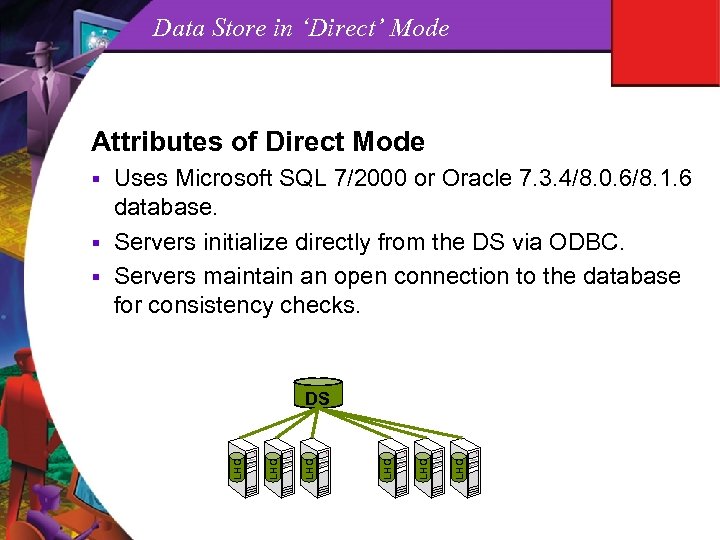
Data Store in ‘Direct’ Mode Attributes of Direct Mode Uses Microsoft SQL 7/2000 or Oracle 7. 3. 4/8. 0. 6/8. 1. 6 database. § Servers initialize directly from the DS via ODBC. § Servers maintain an open connection to the database for consistency checks. § LHC LHC LHC DS
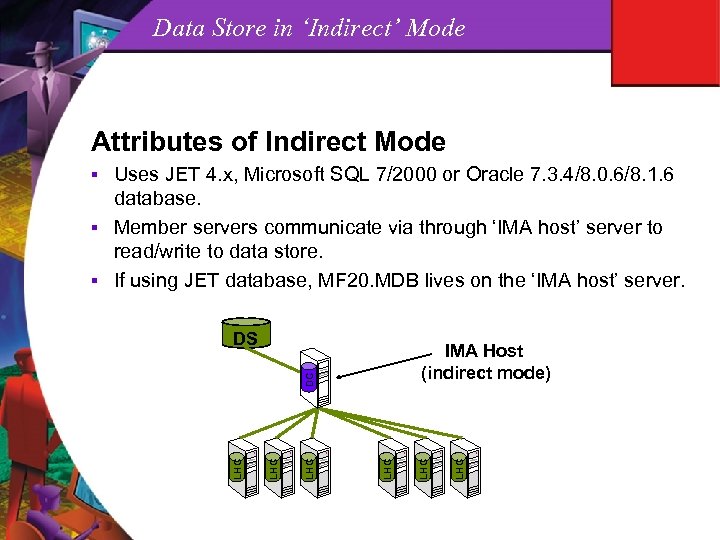
Data Store in ‘Indirect’ Mode Attributes of Indirect Mode Uses JET 4. x, Microsoft SQL 7/2000 or Oracle 7. 3. 4/8. 0. 6/8. 1. 6 database. § Member servers communicate via through ‘IMA host’ server to read/write to data store. § If using JET database, MF 20. MDB lives on the ‘IMA host’ server. § DS LHC LHC LHC DC IMA Host (indirect mode)
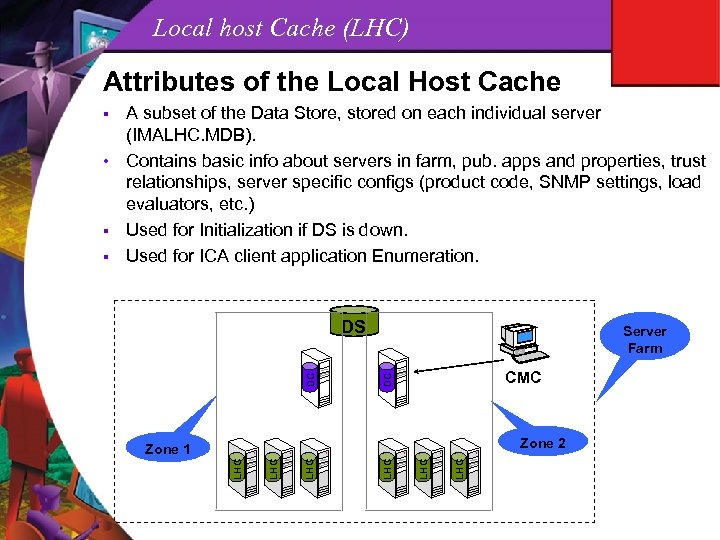
Local host Cache (LHC) Attributes of the Local Host Cache A subset of the Data Store, stored on each individual server (IMALHC. MDB). • Contains basic info about servers in farm, pub. apps and properties, trust relationships, server specific configs (product code, SNMP settings, load evaluators, etc. ) § Used for Initialization if DS is down. § Used for ICA client application Enumeration. § Server Farm CMC DC DC DS Zone 2 LHC LHC LHC Zone 1
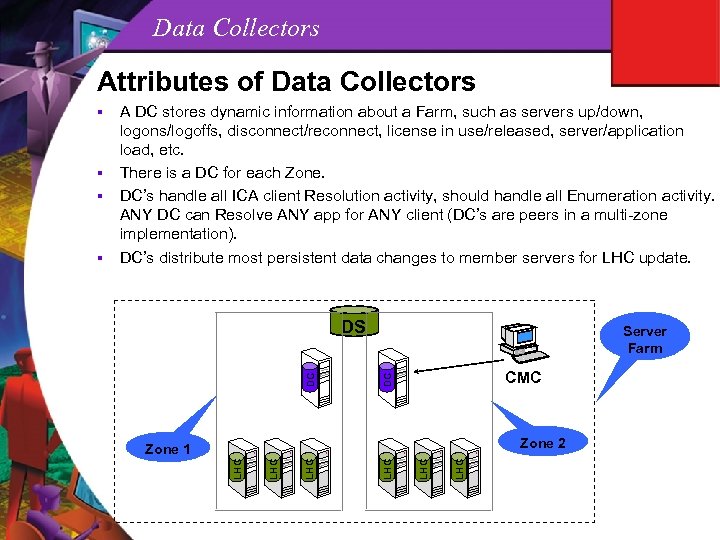
Data Collectors Attributes of Data Collectors DS Server Farm CMC DC DC Zone 2 LHC Zone 1 LHC § A DC stores dynamic information about a Farm, such as servers up/down, logons/logoffs, disconnect/reconnect, license in use/released, server/application load, etc. There is a DC for each Zone. DC’s handle all ICA client Resolution activity, should handle all Enumeration activity. ANY DC can Resolve ANY app for ANY client (DC’s are peers in a multi-zone implementation). DC’s distribute most persistent data changes to member servers for LHC update. LHC §
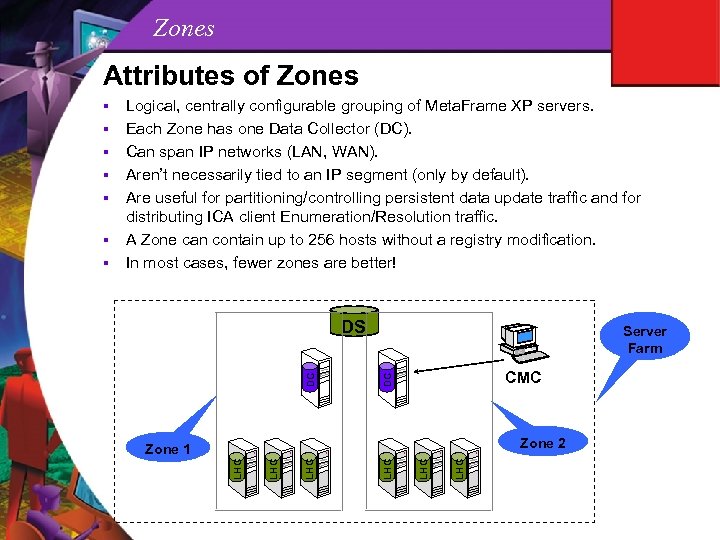
Zones Attributes of Zones DS Server Farm CMC Zone 2 LHC Zone 1 LHC § DC § LHC § Logical, centrally configurable grouping of Meta. Frame XP servers. Each Zone has one Data Collector (DC). Can span IP networks (LAN, WAN). Aren’t necessarily tied to an IP segment (only by default). Are useful for partitioning/controlling persistent data update traffic and for distributing ICA client Enumeration/Resolution traffic. A Zone can contain up to 256 hosts without a registry modification. In most cases, fewer zones are better! LHC §
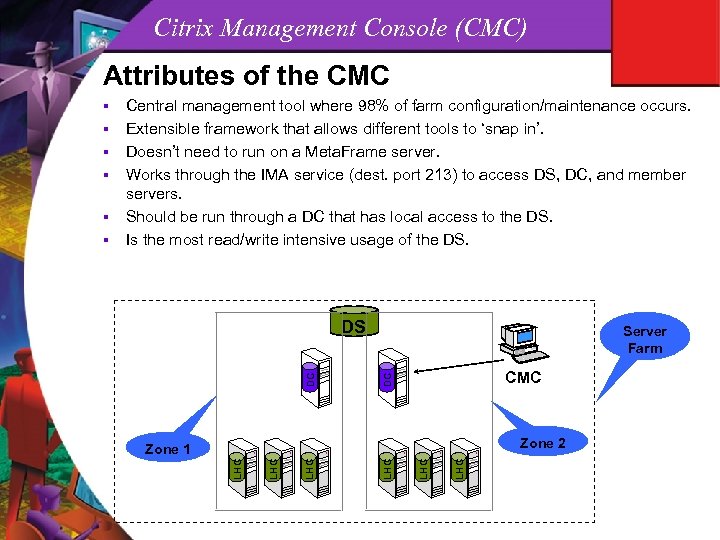
Citrix Management Console (CMC) Attributes of the CMC DS Server Farm CMC DC Zone 2 LHC Zone 1 LHC § DC § LHC § Central management tool where 98% of farm configuration/maintenance occurs. Extensible framework that allows different tools to ‘snap in’. Doesn’t need to run on a Meta. Frame server. Works through the IMA service (dest. port 213) to access DS, DC, and member servers. Should be run through a DC that has local access to the DS. Is the most read/write intensive usage of the DS. LHC §

Demonstration: CMC in Action

Understanding XP Communication ‘Layers’ (5 of them) § IMA (server to server) Communication • Persistent Data Events (1) • Dynamic Data Events (2) • Printer Management Events/Processes (3) § ICA Session (client to server) Communication • Client Enumeration/Resolution (4) • ICA Client to Server (5)
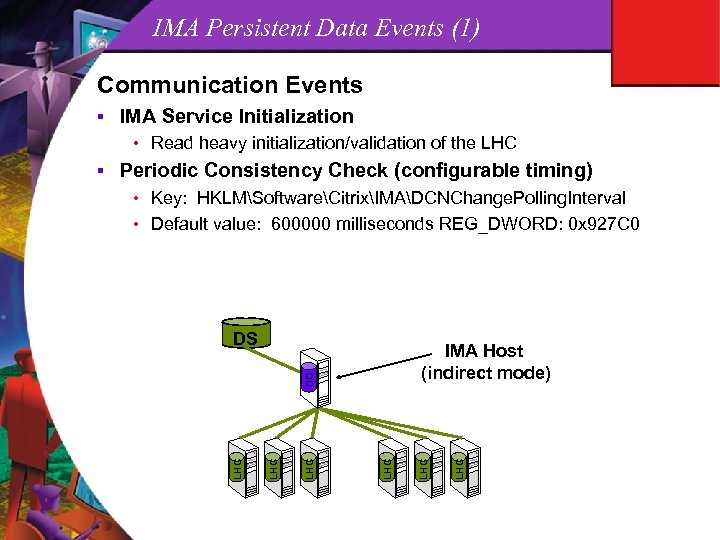
IMA Persistent Data Events (1) Communication Events § IMA Service Initialization • Read heavy initialization/validation of the LHC Periodic Consistency Check (configurable timing) • Key: HKLMSoftwareCitrixIMADCNChange. Polling. Interval • Default value: 600000 milliseconds REG_DWORD: 0 x 927 C 0 DS LHC LHC IMA Host (indirect mode) DC LHC LHC §
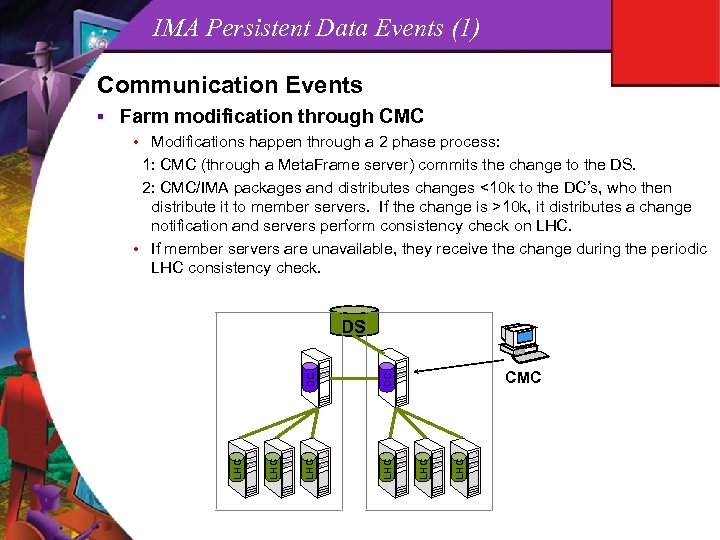
IMA Persistent Data Events (1) Communication Events Farm modification through CMC • Modifications happen through a 2 phase process: 1: CMC (through a Meta. Frame server) commits the change to the DS. 2: CMC/IMA packages and distributes changes <10 k to the DC’s, who then distribute it to member servers. If the change is >10 k, it distributes a change notification and servers perform consistency check on LHC. • If member servers are unavailable, they receive the change during the periodic LHC consistency check. LHC DC LHC CMC LHC DC LHC DS LHC §
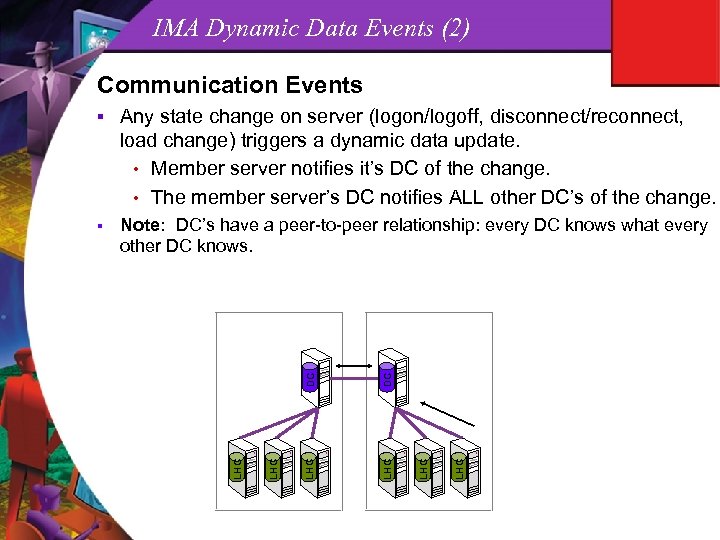
IMA Dynamic Data Events (2) Communication Events LHC LHC DC Note: DC’s have a peer-to-peer relationship: every DC knows what every other DC knows. LHC § DC Any state change on server (logon/logoff, disconnect/reconnect, load change) triggers a dynamic data update. • Member server notifies it’s DC of the change. • The member server’s DC notifies ALL other DC’s of the change. LHC §
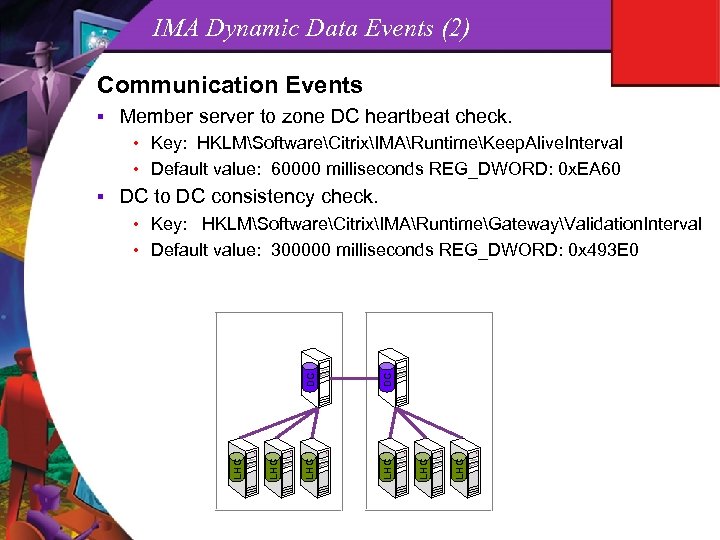
IMA Dynamic Data Events (2) Communication Events § Member server to zone DC heartbeat check. • Key: HKLMSoftwareCitrixIMARuntimeKeep. Alive. Interval • Default value: 60000 milliseconds REG_DWORD: 0 x. EA 60 DC to DC consistency check. • Key: HKLMSoftwareCitrixIMARuntimeGatewayValidation. Interval LHC DC LHC LHC • Default value: 300000 milliseconds REG_DWORD: 0 x 493 E 0 LHC §

IMA Printer Management Events (3) Communication Events Why is this slide blank? § Printer Management has a relatively substantial impact upon IMA traffic. §
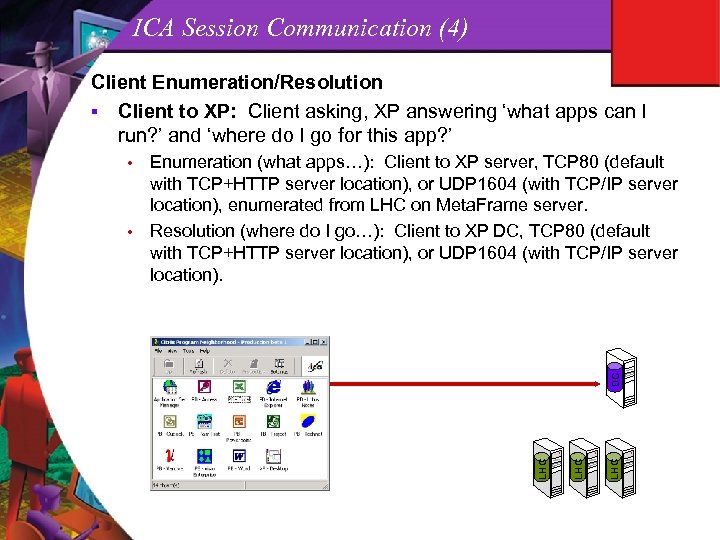
ICA Session Communication (4) Client Enumeration/Resolution § Client to XP: Client asking, XP answering ‘what apps can I run? ’ and ‘where do I go for this app? ’ Enumeration (what apps…): Client to XP server, TCP 80 (default with TCP+HTTP server location), or UDP 1604 (with TCP/IP server location), enumerated from LHC on Meta. Frame server. • Resolution (where do I go…): Client to XP DC, TCP 80 (default with TCP+HTTP server location), or UDP 1604 (with TCP/IP server location). LHC LHC DC •
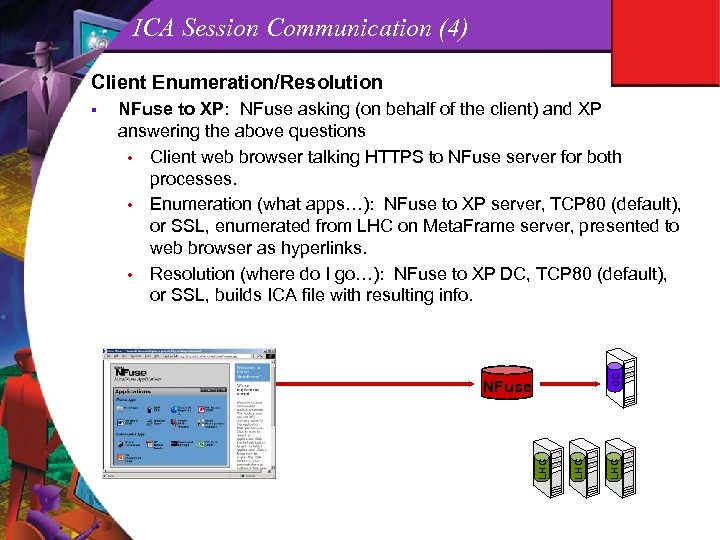
ICA Session Communication (4) Client Enumeration/Resolution LHC NFuse LHC DC NFuse to XP: NFuse asking (on behalf of the client) and XP answering the above questions • Client web browser talking HTTPS to NFuse server for both processes. • Enumeration (what apps…): NFuse to XP server, TCP 80 (default), or SSL, enumerated from LHC on Meta. Frame server, presented to web browser as hyperlinks. • Resolution (where do I go…): NFuse to XP DC, TCP 80 (default), or SSL, builds ICA file with resulting info. LHC §
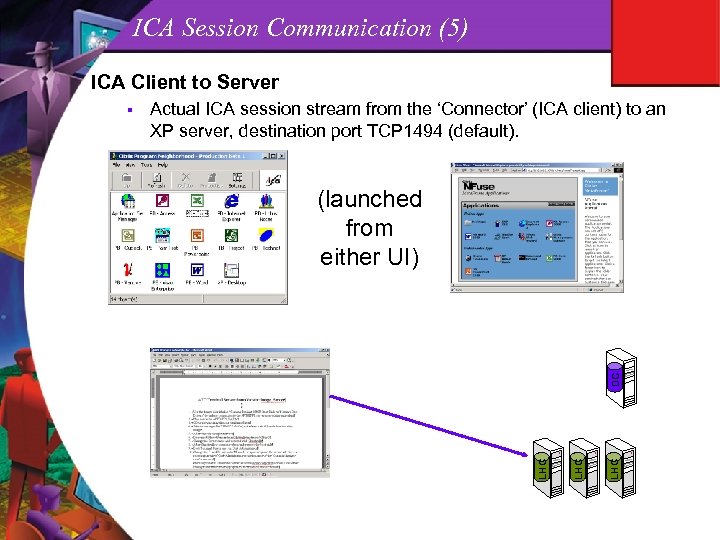
ICA Session Communication (5) ICA Client to Server Actual ICA session stream from the ‘Connector’ (ICA client) to an XP server, destination port TCP 1494 (default). LHC DC (launched from either UI) LHC §
Meta. Frame XP Features Revealed

Meta. Frame XP Management Centralized Administration Single Point Command Control n All administration, configuration, monitoring and control of the Citrix Server Farm is managed centrally Independent Management Architecture n IMA compliant servers and management products share a common and extensible management infrastructure Unified Management Console n The Citrix Management Console communicates across a single Management Scope of the server farm using the IMA protocol Central Data Store n Configuration information for the Server Farm is stored centrally in the Citrix Data Store.
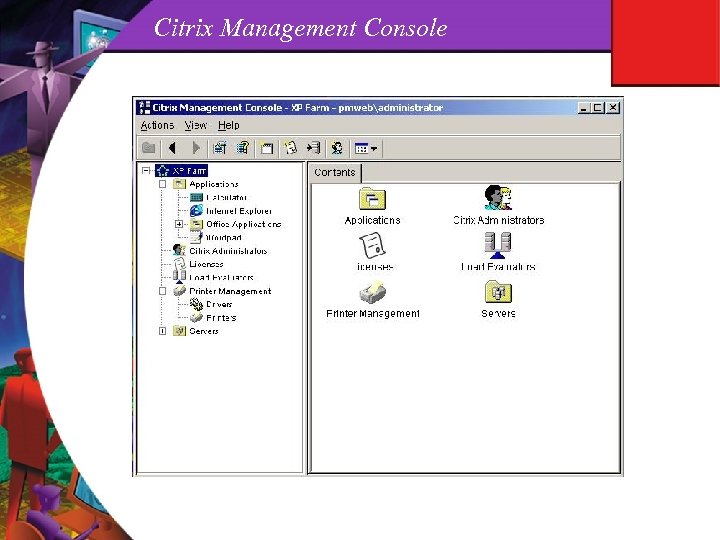
Citrix Management Console
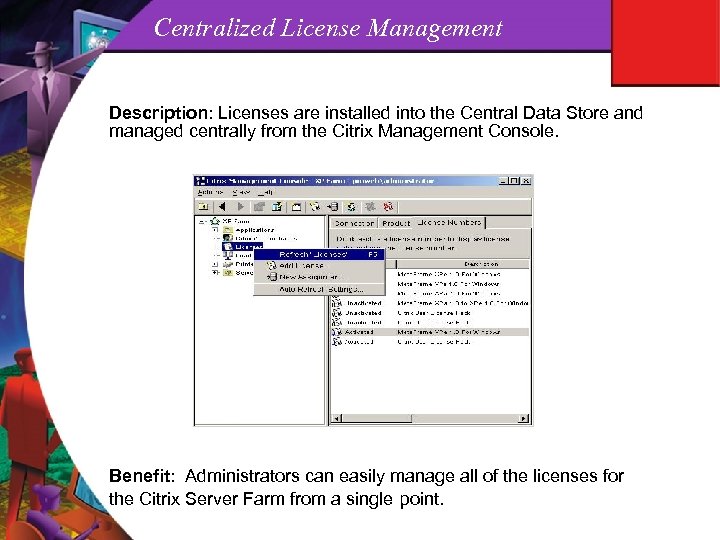
Centralized License Management Description: Licenses are installed into the Central Data Store and managed centrally from the Citrix Management Console. Benefit: Administrators can easily manage all of the licenses for the Citrix Server Farm from a single point.
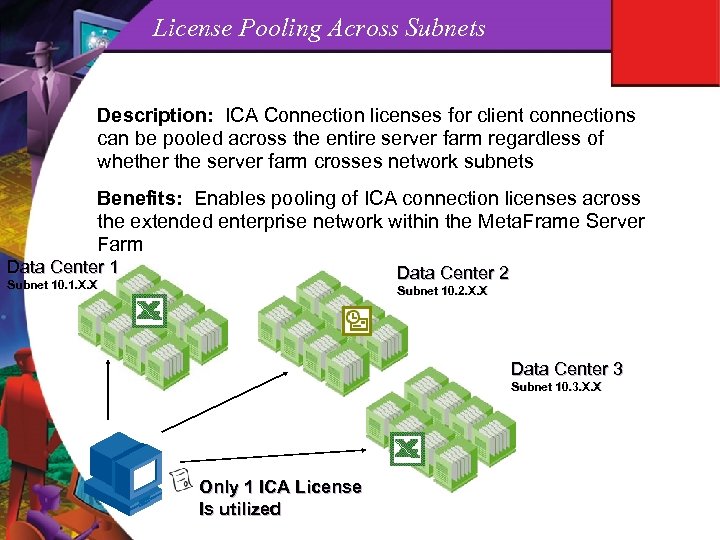
License Pooling Across Subnets Description: ICA Connection licenses for client connections can be pooled across the entire server farm regardless of whether the server farm crosses network subnets Benefits: Enables pooling of ICA connection licenses across the extended enterprise network within the Meta. Frame Server Farm Data Center 1 Data Center 2 Subnet 10. 1. X. X Subnet 10. 2. X. X Data Center 3 Subnet 10. 3. X. X Only 1 ICA License Is utilized
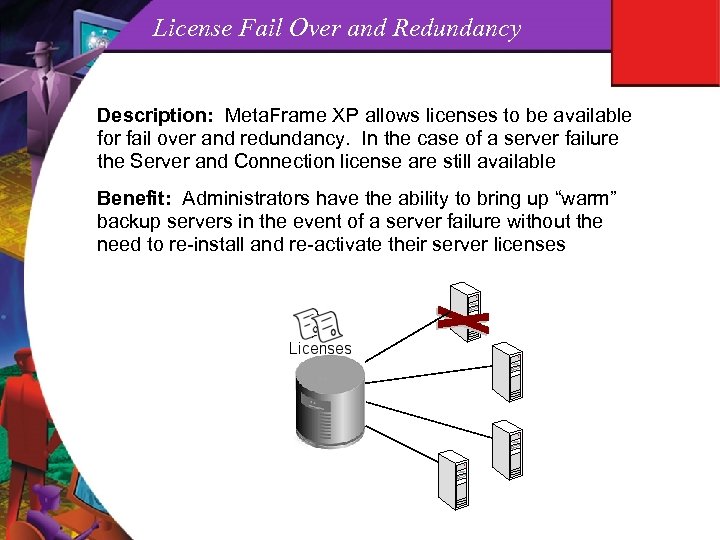
License Fail Over and Redundancy Description: Meta. Frame XP allows licenses to be available for fail over and redundancy. In the case of a server failure the Server and Connection license are still available Benefit: Administrators have the ability to bring up “warm” backup servers in the event of a server failure without the need to re-install and re-activate their server licenses
Meta. Frame XP License Management Centralized License Management Flexible Licensing for emerging business models n Increased flexibility to support Citrix Licensing Programs (Shrink Wrap, CLP, ELP, and i. License) Single Point of License Installation and Activation n License installation and activation can be done centrally via the Citrix Management Console Support for Multiple Server/Product Platforms n The new licensing system supports all types of Citrix licenses: Server, Connection, and Management Connection License Sharing across Platforms n Ability to share connection licenses across other IMA compliant server platforms in the future: Solaris, HP-UX, AIX

Meta. Frame XP Directory Integration Active Directory Integration Application Publishing n Enables application Publishing to users and Groups in Active Directory Account Authority Access n Utilizes Native Active Directory Interfaces to access the Active Directory User Principal Names n Allows users to logon to the Meta. Frame Server using User Principal Names: i. e. user@domain. com NFuse and Program Neighborhood n Enables users to utilize their Active Directory accounts to access Meta. Frame applications via NFuse and Program Neighborhood
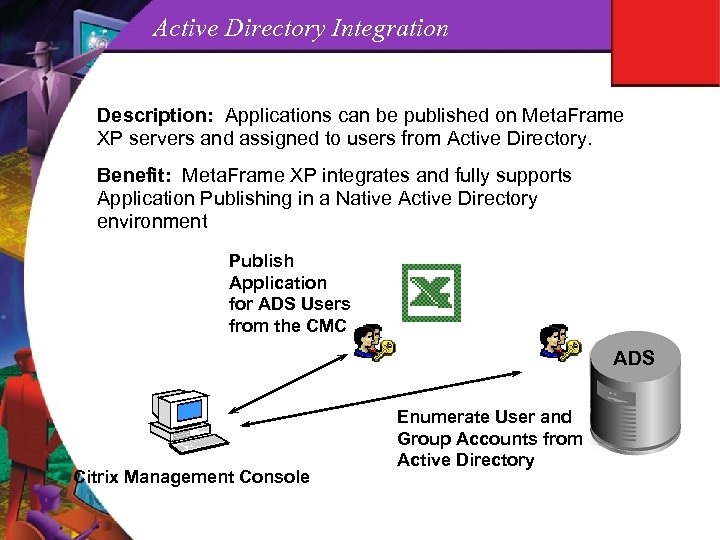
Active Directory Integration Description: Applications can be published on Meta. Frame XP servers and assigned to users from Active Directory. Benefit: Meta. Frame XP integrates and fully supports Application Publishing in a Native Active Directory environment Publish Application for ADS Users from the CMC ADS Citrix Management Console Enumerate User and Group Accounts from Active Directory
Meta. Frame XP Printer Management n Print Driver Replication n Printer Mapping n Network Printer Auto-Creation n Printer Compatibility n Printer Bandwidth Control n Terminal Printer Auto-Creation n Client Printer Creation Logging
Meta. Frame XP Printer Management Printer Mapping n Ability to create mappings for Windows 9 X Client Printers on the Meta. Frame Server and automatically distribute to the Server Farm Printer Bandwidth Control n Allows the administrator to specify the amount of bandwidth that can be used by printing over the client connection Terminal Printer Auto-Creation n Ability for the administrator to setup auto-creation of printers for ICA DOS and Win. CE Terminal Devices Client Printer Creation Logging n Logs all information about auto-creation of client printers, allowing the administrator to proactively detect printer issues and resolve them with the required information
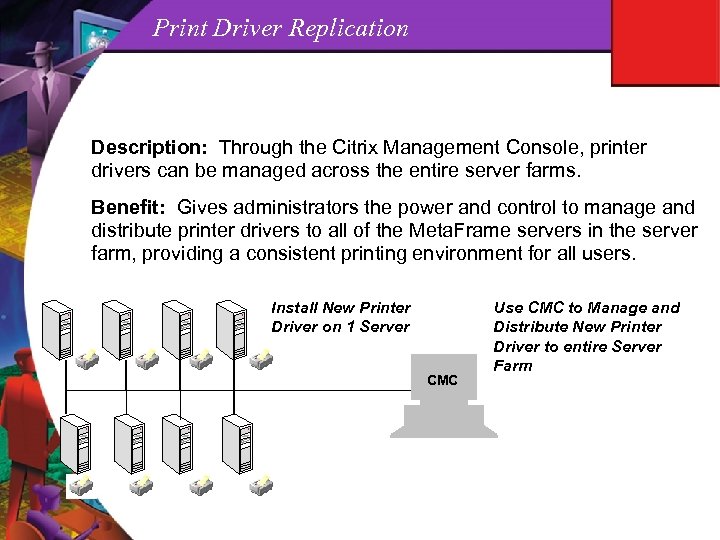
Print Driver Replication Description: Through the Citrix Management Console, printer drivers can be managed across the entire server farms. Benefit: Gives administrators the power and control to manage and distribute printer drivers to all of the Meta. Frame servers in the server farm, providing a consistent printing environment for all users. Install New Printer Driver on 1 Server CMC Use CMC to Manage and Distribute New Printer Driver to entire Server Farm
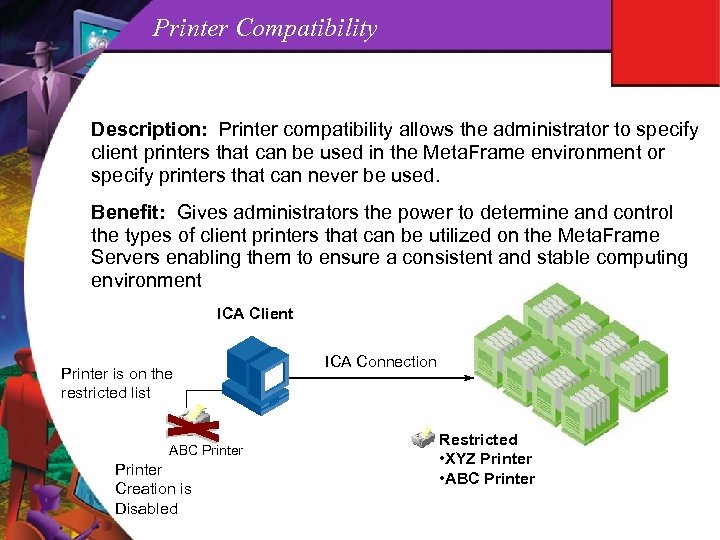
Printer Compatibility Description: Printer compatibility allows the administrator to specify client printers that can be used in the Meta. Frame environment or specify printers that can never be used. Benefit: Gives administrators the power to determine and control the types of client printers that can be utilized on the Meta. Frame Servers enabling them to ensure a consistent and stable computing environment ICA Client Printer is on the restricted list ABC Printer Creation is Disabled ICA Connection Restricted • XYZ Printer • ABC Printer

Print Management Recommendations Print drivers can only be replicated to the servers of the same OS as the source server. § Install drivers on the source server and select any available port on the server. § If installing for the sole purpose of replication there is no need to share the printers or set them as default. § Can be very CPU intensive on the source server so avoid replicating drivers while the source server has a heavy load. §
![Printer Queue Management § #Queue. Entries = [#Drivers] * [#Servers] • Every driver/server combination Printer Queue Management § #Queue. Entries = [#Drivers] * [#Servers] • Every driver/server combination](https://present5.com/presentation/db400c560b4ae4afe7632081d8e79a09/image-47.jpg)
Printer Queue Management § #Queue. Entries = [#Drivers] * [#Servers] • Every driver/server combination creates a queue item in the printer replication queue. • Should not exceed 1500 entries in length • Eg. 30 drivers to 50 servers § QPRINTER Utility • Not installed by default. • supportdebugi 386 • QPRINTER /REPLICA § Expected Performance • Handled by IMA Service at very low priority. • Depends on network traffic and server load.

New! XP Shadow Management Shadowing Installation Option: • Ability to select whether ICA Shadowing is available • Lock down the shadowing configuration to avoid changes • Allows administrators flexibility with privacy and security issues involving shadowing Shadow Indicator: • Notifies users that shadowing is in progress • Provides users with a “cancel” button to end the shadow Shadow Activity Logging: • logs all session and user information during a shadow • Enables the creation of a shadow “audit log”

ICA Client Enhancements Published Application Parameter Support n Enables the Meta. Frame server to accept published application parameters provided by a client, and the client to pass published application parameters to the server ICA Client Object Interface n A framework that exposes the functionality of the Citrix ICA Win 32 Client to other objects or Applications. Allows any application that supports embedding of objects, to interface with and pass instructions to the ICA Client Per Connection Timezone n Ability to run applications on the Meta. Frame server in the context of the users local time zone. The Meta. Frame Server can support different users running applications at different time zones on the same server
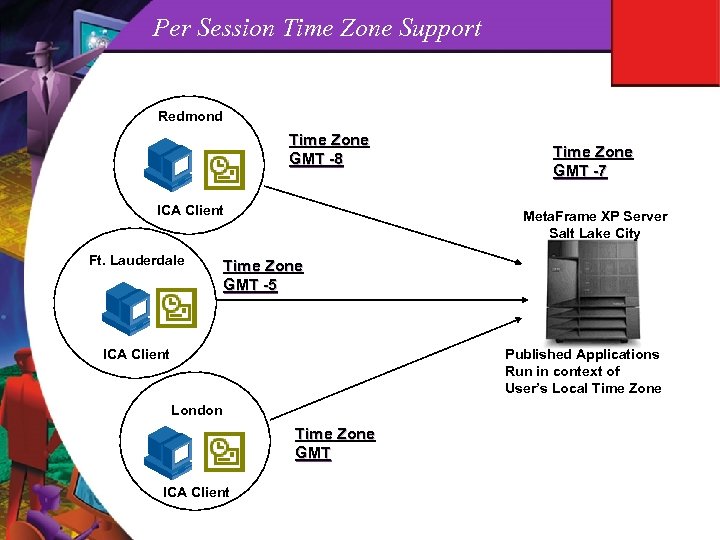
Per Session Time Zone Support Redmond Time Zone GMT -8 ICA Client Ft. Lauderdale Time Zone GMT -7 Meta. Frame XP Server Salt Lake City Time Zone GMT -5 ICA Client Published Applications Run in context of User’s Local Time Zone London Time Zone GMT ICA Client
NFuse Integration Introducing ‘Turnkey’ NFuse install option with XP install if IIS detected. § Sets up default web and startup page. § In short- you can now ACCIDENTLY deploy NFuse! §

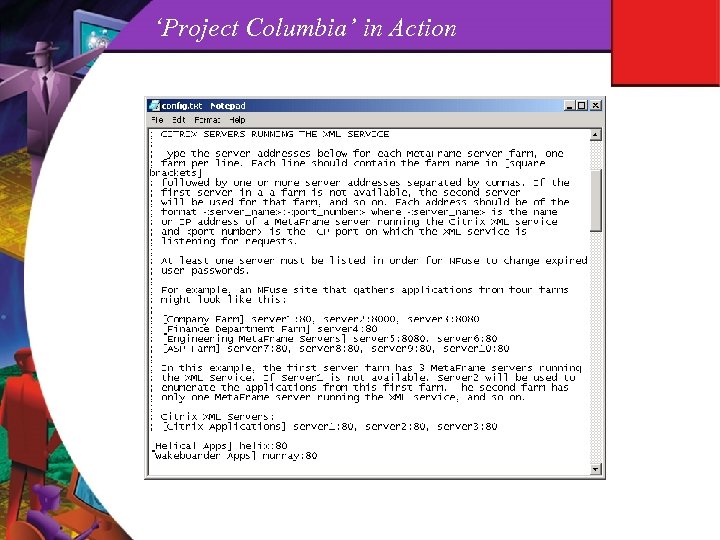
‘Project Columbia’ What is it? n Free, unsupported, NFuse template site n Drop in replacement for XP’s ‘turnkey’ NFuse n Easy feature configuration (config. txt) What does it do? n Tons! For starters… l Multi-farm support l Backup XML server support l Integrated password validation with change function l Detect/install ICA clients l Automatic delivery of win 32 t. cab ICA client

‘Project Columbia’ But wait, there’s more! ; -) n Throw in these functions too. l Display farm names with app sets l Modify application display options and column count l Automatically populate USERNAME/DOMAIN fields l Disable ‘Right Click/Save As’ on ICA file l Enable connectivity for Citrix Extranet clients l Return ALTADDR for external network users l Round robin load balancing of XML servers Current limitations n Win 32/Microsoft server focus n Un-supported

Demonstrations: ‘Turnkey’ NFuse and ‘Project Columbia’
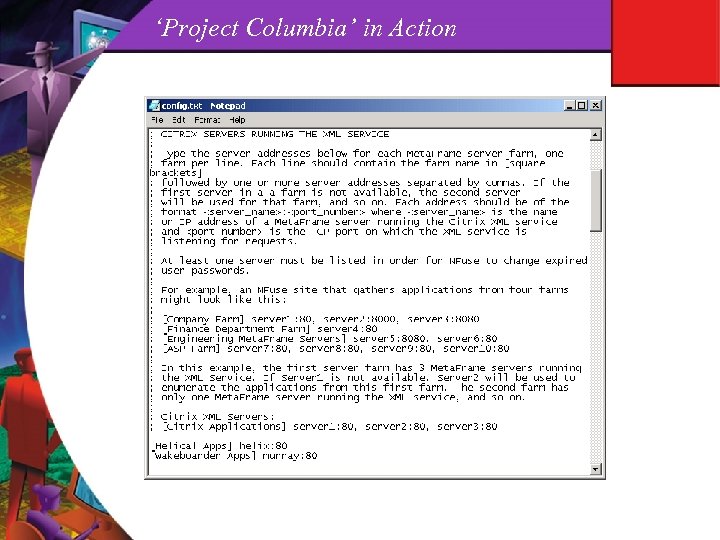
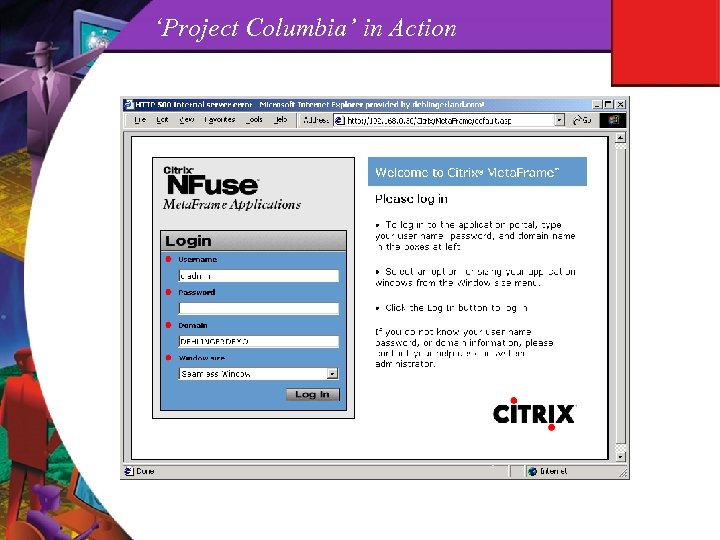
‘Project Columbia’ in Action
‘Project Columbia’ in Action
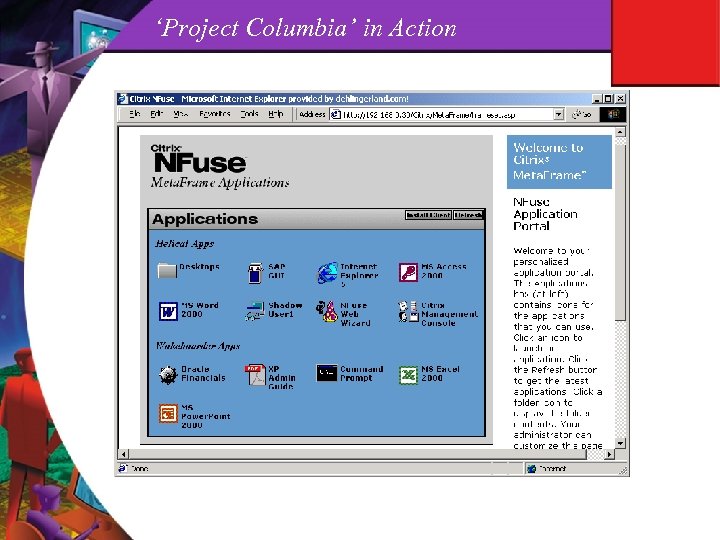
‘Project Columbia’ in Action

Management Tools in Meta. Frame XP

Load Management in XPa and XPe Citrix Load Management Provides: • • Configuration of Application Balancing Monitoring of Application and Server Load Dynamic adjustment of Load Balancing Criteria Citrix Load Management replaces ICA Load Balancing Services in Meta. Frame 1. 8 • Load Management utilizes IMA for communication • Provides the ability to create criteria for Servers and Applications

Load Management in XPa and XPe Major Components of Load Manager § Rules • Measure statistics for high or low loads on servers. • Lower a rule, reach a threshold more quickly • Elevate a rule, a threshold is hard to reach. § Load Evaluators • Used to configure server load measurements. • Use Default for Citrix provided load evaluators. • Use Advanced to create your own. • Can vary on each server. • Can use any combination of rule and load evaluators per server across the farm.

Load Management in XPa and XPe Load Management Criteria Application User Load CPU Utilization Disk Operations Memory Usage Page Swap IP Range New Context Switches Disk Data I/O License Threshold Page Fault Server User Load Scheduling New Administrators can now control accessibility to published applications on the basis of an IP range rule to specify sets of addresses and a scheduling rule to grant access to a specific application only during specified hours
New Criteria in Load Management IP Range: • Using the IP Range rule an administrator can specify a distinct address or set of addresses that can access the published application Scheduling: • The Scheduling criteria enables administrators to control the application load across server based on time sensitive criteria • Using the Scheduling criteria and administrator can create a Load Evaluator that allows access to a specific application or server only during specified times
Load Management in XPa and XPe Default Load Evaluators: Default: • Rule represents the number of users logged onto a Meta. Frame XP server • Contains one rule, Server User Load, that reports a full load when 100 users log on to the attached server Advanced: • The rules in this load evaluator represent server performance using ü Disk I/O ü CPU Utilization ü Disk Operation ü Memory Usage

Demonstration: Load Management

Resource Management in XPe Resource Manager • Ground up re-write! • Resource Management integrates with the Citrix Management Console • Resource Management adds tabs to the CMC • Can control summary data in the CMC** • Configure Alert recipients in the CMC • Adds counters to each server for monitoring, can manage several servers in the CMC • Monitors application usage by published applications • Watcher window requires the CMC to monitor servers

Installation Management in XPe Installation Manager • Nearly a ground up re-write! • Installation Management integrates with the CMC • Configure Network account to be used by the installer service to install packages • Can select to reboot servers post installation • Define how often to expire and remove installation management jobs • Define server groups and application packages • Status can be checked in Job properties
Network Management in XPe Network Manager • Network Management in XPe is an SNMP agent that runs on your citrix servers • It can be managed with any SNMP management service or utility • SNMP agent automatically installed with Meta. Frame XPe • Console plug-ins are available for: ü Tivoli Net. View (v. 5. 1. 2 and above) ü HP Open. View 6. 0 only • Plug-ins are located on a separate “Network Management for XPe” CD in the data pack

Migrating to Meta. Frame XP

Why Move to Meta. Frame XP? • Increased farm scalability and stability • Simplified license management and activation • Printer management • Enhanced NFuse integration • Active Directory User Principal Name support • Client time zone support • Less server to server network traffic • 1. 8 and Feature Release 1 enhancements integrated and available to more clients
Mixed Mode Is… Mixed mode is designed to facilitate migration to Meta. Frame Extended Platform with little or no end user disruption Provides support for: n Published app migration n App load balancing n Subnet license pooling n Existing NFuse, PN, and Custom ICA connections

Mixed Mode Is Not… Mixed mode is NOT designed to be a permanent solution Interoperability is achieved by emulating the services and communication mechanisms used by MF 1. 8
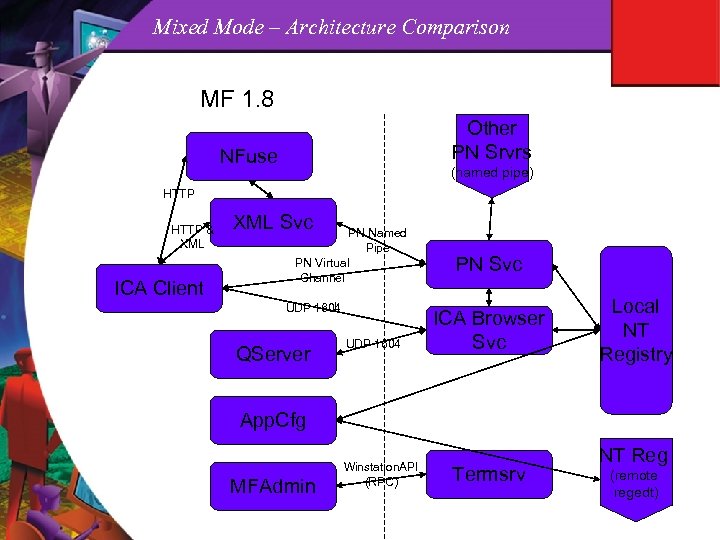
Mixed Mode – Architecture Comparison MF 1. 8 Other PN Srvrs NFuse (named pipe) HTTP & XML ICA Client XML Svc PN Named Pipe PN Virtual Channel UDP 1604 QServer UDP 1604 PN Svc ICA Browser Svc Local NT Registry App. Cfg MFAdmin Winstation. API (RPC) Termsrv NT Reg (remote regedt)
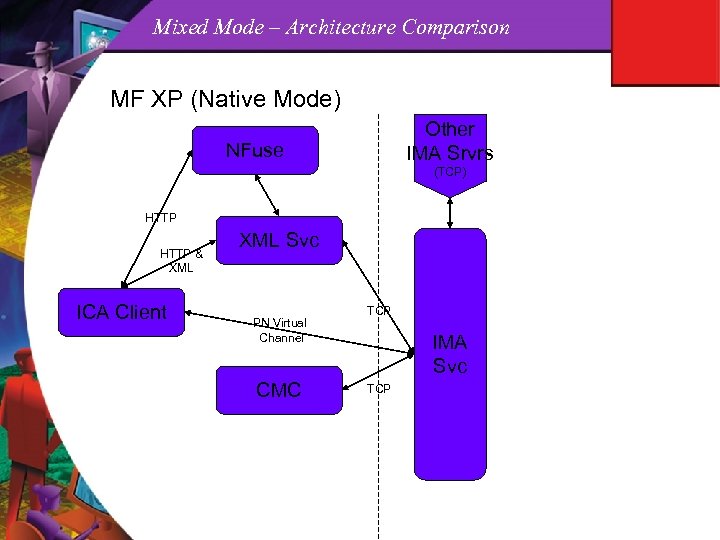
Mixed Mode – Architecture Comparison MF XP (Native Mode) Other IMA Srvrs NFuse (TCP) HTTP & XML ICA Client XML Svc PN Virtual Channel CMC TCP IMA Svc TCP
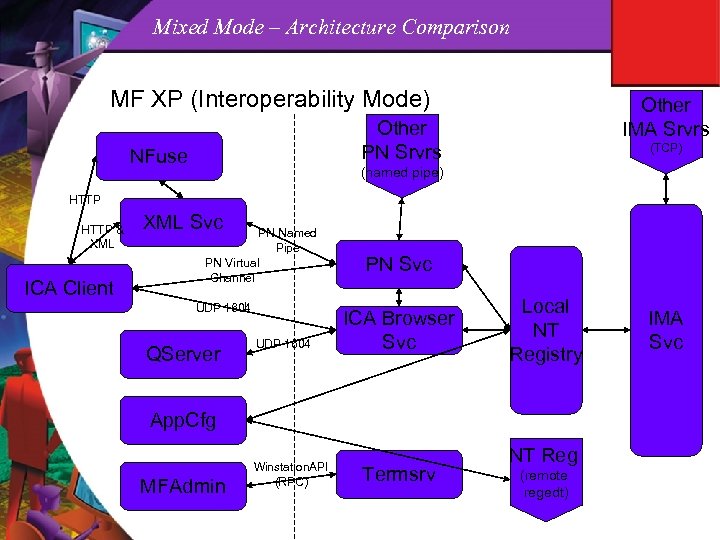
Mixed Mode – Architecture Comparison MF XP (Interoperability Mode) Other IMA Srvrs Other PN Srvrs NFuse (TCP) (named pipe) HTTP & XML ICA Client XML Svc PN Named Pipe PN Virtual Channel UDP 1604 QServer UDP 1604 PN Svc ICA Browser Svc Local NT Registry App. Cfg MFAdmin Winstation. API (RPC) Termsrv NT Reg (remote regedt) IMA Svc

Mixed Mode Until you get to native mode, you can’t take full advantage of: l Increased farm scalability and stability l Advanced printer management l UPN support l Simplified license management and activation n 1. 8 license gateways are not supported Meta. Frame connection licenses are equally distributed among subnets n CMC/Farm/Properties/Interoperability can change licenses assigned to each subnet. n

Mixed Mode (Cont. ) On first XP install, if 1. 8 is detected on the segment, it will offer to run in mixed mode l If yes, legacy tools are automatically installed Admins must use two sets of tools to manage a mixed farm l appcfg shipped on XP is same as 1. 8 sp 2. Older versions may not be able to manage apps published with newer versions. Apps may be published on 1. 8, then XP. Not the reverse

Migration Strategies

Migration Strategies – Flash Upgrade All servers are upgraded to Extended Platform during scheduled network maintenance window n n Consider this for highly centralized and/or cloned server environments Citrix now supports both unattended and cloned installs for all but the first server in an XP farm. See specific documentation in Admin Guide. Note: Repeated licenses will give an error upon migration to IMA Data Store.
Migration Strategies – Parallel XP servers built in native mode 1. 8 and XP servers do not communicate w/ each other Consider this for fast growing installs, new Win 2 K rollouts, or multi-site scenarios n n Requires additional hardware and licenses. Alternately, users may be manually migrated in proportion to servers. XP apps are published manually rather than migrated Publish 1. 8 and XP apps to distinct user groups to prevent redundant icons
Migration Strategies – Mixed Mode Rolling upgrade of existing Meta. Frame servers n Set during install of first server in the farm n XP and 1. 8 farm names must match n XP server will win ICA browser election l (except 1. 8 sp 1 MB hardcode) n Mixed mode applies to all XP servers in the farm n Starts PN and ICA browser services on XP servers. n Existing apps are migrated to IMA data store (1 time) l Any appcfg. changes made to 1. 8 apps after migration are not updated to the data store

Using NFuse to Bridge the Gap
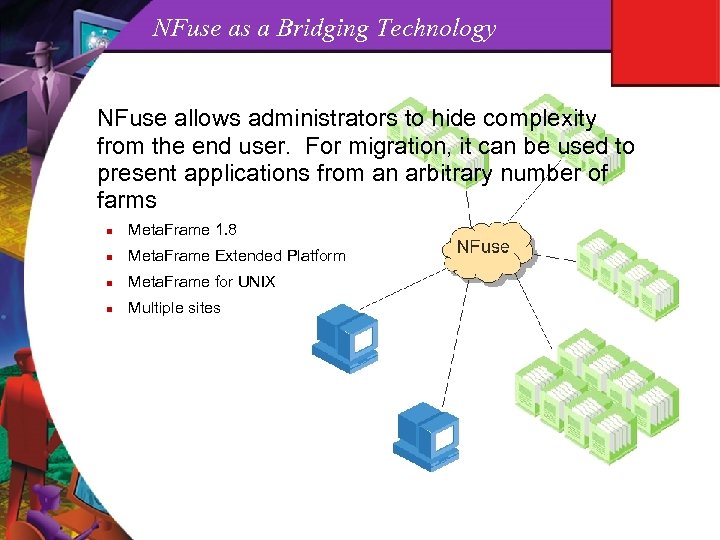
NFuse as a Bridging Technology NFuse allows administrators to hide complexity from the end user. For migration, it can be used to present applications from an arbitrary number of farms n Meta. Frame 1. 8 n Meta. Frame Extended Platform n Meta. Frame for UNIX n Multiple sites
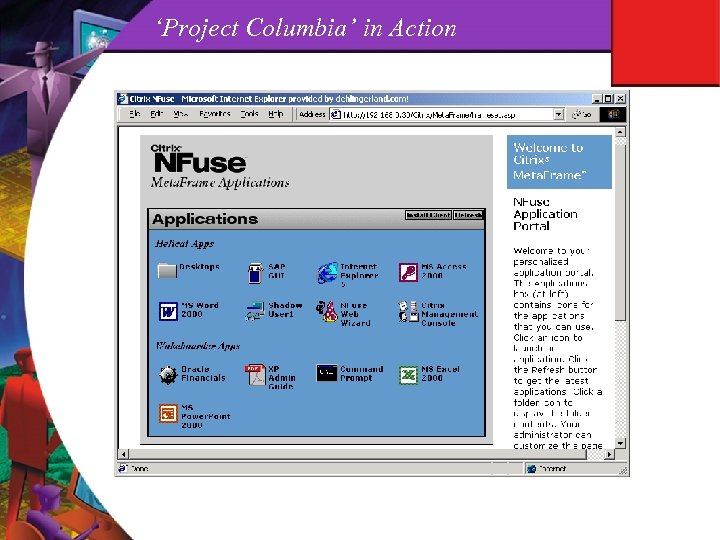
‘Project Columbia’ in Action
‘Project Columbia’ in Action
‘Project Columbia’ in Action

Migration Scenarios

Scenario 1: Single Site Single Farm Migration High level steps (‘rolling’ upgrade): 1. Create IMA Data. Store if necessary 2. Upgrade a server besides the ICA master browser § Install in interoperability mode when prompted § Apply upgrade licenses to XP farm 3. Upgrade remaining servers 4. Switch to XP native mode 5. Enable/disable UDP browsing as needed

Scenario 1: Single Site Single Farm Migration Tips: n n Avoid publishing new apps or changing app configuration while in XP interoperability mode. If necessary, create/modify apps in 1. 8 first then XP. Use NFuse and/or auto-client update to distribute new ICA clients.
Scenario 2: Multi-Farm Consolidation High level steps: n n Ensure IMA server to server communication (default TCP 2512) Upgrade first farm (including switch to native mode) or build new Enterprise XP farm (in native mode) Perform upgrades of other 1. 8 servers (one farm at a time) joining them to the ‘Master’ XP farm Some manual cleanup of duplicate app names may be necessary.
Scenario 2: Multi-Farm Consolidation Multi-Farm consolidation tips: n Key: managing user connectivity. l l n If possible, use an NFuse portal pointing to multiple farms. NFuse can play a HUGE role here! If using PN, add/change Application Set objects and server location/browser type. If usingle published app, may need to modify server location/browser type. If using ICA file(s), may need to modify server location/browser type. Use NFuse and/or auto-client update to distribute new clients.

Useful Command Line Utilities
Useful Command Line Utilities § QUERY FARM (QFARM, replaces QSERVER) • /APP Display app names and server load. • /DISC Display disconnected session data. • /LOAD Display server load. • /PROCESS Display active processes. • /ADDR Display address data on selected server. • /TCP, /IPX, /NETBIOS Display protocol data.

Useful Command Line Utilities § CLICENSE. EXE: Built in, useful for querying licensing information on the farm. • Add_and_activiate • Enumerate • In_use • Servers_using

Useful Command Line Utilities § QUERYHR. EXE: From Support directory on XP CD, useful for querying zone/DC info on the farm. • -z Show all the available zones • -h <zone name> Show all the hosts in a specified • • • zone -l Show the Local Host Record -n <host name> Show the specified Host Record given a host name -I <Host ID> Show the specified Host Record given a host ID -N Show the farm name -d <Host ID> Delete an IMA Host Entry
Useful Command Line Utilities QUERYDS. EXE: From Support directory on XP CD, useful in determining what servers are currently alive in a server farm. § Usage: § • Queryds /table: <tablename>[/query: <querystring>] § Table names: • Subscription. Table • Service. Table • PN_Table • Conn_Sessions • Disc_Sessions
Useful Command Line Utilities § QUERYDC. EXE: From Support directory on XP CD, useful for querying DC info and forcing ‘elections’. • -z <zone name> Show Data Collector name • -e Force Election • -a Show data collectors for all zones
Useful Command Line Utilities § QPRINTER. EXE: From Support directory on XP CD, useful for viewing printer replication queue and importing mapping files into the DS. • /REPLICA Display info about printer replication queue • /IMAPRMAPPING <file name> Import mapping file into DS.

Rick Dehlinger, SSE-NW rick. dehlinger@citrix. com
db400c560b4ae4afe7632081d8e79a09.ppt