1056b83bfcb68e6a1ae87e97fd42dc4a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Meta. Frame XP Interoperability with SQL 2000

Agenda IMA Overview (Review) Farm Data – IMA Service – Change Notification/Polling – SQL BasicsTroubleshooting – – – SQLDIAG Service Packs Monitoring MDAC/Component Checker SQL Profiler Best Practices Maintenance Plans – DB Options/Recovery models/Max Size/Autogrow – Tempdb – FR 3 Information – Q&A 2
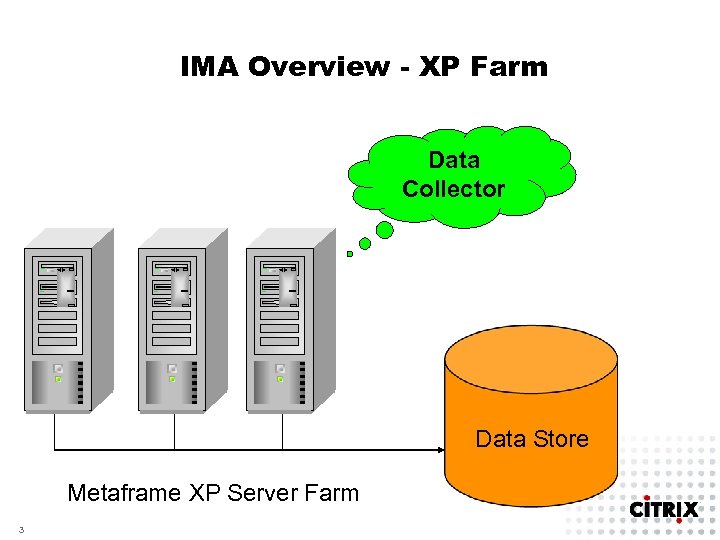
IMA Overview - XP Farm Data Collector Data Store Metaframe XP Server Farm 3
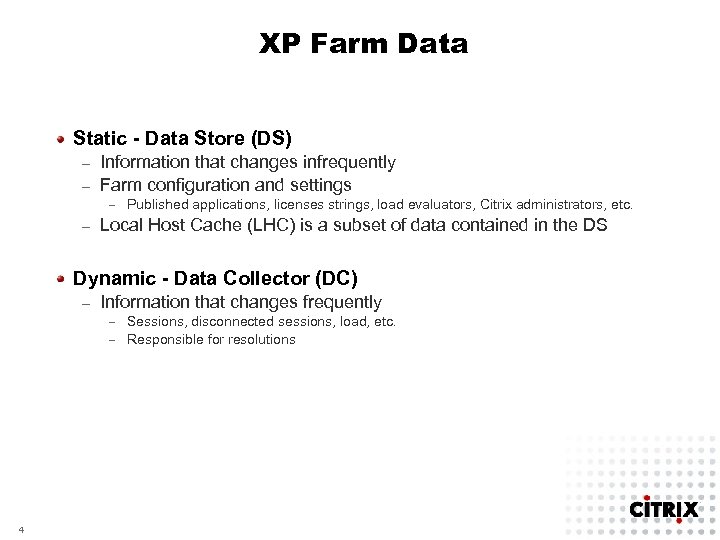
XP Farm Data Static - Data Store (DS) Information that changes infrequently – Farm configuration and settings – – Published applications, licenses strings, load evaluators, Citrix administrators, etc. – Local Host Cache (LHC) is a subset of data contained in the DS Dynamic - Data Collector (DC) – Information that changes frequently – Sessions, disconnected sessions, load, etc. – Responsible for resolutions 4
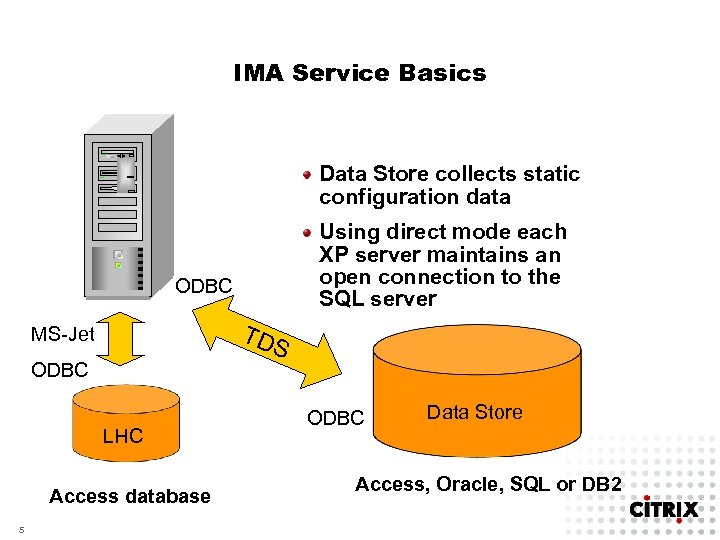
IMA Service Basics Data Store collects static configuration data Using direct mode each XP server maintains an open connection to the SQL server ODBC TD MS-Jet S ODBC LHC Access database 5 ODBC Data Store Access, Oracle, SQL or DB 2
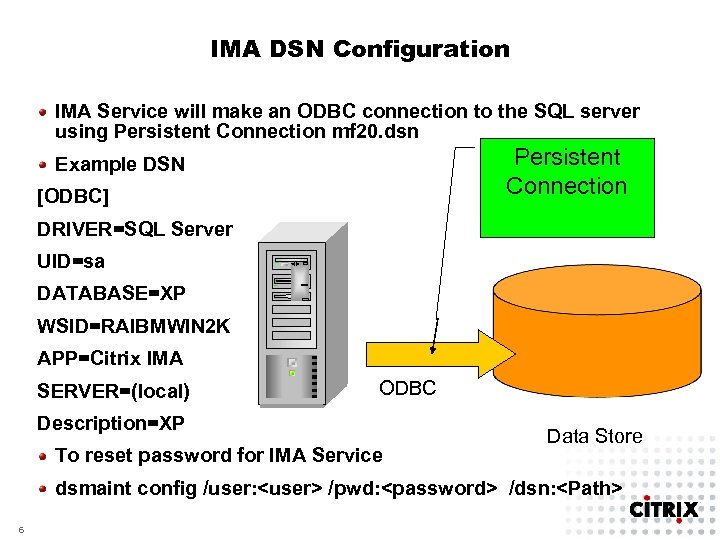
IMA DSN Configuration IMA Service will make an ODBC connection to the SQL server using Persistent Connection mf 20. dsn Persistent Connection Example DSN [ODBC] DRIVER=SQL Server UID=sa DATABASE=XP WSID=RAIBMWIN 2 K APP=Citrix IMA SERVER=(local) ODBC Description=XP To reset password for IMA Service Data Store dsmaint config /user: <user> /pwd: <password> /dsn: <Path> 6

IMA Service Basics How is the LHC kept up-to-date? • Syncing with Data Store at Start-Up • • 7 Change Broadcasts Change Polling
IMA Service Start Up • During start-up each subsystem tells the LHC what data it wants cached. • Initially LHC database is empty and all necessary data is copied over from the Data Store. • On subsequent start-ups, a reconciliation is performed on the LHC against the Data Store. • Only changed data is copied from the Data Store. This catches any changes that occurred while the service was stopped. 8
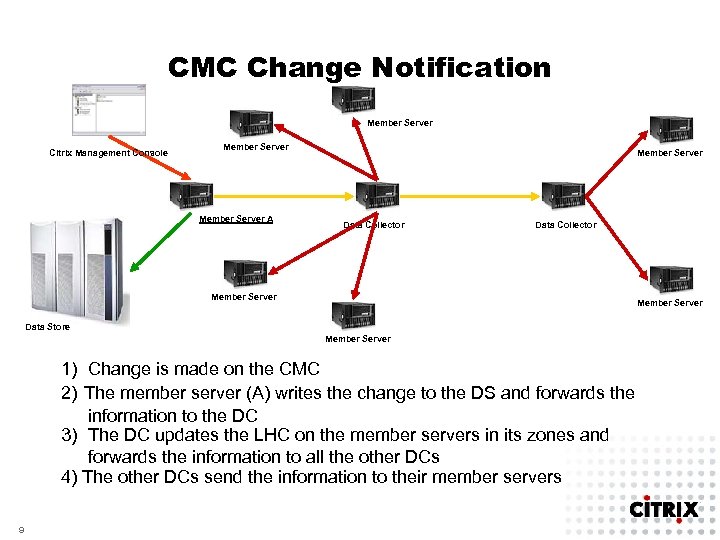
CMC Change Notification Member Server Citrix Management Console Member Server A Member Server Data Collector Member Server Data Store Member Server 1) Change is made on the CMC 2) The member server (A) writes the change to the DS and forwards the information to the DC 3) The DC updates the LHC on the member servers in its zones and forwards the information to all the other DCs 4) The other DCs send the information to their member servers 9
Change Polling Used as a backup method of discovery Occurs by default every 10 minutes (w/o hf XE 102 W 064 – previously XE 102 W 036) FR 3 30 minute interval Configurable in registry under HKLMSoftware-Citrix-IMADCNChange. Polling. Interval Data Store 10
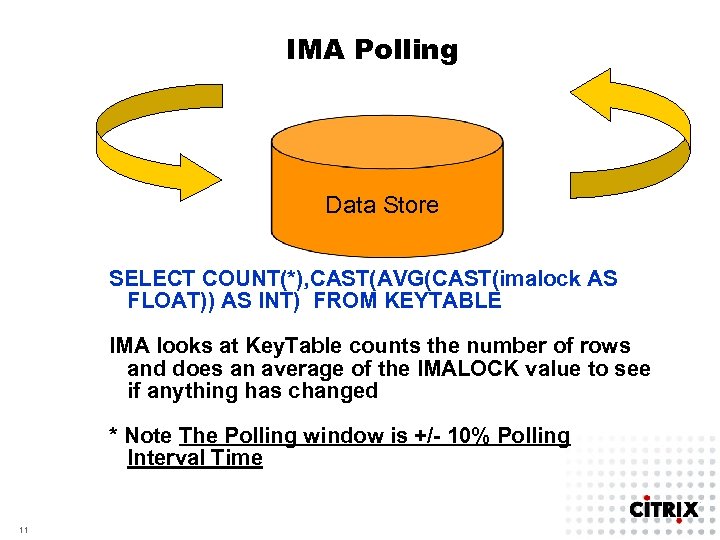
IMA Polling Data Store SELECT COUNT(*), CAST(AVG(CAST(imalock AS FLOAT)) AS INT) FROM KEYTABLE IMA looks at Key. Table counts the number of rows and does an average of the IMALOCK value to see if anything has changed * Note The Polling window is +/- 10% Polling Interval Time 11
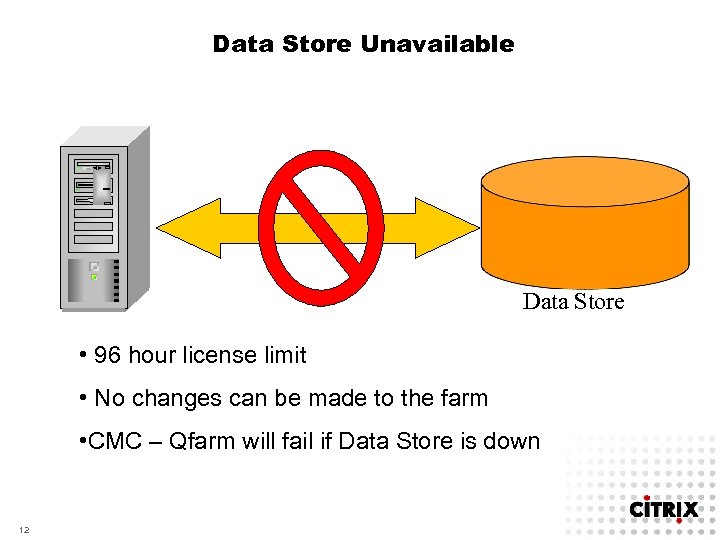
Data Store Unavailable Data Store • 96 hour license limit • No changes can be made to the farm • CMC – Qfarm will fail if Data Store is down 12
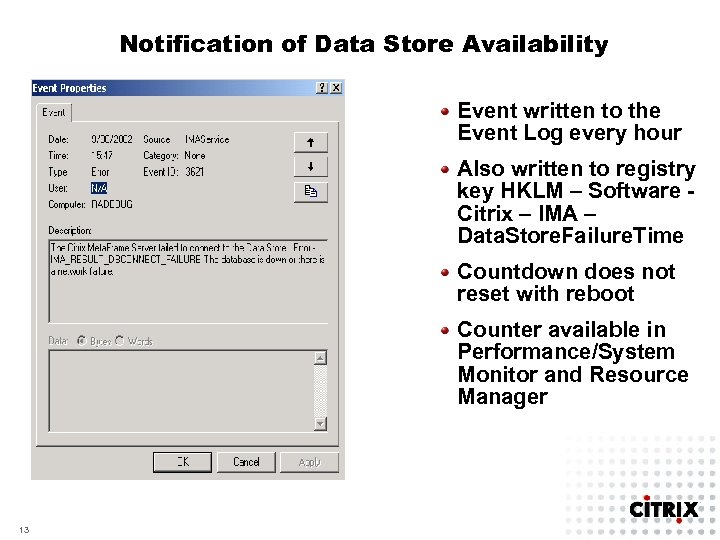
Notification of Data Store Availability Event written to the Event Log every hour Also written to registry key HKLM – Software Citrix – IMA – Data. Store. Failure. Time Countdown does not reset with reboot Counter available in Performance/System Monitor and Resource Manager 13

Microsoft SQL Server 14

SQL Service Packs When installing a new service pack, the sp makes changes to the system tables for maintenance reasons, and upgrades user and distribution dbs that are members of a replication topology. Due to these changes, service packs cannot easily be removed. There is no automated way to remove a service pack. Detach all user databases Stop all SQL Server services Uninstall SQL Server by using the Add/Remove Programs Install SQL Server Apply service pack Restore the master, msdb, and model databases from backup if you have backups that match the version of service pack to which you want to revert. This automatically attaches any user databases that were attached when you created the backup. Attach any user databases that were created after the last backup of the master database 15

Troubleshooting Tools 1. Eventlogs (Critical and Severe Errors) 2. SQL Profiler 3. Performance Monitor 4. Component Checker 5. Enterprise Manager 6. Query Analyzer 7. SQLDiag collects the following information: %systemdrive%Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQLBinn • • Configuration Information • Database Information • 16 Collects SQL error logs Server Information
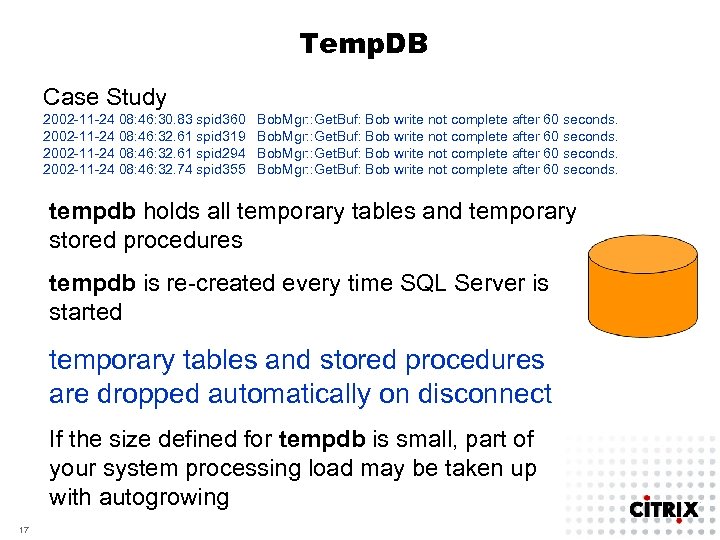
Temp. DB Case Study 2002 -11 -24 08: 46: 30. 83 spid 360 2002 -11 -24 08: 46: 32. 61 spid 319 2002 -11 -24 08: 46: 32. 61 spid 294 2002 -11 -24 08: 46: 32. 74 spid 355 Bob. Mgr: : Get. Buf: Bob write not complete after 60 seconds. tempdb holds all temporary tables and temporary stored procedures tempdb is re-created every time SQL Server is started temporary tables and stored procedures are dropped automatically on disconnect If the size defined for tempdb is small, part of your system processing load may be taken up with autogrowing 17
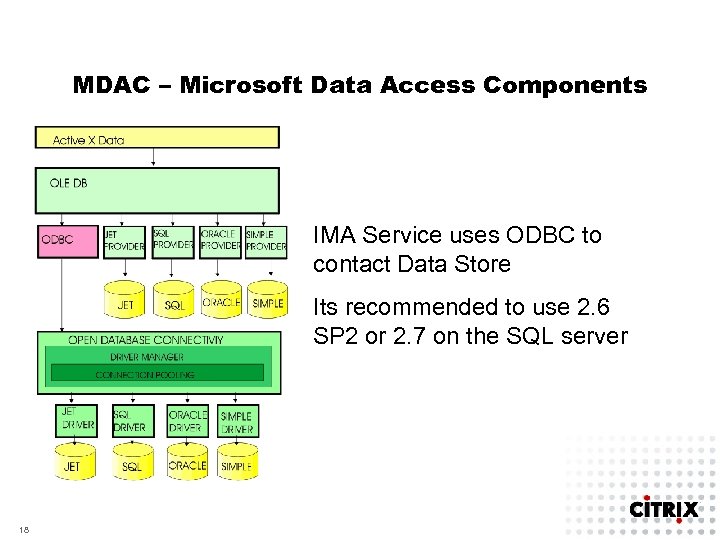
MDAC – Microsoft Data Access Components IMA Service uses ODBC to contact Data Store Its recommended to use 2. 6 SP 2 or 2. 7 on the SQL server 18
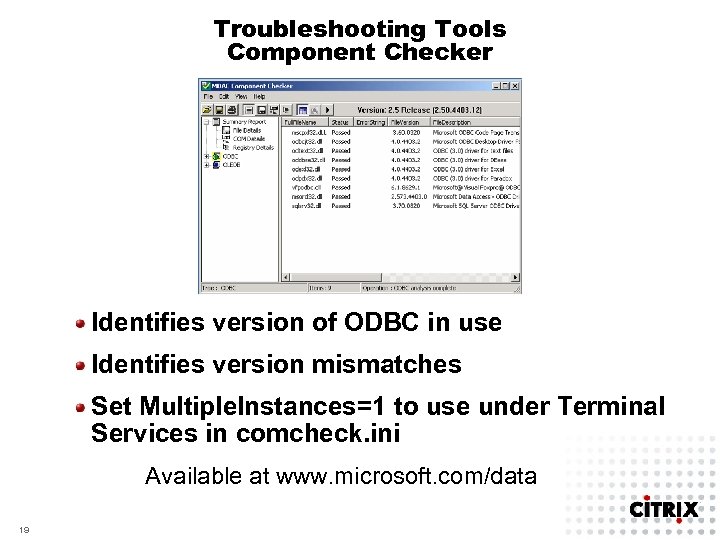
Troubleshooting Tools Component Checker Identifies version of ODBC in use Identifies version mismatches Set Multiple. Instances=1 to use under Terminal Services in comcheck. ini Available at www. microsoft. com/data 19
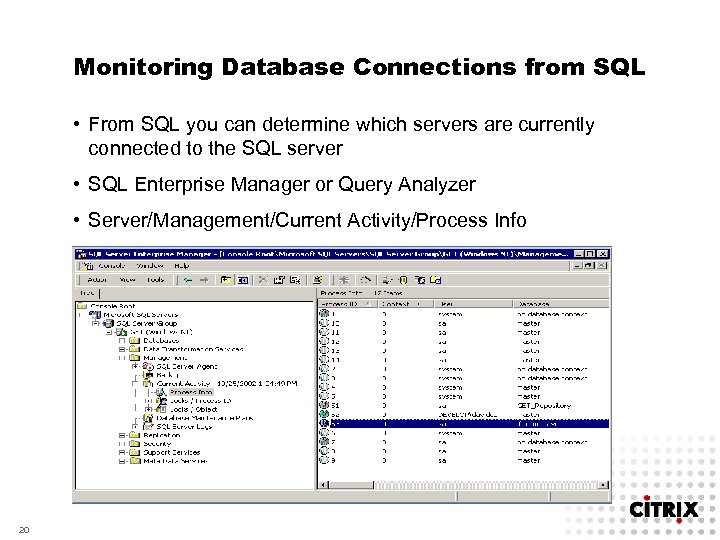
Monitoring Database Connections from SQL • From SQL you can determine which servers are currently connected to the SQL server • SQL Enterprise Manager or Query Analyzer • Server/Management/Current Activity/Process Info 20

T-SQL Commands in Query Analyzer Sp_who, sp_who 2 - Activity information sp_helpdb databasename – Shows size information sp_helptext sp_name – List stored procedure text sp_help – Will list all database objects Print @@version – Displays – Example. SQL version 8. 00. 760 = SP 3 Kill (spid) – Terminates SQL connection on database Sp_configure List and change SQL server settings 21

Best Practices Citrix Support Staff 22
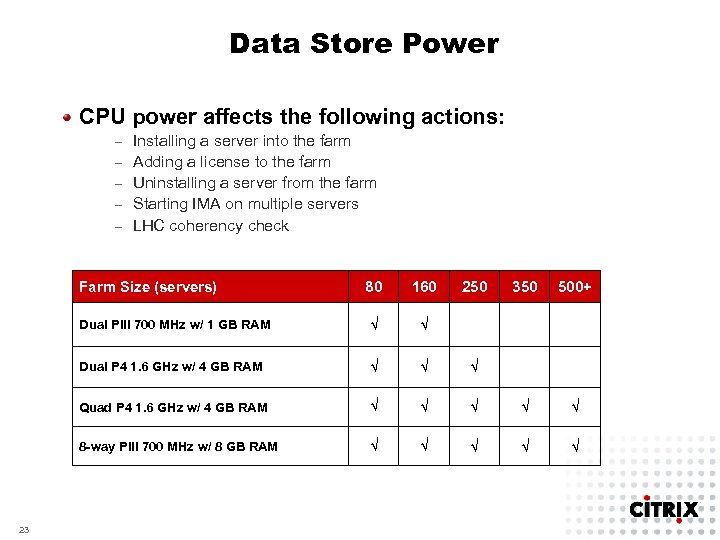
Data Store Power CPU power affects the following actions: – – – Installing a server into the farm Adding a license to the farm Uninstalling a server from the farm Starting IMA on multiple servers LHC coherency check Farm Size (servers) 160 Dual PIII 700 MHz w/ 1 GB RAM √ √ Dual P 4 1. 6 GHz w/ 4 GB RAM √ √ √ Quad P 4 1. 6 GHz w/ 4 GB RAM √ √ 8 -way PIII 700 MHz w/ 8 GB RAM 23 80 250 350 500+ √ √ √ √
Data Store Tuning Increase SQL Server Worker Threads – Increase worker threads if there are more than 250 servers in the farm. (Enterprise Manager or stored procedure/stop and restart SQL service) – Right click properties of server/Processor tab/Max Worker Threads in Enterprise Manager SQL Clustering – Provides redundancy but does not give a performance boost NIC Teaming – Watch the throughput on the data store’s network card. Consider teaming an additional NIC for increased throughput. RAID tuning – 24 Disks should be RAID 5 or 1+0 (recommended). If possible, tune the RAID controller for 100% reads, 0% writes.

Automating Data Store Administration Note: SQLServer. Agent Service must be running to execute plan 25
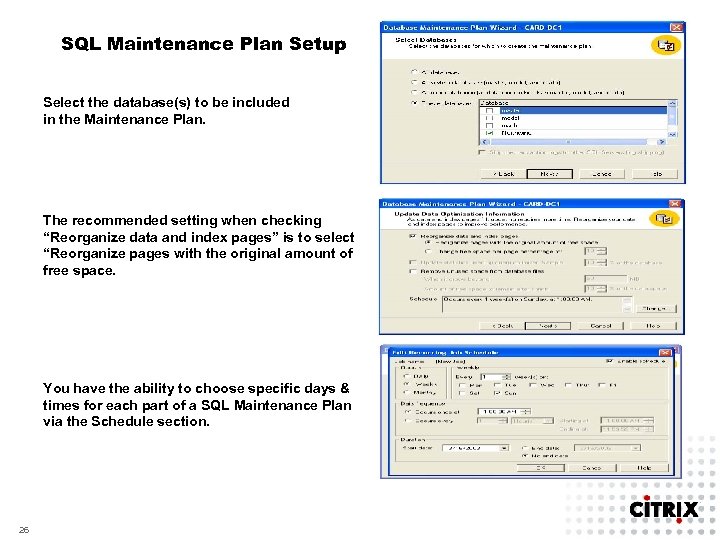
SQL Maintenance Plan Setup Select the database(s) to be included in the Maintenance Plan. The recommended setting when checking “Reorganize data and index pages” is to select “Reorganize pages with the original amount of free space. You have the ability to choose specific days & times for each part of a SQL Maintenance Plan via the Schedule section. 26

SQL Maintenance Plan Setup At the completion of the maintenance plan setup process, ensure that the SQL Server Agent service is running in order for the plan to execute. 27
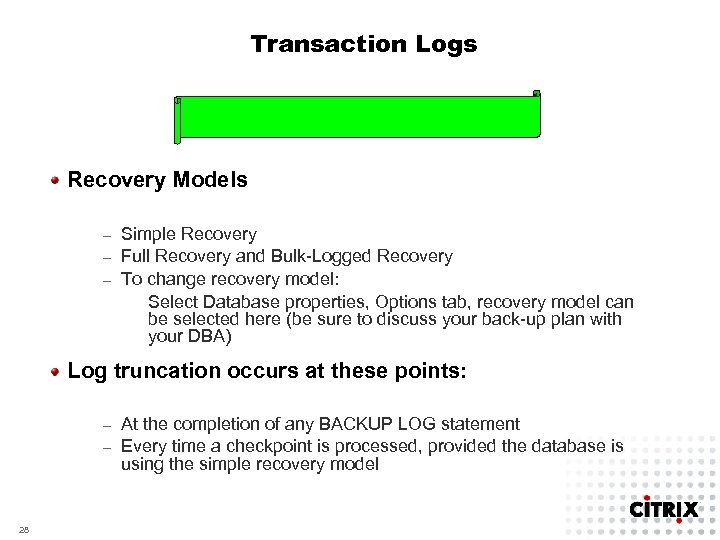
Transaction Logs Recovery Models Simple Recovery – Full Recovery and Bulk-Logged Recovery – To change recovery model: Select Database properties, Options tab, recovery model can be selected here (be sure to discuss your back-up plan with your DBA) – Log truncation occurs at these points: At the completion of any BACKUP LOG statement – Every time a checkpoint is processed, provided the database is using the simple recovery model – 28

Suggested Hotfixes XE 102 W 064 (formerly XE 102 W 036) – Large Meta. Frame XP Feature Release 2/Service Pack 2 server farms sometimes experienced data store contention problems when simultaneously adding or upgrading multiple servers to the farm. XE 102 W 028 – 29 The initialization of a global variable indicating the default name of the ODBC configuration file was moved. As a result, the global variable was not initialized and the DSN file could not be loaded, causing the creation of the database connection to fail.
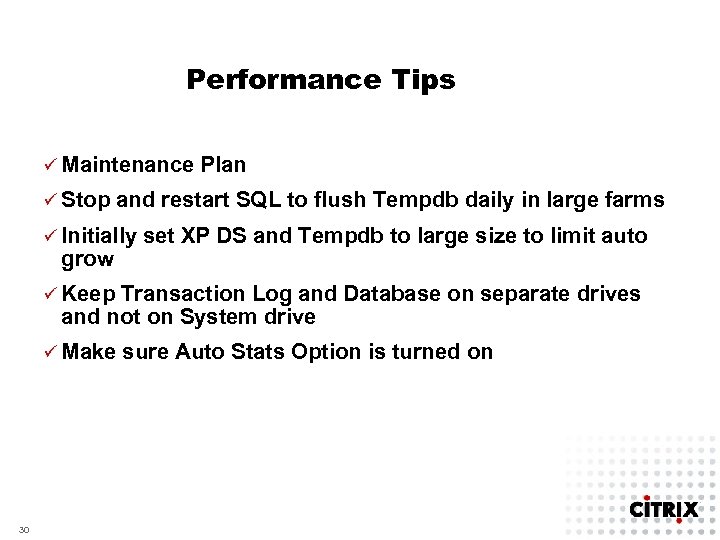
Performance Tips ü Maintenance ü Stop Plan and restart SQL to flush Tempdb daily in large farms ü Initially grow set XP DS and Tempdb to large size to limit auto ü Keep Transaction Log and Database on separate drives and not on System drive ü Make 30 sure Auto Stats Option is turned on

Support SQL Subject Matter Experts Card, Tim Tech Engineer 2 Enterprise NT Support Americas Santos, Ray Tech Support Lead Eng. NT NT Support Americas Aldridge, Michael Technical Relationship Mgr EMEA SE Team Birk, Rob Tech Engineer 2 NT NT Support Americas Bomfim, Jacqueline Tech Engineer 1 NT NT Support Americas Conran, Andre Tech Engineer 2 NT NT Support Americas Davy, Andrew Tech Engineer 2 Enterprise NT Support Americas Garten, Kevin Tech Engineer 1 NT NT Support Americas Harding, Stacy Tech Engineer 2 NT Web/Unix Support Hines, Patrick Technical Relationship Mgr Enterprise Americas Keyzer, Kim Technical Relationship Mgr Enterprise Americas Maharaj, Ken Tech Engineer 2 Enterprise Web/Unix Support Moody, Rob Technical Relationship Mgr Enterprise Americas Nittel, Darnell Tech Engineer 2 NT NT Support Americas Plant, Chris Technical Relationship Mgr EMEA SE Team Rabinowitz, Jon Tech Engineer 2 NT NT Support Americas Sai, Suh Tech Engineer 1 NT Japan Support Engineers Salvatierra, Manuel Tech Engineer 1 NT NT Support Americas Schwalbe, Enrico Technical Relationship Mgr Enterprise EMEA Serriere, Frederic Tech Support Lead Eng. NT Enterprise EMEA Yokohara, Tsuyoshi Sr. Product Readiness Manager Japan Technical Support 31

Questions?
1056b83bfcb68e6a1ae87e97fd42dc4a.ppt