54d3820579f1358163235b05040696c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Mesopotamia in the Second Millennia © John Stevenson, 2017 Maps by David P. Barrett used by permission
Mesopotamia in the Second Millennia © John Stevenson, 2017 Maps by David P. Barrett used by permission
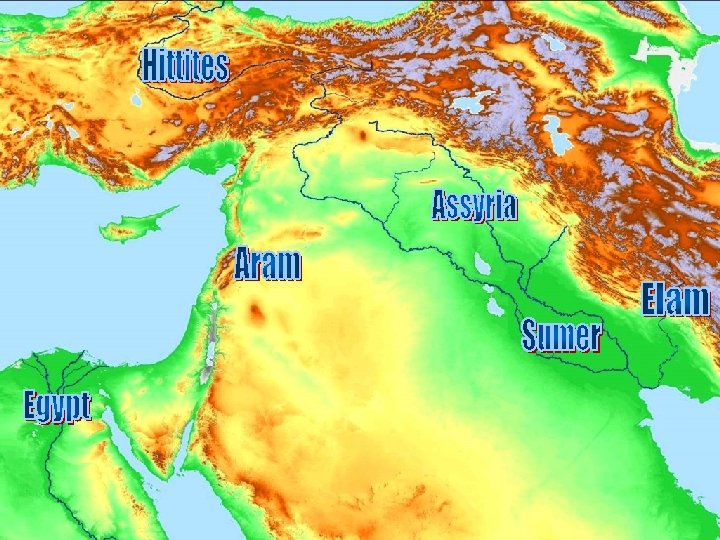
 2330 B. C. • Sargon the Great • Guti invasion
2330 B. C. • Sargon the Great • Guti invasion
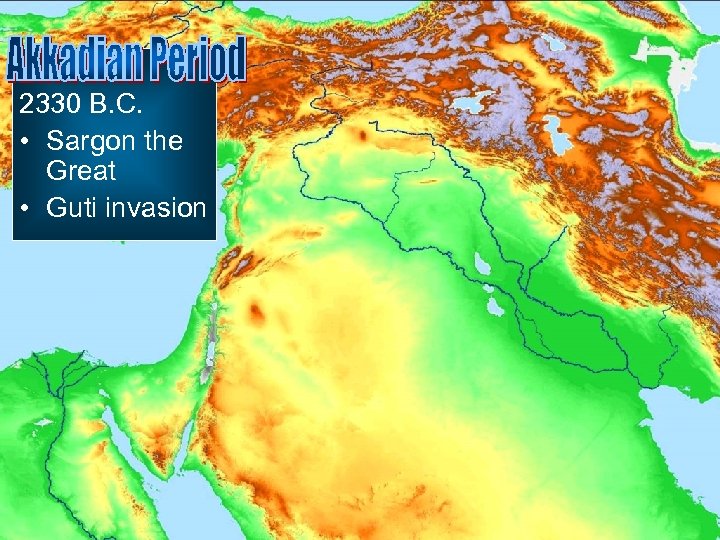
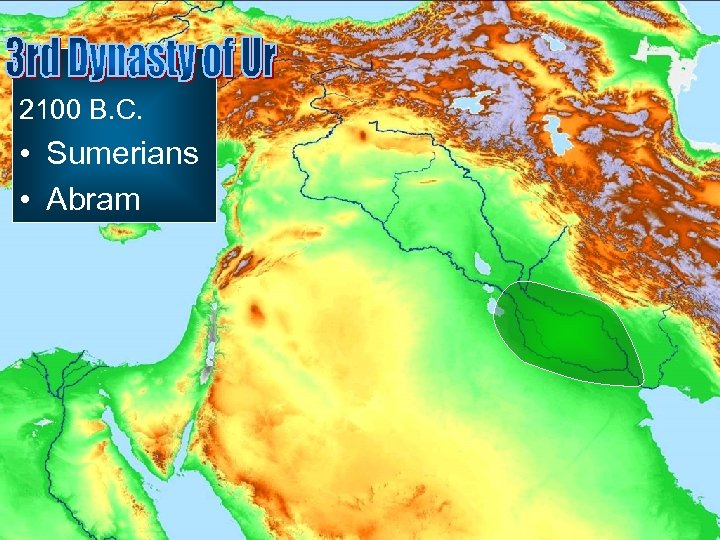 2100 B. C. • Sumerians • Abram
2100 B. C. • Sumerians • Abram
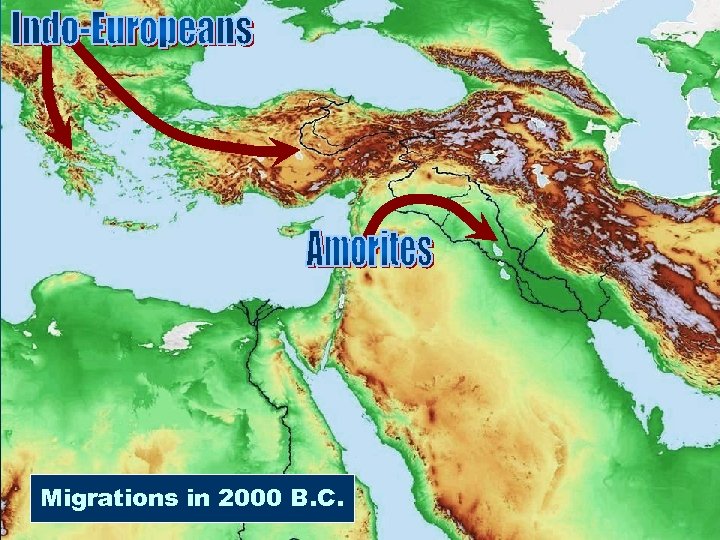 Migrations in 2000 B. C.
Migrations in 2000 B. C.
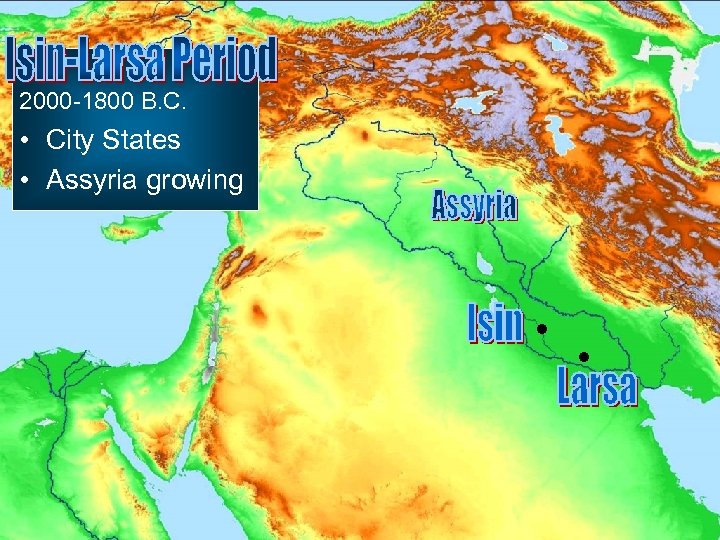 2000 -1800 B. C. • City States • Assyria growing
2000 -1800 B. C. • City States • Assyria growing
 Died around 1750 B. C. • Succeeded father to throne of Babylon • Led coalition against Elam • Unified Mesopotamia – City-state replaced by regional state • Law code
Died around 1750 B. C. • Succeeded father to throne of Babylon • Led coalition against Elam • Unified Mesopotamia – City-state replaced by regional state • Law code
 Code of Hammurabi 1750 B. C. • Found at Susa by de Morgan in 1902 • Divine claim • Caste system • Lex Talionis • Wages • Trial by ordeal
Code of Hammurabi 1750 B. C. • Found at Susa by de Morgan in 1902 • Divine claim • Caste system • Lex Talionis • Wages • Trial by ordeal
 If any one bring an accusation against a man, and the accused go to the river and leap into the river, if he sink in the river his accuser shall take possession of his house. But if the river prove that the accused is not guilty, and he escape unhurt, then he who had brought the accusation shall be put to death, while he who leaped into the river shall take possession of the house that had belonged to his accuser (Hammurabi).
If any one bring an accusation against a man, and the accused go to the river and leap into the river, if he sink in the river his accuser shall take possession of his house. But if the river prove that the accused is not guilty, and he escape unhurt, then he who had brought the accusation shall be put to death, while he who leaped into the river shall take possession of the house that had belonged to his accuser (Hammurabi).
 • Only legal when in writing • Penalty for adultery is death • Wives can own property • Veils mandated
• Only legal when in writing • Penalty for adultery is death • Wives can own property • Veils mandated
 • Monogamy except in case of a barren wife
• Monogamy except in case of a barren wife
 • Payment scaled for healing of… – Citizen: 10 shekels – Freed man: 5 shekels – Slave: 2 shekels • Physicians punished in the death of patient – Citizen or freed man: Physician’s hand cut off – Slave: Cost of the slave
• Payment scaled for healing of… – Citizen: 10 shekels – Freed man: 5 shekels – Slave: 2 shekels • Physicians punished in the death of patient – Citizen or freed man: Physician’s hand cut off – Slave: Cost of the slave
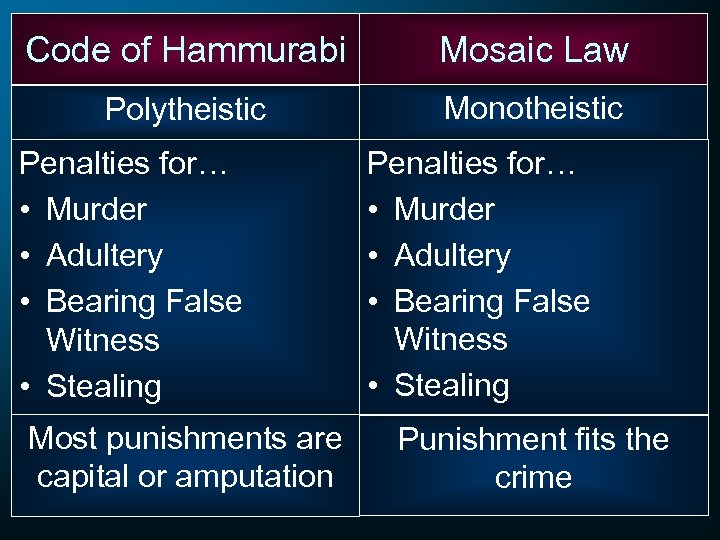 Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law Polytheistic Monotheistic Penalties for… • Murder • Adultery • Bearing False Witness • Stealing Most punishments are capital or amputation Penalties for… • Murder • Adultery • Bearing False Witness • Stealing Punishment fits the crime
Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law Polytheistic Monotheistic Penalties for… • Murder • Adultery • Bearing False Witness • Stealing Most punishments are capital or amputation Penalties for… • Murder • Adultery • Bearing False Witness • Stealing Punishment fits the crime
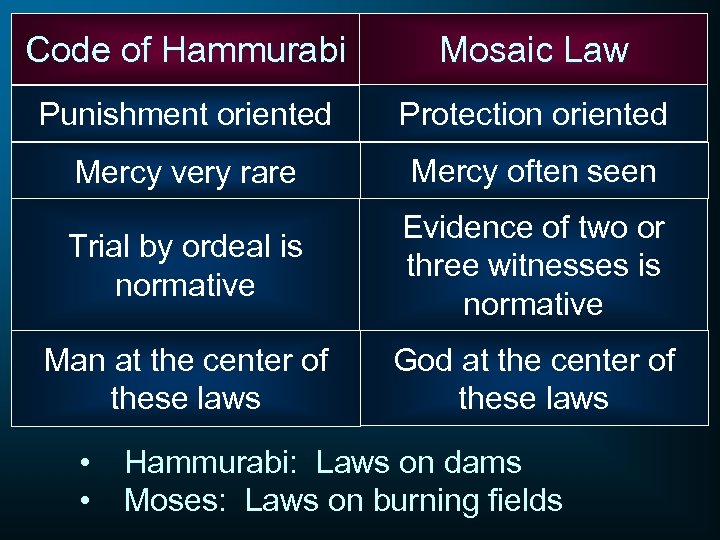 Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law Punishment oriented Protection oriented Mercy very rare Mercy often seen Trial by ordeal is normative Evidence of two or three witnesses is normative Man at the center of these laws God at the center of these laws • • Hammurabi: Laws on dams Moses: Laws on burning fields
Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law Punishment oriented Protection oriented Mercy very rare Mercy often seen Trial by ordeal is normative Evidence of two or three witnesses is normative Man at the center of these laws God at the center of these laws • • Hammurabi: Laws on dams Moses: Laws on burning fields
 Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law No provisions Provisions for the poor Harboring a runaway slave brought death penalty Runaway slaves protected (Deuteronomy 23: 15) Slave who said, “You don’t own me” had his ear cut off Slave who loved his master had his ear pierced Good intentions could be punished (physicians) Good intentions not punished
Code of Hammurabi Mosaic Law No provisions Provisions for the poor Harboring a runaway slave brought death penalty Runaway slaves protected (Deuteronomy 23: 15) Slave who said, “You don’t own me” had his ear cut off Slave who loved his master had his ear pierced Good intentions could be punished (physicians) Good intentions not punished
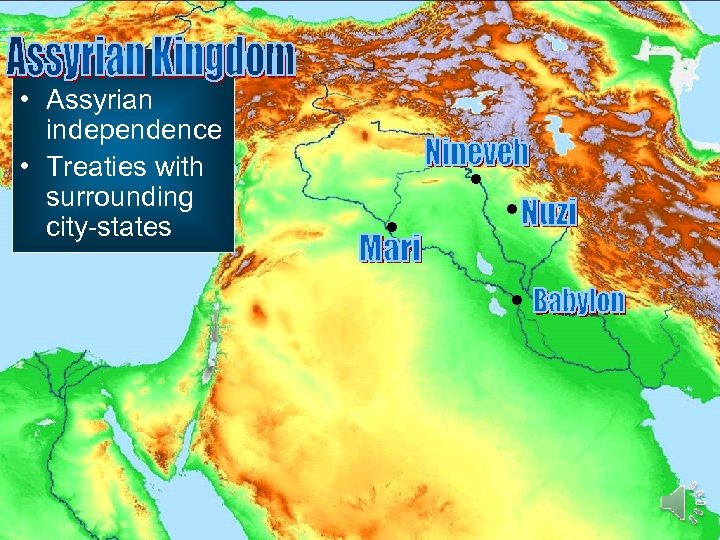
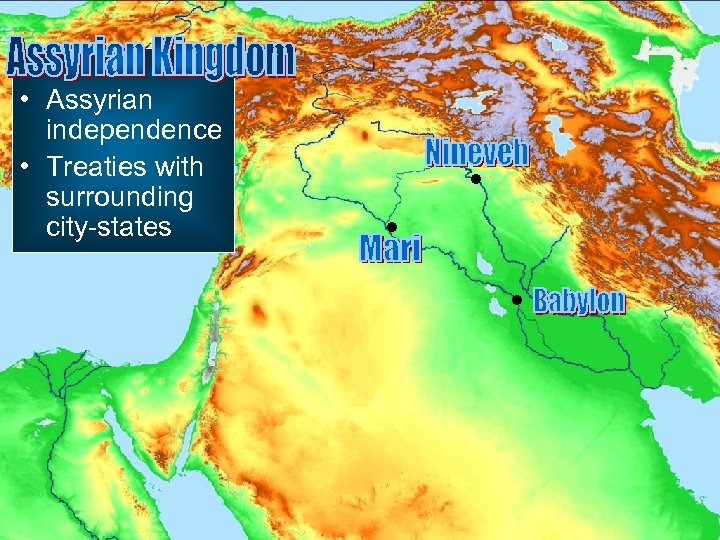 • Assyrian independence • Treaties with surrounding city-states
• Assyrian independence • Treaties with surrounding city-states
 • Mari destroyed by Hammurabi • Andre Parrot excavated from 19331938 and 1952 -1956 • More than 20, 000 tablets • Akkadian from 18001750 B. C.
• Mari destroyed by Hammurabi • Andre Parrot excavated from 19331938 and 1952 -1956 • More than 20, 000 tablets • Akkadian from 18001750 B. C.
 • Biblical names – Noah – Laban – Abram – Jacob • Travel and commerce • Covenant: “To kill a young donkey”
• Biblical names – Noah – Laban – Abram – Jacob • Travel and commerce • Covenant: “To kill a young donkey”
 • Assyrian independence • Treaties with surrounding city-states
• Assyrian independence • Treaties with surrounding city-states
 • • • Smaller town Destroyed around 1450 B. C. Customs and culture similar to that of the Patriarchs
• • • Smaller town Destroyed around 1450 B. C. Customs and culture similar to that of the Patriarchs
 • Children by surrogate for childless couples • Making a slave an heir • Wife who is adopted as a sister has greater rights • Importance of deathbed blessing
• Children by surrogate for childless couples • Making a slave an heir • Wife who is adopted as a sister has greater rights • Importance of deathbed blessing
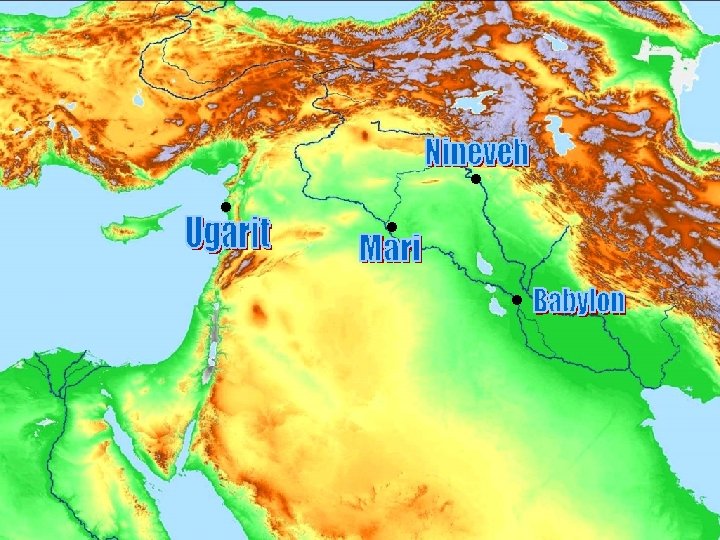
 • Discovered by a farmer in 1928 – Town of Ras Shamra
• Discovered by a farmer in 1928 – Town of Ras Shamra
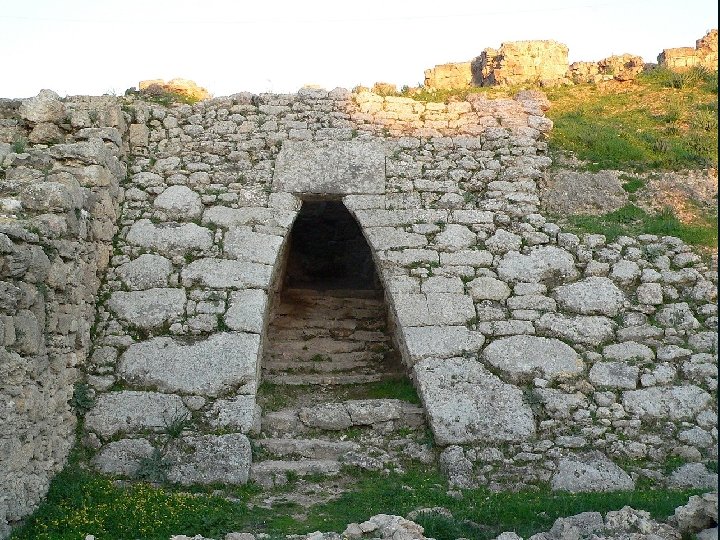
 • • • Discovered by a farmer in 1928 Royal palace with 90 rooms Two temples – Baal, son of El – Dagon • Tablets dating to 1450 -1200 B. C. – Alphabet looks like cuneiform – Semitic language related to Hebrew – Ugaritic poetry similar to Hebrew poets
• • • Discovered by a farmer in 1928 Royal palace with 90 rooms Two temples – Baal, son of El – Dagon • Tablets dating to 1450 -1200 B. C. – Alphabet looks like cuneiform – Semitic language related to Hebrew – Ugaritic poetry similar to Hebrew poets
 Mycenaean ivory box lid found in Ugarit
Mycenaean ivory box lid found in Ugarit

 • Religious Practices: Boiling a kid in its mother’s milk • Sacred prostitution • Use of Aramaic expressions (mirrored in the Bible)
• Religious Practices: Boiling a kid in its mother’s milk • Sacred prostitution • Use of Aramaic expressions (mirrored in the Bible)

 The Hittites: A Canaanite tribe encountered in Palestine by the Israelites, resident and along side the Amorites in the region of Bethel. They were pressed into service by Solomon. Still later, however, an independent and monarchically governed Hittite tribe existed nearer Syria. (Meyers Neus Konversationislexikon, 1871).
The Hittites: A Canaanite tribe encountered in Palestine by the Israelites, resident and along side the Amorites in the region of Bethel. They were pressed into service by Solomon. Still later, however, an independent and monarchically governed Hittite tribe existed nearer Syria. (Meyers Neus Konversationislexikon, 1871).
 For the Lord had caused the army of the Arameans to hear a sound of chariots and a sound of horses, even the sound of a great army, so that they said to one another, “Behold, the king of Israel has hired against us the kings of the HITTITES and the kings of the Egyptians, to come upon us. ” Therefore they arose and fled in the twilight, and left their tents and their horses and their donkeys, even the camp just as it was, and fled for their life. ” (2 Kings 7: 6 -7).
For the Lord had caused the army of the Arameans to hear a sound of chariots and a sound of horses, even the sound of a great army, so that they said to one another, “Behold, the king of Israel has hired against us the kings of the HITTITES and the kings of the Egyptians, to come upon us. ” Therefore they arose and fled in the twilight, and left their tents and their horses and their donkeys, even the camp just as it was, and fled for their life. ” (2 Kings 7: 6 -7).
 Charles Felix-Marie Texier • Traveling through Turkey in 1834 searching for Tavium • Boghazkoy • Unknown ruins
Charles Felix-Marie Texier • Traveling through Turkey in 1834 searching for Tavium • Boghazkoy • Unknown ruins
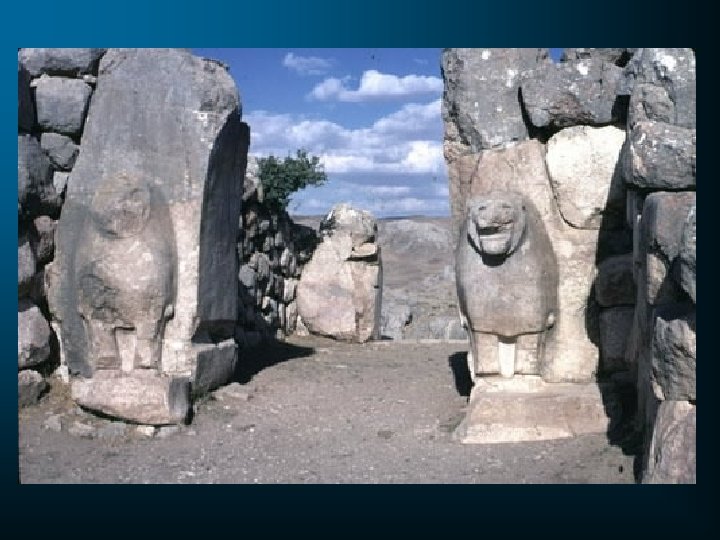
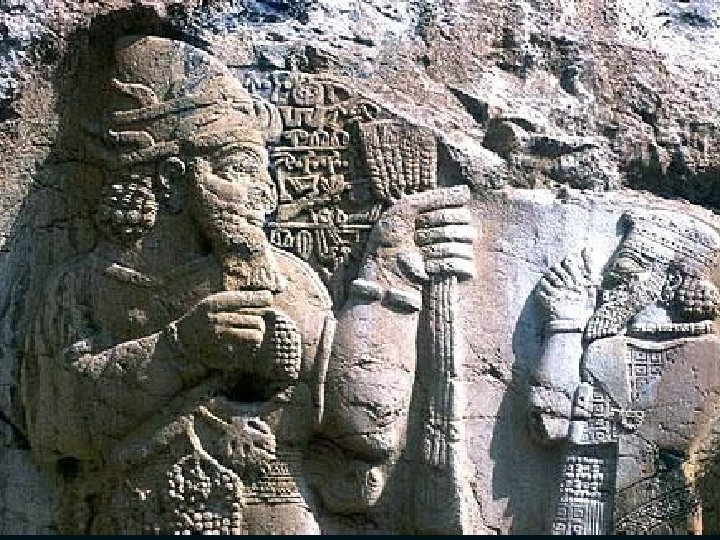




 Archibald Henry Sayce Visited the site in 1889 and suggested they were the Biblical Hittites
Archibald Henry Sayce Visited the site in 1889 and suggested they were the Biblical Hittites
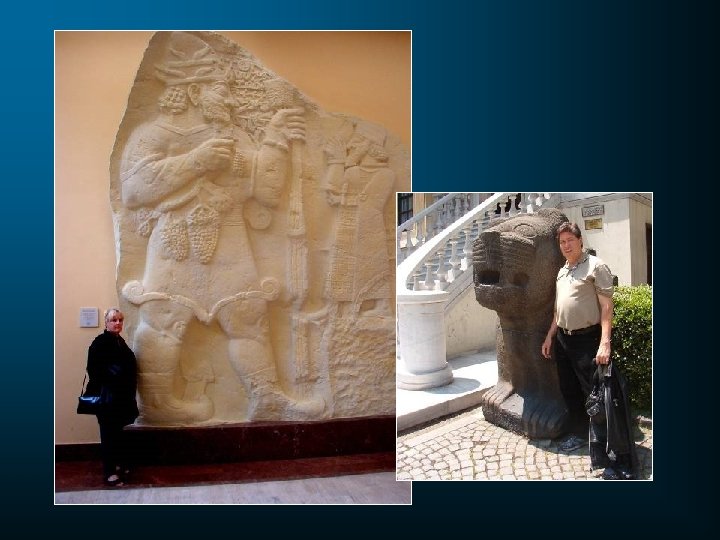
 Hugo Winckler • Two expeditions in the early 1900’s. • Hired local natives to bring fragments of tablets • Akkadian tablet containing a treaty between Rameses II and Hattusilis
Hugo Winckler • Two expeditions in the early 1900’s. • Hired local natives to bring fragments of tablets • Akkadian tablet containing a treaty between Rameses II and Hattusilis

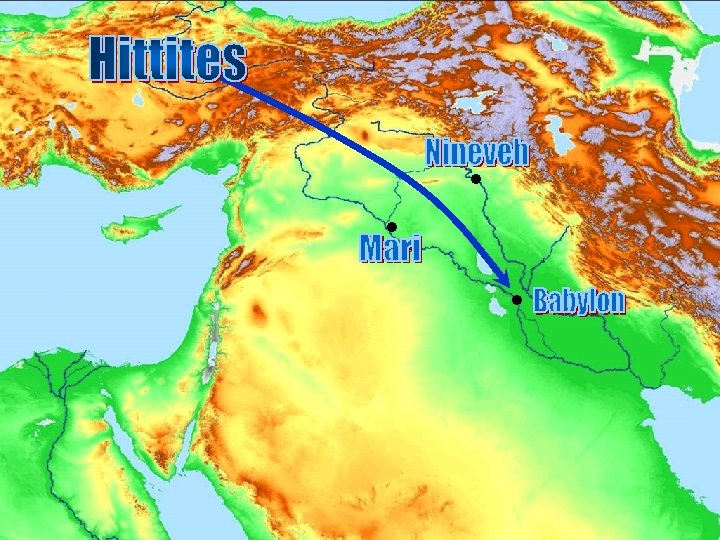
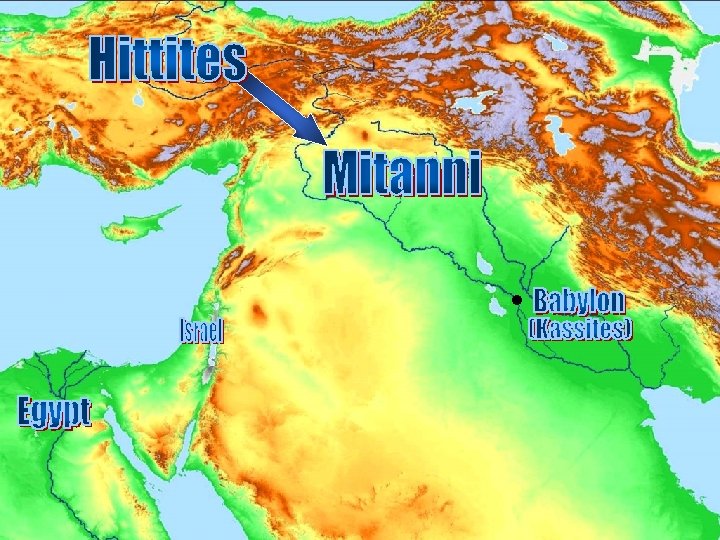
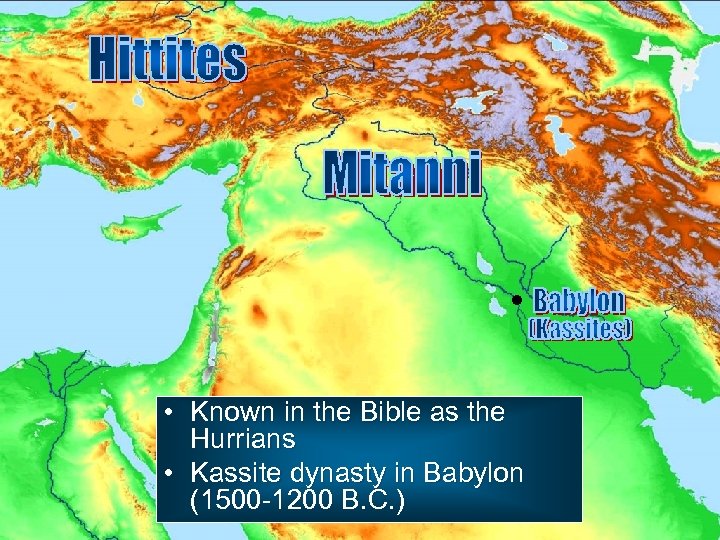 • Known in the Bible as the Hurrians • Kassite dynasty in Babylon (1500 -1200 B. C. )
• Known in the Bible as the Hurrians • Kassite dynasty in Babylon (1500 -1200 B. C. )
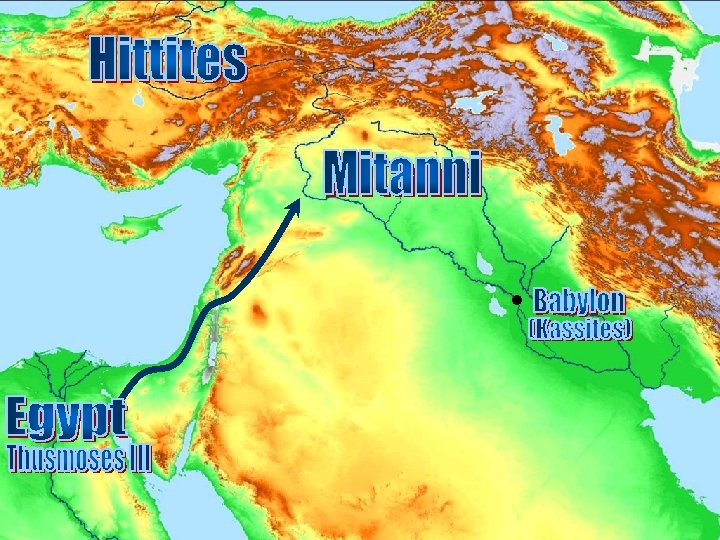
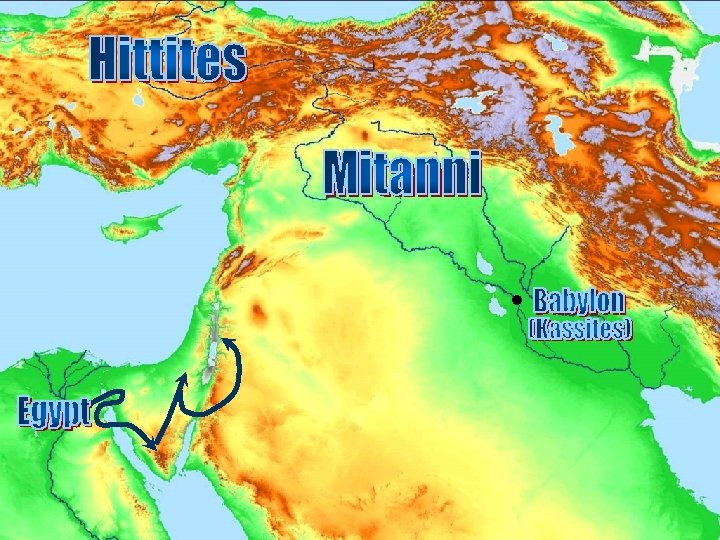
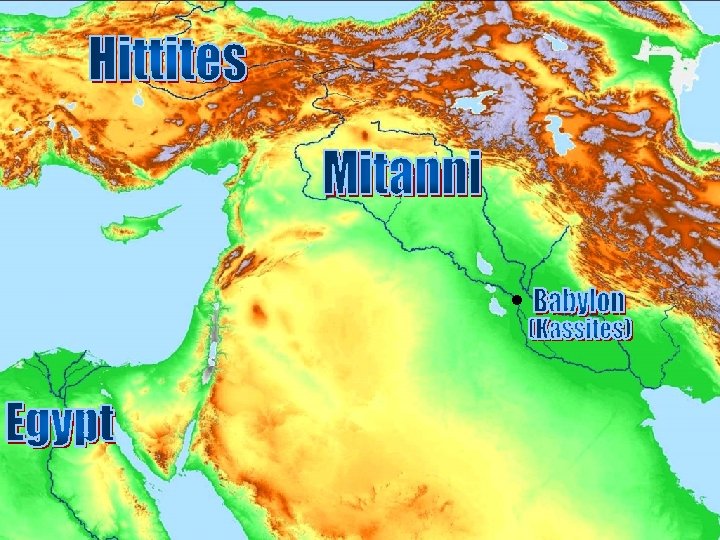
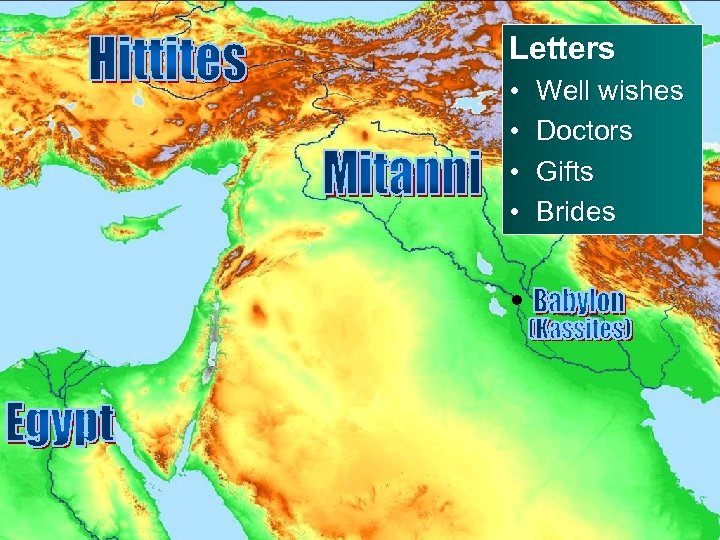 Letters • • Well wishes Doctors Gifts Brides
Letters • • Well wishes Doctors Gifts Brides
 “My husband has died and I have no son. They say about you that you have many sons. You might give me one of your sons to become my husband. I would not wish to take one of my subjects as a husband”
“My husband has died and I have no son. They say about you that you have many sons. You might give me one of your sons to become my husband. I would not wish to take one of my subjects as a husband”
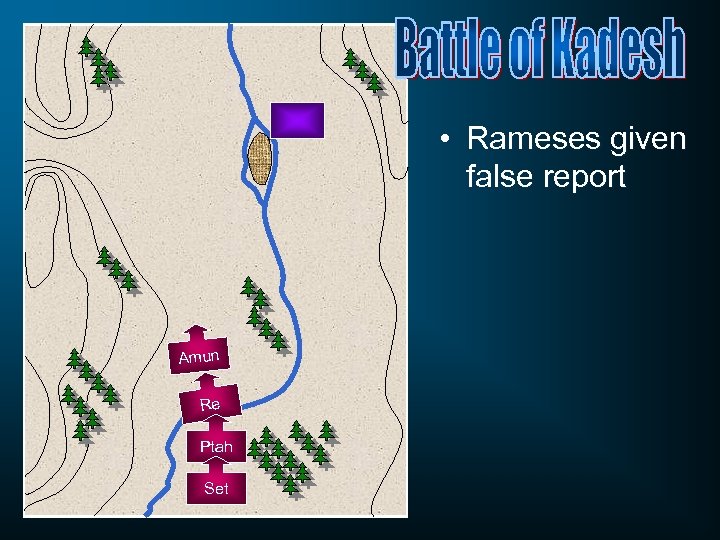 • Rameses given false report Amun Re Ptah Set
• Rameses given false report Amun Re Ptah Set
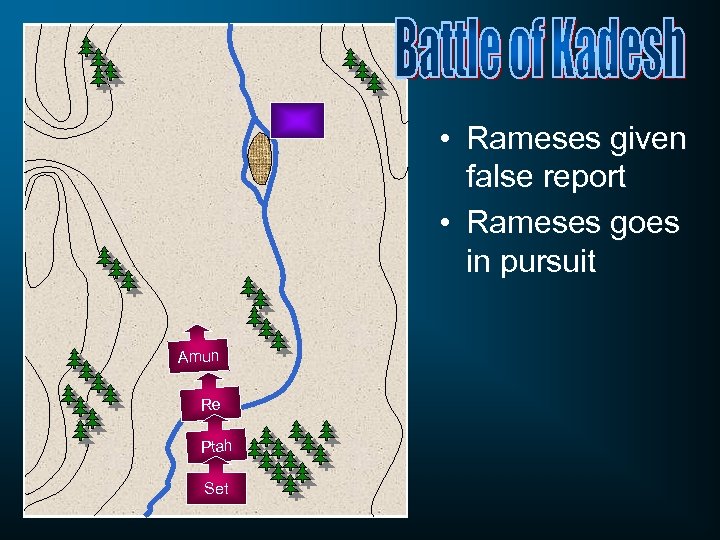 • Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit Amun Re Ptah Set
• Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit Amun Re Ptah Set
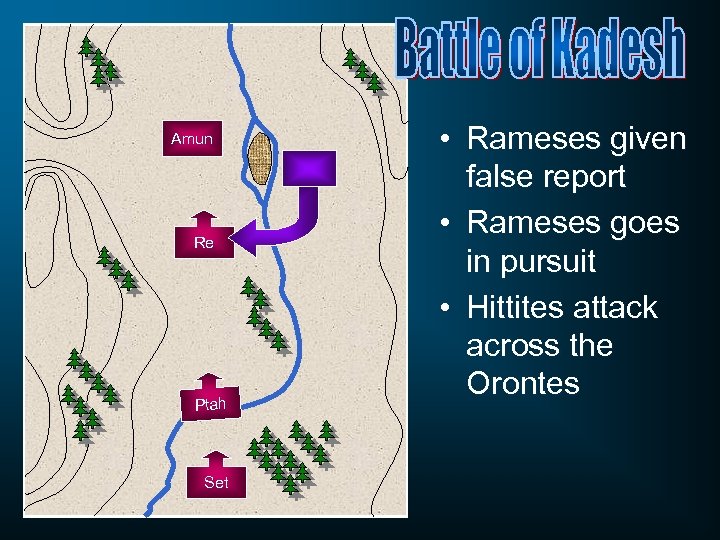 Amun Re Ptah Set • Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit • Hittites attack across the Orontes
Amun Re Ptah Set • Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit • Hittites attack across the Orontes
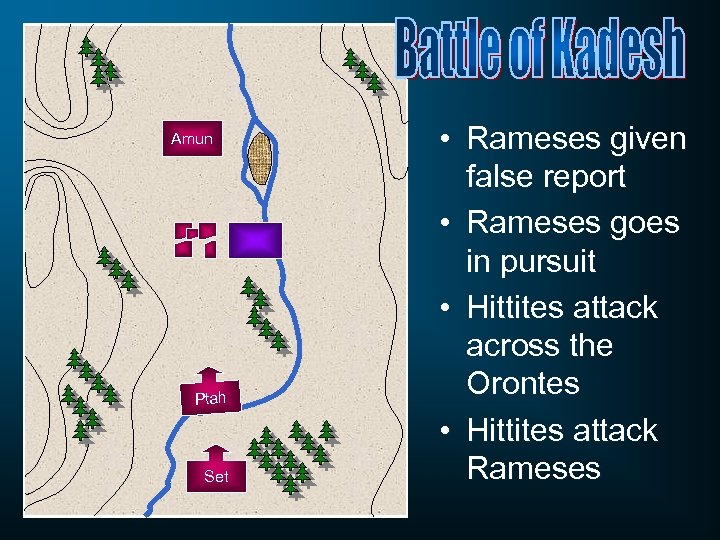 Amun Ptah Set • Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit • Hittites attack across the Orontes • Hittites attack Rameses
Amun Ptah Set • Rameses given false report • Rameses goes in pursuit • Hittites attack across the Orontes • Hittites attack Rameses
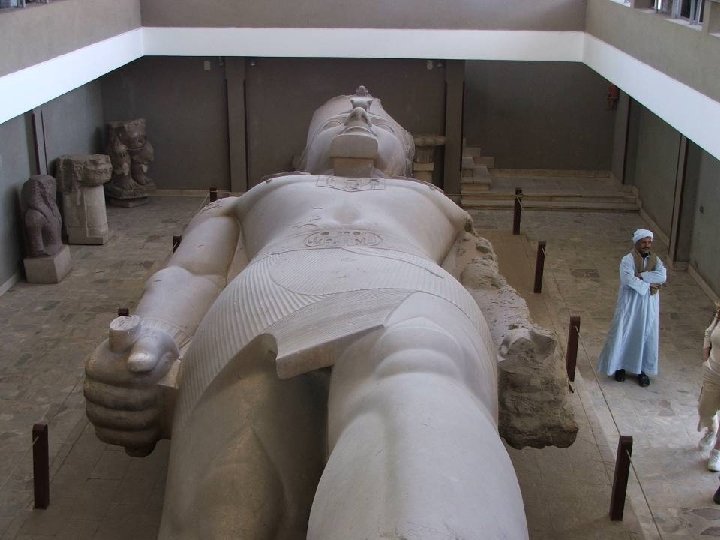
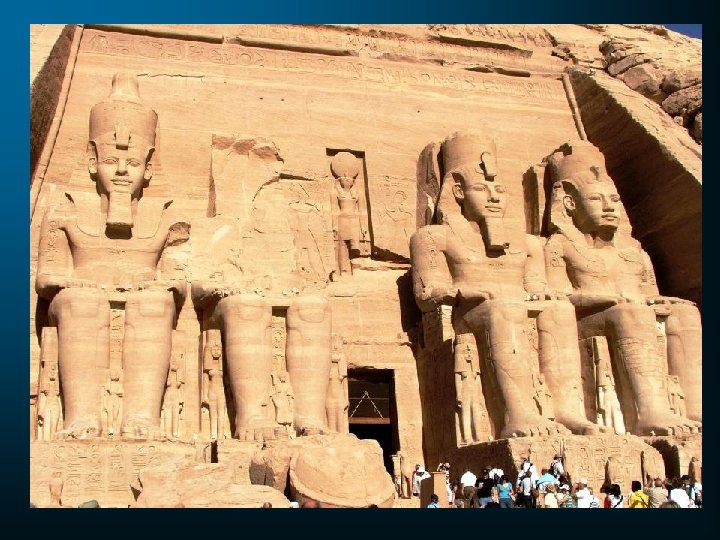





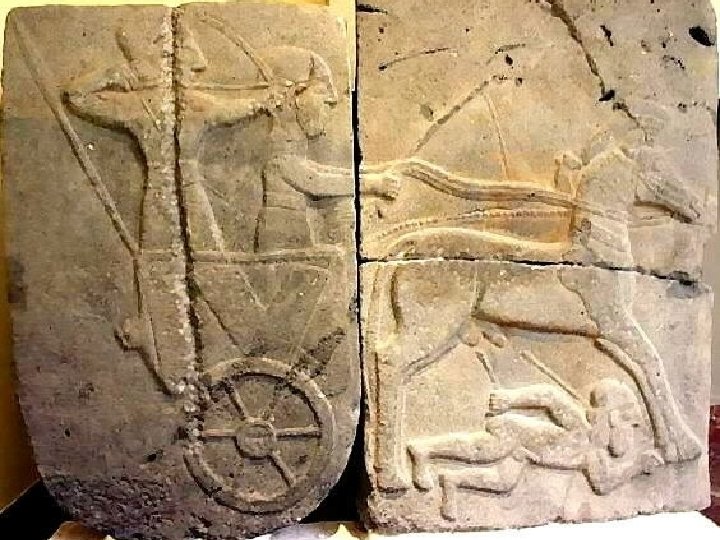
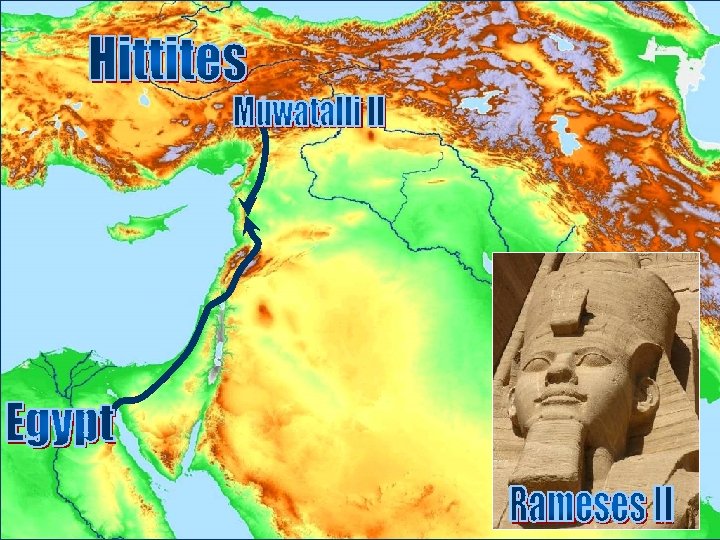
 Rameses II & the Hittites
Rameses II & the Hittites
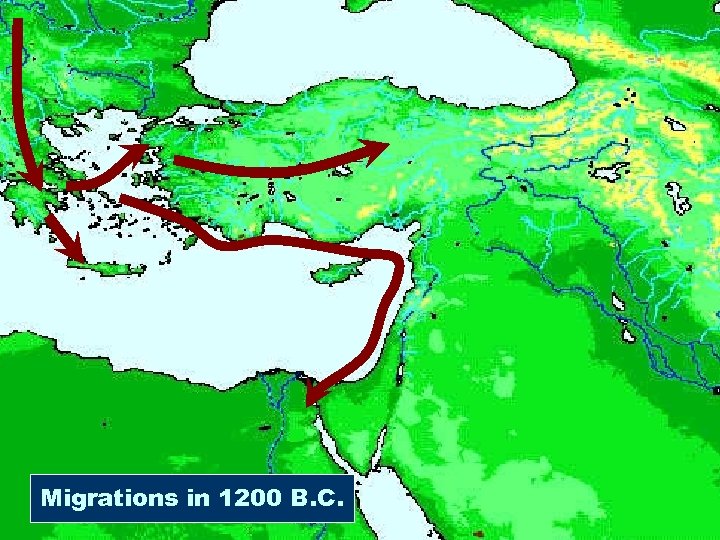 Migrations in 1200 B. C.
Migrations in 1200 B. C.
 Maps provided by David P. Barrett www. Bible. Mapper. com Used by Permission
Maps provided by David P. Barrett www. Bible. Mapper. com Used by Permission


