3d1127204174807897e9ea3add8b0e91.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

MENINGITIS Saima Abbas M. D Fellow of Infectious Diseases November 4 th 2009

Objectives /Goals PROMPT recognition of Meningitis Rapid Diagnostic testing to identify the etiologic pathogen and adjust therapy Rapid Initiation of appropriate Empiric Antimicrobial therapy Targeted Antimicrobial therapy Do’s and Don’ts for the Boards

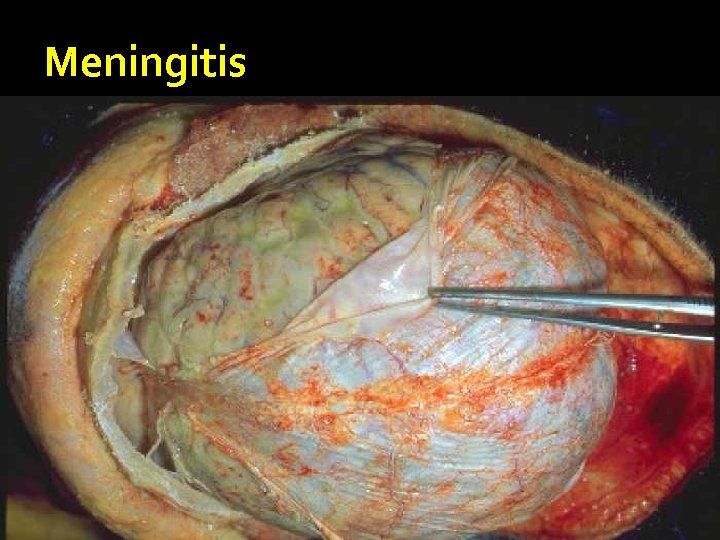
Meningitis
Bacterial Meningitis 1805 -1900’s: ~100% fatal 1913: Flexner: intrathecal meningococcal antiserum. Prevented some deaths 1930’s: Antibiotics. Improved survival Current data: Adults: 25% mortality, 21 -28% neurologic sequelae Bacterial meningitis remains a medical emergency!
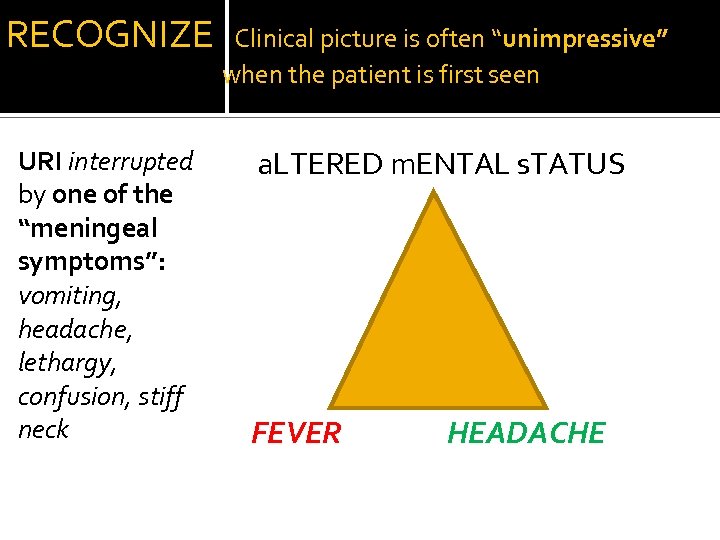
RECOGNIZE Clinical picture is often “unimpressive” when the patient is first seen URI interrupted by one of the “meningeal symptoms”: vomiting, headache, lethargy, confusion, stiff neck a. LTERED m. ENTAL s. TATUS FEVER HEADACHE

Cases ~10 key points 1. AGE 2. SEASON 3. Geography 4. Predisposing factors (immunocompromised state; basilar skull fracture with CSF leak; head trauma; post neurosurgical procedures ~wound and FB) 5. Onset and duration of illness (acute; subacute and chronic) ~community aquired or nosocomial

Key points 6. Travel, occupational and recreational exposures( insect and animal contact) 7. Vaccination history and current meds (ABX) 8. Parameningeal foci or septic emboli from IE 9. Imaging before Lumbar puncture 10. Gram stain and Interpretation of the CSF formula

CASE #1 14 -year-old male with no significant PMH is admitted to the hospital with acute onset of high fever, chills, sore throat, stiff neck, and lethargy T 1040 F, P 120, RR 32, BP 70/30 mm. Hg On examination, he was oriented only to person, and had evidence of nuchal rigidity WBC 25, 000/mm 3 with 20% bands CSF WBC 1, 500/mm 3 (98% neutrophils), glucose 20 mg/d. L, and protein 200 mg/d. L

CASE #1 Which of the following microorganisms is the most likely cause of this patient’s meningitis? A B C D E Haemophilus influenzae type b Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae Enterovirus 71 Cryptococcus neoformans
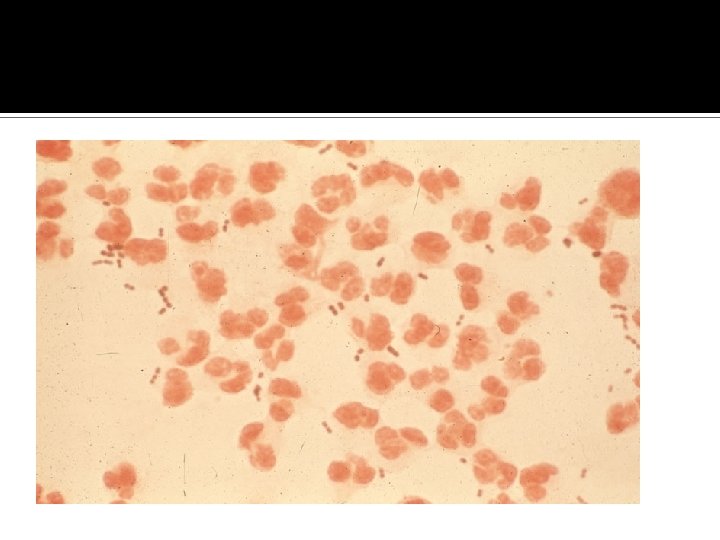
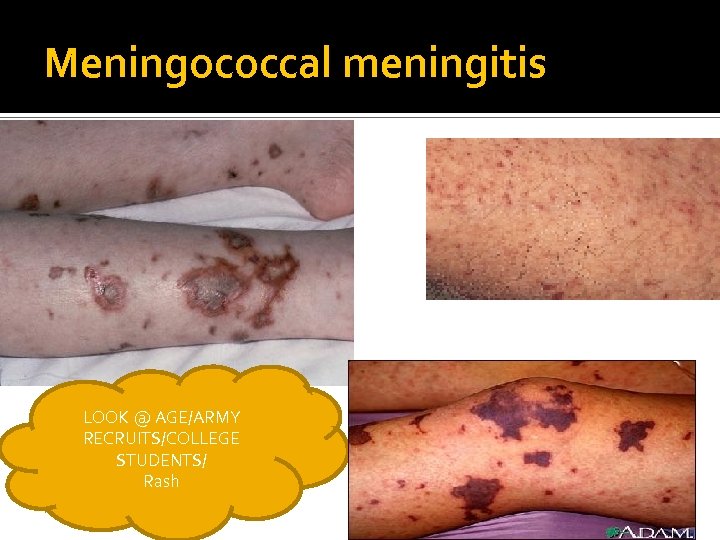
Meningococcal meningitis LOOK @ AGE/ARMY RECRUITS/COLLEGE STUDENTS/ Rash
EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURES OF MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS Affects mostly children and young adults; mortality 3 -13% (SPORADIC 98% cases B) Epidemics usually caused by serogroups A and C Group Y strains associated with pneumonia Serogroup C disease increasing in the US Nasopharyngeal acquisition of infection Predisposition in those with congenital deficiencies in terminal complement components (C 5 -C 9) and properdin deficiencies

Important facts PEN G and AMPICILLIN are DRUGS OF CHOICE Empiric therapy with Third Generation Cephalosporins recommended Nasopharyngeal carrier state 10 to 15% Infection control DROPLET precautions ~surgical mask

CASE #2 21 -year-old male without significant PMH was found difficult to arouse by his roommate in his college dormitory. Patient taken via fire rescue to ER On exam, he was lethargic, febrile to 1030 F, tachycardic, tachypnec, and hypotensve. His neck was stiff and he had a petechial rash on the lower extremities CSF revealed a neutrophilic pleocytosis, low glucose, and elevated protein. Gram’s stain showed gramnegative diplococci The patient received IV penicillin G and made a full recovery. Blood and CSF grew Neisseria meningitidis

Case # 2 For which of the following persons is antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis recommended? The Dean of the college The ambulance driver The emergency room physician The triage nurse The patient

CHEMOPROPHYLAXIS TO PREVENT MENINGOCOCCAL DISEASE Household members Day care center contacts Persons directly exposed to patient’s oral secretions - kissing, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation - endotracheal intubation or endotracheal tube management Index patient if not treated with a third generation cephalosporin Chemoprophylactic regimens - rifampin - ceftriaxone - ciprofloxacin - azithromycin
Pathogenesis
Indications for CT before LP Immunocompromised patients H/O CNS disease New onset SEIZURE Focal neurological signs Altered consciousness Papilledema Delay in performing LP Do Blood Cx STAT Dexamethasone and empiric antimicrobials CT scan LP if CT negative
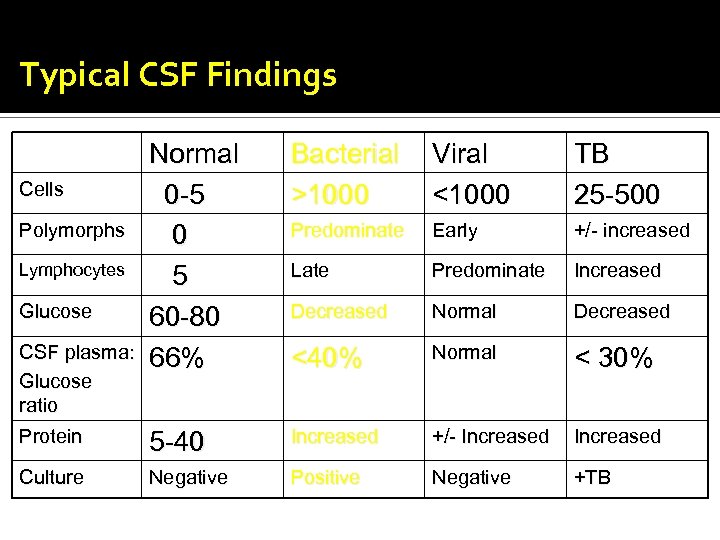
Typical CSF Findings Normal 0 -5 0 5 60 -80 66% Bacterial >1000 Viral <1000 TB 25 -500 Predominate Early +/- increased Late Predominate Increased Decreased Normal Decreased <40% Normal < 30% Protein 5 -40 Increased +/- Increased Culture Negative Positive Negative +TB Cells Polymorphs Lymphocytes Glucose CSF plasma: Glucose ratio
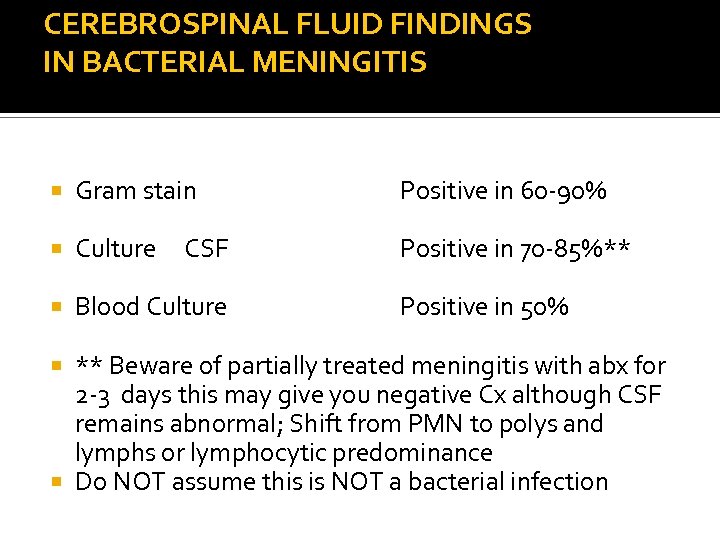
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID FINDINGS IN BACTERIAL MENINGITIS Gram stain Positive in 60 -90% Culture Positive in 70 -85%** Blood Culture CSF Positive in 50% ** Beware of partially treated meningitis with abx for 2 -3 days this may give you negative Cx although CSF remains abnormal; Shift from PMN to polys and lymphs or lymphocytic predominance Do NOT assume this is NOT a bacterial infection
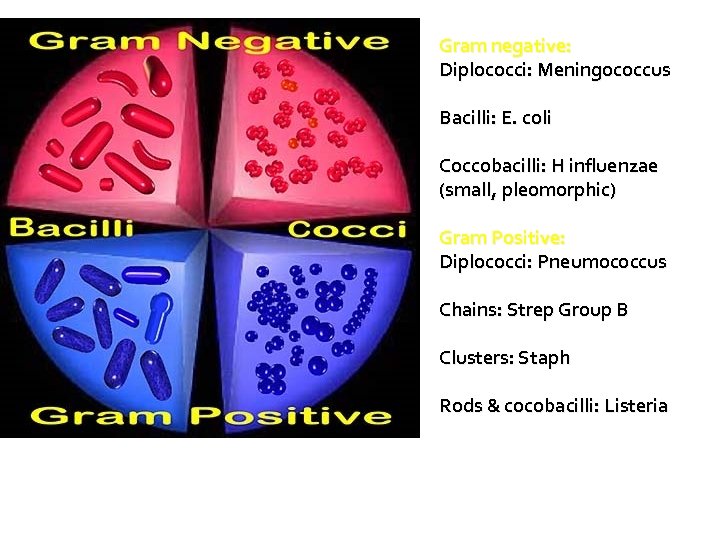
Gram negative: Diplococci: Meningococcus Bacilli: E. coli Coccobacilli: H influenzae (small, pleomorphic) Gram Positive: Diplococci: Pneumococcus Chains: Strep Group B Clusters: Staph Rods & cocobacilli: Listeria

CASE #3 56 -year-old female with a 2 -day history of fever, chills, headache, and confusion. Saw her physician 5 days earlier with complaints of earache; received ciprofloxacin T 1030 F, P 140, RR 32, BP 90/60 mm. Hg Obtunded, stiff neck, purpuric rash on lower extremities CSF showed opening pressure of 280 mm H 2 O, WBC 2, 500/mm 3 (99% neutrophils), glucose 15 mg/d. L, protein 400 mg/d. L

Case # 3 Which of the following regimens should be initiated? A Dexamethasone + Penicillin G B Dexamethasone + Ceftriaxone C Dexamethasone + Vancomycin + Ampicillin D Dexamethasone + Vancomycin + Ceftriaxone E Vancomycin + Ceftriaxone
EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURES OF PNEUMOCOCCAL MENINGITIS Most common etiologic agent in US Mortality of 19 -26% Associated with other suppurative foci of infection ~ Pneumonia (25%) Otitis media or mastoiditis (3 0%) Sinusitis (10 -15%) Endocarditis (<5%) Head trauma with CSF leak (10%)
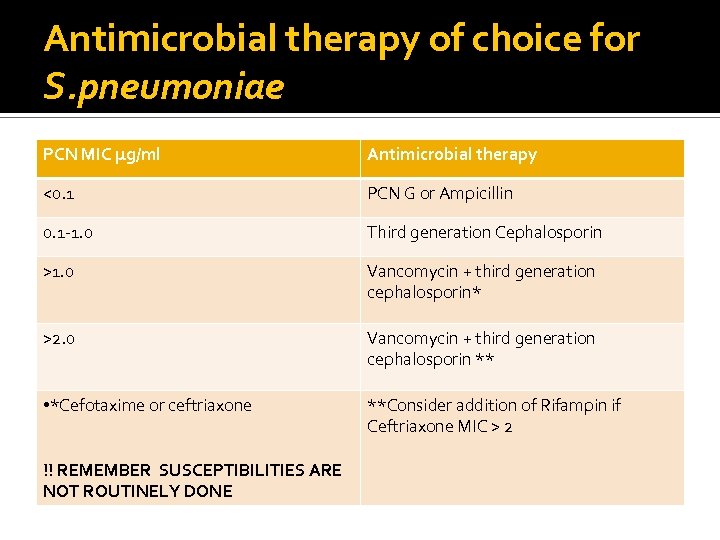
Antimicrobial therapy of choice for S. pneumoniae PCN MIC µg/ml Antimicrobial therapy <0. 1 PCN G or Ampicillin 0. 1 -1. 0 Third generation Cephalosporin >1. 0 Vancomycin + third generation cephalosporin* >2. 0 Vancomycin + third generation cephalosporin ** • *Cefotaxime or ceftriaxone **Consider addition of Rifampin if Ceftriaxone MIC > 2 !! REMEMBER SUSCEPTIBILITIES ARE NOT ROUTINELY DONE
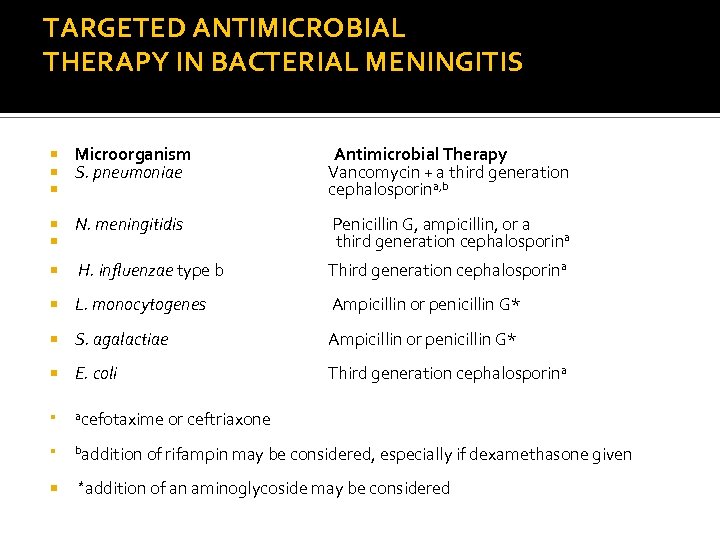
TARGETED ANTIMICROBIAL THERAPY IN BACTERIAL MENINGITIS Microorganism S. pneumoniae Antimicrobial Therapy Vancomycin + a third generation cephalosporina, b N. meningitidis Penicillin G, ampicillin, or a third generation cephalosporina H. influenzae type b Third generation cephalosporina L. monocytogenes Ampicillin or penicillin G* S. agalactiae Ampicillin or penicillin G* E. coli Third generation cephalosporina acefotaxime baddition or ceftriaxone of rifampin may be considered, especially if dexamethasone given *addition of an aminoglycoside may be considered

ADJUNCTIVE DEXAMETHASONE IN BACTERIAL MENINGITIS Attenuates subarachnoid space inflammatory response resulting from antimicrobial-induced lysis Recommended for infants and children with Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis and considered for pneumococcal meningitis in childhood, if commenced with or before parenteral antimicrobial therapy Clinical trials (predominantly in infants and children) have demonstrated reduction in neurologic and/or audiologic sequelae Recommended in adults with pneumococcal meningitis Administer at 0. 15 mg/kg every 6 hours for 2 -4 days concomitant with or just before first antimicrobial dose

ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY IN MENINGITIS Tuberculous Meningitis – Corticosteroids (extreme neurologic compromise, elevated ICP, impending herniation, impending or established spinal block; CT/MR evidence of hydrocephalus or basilar meningitis) Cryptococcal Meningitis – Reduction in intracranial pressure (frequent high- volume lumbar punctures, VP shunts)

CASE #4 60 -year-old male with acute myelogenous leukemia presented with fever, headache, ataxia, and altered mental status. Recently traveled to an outdoor family picnic in rural Virginia. He is allergic to penicillin (anaphylaxis) T 102 o. F, P 120, RR 24, BP 100/60 On examination, he was obtunded and had nuchal rigidity. Funduscopic exam revealed no papilledema. Babinski responses were positive bilaterally WBC was 25, 000/mm 3 (30% bands) LP revealed a WBC 1500/mm 3 (50 neutrophils, 50% lymphocytes), glucose 30 mg/d. L, and protein 200 mg/d. L

CASE #4 Which of the following antimicrobial regimens should be initiated? A Vancomycin administered intravenously and intrathecally B Vancomycin + rifampin C Chloramphenicol D Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole E Erythromycin

EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURES OF LISTERIA MENINGITIS Mortality 15 -29% Rare cause of bacterial meningitis in US (8%) Outbreaks associated with consumption of contaminated coleslaw, raw vegetables, milk, cheese, processed meats Common in neonates (~20% of cases) Disease in adults associated with: Elderly Alcoholism Malignancy Immune suppression Diabetes mellitus Hepatic and renal disease Iron overload Collagen-vascular disorders

Case # 5 CASE #2 46 -year-old male executive from Phoenix, Arizona presents to the ER with recent history of going on a cruise to Jamaica. One week after returning, he developed headaches, stiff neck, and vomiting. He had no significant PMH and was sexually active with multiple partners. Physical exam revealed low-grade fever and meningismus, but was otherwise negative. CSF examination revealed a WBC count of 300/mm 3 with 60% eosinophils, glucose of 45 mg/d. L and protein 150 mg/d. L. Gram stain was negative.

CASE #5 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s illness? Treponema pallidum Mycobacterium tuberculosis Coccidioides immitis Angiostrongylus cantonensis Lymphoma

FEATURES OF ANGIOSTRONGYLUS CANTONENSIS MENINGITIS~ rat lungworm Most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis Reported from many countries of the world (Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Taiwan, Pacific Islands); recent outbreak in Jamaica Rat infection rate in urban Bangkok ~40% May spread as rats move freely from port to port on ships Symptoms begin 6 -30 days after ingestion of raw mollusks or other sources of the parasite. Clinical findings are headache (90%), stiff neck (56%), paresthesias (54%), and vomiting (56%) CSF reveals a moderate pleocytosis with 16 -72% eosinophils; larvae are occasionally found in CSF

Treatment Usually self limited course and recover completely Analgesics Corticosteroids Frequent but careful LPs if increased intracranial pressure
FEATURES OF COCCIDIOIDAL MENINGITIS May present acutely, although usually subacute to chronic Patients generally complain of headache, low-grade fever, weight loss, and mental status changes; signs of meningeal irritation are usually absent Serum complement-fixing antibody titers >1: 32 to 1: 64 suggest disseminated disease CSF examination may occasionally reveal a prominent eosinophilia; CSF protein is almost always elevated Only 25 -50% of patients have positive CSF cultures CSF complement-fixing antibodies present in at least 70% of cases; titers parallel course of meningeal disease

Case #6 60 year old male with ESRD immigrated from Brazil to US and underwent a cadaveric renal transplant. Prior to transplant, he had recurrent epigastric pain. WBC 6, 500 with 15% eosinophils After transplant received Prednisone and Azathioprine Presented 1 month later with T 39ºC, headache, meningismus and altered mental status

Case#6 Lumbar puncture showed WBC 2500/mm³ (98% neutrophils) Glucose 20 mg/dl Protein 450 mg/dl Placed on Empiric Vancomycin, Ampicillin and Ceftriaxone Blood cultures and CSF Cx grew E. coli

Which of the following diagnostic test would most likely establish the pathogenesis of E. coli meningitis in this patient? A. CT scan of the head and sinuses B. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial lung biopsy C. Serial stool examinations D. Meningeal Biopsy E. Metrizimide cisternography

EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURES OF MENINGITIS CAUSED BY AEROBIC GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI Klebsiella species, Escherichia coli, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella species Isolated from CSF of patients following head trauma or neurosurgical procedures Cause meningitis in neonates, the elderly, immunocompromised patients, and in patients with gram- negative septicemia Associated with disseminated strongyloidiasis in the hyperinfection syndrome

CASE #6 An 80 -year-old male is brought to the hospital by his family because of personality changes and olfactory hallucinations On exam, T 1010 F, P 90, RR 16, BP 120/90 mm. Hg He is confused and oriented only to person. There is no meningimus or evidence of focal neurologic deficits CT of head without contrast is negative; CSF reveals a WBC of 90/mm 3 (95% lymphocytes), glucose of 80 mg/d. L (serum 100 mg/dl), and protein of 70 mg/d. L

CASE #6 Which of the following is the best test for establishing the diagnosis in this patient? A Electroencephalogram B MRI of head with gadolinium C Brain biopsy D CSF polymerase chain reaction E CSF antibody studies
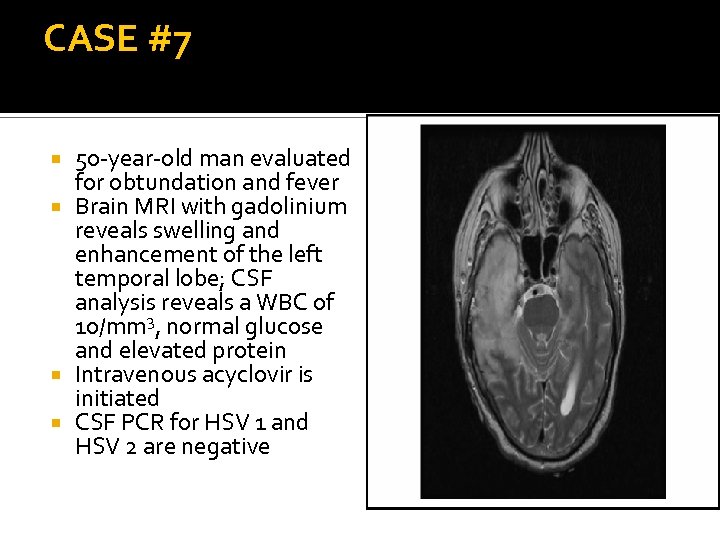
CASE #7 50 -year-old man evaluated for obtundation and fever Brain MRI with gadolinium reveals swelling and enhancement of the left temporal lobe; CSF analysis reveals a WBC of 10/mm 3, normal glucose and elevated protein Intravenous acyclovir is initiated CSF PCR for HSV 1 and HSV 2 are negative

CASE #7 Which of the following is the appropriate management for this patient? A. Discontinue acyclovir B. Perform a brain biopsy C. Begin ganciclovir + foscarnet D. Send CSF for HHV 6 PCR E. Perform HSV PCR on a new CSF specimen
HERPES SIMPLEX ENCEPHALITIS (DIAGNOSIS) Neuroimaging – MRI is procedure of choice (AFTER LP) – Edema and hemorrhage in temporal lobes – Bilateral temporal lobes (pathognomonic) CSF Analysis – Lymphocytes, increased protein, normal glucose – Polymerase chain reaction EEG – Periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges
False Negatives Published reports have found that false negatives can occur due to testing Too early or too late, improper sample transport, or low volumes of CSF tested. HSVE is frequently fatal untreated. Therefore, if MRI shows compatible temporal lobe findings and no alternative diagnosis is established, continued treatment with acyclovir should be strongly considered. A second spinal tap with repeat CSF PCR or a brain biopsy may be indicated.

Case # 8 75 year old woman from Colorado presents with acute onset of altered mental status and fever Neurological examination reveals bilateral tremors of theextremities and cogwheel rigidity Brain MRI reveals T 1 hypodense lesions in the thalamus and basal ganglia that are hyperintense on T 2 images

CSF Analysis reveals a WBC of 300/mm³ glucose of 70 and protein of 105. Which of the following tests is most likely to confirm the diagnosis in this patient? A. Serum Ig M antibody B. Serum Ig G antibody C. CSF Ig. M antibody D. CSF PCR E. Brain Biopsy

WEST NILE VIRUS First US cases reported in 1999 in New York City Birds are main reservoirs Transmission -mosquito vector -transfusion -transplantation -Breast feeding
Clinical features of WNV Age >50 years~ increased incidence 1/150 develop neuroinvasive disease Tremors and Myoclonus Parkinsonism Poliomyelitis like flaccid paralysis Serum Ig. M and Ig. G capture ELISA (cross reactivity with other flaviviruses) CSF Ig. M antibodies (diagnostic of neuroinvasive disease) CSF PCR (positive in <60%)
Etiologies of Viral encephalitis Echo virus Coxsakie and Enteroviruses Herpes Simplex West Nile virus Un identified etiology 32 - 75% Herpes Encephalitis is “NOT SEASONAL” sporadic **Clues !!! epidemiological factors THERAPY FOR ENCEPHALITIS Etiology Therapy HSV Acyclovir VZV Acyclovir CMV Ganciclovir + foscarnet HHV-6 Ganciclovir or foscarnet HIV HAART JC virus HAART
Case # 9 56 year old man s/p Kidney transplant in 2006 s/p Left mastectomy for a painful mass on Sept 1 st 2009 discharged POD # 3 re-admitted a week later with urinary retention and rectal bleeding. Unclear cause of urinary retention relieved after foley catheter insertion Rectal bleeding attributed to constipation and a bowel regimen ordered by general surgery
Day 4 of admission patient began to have some hallucinations and beginning confusion. Agitation increased gradually over the next few days. CT Brain No acute abnormality MRI ( X AICD ) Day 7 after admission; after a bowel movement patient is turned back to supine position turns gray codes and is intubated ( ? Aspiration) Day 14 ID is consulted for a persistent fever on Vancomycin and Cefepime with a RLL Pneumonia

Patient was on Haldol round the clock for severe agitation attributed to ICU delirium. . initially sleep deprivation WHAT ARE WE MISSING? Fever, altered mental status in an Immuno-compromised host ? ? ? ? CONFOUNDERS pneumonia with Achromobacter Xylosoxidans I to cefepime

Noninvasive testing was ordered and so was and LP Serum Cryptococcal Antigen was 1: 1024!!!! CSF Cr. AG was 1: 2084 Protein was 594 Glucose was 37 CSF wbc Neutrophils Lymphocytes

Patient was initiated on High dose Fluconazole and 5 Flucytosine without reversal of neurological status. He underwent trach and peg and died 2 weeks after initiation of therapy.
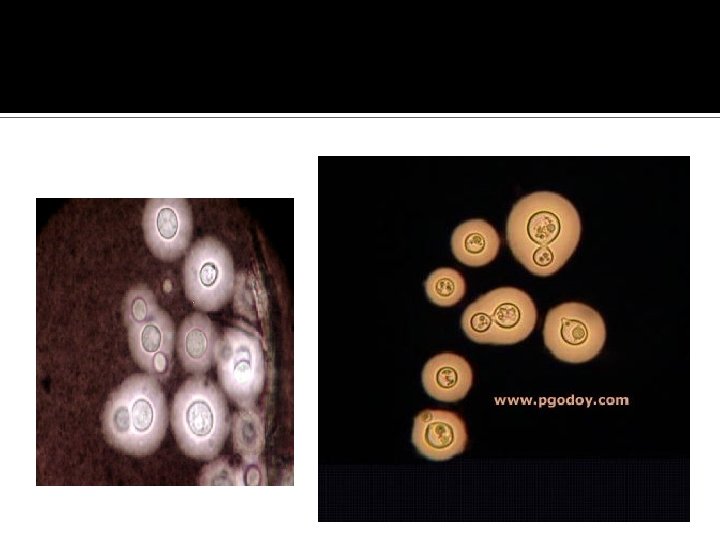
LABORATORY AND CEREBROSPINAL FLUID FINDINGS IN CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS CSF parameter NON –AIDS(%) Blood cultures - 30 - 63% Serum Cr. AG 66% 99% Opening pressure>200 mm H 2 O 72% 62 - 66% CSF Glucose < 40 mg/dl 73% 33% CSF protein>45 mg/dl 89% 58% CSF Leukocytes > 20/mm³ 70% 13 -31% CSF Culture 96% 95% CSF Cr. AG 86% 91 -100%

d/d of Meningitis SYNDROME Septic Emboli with Infective Endocarditis Brain Abscess Secondary Syphilis Parameningeal focus Rocky mountain Spotted fever ~ Doxycycline Aspetic Meningitis like picture Leptospirosis~ water rodent exposure Hepatitis/ meningitis LYME disease Lymphocytic choriomeningitis ~grip like illness Influenza like 2000 -3000 lymphocytes / winter peak Mumps~ peaks in winter with orchitis and parotitis Brucellosis Midline tumors craniopharyngiomas MEDS NSAIDs ( afebrile)

Suggested reading Tunkel AR, Hartman BJ, Kaplan SL, et al. Practice guidelines for the management of bacterial meningitis. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 11267 -84. Spanos A, Harrell FE Jr, Durack DT. Differential diagnosis of acute meningitis: an analysis of the predictive value of initial observations. JAMA 1989; 262: 2700 -7.
3d1127204174807897e9ea3add8b0e91.ppt